In-Semester Exam L6 Evolution
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
27 Terms
How was the diversity of animals classified before modern molecular biology?
Linnaeus developed a classification scheme called taxonomy.
Linnaeus assigned binomial nomenclature of genus and species, for example, Homo sapien and Felis catus.
List the ranking of groups into taxa
Kingdom
Phylum
Class
Order
Family
Genus
Species
What is the definition of species?
A group of organisms capable of interbreeding and producing fertile offspring
What suffix does the family name always end in?
-idae
Or for a super family -oidae
Outline the taxonomy of a domestic cat
Domain - Eukarya
Kingdom - Animalia
Phylum - Chordata
Class - Mammalia
Order - Carnivora
Family - Felidae
Genus - Felis
Species - Felis catus
Describe scientific names of animals
Scientific names of animals are descriptors of that species in Latin
Briefly describe dichotomous key
Dichotomous key is a tool used to identify different organisms based on the organisms observable traits. Dichotomous keys consist of a series of statements with two choices in each step that leads users to identification. Dichotomous keys ignore the true relationship of organisms.
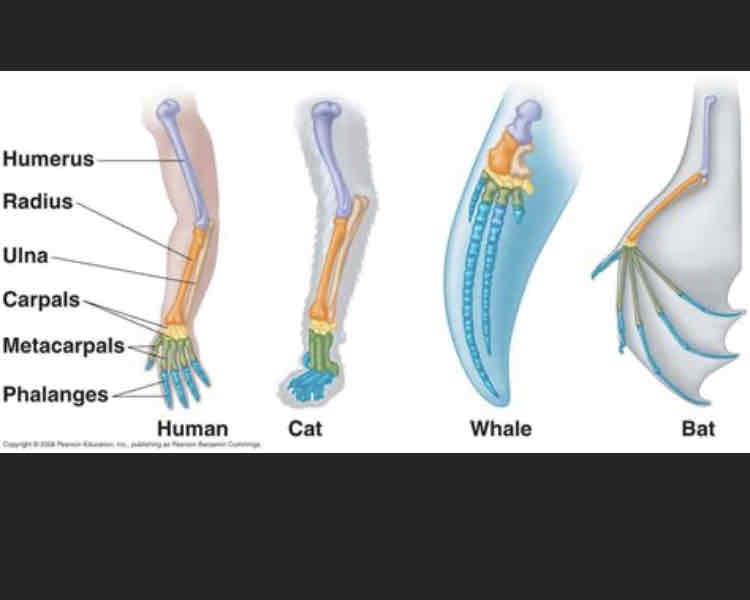
Define homologous structures.
Homologous structures are similar physical features in organisms that share a common ancestor, but the features serve completely different functions. An example of homologous structures are the limbs of humans, cats, whales and bats.
Define analogous structures
Analogous structures are features of different species that are similar in function, but not necessarily in structure. They do not derive from a common ancestor and evolved in response to similar environmental challenges. The wings of birds and butterflies are examples of analogous structures.

Define morphology
Morphology is the study of the size, shape and structure of animals, plants, and microorganisms and of the relationship of their constituent parts.
Describe phylogeny
It is the study of the evolutionary history of species
It infers the relationships of organisms
It uses more homologous characteristics as these are the most informative in inferring evolution
It traces changes in species over time
What are some of the ways we can identify species?
Morphology, ecology, geographic distribution, biochemistry and physiology, nucleic acid sequence
Describe the chromosomes of prokaryotes
Prokaryotes usually have one circular chromosome and no nucleus
Describe the chromosomes of eukaryotic cells
Eukaryotic cells have chromosomes located in the nucleus. Most eukaryotic cells have multiple chromosomes, which are linear in shape. The DNA is wrapped tightly within chromosomes.
There is also DNA in mitochondria for animals and the mitochondria and chloroplasts for plants.
What is an orthologous gene
It is a gene found in different species that evolved from a common ancestor by speciation
What do genes code for?
Each gene has the instructions for making a specific protein, and each protein does a specific job in the cell. Some proteins are used to replicate or reproduce, some produce energy, some form structure and perform specific functions.
Briefly describe genetic similarity
There are similarities in every organism with respect to their DNA, replication and protein synthesis
There are orthologous genes across all lifeforms in both prokaryotes and eukaryotes
Define phenotype
Observable characteristics of an individual based on the expression of the gene, such as size and colour.
Genetic diversity occurs due to mutations within the genome. Describe the two types of mutations.
Defective chromosomes (usually occurs during division) through rearrangement, recombination, insertions or deletions.
Point mutation occurs in the genome when a single base pair is added, deleted or changed.
What are endogenous mutations?
Endogenous mutations are produced by the body. They are spontaneous and due to normal cellular division or cell metabolism by-products. Spontaneous mutation rates are low.
What are exogenous mutations?
Exogenous mutations come from environmental agents such as chemicals, radiation, transposable elements and viruses.
When are genetic mutations heritable?
Genetic mutations are only heritable if they occur in germ cells (tissues) they’re not heritable if they occur in somatic cells (tissues).
When there is a mutation in the DNA or RNA code, the genetic information is changed, which leads to the translation of the mutated protein. What three things could this result in?
No change in protein function, called a synonymous mutation
Change in protein function, leading to a new phenotype
Loss of protein function, leading to a new phenotype or disease.
One of the driving forces of evolution is natural selection. Describe this process.
Organisms that are more adapted to their environment are more likely to survive and pass on their genes.
This process causes species to change and diverge over time. Individuals that have a trait that is better adapted to the environment survive and produce more offspring.
An example of this is the peppered moth. In the United Kingdom in the 1800s trees were becoming covered in soot. The numbers of dark coloured moths increased as they were camouflage better while the lighter moths were predated upon. Later, when the pollution was reduced the light coloured moths once again became more dominant.
What are four factors that affect the genetic diversity of the population and species evolution.
Mutations, natural selection, migration and random genetic drift.
A bottleneck can cause genetic drift. Describe a bottleneck.
A bottleneck occurs when there is a large amount of predation, or a catastrophic event which significantly reduces the numbers of a population. When the population subsequently increases the animals have much less genetic variation than expected for a population of that size.
Phylogenetics on a genetic level uses gene sequences and looks at the differences in gene sequences. Animals with the least differences in their gene sequences would be closer on the phylogenetic tree. True or false.
True