Cell Bio 2020 Exam 1: University of Utah
1/92
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
93 Terms
What is the cell theory? (3 parts)
1. All living things are made up of cells
2. Cells are the basic units of structure and function in living things
3. New cells are produced from existing cells
What are common cell features? (3)
1. Boundary
2. Metabolism
3. Mechanism of Inheritance
What are the steps of the central dogma?
replication, transcription, translation
Features of prokaryotic cells
- Circular DNA
- No membrane bound organelles
- No nucleus
- Double boundary
Features of Eukaryotic cells
- Linear DNA
- Membrane bound organelles
- Nucleus
- Single or Double boundary
Nucleus
A part of the cell containing DNA and RNA and responsible for growth and reproduction (Site of DNA replication and RNA transcription)
Mitochondria
Powerhouse of the cell, organelle that is the site of ATP (energy) production
Chloroplasts
Site of photosynthesis
Endoplasmic Reticulum
synthesizes proteins (rough) and lipids (smooth)
Golgi apparatus
processing and sorting
lysosomes
Uses chemicals to break down food and worn out cell parts
light microscopy
light lenses to magnify objects
scanning electron microscope
uses electrons to image the surface of dried gold-coated cells
confocal microscopy
optical sectioning and 3D reconstruction of cells or tissues
fluorescence microscopy
uses a fluorescent dye that emits fluorescence when illuminated with ultraviolet radiation
live cell fluorescence
