Human Responses to the Environment
1/101
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
102 Terms
Stimulus
a signal to which an organism responds
environment
the surroundings or conditions in which a person, animal, or plant lives or operates.
Receptors
structures specialized to detect certain stimuli
Interoceptors
detect internal stimuli, usually chemical stimuli
Exteroceptors
detect external stimuli, are therefore located on the surface of the body.
Propioceptors
Provide information about body position and motion, are located in the inner ear.
sight
the sense through which we detect light stimuli
Photoreceptors
cells in the retina that initially transform light stimuli into nerve impulses
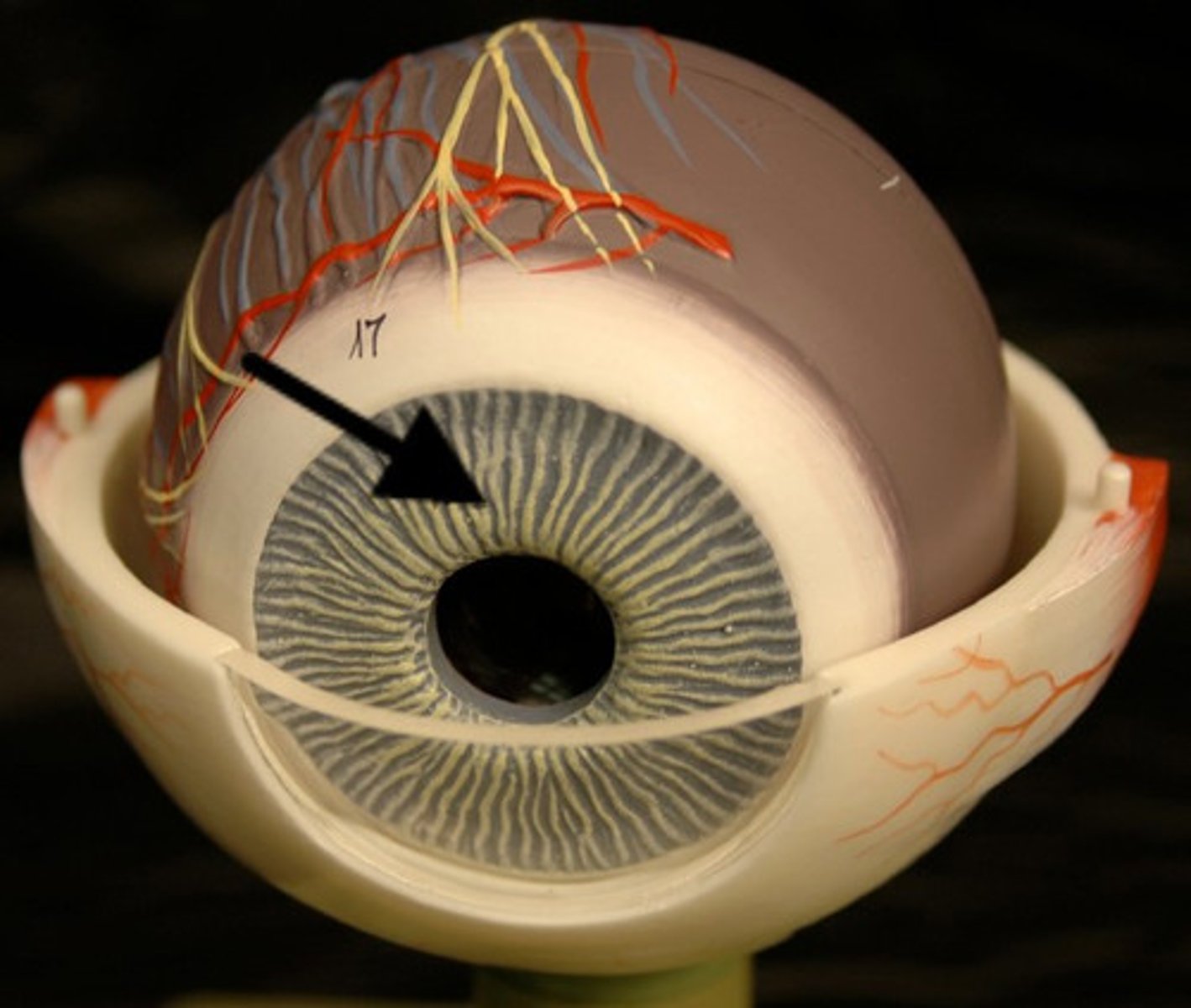
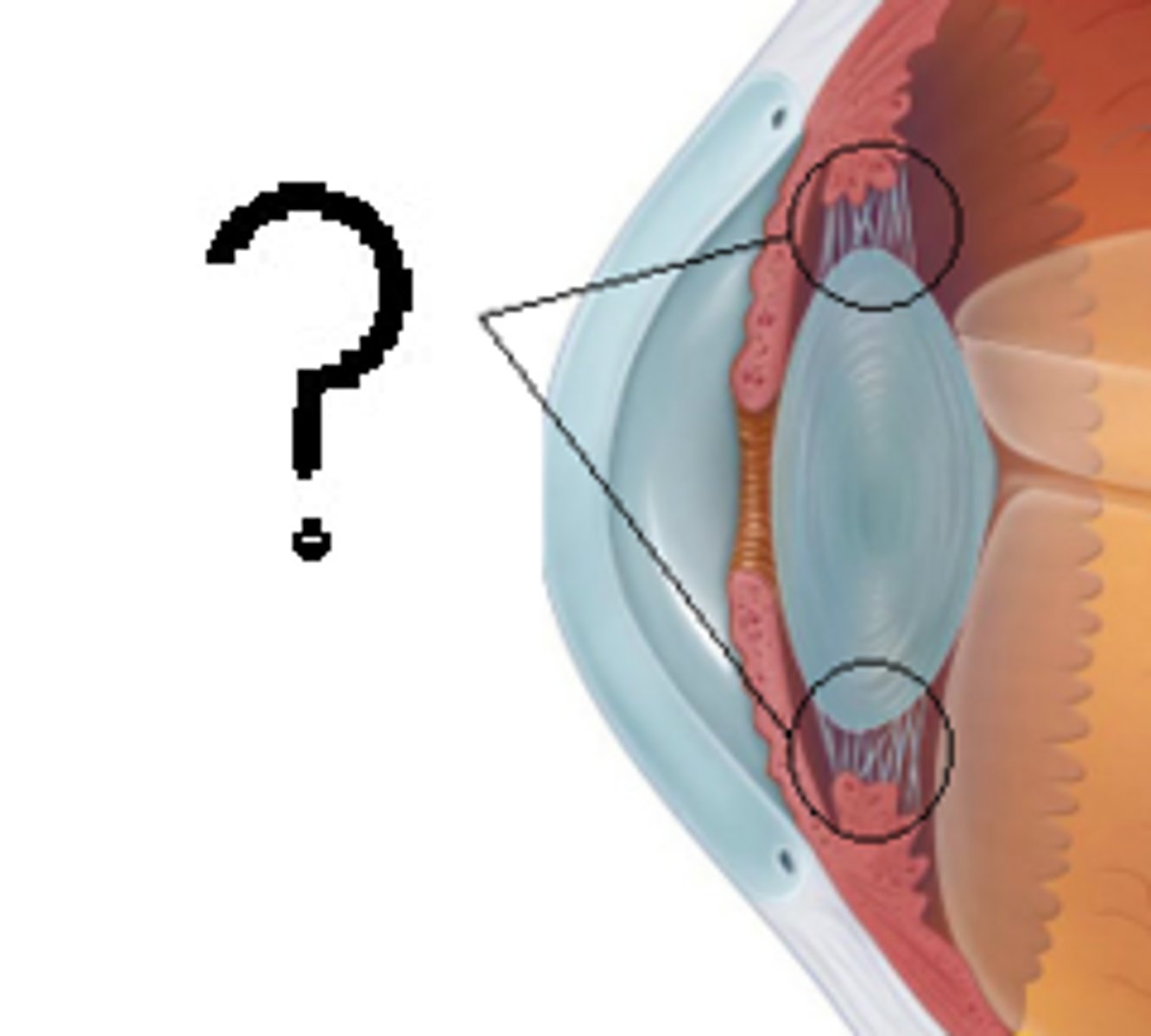
Iris
a ring of muscle tissue that forms the colored portion of the eye around the pupil and controls the size of the pupil opening
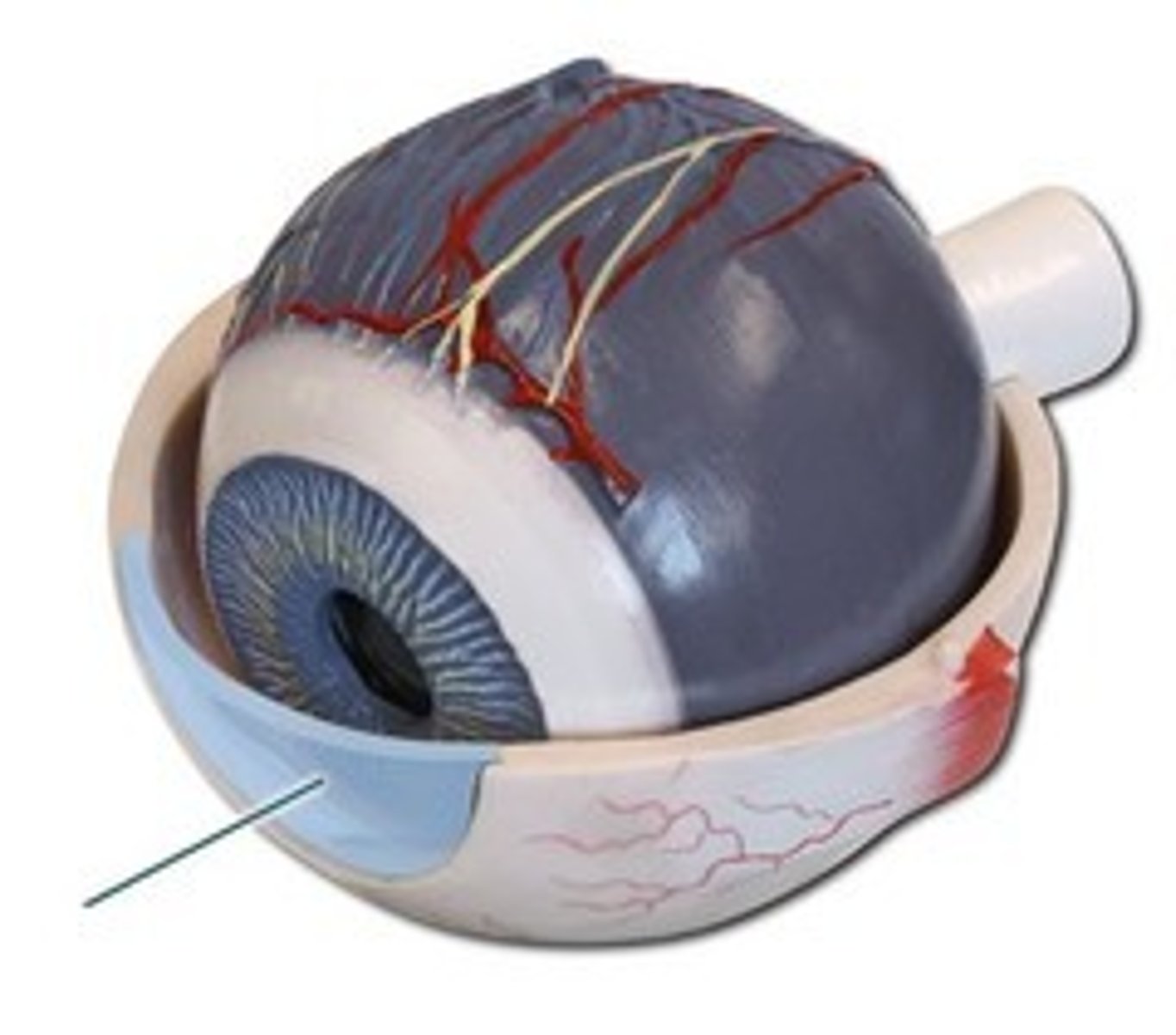
Cornea
The clear tissue that covers the front of the eye. It acts like a lens to focus the light rays into the pupil
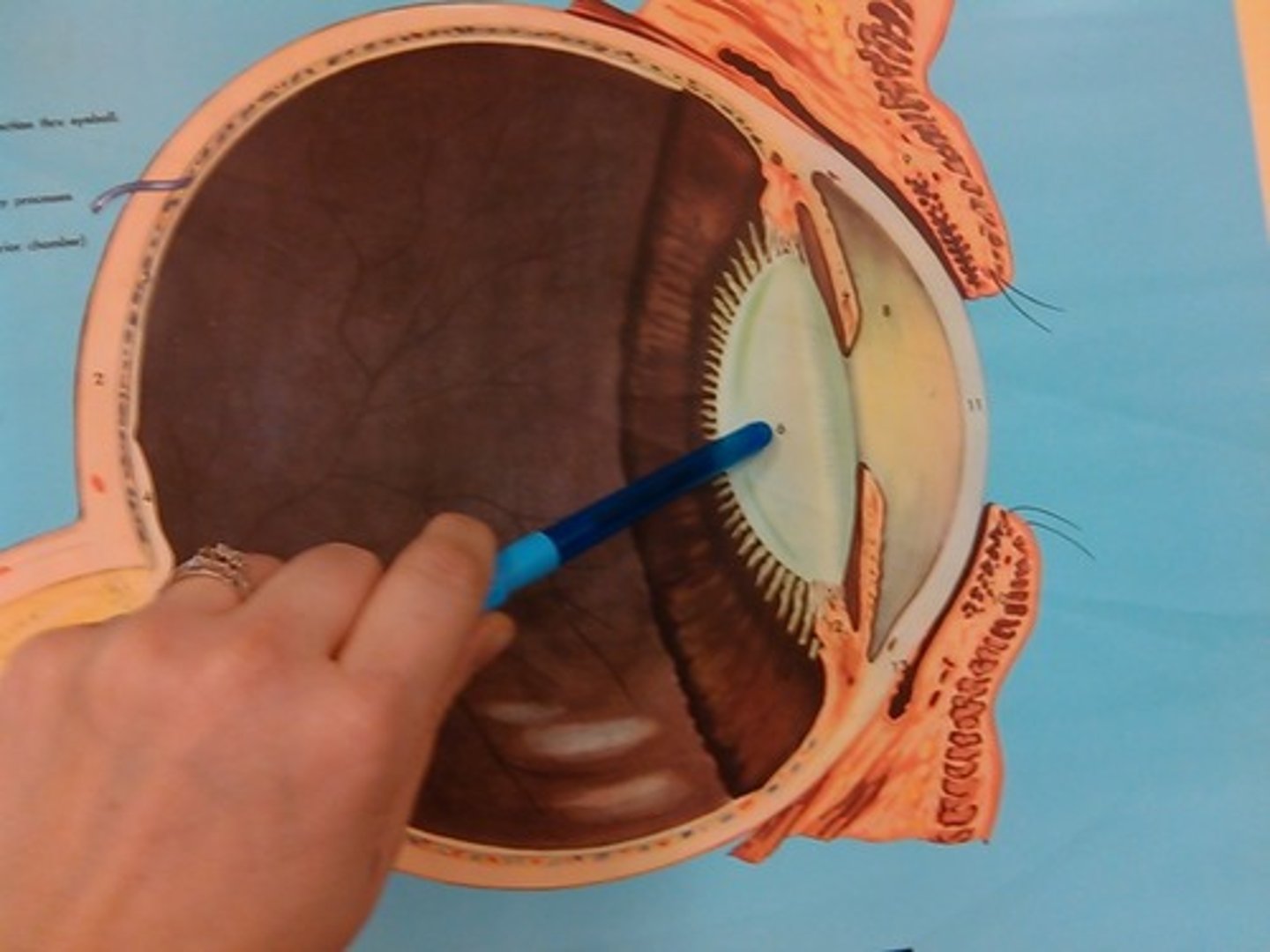
crystalline lens
the lens inside the eye, which focuses light onto the back of the eye
accommodation
the process by which the eye's lens changes shape to focus near or far objects on the retina
pupil
the adjustable opening in the center of the eye through which light enters
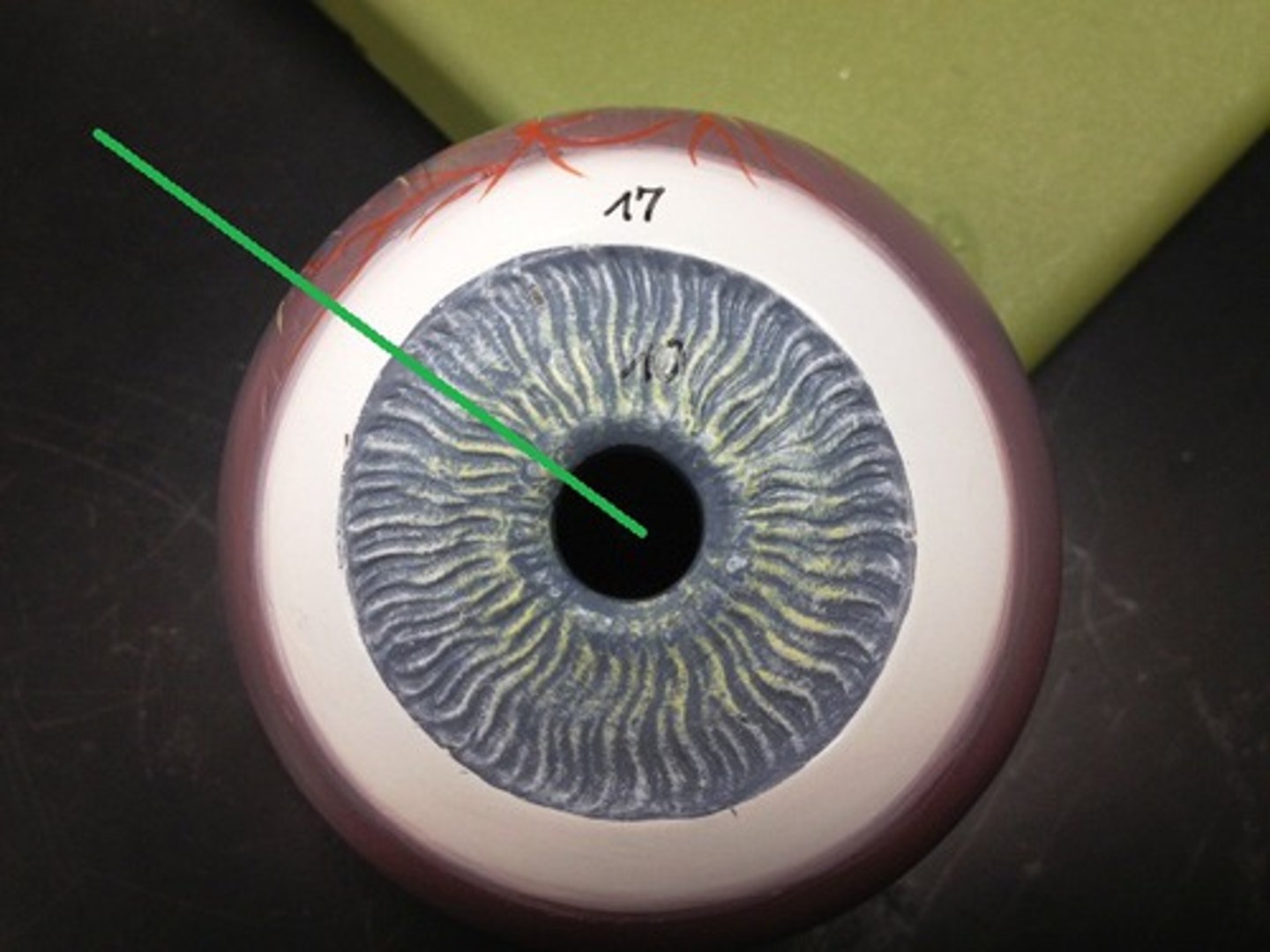
Retina
the light-sensitive inner surface of the eye, containing the receptor rods and cones plus layers of neurons that begin the processing of visual information
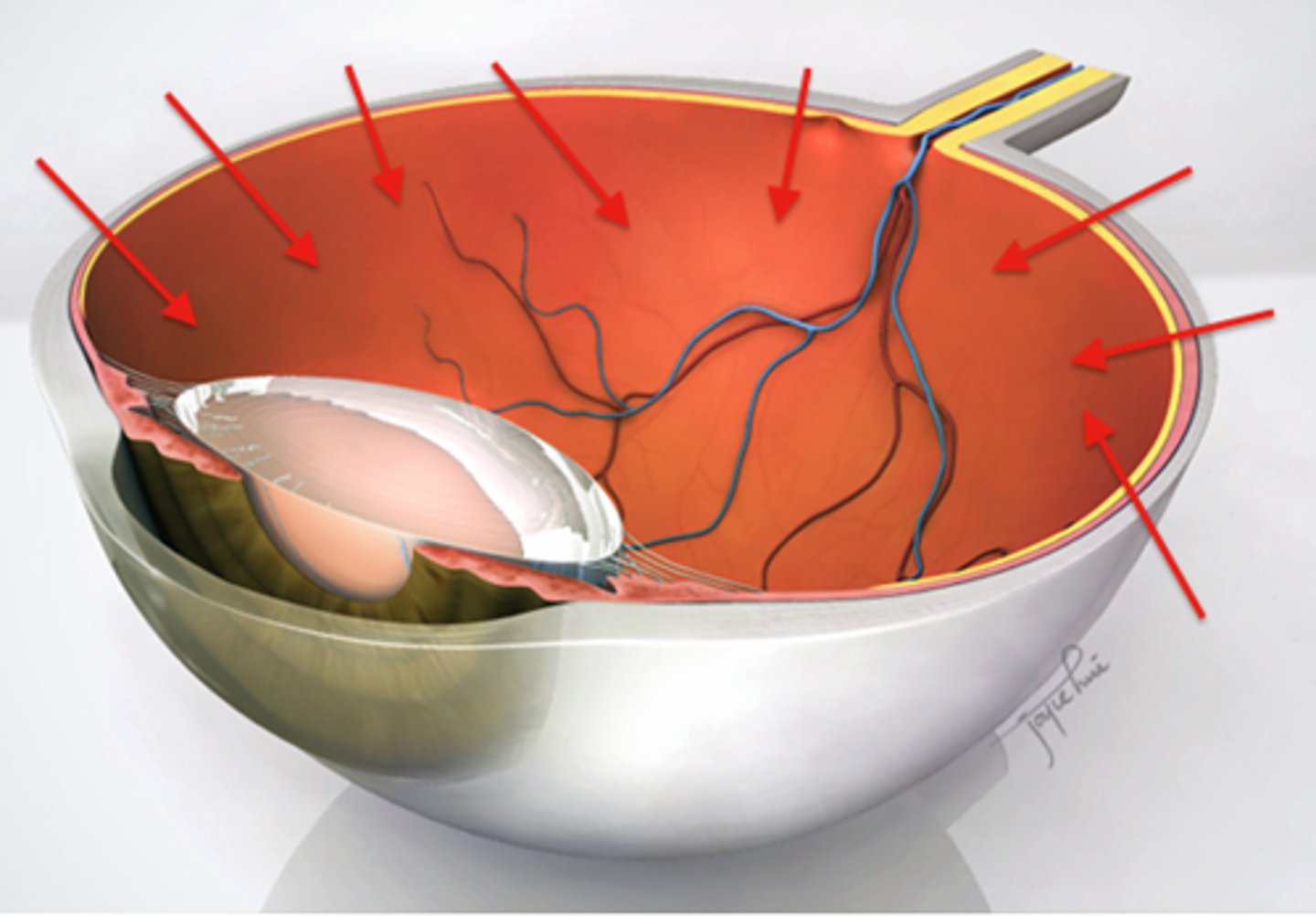
optical nerve
something that transmits visual information from the retina to the brain
Rods
Specialized visual receptors that play a key role in night vision and peripheral vision.
