AP HUMAN EXAM UNIT 2
1/76
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
77 Terms
Ecumene
Where people set
Arithmetic Density
Total number of people/ total area (includes non-livable land
Physiological Density
People/livable land
Agricultural Density
Farmers/Arable land
Carrying Capacity
Max population size environment can sustain
Overpopulation
Not enough resources to support a population
Age/Sex ratio
Ratio of males to females of different ages
Crude Birth Rate (CBR)
Births per one thousand ppl
Crude Death Rate (CDR)
Number of deaths per one thousand ppl
Doubling Time
Time it takes for population to double
Infant Mortality Rate (IMR)
Number of dead children under one per 1,000 live births
Natural Increase Rate (NIR)
Birth rate - Death rate
Total Fertility Rate (TFR)
Average number of children a woman has in her fecund years
Describe stage one of the demographic transition model.
High death and birth rates,Stable or slow NIR, disease and famine prevalent
Describe stage two of the demographic transition model
High birth rate, rapidly falling death rate, high NIR, lower IMR
Describe stage three of the demographic transition model
Falling birth rate, falling death rate, slower NIR
Describe stage four of the demographic transition model
Low death and birth rates, stable or slow NIR, reliable health care, food, and family planning
Describe stage five of the demographic transition model
Very low birth rate, low death rate, slow NIR
Antinatalist policies
Policies that discourage birth
Pronatalist policies
Encourage birth
Ravenstein’s Law of Migration
Majority go a short distance
Migration proceeds step by step
Migration produced counter-stream
People in urban areas are less likely to migrate
Migrants go to large economic centers
Women are more migratory in their area of birth, but men migrate more internationally
Families rarely migrate
Urban areas grow more bc of migration than births
Migration increases when infrastructure improves
Major direction is rural to urban
Dependency Ratio
Number of people not in the workforce compared to number of people in the workforce
Push Factors
Drives people away
Pull Factors
Attract people
Intervening opportunity
Opportunity that stops migration
Intervening obstacle
Obstacle that stops migration
Asylum Seeker
Seeking residence in foreign country due to persecution
Chain Migration
Migrants move to follow earlier migrants
Step Migration
Takes place in stages
Internally Displaced Persons (IDP)
Forced to flee home, remains in home country
Refugee
Flees home country and is unable to return
Guest Worker
Legal migrant in a country for a job
Transhumance
Moving herds of animals to highlands in the summer and lowlands in the winter
Transnational Migration
Moving into another country
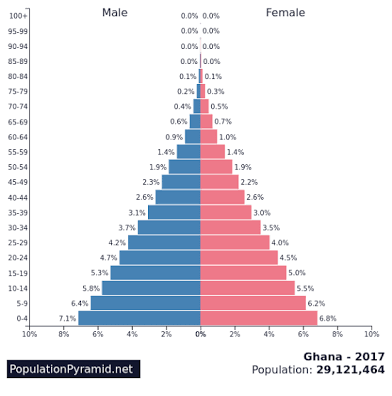
What stage is this?
