Biol 266 : Unit 6-2
1/59
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
60 Terms
Mechanisms that control exit of proteins from the ER include:
Quality control and Active cargo selection
Active cargo selection : _______________ are collected in regions of the ______ that will pinch off to form a ___________. Soluble cargo are recognized by membrane proteins that span the ER bilayer. Membrane cargo can be recognized by cytosolic proteins that will aid in vesicle formation.
specific cargo ; ER ; transport vesicle
Some proteins that are resident ER proteins may mistakenly exit the ER. The soluble proteins contain the targeting signal ____________ at the C-terminus that interacts with the _______________. The receptor cycles between the Golgi and the ER, binding KDEL-containing proteins at the Golgi and releasing them in the ER.
For resident ER membrane proteins the retrieval signal is ____________ at the C-terminus in the cytosol. It is recognized by the ______________ (a set of proteins that are needed to form transport vesicles from the Golgi to the ER)
KDEL ; KDEL receptor ; KKXX ; COP I coat
_______________________________ were used to identify many of the proteins needed for this process and to understand the mechanism.
Yeast temperature-sensitive mutants
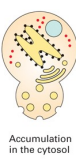
What is the defective function, if the secretory proteins accumulate in the cytosol ?
Transport into ER
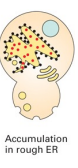
What is the defective function, if the secretory proteins accumulate in the rough ER?
Budding of vesicles from the rough ER
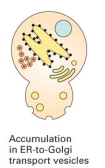
What is the defective function, if the secretory proteins accumulate in ER-to-golgi transport vesicles ?
Fusion of transport vesicles with golgi
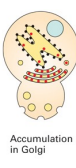
What is the defective function, if the secretory proteins accumulate in the Golgi ?
Transport from Golgi to secretory vesicle
What is the defective function, if the secretory proteins accumulate in the Secretory vesicles ?
Transport from secretory vesicles to cell surface
Three main classes of vesicle coats:
Clatherin / COP I /COP II
Clathrin – mediates transport vesicle formation at the ____________ (for transport to lysosomes via endosomes) and at the ________________ (for transport to endosomes).
trans-Golgi ; plasma membrane
COP I – mediates transport from the ________________ and between various __________________.
cis-Golgi to the ER ; Golgi cisternae
COP II – mediates transport from the _____ to the _________.
ER ; cis-Golgi
Set of proteins that help deform the ER membrane to allow budding of vesicles from the endoplasmic reticulum, to their destination of the Cis-golgi.
COP II
Two functions of protein coat on the cytosolic surface of budding vesicles:
1. ________ the donor membrane into a bud
2. Helps to ______________ into budding vesicles
Shapes ; capture cargo proteins
Coat formation and other steps of vesicle transport require small GTP binding proteins called ___________. These proteins cycle between ________ (GTP-bound) and ________ (GDP-bound) forms.
Rab proteins ; active ; inactive
For ER to golgi trafficking in between the endomembrane systems, the rab GEF and the GAP are in the __________.
Cytosol
1,2 step involved for COP II coat formation : The Rab protein ______ is activated by its _______ . It then inserts into the membrane and begins to curve the membrane.
Sar1 ; GEF
3 step involved for COP II coat formation : Activated Sar1 recruits the inner portion of the COP II coat made up of the proteins _______ and ________. These proteins further bend the membrane. ________acts as a cargo receptor for membrane proteins
Sec23 ; Sec24 ; Sec24
4 step involved for COP II coat formation : Sec23 and Sec24 recruit the _______ of the COP II coat made up of the proteins _________ and _____________.
outer layer ; Sec13 ; Sec31
Continuous recruitment of Sar1 and the COP II coat proteins eventually _______ the membrane to the point of _______________.
deforms ; vesicle release
Fusion of all three types of transport vesicles with their target membranes exhibits several common features:
1. The vesicle coats must be completely or mostly ____________ from the vesicle.
2. The vesicle must be specifically _________ by the correct destination membrane.
3. The vesicle and target membrane must _____________ to deliver the contents of the vesicle to the target organelle
removed ; recognized ; fuse and mix
Formation of the COP I coat at the Golgi requires:
• __________________ (a Rab protein) activation
• __________________ composed of 7 subunits that are recruited en bloc (_________)
Arf1 ; COP I complex ; as one unit
For both _______________________ vesicles, removal of the coat (uncoating) requires ______________________ protein (hydrolysis of GTP to GDP and Pi).
