310 - Binomial Trees
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
18 Terms
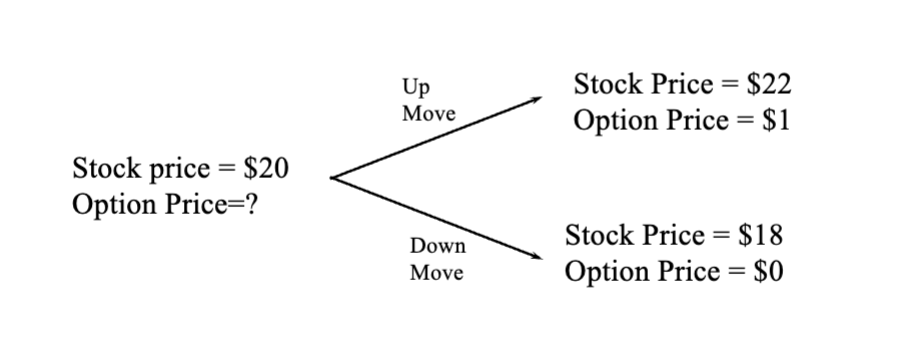
Generalized simple binomial tree
u is larger than 1
d is smaller than 1
payoff function is a function of the derivative, whether call, put, or to the power of x, where x is any variable, generally speaking, f is a function of S(T)
This allows us to construct a risk free portfolio
Delta formula for risk free portfolio
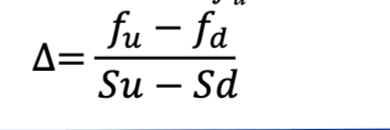
risk free in binomial context
no matter what happen, value of portfolio will always be constant.
Value of portfolio at time T
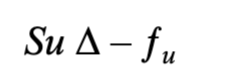
Value of portfolio today

