Anatomy and Physiology - Nervous System
1/78
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
79 Terms
What makes up the central nervous system?
brain, spinal cord
What makes up the peripheral nervous system?
cranial nerves, spinal nerves
What makes up the somatic nervous system and is it voluntary or involuntary?
voluntary
made of skeletal muscles
What makes up the autonomic nervous system? Is it voluntary or involuntary?
Is the motor subdivision of the PNS
Involuntary
Regulates heart, viscera and glands
2 branches: sympathetic and parasympathetic
2 motor neurons
preganglionic and postganglionic
Synapse in a ganglia in PNS
fight or flight - sympathetic effects
rest and digest - parasympathetic
Neuroglia
supporting cells or glial cells
Do not transmit impulses
Are mitotic
Microglia
Phagocytes
Oligodendrocytes
Form myelin sheath in CNS
Ependymal cells
Are ciliated. Line cavities of the brain and spinal cord to circulate Cerebrospinal Fluid (CSF)
circulation of CSF
Astrocytes
make up ½ of all nervous tissue
“bouncers” of the CNS – regulate movement of substances out of brain capillaries into neurons
Schwann Cells
Form myelin sheath in PNS
Satellite Cells
Similar functions as astrocytes in CNS
Neurons
~100 billion, amitotic, transmit electrochemical messages
what are neurons functionally classified as?
Afferent neurons: sensory
Efferent neurons: motor
Interneurons (association neurons): in the CNS - between a sensory and a motor neuron
Cell body
soma
axon
conduct outgoing info
myelin sheath
increases speed of action potential transmission down axon
Nodes of Ranvier
spaces of “naked” axon between myelin
Dendrites
receive incoming info
What is the terminology for groups of neurons in the CNS
Nucleus (nuclei), tract
what is a nucleus (nuclei) and where is it found?
a cluster of neuron cell bodies in the central nervous system
what is a tract and where is it found?
a bundle of axons in the central nervous system
What is the terminology for groups of neurons in the PNS
ganglion (ganglia), nerve
what is a ganglion (ganglia) and where is it found?
a cluster of neuron cell bodies in the PNS
what is a nerve and where is it found?
a bundle of axons in the PNS
reflex
a rapid, predictable, involuntary response to a stimulus
refex arc
neural pathway over which a reflex occurs
components of a reflex arc
sensory receptor, afferent neuron, interneuron, efferent neuron, effector (muscle or gland)
autonomic reflexes
stimulate smooth muscle, cardiac muscle or glands (ex. Emptying bladder and rectum)
somatic reflexes
stimulate skeletal muscle (ex. Patellar knee jerk)
Meninges
connective tissue membranes covering CNS
Dura mater
Outermost, double-layered (one layer adheres to inside of skull), tough/leathery
arachnoid membrane
Middle layer, webby, has villi that return CSF to blood
pia mater
Innermost, clings to gyri and sulci
what is cerebrospinal fluid formed by?
Formed by choroid plexuses
cerebrospinal fluid functions
Is a watery cushion for the brain and spinal cord
Gives buoyancy to the brain so pressure at the base of the brain is reduced.
As CSF flows to the blood via the arachnoid villi, it takes potentially harmful substances away from the brain.
transports hormones to areas of the brain
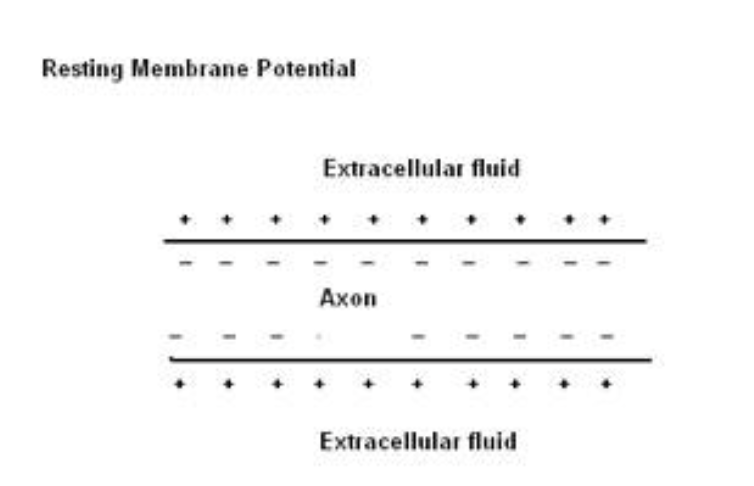
membrane potential of a neuron
a difference between the net charge inside and outside the cell
resting membrane potential
-70mV in avg neuron
Inside is more negative than outside b/c there are fewer + ions inside
K+ is the primary ion inside
Na+ is the primary ion outside
depolarization
Stimulated neurons depolarize (membrane potential becomes more +)
Na+ gates open and Na+ enters cell
Think….WHY does the Na+ enter?
