UNIT 1: BIOLOGICAL MACROMOLECULES
1/54
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
55 Terms
carbon
central atom to all living things; necessary for ORGANIC molecules; has tetravalence
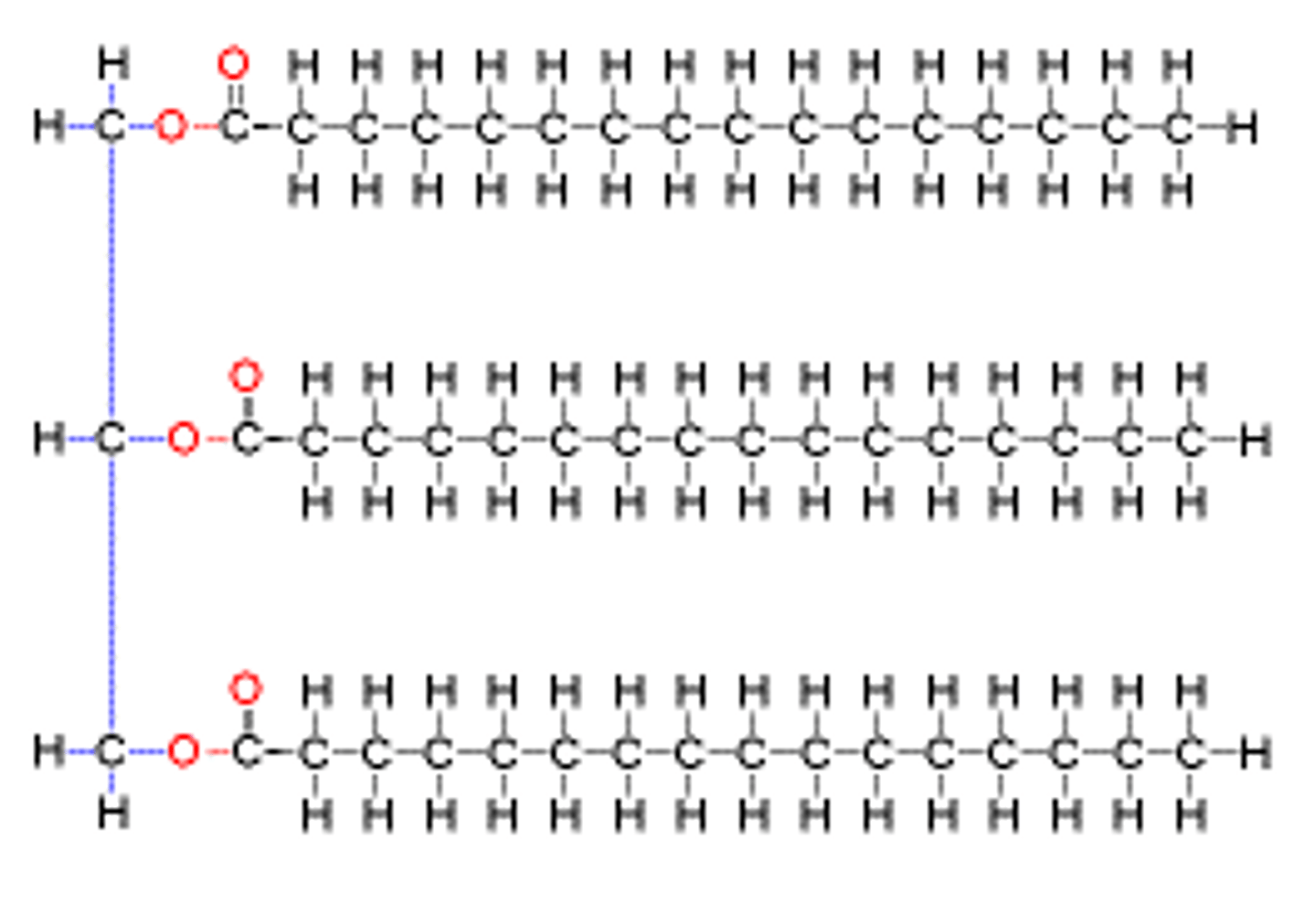
polymer
long chains of smaller monomers/building blocks
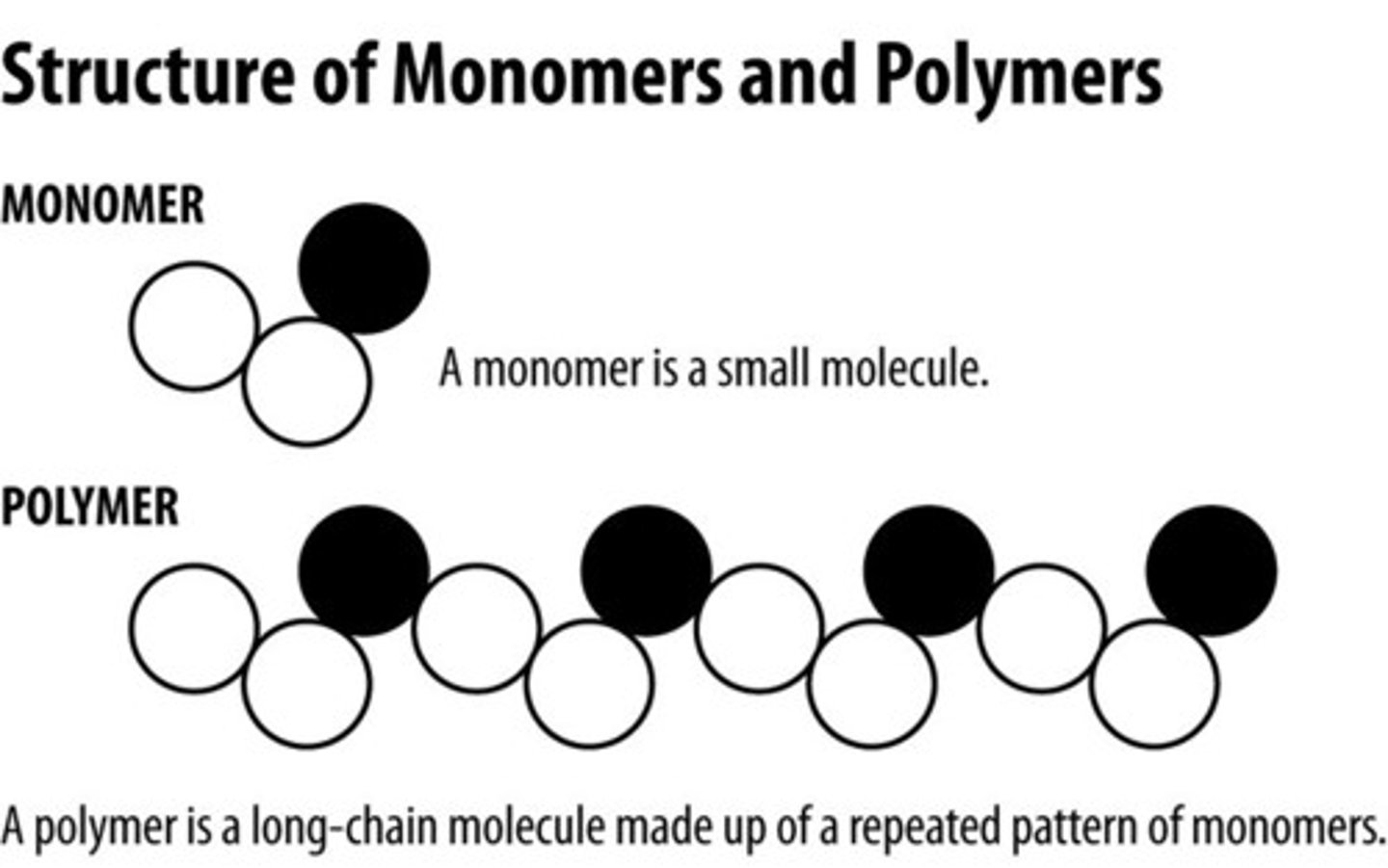
monomer
small building blocks that make up polymers
hydrocarbons
long chains of carbon and hydrogen covalently bonded together
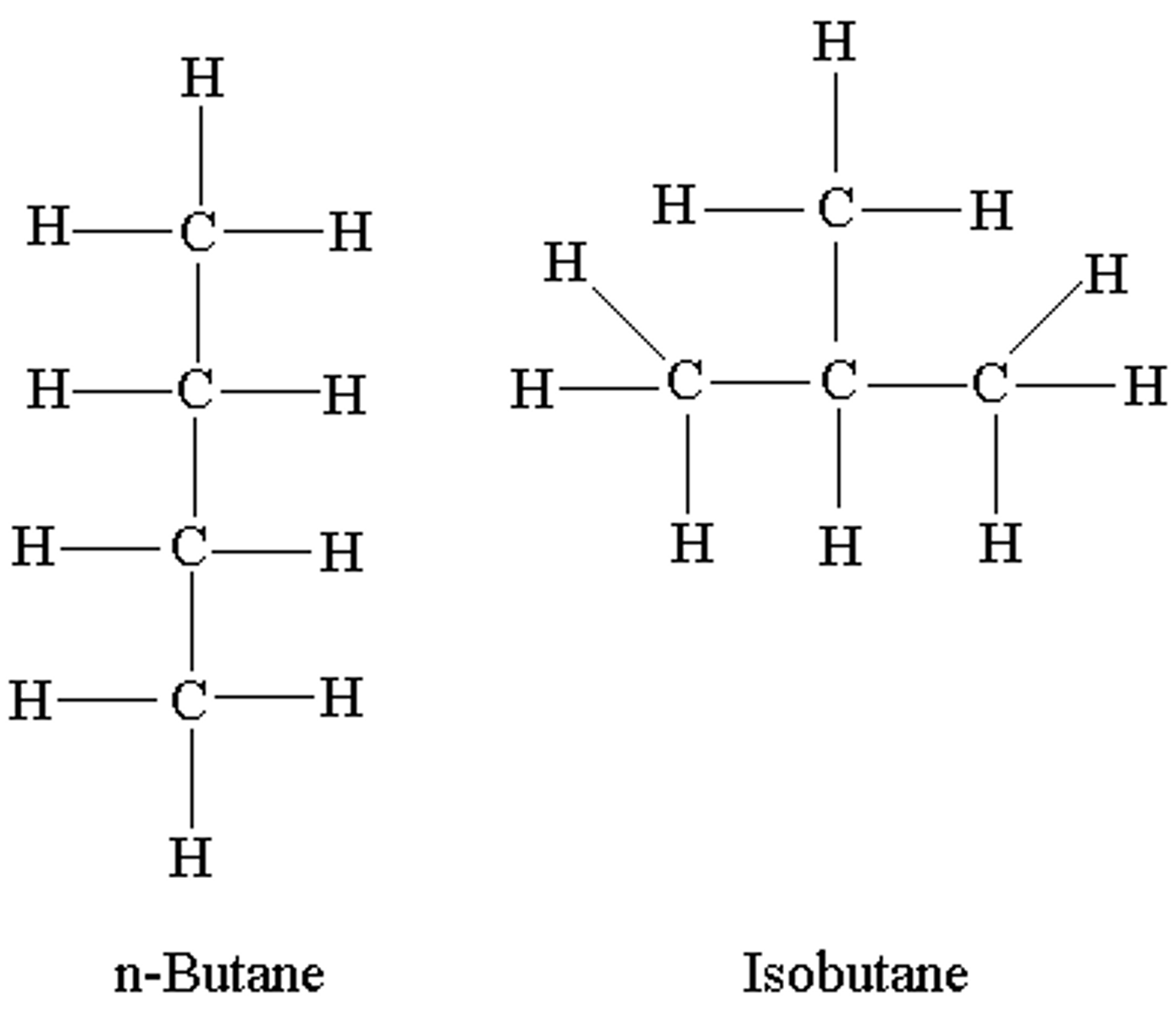
isomer
molecules with the same number of atoms and same elements, but different structures (and thus different properties and functions)