watch living cells
Endosymbiosis theory
A theory that mitochondria and chloroplasts originated from bacteria that took up residence within a primordial eukaryotic cell.
What is the subunit of a polysaccharide
sugar
What is the purpose of a polysaccharide?
Energy source; cell structures
Sugars are linked via...
condensation
Sugars are split via...
hydrolysis
What is the subunit of a lipid
fatty acid
What are lipids used for?
long term energy storage; cell membranes
Amphipathic
A molecule that has both a hydrophilic region and a hydrophobic region.
A fatty acid hydrocarbon tail is
hydrophobic
A fatty acid carboxylic head is
hydrophilic
Saturated fats
have no double bonds
Unsaturated Fats
have double bonds
Phospholipid structure
2 fatty acids, 1 glycerol, 1 phosphate group
Subunit of Proteins
amino acids
side chains of amino acids
can be:
polar
non-polar
aromatic
nonaromatic
charged
uncharged
Proteins form in
linear chains
What bond joins amino acids?
peptide bonds
What process creates proteins
translation
Folding of proteins happens because of
non-covalent interactions (electrostatic attractions, hydrogen bonds, van der waals)
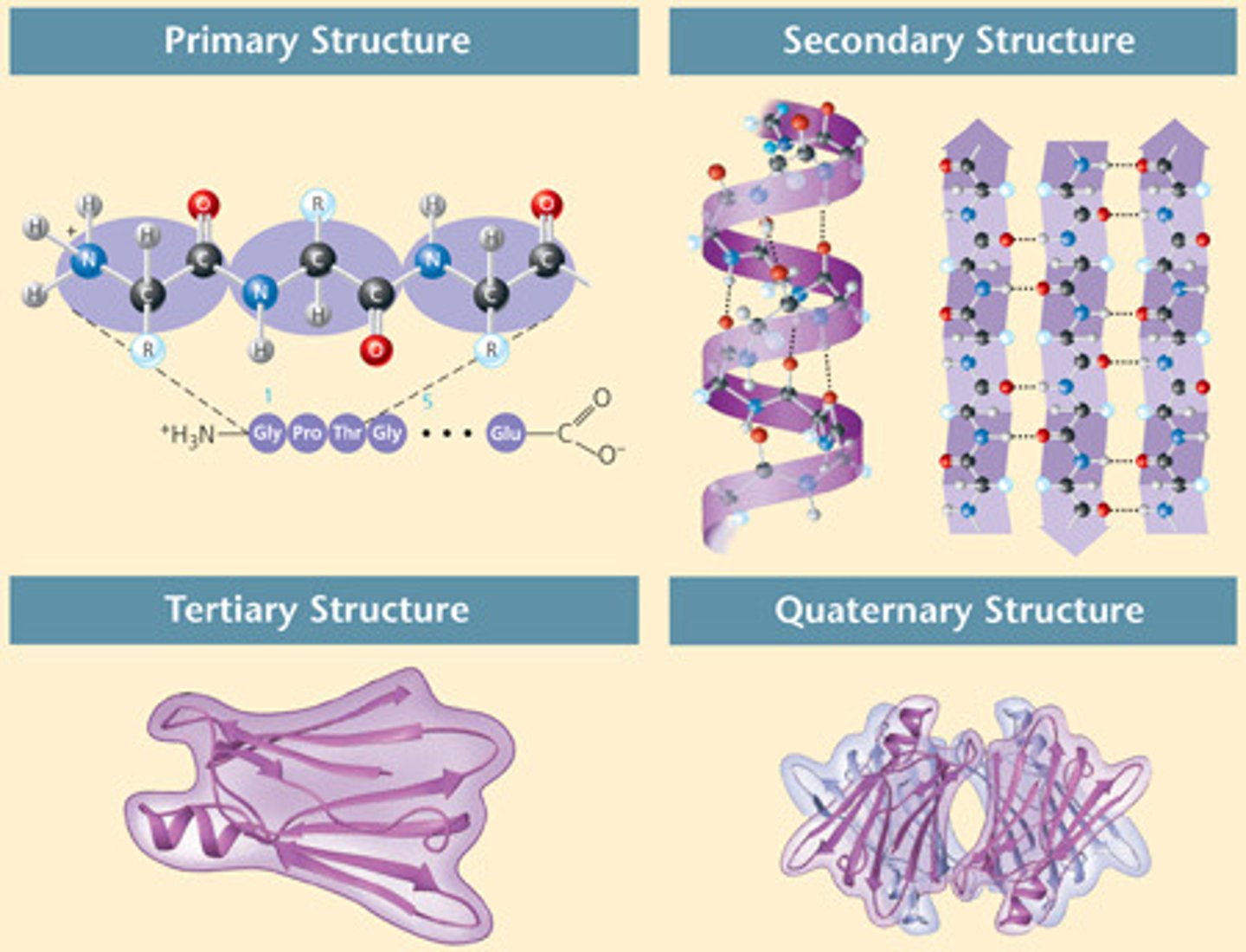
primary structure
linear sequence of amino acids
secondary structure
alpha helix and beta sheet
tertiary structure
three-dimensional shape of a polypeptide due to interactions of the R groups of the amino acids making up the chain.
quaternary structure
the shape resulting from the association of two or more polypeptide subunits.
