Virology
1/68
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
69 Terms
Viruses were widely a mystery until...
the 1930's when the elcetron microscope was invented
Size of viruses
SMALL
*100x smaller than bacteria
*20-150nm in diameter
Characteristics of Viruses
need a living cell
have either DNA or RNA (not both)
have a 'receptor-binding' protein
structure of a virus
nucleic acid
protein coat
lipid envelope
Nucleic Acid
either RNA or DNA
where all herditity information is located(aka viral genome)
must be translated into protein for virus to reproduce
virus needs host cell machinery for transcription/translation of genome
genome may be cirucular, linear, or segmented
Viral genome
the information is the genes for viral proteins
size ranges from 3,000 bp to 200,000 bp
number of genes ranges from 3 to 200 but typically only 10-15 genes
DNA genomes
double stranded
DNA must be transcribed into mRNA, than translated to protein
RNA genomes
single-stranded
have smaller genomes because less stable than DNA
change more rapidly due to no mechanism for repair (up to 2% change a year)
RNA positive stranded
positive sense
acts directly as mRNA
directly translated into protein
no need for transcription
RNA negative stranded
negative sense
contain a "virion-associated" polymerase
transcribes into positive sense mRNA
Protein Coat
Capsid
capsomeres-individual proteins that make up the capsid
2 general shapes- helical, icosahedral
nucleocapsid
nucleic acid with the capsid
