CVP 2.2 - CAD and heart valves
1/149
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
150 Terms
heart disease
what is the leading cause of death n the US
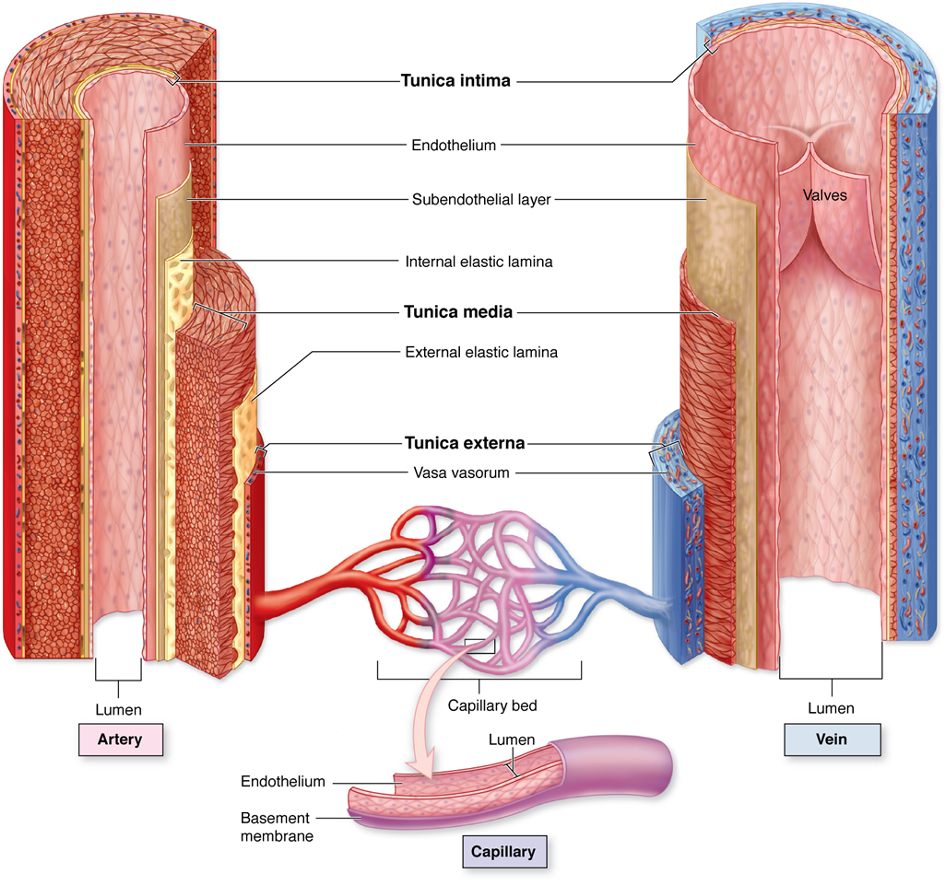
veins
(arteries or veins) have a bigger lumen
tunica externa
tunica media
tunica intima
what are the layers of a vessel? list from outer to inner
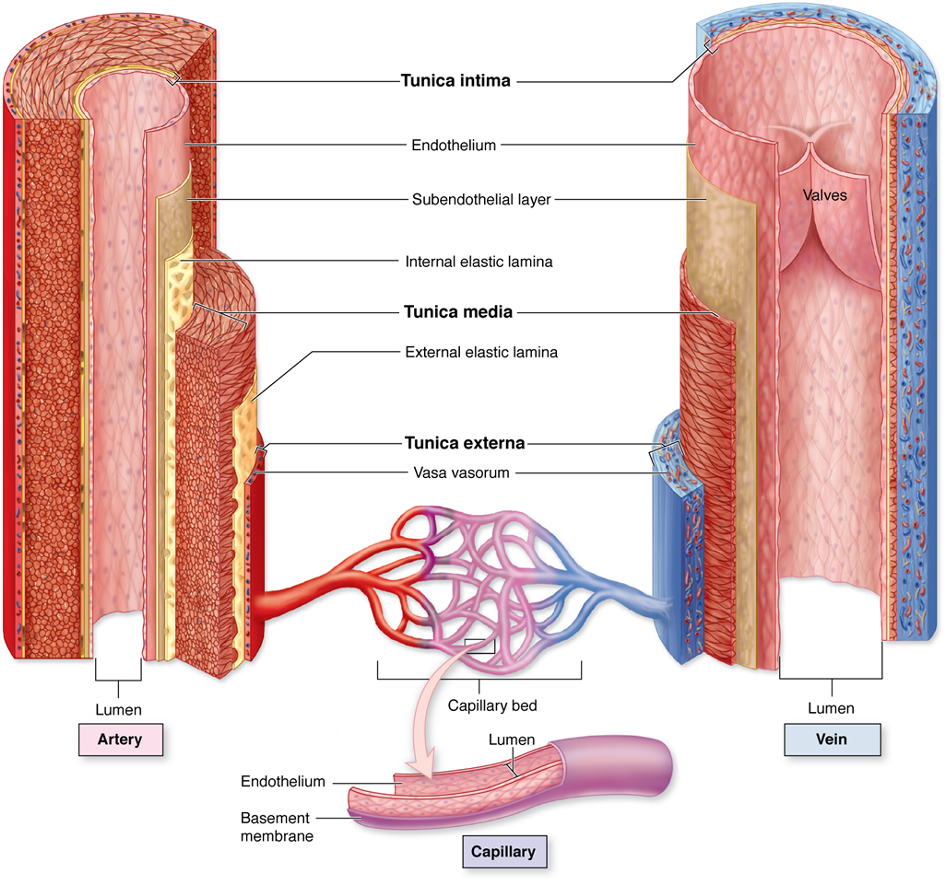
intinma
tunica __________ is a single layer of endothelium
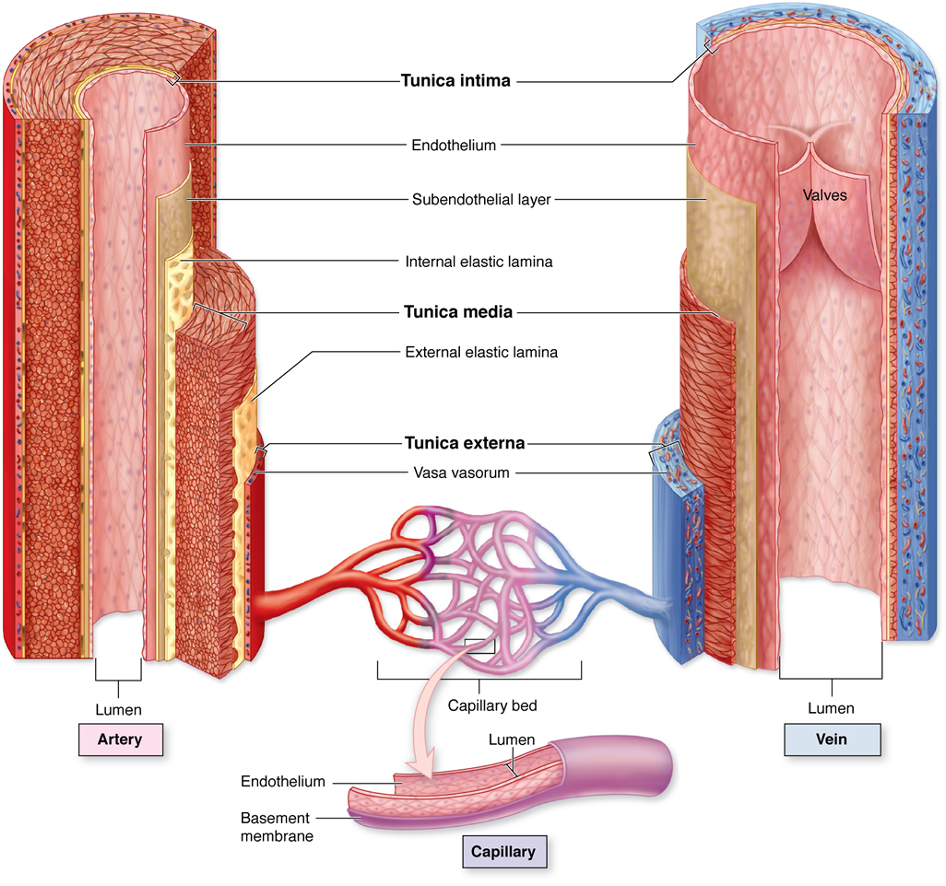
media
tunica ___________ allows vessels to stretch and rebound - in the arteries if helps with forward flow and in the veins it helps with storage of excess fluid
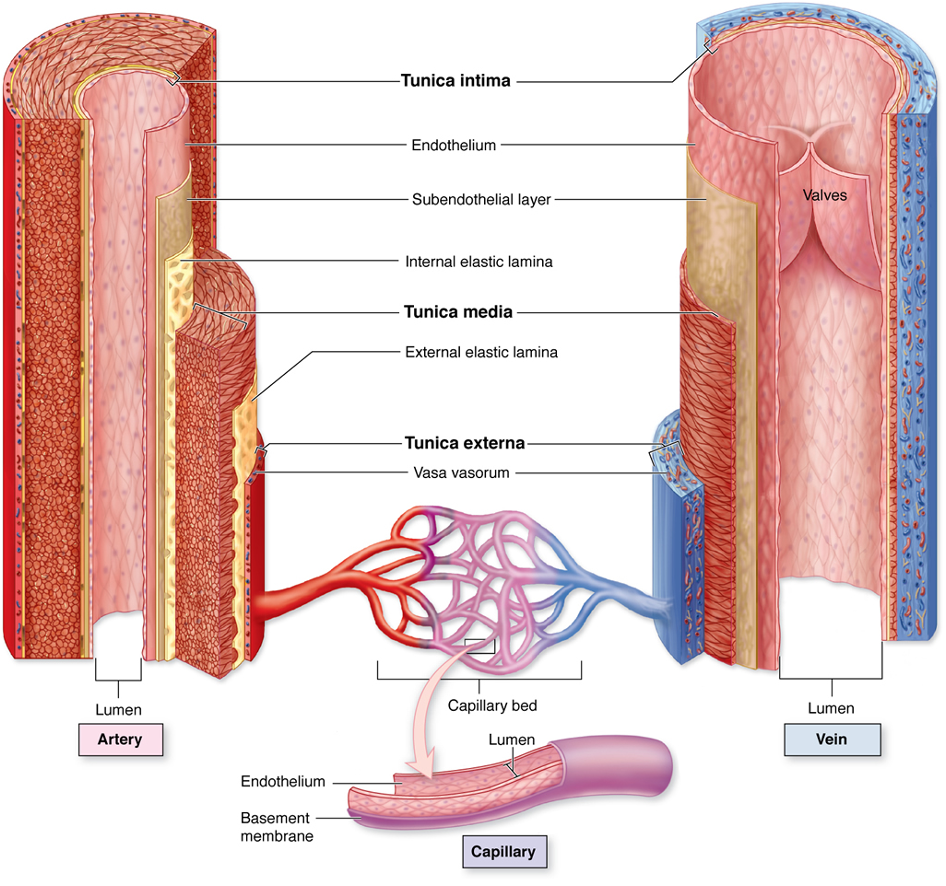
elastic fibers
collagen fibers
smooth muscle
what is the tunica media made out of
loose connective tissue
elastin
collagen
what is the tunica externa made out of
tunica externa (vasovasorum are small vessels that supply the walls of the large blood vessel)
which blood vessel layer is the vasovasorum location
tunica media (becasue of the smooth muslce)
which blood vessel layer controls vasoconstriction and vasodilation
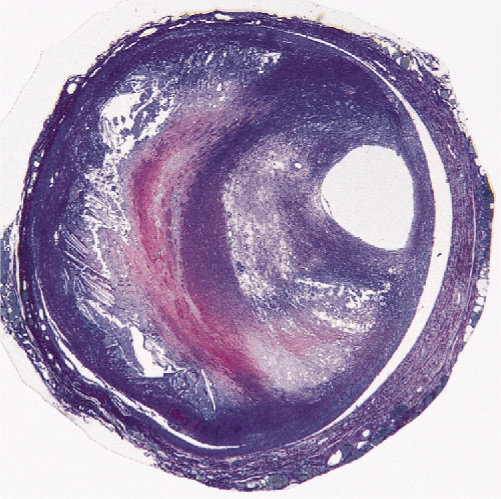
atherosclerosis