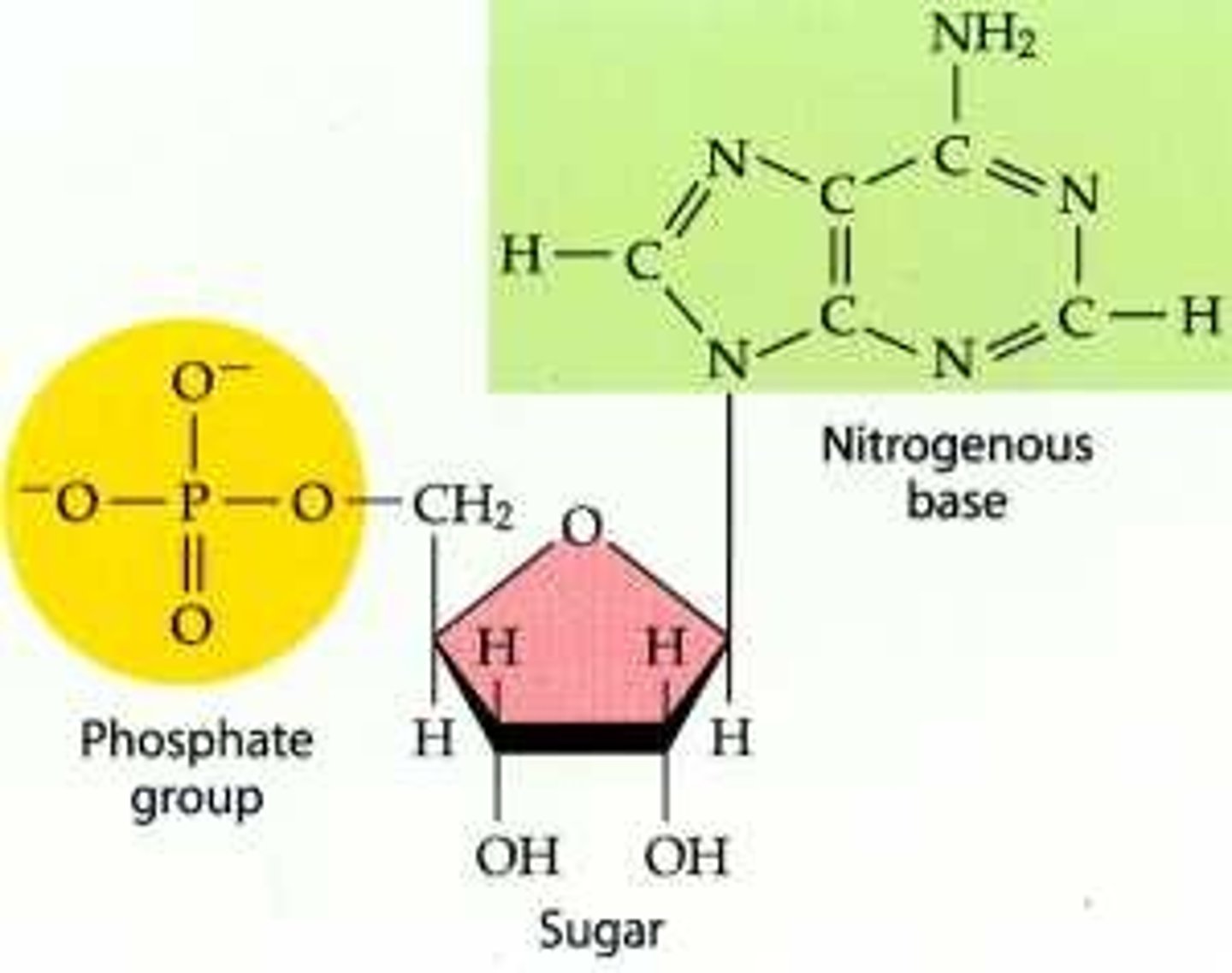
What is the subunit of a nucleic acid?
