4th Quarter Vocabulary - Life Science - 8th Grade
1/35
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
36 Terms
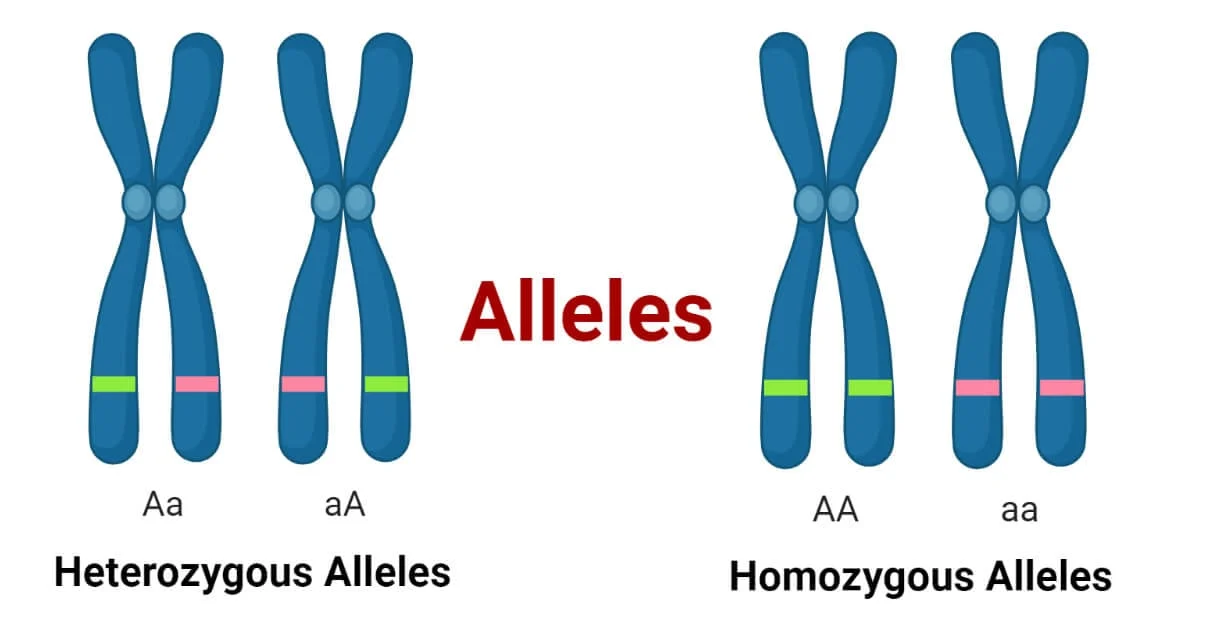
Allele
One of two or more versions of a gene.
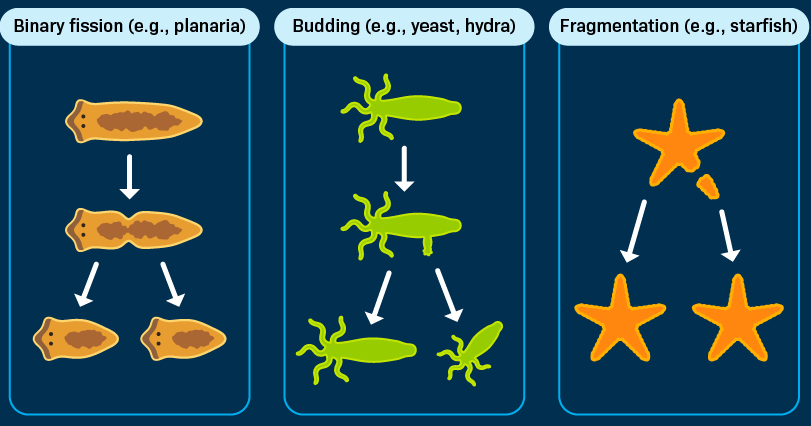
Asexual reproduction
Reproduction without the joining of sperm and egg (single parent produces offspring).

Biological evolution
The process by which species changes over time through variation and natural selection.
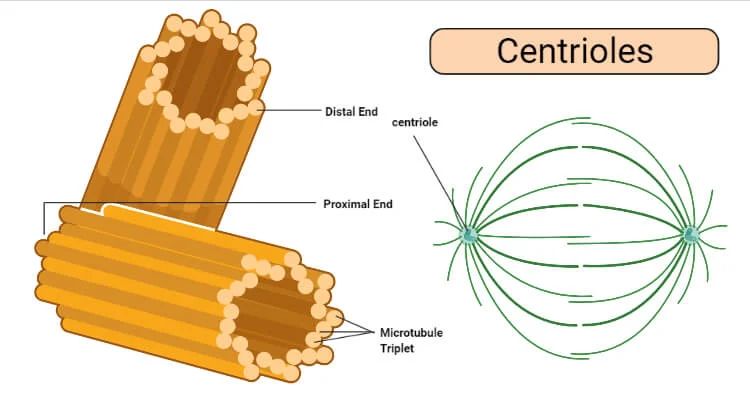
Centriole
A tiny part in the cell that helps the cell split into two during cell division.
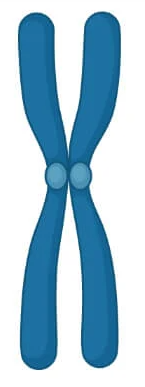
Chromosome
Structure in a cell’s nucleus that contains DNA and genes.