Cones
retinal receptor cells that are concentrated near the center of the retina and that function in daylight or in well-lit conditions. The cones detect fine detail and give rise to color sensations.
Sclera
white part of the eye
Hearing
the sense through which we detect sound
Mechanoreceptors
sensory cells that are sensitive to vibrations in the surrounding environment, therefore detection sound waves.
outer ear
the outermost part of the ear, consisting of the pinna and the ear canal
Pinna
the visible part of the ear that intercepts sound waves and focuses them into the ear canal
ear canal
A narrow region leading from the outside of the human ear to the eardrum. The sound waves travel through it
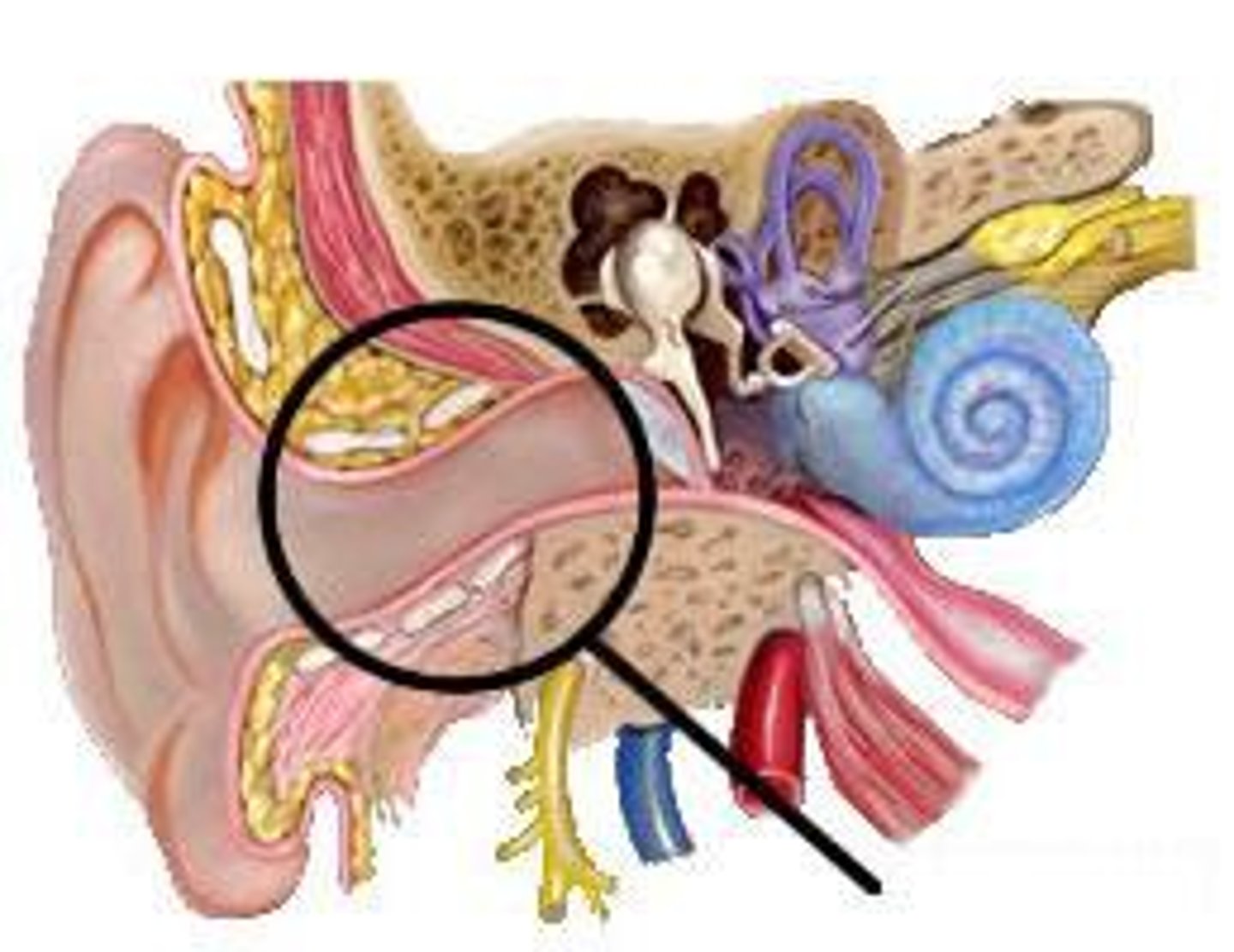
eardrum
a thin membrane that marks the beginning of the middle ear; sound waves cause it to vibrate
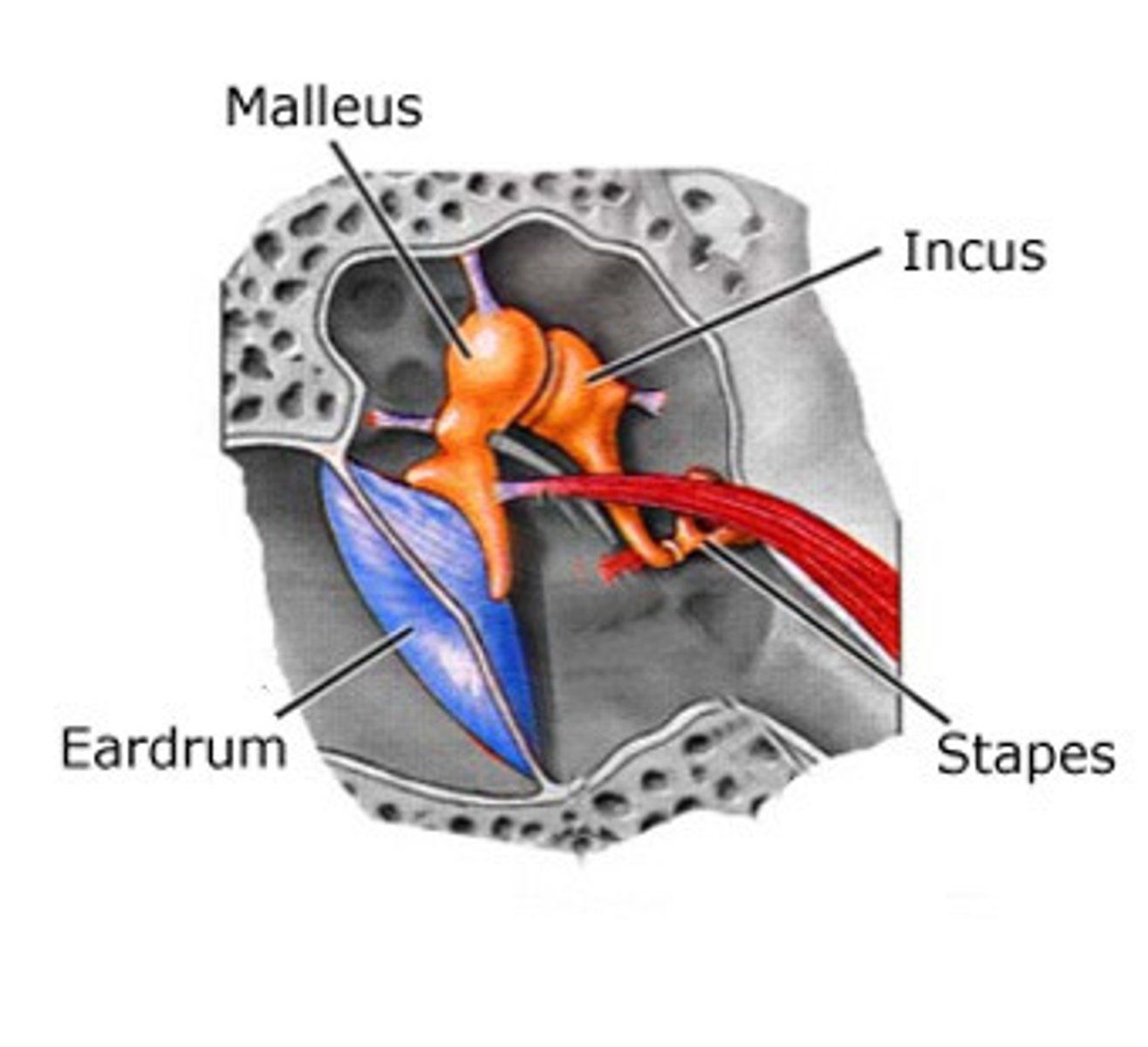
ear bones
malleus, incus, stapes
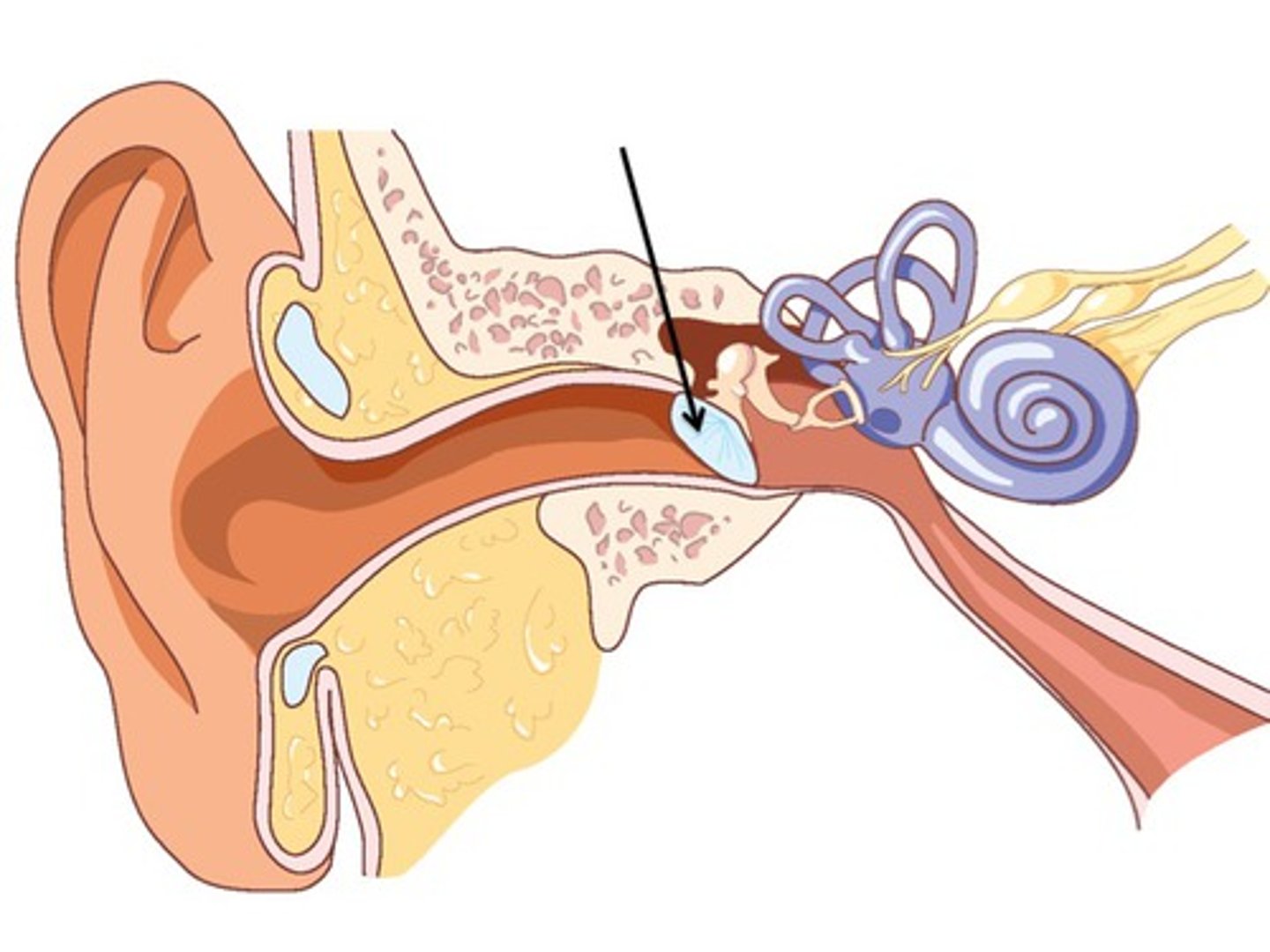
Eustachian tube
A narrow tube between the middle ear and the throat that serves to equalize pressure on both sides of the eardrum
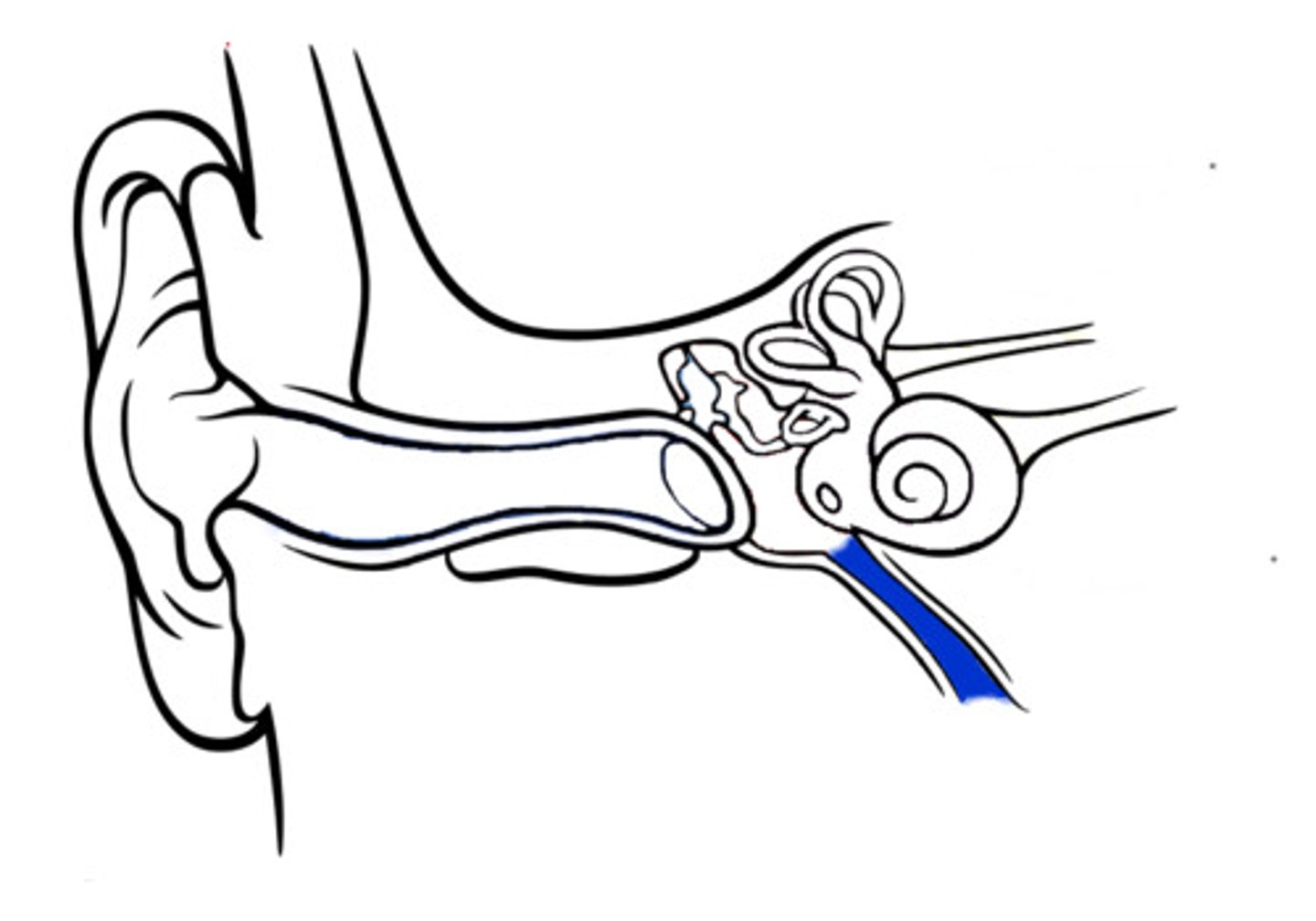
middle ear
the chamber between the eardrum and cochlea containing 3 tiny bones that concentrate the vibrations of the eardrum on the cochlea's oval window
inner ear
the innermost part of the ear, containing the cochlea, Vestibular system and auditory nerve
cochlea
a coiled, bony, fluid-filled tube in the inner ear through which sound waves trigger nerve impulses
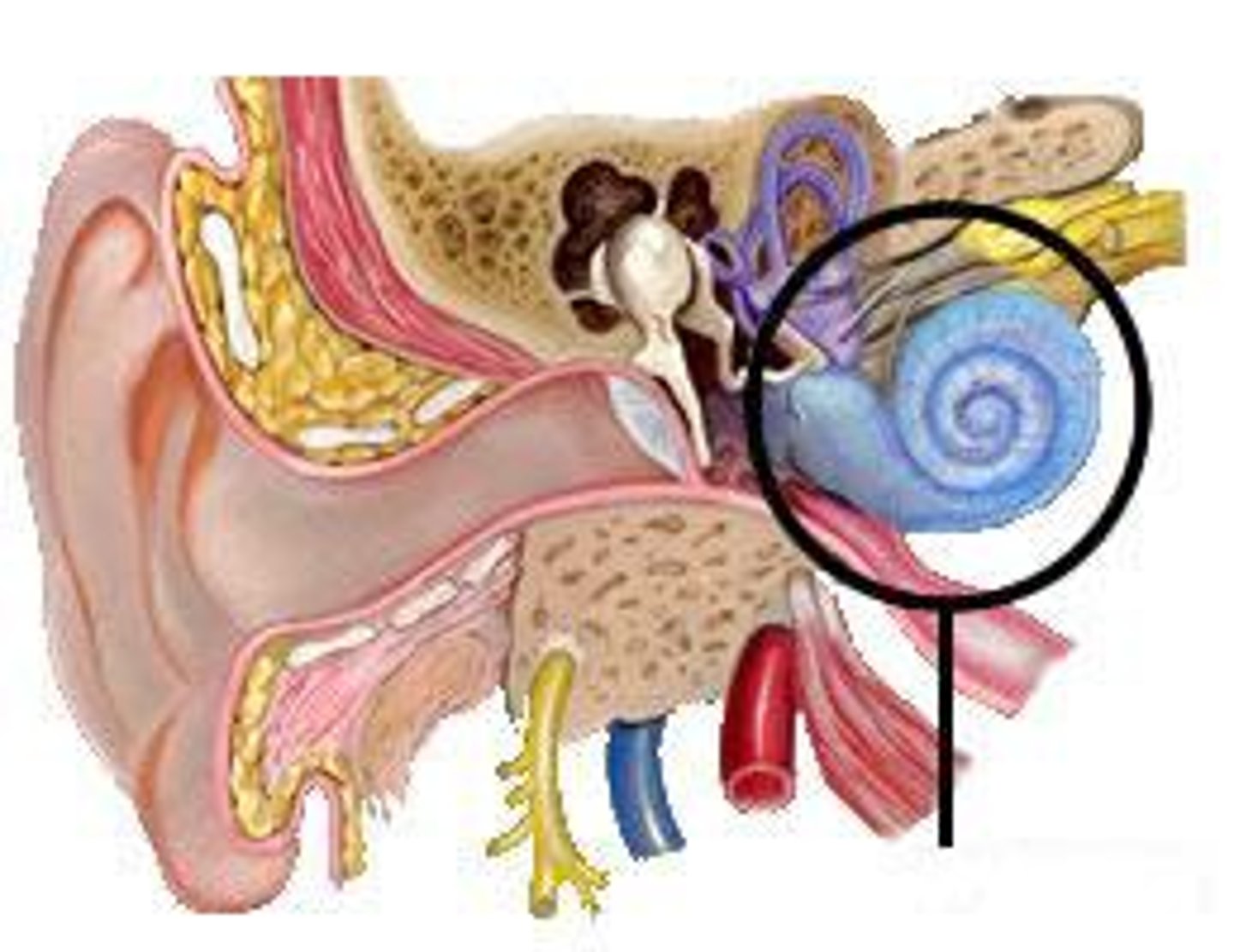
vestibular system