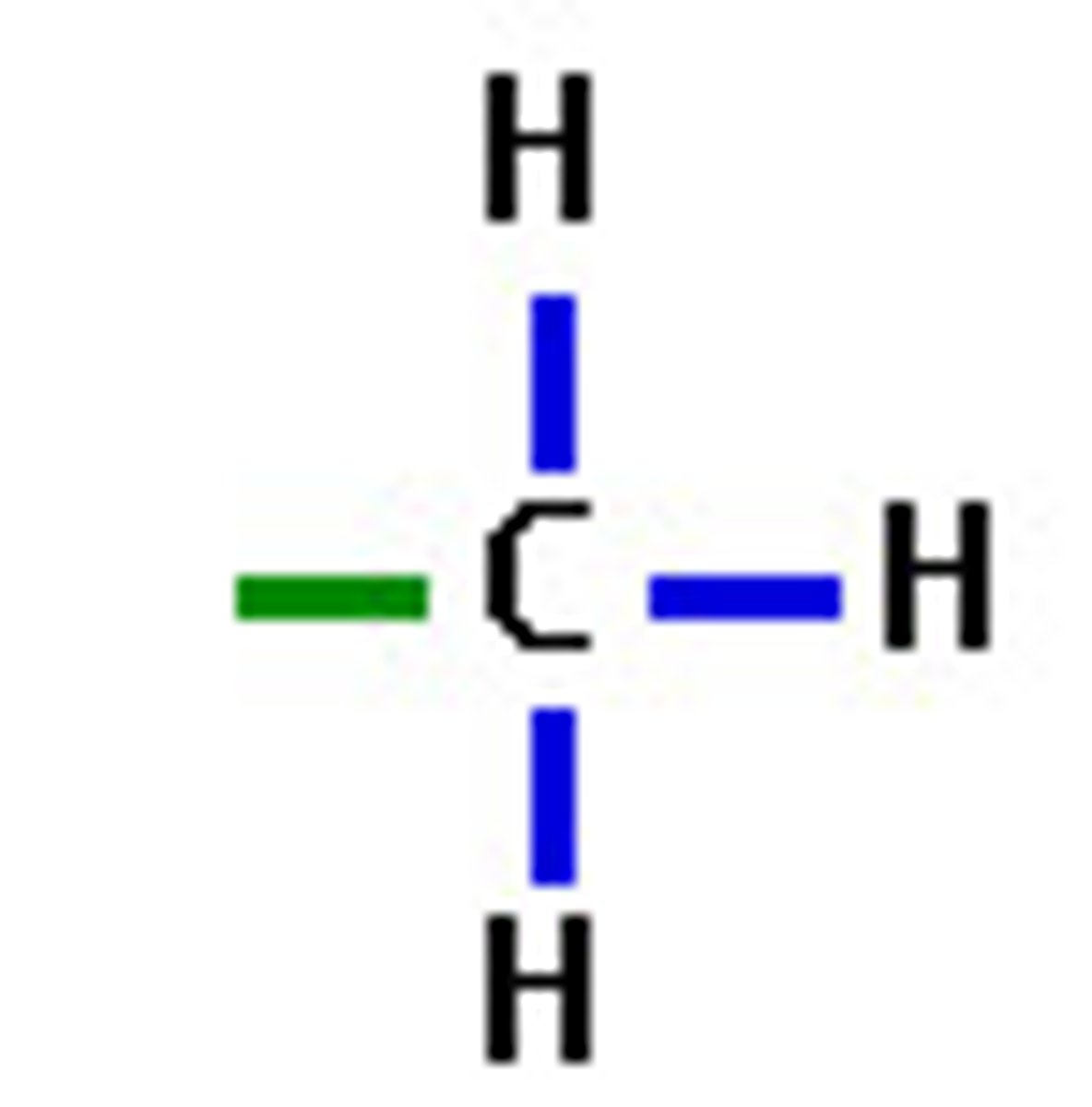
methyl group
Consists of a carbon atom bonded to three hydrogen atoms. Affects gene expression; often tags DNA
hydroxyl group
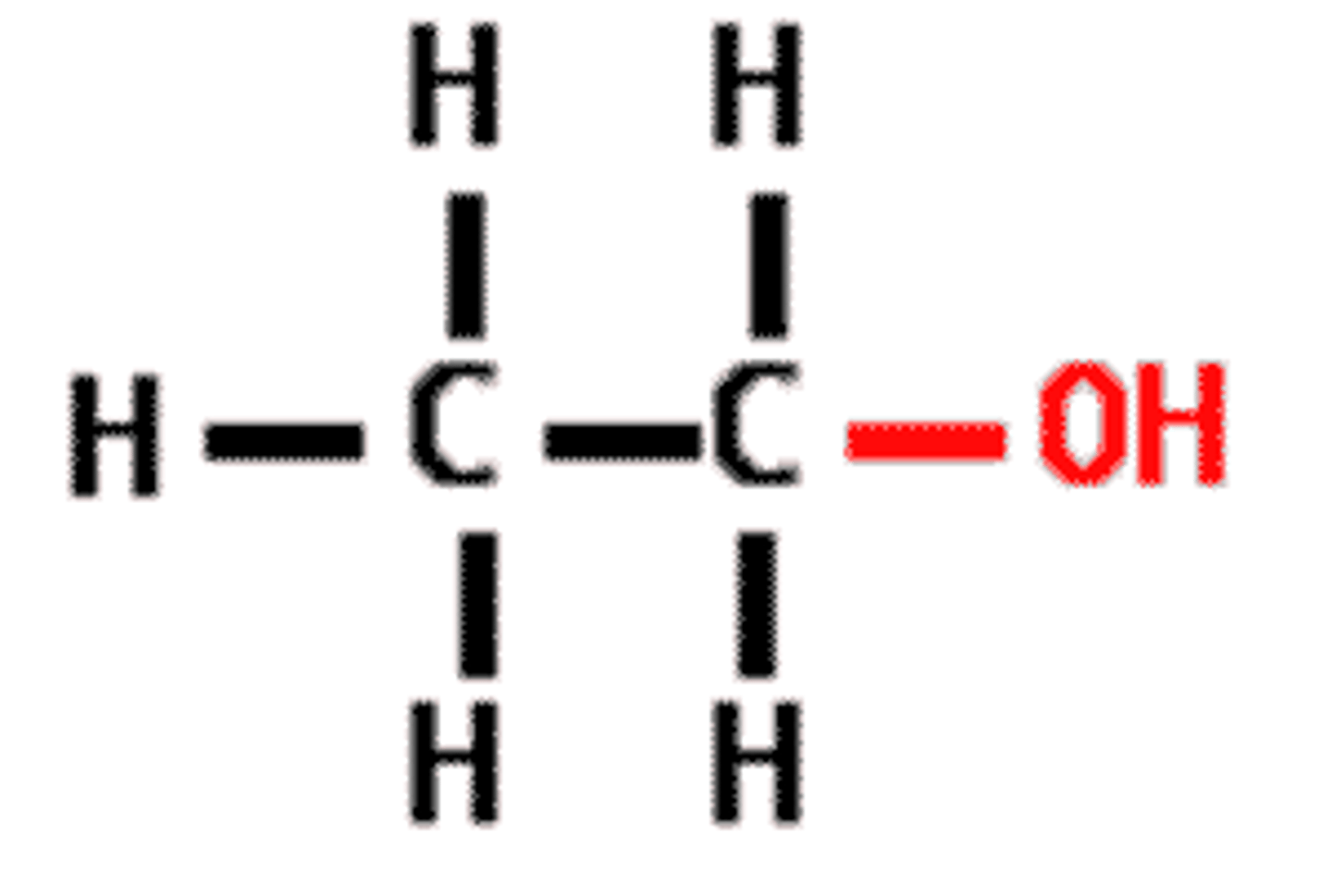
functional group - alcohols, polar, helps dissolve organic compounds like sugar
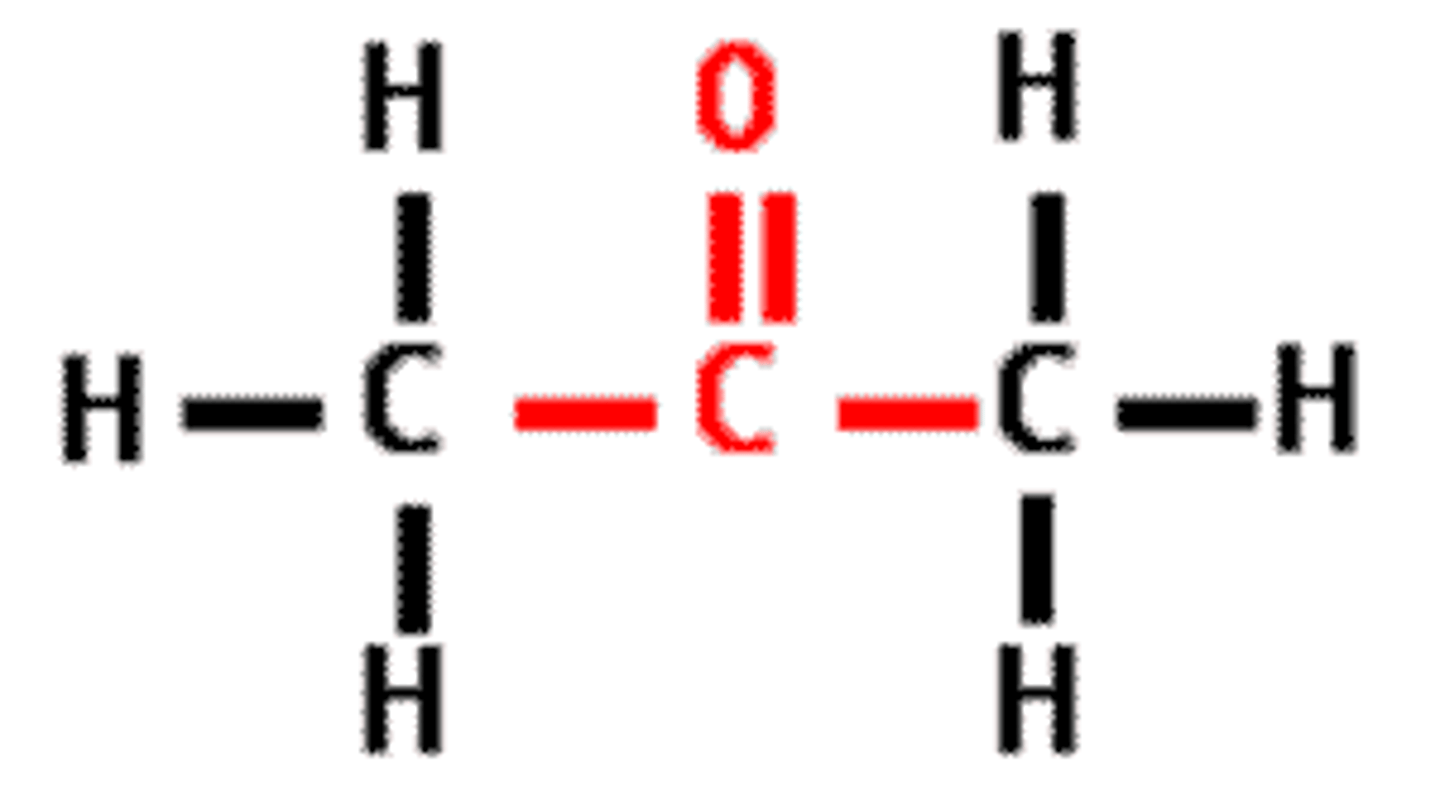
carbonyl group
functional group - ketones or aldehydes, sugars
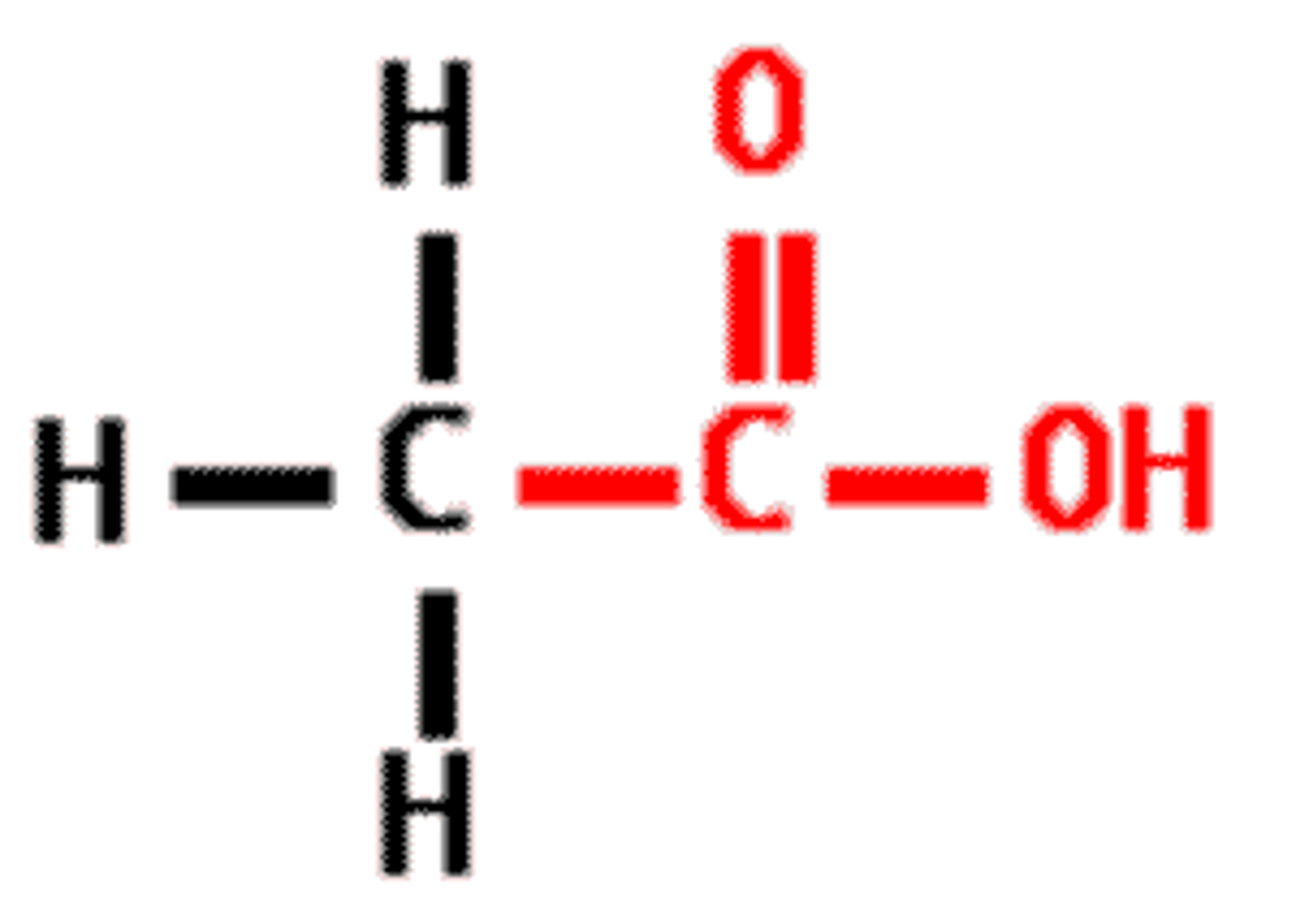
carboxyl group
found in an amino acid
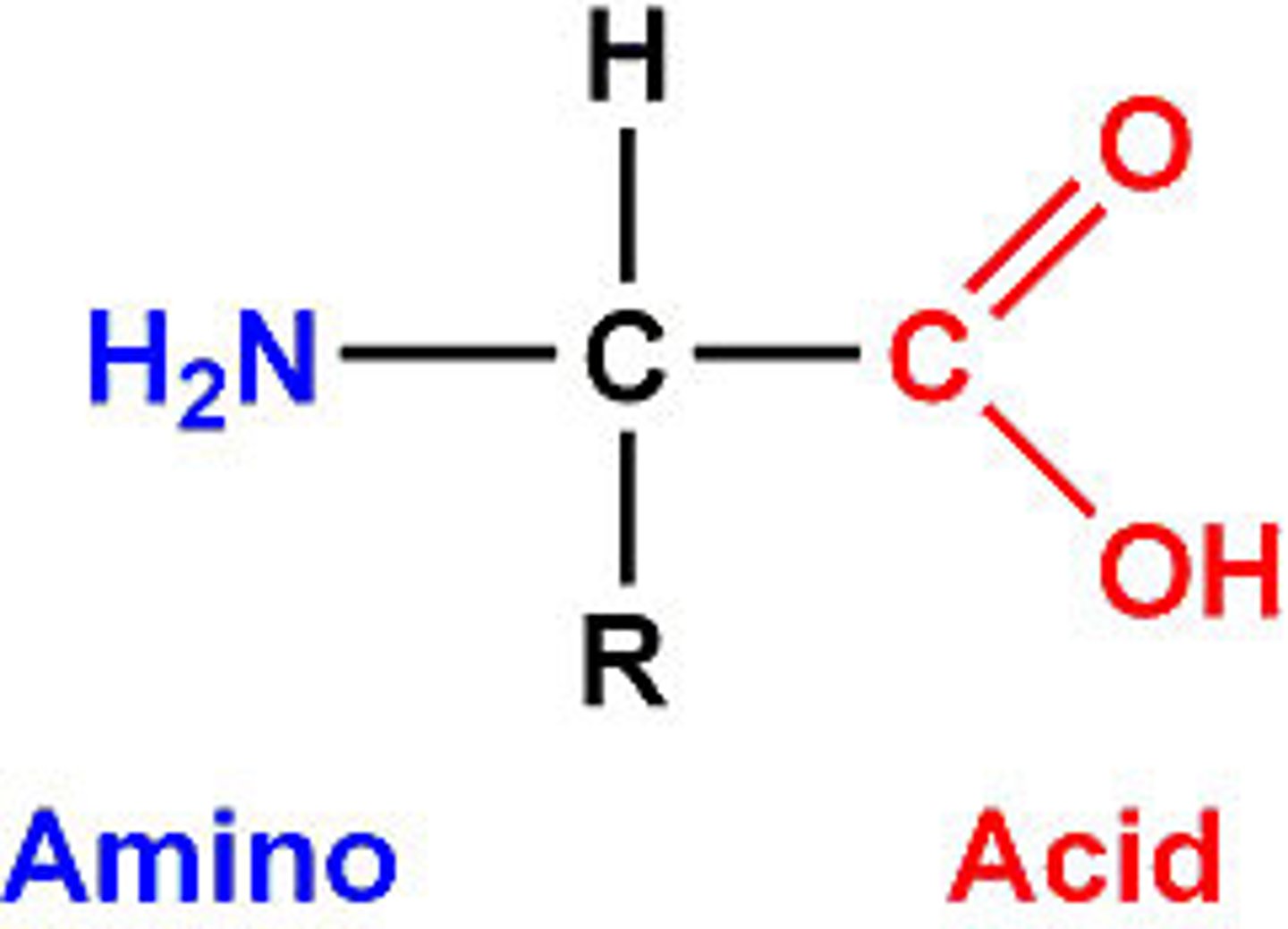
amino group
nitrogen bonded to two hydrogens;one part of an amino acid