nucleotide
Nucleotide bases
Adenine, Thymine, Guanine, Cytosine
Pyrimidines (3)
cytosine, thymine, uracil
Purines (2)
Adenine and Guanine
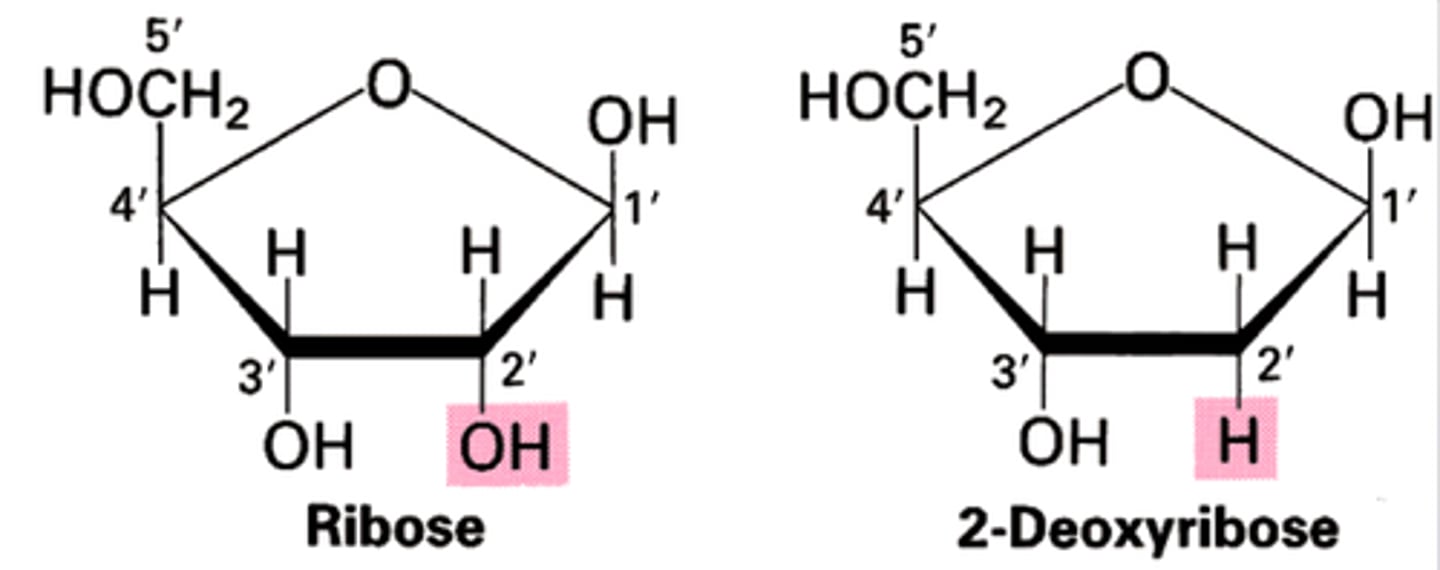
Nucleic acid sugars
deoxyribose and ribose
deoxyribose vs ribose
deoxyribose lacks an oxygen atom on the second carbon in the ring
what makes up a nucleic acid
The phosphates, the sugars and the nitrogenous bases
A favorable reaction has a ________ deltaG
negative
An unfavorable reaction has a _____ deltaG
positive
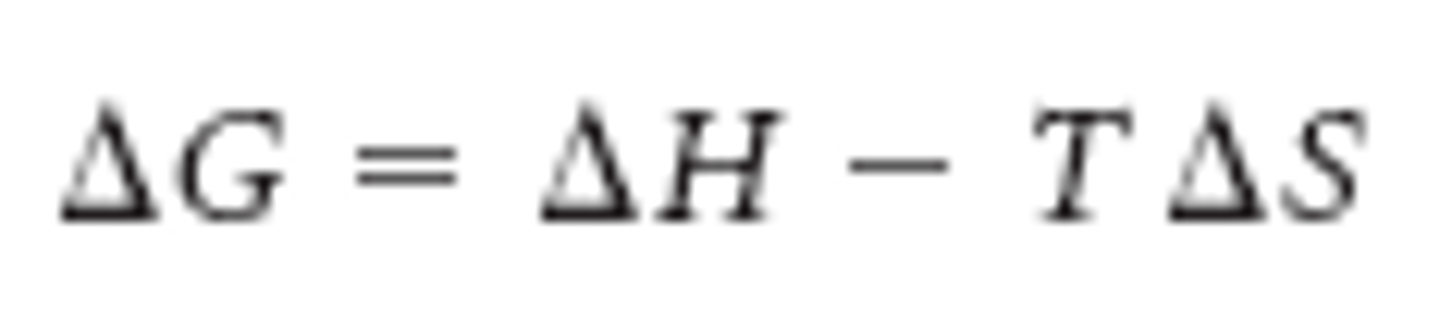
Favorability of a reaction depends on:
- concentrations
- intrinsic chemistry (enthalpy and entropy)
Enzymes
lower the Ea and don't affect delta G
Energetically unfavorable reactions must...