Stage two
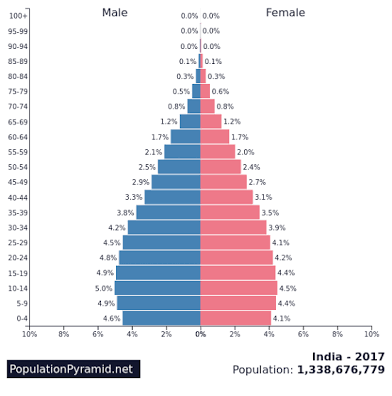
What stage is this
Stage three
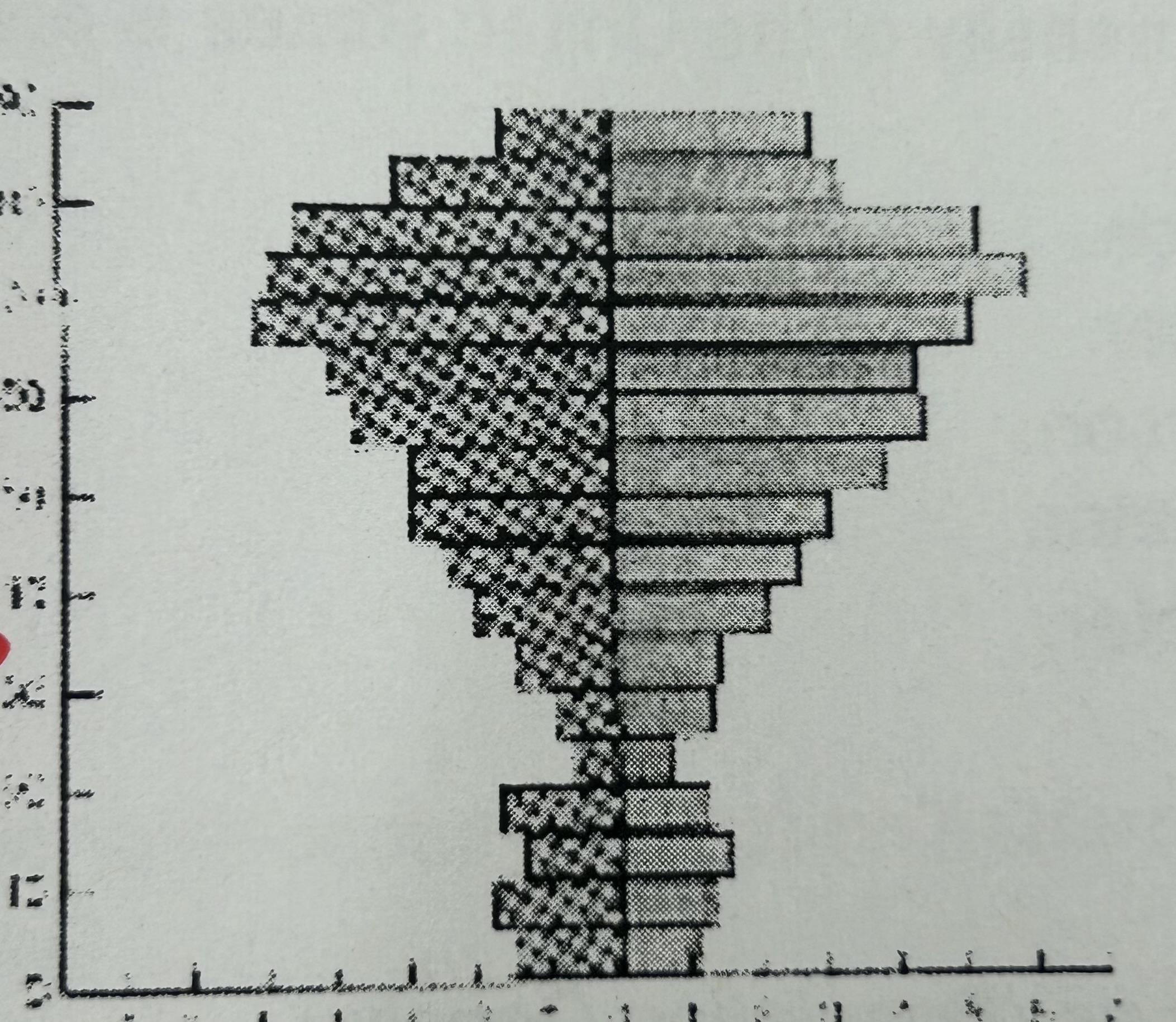
What stage is this?