three semicircular canals that provide the sense of balance, located in the inner ear and connected to the brain by a nerve
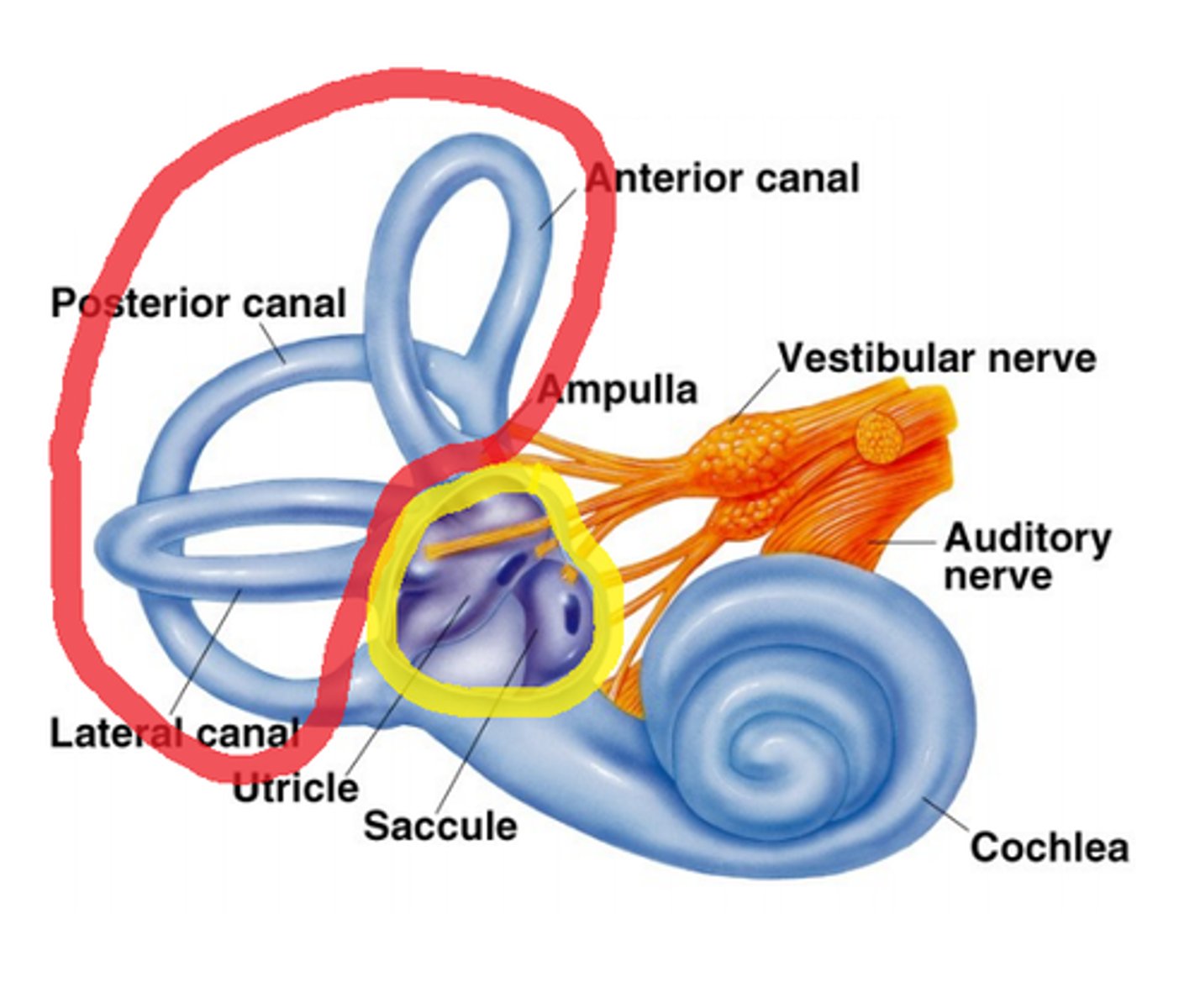
auditory nerve
the nerve that carries impulses from the inner ear to the brain, resulting in the perception of sound
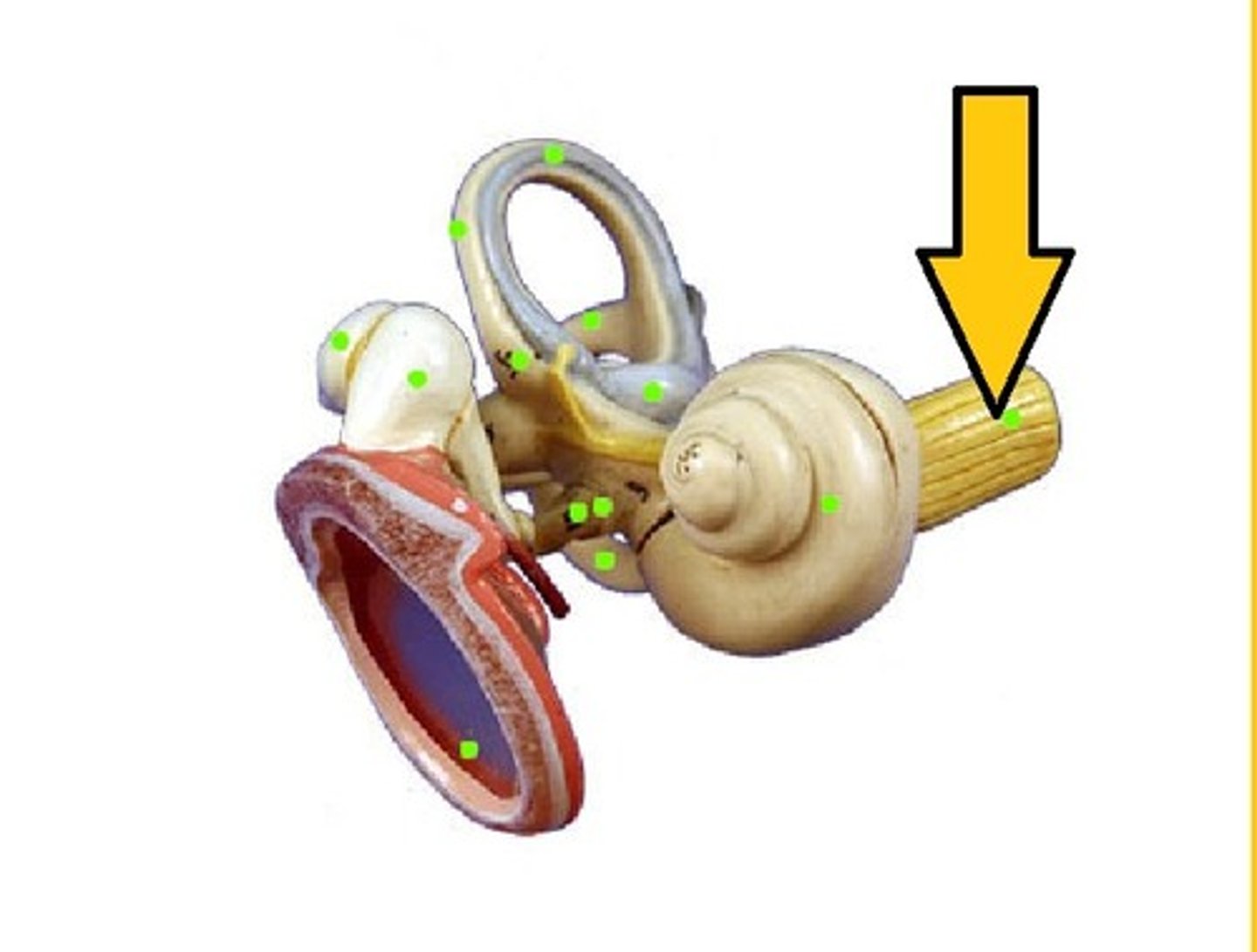
aqueous humor
fluid in the eye, found between the cornea and the lens
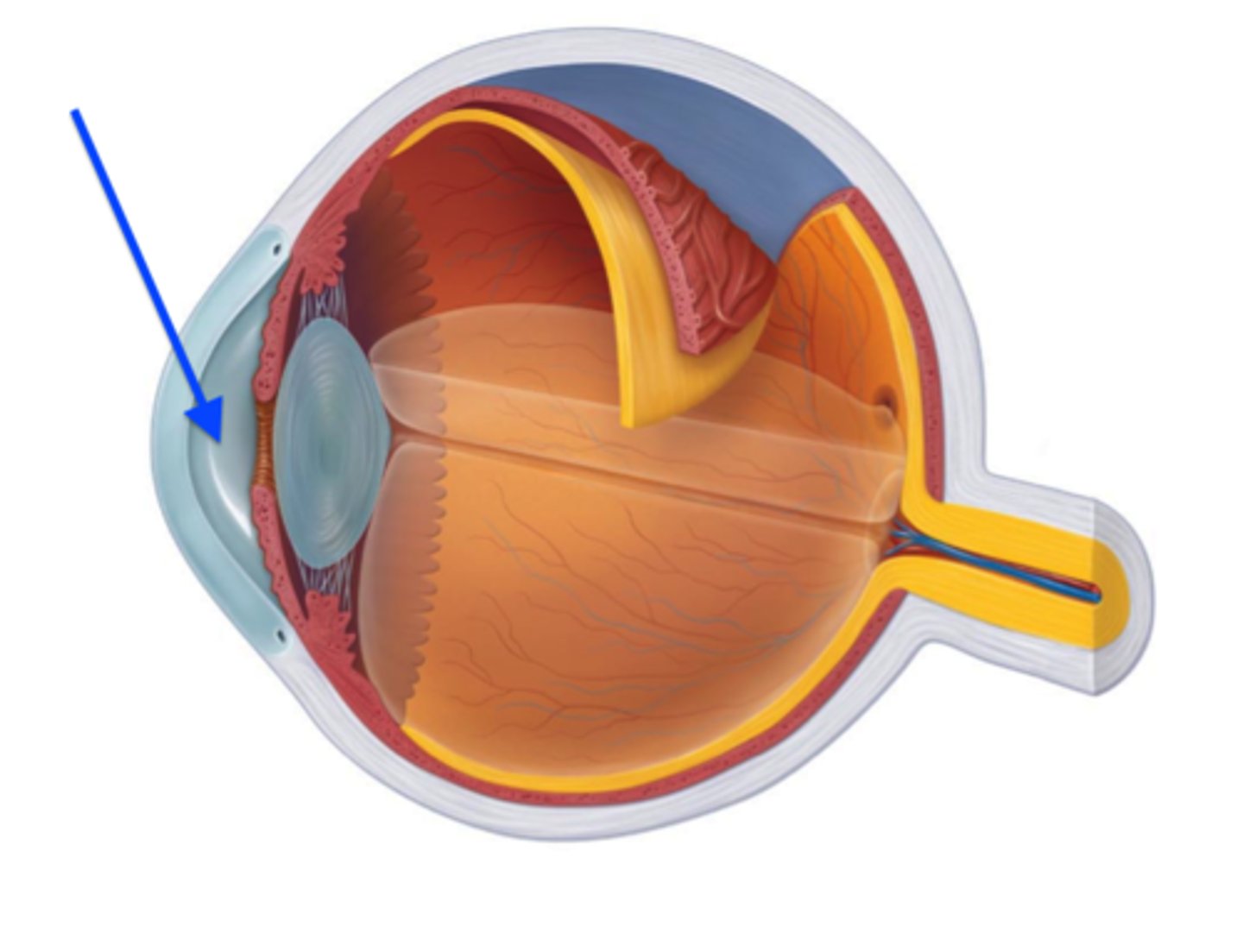
cilliary muscle
adjusts shape of the lens to focus objects on the retina.
the nervous system
the network of nerve cells and fibers that transmits nerve impulses between parts of the body.
the endocrine system
the body's "slow" chemical communication system; a set of glands that secrete hormones into the bloodstream
reflex
a simple, automatic response to a sensory stimulus, such as the knee-jerk response
Photomotive reflex
when the pupil/iris adjusts to the amount of light in the environment
patellar reflex
The knee-jerk reflex; a spinal reflex in which tapping below the knee produces a reflexive contraction of the quadriceps muscle of the thigh, causing the foot to kick.
nervous reaction
A reaction triggered by the nervous system that has to be processed before causing a reaction
Reaction capacity
The immediacy with which an individual can react to stimuli or a task
Chemoreceptors
Receptors that detect chemicals
taste buds
Tiny bumps covering the upper surface of the tongue. They contain chemoreceptors and nerve endings
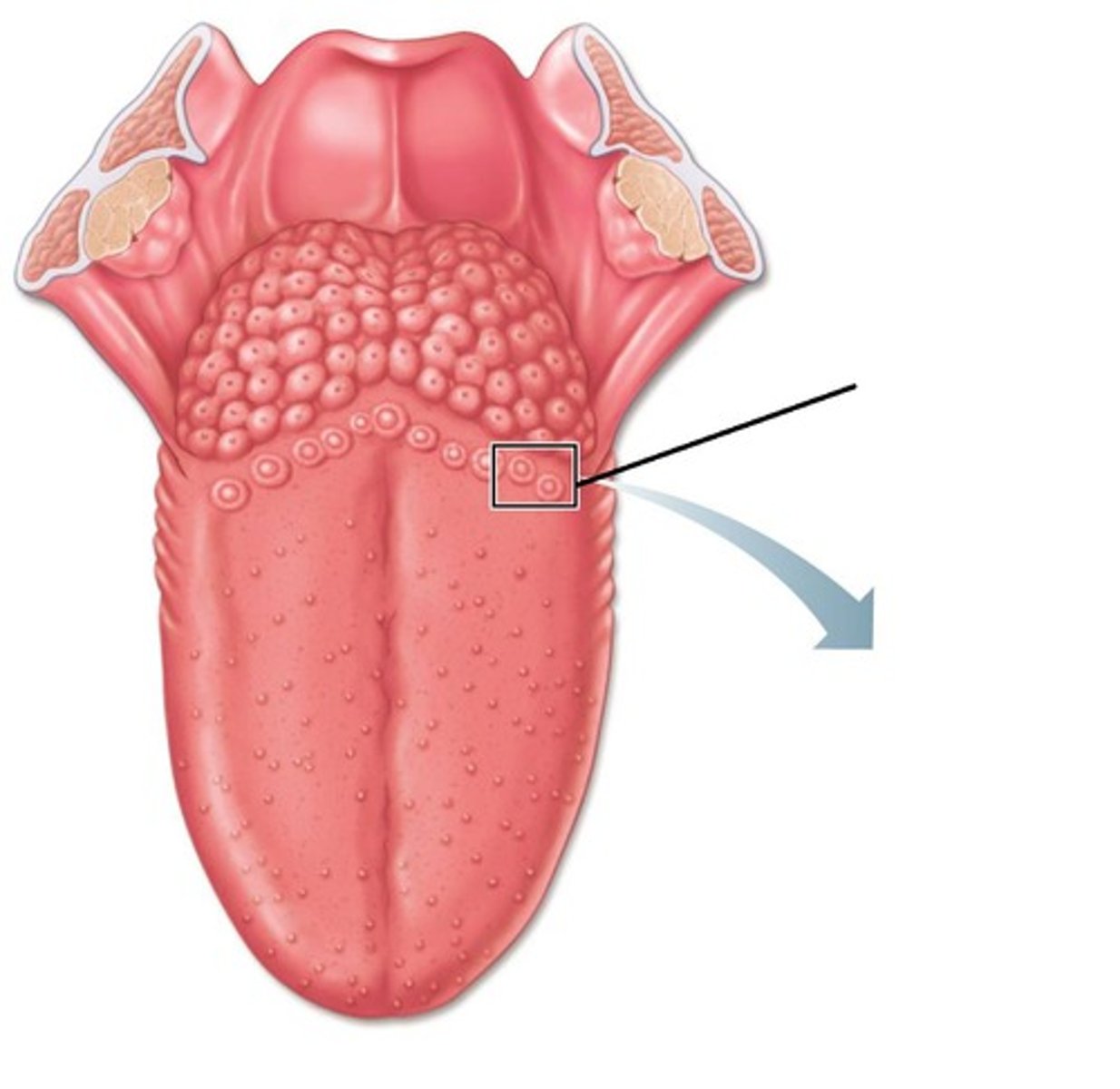
taste receptors