be coupled with energetically favorable reactions (via peptide bond formations)
Ways to damage DNA (3)
1- Depurination
2- Deamination
3- Thymine Dimers
Depurination
Chemical reaction that removes the purine bases from DNA
Deamination
the removal of an amino group from an amino acid
Thymine Dimers
two neighboring thymines attached to one another by covalent bonds bond together on a single strand of DNA
Ways to repair DNA (3)
1- DNA Polymerase
2- Mismatch repair
3- Double Strand breaks
Nonhomologous end joining
A quick-and-dirty mechanism for repairing double-strand breaks in DNA that involves quickly bringing together, trimming, and rejoining the two broken ends; results in a loss of information at the site of repair. (done by DNA Ligase)
Homologous recombination
uses intact chromosome as a template for error-free repair by nuclease
What does CRISPR do
makes it possible to change or remove a specific gene in living cells
What does CRISPR need to work
- Cas9 protein (cuts DNA)
- gRNA (guide RNA; finds target gene)
CRISPR process
1- gRNA binds to Cas9
2- Cas-9:gRNA complex finds matching DNA site
3- generates a double strand break
4- repaired by non homologous end joining
What direction is DNA synthesized
5' to 3'
Helicase
An enzyme that untwists the double helix at the replication forks
Topoisomerase
Enzyme that functions in DNA replication, helping to relieve strain in the double helix ahead of the replication fork.
Primase
synthesizes RNA primer
DNA Polymerase
principle enzyme involved in DNA replication
RNA polymerase
enzyme that links together the growing chain of RNA nucleotides during transcription using a DNA strand as a template
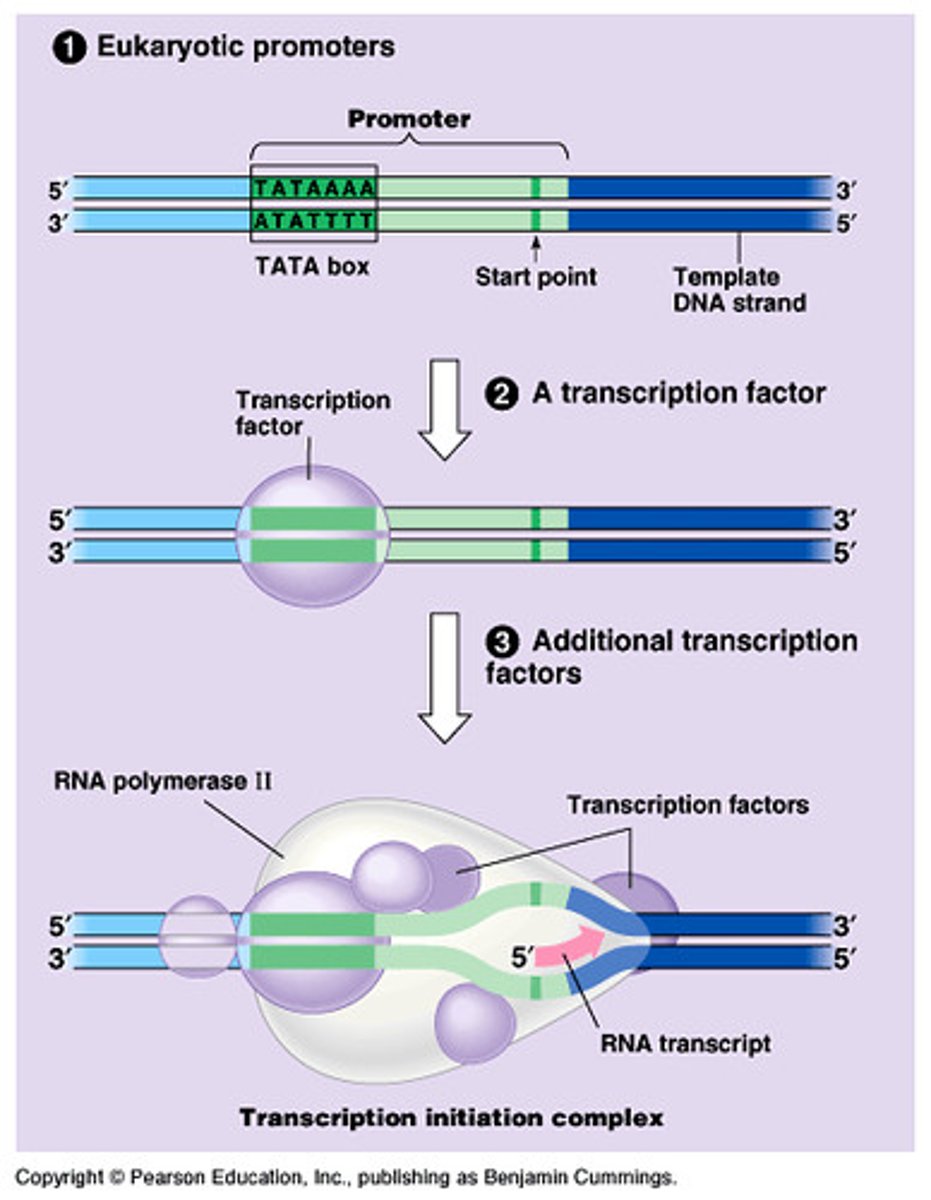
Transcription process (8)
1. TATA-binding protein (TBP) recognizes the TATA box.
2. TFIID (transcription factor II D) recruits TFIIB.
3. RNA polymerase II and the rest of the transcription factors assemble at the promoter.
4. Helicase opens DNA.
5. TFIIH phosphorylates RNA polymerase