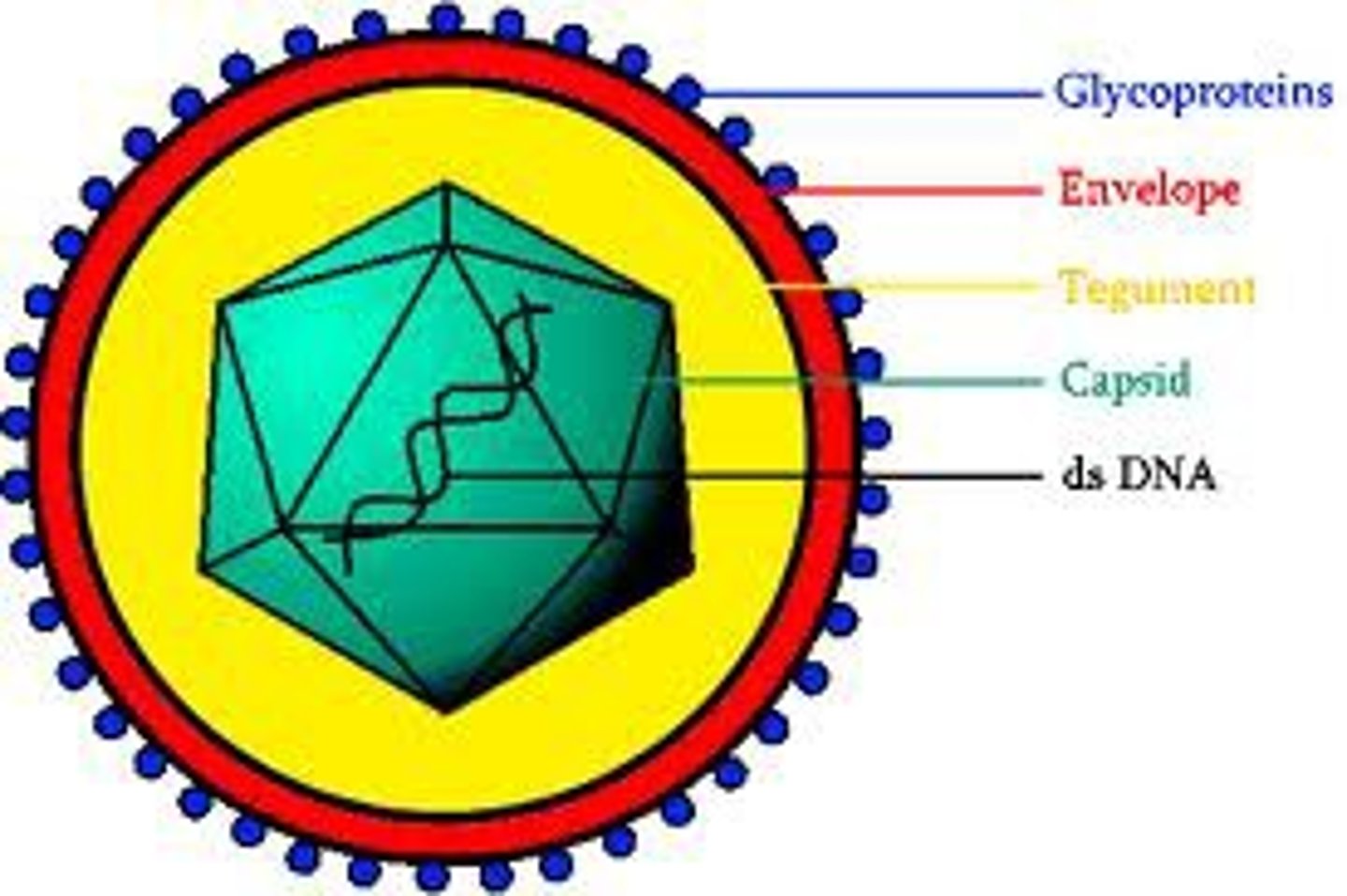
Lipid envelope
enveloped viruses have an outer lipid envelope surrounding the protein coat
comes from host cell
have protein spikes sticking out that bind to the host cell
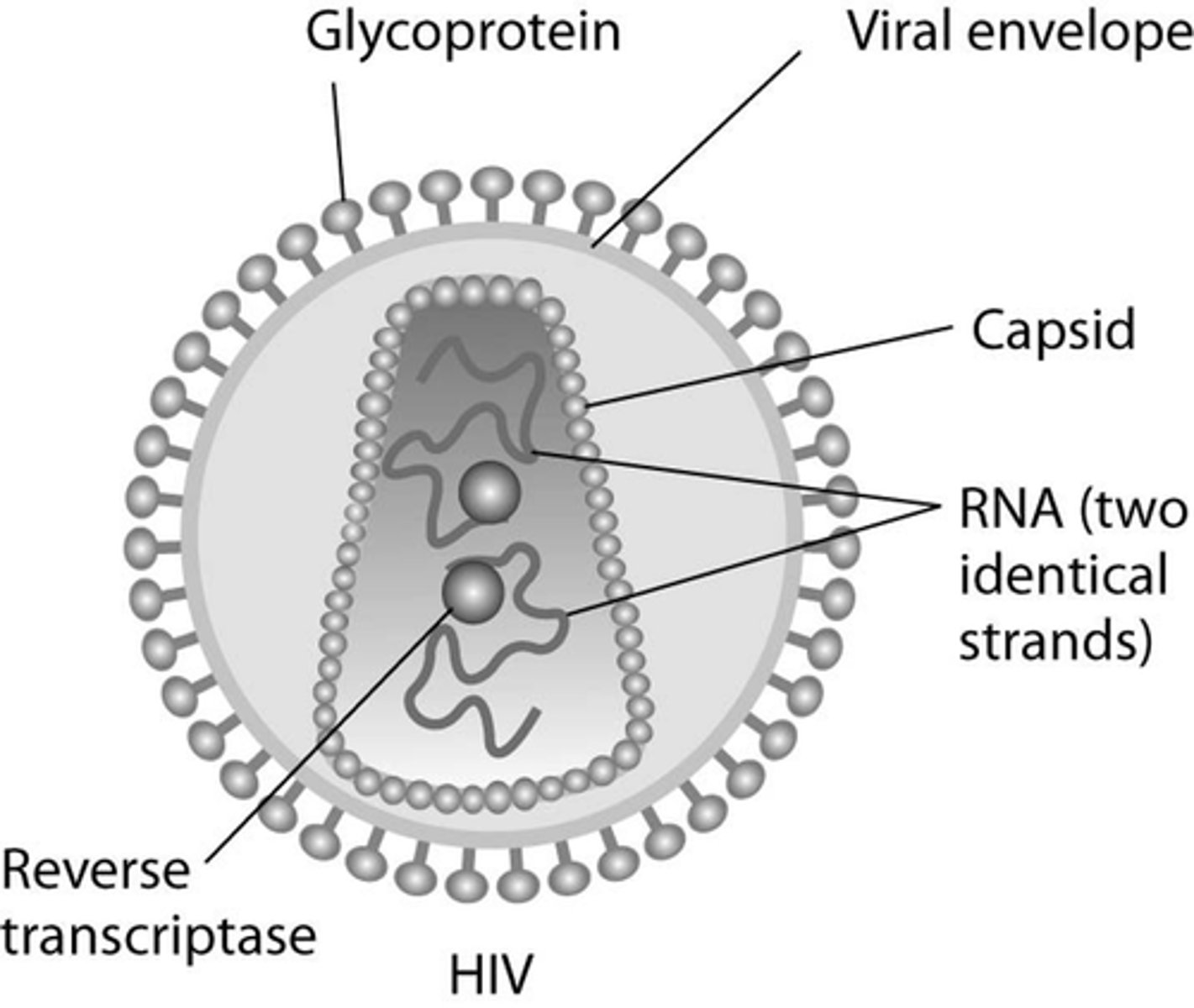
Virion
nucleocapsid + envelope
1 virion= 1 virus particle
Viral classificaiton
genome type (RNA or DNA)
polarity of genome (Pos or Neg)
symmetry of nucleocapsid (helical or Icosahedral)
presence or absence of lipid envelope
Viral infection
infect nearly every life-form on the planet
Virus Life cycle
6-8hrs
1. host cell recognition and binding
2. internalization of genetic material
3. transcription
4. translation of 'early genes'
5. early gene action
6. genome replication
7. translation of 'late' genes
8. assembly
9. release
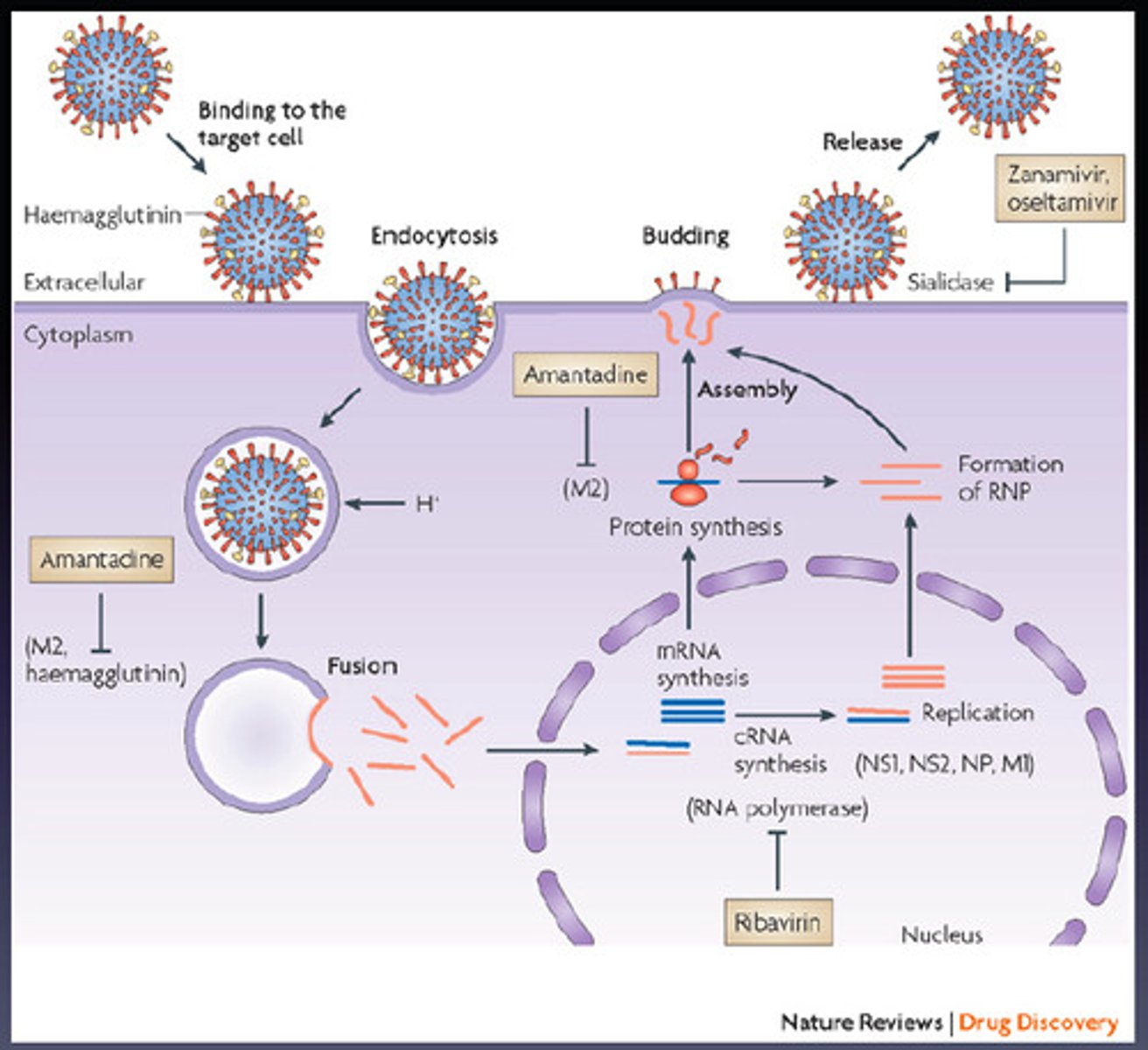
host cell recognition
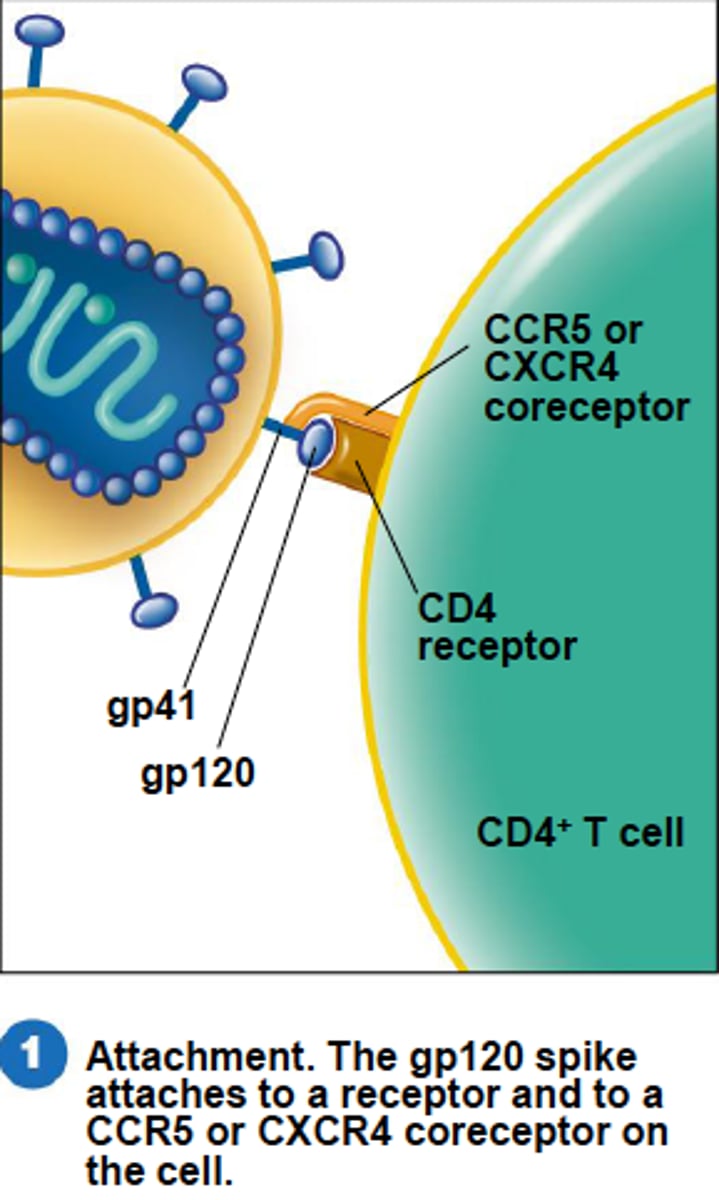
viruses have a receptor-binding protein on their surface
binds to receptor on host cell surface (viruses exploit the normal function of the receptor)
Very Specific and Very Strong
Viruses only infect particular types of cells
fusion
virus has fusion proteins on its surface
cause fusion of the viral membrane with host plasma membrane
virla genome enters cytoplasm
internalization
virus gets into the cell
fusion
receptor mediated endocytosis (viropexis)
Receptor-mediated endocytosis
(viropexis)
most common
virus binds to receptor
"coated-pit" forms in cell membrane
