Ap psychology ALL UNITS!
1/942
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
943 Terms
Wihelm Wundt
Wilhelm Wundt combined physiology and philosophy to create psychology and established the first psychology lab in Germany 1879. He believed in introspection and structuralism
Structuralism
structure is more important than function. structuralists believe that the mind must be broken into elements to understand its function using introspection.
Introspection
Self examination of one's own thoughts and feelings.
Functionalism
A psychological philosophy that considers mental life and behavior in terms of active adaptation to the persons environment. Was created to understand how the conscious mind is related to behavior.
William James
founder of functionalism; studied how humans use perception to function in our environment.
Early Behaviorism
Study of observable events. theory that states our responses to environmental stimuli shape our actions.
John Watson
Father of behaviorism. Studied observable behaviors and led the little Albert experiment where he trained young boy to fear white rat.
Gestalt Psychology
the whole is greater than the sum of its parts. looks at the mind and behavior as a whole
Sigmund Freud
Founder of psychoanalysis. Proposed theories about the role of the unconscious mind and childhood experiences.
Humanstic approach
humans have free will and ability to grow
self-actualization
The process of of fulfilling ones potential capabilities.
Evolutionary approach
An approach to psychology centered on evolutionary ideas such as adaptation, reproduction, and natural selection as the basis for explaining specific human behaviors.
biological perspective
The perspective assumes personality characteristics are a function of various biological factors, including behavioral genetics, the neurological perspective, and an evolutionary perspective.
Cognitive approach
Thought processes impact the way people behave.
biopsycholosocial approach
an integrated approach that incorporates biological, psychological, and social-cultural levels of analysis
Sociocultural Approach
examines the ways in which social and cultural environments influence behavior.
biological psychology
Physical processes shape behavior. (ex-anger is due to hormonal imbalance in the brain)
clinical psychology
focuses on diagnosing and treating mental, emotional, and behavioral disorders
Cognitive psychology
Scientific study of the mind as an information processor. Studies the mental processes associated with thinking, knowing and communicating.
Counseling psychology
a branch of psychology that assists people with problems in living.
developmental psychology
Studies social, physical and cognitive changes throughout life span and how and why human beings change in life;used in cross sectional research
educational psychology
the study of how psychological processes affect and can enhance teaching and learning
experimental psychology
the study of behavior and thinking using the experimental method
industrial-organizational psychology
studies the relationships between work and people in order to help companies increase productivity, boost morale, and select and train employees.
personality psychology
studies personality along with its variation among individuals.
social psychology
studies how humans are influenced by one another.
positive psychology
Focuses on studying positive emotions to improve peoples lives.
psychodynamic approach
Made by sigmund freud. regards personality as formed by needs, strivings, and desires largely operating outside of awareness-motives that can also produce emotional disorders
Behaviorism
created by Ivan Pavlov.Rejection of psychodynamic approach. the view that psychology should be an objective science that studies behavior without reference to mental processes.
correlational studies
Involves looking at the relationship between two or more variables. Is used when performing an experiment is not possible.
Survey research
The collection of information reported by people about a topic.
naturalistic observation
observing and recording behavior in naturally occurring situations without trying to manipulate and control the situation
case studies
a research method that is in depth, time consuming that provides detailed info on unusual people.
longitudinal studies
A research method that studies the same participants over a period of time
cross-sectional study
Examines people from different groups at the same time. quick and easy to conduct.
Basic research
To increase knowledge about a topic
Applied research
scientific study that aims to solve practical problems
Scientific Method
A series of steps followed to solve problems including collecting data, formulating a hypothesis, testing the hypothesis, and stating conclusions.
operational definition
a statement of the exact procedures used in the study which would eventually allow other researchers to replicate the research.
independent variable
The variable that changes in the experiment
dependent variable
The effect of the change in the experiment. This is what gets measured.
Confounding variable
An outside influence that changes the effect of the independent and dependent variables.
control variable
A variable that is kept the same during an experiment.
random assignment
participants are assigned to each experiment group with an equal chance.
random sample
each individual in a large population has equal chance of being selected
sampling bias
a flawed sampling process that produces an unrepresentative sample
experimenter bias
when researchers influence the results of an experiment to portray a certain outcome.
double-blind procedure
when neither the participants nor the researcher are able to affect the outcome of the research because they don't know what group they have been assigned to.
hindsight bias
the tendency to believe that you knew what was going to happen all along.