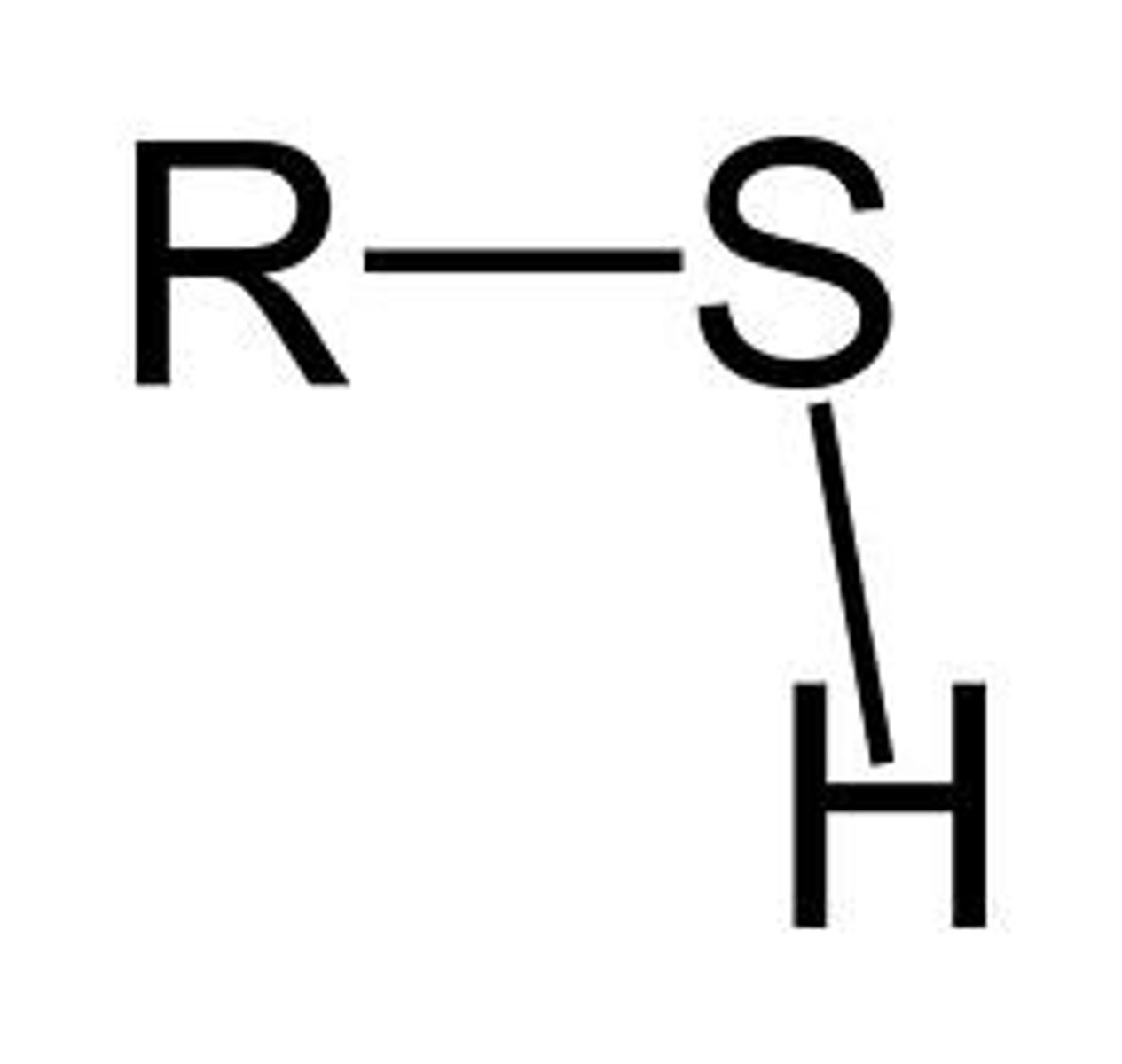
sulfhydryl
forms "bridges" in proteins, "cross-linking" to stabilize protein structure
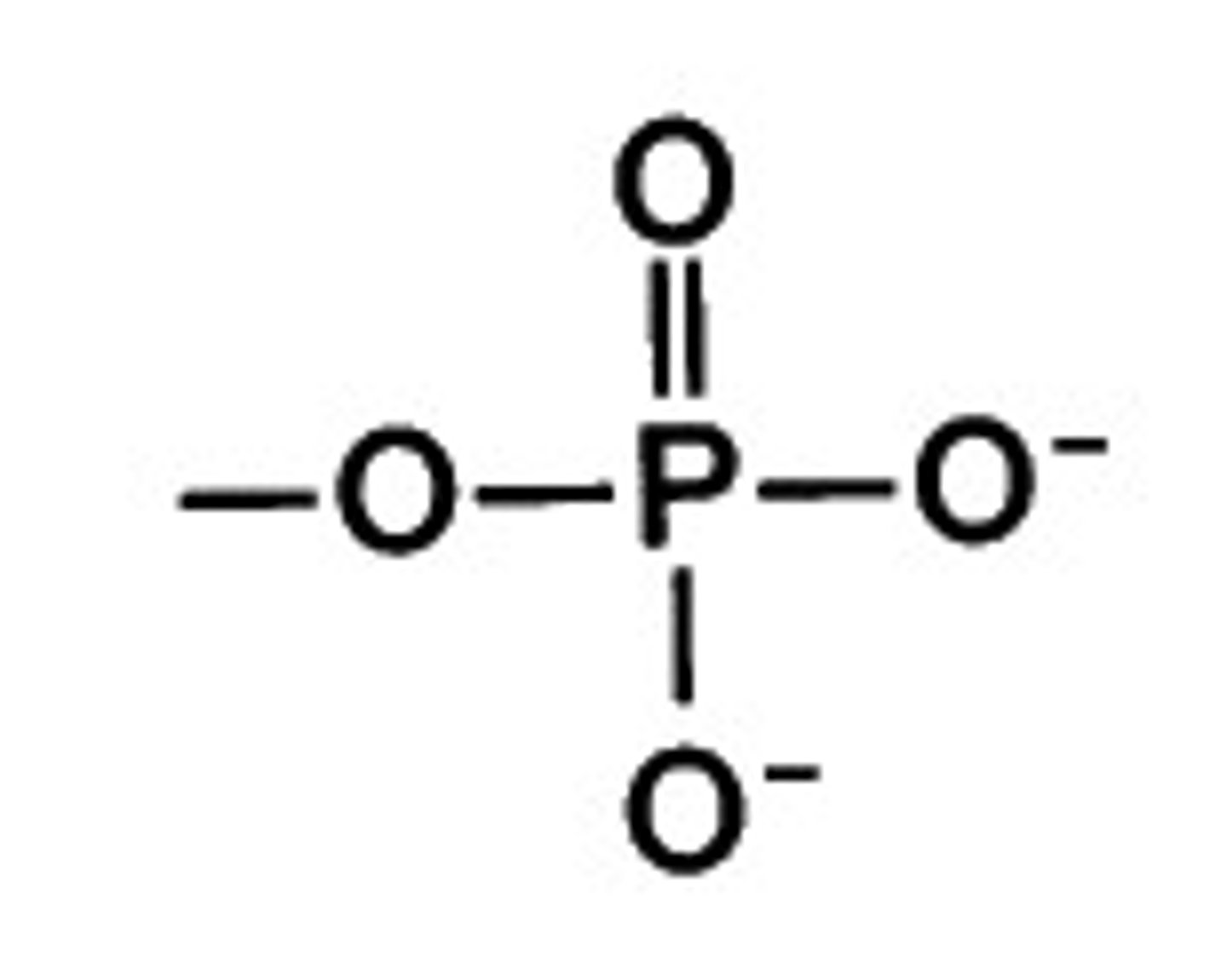
phosphate group
activates molecules, transfers energy between organic molecules; found in nucleic acids
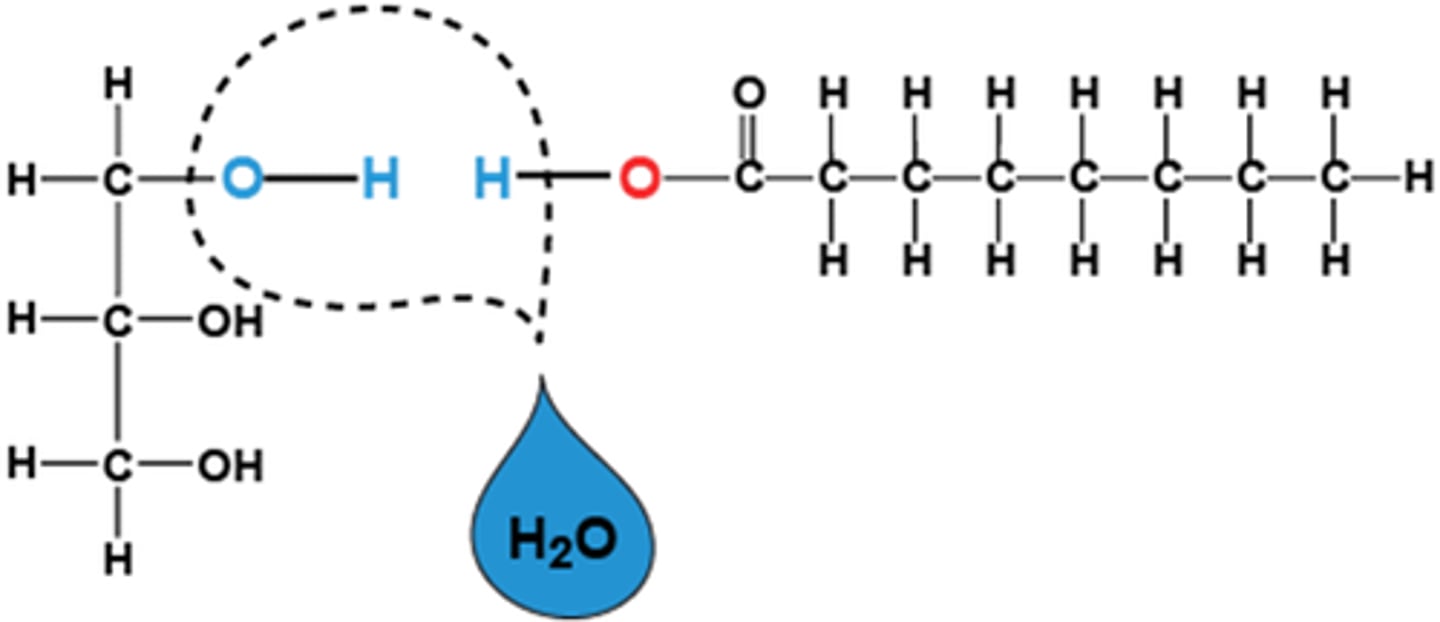
dehydration synthesis
builds polymers by joining monomers; requires removal of H2O
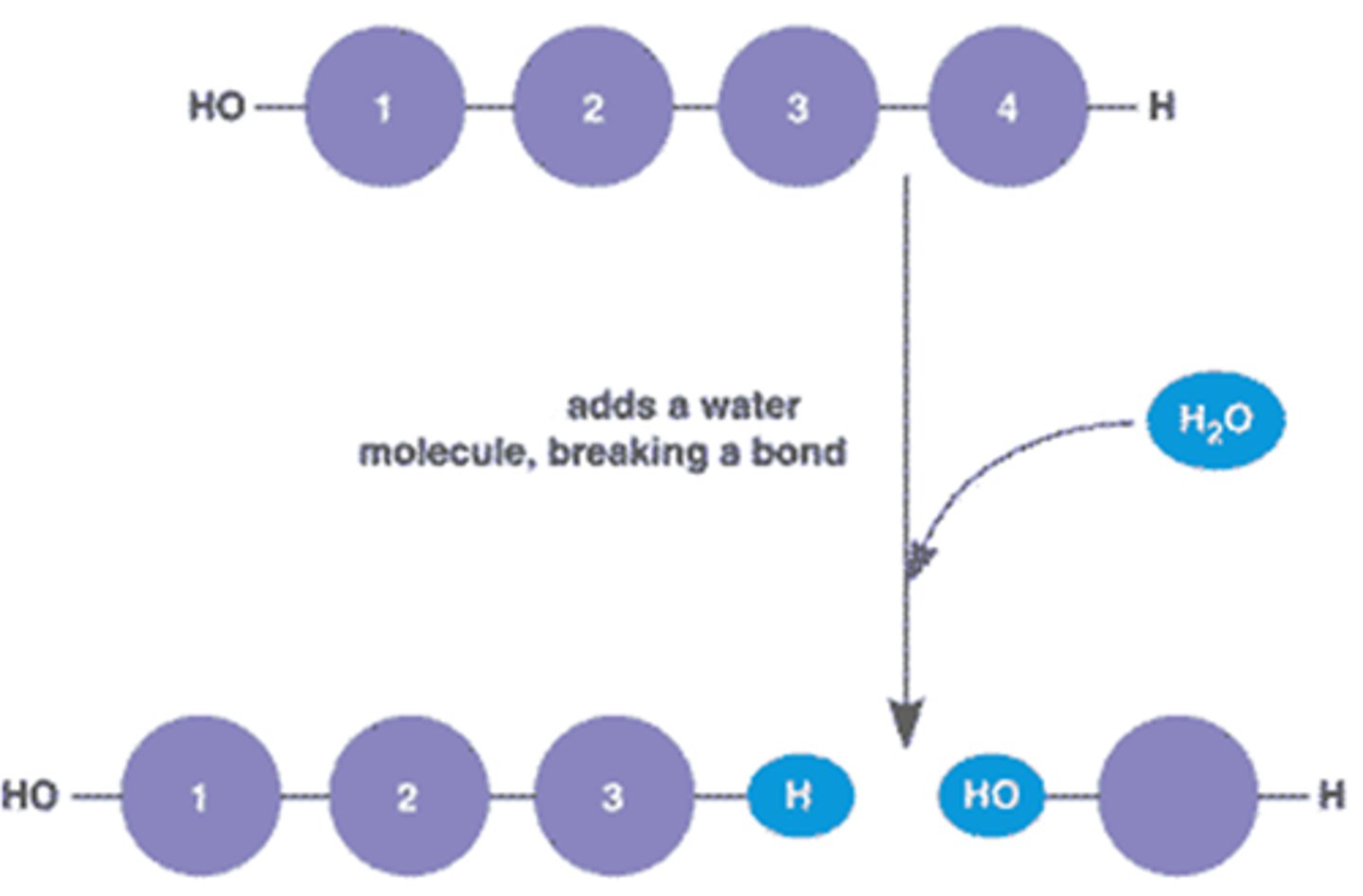
hydrolysis
breaks down polymers by removing monomers; requires addition of H2O
carbohydrates
