Mycology
1/133
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
134 Terms
what is mycology?
study of fungi
where is fungi found?
environment - decaying vegetation, moldy hay
skin and mucous membranes - host adapted or contaminants from enrivonment
what are the major characteristics of fungi?
eukaryotes, majority saprophytes and non-pathogens
how do fungi reproduce?
asexually by fragmentation, budding and through spores; sexual reproduction is also seen
what do fungi cell membranes contain?
sterols (ergosterol)
true/false - fungi contain a cell wall
true; contains glucan, mannan, chitin
what are the unicellular forms of fungi called?
yeast
what are the multicellular fungi called?
mold
what does mold contain to spread?
hyphae and fruiting bodies which contain spores
what are a tangled group of hyphae called?
mycelium
what is the colonial morphology of yeast?
opaque, creamy, smooth
what is the microscopic morphology of yeast?
unicellular forms round single cells, budding
what is the colonial morphology of molds?
wooly-fluffy-powdery colonies, aerial growth
what is the microscopic morphology of molds?
hyphae
what is the colonial morphology of dimorphic fungi?
combination of yeast and mold depending on temperature
what is the microscopic morphology of dimorphic fungi?
yeast or hyphal, depending on temperature
what is used to differentiate between fungi organisms?
hyphae divided based on presence of septa
what is the general pathogenesis of fungal infections?
fungus invade tissue and induce pathogenic effect; environment/opportunistic organisms infect mainly immunocompromised hosts; fungal infection results in induce chronic granulomatous infection; infections uncommon, but serious; limited antimicrobial agents
what is mycotoxicosis?
fungal contamination or growth on food material leads accumulation of toxins and when consumed induce severe disease
how does fungi impact allergies?
inhaled fungal spores induce hypersensitivity and allergy
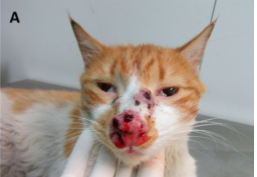
where is this fungal infection?
superficial - outermost layers of the skin and hair
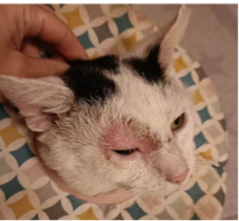
where is the fungal infection?
cutaneous - extend deeper into the epidermis, invasive hair and nail
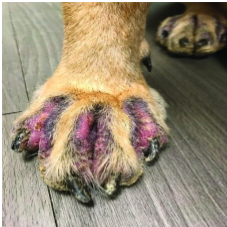
where is the fungal infection?
subcutaneous - dermis, SQ, muscle and fascia
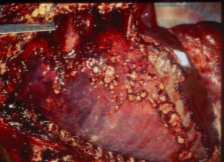
where is the fungal infection?
systemic - primarily in lung, spreads to other organs
how are fungal infections diagnosed?
morphology recognition - cytology, histopathology, went mounts
detection of fungal components - Beta D-glucan assay
detection of host immune response - antibodies, agar gel, ELISA
culture and ID
PCR
what is the stain used on fresh tissue to detect fungi?
calcofluor stain - binds to chitin in cell wall; requires UV microscope
what are the 3 agars used to culture fungi?
sabouraud dextrose agar, sabouraud dextrose agar with cycloheximide, dermatophyte test media
what is used to definitive id fungi?
by DNA probes/sequencing, serotyping, mating studies, virulence testing
when are beta-d glucan assay performed?
general screening of invasive fungal disease
what species of fungi is diagnosed by latex agglutination test or lateral flow tests?
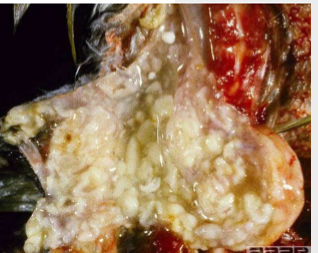
cryptococcus neoformans - in cats
what is a great tool used to detect antigen from fungal infection?
fungal serology-A
what are the 5 examples of antifungal drugs?
polyenes (amphotericin B, natamycin, nystatin)
flucytosine
azoles
allylamines
griseofulvin
how do polyenes, azoles, allylamines work?
inhibit ergosterol
how do flucytosines work?
inhibit nucleic acid synthesis
how do griseofulvin work?
binds to mitotic spindles, inhibits mitosis; administered orally, accumulates in skin
why are antibodies usually not protective in fungal infections?
immunity against fungal infections are usually cell-mediated; most lesions are granulomatous
what is the fungal parasites of keratinized epithelium of skin and nails?
dermatophytes (ringworm)
what are the common dermatophytes?