inversion of pit around virus allows virus to enter cytoplasm
viral genome enters nucleus/cytoplasm
after internalization....
production of viral proteins
replication of genome
production of viral proteins
1. production of mRNA from DNA (Transcription)
2. production of protein from mRNA (translation)
Production of Viral proteins Positive stranded
genome used directly as mRNA
translated to protein
Polio
Production of viral proteins Neg stranded
RNA genome is complementary to mRNA
Replicase: RNA-dependent RNA polymerase (virus brought into the cell with itself) (makes complementary copy of RNA genome)
Rabies
Retroviruses
RNA virus (HIV)
1. RNA genome transcribed by Reverse Transcriptase (virus-associated)
2. RNA digested and is replaced by DNA (created double stranded DNA)
3. Integrase (virus-associated) integrates DNA into Host cell genome!
4.mRNA is translated to protein
Integrase integrate DNA into host cell genome
viral DNA is now called "pro-viral" DNA
pro-viral DNA is now transcribed to mRNA along with host-cell genome
Reverse Transcriptase
makes DNA copy of RNA (DNA and RNA form double strand)
known as 'RNA dependent DNA polymerase" RNA polymerase II. mRNA is then translated to protein by host-cell. Reverse transcriptase is prone to making many errors that leads to frequent mutation of the virus
DNA Viruses
Viral genome is transcribed to mRNA by host-cell "DNA- dependent RNA polymerase" RNA polymerase II
mRNA is then translated to protein by host-cell