polymer that functions as an immediate source of energy, storage, or structural support. Monomers are monosaccharides

types of polysaccharides
starch, glycogen, cellulose, and chitin
function of starch and glycogen
short-term energy storage in plants (starch) and animals (glycogen)
lipids
long-term energy storage, insulation, protection, shock absorption; polymer that includes fats, phospholipids, steroids
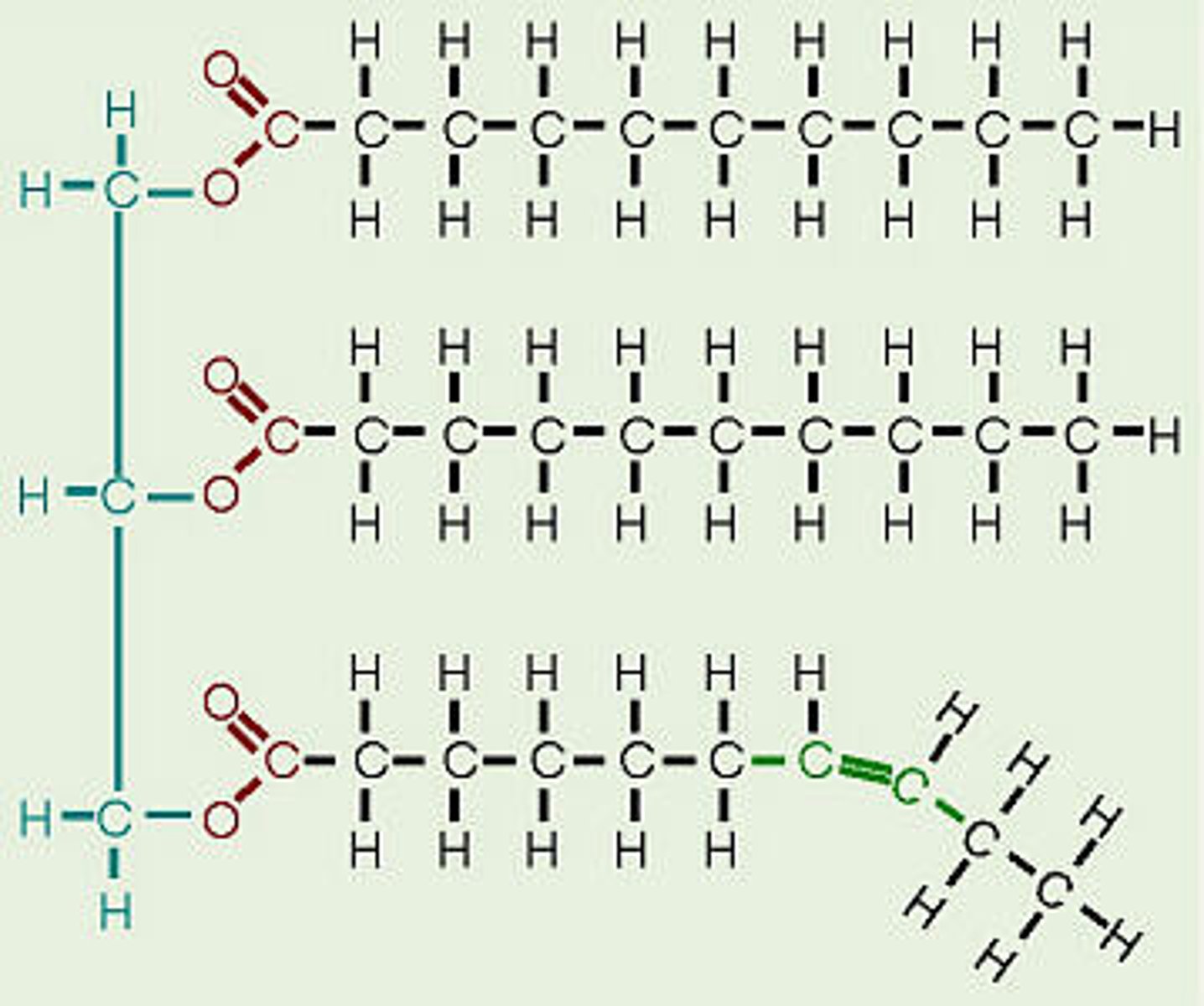
difference between saturated and unsaturated fat
saturated - solid at room temp, comes from animals, contains only single bonds
unsaturated - liquid at room temp, comes from plants, contains at least one double bond
