Endocrine disorders - The Thyroid Gland: Hypothyroidism
1/6
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
7 Terms

Hypothyroidism
Deficiency in thyroid hormone
Most commonly found in dogs
Usually caused by lymphocytic thyroiditis - autoimmune
Usually 6-10 years of cages
Causes inflammation within the thyroid gland
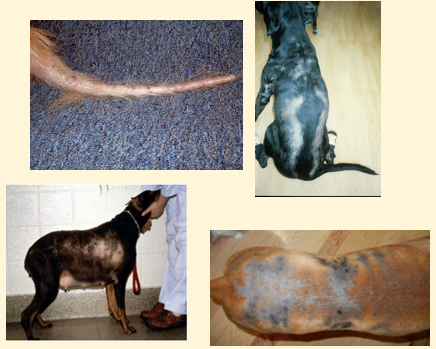
Clinical signs of HypoT4
‘Great impersonator’
Lethargy - lack of thyroid hormone
Weight gain
Symmetrical alopecia - patchy, ‘rat-tail’
Skin disease - pyoderma, seborrhoea
Occasionally see cardio and neuro abnormalities
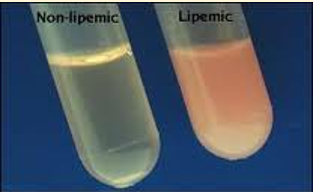
Diagnosis of HypoT4
Clinical signs
Routine blood tests - Hypercholesterolemia, Mild non-regenerative anaemia
Low Total T4
Raised TSH
Management of HypoT4
Levo-thyroxine replacement
Tablet - Thyforon - Recommends trough (pre dose) and peak (3h post)
Liquid - Leventa - Recommend at peak (4-6h post)
Monitor serum T4 concentration - ‘post-pill’ (differs with drug)
Improvement can take 6-8 weeks
Levo-thyroxine
Identical to endogenous thyroxine
Binds thyroxine receptors to regulate metabolism, cardiac function and blood flow, lipid and carbohydrate metabolism
Levo-thyroxine - Pharmacology
Oral administration
Variable Tmax and half life
Variable dose frequency recommendation (once or twice daily)
Consistent with feeding routine
Nursing care for HypoT4
Care when handling
Skin care
Nutrition - weight loss
Regular diagnostic tests
Owner support