302A: ATC Support
1/69
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
70 Terms
What is the primary responsibility of a Flight Service Specialist regarding IFR aircraft?
To provide ATC support services, including relaying clearances and movement information, on behalf of ATC.
According to MATS, what is the definition of an Instrument Approach Procedure (IAP)?
A series of predetermined manoeuvres by reference to flight instruments with specified protection from obstacles from the initial approach fix, or where applicable, from the beginning of a defined arrival route to a point from which a landing can be completed and thereafter, if a landing is not completed, to a position at which holding or enroute obstacle clearance criteria apply.
In which official publication are instrument approach procedures for specific Canadian airports published?
The Canada Air Pilot (CAP).
CARs 602 prohibits pilots on instrument approaches from descending below the Decision Height (DH) or Minimum Descent Altitude (MDA) unless what condition is met?
The required visual reference is established and maintained to complete a safe landing.
What are the 10 specified items that a pilot must be required to have visual reference to in order to continue an approach below DH/MDA?
the runway or runway markings;
The runway threshold or threshold markings;
the TDZ or TDZ markings;
the approach lights;
the approach slope indicator system;
the runway identification lights (RILS);
the threshold and runway end lights;
the touchdown zone lights (TDZL);
the parallel runway edge lights; or
the runway centreline lights
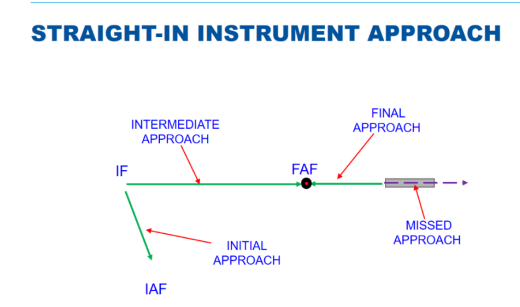
An instrument approach procedure may have up to four separate segments:
Initial Approach, Intermediate Approach, Final Approach, and Final Approach.
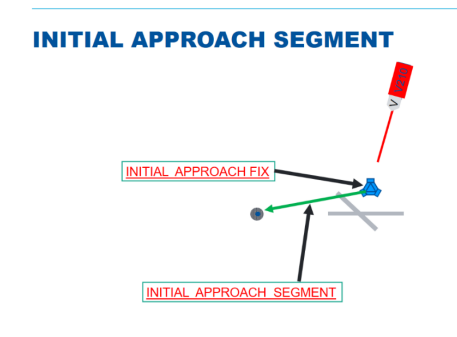
MATS definition of Initial approach segment?
That part of an instrument approach procedure between the initial approach fix or waypoint and the intermediate approach fix or waypoint during which the aircraft departs the enroute phase of flight and manoeuvres to enter the intermediate segment
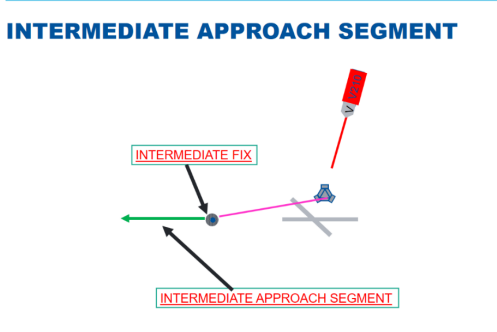
MATS definition of the Intermediate Approach Segment?
That part of an instrument approach procedure (IAP) between the intermediate approach fix (IF) or waypoint and the final approach fix (FAF), waypoint or point, or between the end of a track reversal, racetrack or dead-reckoning track procedure and the FAF, waypoint or point, as appropriate. It is in this part of the procedure that aircraft configuration, speed, and positioning adjustments are made for entry into the final approach segment.
