Sustainable Development and Energy
1/33
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
34 Terms
Solar Energy
conversion of sunlight into usable energy forms
Solar photovoltaics (PV) and solar thermal electricity
estaSun radiation arrives outside the Earth with a specific spectral distribution, which is modified throughout the atmosphere until reaching the Earth’s surface.
Geographic latitude
Time of day
Year
The amount of solar energy available on a given location of the earth differs depending on the:
Solar radiation components
Direct radiation
Diffuse radiation
Direct radiation
radiation from the sun that reaches the Earth without scattering
Direct radiation
it can be concentrated using technological devices
Diffuse radiation
radiation that is scattered by the atmosphere and clouds
Established Solar Technologies
Solar PV
Solar Thermal
Solar PV
Directly converts solar energy to electricity
Solar PV
Absorbs 80% incident solar radiation but convert only small portion to electricity
Solar PV
Release excess heat during the operation
Solar Thermal
Harnessing solar energy for thermal applications – domestics, industries, hotels, hostpitals, leisure, etc.,
Solar Thermal
Use thermal energy for space heating, fluid and generate electricity
Solar Thermal
Has been accepted worldwide as solar thermal power
Solar Thermal Collector
converts solar radiation into useful heat and its performance depends both on optical and thermal features.
Different Solar Thermal Technologies
Parabolic Trough Solar Thermal System
Central Tower Solar Thermal System
Linear Fresnel Solar Thermal System
Parabolic Dish Solar Thermal System
Flat plate solar collectors
Parabolic Trough Solar Thermal System
System where the troughs concentrate sunlight onto a receiver tube that is positioned along the focal line of the trough.
Example: SEGS in California, with 936,384 mirrors
Central Tower Solar Thermal System
system takes advantage of numerous heliostats to reflect sunlight onto the surface of the high-temperature heat absorber on the top of the center tower.
Example: Ivanpah 440 MW Power Facility, California, 214,000 heliostats
Linear Fresnel Solar Thermal System
one-axis solar tracking device, with the parola divided into many small nearly flat mirrors with independent movement, simultaneously focusing the linear absorber located in optical focus.
Example :Murcia, Spain with 100MW/km2 land use
Parabolic Dish Solar Thermal System
heliostats with sunlight focused on the engine with a cavity receiver on the focal point. One of the most efficient solar electric technologies.
Example: Arizona, US
Flat plate solar collectors
mostly used in heating water for showers.
Example: small-scale than other examples, used in heating water in swimming pools and showers
Heliostats
two-axis tracking mirrors which concentrate solar radiation maintaining the reflected image at fixed position over the course of the day.
Solar Collector
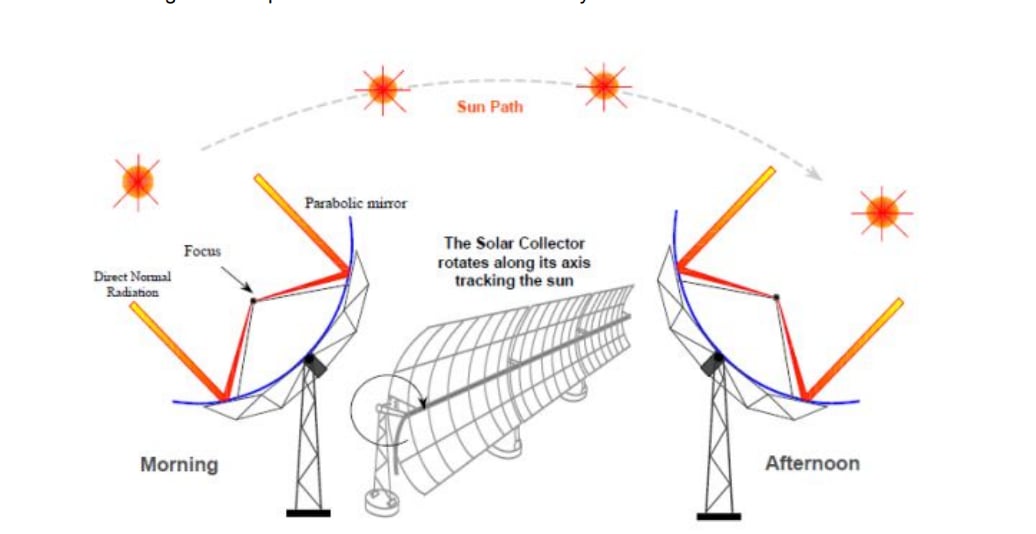
Solar photovoltaics Advantage
Module manufacturing is being done in large plants, which allows for economies of scale, and it can be deployed in very small quantities at a time
Solar photovoltaics Disdvantage
As PV generates power from sunlight, power output is limited to times when the sun is shining. However, a number of options (demand response, flexible generation, grid infrastructure, storage) exist to cost-effectively deal with this challenge.