chemical receptors on the tongue that detect the presence of substances dissolved in saliva or in liquids inside the oral cavity, then turn these stimuli into electrical impulses
Nerve endings
carry information from the taste buds to the brain. These receive nerve impulses from the taste receptor they're connected to
olfactory mucosa
covers the upper region of the nasal cavity. It holds chemoreceptors that are connected to nerve endings from the olfactory bulb. (3)
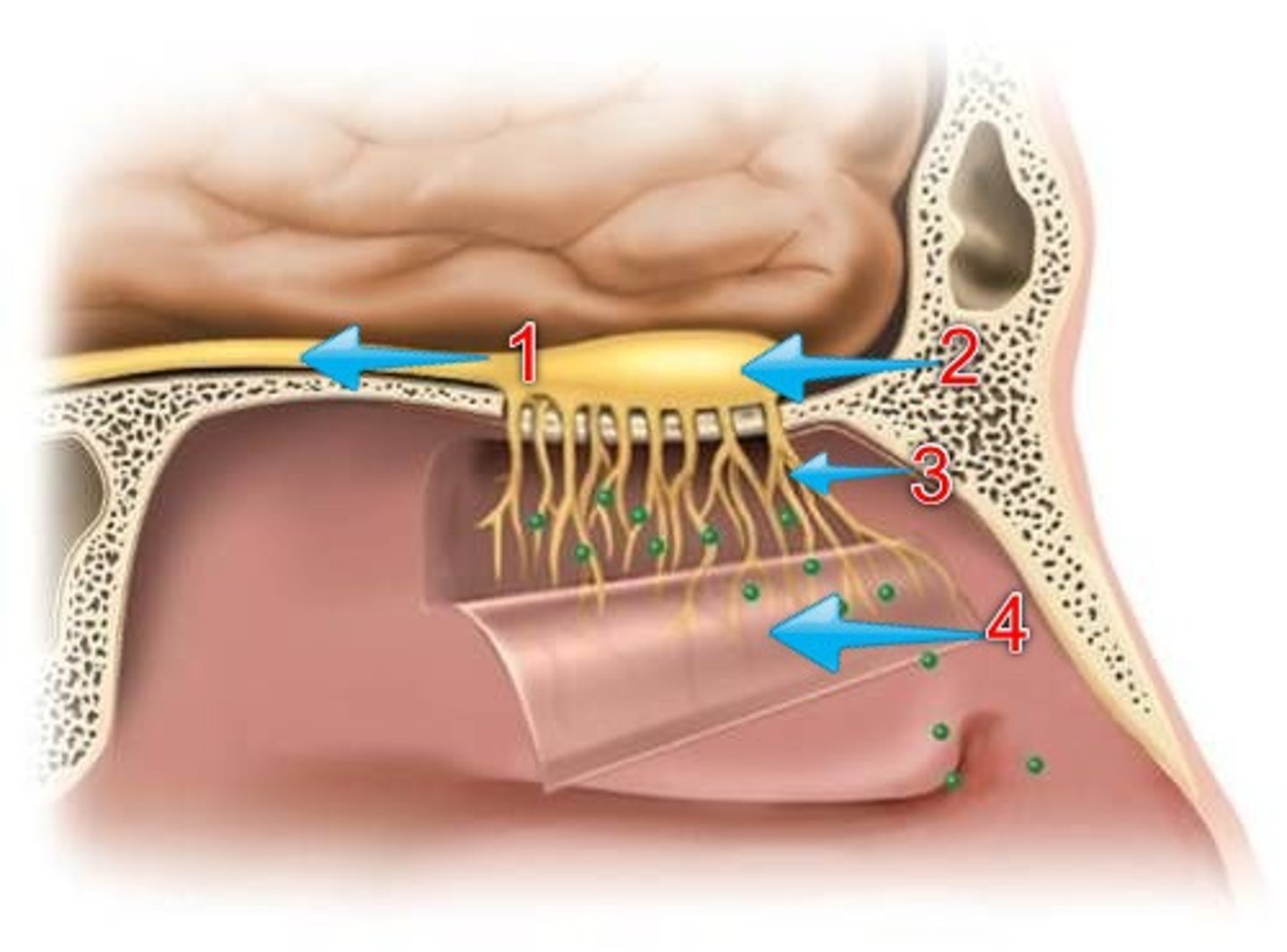
olfactory bulb
Collects electrical impulses from the olfactory mucosa and directs them to the olfactory nerve
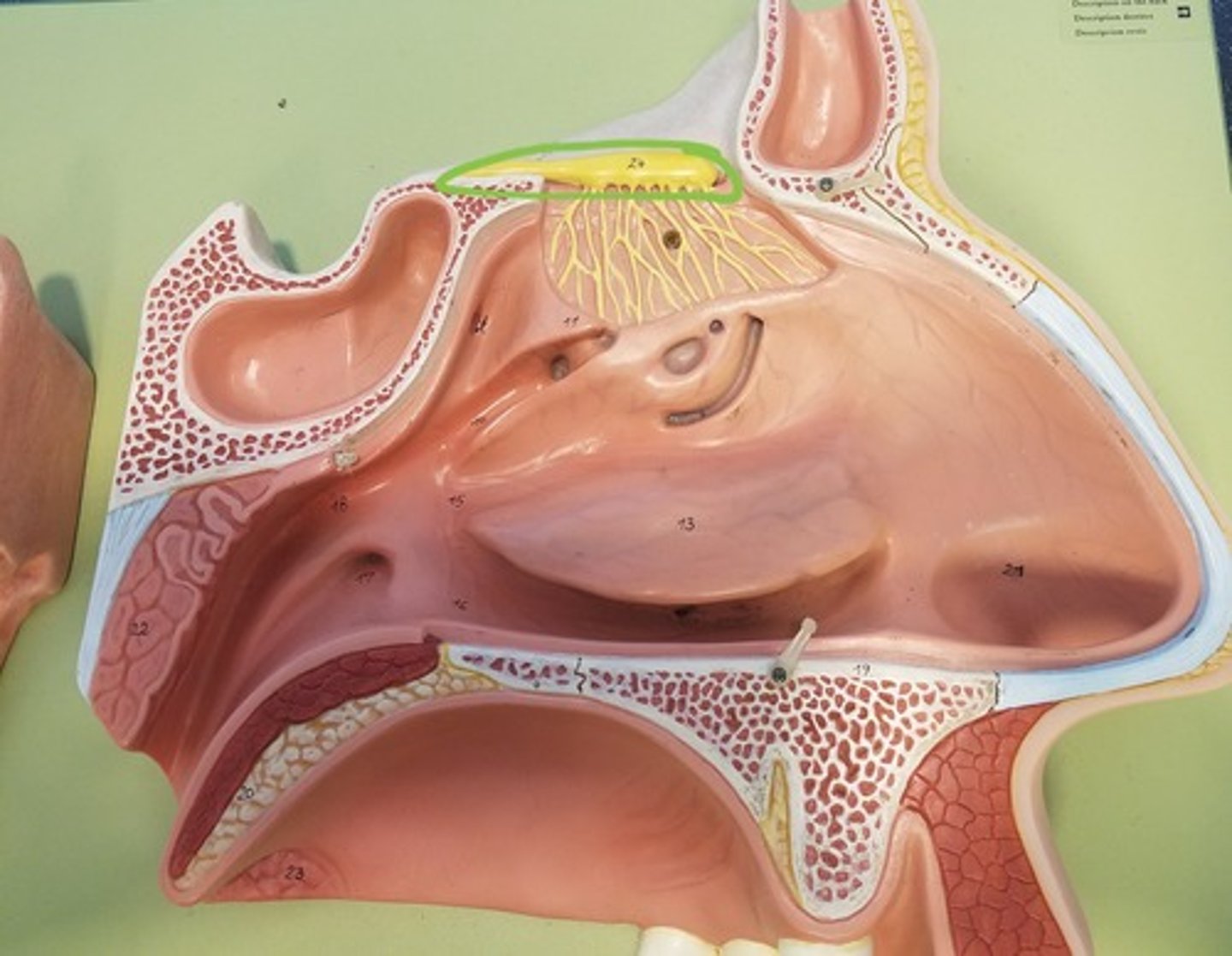
olfactory nerve
the nerve that carries smell impulses from the nose to the brain (1)
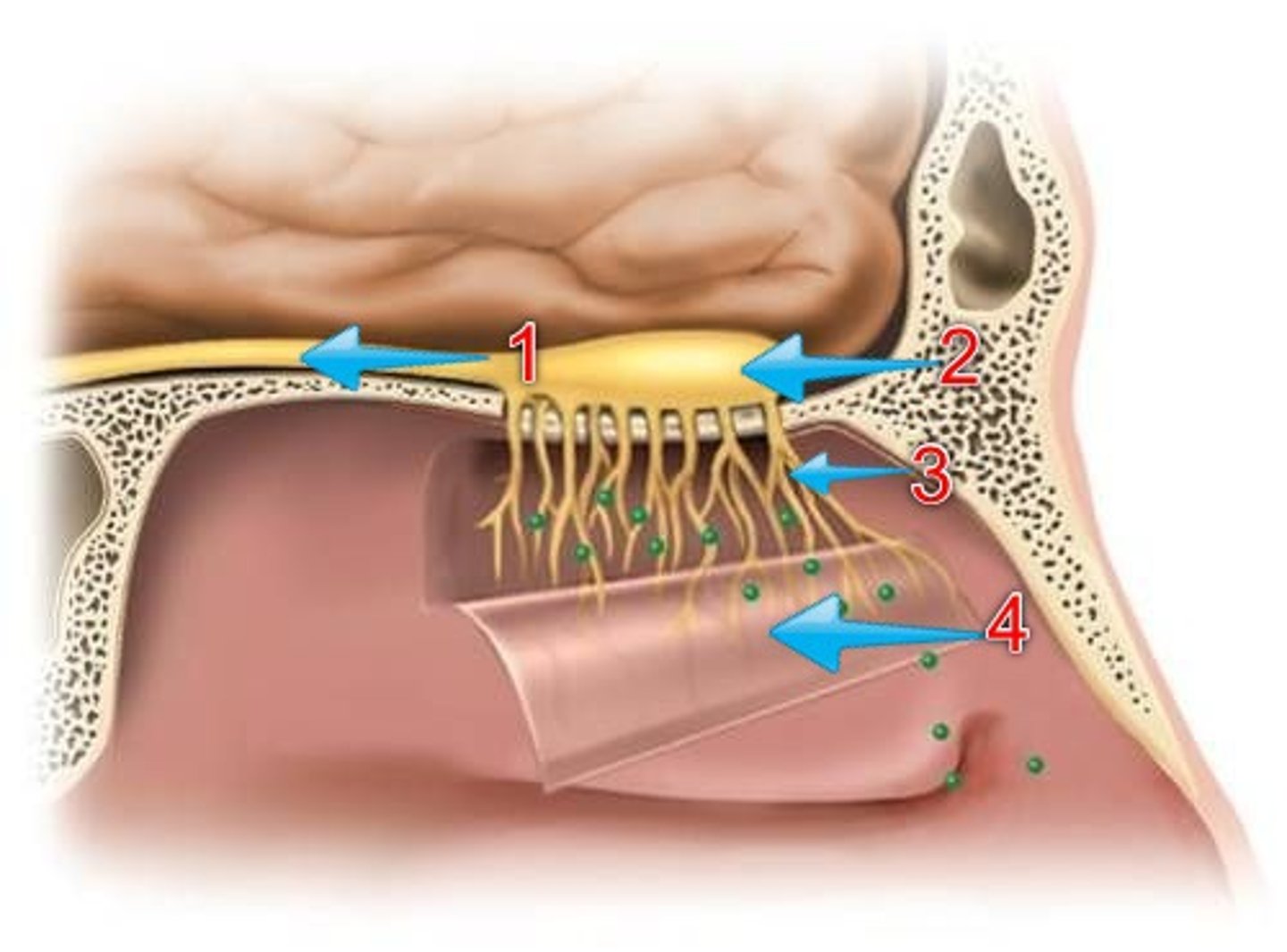
Thermoreceptors
detect changes in temperature
Nocioreceptors
pain receptors
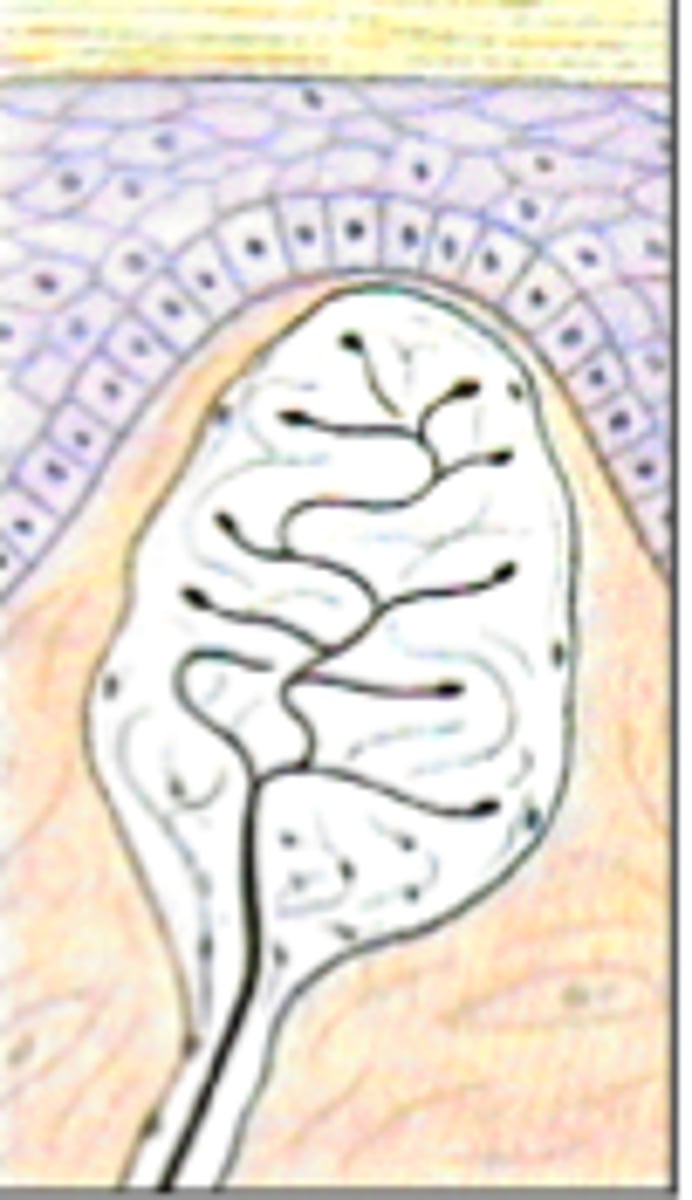
Meissner's corpuscles
detect slight pressure changes
Pacinian corpuscles
respond to deep pressure and vibration
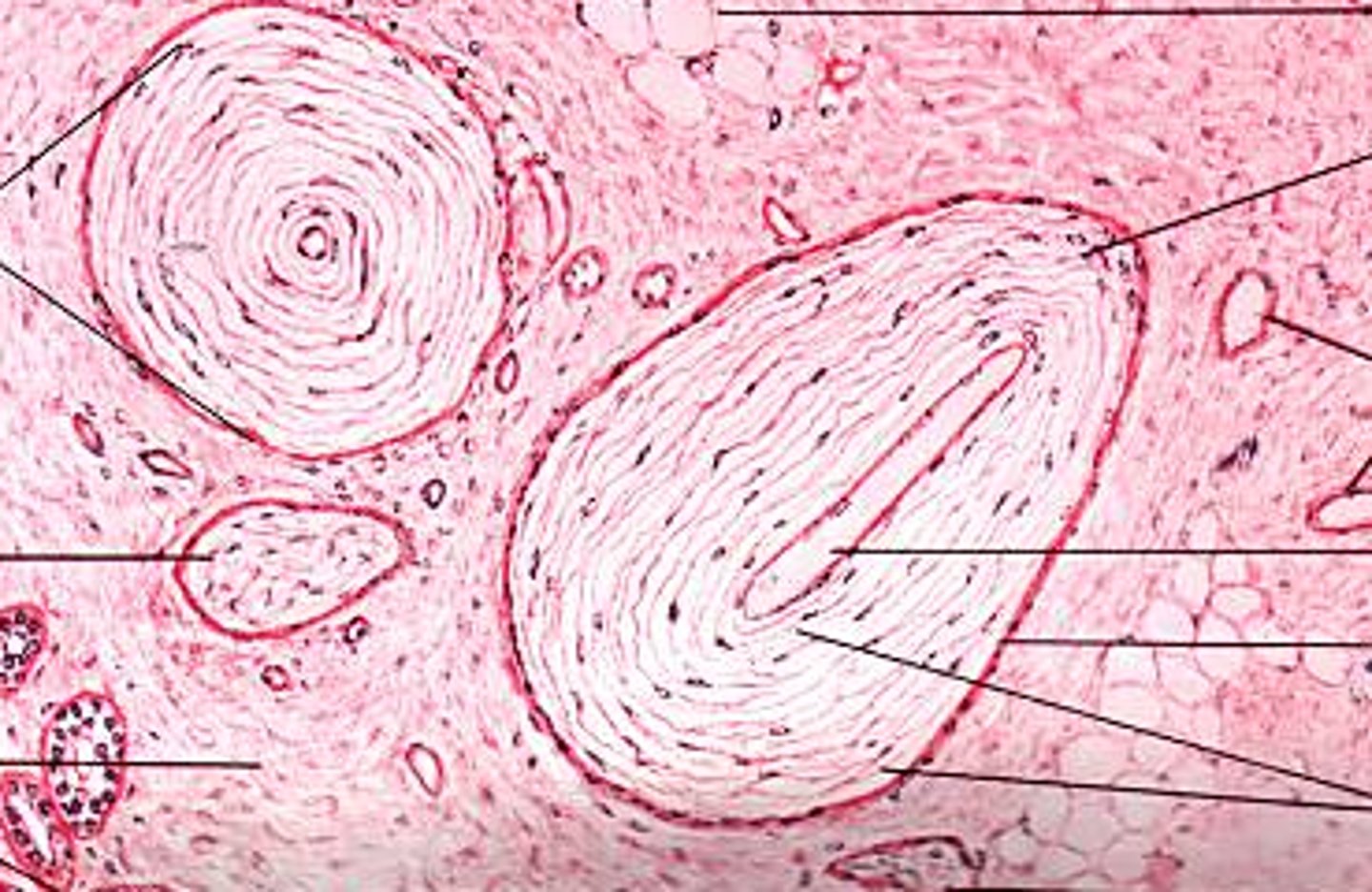
Ruffini's corpuscles
Detect increases in temperature
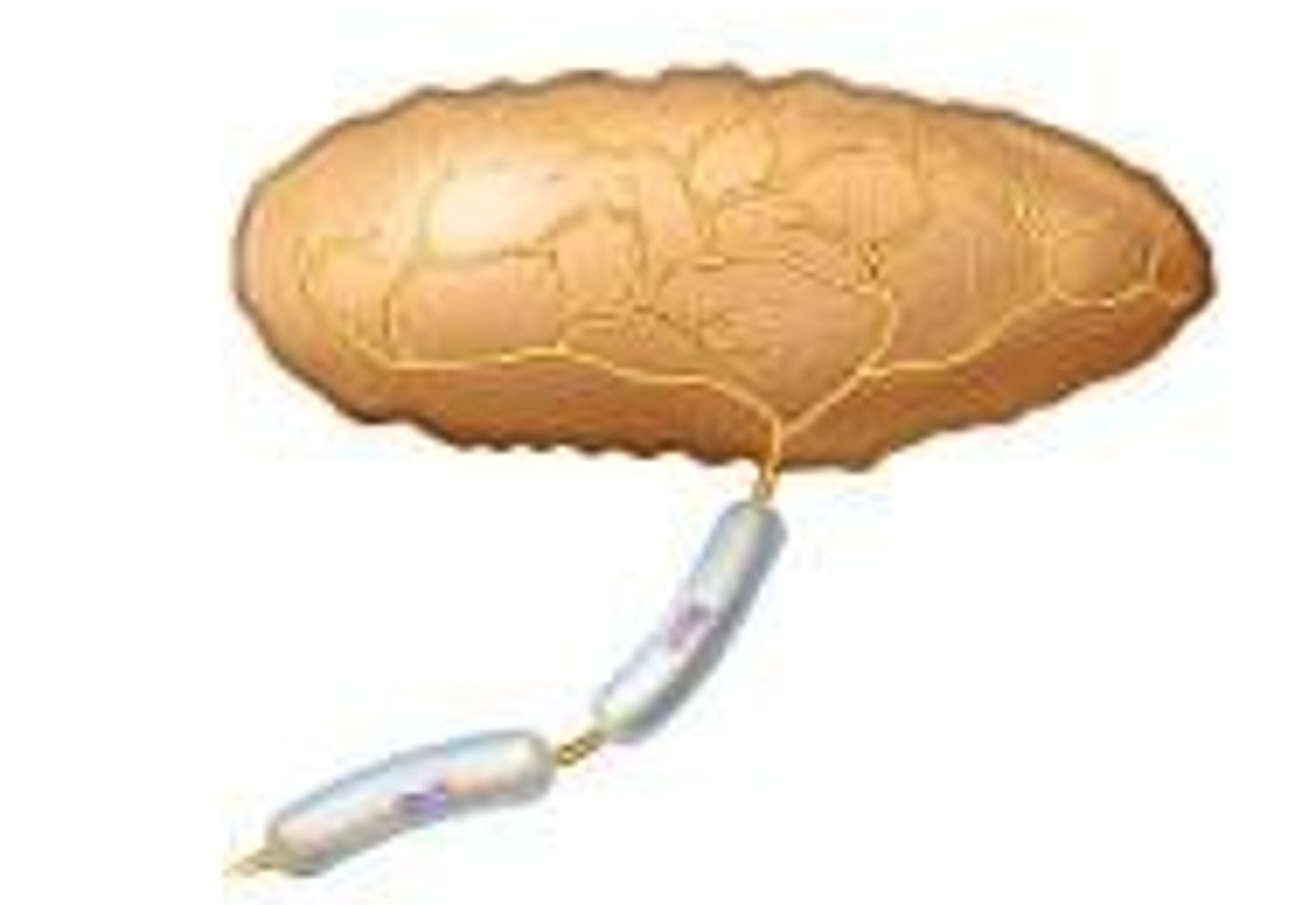
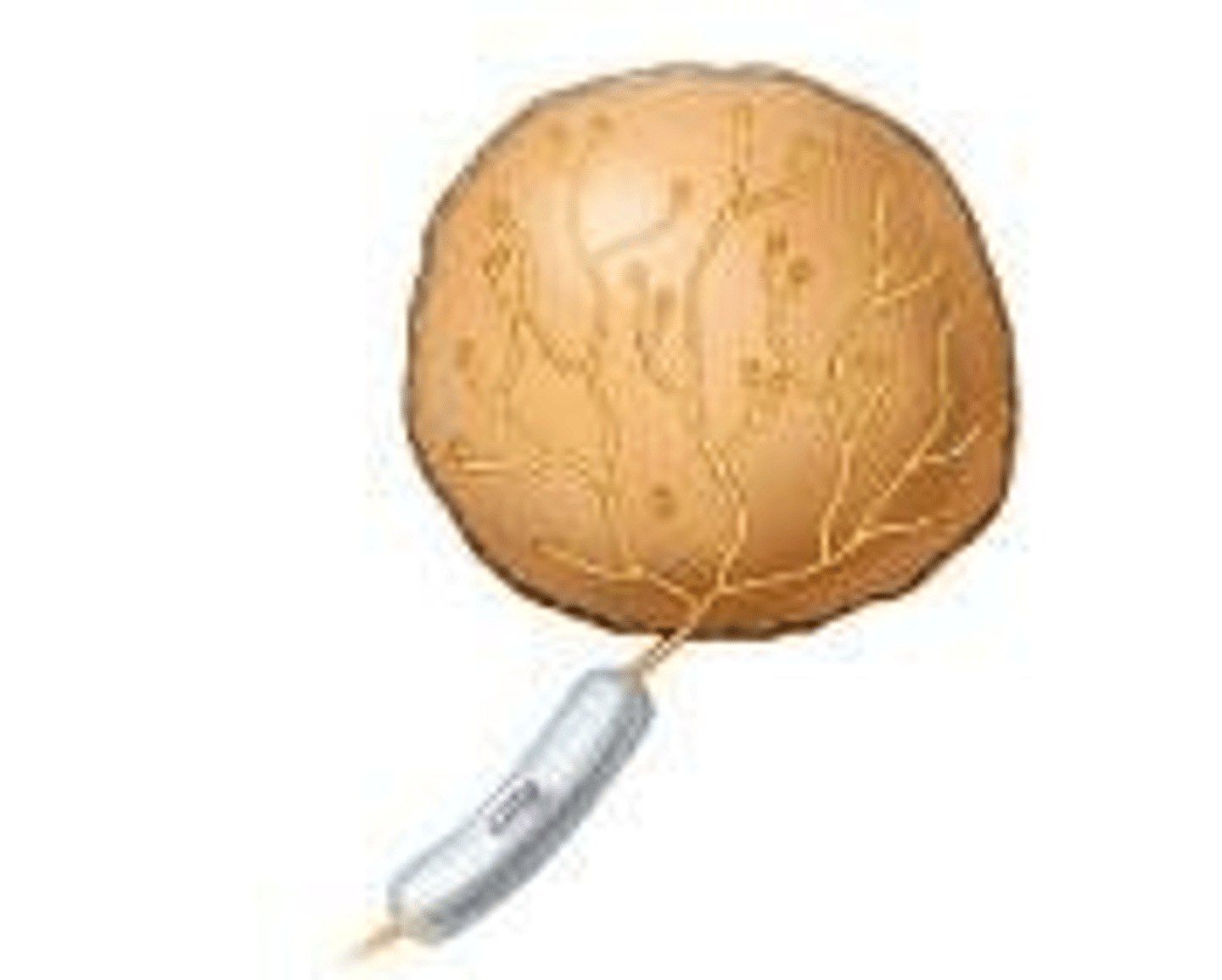
Krause's corpuscles
detect decreases in temperature

free nerve endings
transmit sensation of pain
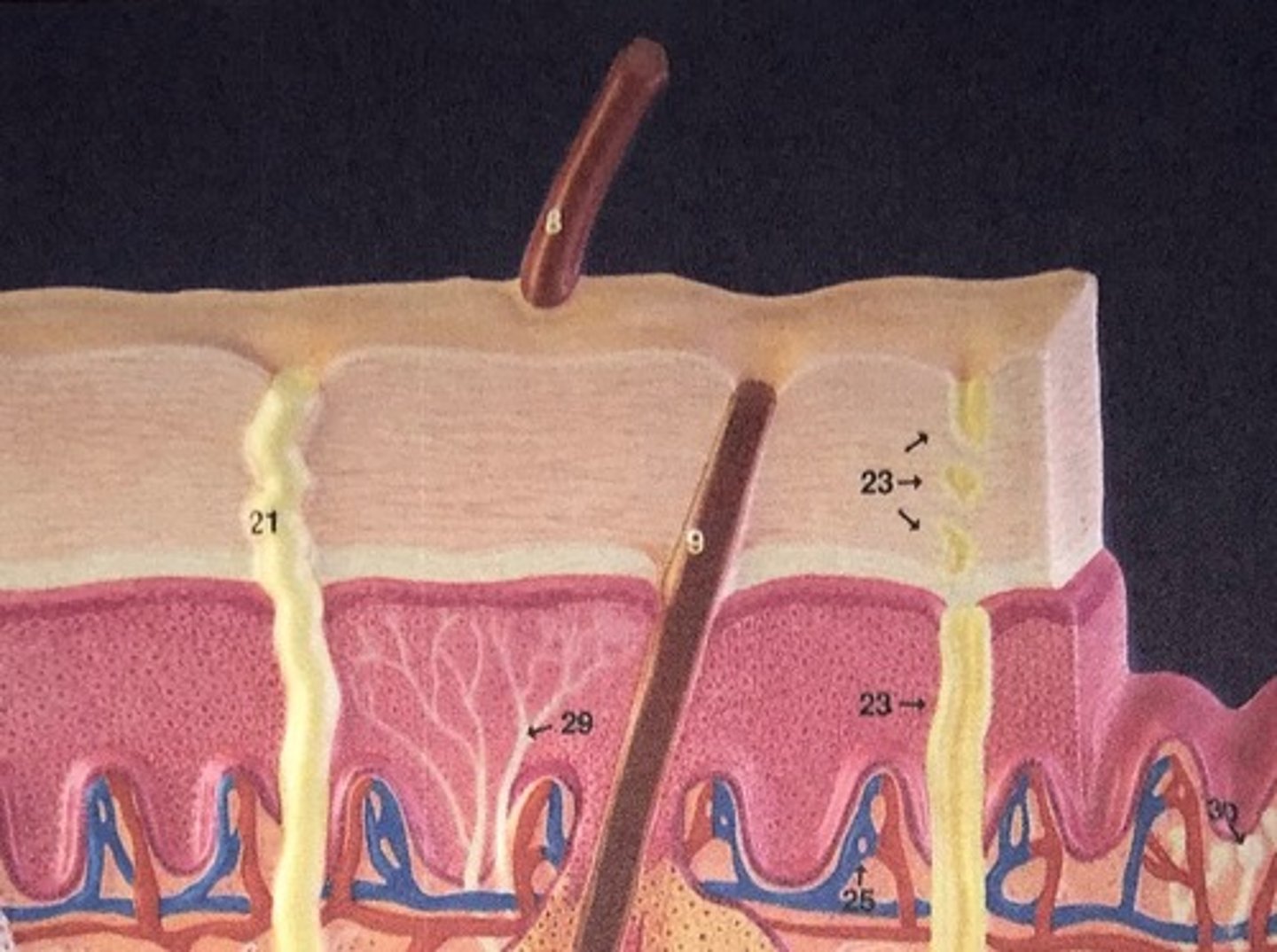
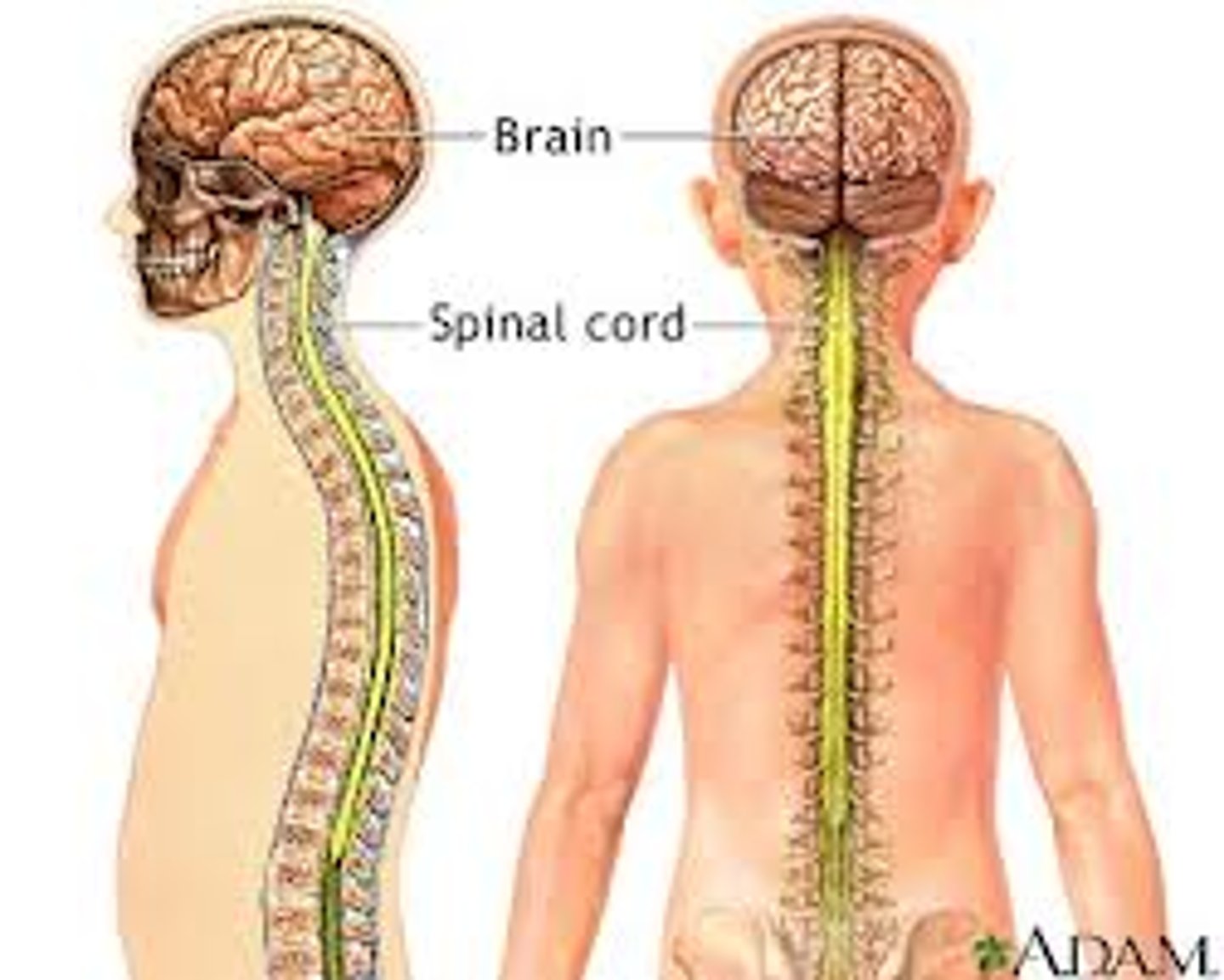
central nervous system
A subdivision of the human nervous system comprising the brain and spinal cord. Receives information from the receptors and creates an appropriate response to the stimulus.
Encephalon
another word for brain
Cerebrum