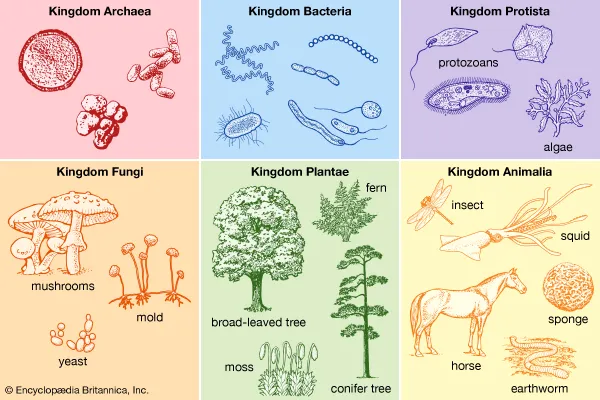
Classification
The system of grouping organisms based on similarities and differences.
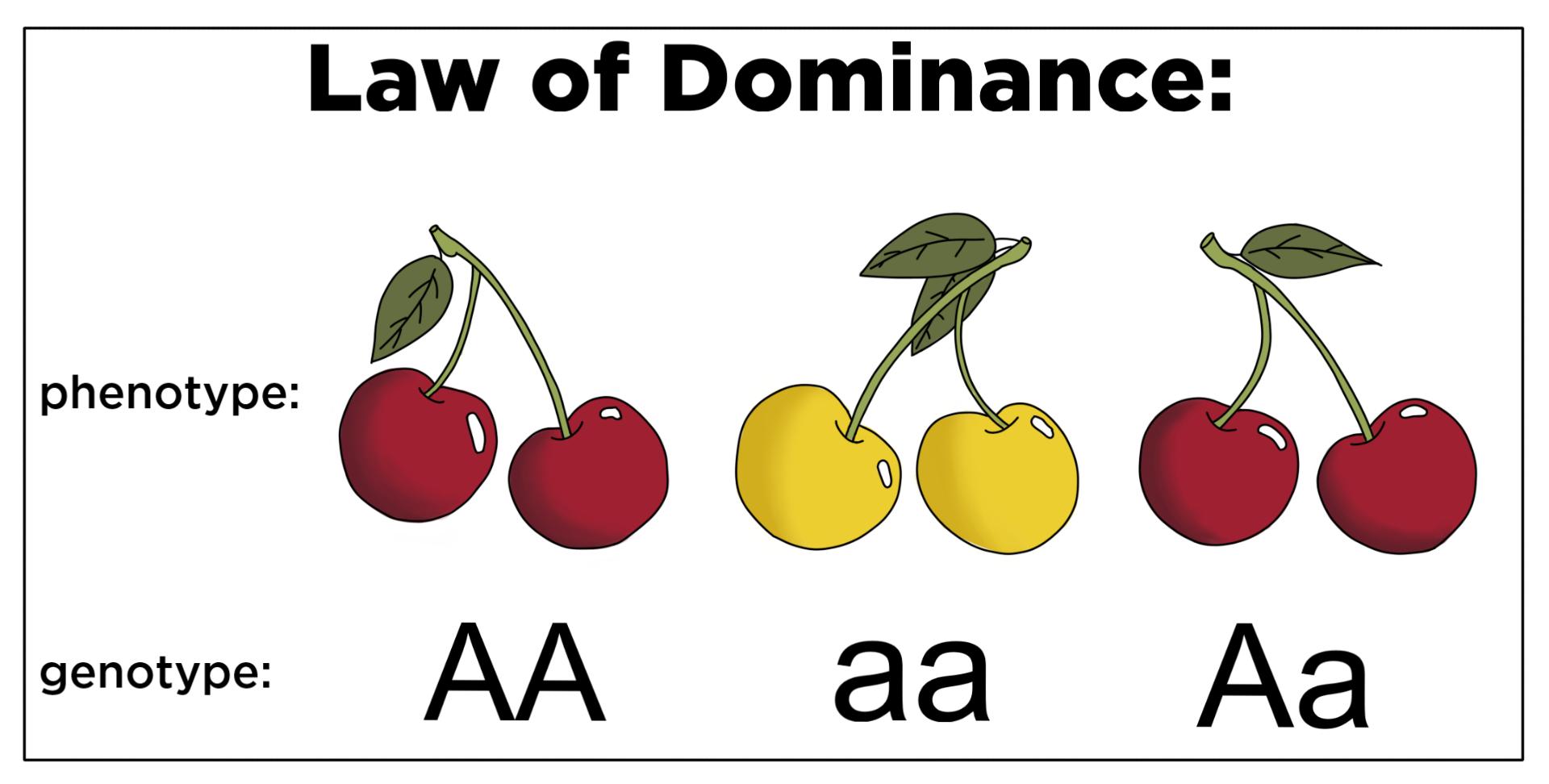
Dominant trait
A trait that appears when at least one dominant allele is present.

Extinction
The complete disappearance of a species.