Microsporum canis, Trichophyton mentagrophytes, Trichophyton verrucosum
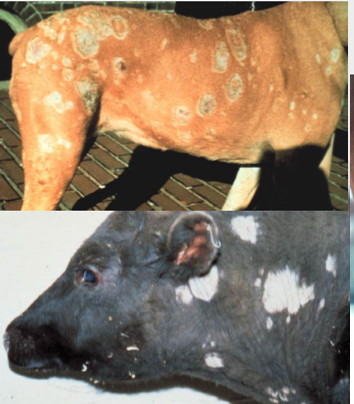
what disease is seen in this image?
ringworm
what can some ringworm lead to?
folliculitis, granulomatous lesions, nodular lesions
what is the ringworm species that affects cattle?
trichophyton verrucosum
what is the ringworm species that affects dogs and cats?
microsporum canis
which species is a major asymptomatic carrier of ringworm?
cats
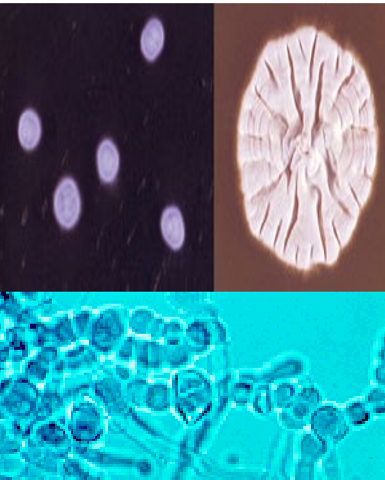
what is this?
Trichophyton verrucosum
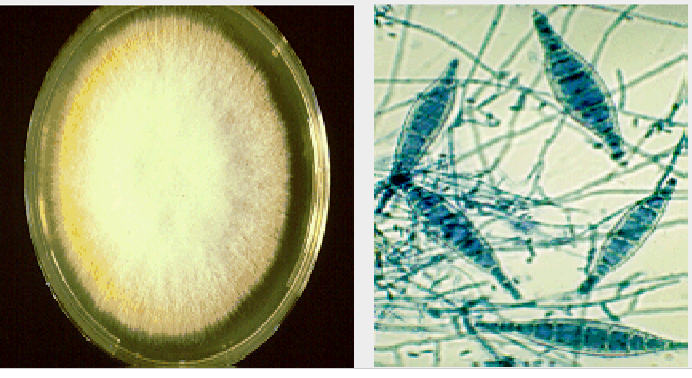
what is this?
Microsporum canis
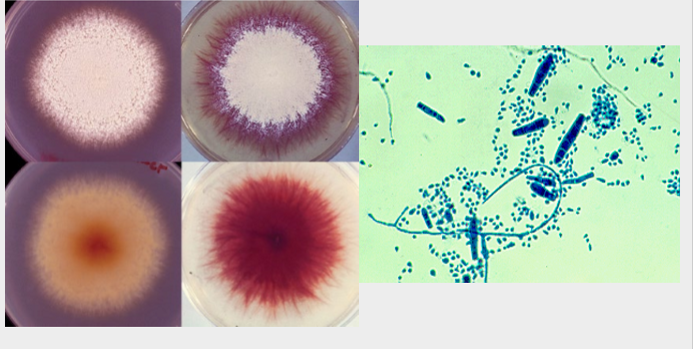
what is this?
trichophyton mentagrophytes
what are the nodular lesions called caused by dermatophytes?
kerion; localized or generalized folliculitis, often with furunculosis
what is the subcutaneous nodule that persian cats can develop from microsporum canis?
pseudomycetoma
what is the ringworm that affects chickens?
microsporum gallinae
how is ringworm diagnosed?
fluorescence using woods lamp, biopsy, direct examination using wet mount of plucked hair or tape mounts
where should the sample be collected for ringworm?
sample should be collected from the periphery of the lesion, or combing with a tooth brush if lesions are not visible
how is a ringworm sample collected?