Inside rapidly becomes positively charged (+35mV)
repolarization
Membrane potential becomes more – again
K+ channels open and K+ exits the cell
Inside hyperpolarizes to -75mV but quickly returns to -70mV (resting membrane potential)
action potential
If the neuron membrane depolarizes to threshold then an Action Potential is generated.
Is a rapid change in membrane potential that communicates information
Is an all or none event of fixed amplitude that travels in one direction
Na+ channels (open)
During depolarization
Channel-blocking and channel-inactivating segments open
Na+ channels (Closed and locked - inactivated)
During repolarization
Channel-blocking and channel-inactivating segments closed
Na+ channels (Closed and unlocked)
When neuron is at rest
Channel-blocking segment closed but channel-inactivating segment open
absolute refractory period
The cell membrane cannot immediately produce a second AP because the majority of voltage-gated Na+ channels are open and/or inactivated
no amount of depolarizing current can cause another action potential
gyrus (gyri)
elevated ridges
sulcus (sulci)
shallow grooves
Ex. Central sulcus separates frontal and parietal lobes
fissure
a deep sulcus
Ex. longitudinal fissure separates left and right cerebral hemispheres
corpus callosum
fiber tract allowing communication between left and right cerebral hemispheres
what structures make up the forebrain
cerebral cortext, basal nuclei, limbic system (amygdala, hippocampus, cingulate (gyrus) cortex), diencephalon (hypothalamus, thalamus, epithalamus)
what structures make up the epithalamus
pineal gland, choroid plexus
Cerebral cortex
regulates perception, planning, and other mental activities – 80% of brain mass
basal nuclei
play role in control of movement (includes striatum, caudate nucleus, putamen, globus pallidus)
the limbic system (parts too)
Part of the brain that regulates emotions and motivations, especially those related to survival, such as fear, anger, pleasure (from eating, sex, nurturing).
amygdala, hippocampus, cingulate (gyrus) cortex
how does the limbic system work
Generates responses to situations by using:
Memories
Information about how your body is working at that moment
Current sensory input
Example: A dog runs and jumps up on you. Your response can vary depending on the 3 factors listed above.
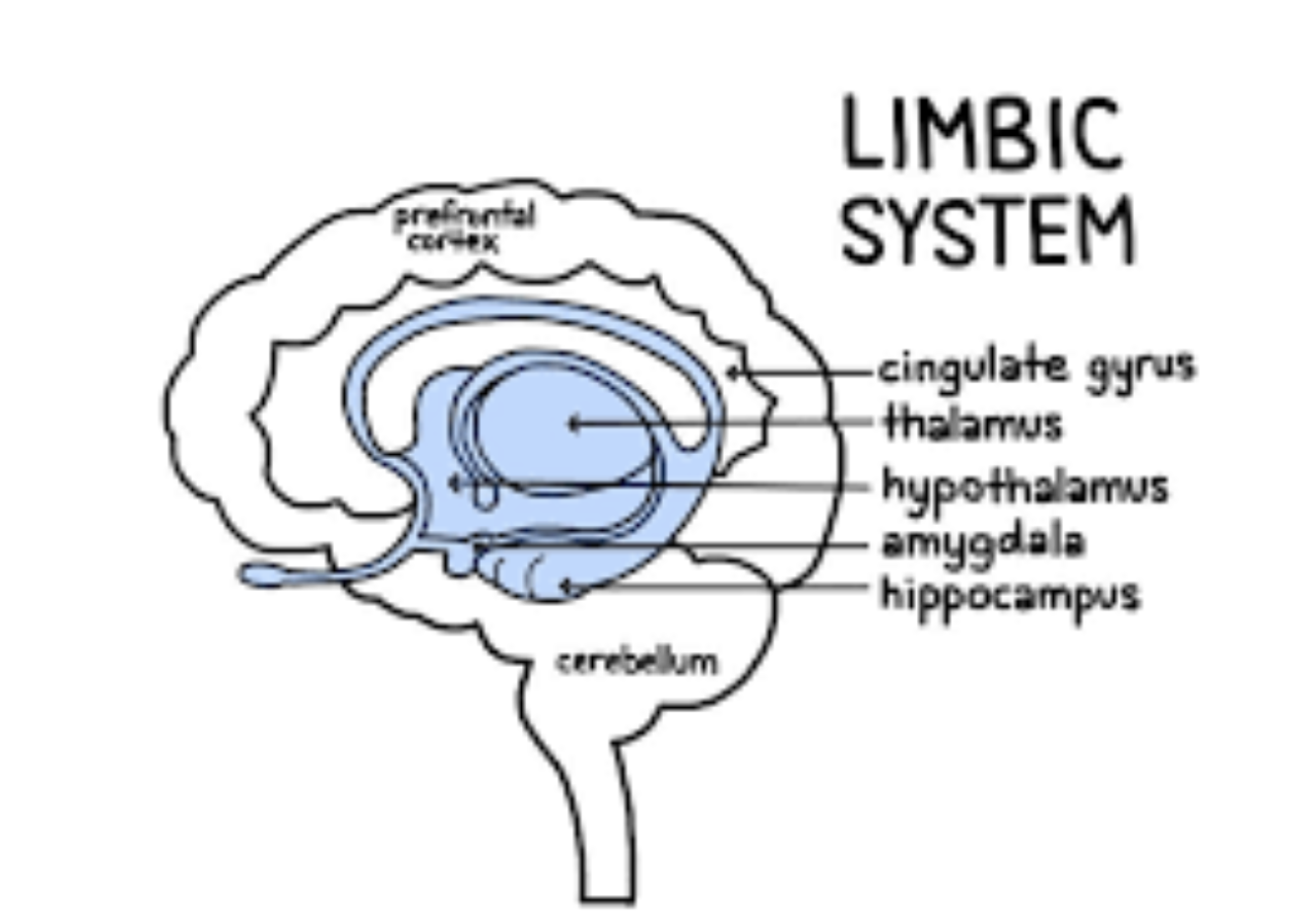
amygdala
involved in emotional response and memory
hippocampus