Biomass Energy
burning of wood, bark, branches, starchy roots, manure and other plant and animal materials to produce energy
Example: San Carlos Biopower Inc. in Negros Occidental
Biomass Energy Conversion Process
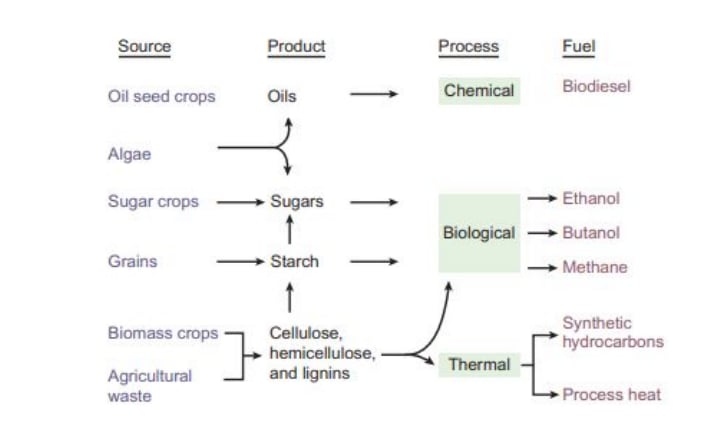
Hydropower
falling water produces energy which is harnessed as a valuable contribution to total energy supply.
Example: Maria Cristina Falls and Agus VI Hydroelectric Plant, supplying 200 MW of electricity
Less destructive alternatives to dams
low-head hydropower technologies
Wind
Wind energy comes from capturing kinetic energy using turbines to generate electricity, and can be onshore or offshore.
Example: Pililla Win Farm in Rizal, supplying 54 MW to Meralco
Energy Mix
refers to how final energy consumption in a given geographical region breaks down by primary energy source
PH Energy MIx
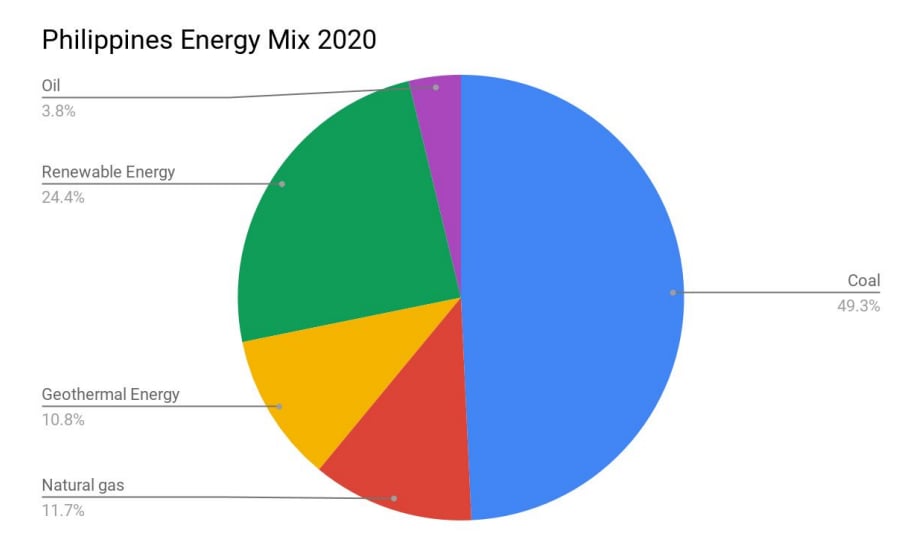
Renewable Energy in the Philippines
Hydropower
Geothermal
Biomass
Solar, wind, ocean
Biofuels