clean with alcohol, pluck/scrape/brush area of concern, place sample in appropriate container, can send to lab or inoculate media in clinic
what is the stain used for a fungal culture and scotch tape prep?
lactophenol cotton blue
what type of media can be used in clinic to help diagnose ringworm?
dermatophyte test medium; contains phenol red indicator for a color change with a positive test
how is ringworm tested?
spontaneous recovery possible, topical or systemic antifungals (azols, natamycin, terbinafine; Griseofulvin (only with dermatophytes, systemic drug that reaches the keratinized epithelium)
how is ringworm controlled?
hygiene, environmental decontamination, isolate infected animals, clip hair, disinfect bedding and grooming tools, some vaccines available for cattle
how is ringworm prevented in shelters?
examination of animals at admission, detection of animals using wood’s lamp/culture, use of isolation facilities, use of protective clothing and gloves, topical treatment of exposed animals, post treatment testing, cleaning and disinfection
what is the superficial fungal infection that can cause dermatitis and otitis externa?
Malassezia spp (M. pachermatis, M. furfur)
what are the characteristics of M. pachydermatis?
bottle shaped, small lipophilic yeast, commensals on skin of animals and ears; causes otitis externa
what is the species that is normal flora of the mouth, intestine, lower urogenital tract in animals and humans, but can cause thrush?
candida albicans
what are the clinical signs of candida albicans?
whitish-yellow hyperkeratotic lesions in tongue, mouth, proventriculus, stomach; predisposed by antibiotic treatment, immunosuppression, moisture
what is the species in this image?
candida albicans
how is candida albicans diagnosed?
staining and direct demonstration of the organism, culture
how is candida albicans treated?
local or systemic antifungals; susceptibility tests available
what is the fungus that is large, round to oval, budding yeast with mucopolysaccharide capsule prominent in vivo?
Cryptococcus
what does cryptococcus spp cause?
chronic infection upper respiratory tract, CNS of dogs and cats, and sometimes skin, eye, lymph nodes, pneumonia
what is cryptococcus common presentation?
CNS manifestations, reaches CNS directly or via blood; gelatinous masses and polyps with numerous organism and minimal inflammation
how cryptococcus diagnosed?
microscopic detection, fungal culture, test for capsular antigen in serum or CSF
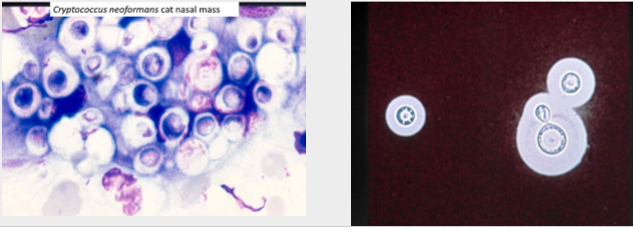
what species is seen here?
cryptococcus - containing capsule
how is cryptococcus treated?
amphotericin B, flucytosine, azoles, surgical removal, long term treatment
how is cryptococcus prevented?
avoid areas with high concentrations of dried pigeon/bird dropping, clean and disinfect bird habitat
what is thermally dimorphic fungi?
single cell or spherule form at mammalian body temp, mold form at ambient environment temperatures
what are the top four organisms that can cause thermally dimorphic fungi infections?
histoplasma, blastomyces, coccidioides, sporothrix
what is the most common systemic mycoses endemic to the ohio-mississippi river valley?
blastomyces dermatitidis
how is blastomycosis transmitted?
inhalation of spores; disease most common in dogs, human
what type of disease is caused by blastomyces?
disseminated disease - cutaneous, ocular, bone, pulmonary
how is blastomyces diagnosed?
cytology - large spherical yeast with broad base budding, biopsy and histopathology, culture, serology
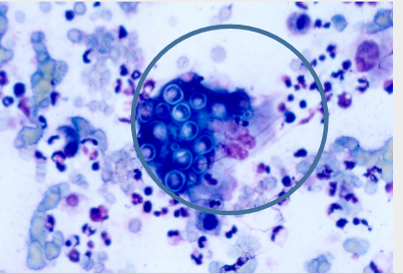
what is seen in this image?
blastomyces - broad base budding
how is blastomyces treated and prevented?
early recognition, antifungal treatment
what is the species that is a thermally dimorphic fungus that is a small oval yeast usually seen in macrophages?
histoplasma capsulatum
what areas are endemic with histoplasma capsulatum?
