B4 - Phloem and Bark
1/14
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
15 Terms
identify the functions of phloem and what it transports and it’s direction.
transport tissue. cells are alive. transports photosynthate and nutrients. goes both up and down to growing points.
phloem structure
stucture is long, continuous root to tip. external to xylem.
phloem functions
it functions as a continuous highway for most materials. the external position means its not buried when xylem grows.
sugar source
part that makes or releases more stored sugar than it uses.
sugar sink
part that uses or stores more sugar than it makes.
how is photosynthate transported throughout plant
1) Sugar actively transported from source to phloem
2) H2O flows passively from the xylem into the phloem
3) H2O and sugar passively transported toward sink
4) Sugar actively transported into sink
understand the role of phloem in food chains
phloem feeding insects.
direct defense
plants produce physical barriers against insect herbivores, or compounds that exert repellent, antinutritive, or toxic effects
indirect defense
plants attract or nourish other organisms to reduce energy pressure.
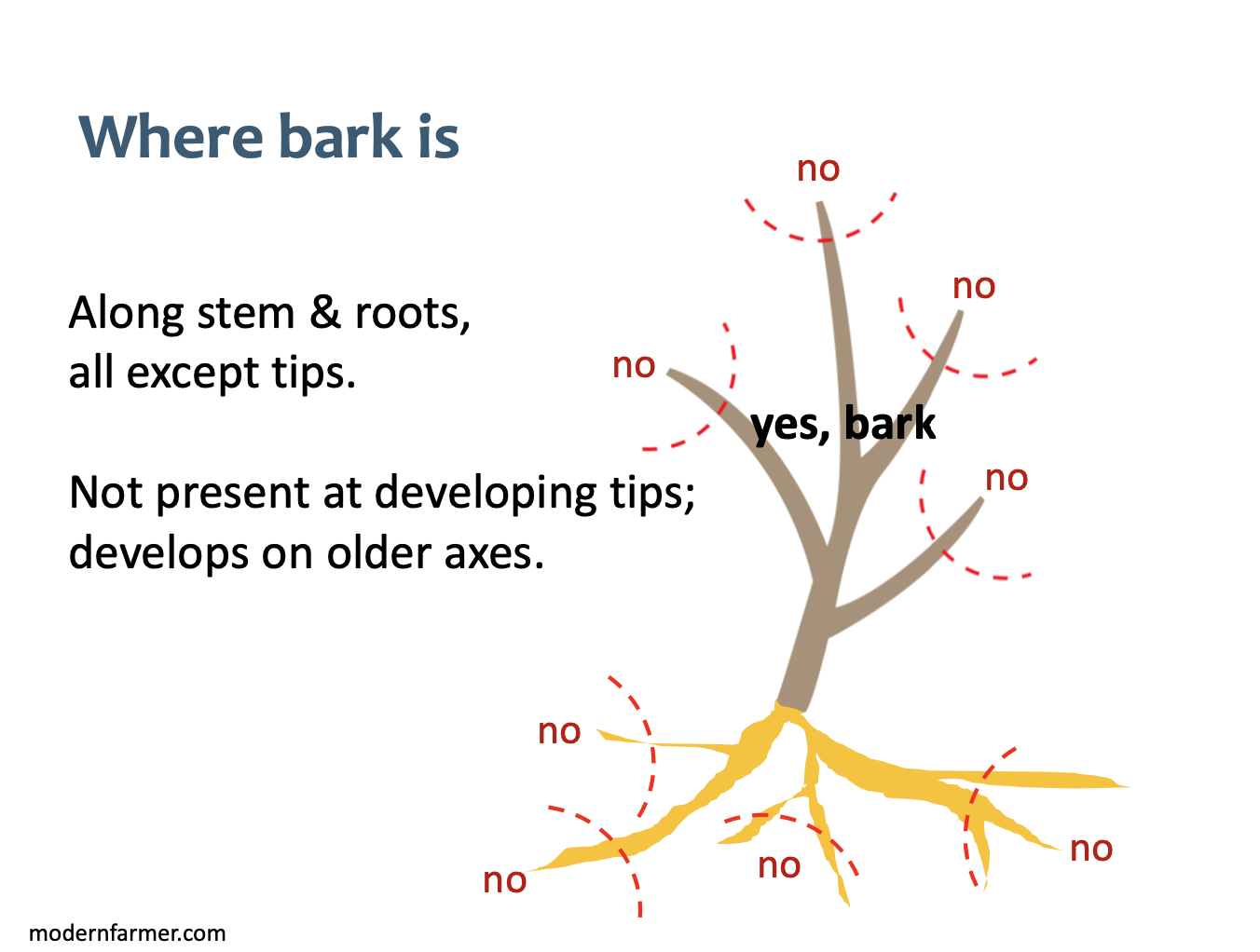
outer bark
along stems and roots, all except tips
vascular cambium
secondary phloem and xylem are developed by vascular cambium.
cork cambium
develops outer bark
inner bark
layer of inner cells that transport nutrients from leaves to the rest of the tree
outer bark
protective layer of dead cells that protect the tree from defense.
identify three functions of outer bark for the plant
physical protection, photosynthesis, channel rain flow, not supporting parasites