RNA Virus Genome Replication
Replicase (RNA-dependent RNA pol):
*enzyme that synthesizes a complementary RNA strand of RNA genome
*forms double-stand of RNA (unstable)
*New, complementary strand serves as a template for synthesis of new RNA viral genome
Replicase
positive stranded- replicase is translated directly from genome ('early gene')
negative stranded- replicase is carried by virus as a protein
Replication is RAPID
DNA virus genome replication
occurs in nucleus
occurs by formation of "replication fork"
both strands copied simultaneously
RAPID: 100 nuecleotides per second
late genes
genes that are expressed later in the cycle
usually form replicated viral genomes
structural proteins
early genes
genes that are expressed immediately after infection from viral genome
polymerases and enzymes
assembly
viral proteins assemble
capsid forms around nucleic acid
assembly may occur in cytoplasm or at membrane
release- lytic viruses
cell bursts and viruses are released
no envelope
release- enveloped viruses
"bud" from surface
assembly takes place on membrane
virus buds off from membrane
lipid envelope surrounds new virions
Pathogenicity
compares severity of disease caused by Different viruses
Virulence
Compares severity of disease caused by same virus
viruses effects on cellular level
lysis
cells fuse together (syncytia)
malignancy
inclusion bodies
triggers immune response
how disease enters body
invade host
replicate
overcome defenses
spread to other areas via bloodstream