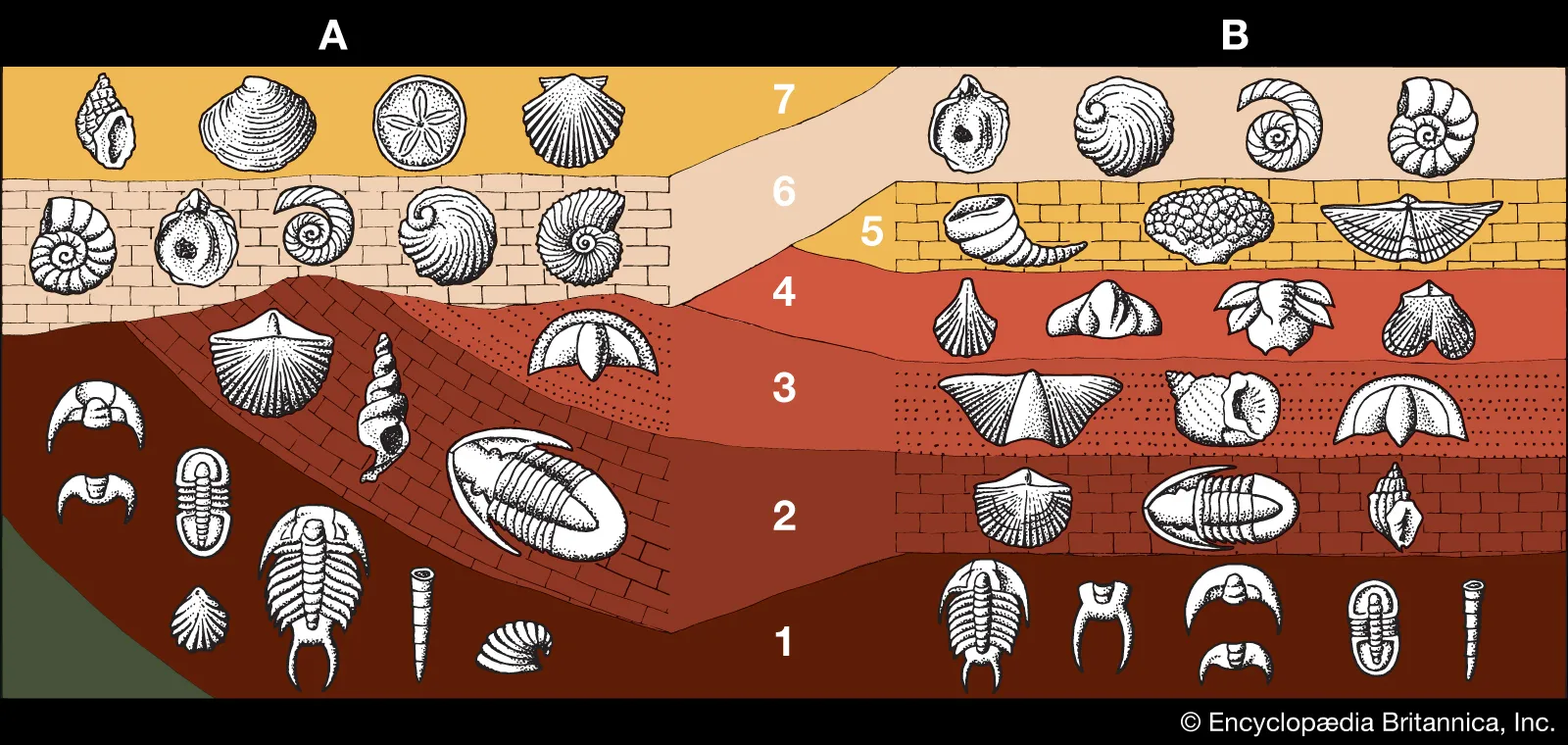
Fossil record
The history of life as documented by fossils preserved in rock layers.

Gene
A segment of DNA that codes for a particular trait.
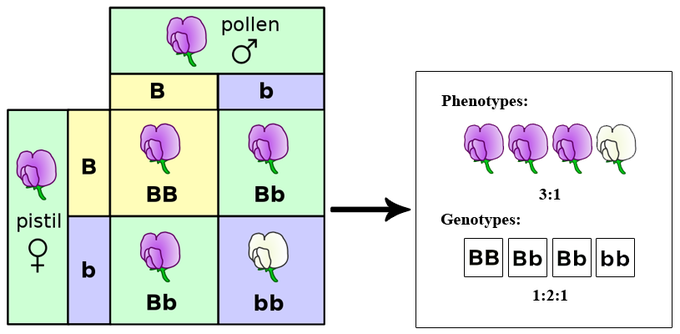
Genotype
The genetic makeup of an organism (the alleles it has).

Heredity
The passing of traits from parent to offspring.
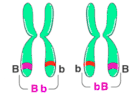
Heterozygous
Having two different alleles of a particular gene.
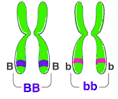