involved in memory/learning – sends memories out for long-term storage
Cingulate (gyrus)cortex
plays a role in expression our emotions through gestures
parts of the diencephalon
hypothalamus, thalamus, epithalamus (pineal gland, choroid plexus of 3rd ventricle)
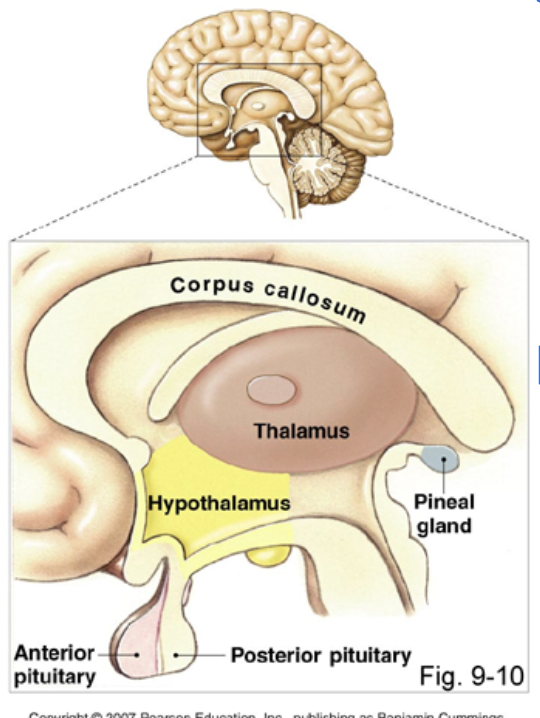
hypothalamus
Regulation of temp, H2O balance, blood pressure. Controls drives (hunger, thirst, sex, rage), controls production of some hormones (interacts with pituitary gland)
thalamus
gateway for all sensory impulses (except smell) passing up to the cerebral cortex for interpretation. Crude recognition of pleasant vs. pain
epithalamus
pineal gland, choroid plexus of 3rd ventricle
pineal gland
makes melatonin
choroid plexus of 3rd ventricle
makes CSF
brain stem parts
midbrain (corpora quadrigemina (tectum), superior collicus, inferior collicus), tegementum, hindbrain (pons, medulla, reticular formation)
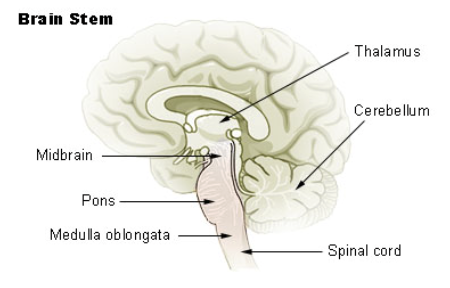
midbrain parts
corpora quadrigemina (tectum), superior collicus, inferior collicus
superior collicus and inferior collicus roles
superior collicus: reflex center for vision
inferior collicus: reflex center for hearing
tegmentum parts and roles
red nucleus: relay nuclei in some descending motor pathways
substantia nigra: dopamine producing neurons – causes Parkinson’s when they degenerate
hindbrain parts
pons, medulla oblongata
pons
one of 2 respiratory centers, bridge for info between cerebrum and cerebellum
medulla oblongata
controls respiration, rate & force of heart contractions, vasomotor control of BP, swallowing, vomiting, gagging, sneezing, hiccupping,
reticular formation
(reticular activating system RAS) – sleep/wake behavior, consciousness, filters out repetitive sensory input (ex. Feeling of shirt on your back)
cerebellum
provides coordination for skeletal muscle activity (timing, precision)
somatic sensory area
located on the postcentral gyrus
crossed pathways; interprets sensory info from sensory receptors
primary visual cortex
receives visual input from the eye
visual association area
interprets visual stimuli
frontal association area (prefrontal cortex)
intellect, cognition, personality, judgement, reason, planning
where is the primary motor area
on the precentral gyrus
brocas area
directs the muscles involved in speaking (“bro-ducing” speech)
Wernicke’s area
in the junction of the temporal, parietal and occipital lobes
Interpreting words we read or hear