Chapter 12 - Solids and Modern Materials
Classifying solids based on bonds
- Metallic solids - Held together by a sea of collectively shared electrons.
- Ionic solids - Sets of cations and anions mutually attracted to one another.
- Covalent-network solids - Joined by an extensive network of covalent bonds.
- Molecular solids - Discrete molecules held together by weak forces.
Types of solids
- Polymers - Contain a long chain of atoms connected by covalent bonds. They have different properties than small molecules or metallic ionic compounds.
- Nanomaterials - Crystalline compounds with the crystals on the order of 1-100nm. They have different properties than larger crystalline materials.
- Crystalline - Solids with a repeating pattern of atoms.
- Amorphous - Lack of order in the arranged atoms.
Unit Cell
- Unit cell - The basis of a repeating pattern.
- The structure of a crystalline solid is defined by
- Size and shape of unit cell
- Location of atoms in the unit cell
- Crystal lattice - Geometric pattern on which the unit cell is.
- Lattice points - Positions that define the overall structure of the crystalline compound.
- Each point has an identical environment.
Basic 3D lattices
- Cubic
- Tetragonal
- Orthorhombic
- Rhombohedral
- Hexagonal
- Monoclinic
- Triclinic
- Centered lattices - Have atoms in another regular location, most common in the body center (body-centered) or center of the face (face-centered).
- Alloys - Materials that contain more than one element and have the characteristic properties of metals.
- Substitutional alloys - A second element takes the place of a metal atom.
- Interstitial alloys - A second element fills a space in the lattice of metal atoms.
- Heterogeneous alloys - Components are not dispersed uniformly.
- Electron sea model - Where we assume a metal is a group of cations suspended in a sea of electrons.
- Molecular solids - Consist of atoms of molecules held together by weaker forces.
- Shape - Ability to stack, it has influence on some physical properties like boiling point.
- Covalent-network solids - Atoms are covalently bonded over large network distances with regular patterns of atoms.
- They have higher melting and boiling points.
- Coordination number - The number of nearest-neighbor atoms of an atom.
Polymers
- Polymers - Molecules of high molecular weight made by joining smaller molecules called monomers.
- They are mostly carbon-based.
- They are formed by covalent bonding.
Primary polymers
- Addition - Formed when a bond breaks and the electrons in that bond make two new bonds.
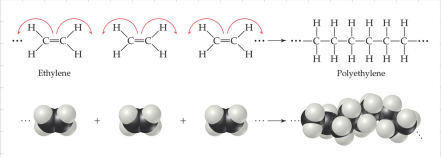
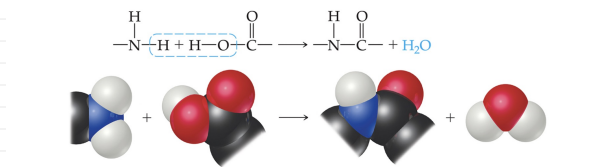
- Condensation - Formed when a small molecule is removed between two larger molecules.
- Copolymers - Formed by two different monomers.
Semiconductors on nanometers
- Quantum dots - Semiconductor particles that are about 1-10nm.
- Bond energy - Gap between highest occupied level and lowest unoccupied level.
- Buckminsterfullerene or Buckyballs - Soccer ball-shaped C60 molecule.