Stage four
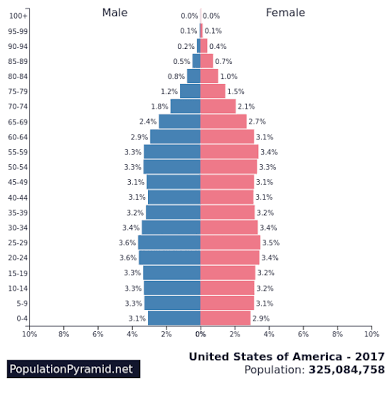
What stage is this?
Stage five
Counterurbanization
Shift from urban to rural
External Migration
Migration between countries
Internal Migration
Migration within a state
Net Migration
In migration - out migration
Brain Drain
Talented people leave an area
Choose the cause of the other two
Water
Population Growth
Agriculture
Water
Choose the cause of the other two
Columbus discovers America
Crop exchange between west and east
Natives die by disease
Columbus discovers America
Choose the cause of the other two
One child policy
Overpopulation
Poverty
Overpopulation
Choose the cause of the other two
Poverty
Drug trafficking
Guestworkers
Poverty
Choose the cause of the other two
High standard if living
Large metropolitan population
Stage 3 of dtm
Large metropolitan population
Choose the cause of the other two
Immigration
Remittances
Stage 4 of the dtm
Immigration
Choose the effect of the other two
Poverty
War
Migration
Migration
Choose the effect of the other two
Racism
Exclusion of non-white immigrants
Quota laws from 1920s-1960s