________________ is progressive hardening and narrowing of medium and large arteries
intima
the tunica ____________ is affected with atherosclerosis
coronary
cerebral
peripheral regions
what 3 locations are common for atherosclerosis
macro (affects the medium and large vessels)
is atherosclerosis a macro or micro vascular disease
fatty streak
(LDL moves into vessel → leukocytes → inflammatory response but lumen size and blood flow is fine)
plaque progression
(more lipoproteins → lumen starts to decrease in size)
plage disruption
(plaque becomes unstable → can result in emboli and thrombus formation)
what is the 3 progression phases of developing atherosclerosis
endothelial (inner layer)
with atherosclerosis, the fatty streak affects the ________ cells in the blood vessel
lipoprotein (LDL… bad cholestrol); inflammatory
with atherosclerosis, the fatty streak is caused by ___________ entry into the vessel, this leads to a __________ response
leukocytes; macrophages
when there is a atherosclerosis fatty streak, extra inflammation happens in the vessel which recruites ____________ cells which later turn into ____________ which get stuck and can lead to blood clots and promote the formation of the atherosclerotic plaques/plaque progression
thrombogenic lipid core
during the plaque formation in atherosclerosis, there is a _______________ beneath the protective fibrous cap that promotes blood clot formation
intima
during the plaque formation in atherosclerosis, smooth muscle migrates from the tunica media to the tunica ___________ which increases collagen synthesis
extracellualr matrix
during the plaque formation in atherosclerosis, metabolism of the ____________ that creates a either stable or unstable fibrous cap (plaque is now more likely to rupture → plaque disruption)
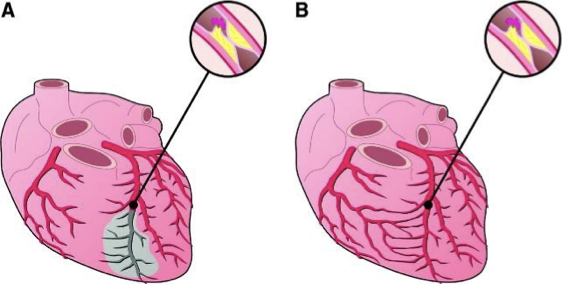
rapid (picture A)
with atherosclerosis, (rapid or slow) occlusion causes myocardial death
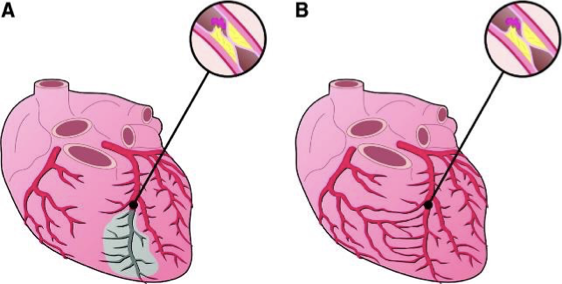
slow (picture B - this is why someone can have a 100% occlusion and no symptoms of a MI)
with atherosclerosis, (rapid or slow) occlusion causes collateral formation
EDUCATION
diet
exercise
meds to control hyperlipidemia (bad cholesterol that builds up in the tunica intima)
what are the 4 ways to medically manage atheroclerosis
men
(men or women) are more likely to develop atherosclerosis
diastole
the coronary arteries are perfused during ventricular (systole or diastole)
ischemic heart disease
_______________ is the imbalance between supply and demand of oxygen
tissue hypoxemia
accumulation of waste
what are the two results of ischemic heart disease
stable angina
on the spectrum of angina pectoris, which is narrowing of the vessel and vasoconstriction - epidose of ischemia
normal
stable angina
unstable angina
variant angina
unstable angina
on the spectrum of angina pectoris, which is where the atherosclerotic plaque has been disrupted - vessels always vasoconstricted without medication
normal
stable angina
unstable angina
variant angina
variant angina
on the spectrum of angina pectoris, which has no atherosclerosis and intense vasospasm
normal
stable angina
unstable angina
variant angina
levine; chronic stable angina
when someone places a clenched fist over the sternal region it is called the __________ sign which is a common sign/sx of _____________
“a few minutes” (but less than 5-10min)
how long do the symptoms of a chronic stable angina last
common locations
retrosternal or left precordium - most common
chest
arms
neck
lower face
upper abdomen
radiating
shoulders
inner aspect of arm - usually left arm
where are the 6 common locations of chronic stable angina? which are the most common?