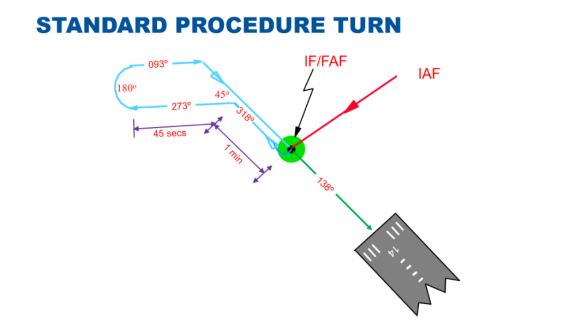
MATS definition of Procedure Turn?
On the plan view of an approach, a manoeuvre in which a turn is made away from a designated track followed by a turn in the opposite direction, both turns being executed so as to permit the aircraft to intercept and proceed along the reciprocal of the designated track. Procedure turns are designated "left" or "right" according to the direction of the initial turn. However, if possible, the procedure turn is designated "left."
Under what circumstance are the initial approach fix (IAF) and the final approach fix (FAF) the same, requiring the pilot to make a procedure turn?
When no suitable fix is available to construct a straight-in approach procedure.
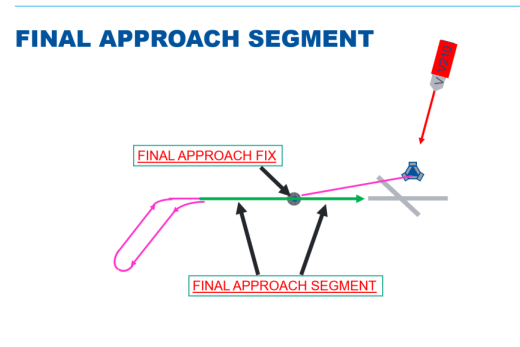
MATS definition of Final Approach Segment?
That part of an instrument approach procedure (IAP) from the time that the aircraft does one of the following:
Completes the last procedure turn or base turn, where one is specified
Crosses the final approach fix (FAF), waypoint or point
Intercepts the last track specified for the procedure until it reaches the missed approach point (MAP); alignment and descent for landing accomplished here
MATS definition of Missed Approach Procedure?
Missed approach procedure The procedure to be followed after an instrument approach procedure if, for any reason, a landing is not effected and that occurs normally when the aircraft either:
Has descended to the decision height, or has descended to the minimum descent altitude and reached the missed approach point or waypoint, and has not established the required visual reference to land
Is directed by ATC to pull up or to go around.
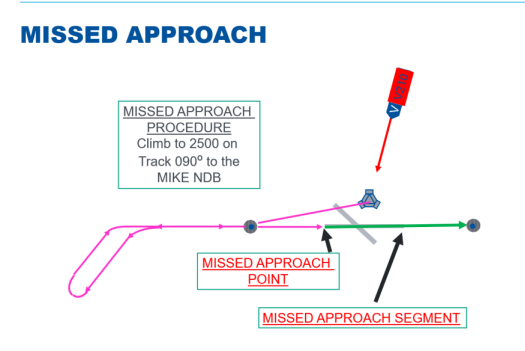
At what point is a missed approach procedure initiated on a precision approach?
At the decision height (DH).
What are the two basic types of instrument approach procedures?
Precision and Non-Precision.
What type of instrument approach procedure uses both azimuth (lateral) and glide path (vertical) information?
A Precision Approach Procedure.
A Non-Precision Approach Procedure provides only _ information.
electronic azimuth (lateral)
What is the definition of Decision Height (DH)? (Precision)
A specified height in a precision approach at which a missed approach must be initiated if the required visual reference has not been established.
What is the definition of Minimum Descent Altitude (MDA)? (Non-precision)
The altitude specified for a non-precision approach, below which descent must not be made until required visual reference is established.
What type of precision approach consists of a high-definition radar that provides the controller with altitude, azimuth, and range information to assist the pilot?
Precision Approach Radar (PAR).
For IFR traffic, what is a straight-in approach?
An IFR approach where the aircraft begins the final approach without first executing a course reversal manoeuvre like a procedure turn.
What conditions must be met to conduct a Contact Approach?
Clear of cloud
At least 1NM flight visibility
Reasonable expectation to continue in this weather
Proceed with visual reference to the earth
Approved, functioning I.A.P or GPS approach
What is the key difference between a Visual approach and a Contact approach?