Quota laws from the 1920s-1960s
Choose the effect of the other two
Young age structure
Not married
High level of migration
High level of migration
Choose the effect of the other two
Cold weather
Warm coastal waters
Population clusters near the equator and coast
Population clusters near the equator and coast
List push factors
Ethnic cleansing, natural disaster, war, and overpopulation
List pull factors
Jobs, chain migration
The four regions where 2/3rds of the world’s population is clustered
East Asia, Southeast Asia, Europe, and South Asia
Compared to the Netherlands, Egypt has
Low arithmetic density, high physiological density, and high agricultural density
Countries with high fertility rates usually have high
infant mortality
Malthus’s theory is partially correct because
Life spans have increased due to advancements in agricultural tech
Which stage of the dtm has the best medical care with a low dependency ratio?
Stage four
The epidemiological transition model does not involve
Birth rates
In the early 1900s, migration patterns in the US were mostly
Rural to urban
What policies would a country at stage five of the dtm pursue to decreases its dependency ratio?
Pronatalist policies and guestworkers
What countries have zero or negative population growth as of 2018?
Italy, Japan, Russia
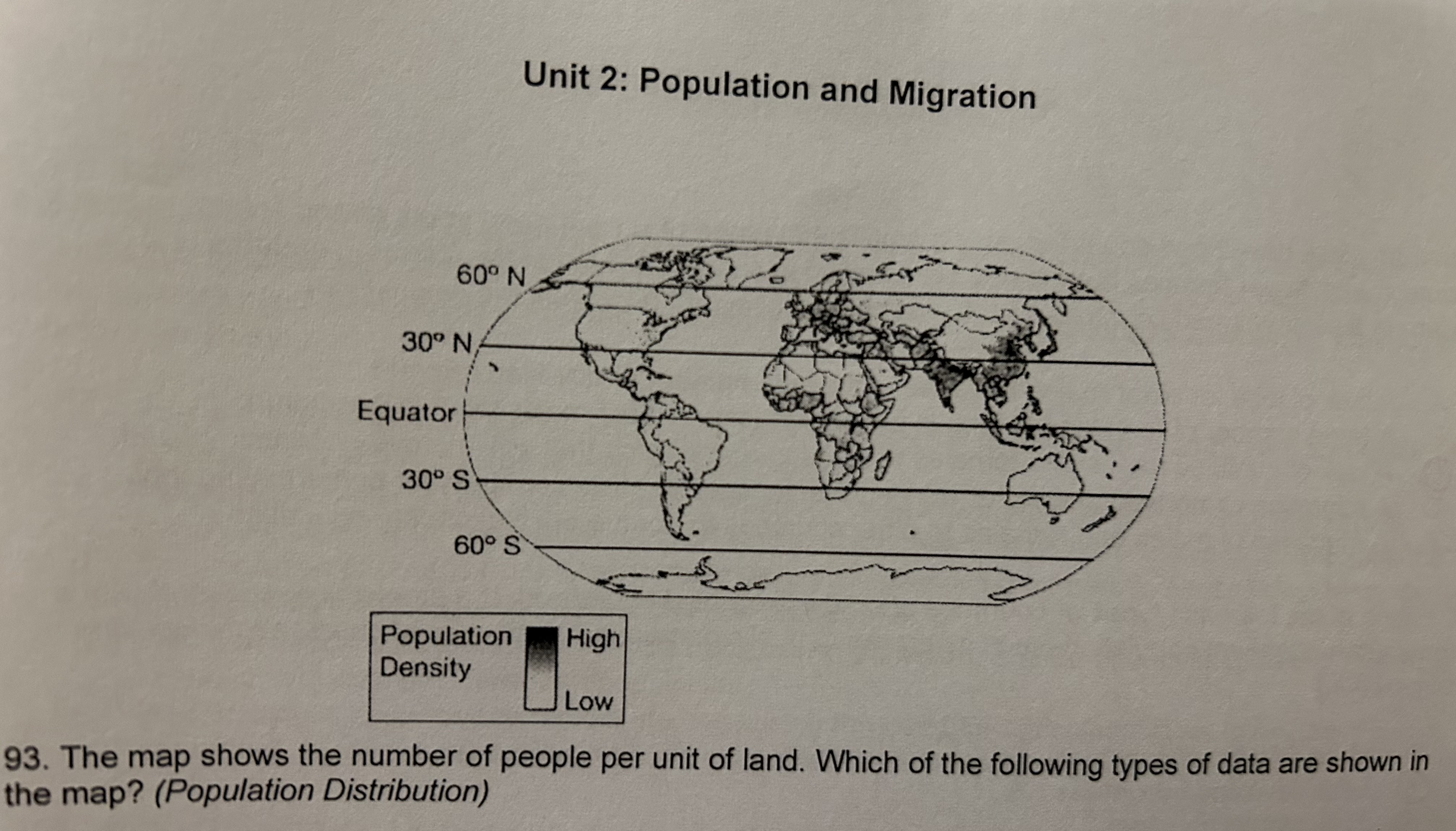
What data is shown in the map?
Arithmetic density
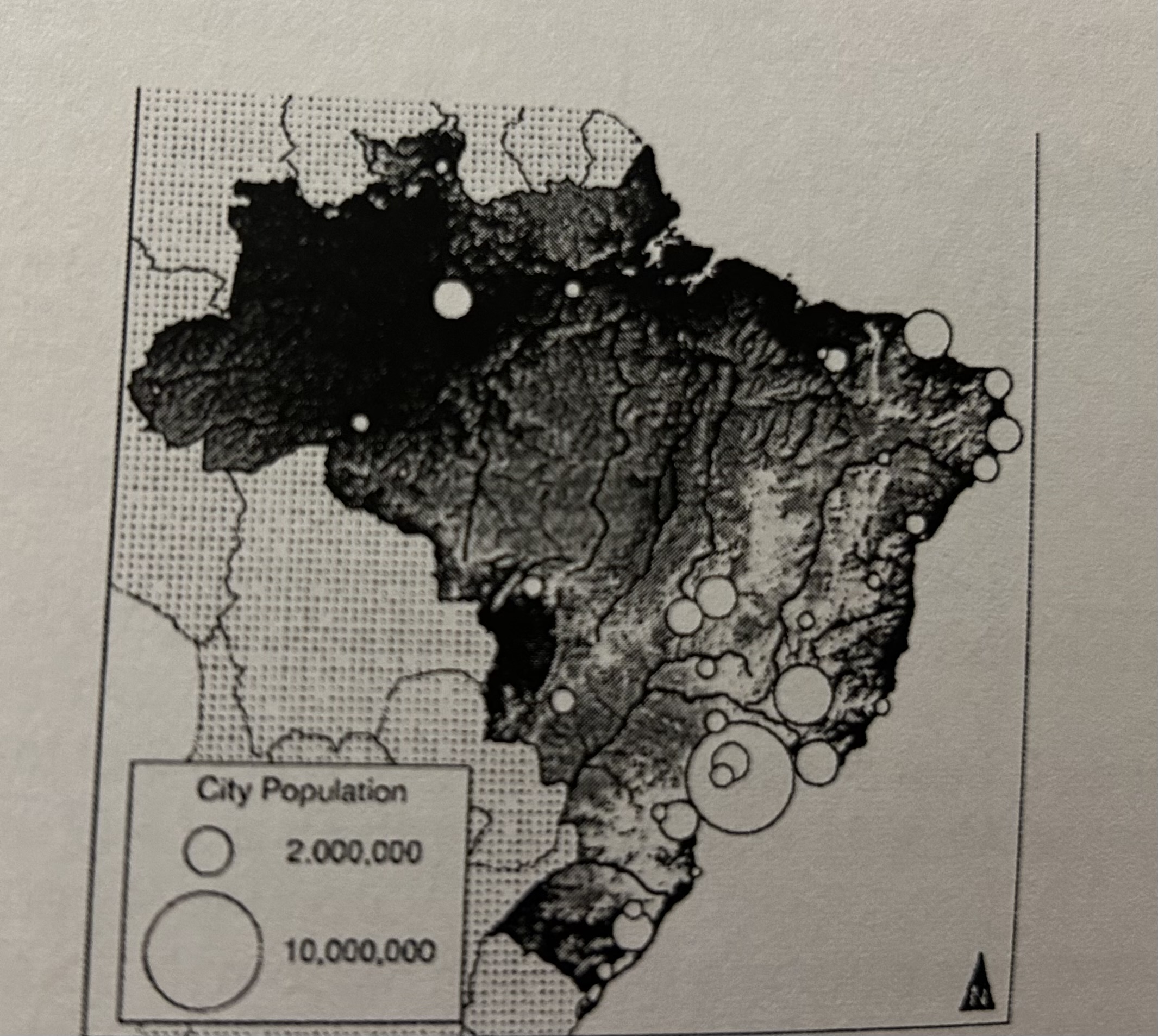
Describe the information a geographer could identify from the map of urban populations in Brazil
Patterns of arithmetic density in specific regions
Describe a country with a rate of natural increase of 0.4
Slow population growth
What pattern is a concern in LDCs with low school enrollment?
Lack of qualified people to develop a workforce to improve economic growth
Which countries are challenged by a large youth-dependent population
Less developed countries
Which country is in stage three of the dtm?
China: Birth rate = 13 Death rate = 7
DRC: Birth rate = 44 Death rate = 10
Bolivia: Birth rate = 24 Death rate = 7
Ivory Coast: Birth rate = 37 Death rate = 13
Hungary: Birth rate = 10 Death rate = 13
China: Birth rate = 13 Death rate = 7
What was Thomas Malthus’s theory?