Homozygous
Having two identical alleles for a gene.
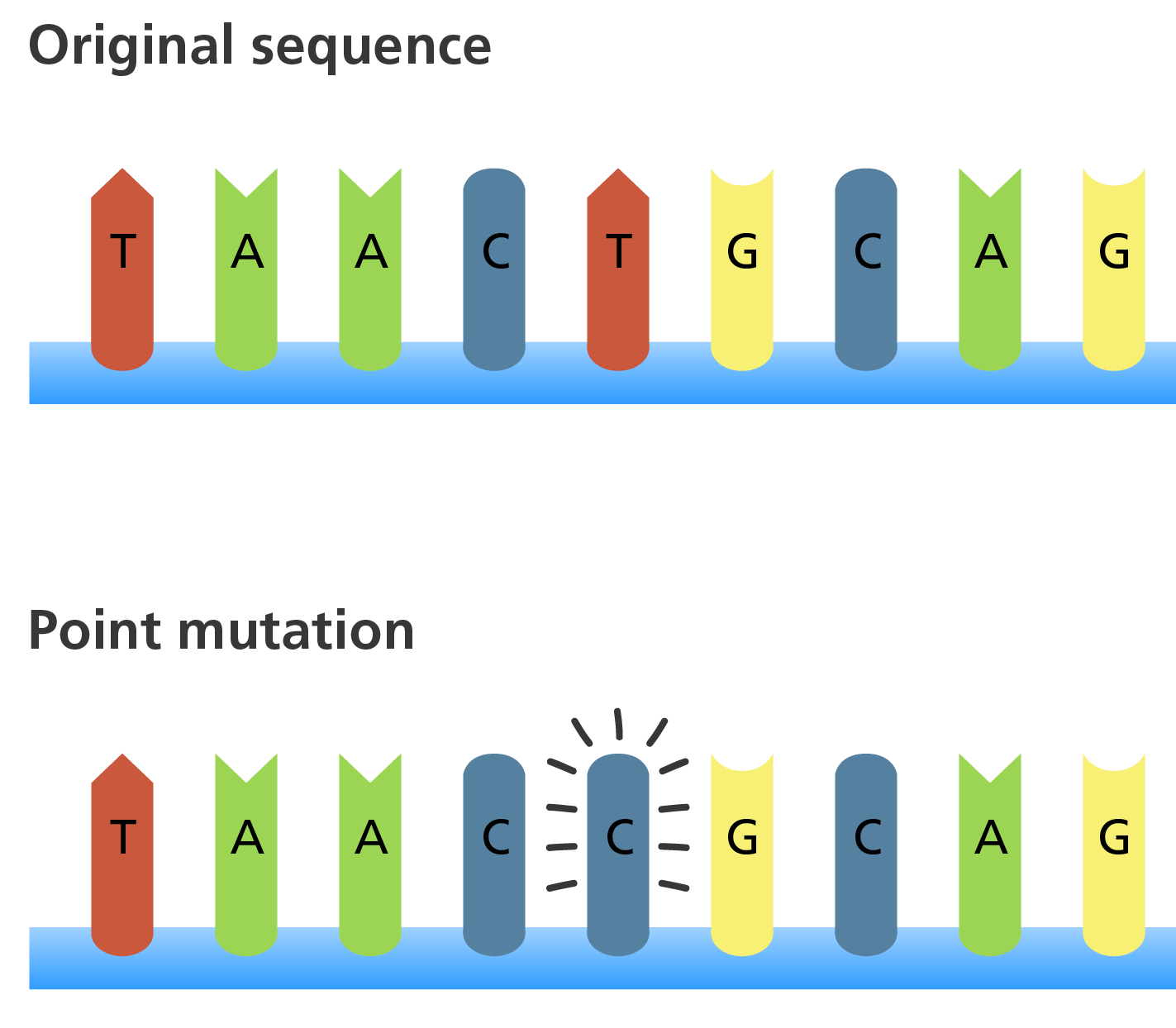
Mutation
A change in a gene or chromosome that can lead to variation.
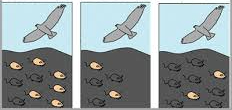
Natural selection
The process where organisms that are better adapted to their environment tend to survive and produce more offspring.
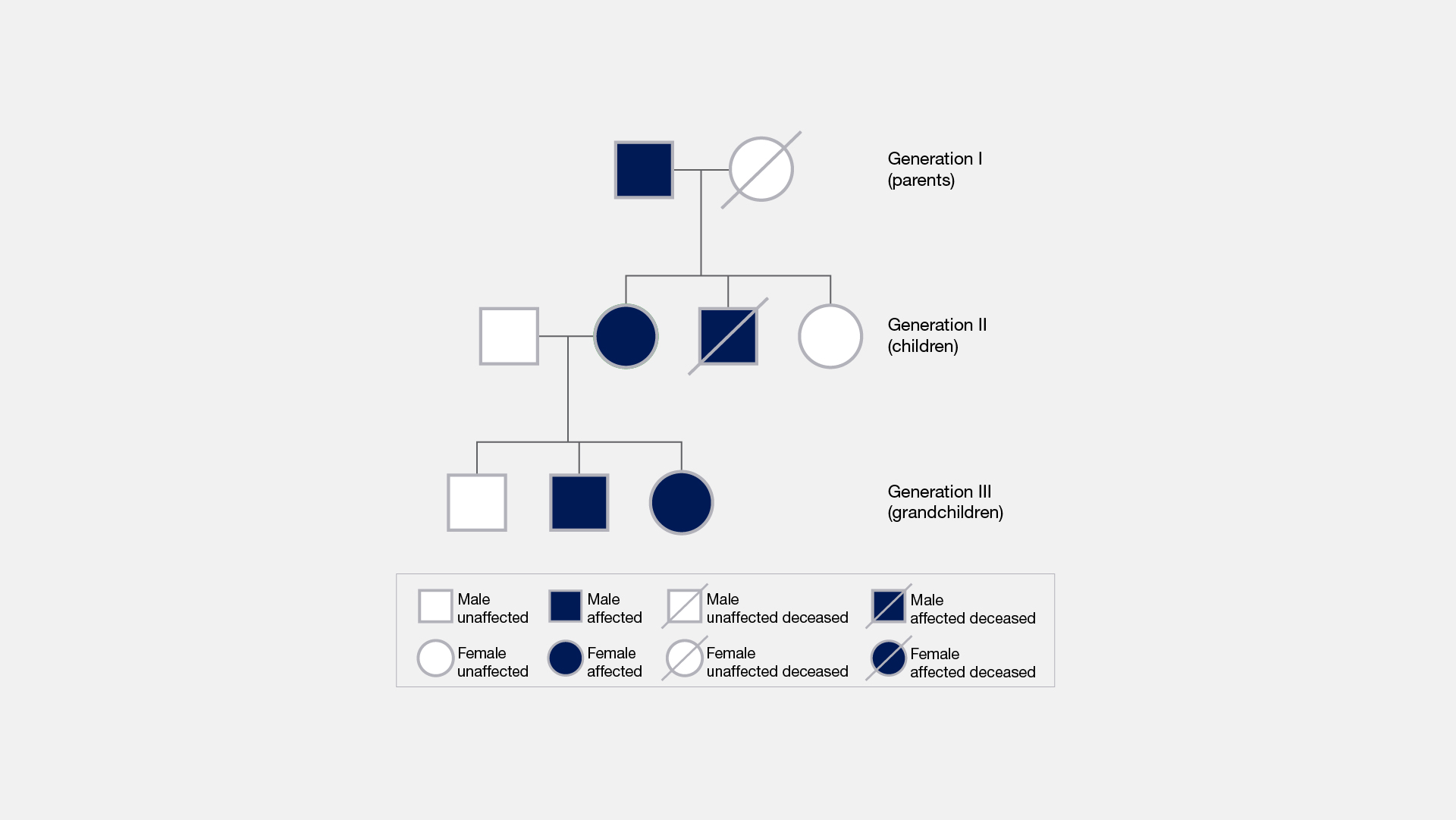
Pedigree
A chart showing the inheritance of a trait through several generations.