Part of the brain that initiates movement, interprets information from the senses, and enables complex cognitive skills (speaking, thinking, memory and emotions etc.)
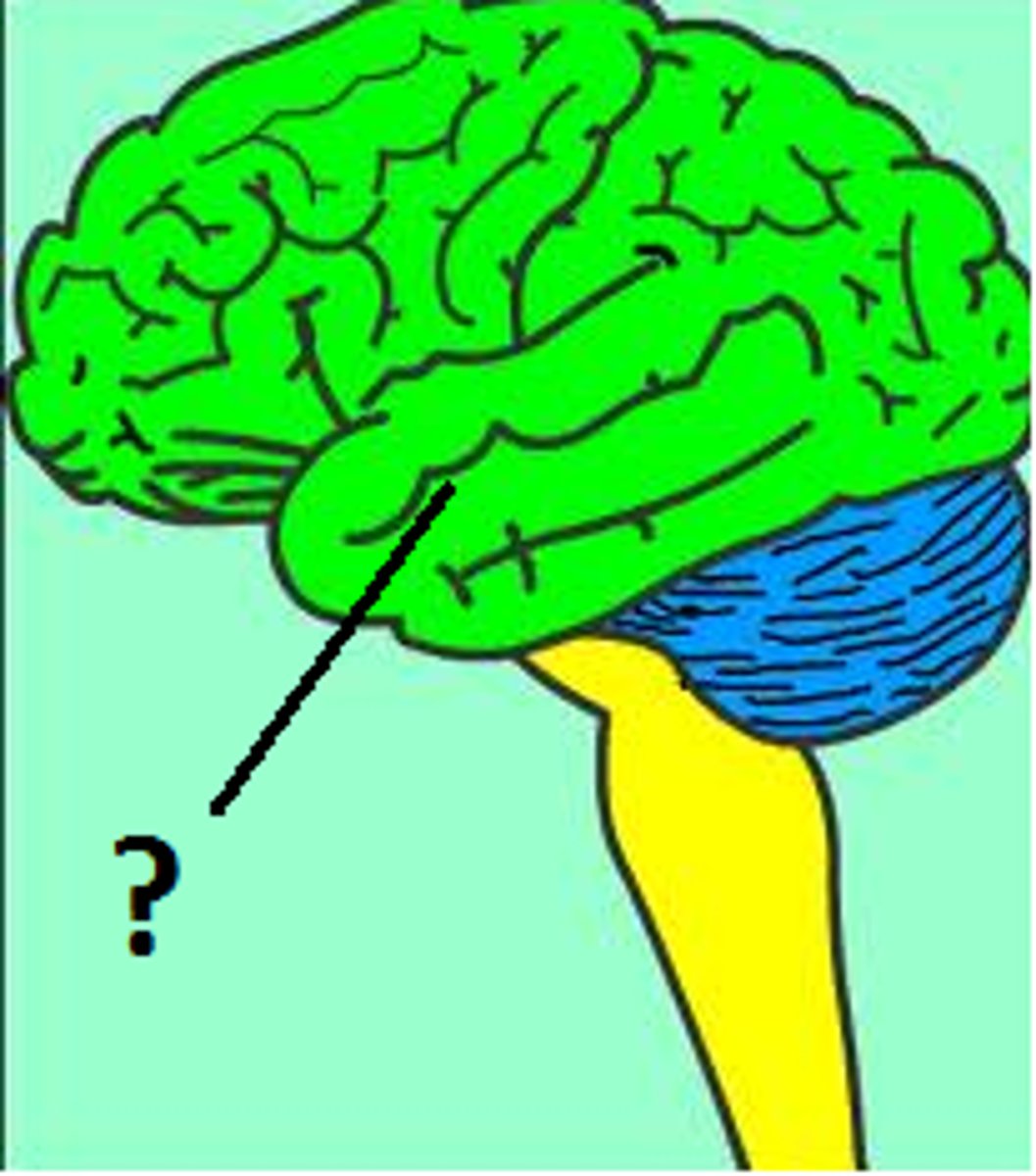
Cerebellum
an area at the base of the brain that coordinates muscle movement in the body, but doesn't initiate it.
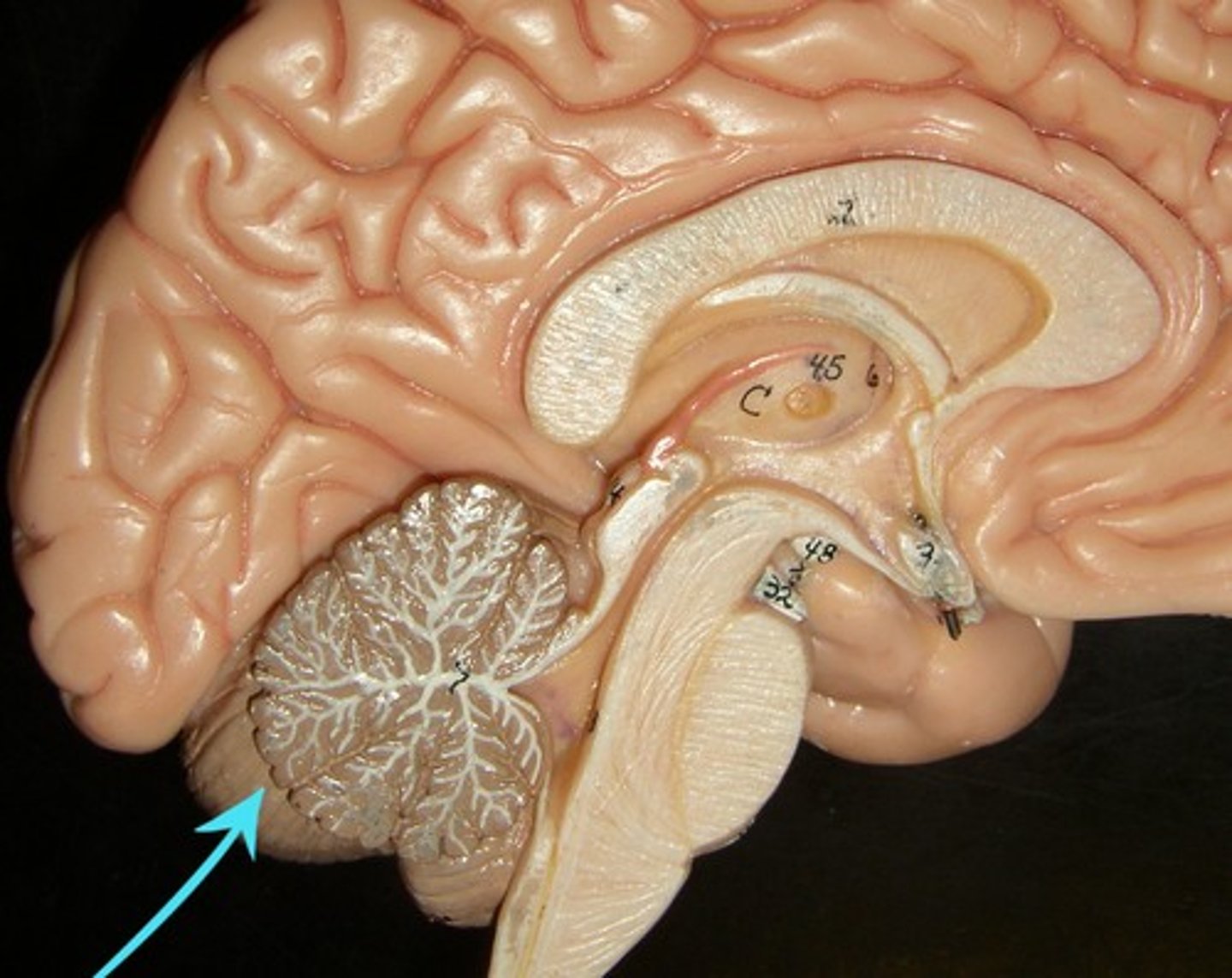
Brainstem
central core of the brain, beginning where the spinal cord swells as it enters the skull; the brainstem is responsible for automatic survival functions (heartbeat, breathing, sleep-wake cycles, etc.)
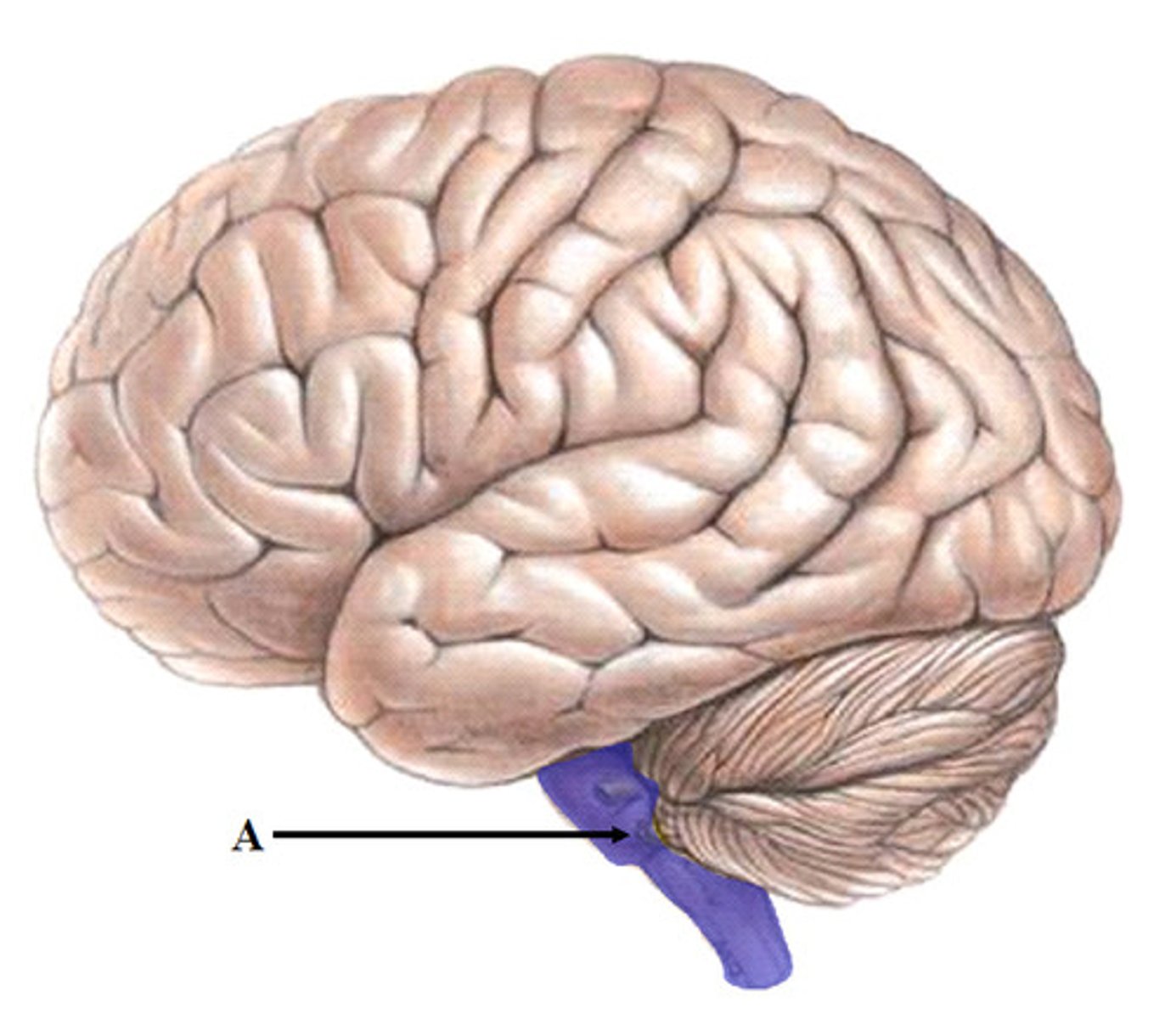
circumvolutions
The "rugouseness" on the brain that is there to increase surface area
spinal cord
a major part of the central nervous system which conducts sensory and motor nerve impulses to and from the brain, is protected by the vertebral column
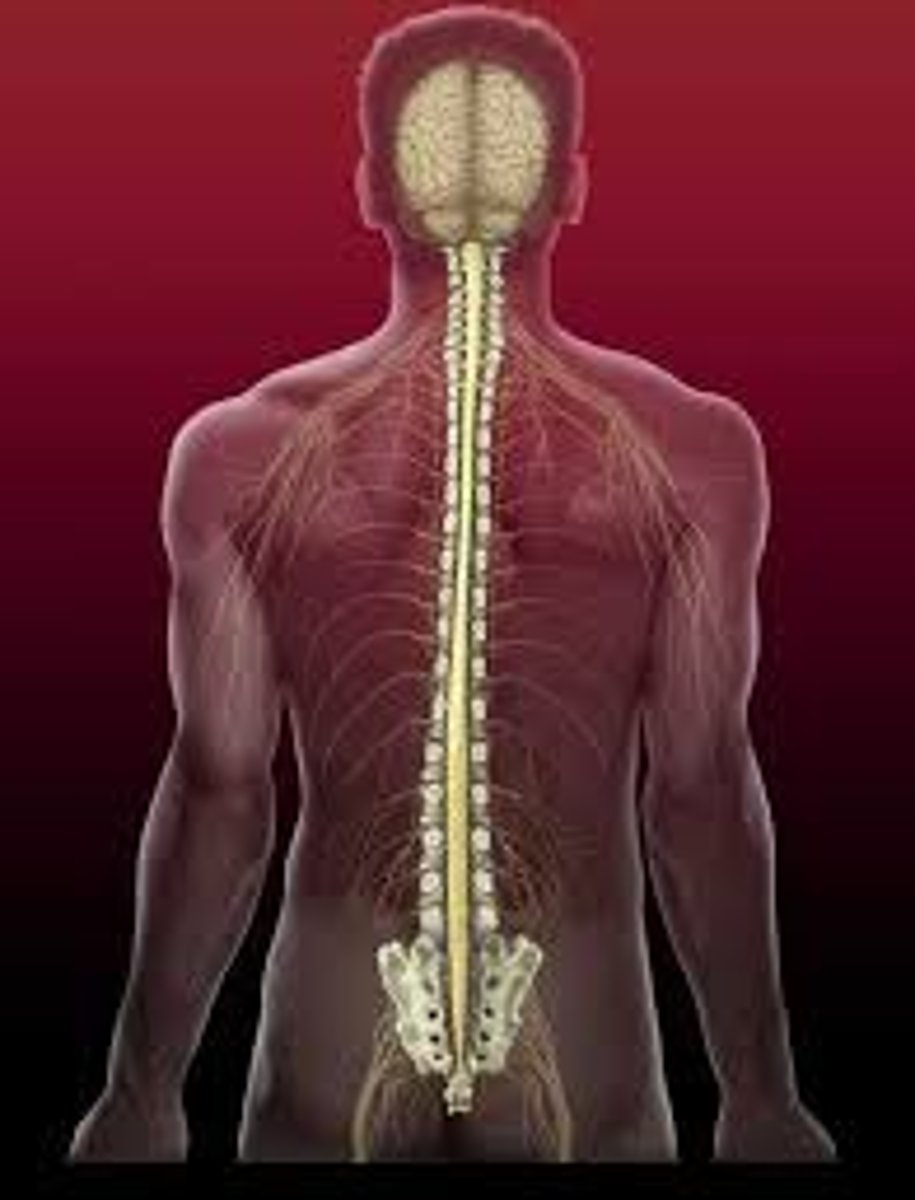
peripheral nervous system
the sensory and motor neurons that connect the central nervous system to the rest of the body
autonomic peripheral nervous system
The group of nerves in the PNS that innervates smooth muscle, cardiac muscle, and glands. It controls the body's involuntary processes such as heartbeat or bowel movement
somatic peripheral nervous system
part of the peripheral nervous system that controls voluntary actions such as moving your arms
sympathetic autonomic peripheral nervous system
directs the body's rapid involuntary response to dangerous or stressful situations. It is your "fight or flight" response and prepares all your organs to face a treat.