replicate
exit from host
how virus gets in
skin
mucous membranes
transplant
mother to fetus
localized infections
remains at or near site of entry
short incubation period (1-3 days)
generalized infection
spreads to 1 or more organs
not at site of entry
long incubation period (2 weeks)
steps: 1. enter epithelium
2. replicate in epithelium
3. migrate lymph nodes
4. enter bloodstream (fever and fatigue)
5. enters large organs and replicate
6. enter bloodstream and infects target organs
target organs
skin: local or general infection: rash (exanthema)
buccal mucous membrane
lung: local
liver
kidney
CNS
incubation periods
short: 1 week:localized
medium: 1-3 weeks
long: months
extra long: years
patterns of disease
acute non-persistant infection: nearly immediate: single episode
persistent infection with acute onset: primary infection has symptoms: recurring infection b/c of latency (2-3 years after primary infection)
chronic infection: virus continually being produced
R0
reproduction number
average number of secondary cases cause by a single primary case
epidemiology
the study of diseases affect a community
predict trends
guide control measures
evaluate success of control measures
aid in diagnosis
seriological epidemiology
study of the presence of antibodies in the people of a community
antibodies vs age: history of viral infections
charactertistics of the virus
how well doe sit survive between/outside hosts
resist to temp. pH. sunlight/drying
