Env. Sci. Ch. 12: Geology & Earth Resources
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
22 Terms
Tectonic plates
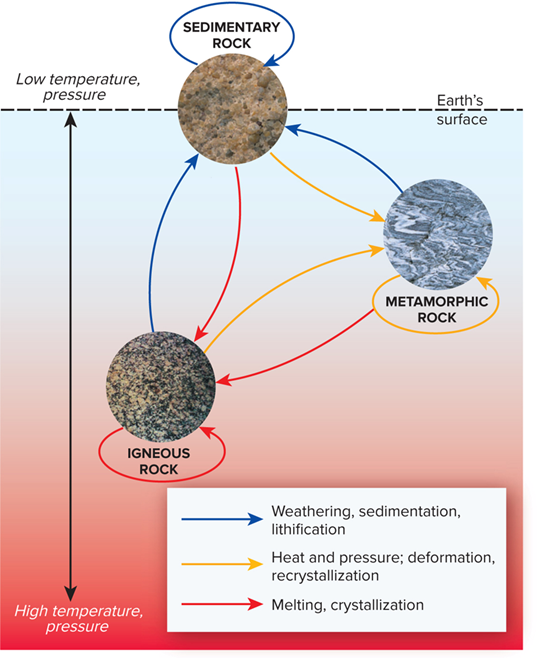
3 major rock classification
•Igneous rocks are solidified from hot, molten magma or lava.
•Metamorphic rocks form from the melting, contorting, and recrystallizing of other rocks.
•Sedimentary rocks are formed when loose grains of other rocks are consolidated by time and pressure.
What products are rare metals used in?
transportation, electronics, food and beverage packaging, steel alloys, chemicals, medical products and equipment, machinery, gasoline, etc.

tectonic plates
huge blocks spanning across Earth’s crust which slide slowly across its surface
What are earthquakes caused by?
jerking as tectonic plates grind past each other
magma
molten rock
rock cycle
a relentless cycle of formation and destruction
mineral
a naturally occurring, inorganic solid with a specific chemical composition and a specific internal crystal structure
metals
(such as iron, copper, aluminum, or gold) come from mineral ores, but once purified, are no longer crystalline and thus are not mineral
rock
a solid, cohesive aggregate of one or more minerals
sedimentation
deposition of particles of rock
Impacts of fracking operations
pollution, earthquakes,
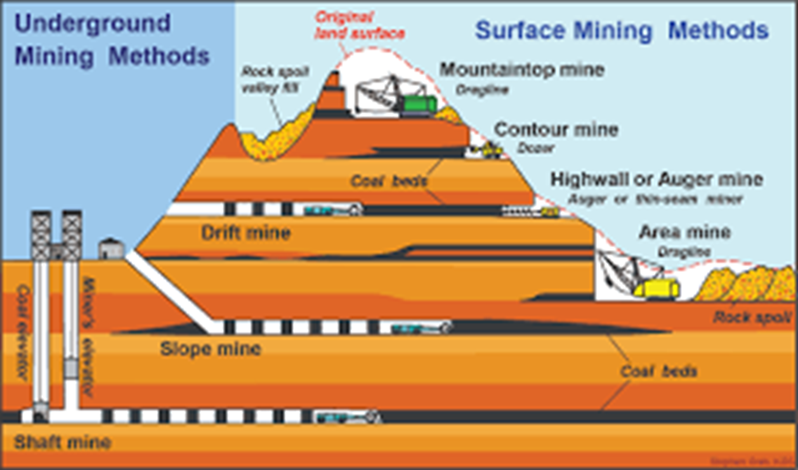
Types of mining
surface mining: mountaintop mine, contour mine, highwall/auger mine, area mine
underground mining: shaft mine, slope mine, drift mine
Open-pit mines
are used to extract massive beds of metal ores and other minerals, accumulates groundwater which turns into toxic soup
strip mining
The entire land surface is stripped away to cheaply and quickly expose the coal
smelting
roasting ore to release metals—is a major source of air pollution
chemical extraction
is used to dissolve or mobilize pulverized ore but it uses and pollutes a great deal of water. Chemicals used include toxins like cyanide
Where do earthquakes most frequently occur?
frequently occur along the edges of tectonic plates, but sometimes also occur in the centers of continents
landslides
are sudden collapses of hillsides
core
dense, hot, metal center of Earth composed of mostly iron, 3rd layer of Earth
mantle
surrounds molten hot core, hot pliable layer of rock, 2nd layer of Earth
crust
cool, outer brittle layer of Earth, 1st and outermost layer of Earth