parasympathetic autonomic peripheral nervous system
works to calm your body down after a SAPNS response, and encourages your body to "rest and digest". Settles the body back into homeostasis or equilibrium after a stressful event.
nerve impulse
the message carried by a neuron
sensory nerves
Nerves that carry information from the sense receptors to the spinal cord and brain.
motor nerves
Nerves that carry information from the central nervous system to the muscles of the body.
relay neuron (interneuron)
nerve cells linked to other neurons that form networks within the CNS. They take part in producing responses
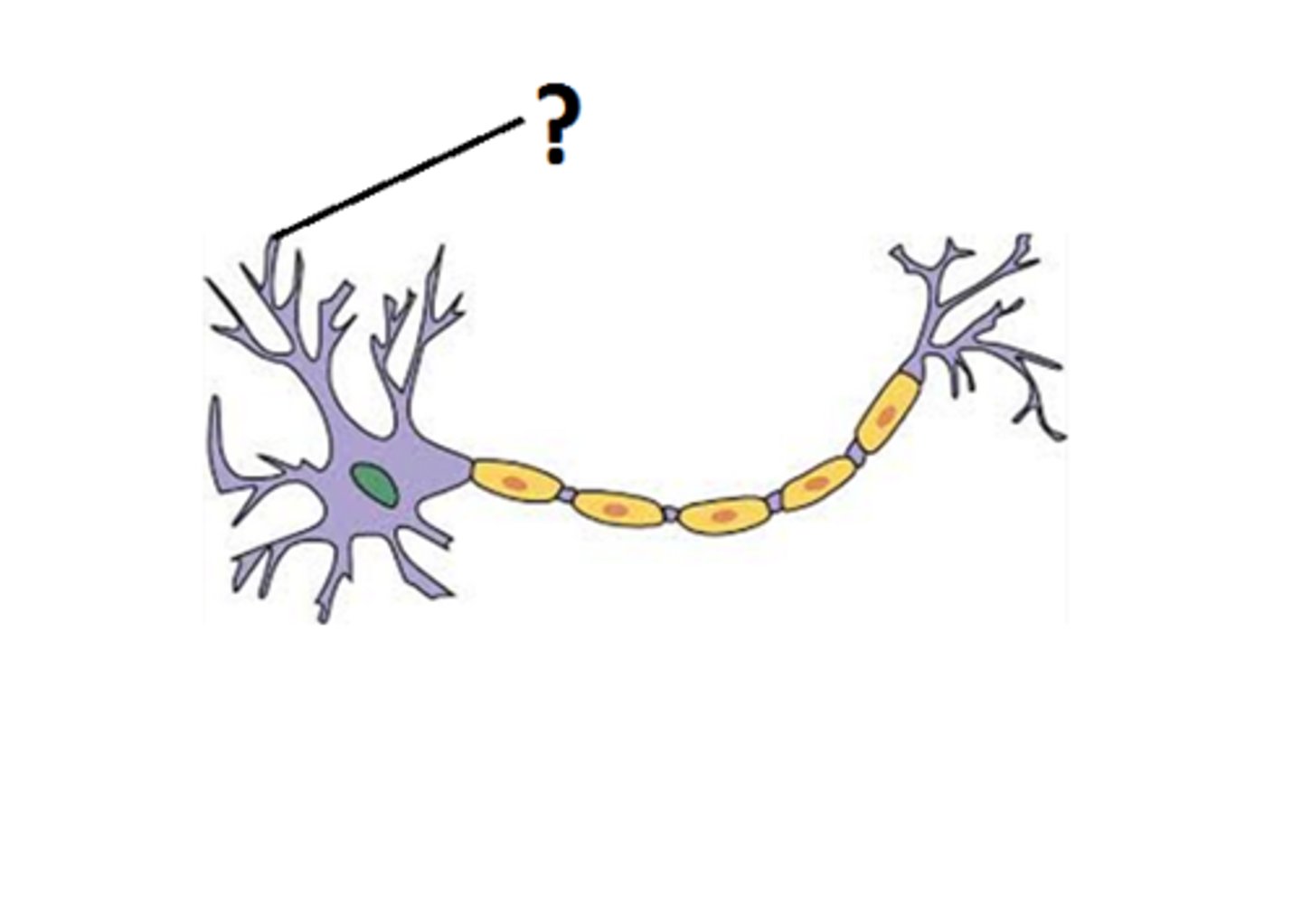
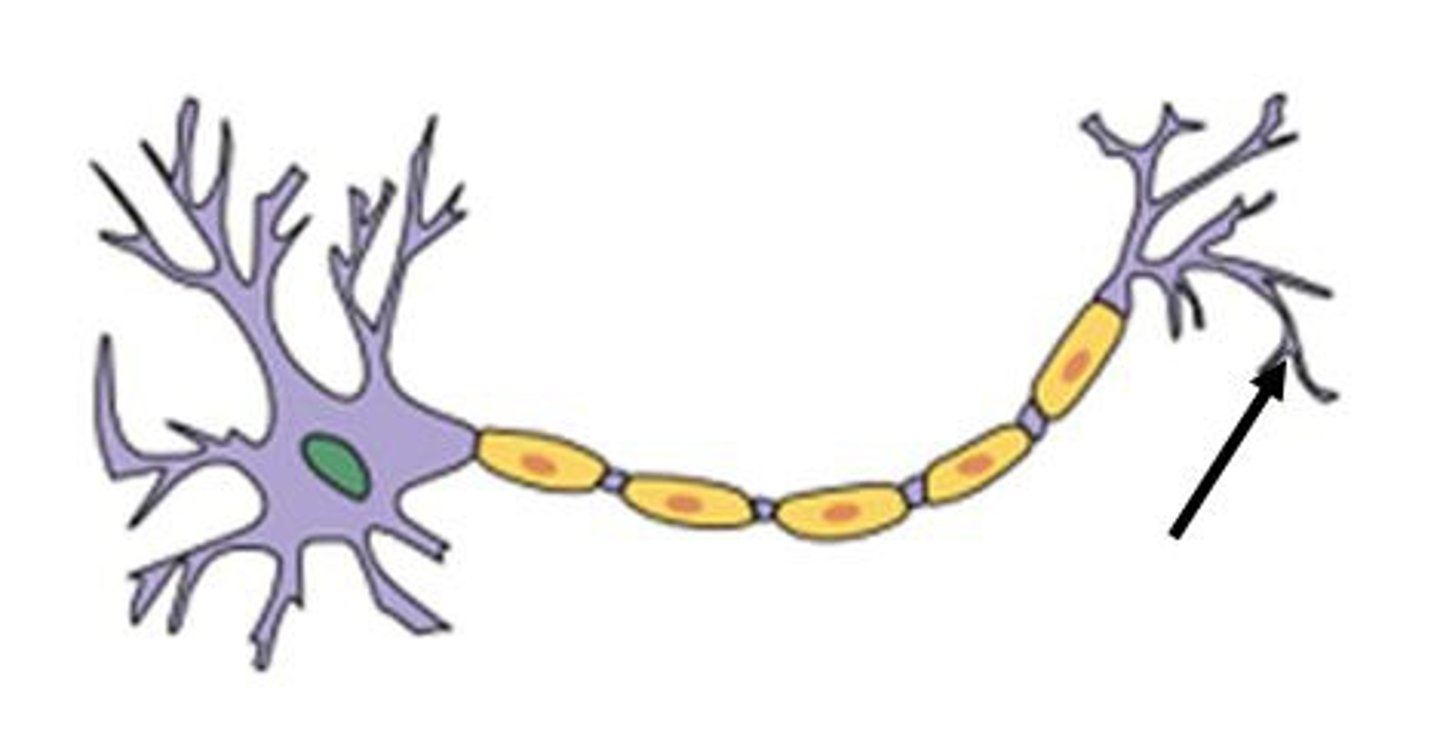
Dendrites
Branchlike parts of a neuron that are specialized to receive information.
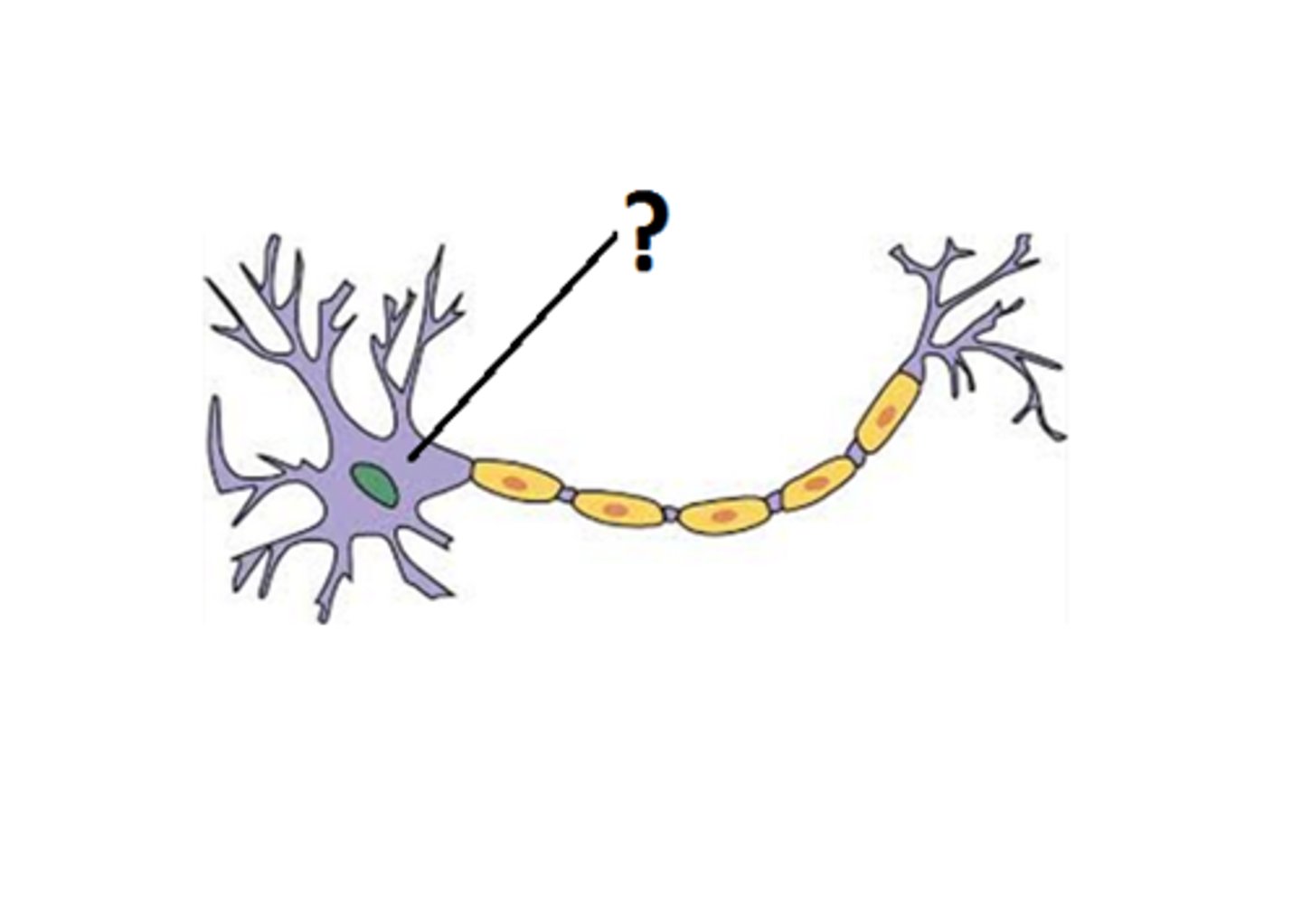
Soma
cell body of a neuron
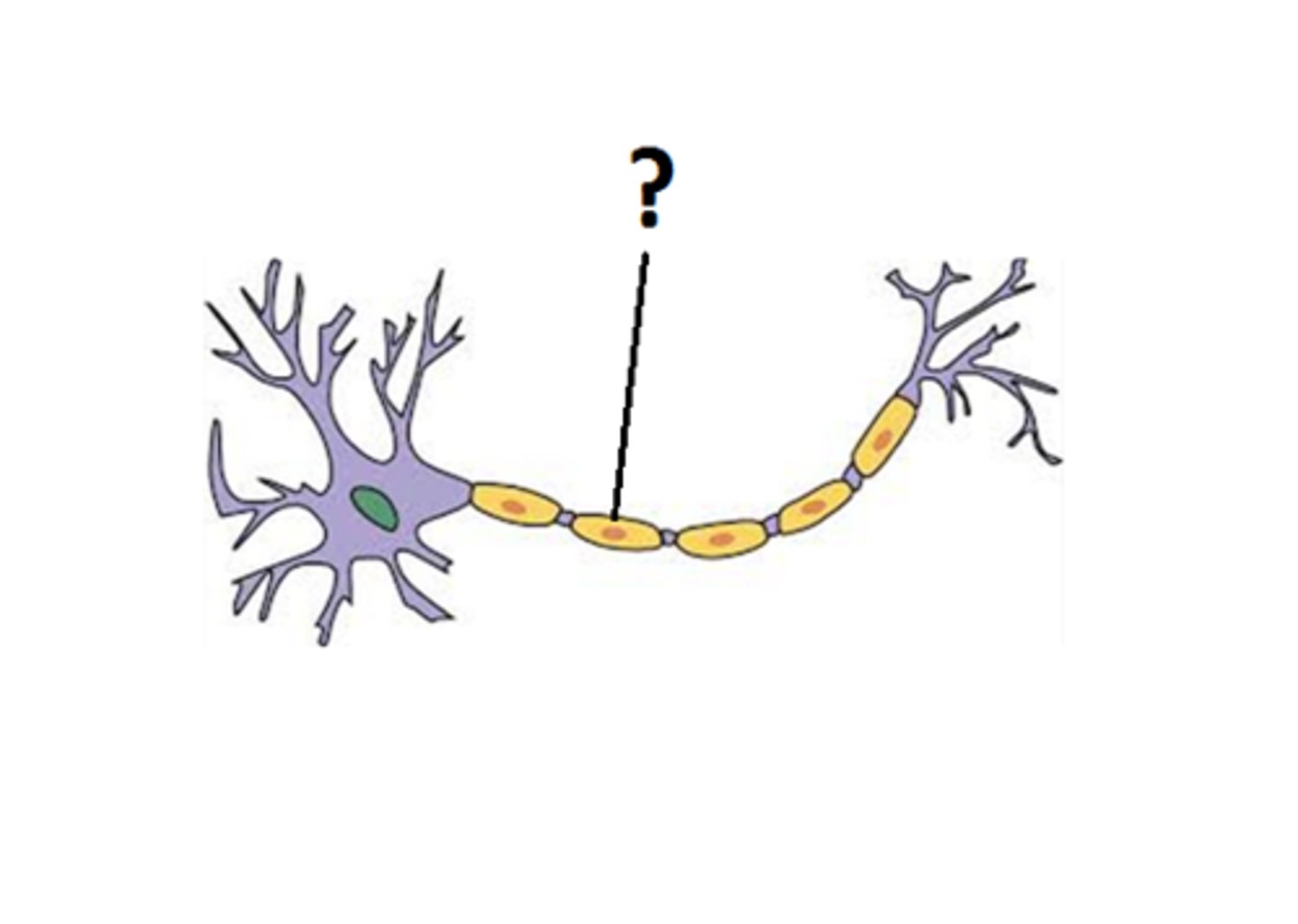
Ranvier nodes
breaks in the myelin sheath; places where action potentials are generated
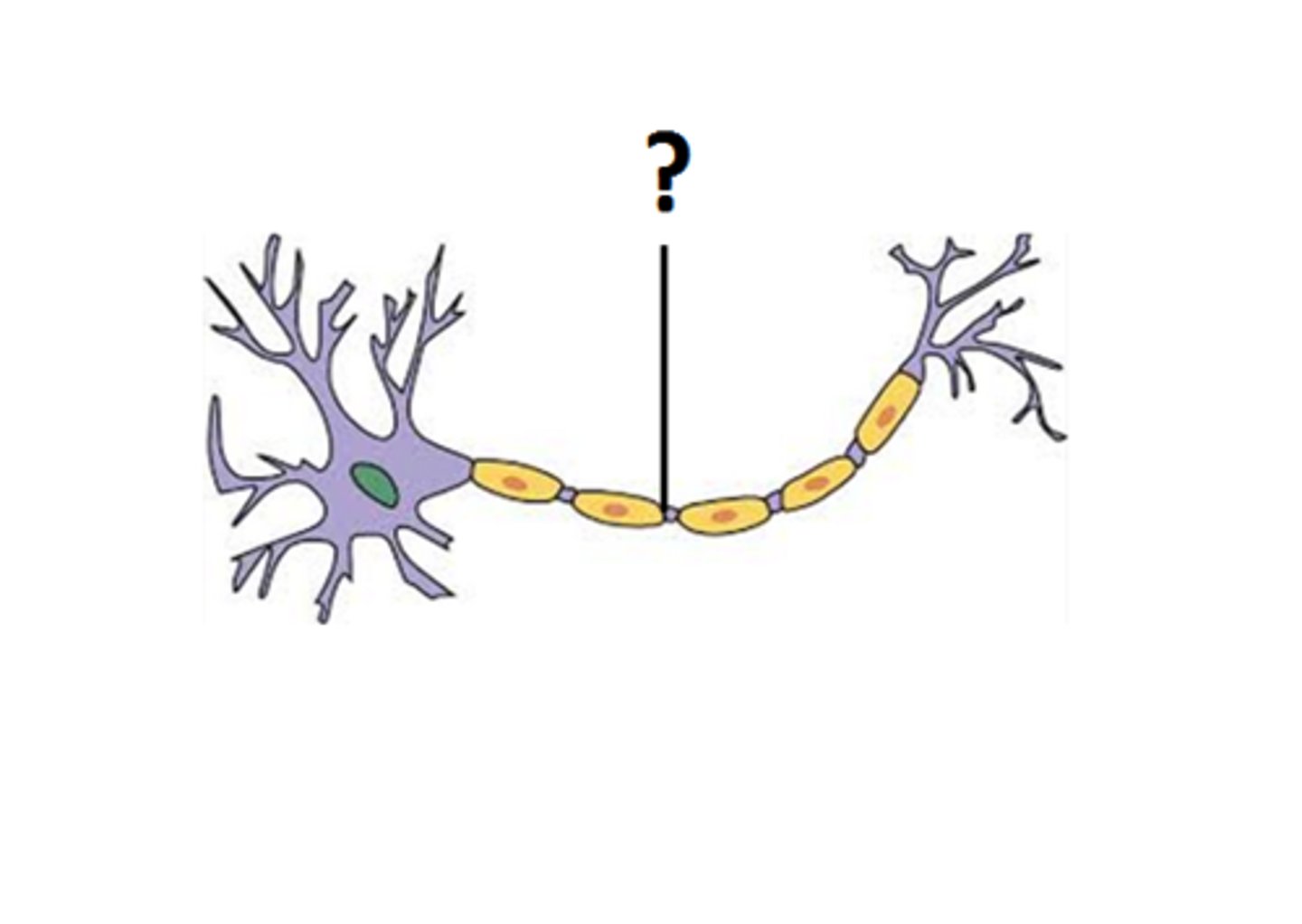
myelin sheath