A Visual approach is initiated by ATC in VMC, while a Contact approach must be requested by the pilot and has specific weather minima (clear of clouds, 1-mile visibility).
An instrument approach procedure conducted in VMC by an aircraft not on an IFR clearance, mainly for training purposes, is called a _ approach.
Simulated
What is a Restricted Instrument Procedure (RIP)?
An instrument procedure not authorized for public use but approved by Transport Canada for restricted use by specific operators. (Known as Company approaches)
A _ procedure is a manoeuvre initiated by the pilot to align the aircraft with a runway for landing when a straight-in landing is not possible or desirable.
Circling
According to CAR 602.104, What are Reporting Procedures for IFR Aircraft at Uncontrolled Aerodromes?
Pilot-in-command shall report their intentions:
5 minutes before estimated time of commencing the approach procedure
When commencing circling manoeuvre
As soon as practicable after initiating a missed approach procedure
Pilot-in-command shall report aircraft’s position:
When passing the fix outbound, if conducting a procedure turn or if no procedure turn intercept final approach course.
When passing the final approach fix or three minutes before the ETL where no final approach fix
On final approach
What are the 5 sections of an approach chart?
The five distinct sections of an approach chart are: Procedure identification, Plan view, Profile, Landing chart, and Minima Box.
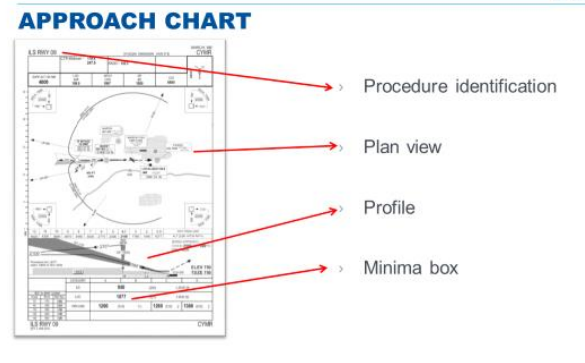
On an approach chart's Profile view, what symbol is used to denote the Final Approach Fix (FAF) for a non-precision approach?
A Maltese cross.
On an aerodrome chart, what are the 4 different Declared Distances?
TORA Take Off Run Available - Length of runway declared available and suitable for the ground run of an aeroplane taking off.
TODA Take Off Distance Available - Length of the take-off run available plus the length of the clearway, if provided.
ASDA Accelerate Stop Distance Available - Length of the take-off run available plus the length of the stopway, if provided.
LDA Landing Distance Available - Length of runway which is declared available and suitable for the ground run of an aeroplane landing
What is the key difference between an ATC clearance and an ATC instruction?
A pilot has the option to accept or refuse a clearance, whereas an instruction is a command that must be complied with unless safety is jeopardized.
According to CAR 602.31, what must a pilot of an IFR flight do after receiving an air traffic control clearance?
Read back the text of the air traffic control clearance to the appropriate air traffic control unit.
When a Flight Service Specialist relays a clearance from ATC, what prefix must be used?
A-T-C CLEARS.
When a Flight Service Specialist relays an instruction from ATC, what prefix must be used?
A-T-C INSTRUCTS.
Requests for ATC clearances for departing aircraft should be relayed by the FSS before the aircraft _, if possible.
begins to taxi
An ATC clearance is normally stated in a specific order, beginning with the prefix, clearance limit, SID, route, and _.
altitude
What is a 'clearance limit' in an ATC clearance?
The point to which an aircraft is cleared, with further clearance expected before arrival at that point.
When manually recording an ATC clearance, what must be done if the clearance is cancelled?
A single diagonal line must be drawn through it with the word 'CANCELLED' written.
What two time-related items must be included in the endorsement of a completed ATC clearance form?
The time the clearance was received and the time it was delivered.
After a pilot reads back an ATC clearance, what must the FSS state if the readback is correct?
READ BACK CORRECT.
Instead of reading back traffic information included in a clearance, what phrase may an FSS use when confirming the clearance with ATC?