where would one with chronic stable angina feel radiation pain
fixed
when the level of activity to trigger symptoms is relatively constant, it is referred to as ________ threshold angina
variable
when the level of activity to trigger symptoms is dynamic, it is referred to as ________ threshold angina
3-5 min
symptoms of chronic stable angina will usually resolve in ___________
variant
___________ angina is caused by coronary artery spasm
decubitus or resting
____________ angina occurs most often when at rest and frequently occurs at the same time every day
unstable; 2 weeks
new onset angina is considered (stable or unstable) and is defined as having developed for the first time within the last ___________
nocturnal (usually due to inc HR in sleep or in response to underlying heart failure)
____________ angina may awaken a person from sleep with the same sensation experienced with exertion
pre-infarction
______________ angina is defined as lasting over 15 minutes, worsening cardiac ischemia symptoms, and an abrupt change in intensity and/or frequency of symptoms or decreased threshold to onset of sx
post-infarction
______________ angina occurs after MI when residual ischemia triggers episode of pain
organic nitrates
____________ medication for angina pectoris decreases O2 demand by…
decreasing preload
increasing O2 supply by…
inc coronary perfusion
dec coronary vasospasm
beta blockers
____________ medication for angina pectoris decreases O2 demand by…
decreasing contractility
decreasing HR
calcium channel blockers
____________ medication for angina pectoris decreases O2 demand by…
decreasing preload
decreasing BP
decreasing contractility
increasing O2 by…
inc coronary perfusion
dec coronary vasospasm
ranolazine
____________ medication for angina pectoris decreases O2 demand by…
decreasing late phase inward sodium current
beta blockers
which medication for angina pectoris can cause bronchoconstriction and can mask hypoglycemia sx
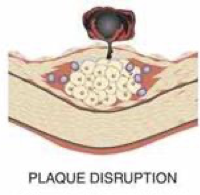
plaque disruption; intracoronary thrombus
acute coronary syndrome is caused by the _____________ phase of atherosclerosis and the formation of ______________
partially; completely
acute coronary syndrome can either be ___________ or ___________ occlusive thrombus
partially
an acute coronary syndrome that has (partially or completely) occlusive thrombus is caused by unstable angina or non-ST segment elevation MI