function of steroids
signaling, hormones, some vitamins
proteins
polymer that is used for transport, structural support., includes enzymes; Monomers are amino acids
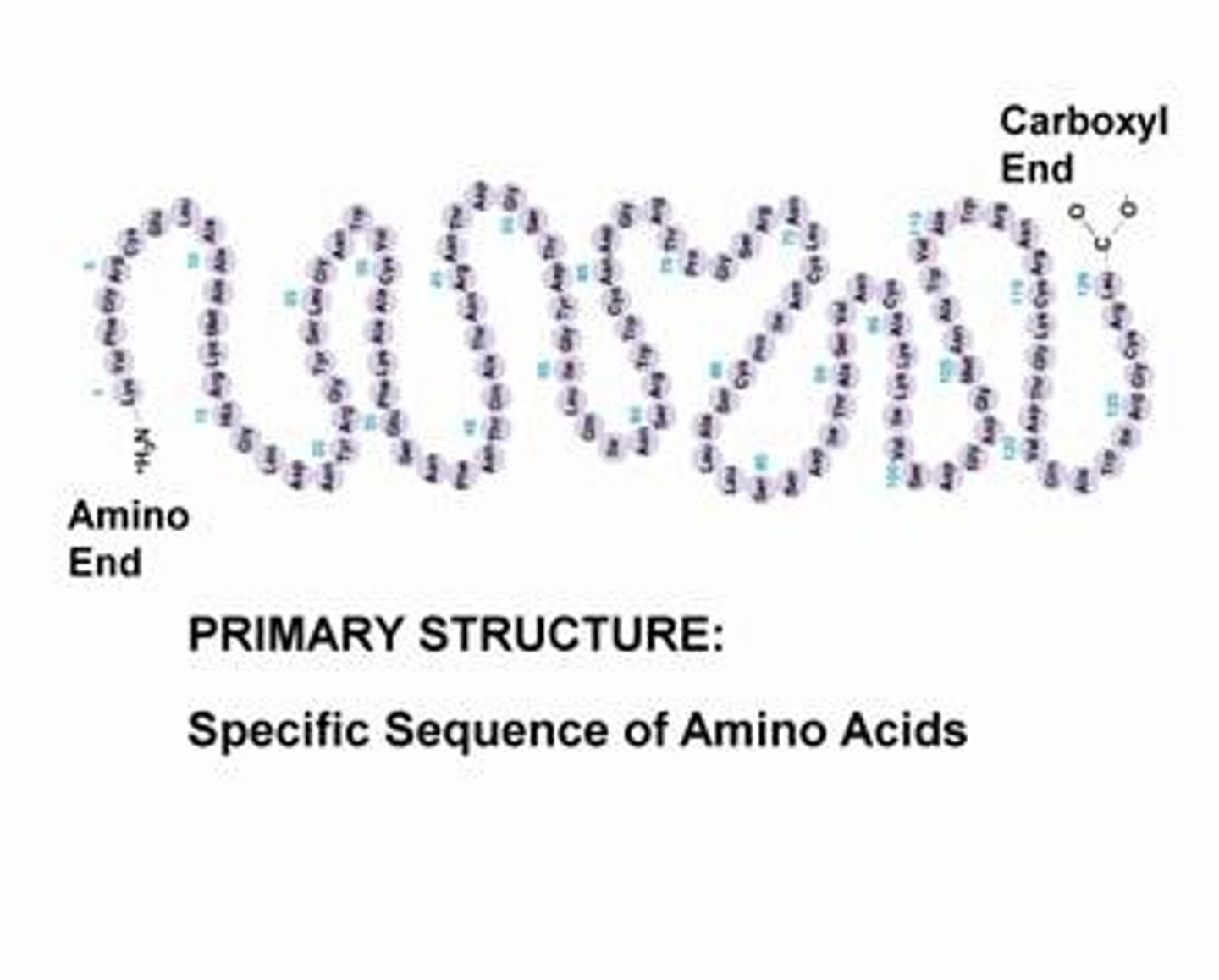
primary protein structure
sequence of amino acids
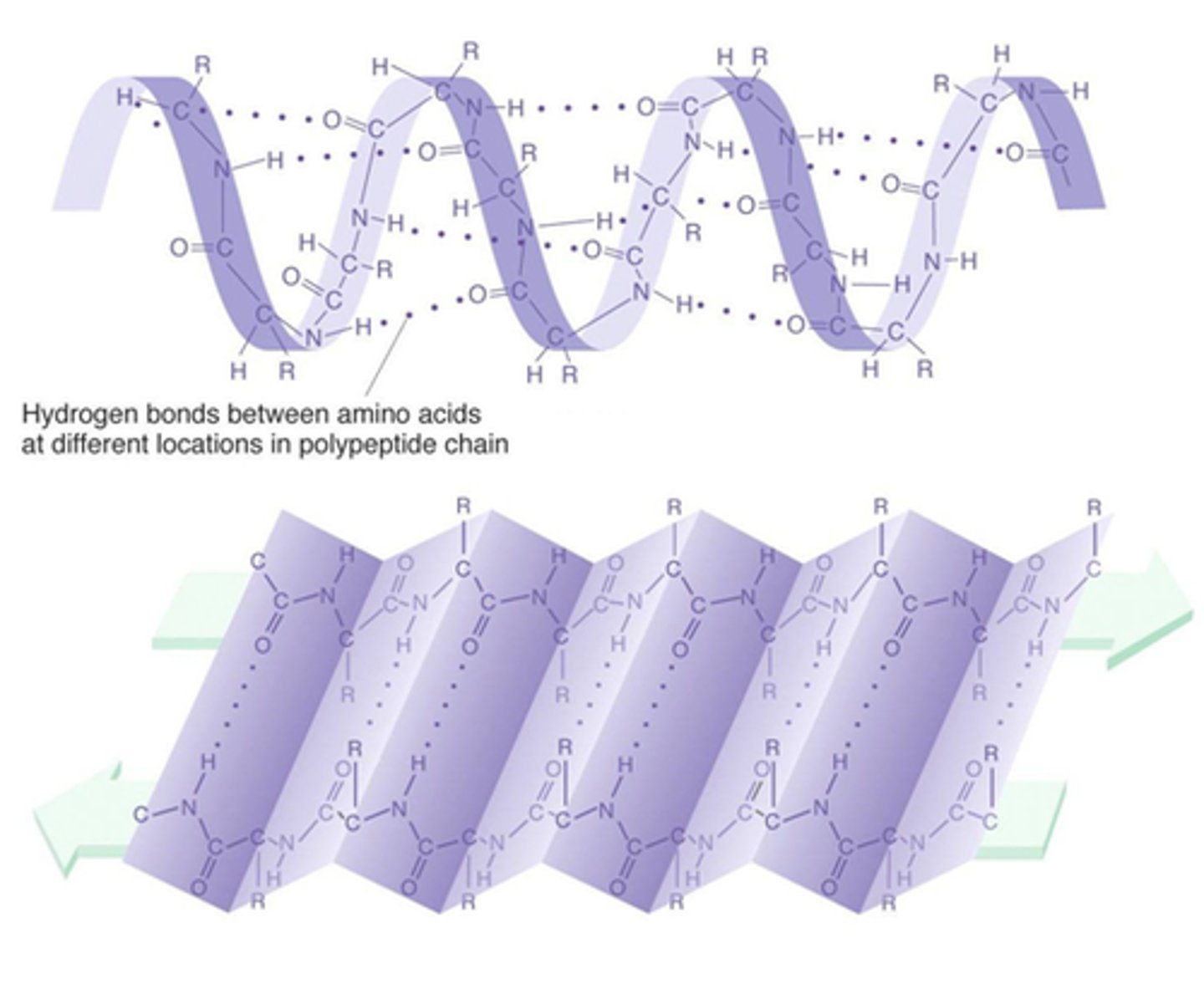
secondary protein structure
amino acid sequence interacts to form alpha helices and beta-pleated sheets
tertiary protein structure
alpha helices and beta-pleated sheets interact within the same polypeptide chain; some proteins only reach this level
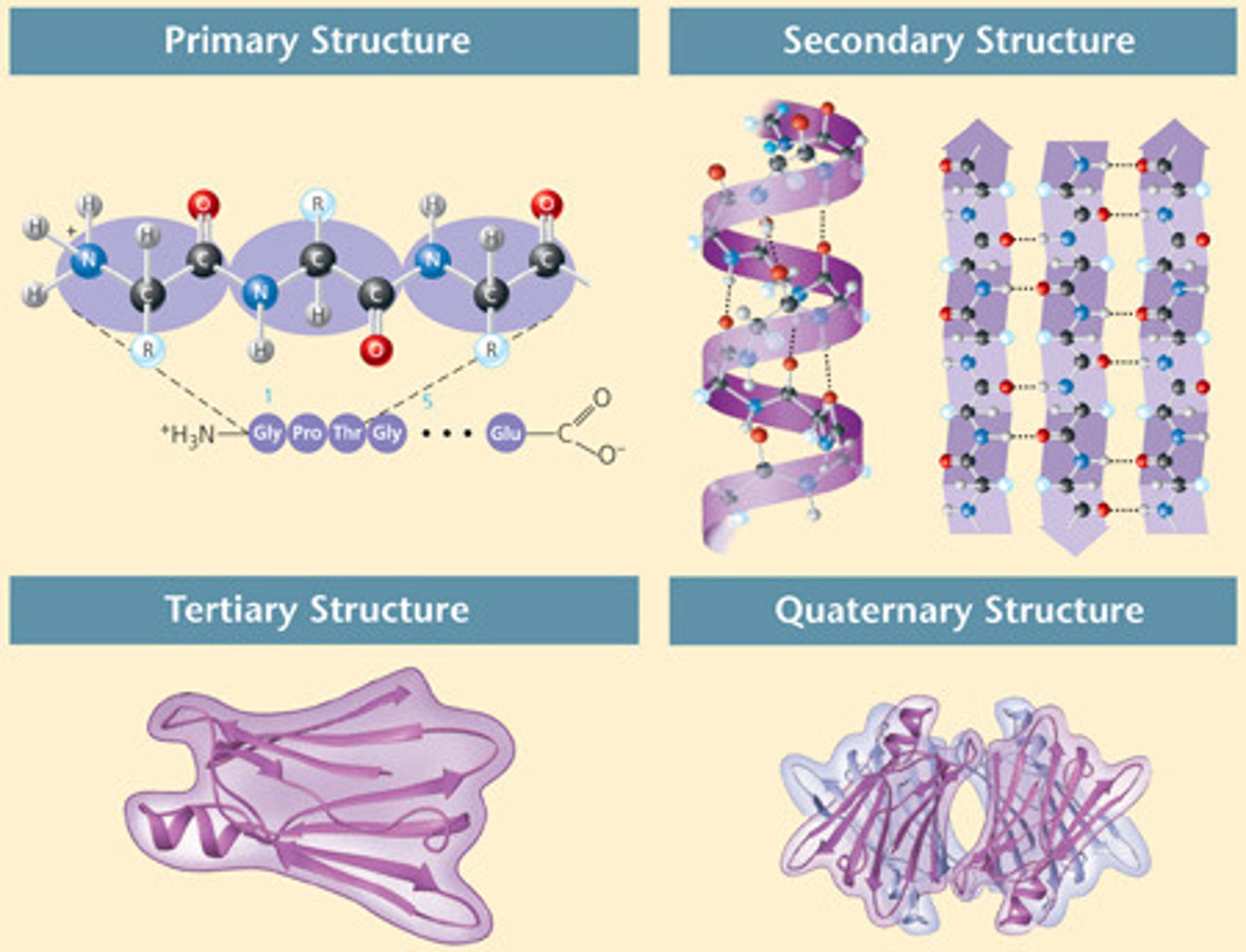