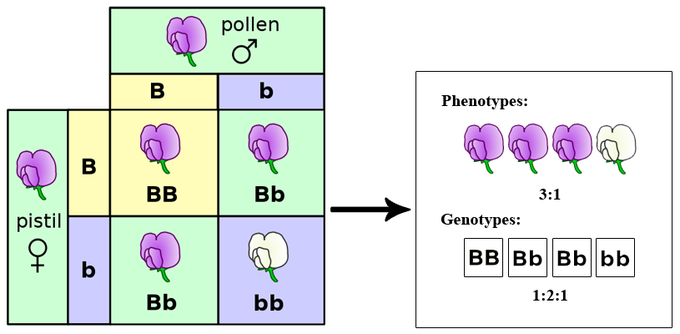
Phenotype
The physical appearance or expression of a trait.

Recessive trait
A trait that only appears when two recessive alleles are present.
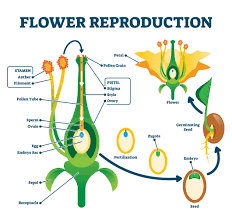
Sexual reproduction
Reproduction involving the fusion of sperm and egg producing offspring with genetic variation.

Species
A group of organisms that can interbreed and produce fertile offspring.
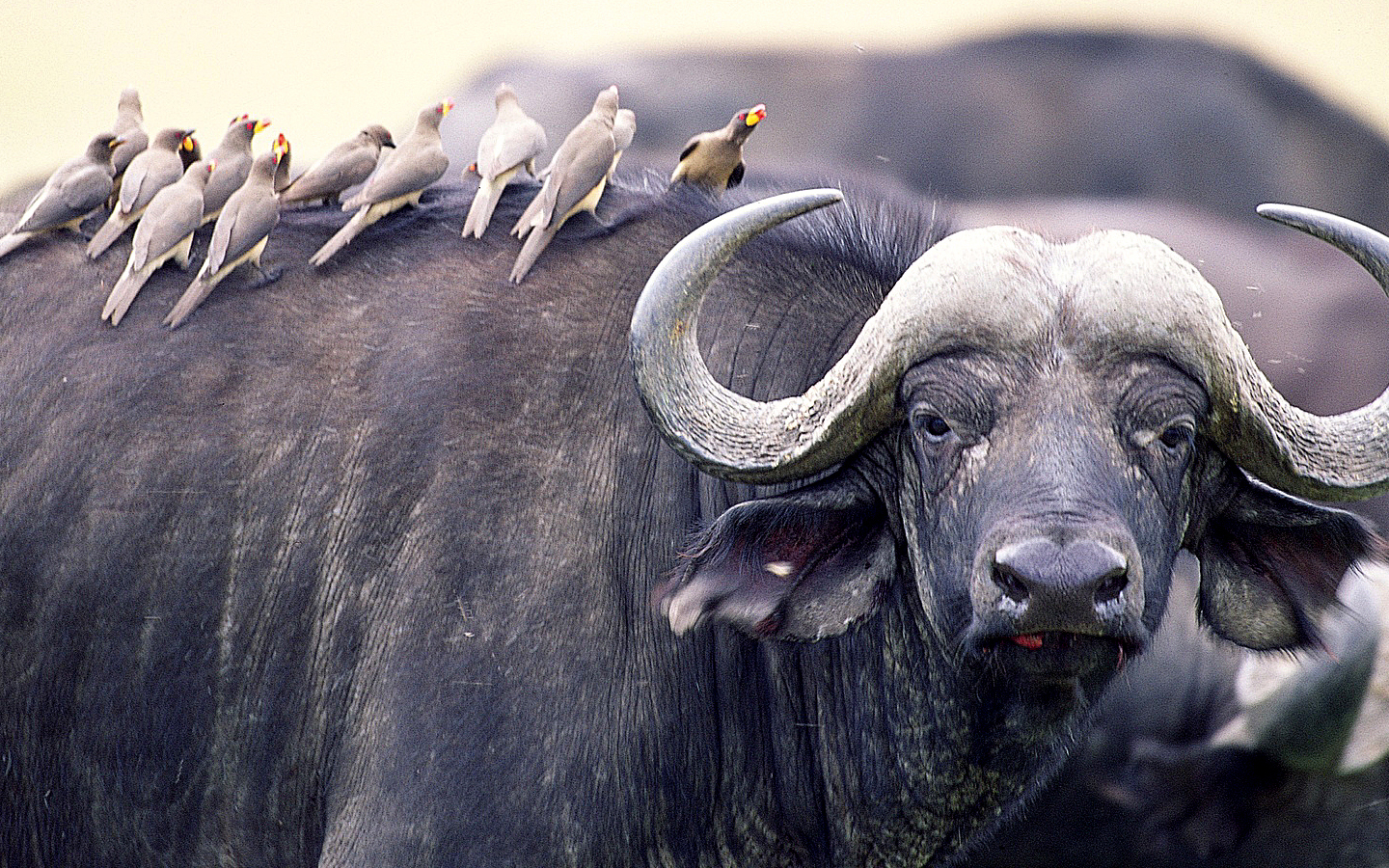

Symbiosis
A close relationship between organisms of different species.