completely
an acute coronary syndrome that has (partially or completely) occlusive thrombus is caused by ST segment elevation MI
both (they both result in necrosis)
with acute coronary syndrome, does a non-ST segment elevation MI or ST-segment elevation MI result in necrosis
no (but it is a high risk for MI)
can an unstable angina cause necrosis
myocyte necrosis
_____________ is secondary to prolonged ischemia
20-24
ischemia that lasts ______-______ minutes leads to irreversible cell injury
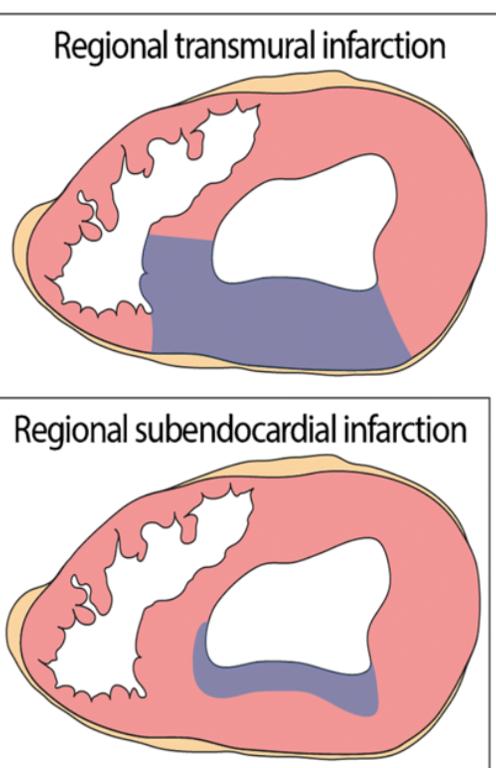
transmural
a _____________ infarct is necrosis that spans to the myocardial wall
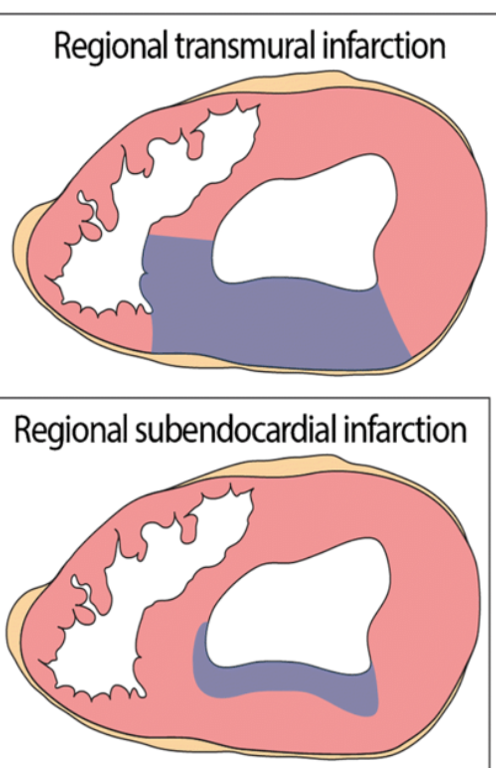
subendocardial
a _______________ infarct is necrosis of the inner layers of myocardium
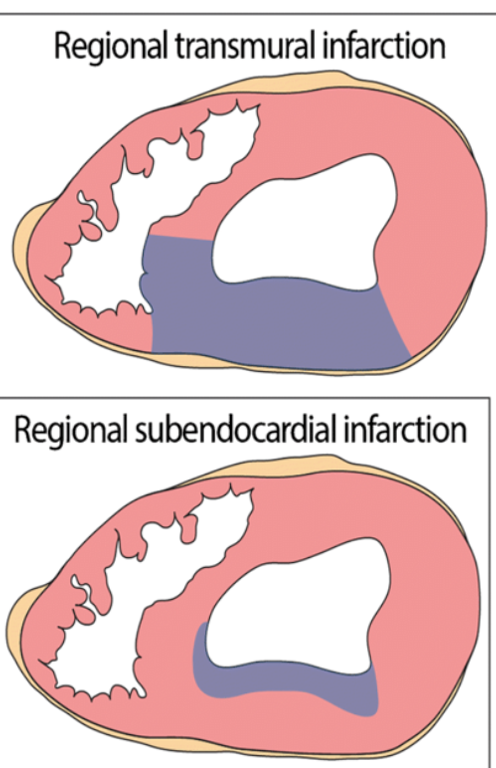
transmural (transmural has much more wall stiffness, outer walls with subendo can still produce force)
the (transmural or subendocardial) infarct produces less contractile force
MI
prompt medical treatment of an unstable angina with acute coronary syndrome can prevent __________
do not
rapid
nitroglycerine
the main clinical presentations that acute MI of acute coronary syndrome is:
symptoms (do or do not) change with rest
(rapid or insidious) onset of symptoms
little effect from use of ________________
ST segment; T
the EKG of an acute coronary syndrome - acute MI will present with the ________ wave depressed and the _______ wave inverted
<14
the normal level of troponins is __________ng/L
NOOOOOOO (indicates cell death and/or heart damage)
can you still do PT with a patient that has increasing levels of troponin
3-5
the normal level of creatine kinase is _____-_____%
nope
can you still do PT with a patient that has increasing levels of creatine kinase
anti-ischemic (beta-blockers, nitrates, Ca channel antagonists)
antithrombotic (antiplatelet, anticoagulant)
a pt with acute coronary syndrome should be on ___________ medication with ___________ therapy
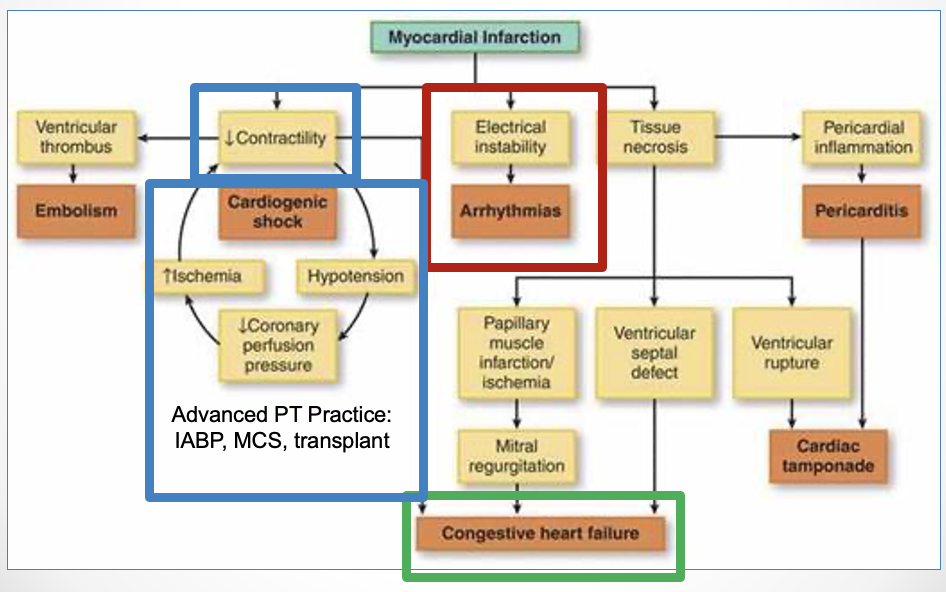
arrhythmias
heart failure
cardiogenic shock
what are the 3 main complications of acute coronary syndrome - acute MI for PT
percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI)
the surgical treatment for acute coronary syndrome is ______________
radial
femoral