have alternative host?: reservoir or vector
pathogenesis: incubation period
evasivness of immune system: rapid replication at site if infection: mutagenesis
route by which virus shed: skin, feces, blood
characteristics of host
age, sex, ethnic group, occupation, nutrition, immunity
characteristics of environment
geographic location, urban/rural
existence of vectors/reservoirs
socio-economic status (hygiene, overcrowding, education)
prevalence
proportion of a population that are affects by a disease at a given point in time
incidence
the number of cases (per thousand) of a particular disease recorded during a particular PERIOD of time
endemic
refers to a disease that is CONSTANTLY present at a significant level within a community
epidemic
an unusual increase in the number of cases within a community (outbreak)
pandemic
epidemic involving several CONTINENtTS at the same time
herd immunity
proportion of people in a population that are immune to a particular virus
innate immune system components
toll-like receptors; recognize protein spikes/double-stranded RNA
cytokines: interferons (IFNS), chemokines, interleukins
Natural killer cells
interferons
produced/secreted by virus-infected cells
protects neighboring cells freom infection
NOT virus specific
ARE species specific
virus infect through toll receptor; expresses IFNs; IFN diffuse out of cell to neighboring cell receptors; activate enzymes that degrade RNA (stop protein synthesis); activate natural killer cells; enhances ADAPTIVE IMMUNE system
