bio exam 3 -- new content only
1/322
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
323 Terms
human genetics
study of inherited variation in humans
difficulties in studying humans
few offspring, long gens, human ethics
pedigree
family tree showing inheritance of multiple generations
what can determine pattern of inheritance based on prevalence and distribution of a trait
pedigree
human traits w mendellian inheritance: _____ —> protein —> function
genes
human traits w mendellian inheritance:
genes —> ______—> function
protein
human traits w mendelian inheritance:
genes —> protein —> ____
function
human traits w mendelian inheritance: __________→ non-functional or absent protein → no function
mutated allele
human traits w mendelian inheritance: Mutated allele → __________ → no function
non-functional or absent protein
human traits w mendelian inheritance: Mutated allele → non-functional or absent protein → ______
no function
is a heterozygote a carrier
yes
to have an autosomal recessive disorder, must be
homozygous recessive
parents of somebody with a autosomal recessive disorder are
carriers / heterozyg
autosomes are
non sex chromosomes
is an autosomal trait inherited dependently or independently of sex
independantly
autosomal traits follow
mendellian inheritance patterns
autosomal recessive
two recessive alleles required
autosomal domnant
one dominant allele is enough to show trait
disomy
having 2 of each chromosomes
typical chromo state / number is
disomy
aneuploidy
presence of atypical number of a chromo
trisomy
having 3 of a chromosome; 2n+1
monosomy
lacking 1 member of a pair of chromosomes; 2n-1
monosomies and trisomys are ______ for human life
inviable
deletion
region of chromo is duplicated
inversion
orientation of a region of a chromo is reversed
translocation
segment of a chromo is moved to a diff chromo
if a trait appears in every generation of a pedigree it is probably
autosomal dominant
if a trait skips gens in a pedigree it is
autosomal recessive
the parents of an autosomal recessive are both
carriers / heterozygotes
carriers in a pedigree are
individuals who do not show the trait but have affected offspring
used to predict the probability of inheriting a disorder
pedigree
what is required for expression of an autosomal recessive trait
2 mutated alleles — homo recessive
what is required for expression of an autosomal dominant trait
one mutated allele — heterozyg or homozyg dom
autosomal recessive heterozygotes are
unaffected carriers
autosomal dominant heterozygotes
show the trait
what is more common autosomal recessive or auto dom
auto recess
many autosomal dom traits appear
after reproduction , so allele is passed on reguardless of it is harmful
mendelian inheritance
determined by allele dominance
non-mendelian traits
caused by chromo number or structure changes
most autosomal aneuploidies are
inviable
aueoploidy is
improper chromosome number
autosomal aneuploidy are
lethal
sex chromo aneuploidy are
often viable but infertile
genetic testing is valuable because
eary diagnosis so prevention or symptom management is good
fetal testing
detects disorders before birth
newborn screening detects disorders at
birth
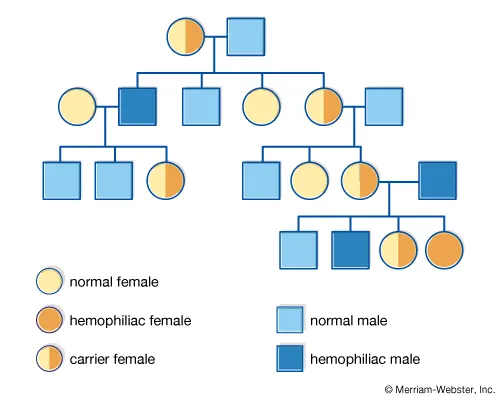
what is this
pedigree
gradualism
observable processes produce small changes accumulate over time
uniformitarianism
geological processes uniform over time so earth is very old
use and disuse theory
body pts used —> larger stronger better at funct , not used = deteriorate
inheritance of acquired traits
traits aquired during lifetime passed down to offspring
overproduction
more offspring born each gen than will survive and reproduce
unequal survival and reproduction
some survive longer and have more offspring and thus competition
adaptations
beneficial traits = greater reprod success
natural selection
beneficial traits (adaptations) à greater reproductive success
Beneficial heritable traits accumulate in populations over generations
Necessarily mathematically true
pops change over time as beneficial traits increse in frecuqncy
descent w mod
evol by natural selection is one
mechanism of evolition
homology
similar due to common ancestory
before darwin, we thought
species were unchanging and earth was young
varous linneaus
gave the binomial nomenclature / sci naming system
pre darwin geology
gradualism — slow observable proccessed so earth is old
james hutton
gradualism — influenced darwin
charles lyell
Refined gradualism into uniformitarianism”
“Geological processes uniform over time”
uniformitarianism
geolog processes are consistant over time so earth is old
lamarack
use and disuse and inheritance of aquired traits
lamarack said evolution occurs at the
individual level
lamarack established
evolution is a natural process
what experiences influenced darwins thinking on evol
Voyage on the Beagle”
“Collected plant and animal specimens, fossils”
whas darwin reluctant to publish his theory
yes
who reached same conclusions as darwin independently and then they collabled and published
wallace
darwin’s first observation
over production — more offspring born each gen than will survive and reproduce
darwins second observation
unequal survival and reproductino
darwins third observation
heritable variation
heritable variation
individuals have variation, offspring tend to resemble parents
darwins fourth observation
non random survival and reproduction
survival and repdocuction are based on
phenotype
better adapted individuals produce -____ offspring
more
we illustrated evolution because of
artificial selection, direct observations, homology, fossil record
evolution
change in allele frequency in populations over generations
phenotypic variation
observable differences between individuals
genetic variation
differences amoung individuals in gene or nucleotide sequence
mutation, recombination, and rapid reproduction are all
sources of genetic variation
population
group of orgs in same species same area same time that fuck
allele
one of two or more forms of a gene
gene pool
all alleles of all genes in a pop at any given time
allele frequency
proportion of a specific allele at a pocus within a populatino
fixed allene
allele frequency of one in a population — the only allele at a locus
genetic equilibrium
no change in allele frequency gen to gen, no evol in pop at equilib
who developed the idea of geneetic equlibrium
hardy weinberg
is hardy weinbery equilib common in nature
no
in hardy weins the p is
frequency of dominant allele in a pop
in hardy wein s q is
frequency of recessive allele in pop
equation for genotype frequencies
p2 + 2pq + q2 = 1
equation for allele frequencies
p+q=1
if no mutation, yes rand mating, no selection, no genetic drift, no gene flow, then it
meets conditions for hardy wein
non random mating
unequal chances to mate, no random mixing of gamettes/alleles,
mutation
any heritable change in dna, 1 allele becomes a diff allele, raw material for natural selection
random matinge
each individ in pop equally likley to mate with any indiivid of opposite sex
natural selection
non random changes in allele frequency based on fitness