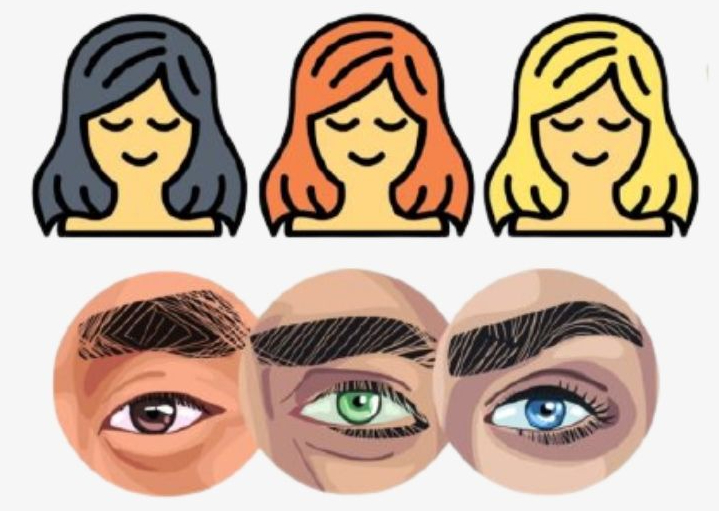
Trait
A characteristic of an organism (such as eye color or leaf shape).

Variation
Differences among individuals of the same species.
Vestigial structure
A body part that no longer serves its original function but was important in an ancestor.
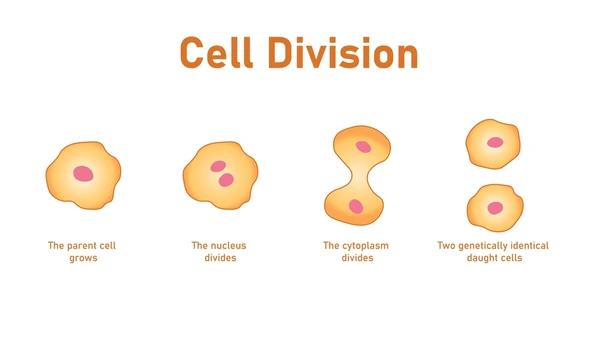
Cell division
When one cell splits into two new cells so living things can grow or heal.
DNA
The instructions inside the nucleus that tell how the living thing looks and works.

Habitat
The natural home or environment of an organism.

Adaptation
A special characteristic or behavior that helps a living thing survive in its environment.
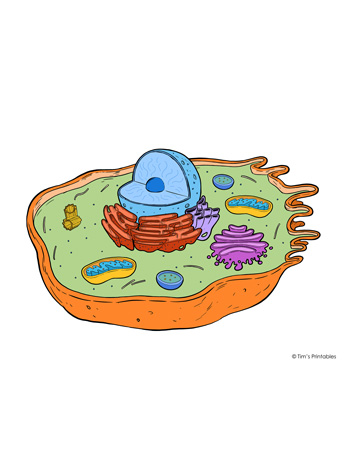
Cell
The tiny building block that makes up all living things.
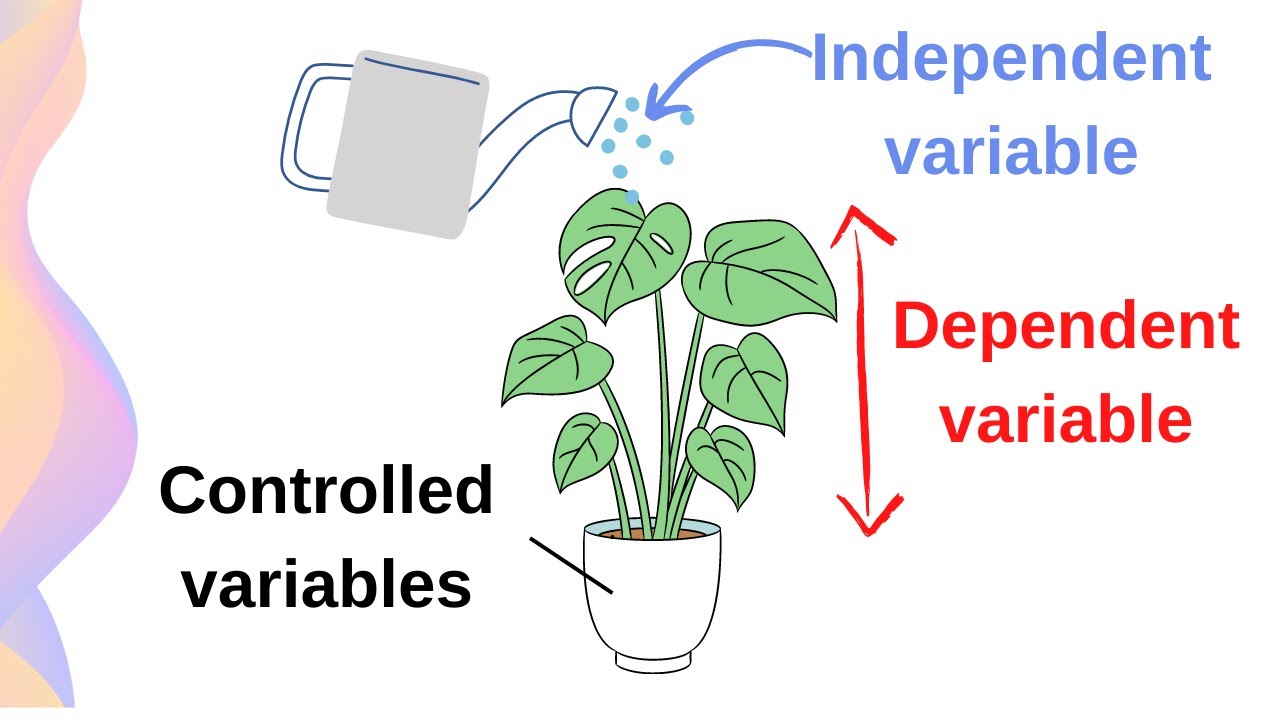
Dependent variable
In an experiment, the factor that you measure in response to changes you make.