covers the axon of some neurons and helps speed neural impulses
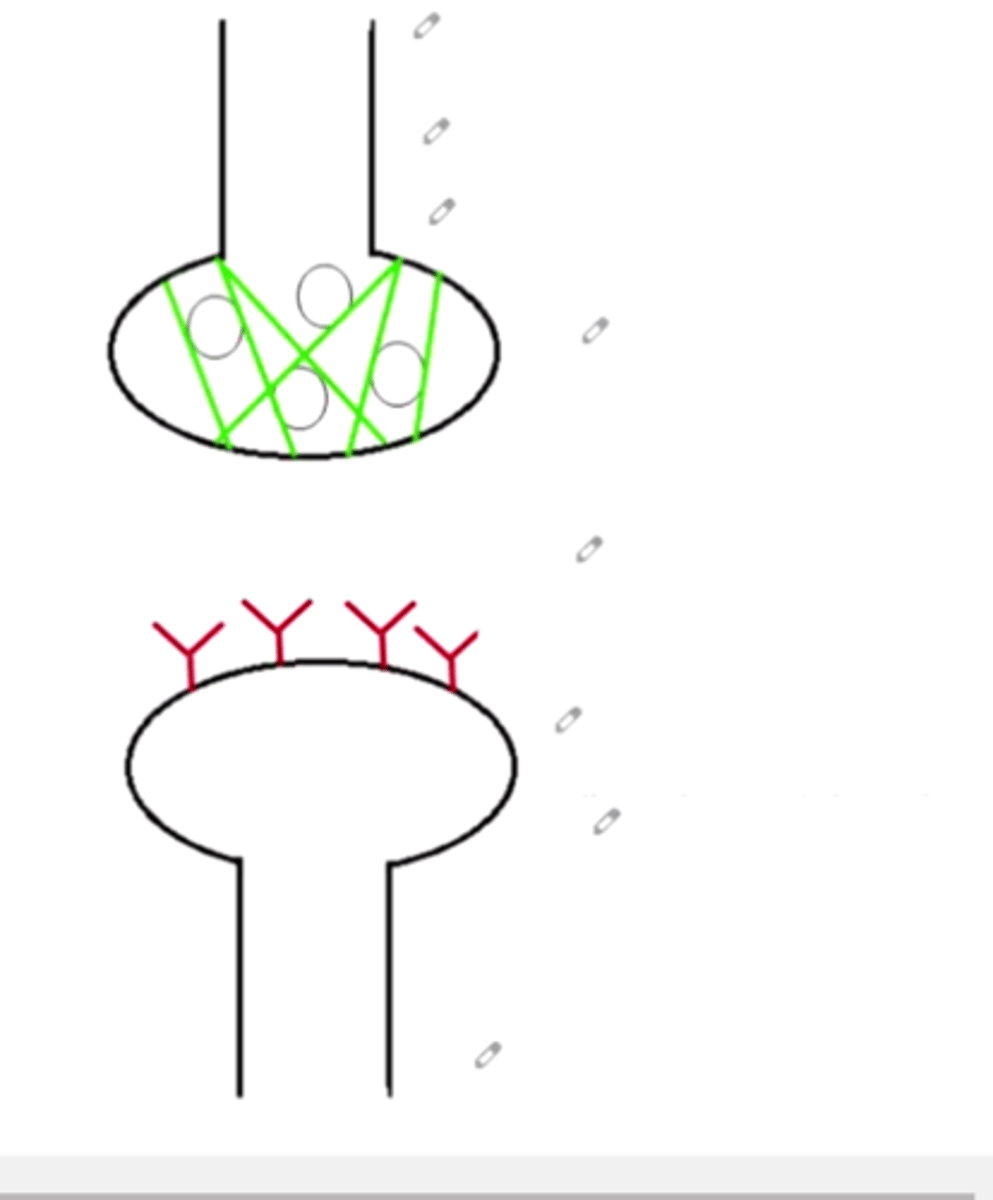
sysnapse
Location at which a neuron can transfer an impulse to another cell
Schwann cell
Section of myelin sheath on the cell
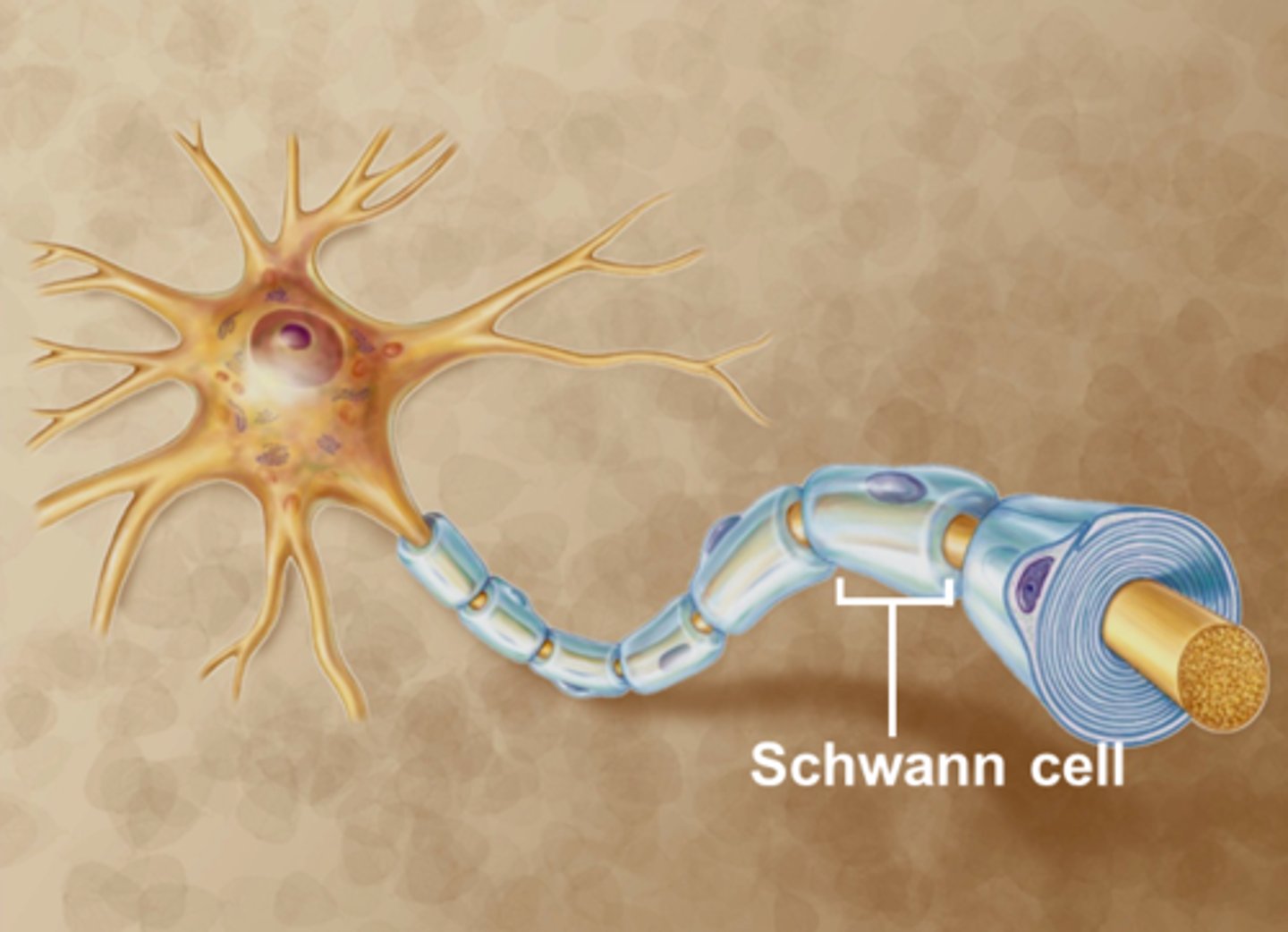
Axon
the extension of a neuron, ending in branching terminal fibers, through which messages pass to other neurons or to muscles or glands
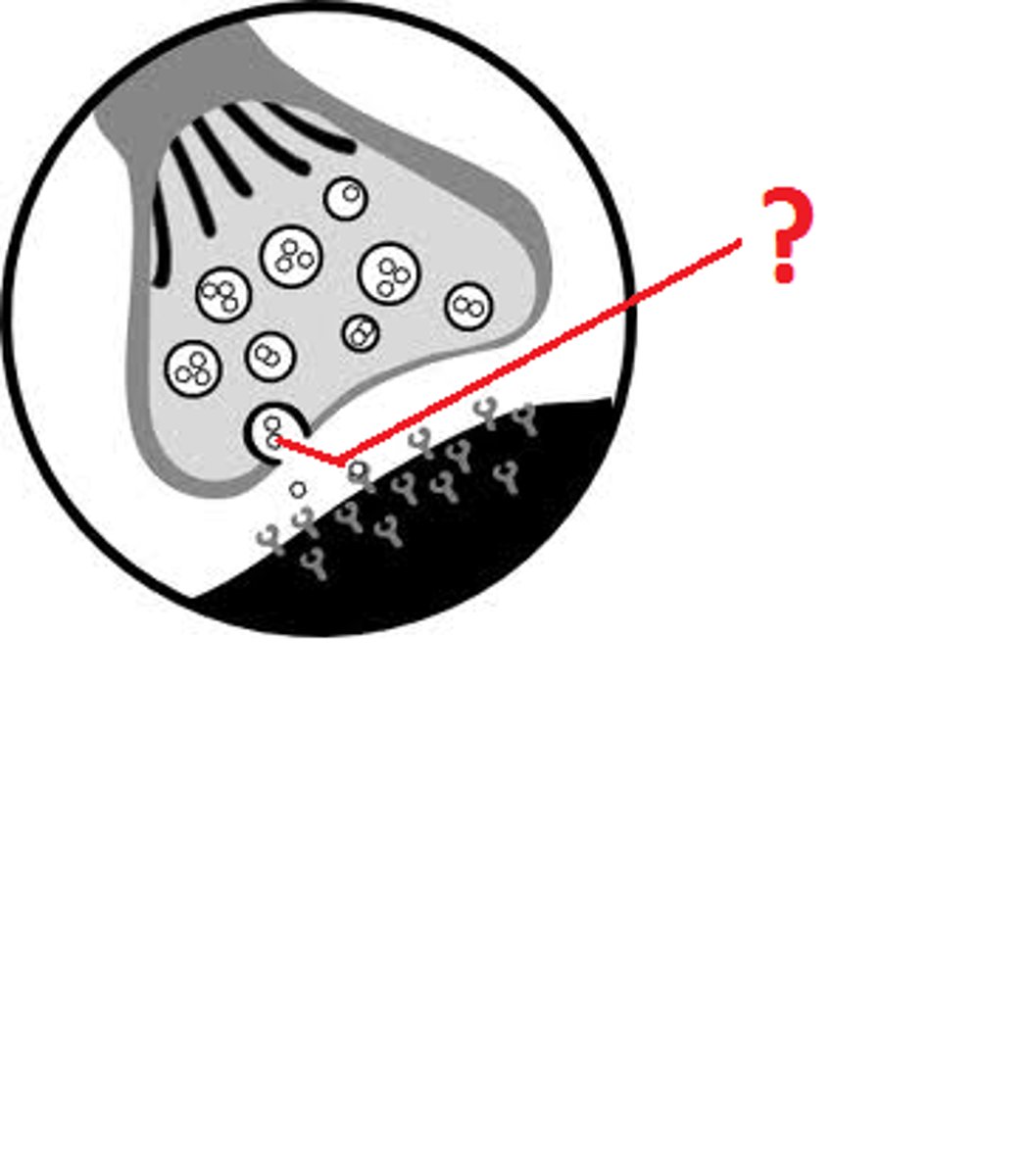
Neurotransmitters
chemical messengers that cross the synaptic gaps between neurons
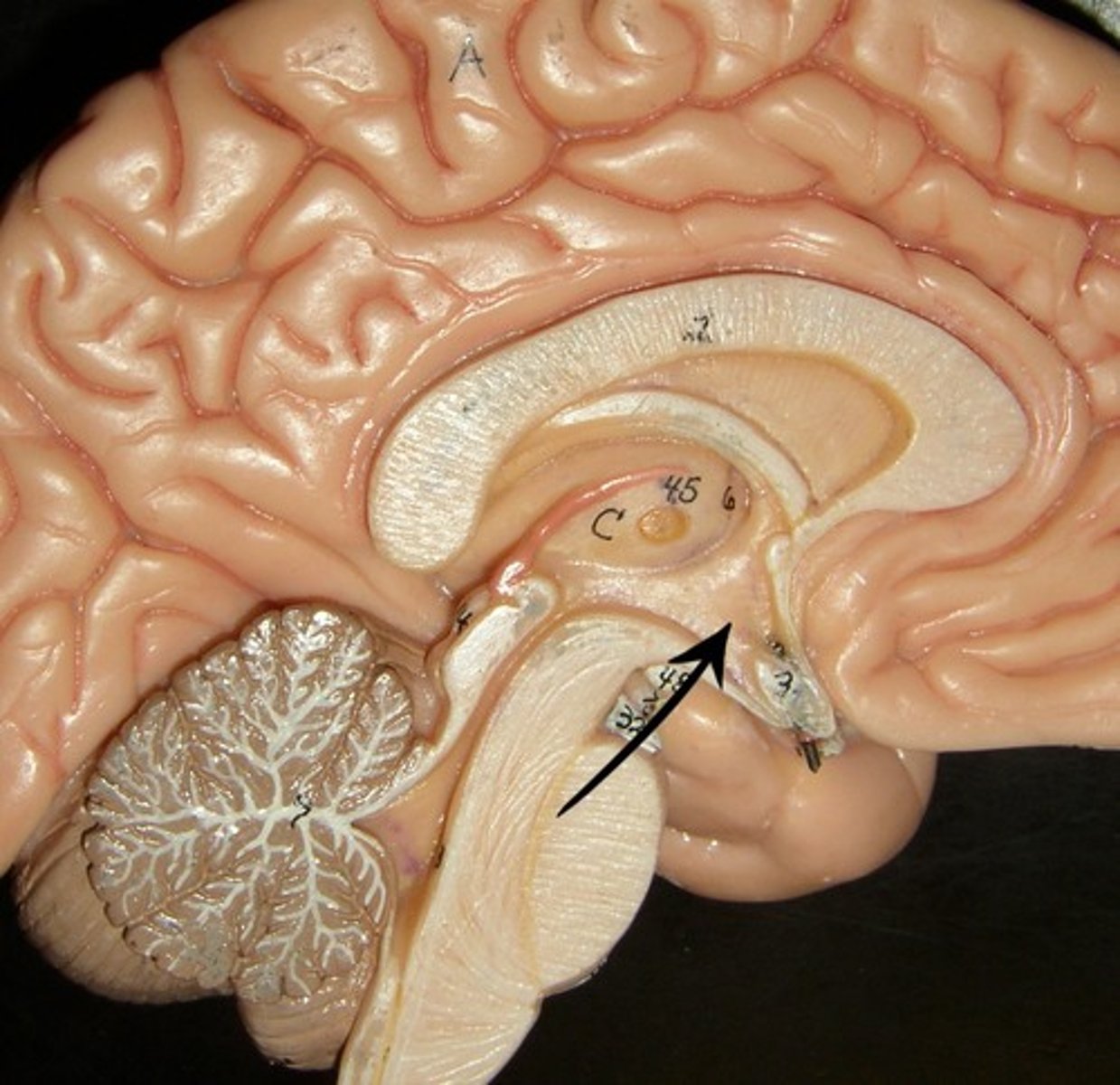
Hypothalamus
brain region connecting the nervous system and endocrine system and also controls the pituitary gland
pituitary gland
endocrine gland at the base of the brain that secretes hormones that activate other endocrine glands
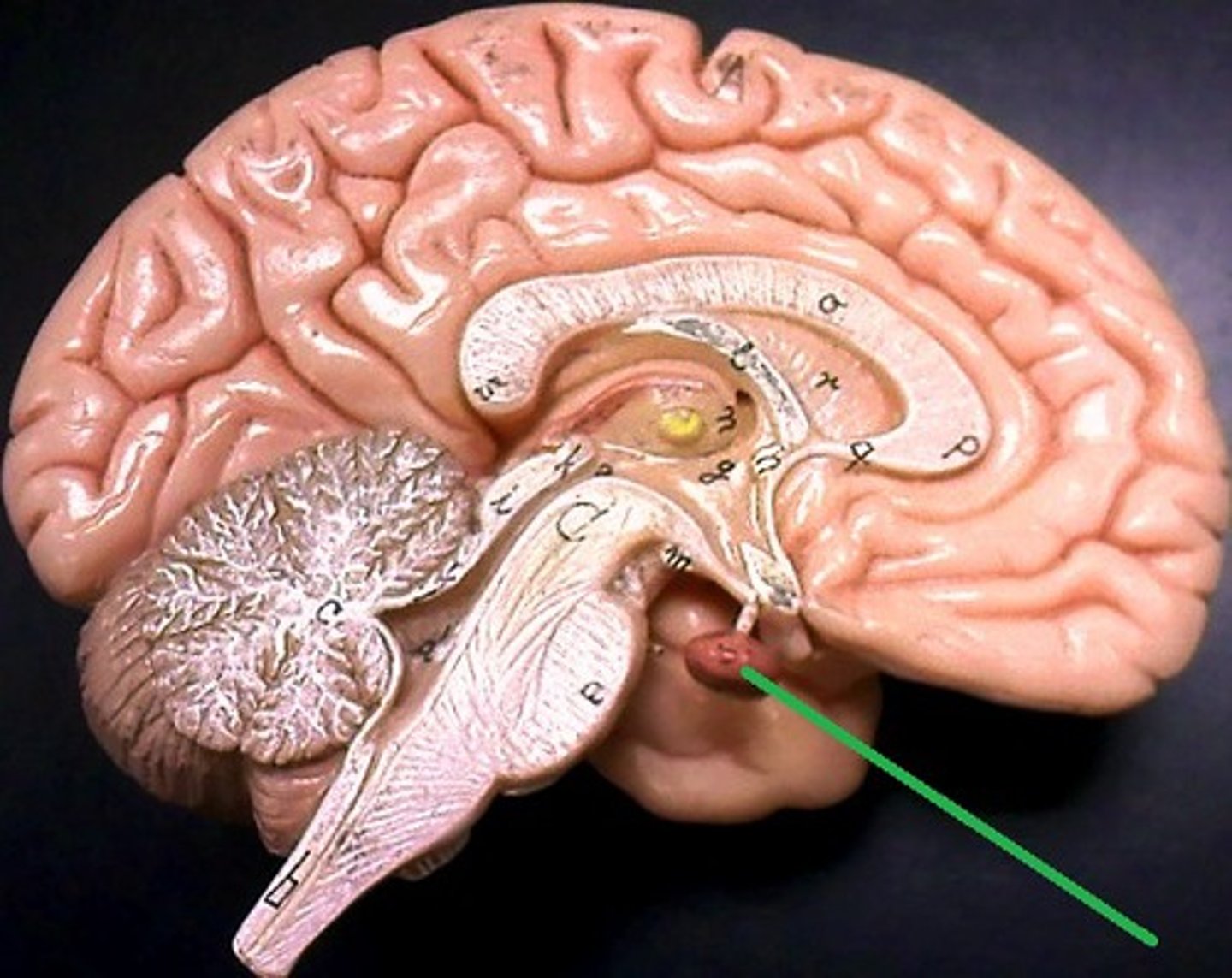
pineal gland
endocrine gland that secretes melatonin
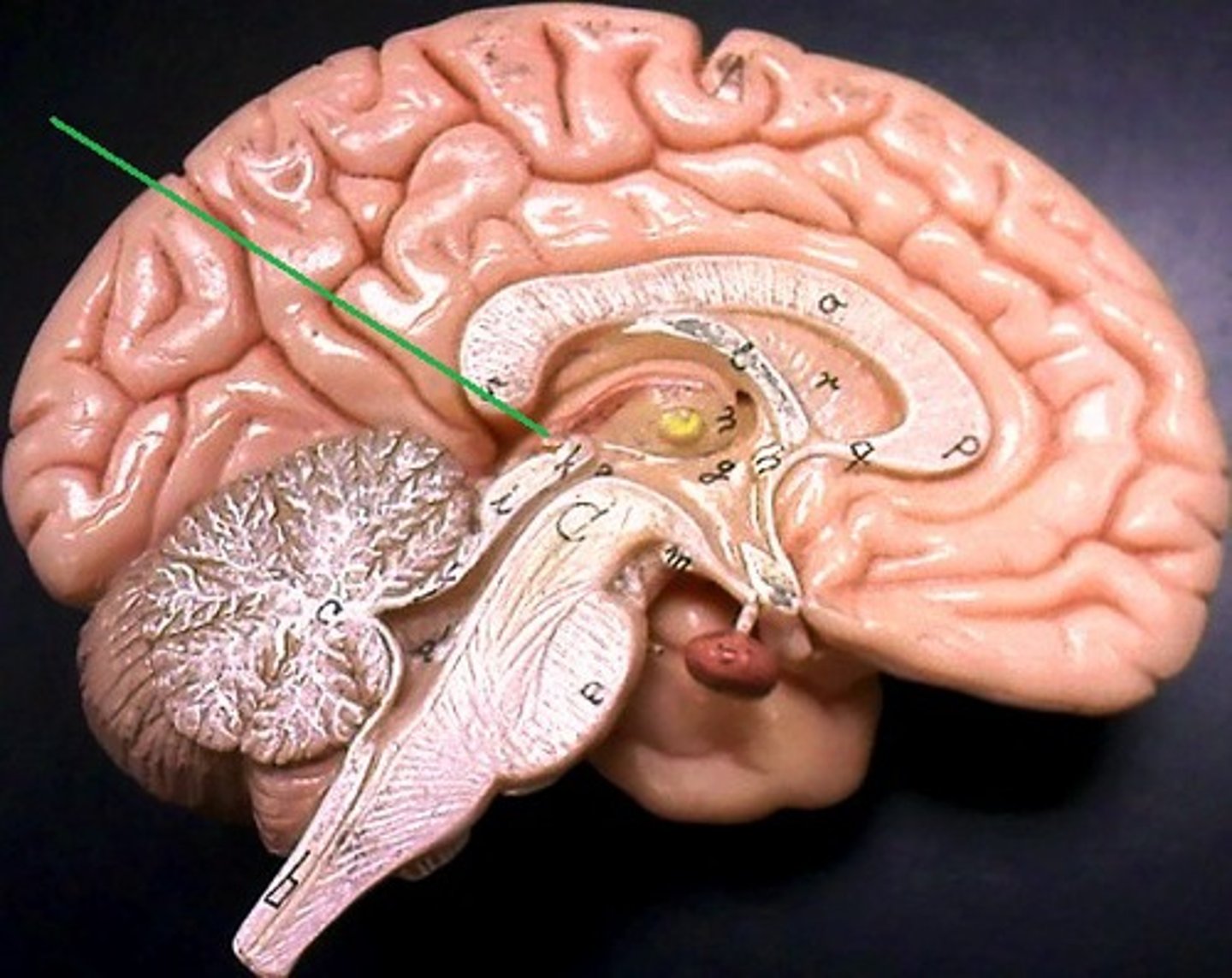
Melatonin
A hormone manufactured by the pineal gland that produces sleepiness.