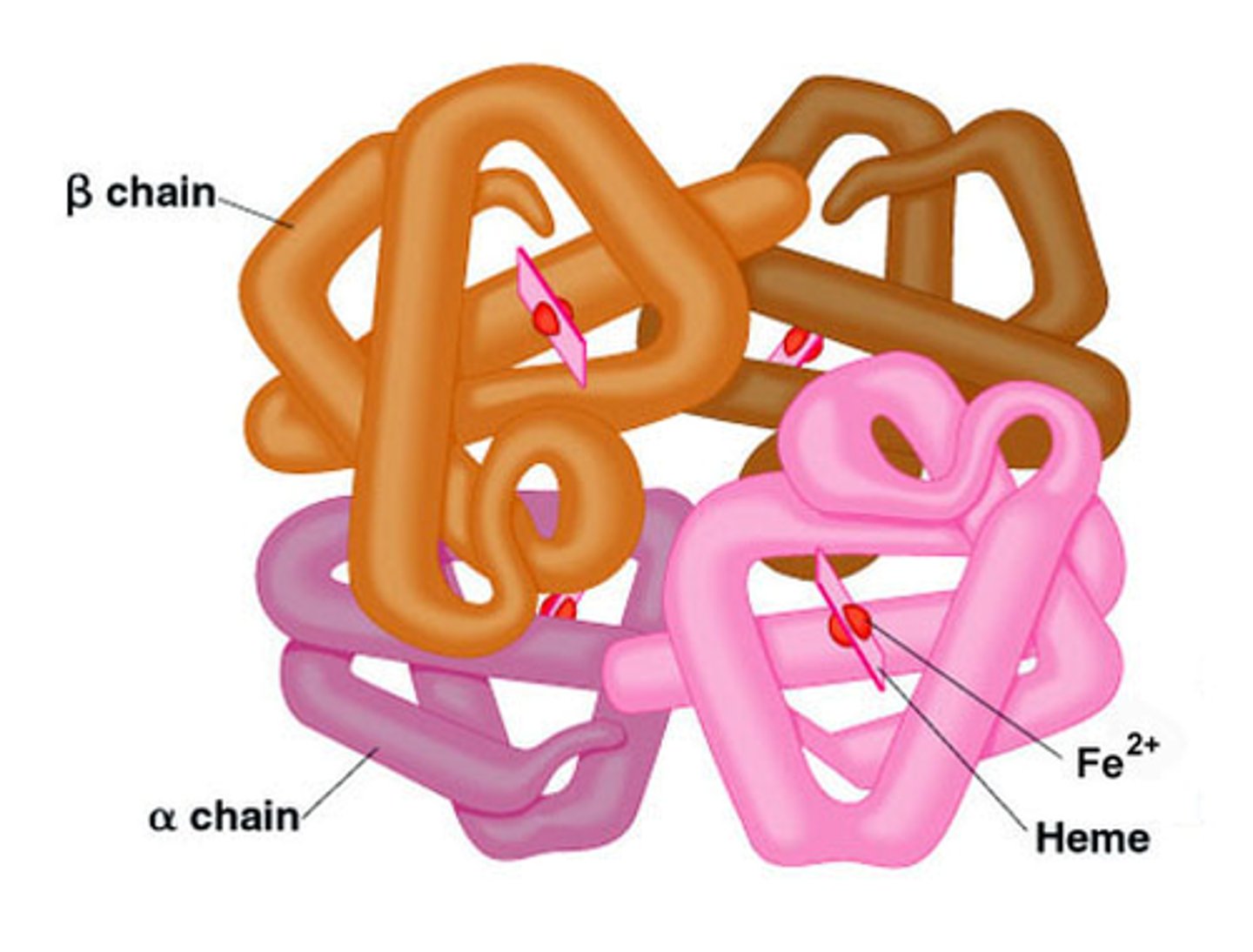
quaternary protein structure
multiple polypeptide chains interact to form a protein
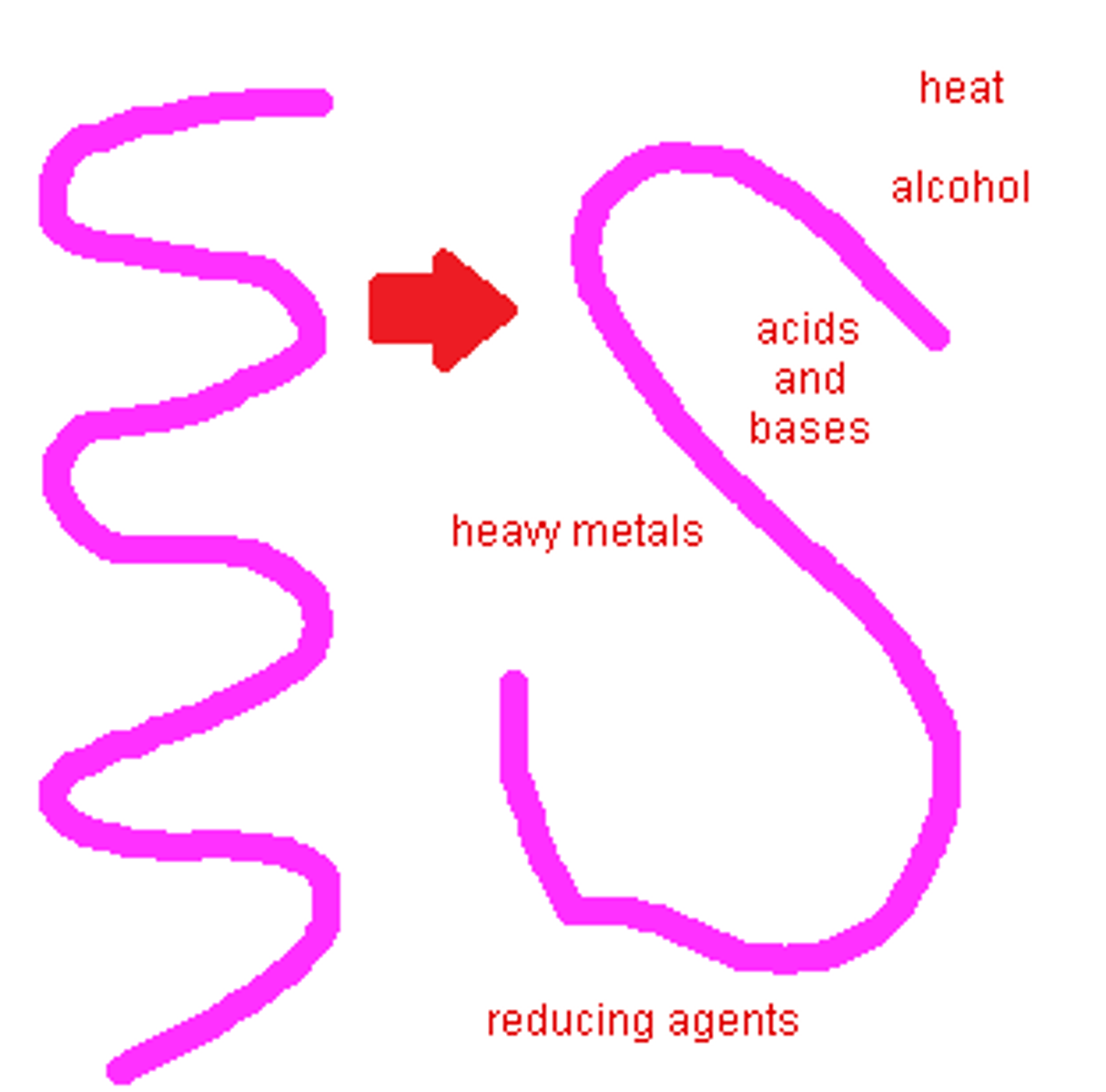
denaturation
process of protein structure being disrupted and unfolding; renders protein nonfunctional
nucleic acids
stores and transports genetic information; Monomers are nucleotides; types include RNA & DNA;
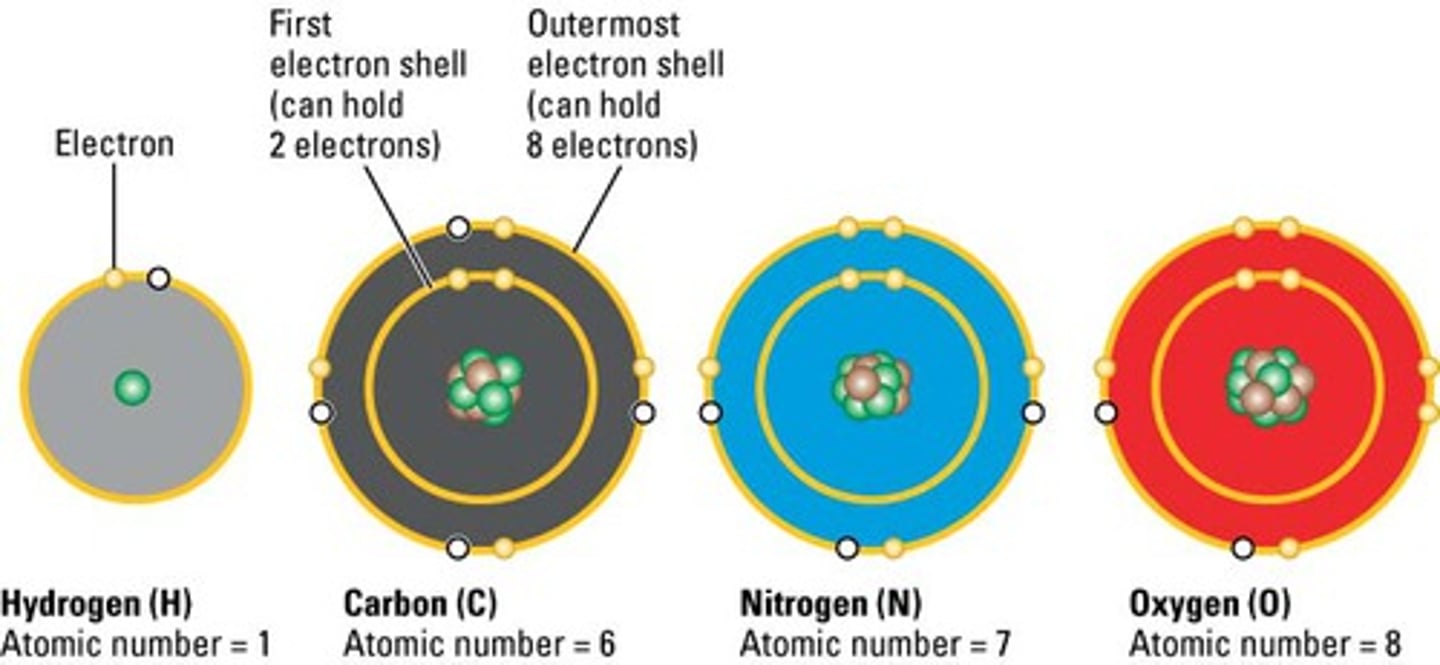
Elements necessary for life
oxygen (O), carbon (C), nitrogen (N), and hydrogen (H), phosphorus (P), sulfur (s)
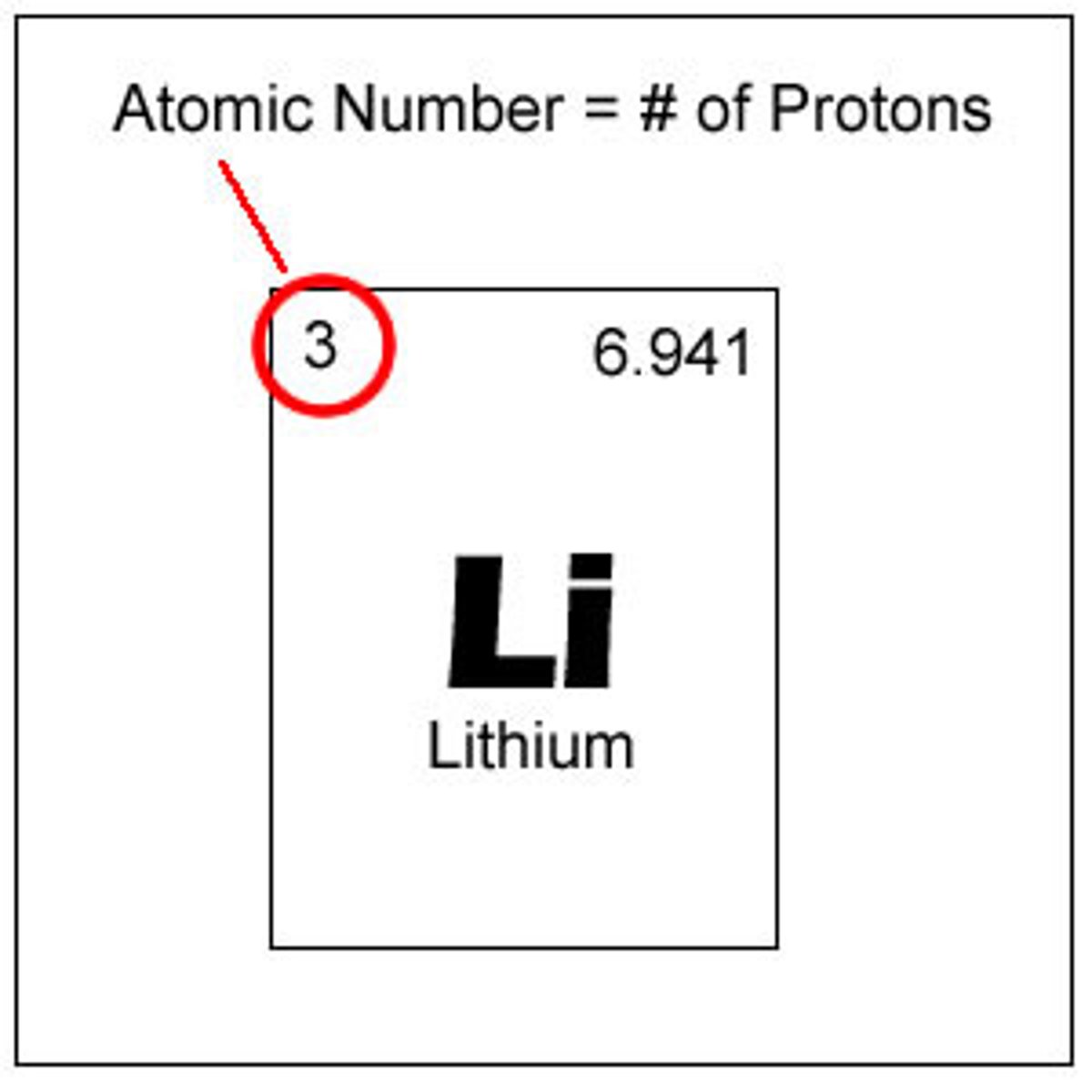
atomic number
number of protons in an element