Ohio, missouri, mississippi river valleys; grows in bird feces
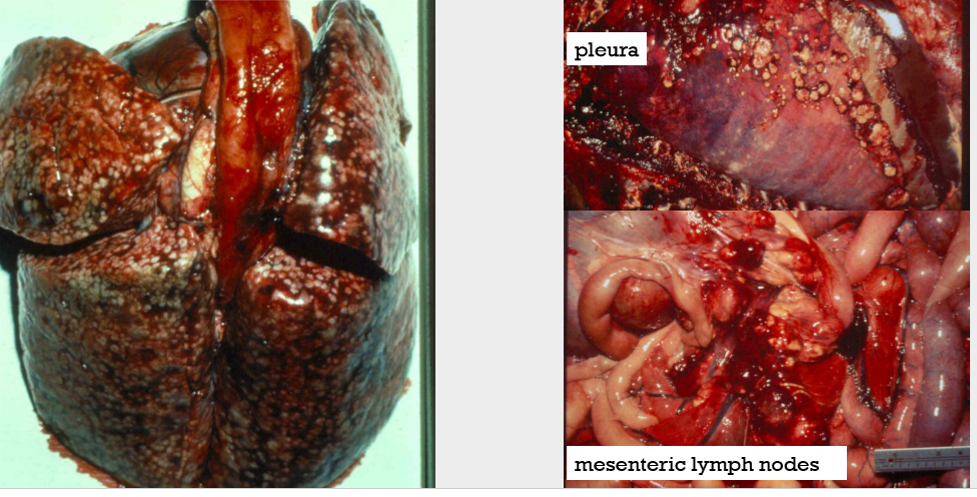
what is the cause of these nodules?
histoplasma capsulatum
what is the route of entry for histoplasmosis?
inhalation, disease most common in cats, dogs, man
which species is the most common systemic fungal infection in cats?
Histoplasmosis
what does histoplasmosis cause in dogs?
intestinal disease
how is Histoplasma diagnosed?
microscopic detection in tissue; small intracytoplasmic yeast cells in macrophages; culture, serology, antigen detection
how is histoplasma treated?
azoles, and amphoterocin B
how is histoplasma controlled?
reduce airborne spread of droppings and contaminated dust
what is the dimorphic fungus that forms a thick walled spherules containing endospores in tissue?
coccidioides immitis
where is coccidioides immitis endemic?
san joaquin va;;er in southwestern regions of US; affects humans and dogs
what is the route of entry for coccidioidomycosis?
inhalation of arthroconidia; transmission favored by dry conditions and soil disturbances
what does coccidioides immitis cause?
chronic/active respiratory and disseminated disease, osteomyelitis
how is coccidioides immitis diagnosed?
microscopic detection; spherules containing endospores in tissues; serology, antigen EIAho
how is coccidioides immitis treated?
azoles, amphoterocin B
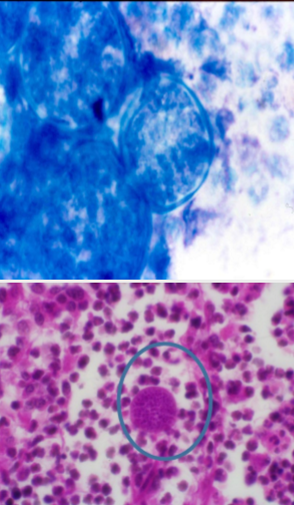
which fungal infection is seen in this slide?
Coccidioides immitis
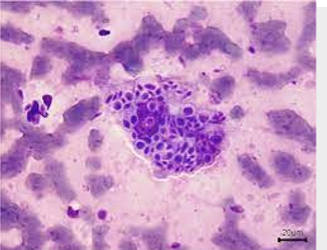
what is the fungus that is cigar shaped, elongated, pleomorphic yeast in tissue?
Sporothrix schenkii
where is Sporothrix schenkii found?
moss, hay, other plant materials and soil
what disease is caused by Sporothrix schenkii?
subcutaneous, restricted to skin nodules with regional lymphatic involvement; most frequent in cats and horses
how is Sporothrix schenkii diagnosed?
microscopic detection of agent; cigar shaped yeast in clinical specimens
how is Sporothrix schenkii treated?
azoles