TRAFFIC RECEIVED.
After relaying a departure clearance and confirming the readback, the FSS advises the aircraft to switch to the ACC frequency when _.
clear of the control zone
What is a Controlled VFR clearance?
A clearance provided to an aircraft operating VFR in class B airspace.
If an IFR pilot indicates their intention to depart VFR, what is the FSS's responsibility?
To advise the ACC of the pilot's intention or request.
Should a Flight Service Specialist suggest a VFR departure to an IFR pilot?
No, an FSS must not suggest a VFR departure or relay that one is available from the ACC.
The primary purpose of the ATC interphone system is the exchange of _ air traffic control messages.
IFR
To interrupt an interphone transmission for a high-priority message, what phraseology should be used?
BREAK FOR EMERGENCY or BREAK FOR CONTROL.
If an ATC clearance contains a time-based restriction (e.g., DO NOT DEPART UNTIL), what must the FSS provide after the pilot's correct readback?
A time check. (ACA121 READBACK CORRECT, TIME ONE FOUR ONE SIX)
A clearance time restriction becomes effective when the _ stated in the restriction is displayed on the clock; the seconds are disregarded.
minute
If an FSS is unable to deliver an ATC clearance within _ minutes of receipt, the ACC must be notified.
three
What does the term APREQ stand for?
APproval REQuest.
What is the purpose of Flow Control (APREQ)?
To adjust the flow of traffic into a given airspace, along a route, or to an aerodrome to ensure effective use of the airspace.
A Pre-Taxi Clearance (PTC) is relayed to a pilot with what specific instruction at the end?
DO NOT DEPART UNTIL DEPARTURE VALIDATION IS RECEIVED.
In the event of an air-ground communication failure with an IFR aircraft, who must the FSS notify without delay?
The appropriate ACC.
An FSS should only transmit ATC messages 'blind' under what circumstance?
Only if specifically instructed to do so by the ACC.
When should the ACC provide inbound IFR aircraft information to the FSS?
At least 15 minutes before the aircraft is expected to establish radio communication with the FSS.
The ACC must provide a revised position report over an approach fix if it differs by _ minutes or more from a previous estimate.
three
What is the difference between the terms 'Estimated' and 'Estimating' in ATS communications?
'Estimated' is used when communicating an ATC estimate, while 'Estimating' is used for a pilot estimate.
If a pilot of an IFR aircraft cancels IFR, what must the FSS do?
Acknowledge the cancellation and advise the ACC. (ROGER CANCELLING IFR.) (ROGER IFR FLIGHT PLAN CLOSED AND ALERTING SERVICE TERMINATED)
4Does the phrase 'CANCELLING IFR' automatically close the IFR flight plan or itinerary in Canadian airspace?
No, it only discontinues IFR separation; the flight plan remains active for alerting purposes.
If an FSS receives a report of a missed approach from an IFR aircraft, who must be advised?
The appropriate ACC. (JAZZ FOUR TWO TWO ON MISSED APPROACH RUNWAY 09 AT ONE FOUR TWO EIGHT)
What is the first item required in an IFR position report?
Aircraft identification.
What is the second item required in an IFR position report?
Position.
What is the third item required in an IFR position report?
Time.
What is the fourth item required in an IFR position report?
Altitude.
What is the fifth item required in an IFR position report?
Type of flight plan or flight itinerary.
What is the sixth item required in an IFR position report?
Next reporting point and ETA.
What is the seventh item required in an IFR position report?
The name only of the next succeeding reporting point.
What must the FSS do immediately upon becoming aware that an IFR aircraft has deviated from an ATC clearance or instruction?
Advise the appropriate ACC.
If communication cannot be established with an inbound IFR aircraft at least 5 minutes prior to its last known estimate, what should the FSS do?
Obtain a position report and an estimated time of landing (ETL) from the ACC.
An FSS must request a 'report off the runway' from an IFR aircraft if the intended runway and taxiway are not visible or if the FSS will not be in a position to _.
see the aircraft leave the runway