mass number
number of protons plus number of neutrons

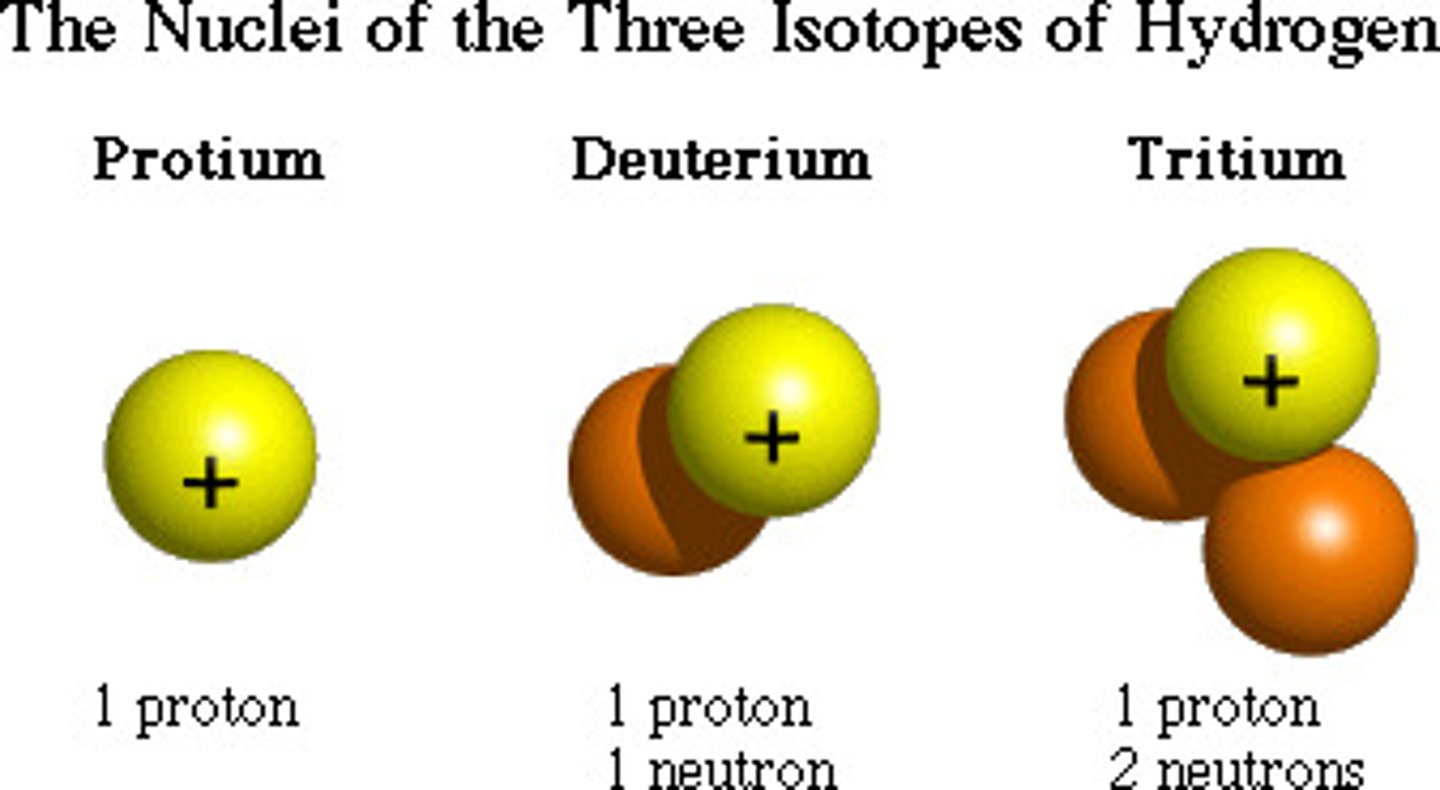
isotopes
atoms that have a different number of neutrons than normal
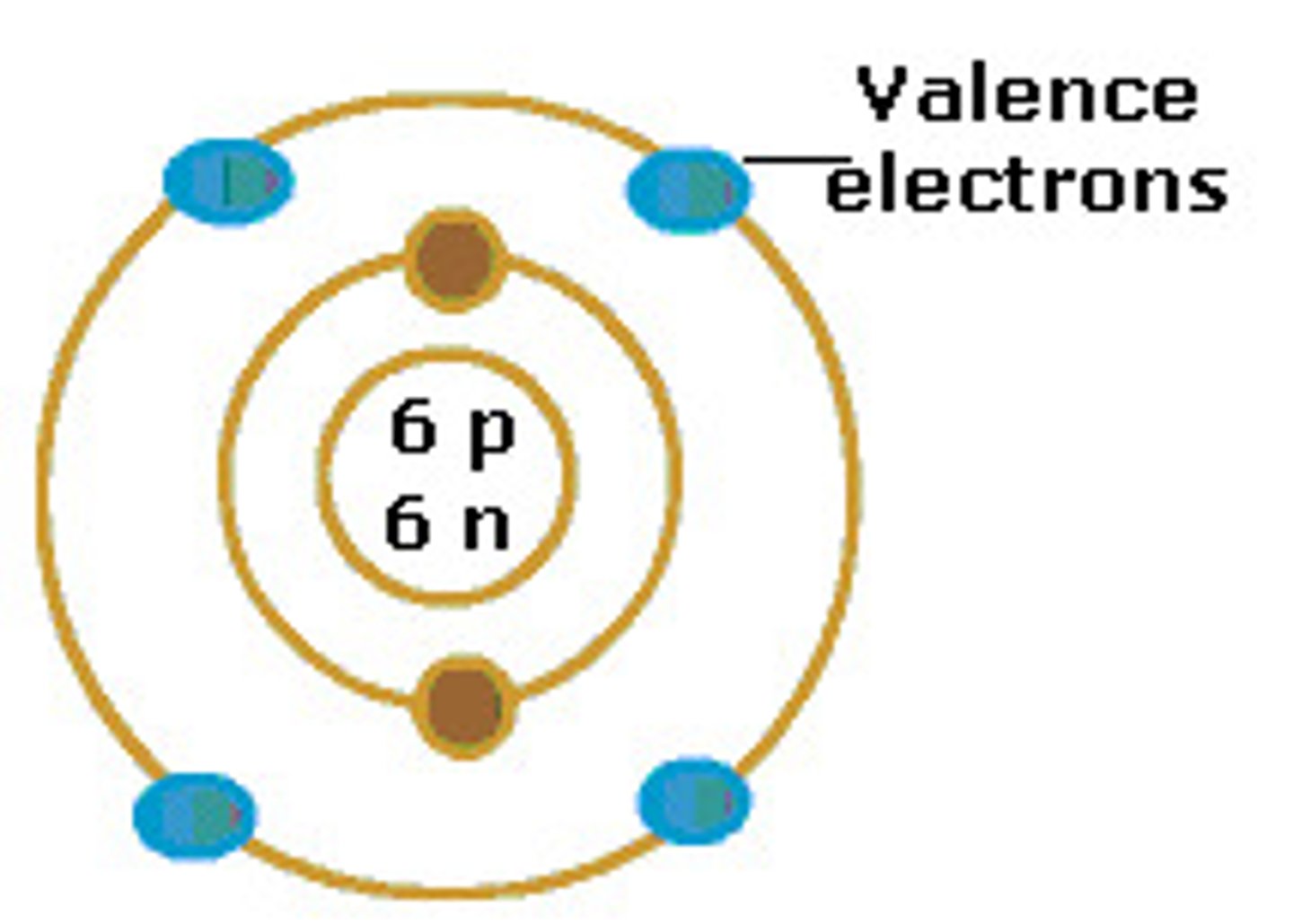
valence electrons
electrons found in the outermost "shell" orbiting the nucleus of an atom
atoms with a complete valence shell...
will not react with any other atom
chemical bonds
attractions that hold atoms together
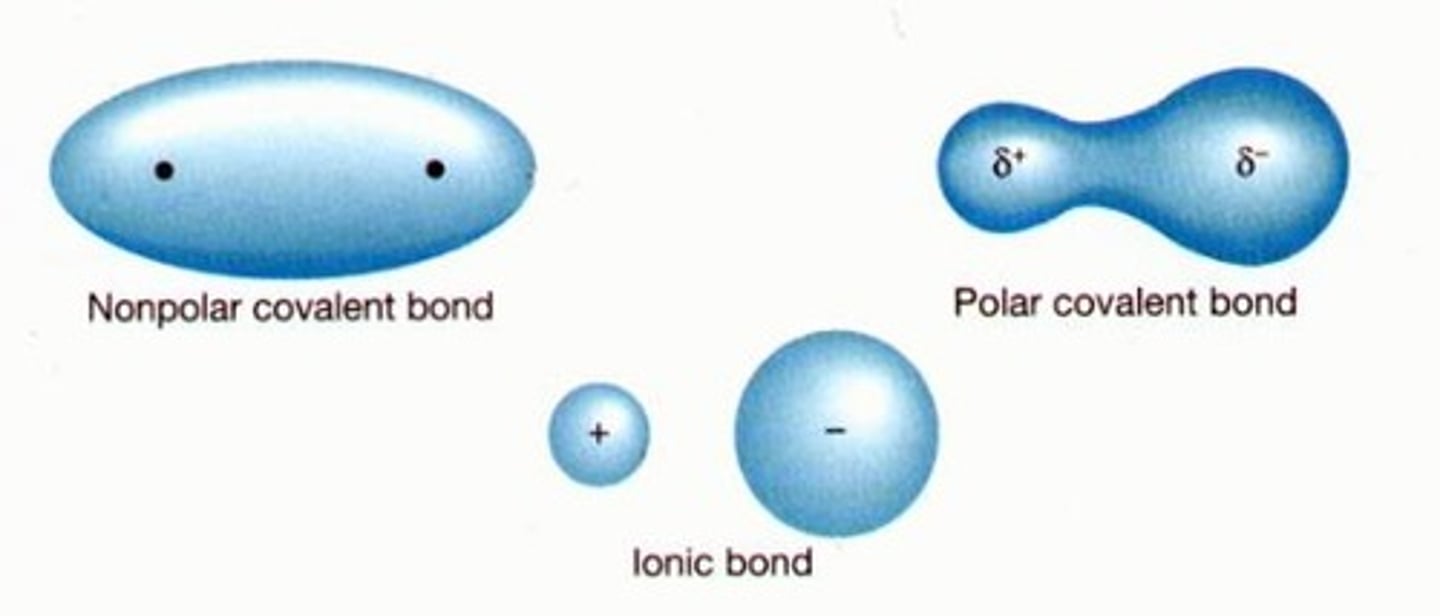
three main types of chemical bonds
covalent, ionic, hydrogen
bonds that share electrons
covalent
polar covalent bonds have...