thyroid gland
endocrine gland surrounding the neck that produces hormones that regulate metabolism, body heat, and bone growth
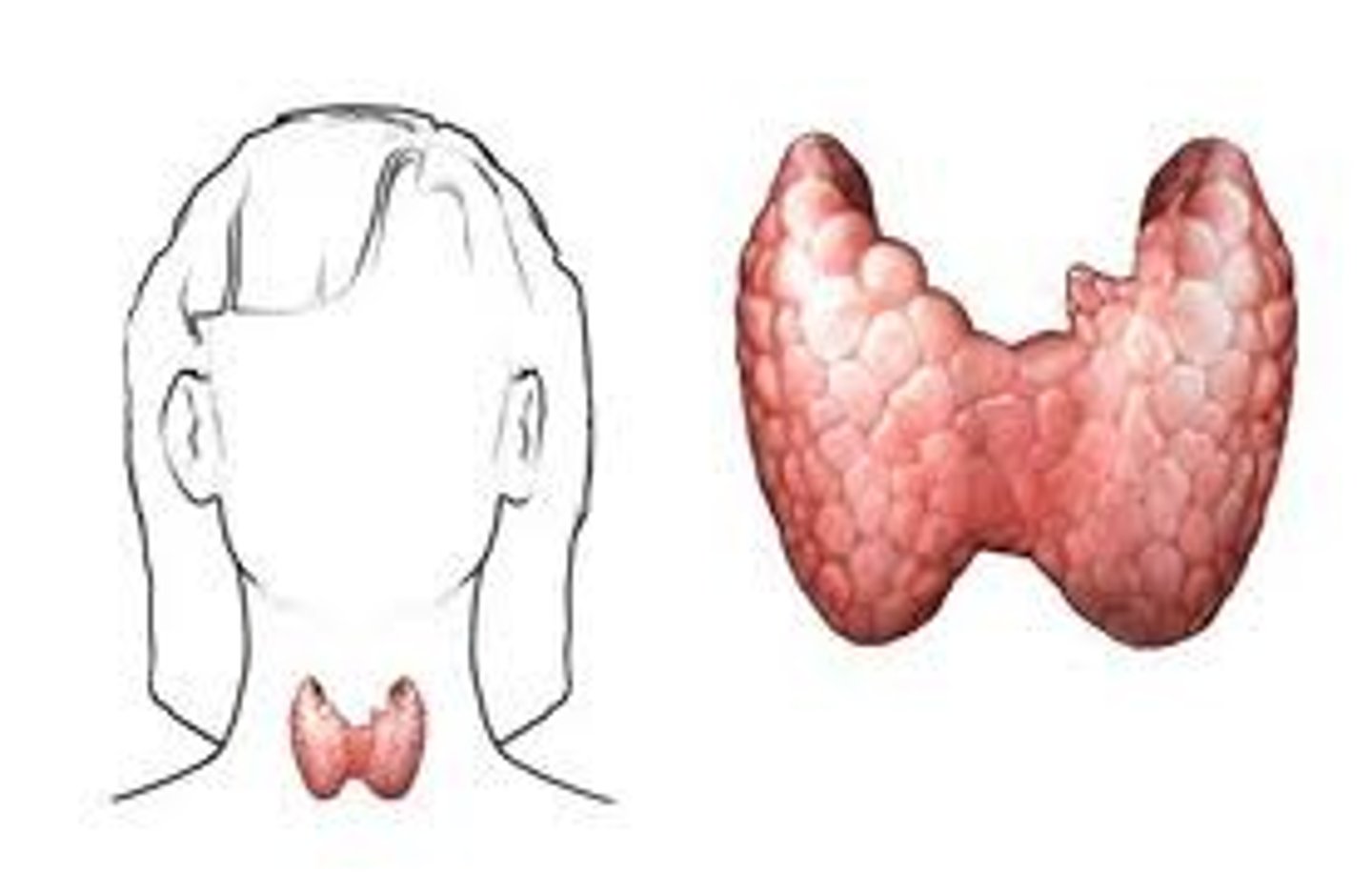
Tyroxin
hormone released by the thyroid gland that controls your cells metabolic rate
parathyroid glands
small pea-like organs that regulate calcium and phosphate balance in blood, bones, and other tissues through the parathyroid hormone
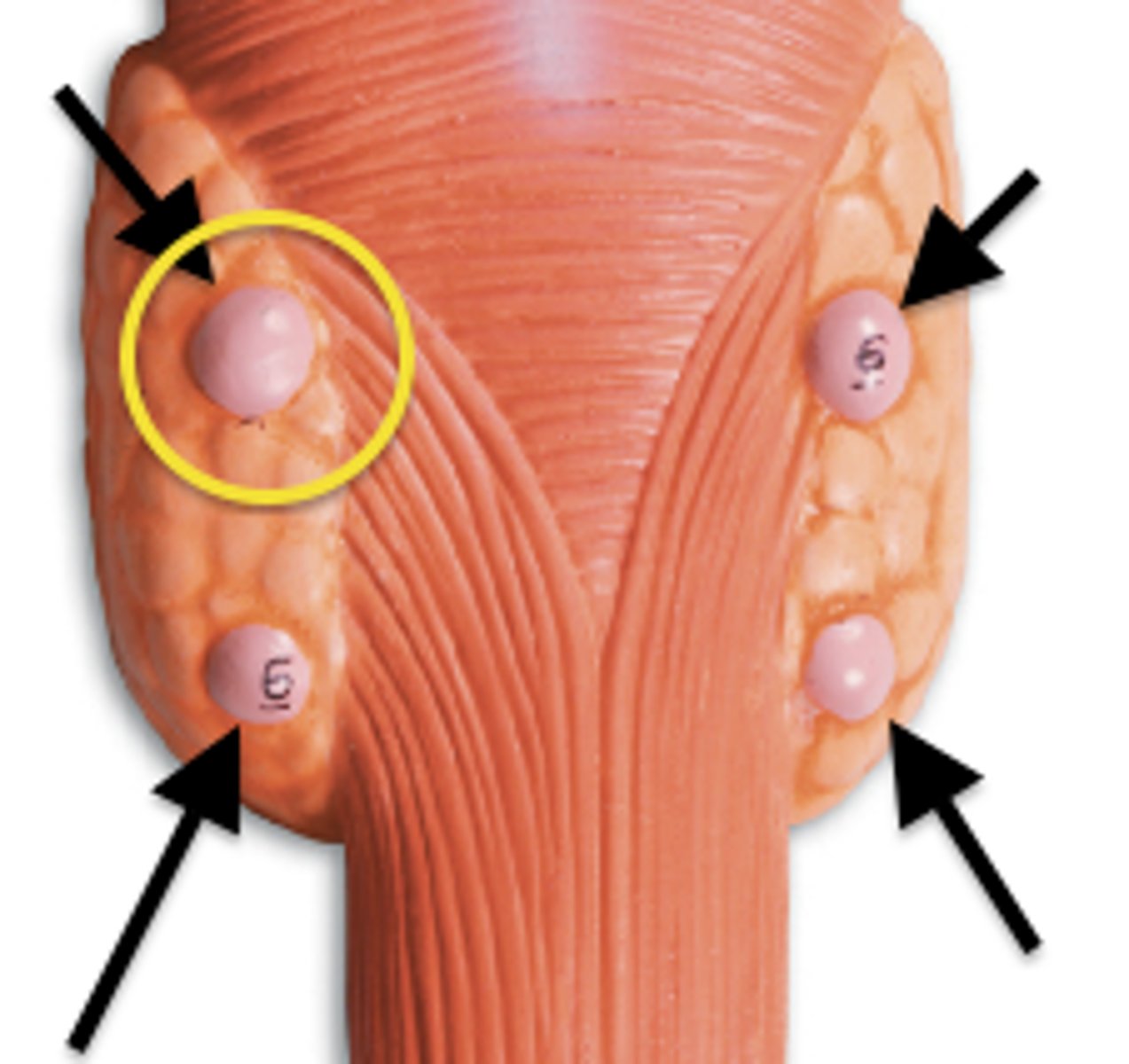
parathyroid hormone
A hormone of the parathyroid gland that regulates the metabolism of calcium and phosphorus in the body.
adrenal glands
a pair of endocrine glands that sit just above the kidneys and secrete hormones (adrenaline and corticosteroids) that help arouse the body in times of stress.
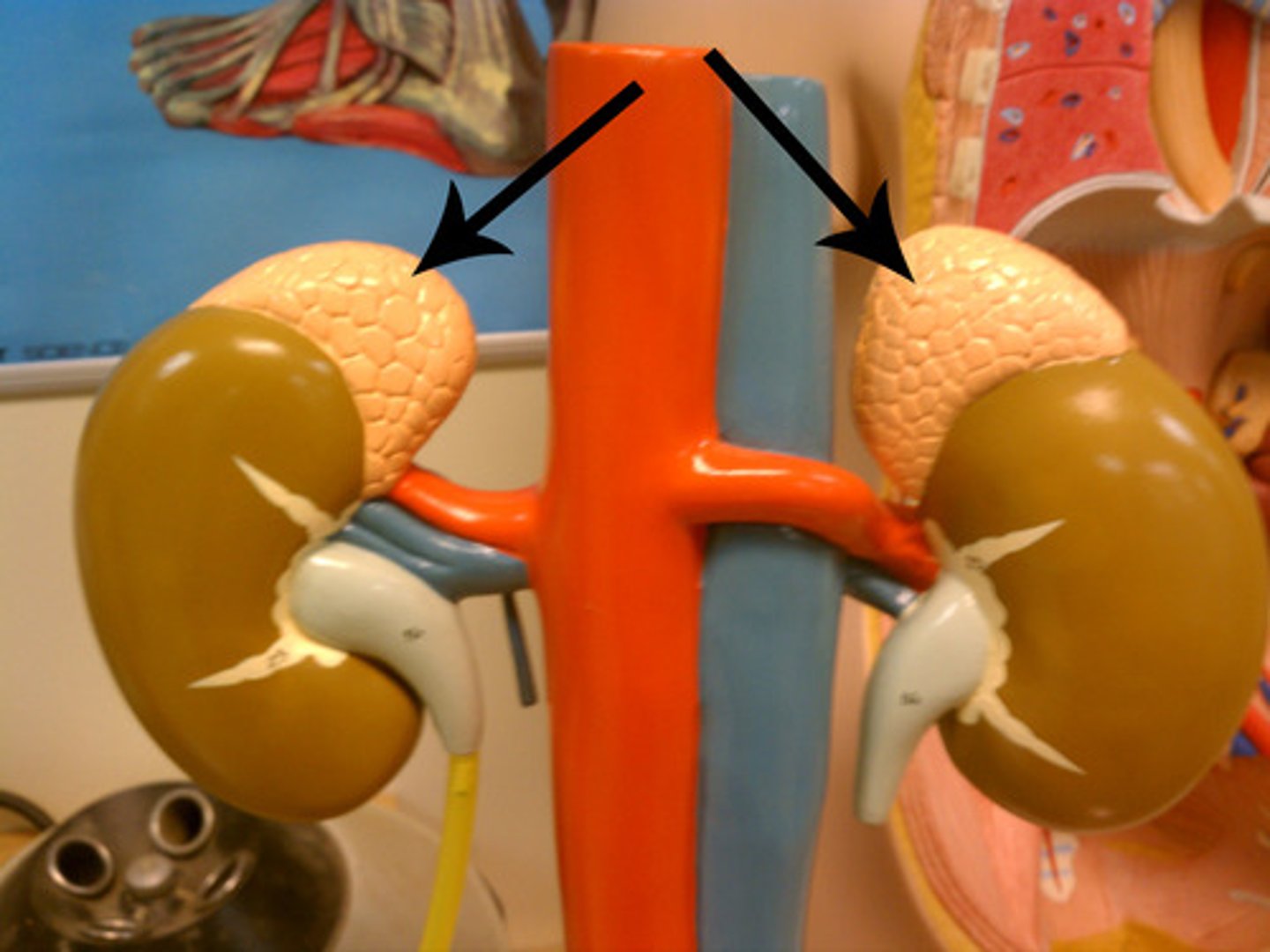
Corticosteroids
A group of hormones, including cortisol, released by the adrenal glands at times of stress
Adrenaline
a hormone secreted by the adrenal glands, especially in conditions of stress, increasing rates of blood circulation, breathing, and carbohydrate metabolism and preparing muscles for exertion.
Pancreas
endocrine gland; controls the levels of glucose in the blood, secretes insulin and glucagon
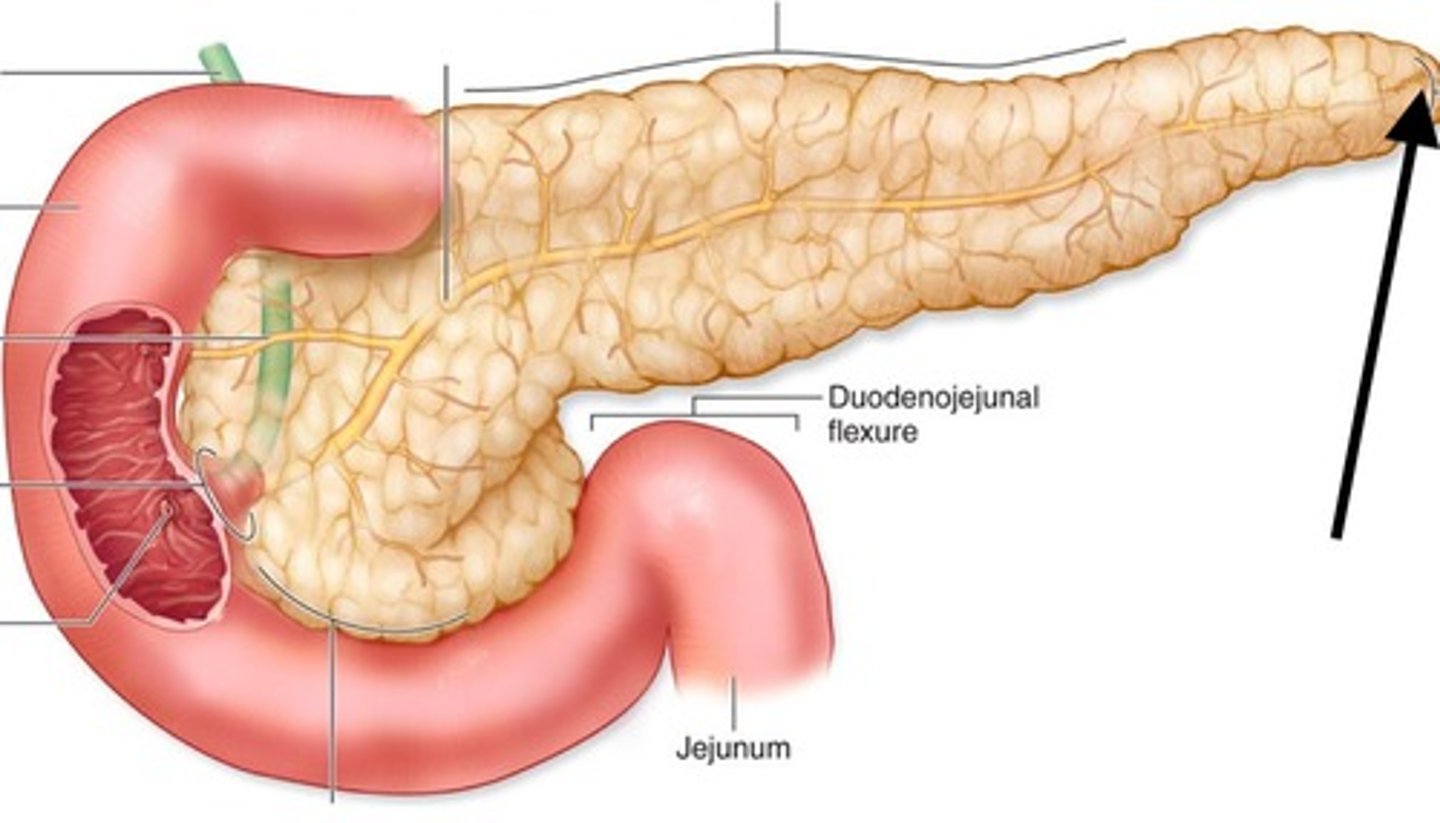
Glucagon
A protein hormone secreted by pancreatic endocrine cells that raises blood glucose levels; an antagonistic hormone to insulin.
Insulin
A protein hormone synthesized in the pancreas that regulates blood sugar levels by facilitating the uptake of glucose into tissues (decreases blood glucose levels)
Ovaries
The female sex glands that store the ova and produce female sex hormones (estrogens and progesterone)
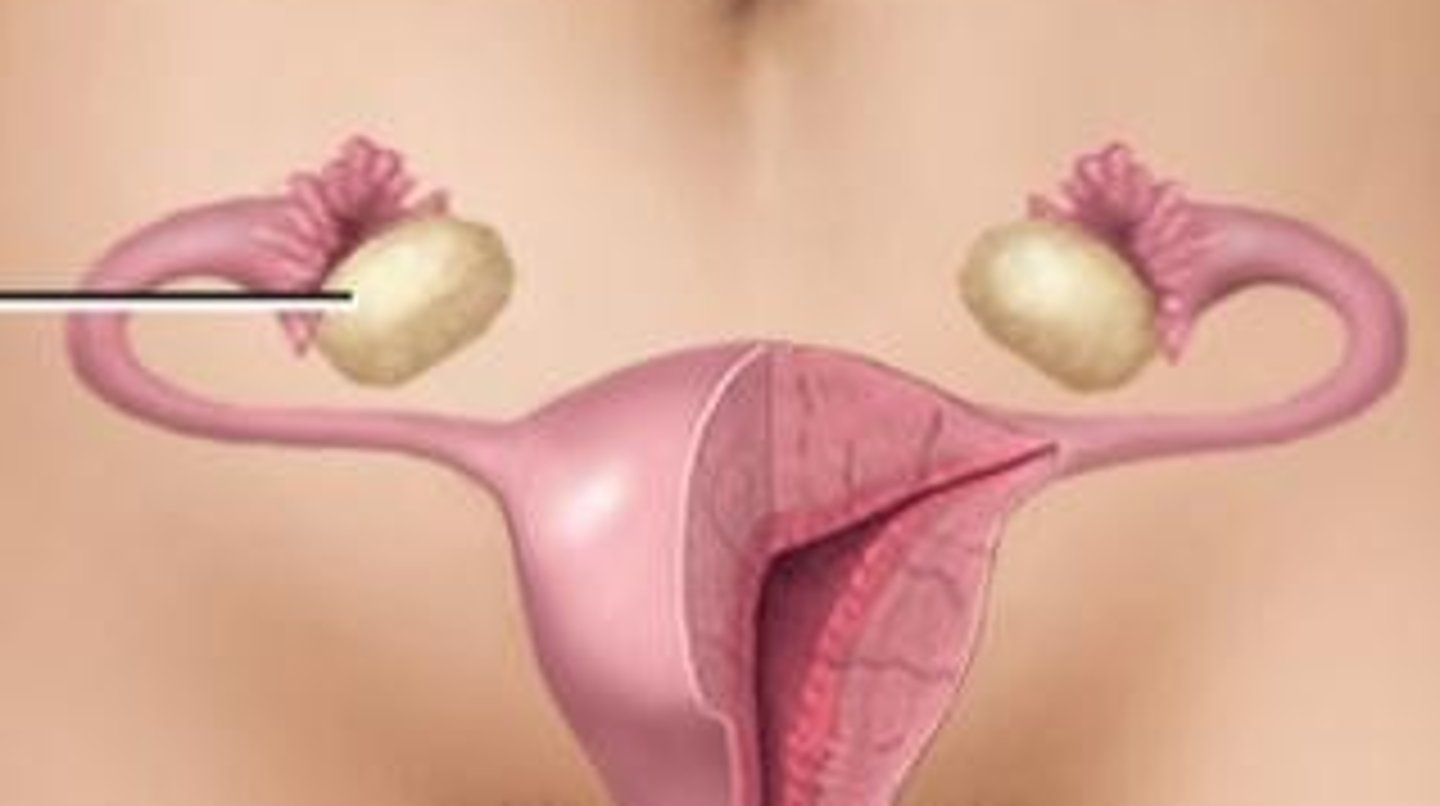
Testes
Male sex glands or gonads that produce the male sex hormone, testosterone.
Estrogen
female sex hormone secreted by the ovaries. In charge of female secondary sex characteristics during puberty
Progesterone
A hormone produced by the ovaries which acts with estrogen to bring about the menstral cycle and participates in pregnancy.
Testosterone
Male sex hormone that controls the development of male secondary sex characteristics
addiction
A physiological and/or psychological dependence on a drug
Depressants
drugs (such as alcohol, sedatives, and heroin) that reduce neural activity and slow body functions
Narcotics
drugs that inhibit the transmission of nerve impulses associated with pain and in addition to dulling pain, they also induce drowsiness and sleep. Cause extreme addiction (morphine, heroin)