COP II and COP I ; inactivation of the Rab
Disassembly of the _______________ is dependent upon _______________________ (removal of phosphate groups from inositol phospholipids leads to uncoating).
clathrin coat ; lipid composition
Sec23 is a ________ for Sar1
GAP
In their activated (GTP-bound) form, Rab proteins on the vesicle and target membrane can bind _________________________ that contribute to vesicle tethering (the recognition between the vesicle and the target membrane)
effectors proteins
The main steps in vesicle-mediated transport, after vesicle formation (budding):
Tethering / Docking / Fusion
Tethering – mediated by _____ and their effectors, _______________.
Rabs ; tethering factors and SNAREs
Docking – mediated by _______________.
SNARE pairing
Fusion – driven by ________________.
SNARE “zippering”
Tethering is the ___________ between the vesicle and the target membrane. Occurs over a _____________ (>diameter of the transport vesicle).
initial contact ; long distance
Several classes of tethers:
Multiprotein tethering complexes and Coiled-coil proteins.
Docking is a _________________ between the vesicle and the target membrane. Occurs over a _______________ (<<diameter of the transport vesicle).
stronger interaction ; short distance
Mediated by proteins called __________ proteins on both the vesicle (_________) and the target membrane (_________).
SNARE ; v-SNARE ; t-SNARE
All SNAREs have a __________________ (an a-helix of 60-70 amino acids long) that allow it to interact with another SNARE protein.
Most SNAREs are tail-anchored membrane proteins.
SNARE motif
Membrane Fusion Step 1 : Outer leaflet mixing between the vesicle and target membranes produce a ____________________.
hemifusion intermediate
Membrane Fusion Step 2 : _________ of the hemifusion intermediate provides a surface for the inner leaflets to fuse.
Expansion
Membrane Fusion Step 3 : __________ of the inner leaflets allows access of the soluble material in the vesicle and target membrane to mix.
Fusion
________ Snare complex is Pre-fusion
Trans
_______ SNARE Complex is after fusion.
Cis
Fusion begun but not complete :
Hemifusion
All vesicle-mediated transport reactions require ________ as well as ______ and their _________.
SNAREs ; Rabs ; effectors
Addition of galactose and other carbohydrates takes place in the _______________.
trans Golgi
Addition of GlcNAc, fucose and additional mannose trimming takes place in the _______________.
medial Golgi
Mannose trimming takes place in the ____________.
cis Golgi
A unique modification takes place on soluble lysosomal enzymes resulting in the production of ____________________.
mannose-6-phosphate
The endocytic pathway moves material inside the cell Two main types of endocytosis:
Bulk-phase endocytosis (pinocytosis) and Receptor-mediated endocytosis
Bulk-phase endocytosis (pinocytosis) :
Non-selective, can be clathrin-dependent or clathrin-independent.
Receptor-mediated endocytosis :
Selective, clathrin-dependent, initiated by the binding of a ligand to its receptor.
Clathrin forms the _______________ of the coated vesicles and has a distinctive ________ appearance.
outer layer ; triskelion
Adaptor proteins form the _________________ of the coated vesicles and engage the ____________________. Their recruitment to the “coated pit” is facilitated by a lipid called phosphatidylinositol (4,5) bisphosphate.
inner layer ; cytoplasmic tails of receptors
As the coated pit invaginates, a small ____________ called ________ binds as a ring around the emerging stalk. Using the energy of GTP hydrolysis, it breaks the vesicle free from the plasma membrane. If a _________ form of GTP is used, the stalk continues to _______ with a dynamin ring
GTP binding protein ; dynamin ; non-hydrolyzable ; grow
Uncoating of a clathrin coated vesicle requires:
1. ________________ of the lipids that bind the adaptor proteins
2. _________ provided by the hydrolysis of ATP by _______
Modification ; Energy ; Hsc70
The uncoated clathrin vesicles can fuse to form the ______________.
early endosome
Late endosomes have a ____________ than early endosomes (dissociation of the ligand from its receptor happens in the endosome)
lower pH
Late endosomes associate with a Rab protein called _______ while early endosomes associate with _______.
Rab7 ; Rab5
Late endosomes are found near the Golgi in the ____________ while early endosomes are found near the ______________________.
cell interior ; plasma membrane
Late endosomes are ___________ while early endosomes have a more complex structure (____________).
round or oval ; tubulo-vacuolar