unbalanced partial charges
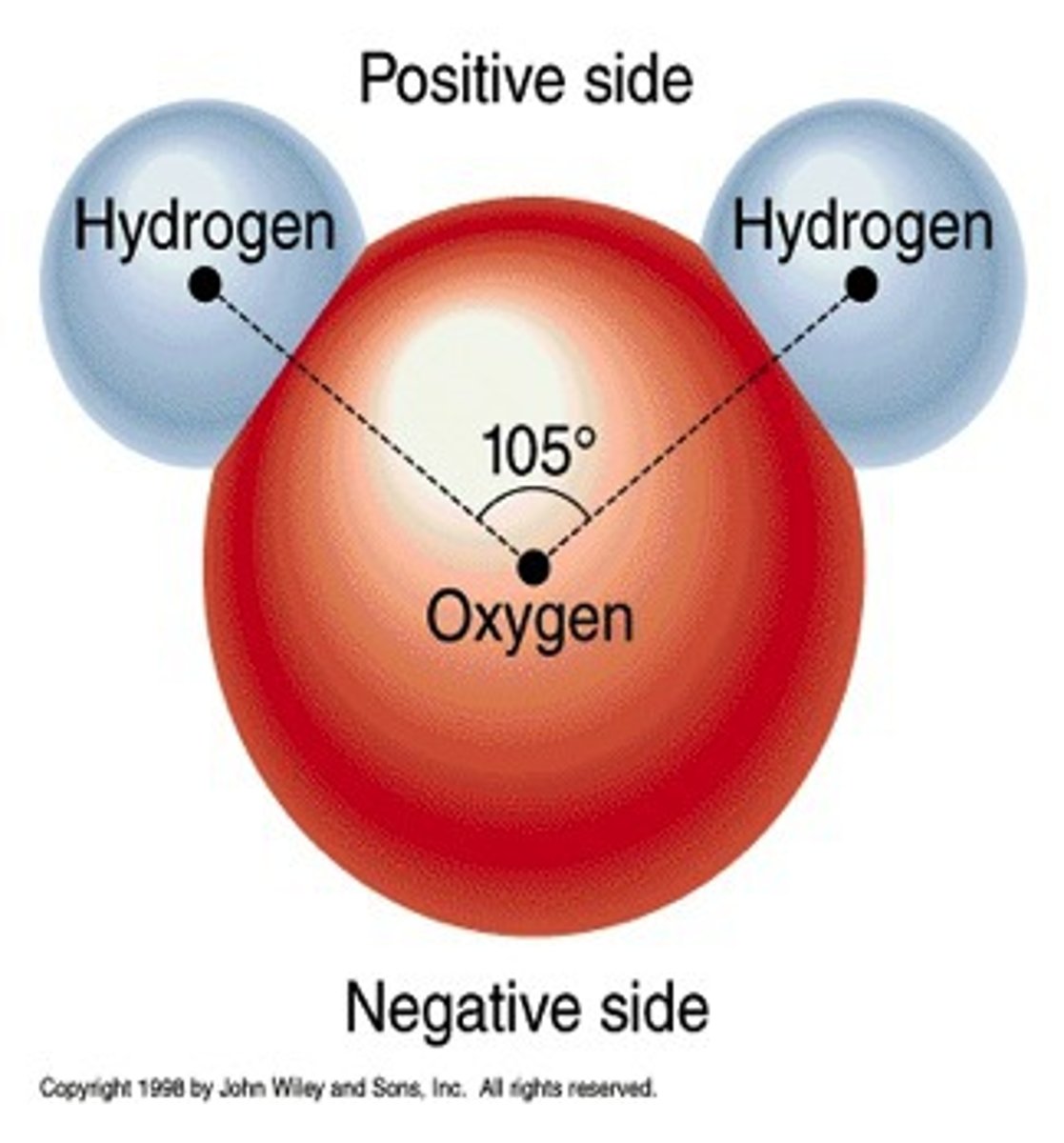
NaCl (sodium chloride) is connected by which type of bond?
ionic
weak attractions that result from polar covalent or ionic molecules being attracted to other polar covalent or ionic molecules.
hydrogen
water and DNA contain these special types of bonds in addition to covalent bonds
hydrogen
cohesion
bonding of water molecules sticking to neighboring water molecules through hydrogen bonds
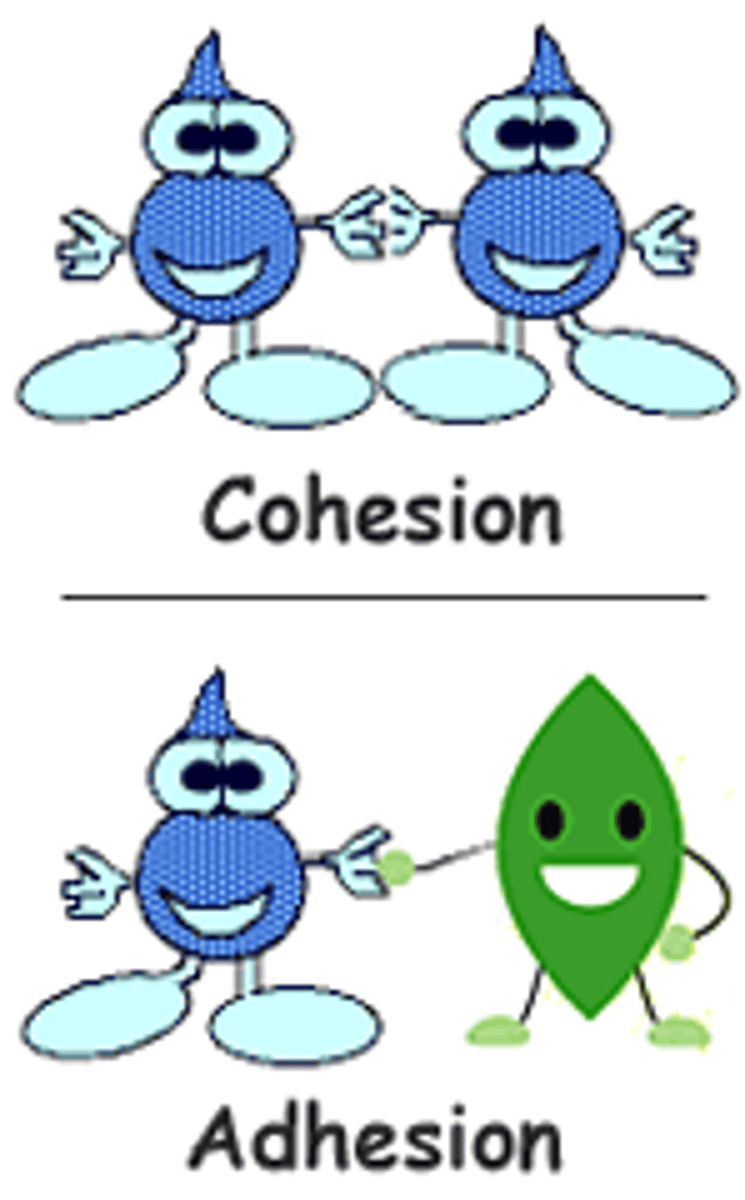
adhesion
clinging of water molecules to other substances
surface tension
a measure of how difficult it is to stretch or break the surface of a liquid

capillary action
transport of water and dissolved nutrients against gravity, usually in plants

what emergent property of water is responsible for water regulating regional and global climate?
high specific heat/high heat of vaporization/evaporative cooling
Water property responsible for ice insulating frozen ponds and lakes rather than killing everything in it?
unique density
Universal solvent
it can dissolve most polar and ionic substances
solvent
dissolving agent in a solution; usually water

solute
substance being dissolved

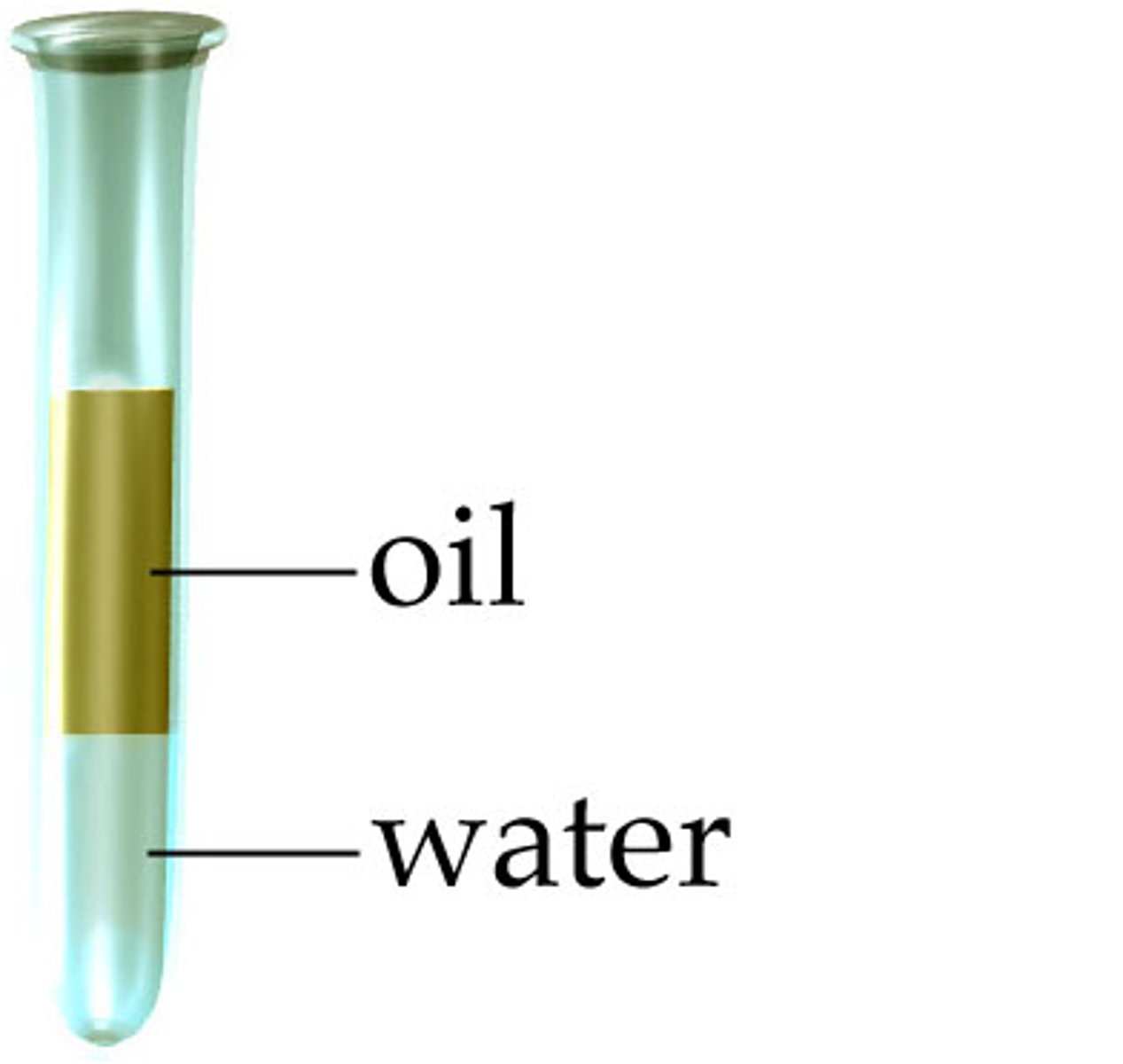
hydrophilic
water-loving; any substance that has an affinity for water; polar substances

hydrophobic
water-fearing; any substance that repels water; nonpolar substances
pH
measure of the concentration of hydrogen ions (H+) in a solution

acid (definition and pH)
substance that increases [H+] of a solution; pH 0 - 6.99
base (definition and pH)
substance that reduces [H+] of a solution; increases [OH-] of a solution; pH 7.01 - 14
buffer
substance that minimizes changes in [H+] and [OH-]; resists changes in pH
![<p>substance that minimizes changes in [H+] and [OH-]; resists changes in pH</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/cd5ec905-ab9a-45c7-8e85-eef385d33ee6.jpg)