6. Polymerase uses NTPs to begin synthesis.
7. Polymerase continues through the gene, generating an mRNA.
8. Eukaryotic terminator sequences cause the polymerase to release from the gene.
Prokaryote Transcription
1. One type of polymerase
2. Sigma factor
3. No nucleosomes
4. Transcript immediately available for translation.
Eukaryote Transcription
1. 3 types of polymerases
2. Many transcription factors
3. Must unpack chromatin structure
4. Transcript must be exported to cytoplasm before translation
RNA Processing (3)
1- Capping
2- Splicing
3- Polyadenylation
What do eukaryotes splice out?
introns
Alternative splicing
allows for a single gene to code for different proteins (opportunity for evolution)
snRNPs
RNA protein complexes that coordinate intron removal.
spliceosomes
Collection of snRNPs that remove introns from pre-mRNA.
ribosome
Makes proteins
What process makes proteins
translation
tRNA
transfer RNA; type of RNA that carries amino acids to the ribosome
A site
acceptor site
P site
holds the tRNA carrying the growing polypeptide chain. Generates the peptide bond
E Site
the exit site, where discharged tRNAs leave the ribosome
small ribosomal subunit
bound to initiator tRNA; Finds AUG
transcription regulator proteins
bind to DNA to switch genes on or off
transcription repressor
decreases transcription
transcription activator
increases transcription
Epigenetics
Heritable information that does not involve changes to DNA
Genetic Variation (6)
1- Mutation within a gene
2- Mutation in regulatory DNA
3- Gene duplication and divergence
4- Exon shuffling
5- Transposition
6- Horizontal transfer
Mutation within a gene
small changes to transcript or protein product
Mutation in regulatory DNA
Changes to expression level, timing, location
Gene duplication and divergence
Genes are copied, and then can evolve separately
Exon shuffling
rearrangement of exons to generate new coding regions
transposition
mobile elements of DNA that 'hop' in and out of genes
horizontal transfer
transfer of genes between organisms