If population growth was left unchecked, it would outstrip the food supply
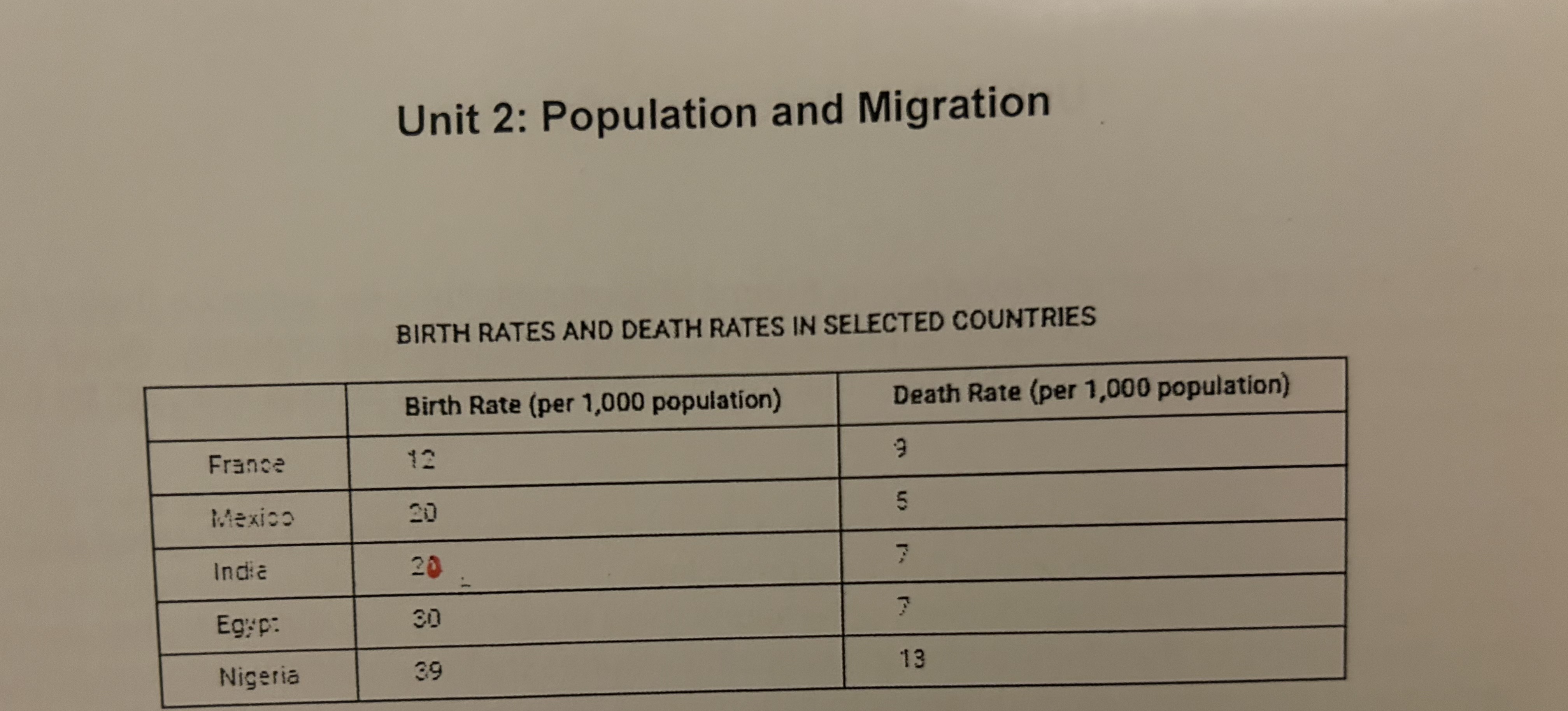
Which country has a high female empowerment?