natural killer cells
recognize and kill infected cells
not kill pathogens
"missing-self" cells with low levels of MHC
adaptive immueen system
slow response
has MEMORY
controlled by phagosytic cells and lymphocytes
humoral response or cellular response
Phagocytic cells- dendritic cells or macrophages
lymphocytes- B-cells (plasma/memorycells) T-cells (helper T-cells/cytotoxic T-cells)
Phagocytic cells
macrophages/dendritic cells
phagocytosis
display parts of foreign particles on surface
cells presenting antigen= Antigen-Presenting Cells (APCs)
lymphocytes
specific type of white-blood cell
T-cell in thymus
B-cell in bone marrow
humoral immunity
anti-body mediated
B-lymphocytes; specific type of antibody to specific antigen; stimulatled by helper T-cell reproduces and form plasma B-cells and memory B-cells
Plasma B-cells; IgM (first) and IgG antibodies (longer lasting)
Helper-T cells; bind to APCs displaying antigens; produces Interleukins; stimulate B-cells and cytotoxic T-cells
cell-mediated immunity
cytotoxic T-cells in blood stream kill cells that have foreign antigen
problem because healthy cells might have receptor
vaccines
active immunization- antigen-containing preparation; starts an immune response produce memory B-cells
passive immunization- antibodies from other organism to fight current infection; no memory B-cells
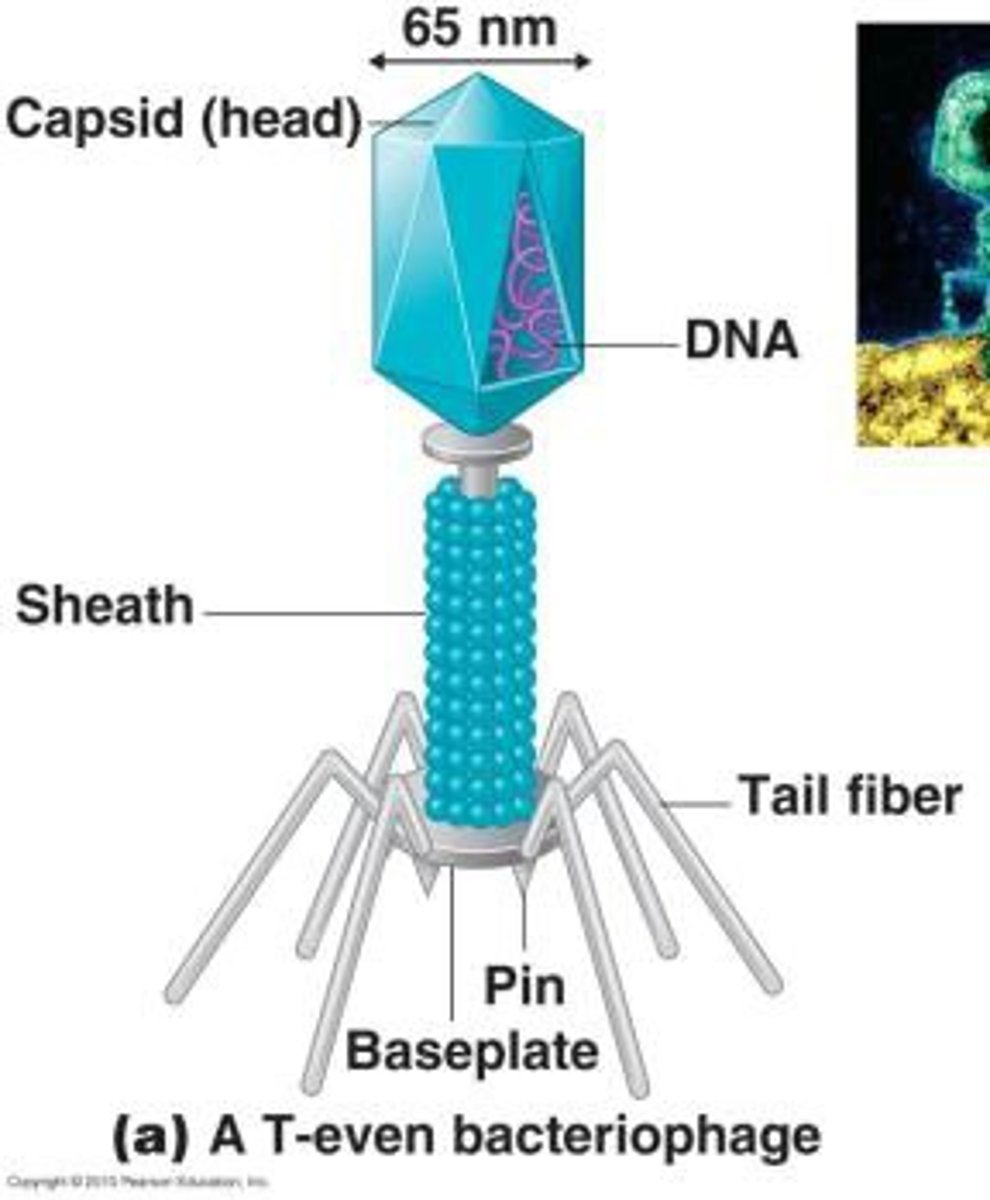
Phage
Phages are specialized viruses that affect bacteria