Ecosystem
The community of organisms that live in a particular area, along with their nonliving environment.
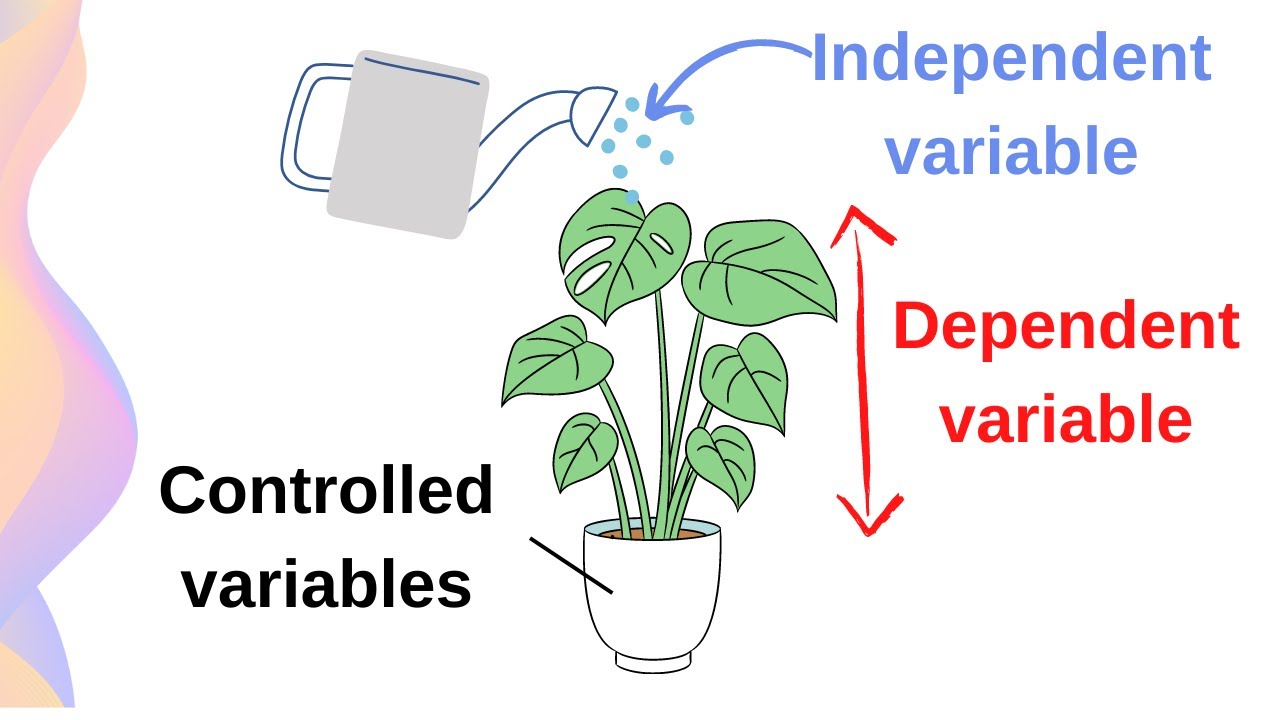
Independent variable
The factor you change in an experiment to see how it affects the outcome.
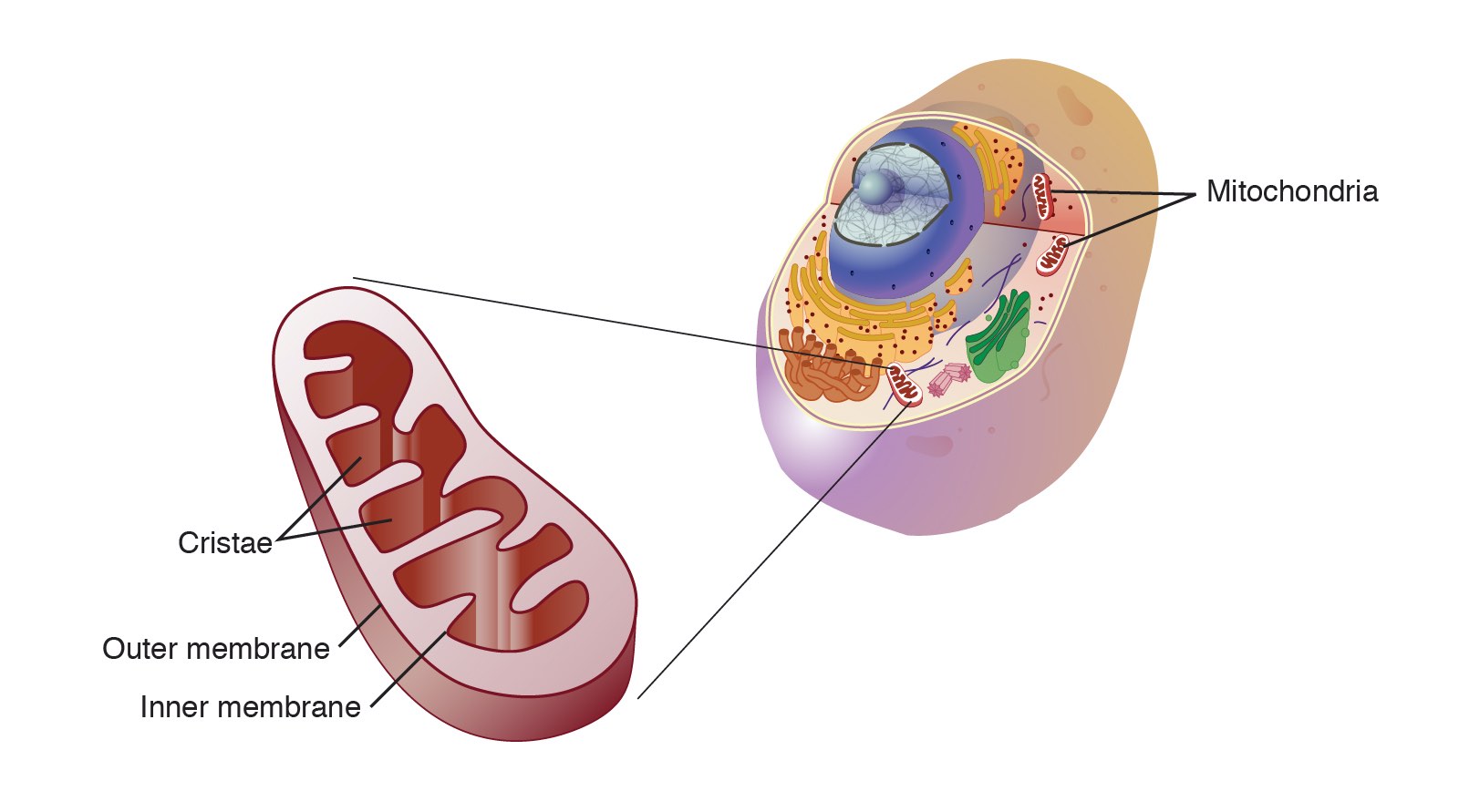
Mitochondria
The part of the cell that makes energy, like a tiny power plant.