Derivative price discounted back to todays date at maturity
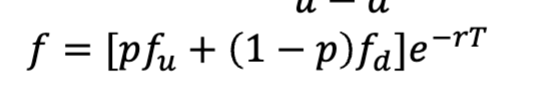
probability
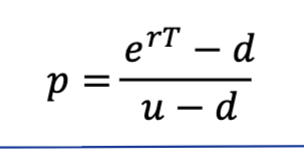
Irrelevance of stock’s expected return
When we are valuing an option in terms of the underlying stock the expected return on the stock is irrelevant.
Risk Neutral valuation
When the probability of an up and down movement are p and 1-p the expected stock price at time T is SerT
This shows that the stock price earns the risk free rate
Binomial trees illustrate the general result that to value a derivative we can assume that the expected return on the underlying asset is the risk free rate and discount at the risk-free rate.
This is know as using risk neutral valuation
Generalisation of two step binomial tree
delta t referes to the length of one time step
Delta hedging
Buy High, Sell Low
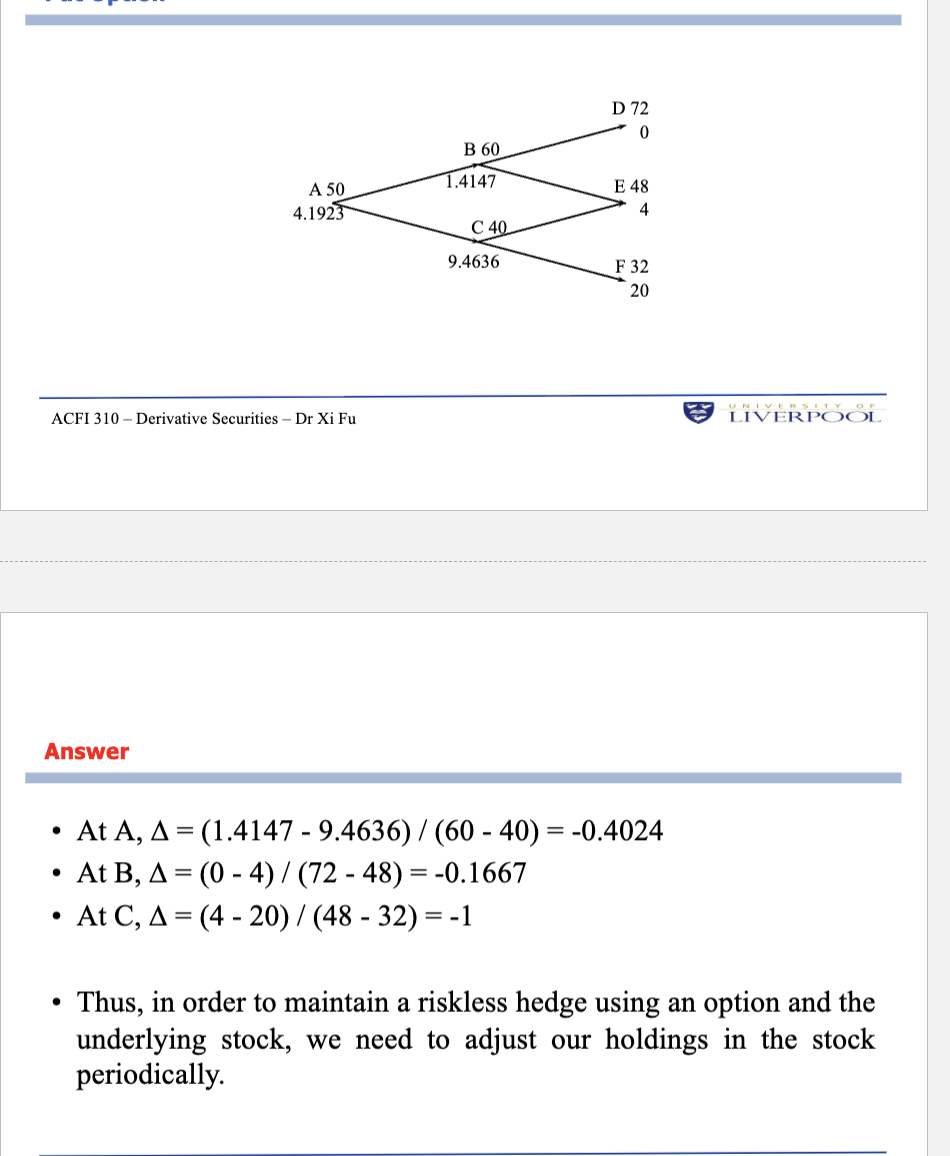
Choosing u and d
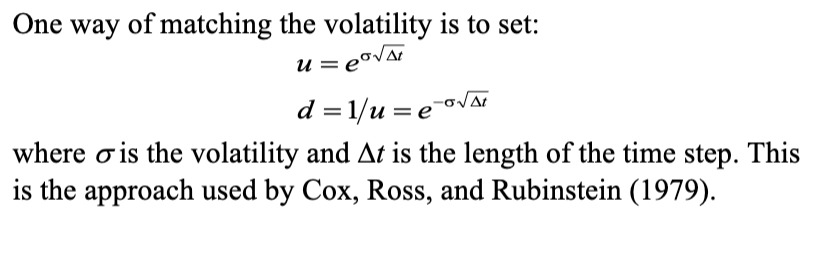
Probability of an up move for non-dividend paying stocks

Increasing time steps

Advantages of Binomial Tree
Primary advantage of binomial trees is that American options become much easier to price
Can factor in dividends;
No calculus needed;
Easy to make a spreadsheet to find option values
American option pricing
For an American option, the value of the option at any given point is the maximum of two values:
- The payoff if the option were exercised now;
- The pullback formula’s output
Note: The pullback formula takes into account American option values at future points
Disadvantages of binomial tree model
Speed:
In order to have accurate results, we want to maximize the number of time periods, but this means creating a lot of nodes which can be slow to calculate even with today’s computers.
For some extreme options, like a cash or nothing, pricing can be inaccurate until a very large number of time intervals is used.
Pros and cons of binomial option pricing
• Pros:
− It uses relatively simple Mathematics.
− It can be used to price American and Bermudan options.
− It can be implemented in computer programs.
− It can be adapted to various kinds of stock features (like dividends).
• Cons:
− Being discrete, it does not produce exact answers.
− By hand, it would take a long time to price an option using a lot of time intervals.
− At least with the Cox-Ross-Rubinstein Model, it must use a constant volatility, a downside
that the Black-Scholes PDE has as well.