France
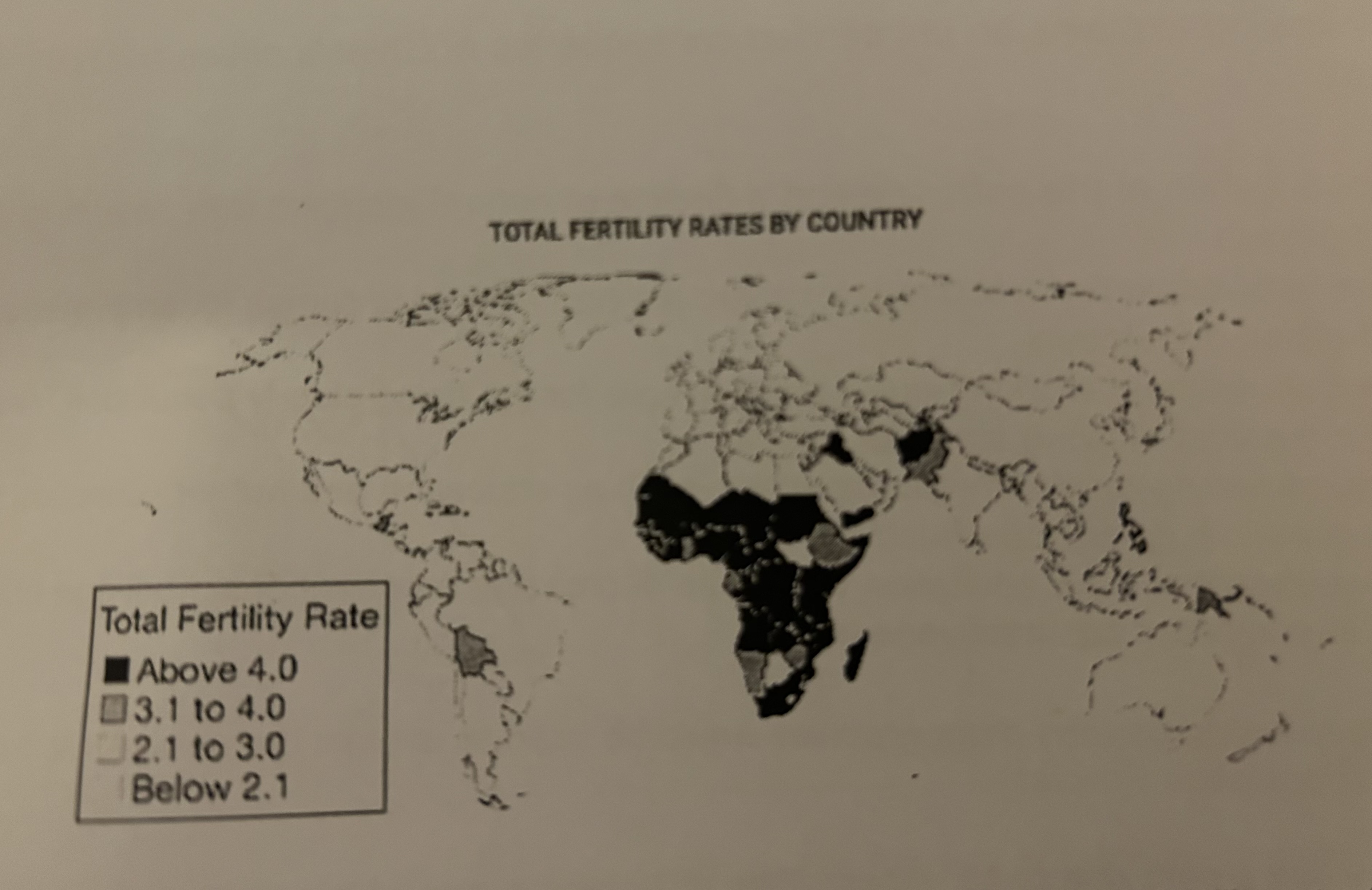
Where are the lowest fertility rates?
Europe, Russia, East Asia, Australia, and Canada
What’s a concern of a country with an aging population?
Fewer young people contribute to support programs
What’s a likely outcome of a country with a low birth rate, a low TFR, a high life expectancy, and a high urban population
Pressure on pensions and social security programs due to an increased elderly population
Majority of migrants from South Asia to the Persian gulf are
Guest workers in oil countries
A positive impact of large Chinese population in Vancouver and Los Angeles
Chinese immigrants establish businesses and religious centers in their new cities