what are the 2 locations for access for percutaneous coronary intervention surgery (treatment for acute coronary syndrome)
but you’re killing it
SO MANY CARDS
4-6
after a pt has percutaneous coronary intervention, PT should ambulate within ______-______ hours
internal mammary artery
saphenous vein
which two vessels can be used for a coronary artery bypass treatment
oICU
o Continuous telemetry
o Ventilator vs. Supplemental O2
o Arterial line
o Central venous catheter (R IJ)
o Epicardial pacemaker
oChest tube
mental note - CABG patients have alllllllllllll the leads
epicardial
the _____________ pacemaker is a “temporary pacemaker”
yes (except immediately after wire removal ~2-6 hours, **note it is a heavy device so it must be secured)
can a pt with an epicardial pacemaker do PT
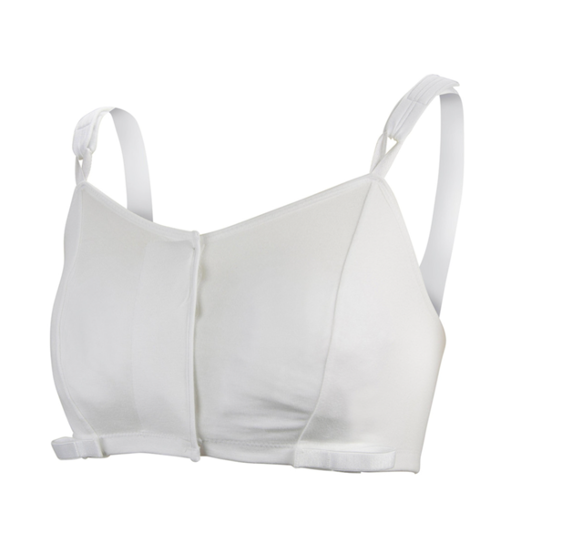

post-op bra
what is a protective device for a female post sternotomy
annulus
the __________ is the base of each valve
chordae tendineae
the ____________ tethers AV valves to papillary muscles
dense connective tissue
fibrocartilage
what is the cardiac skeleton made of
papillary muscles
______________ contract during V systole and pull on chordae and prevent valve from opening during systole
tricuspid; pulmonic
the _________ and _________ valves are on the right side of the heart
mitral; aortic
the __________ and _________ valves are on the left side
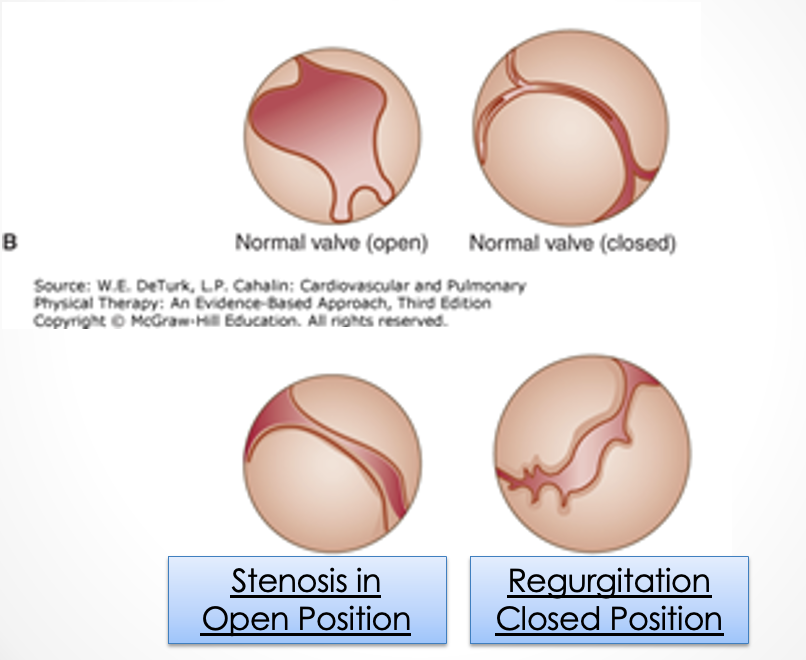
stenosis
___________ is a valve dysfunction where the valve is narrowed or stiff preventing full opening so there needs to be increased pressure to move blood out of chamber
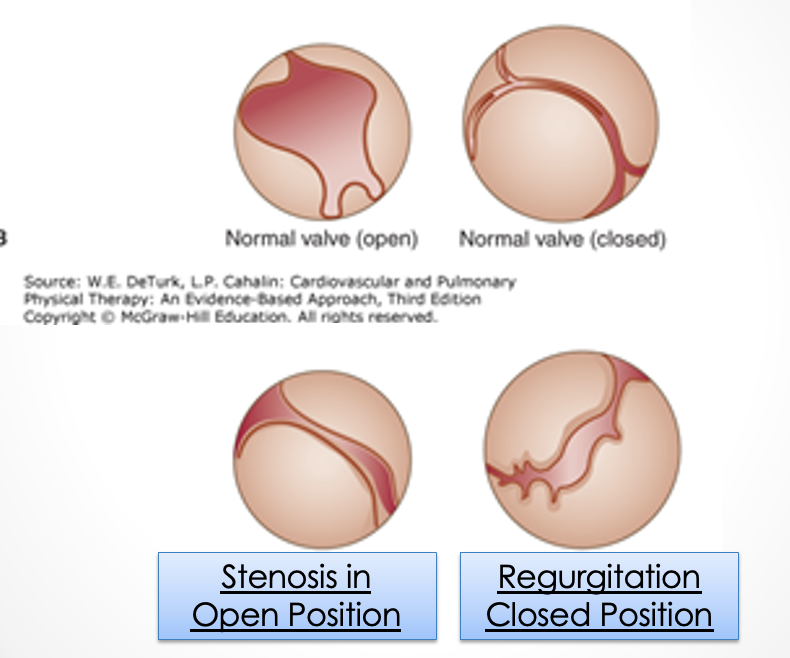
regurgitation
___________ is a valve dysfunction where the valve doesn’t close all the way so some blood flows backward during systole and reduces ventricular output/ejection fraction
false
T/F: males are more likely to have a valve disease
left atria
with mitral valve stenosis, the _________ chamber of heart is unable to completely empty
rheumatic fever
calcification of annulus
infective endocarditis
congenital stenosis
what are the 4 etiologies of mitral valve stenosis
increase; decrease
mitral valve stenosis (increase or decrease) pressure in the LA and (increases or decreases) pressure in the LV
false (decrease CO because less flow to the LV → dec stroke volume → dec CO)
T/F: mitral valve stenosis increases cardiac output
forward (decrease vol → dec SV → dec CO)