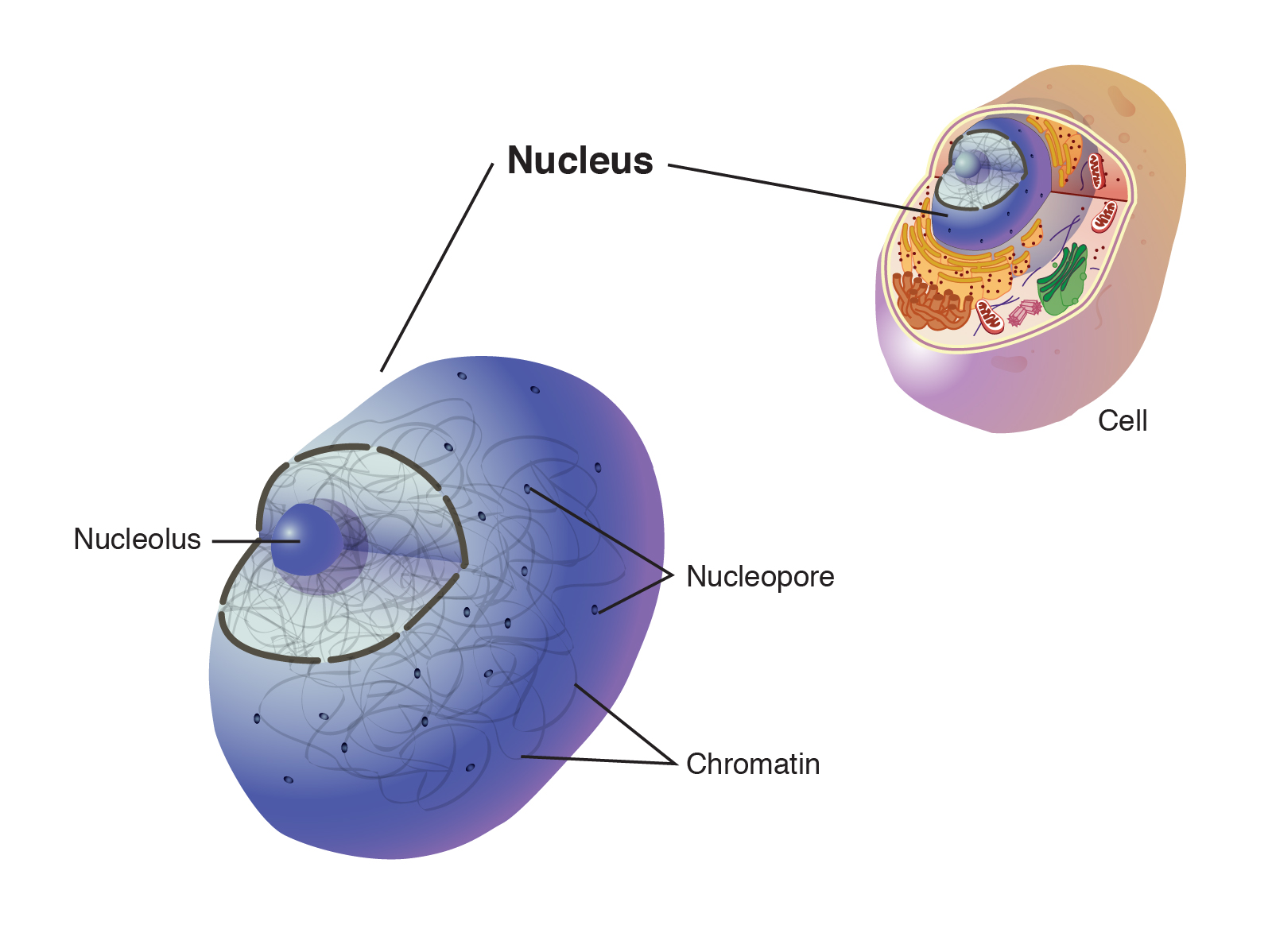
Nucleus
The 'boss' of the cell that tells the cell what to do.
Organelle
The small parts inside a cell that each have a special job.