the effects of (forward or back) flow of mitral valve stenosis is defined as decreased volume in the left ventricle
back
the effects of (forward or back) flow of mitral valve stenosis is defines as increased volume and pressure in the left atria
stays the same (normal)
during forward flow mitral valve stenosis, the pressure in the LV __________
back (causes increased volume and pressure)
the (forward or back) flow of mitral valve stenosis is associated with right sided heart failure, LA enlargement, A-fib, and increased pulmonary pressure
dyspnea
reduced exercise capacity
atrial fibrillation with activity/stress
increased HR and/or CO induce increased symptoms (caused by fever, anemia, hyperthyroidism, pregnancy, emotional stress, sexual intercourse, etc.)
what are the 4 early signs and sx of mitral valve stenosis
dyspnea AT REST
increased fatigue
pulmonary congestion (orthopnea, paroxysmal nocturnal dyspnea)
R sided heart failure
hoarseness (compression of laryngeal nerve by enlarged pulmonary artery or left atria)
what are the 5 late signs and sx of mitral valve stenosis
mitral
S1
pulmonary congestions (remember this is a late sign/sx)
right
exam results of mitral valve stenosis:
diastolic heart murmur loudest over area of ________ valve
change of volume in (S1 or S2)
lung auscultation _______________
______ sided heart failure s/sx
endocardiogram (thickened MV leaflets, possible atrial thrombus, left atrial enlargement)
EKG (possible A fib, increase atrial size, and pulmonary hypertension)
exercise testing with doppler assessment
cardiac catheterization (measures heart pressures)
primary study = endocardiogram
what the 4 diagnostic studies for mitral valve stenosis? which is the primary study?
manage vascular congestion (reduce salt, diuretic medication)
increase diastolic filling time (slow HR: beta blockers, Ca channel blockers)
prevent thromboembolism (anticoagulation therapy)
surgical management
what are 4 treatment options for mitral valve stenosis
cordea tendinaea rupture
papillary muscle dysfunction or rupture
left ventricular enlargement or dysfunction
annular calcification
diseased leaflets
what are the 5 etiologies of mitral valve regurgitation
LV; LA
mitral valve regurgitation is where a portion of the _________ heart chamber stroke volume is ejected backward into the _________ heart chamber