Hawthorne effect
A change in a subject's behavior caused simply by the awareness of being studied
placebo effect
the phenomenon in which the expectations of the participants in a study can influence their behavior
control/placebo group
the group that does not receive the experimental treatment.
edward titchener
Student of Wilhelm Wundt; founder of Structuralist school of psychology.
external validity
How generalizable the results of the experiment are
internal validity
the degree to which changes in the dependent variable are due to the manipulation of only the independent variable
valid
Well-founded reliable evidence and corresponds accurately to the real world.
reliable
research that can be replicated and is consistent
descriptive statistics
Describes data. numerical data used to measure and describe characteristics of groups.
inferential statistics
Tell us what data means. procedures used to draw conclusions about larger populations from small samples of data
central tendency.
mean, median, mode. Identifying an average center from the data.
measures of variation
A measure used to describe the distribution of data
standard deviation
a measure of variability that describes an average distance of every score from the mean. The higher the standard deviation, the less similar to the mean.
range
the difference between the highest and lowest scores in a distribution
correlation coefficient
A statistical measure that describes the strength of the relationship between the two variables. It an range from -1 to 1 -1 indicates a strong negative relationship while 1 indicates a stong positive relationship.
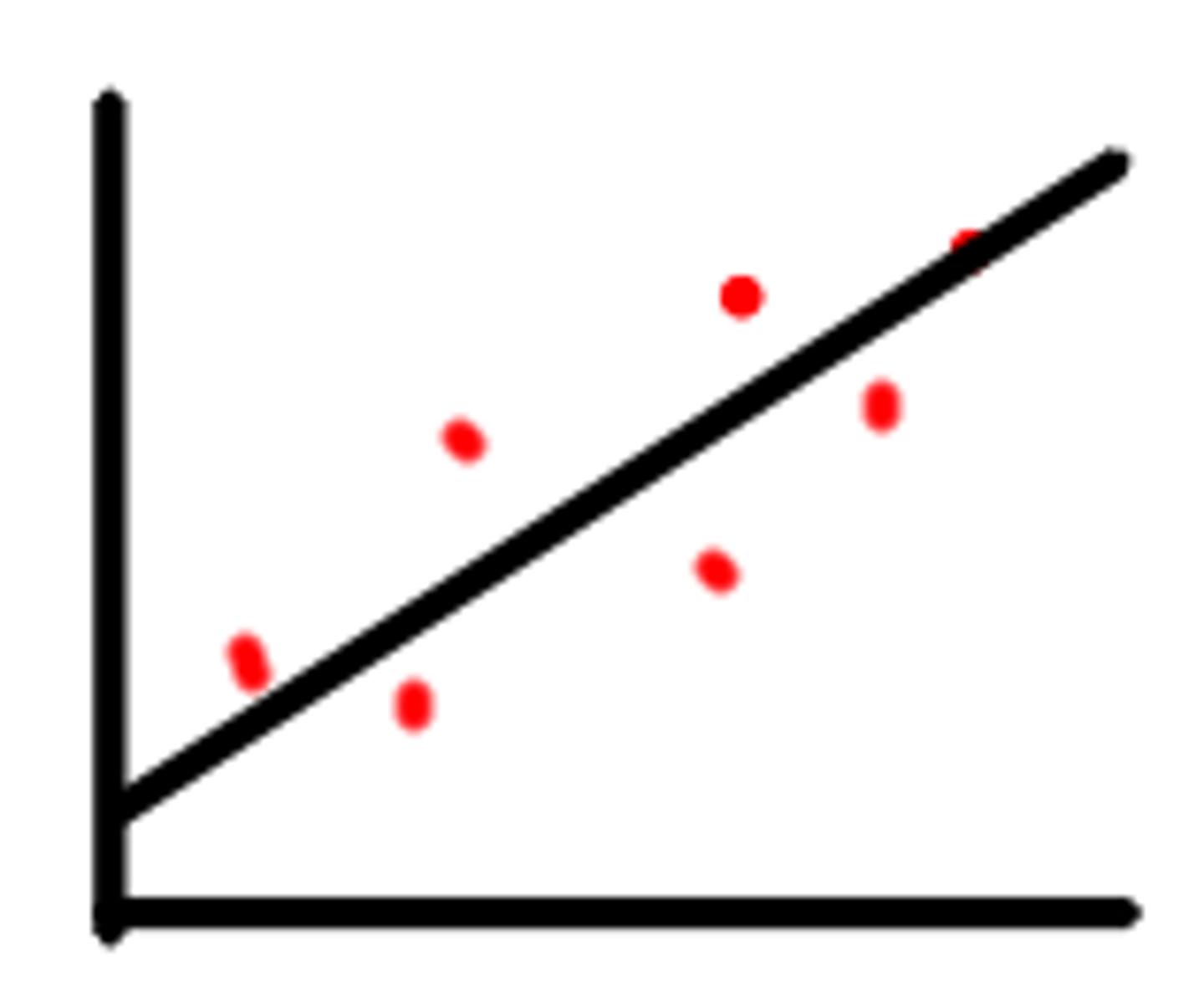
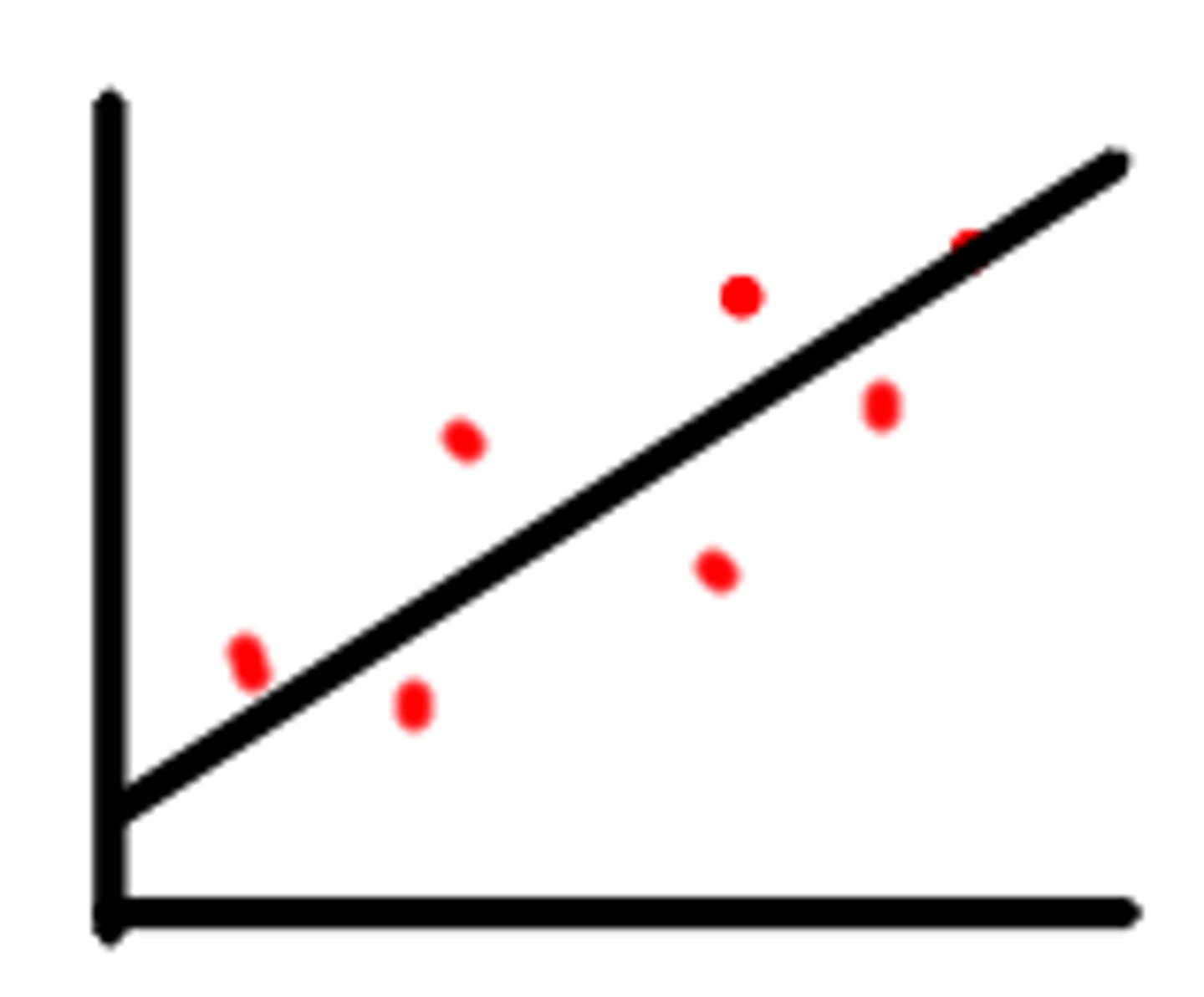
postitive correlation
as x increases, y increases
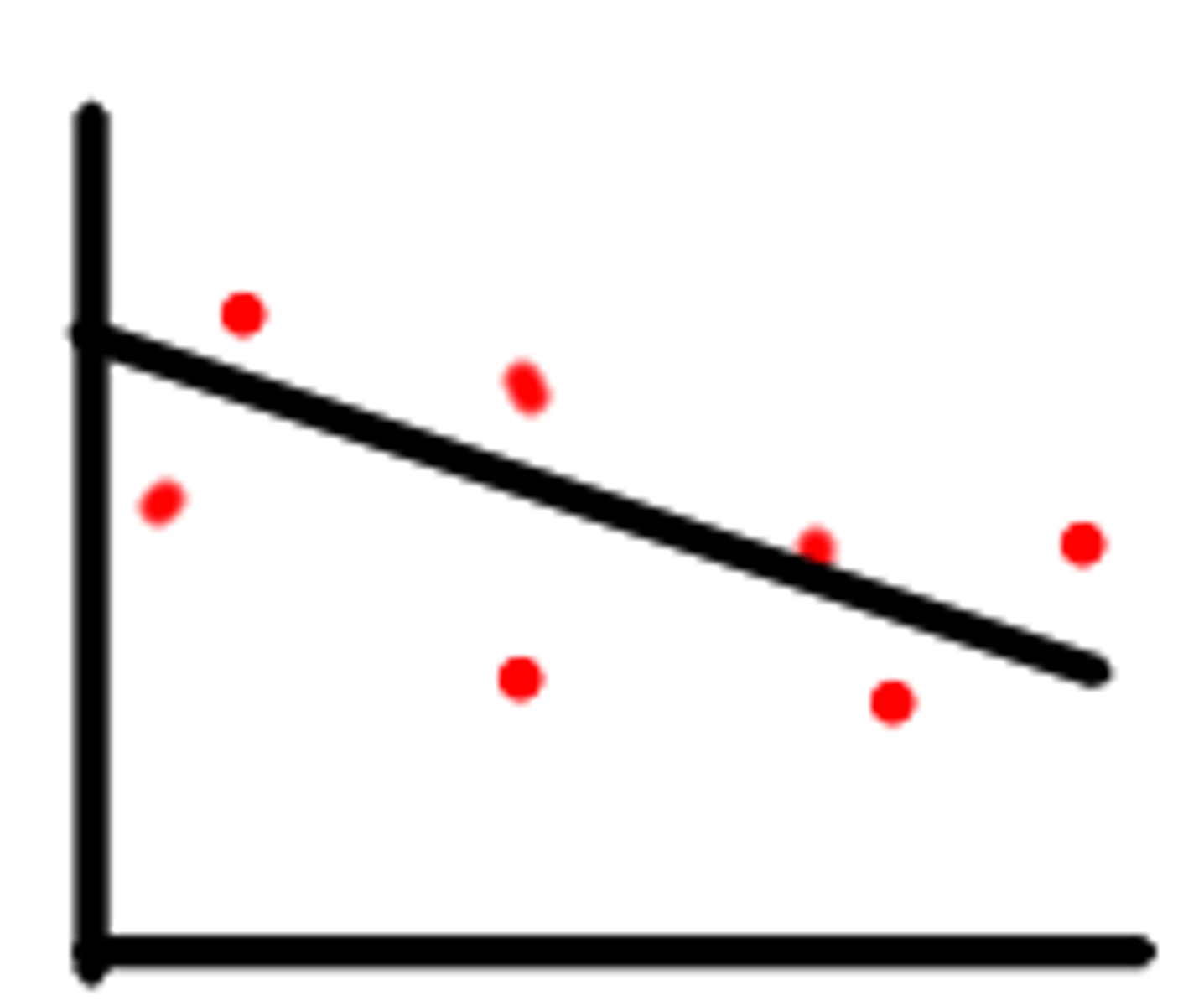
negative correlation
as one variable increases, the other decreases
statistical significance
a statistical statement of how likely it is that an obtained result occurred by chance
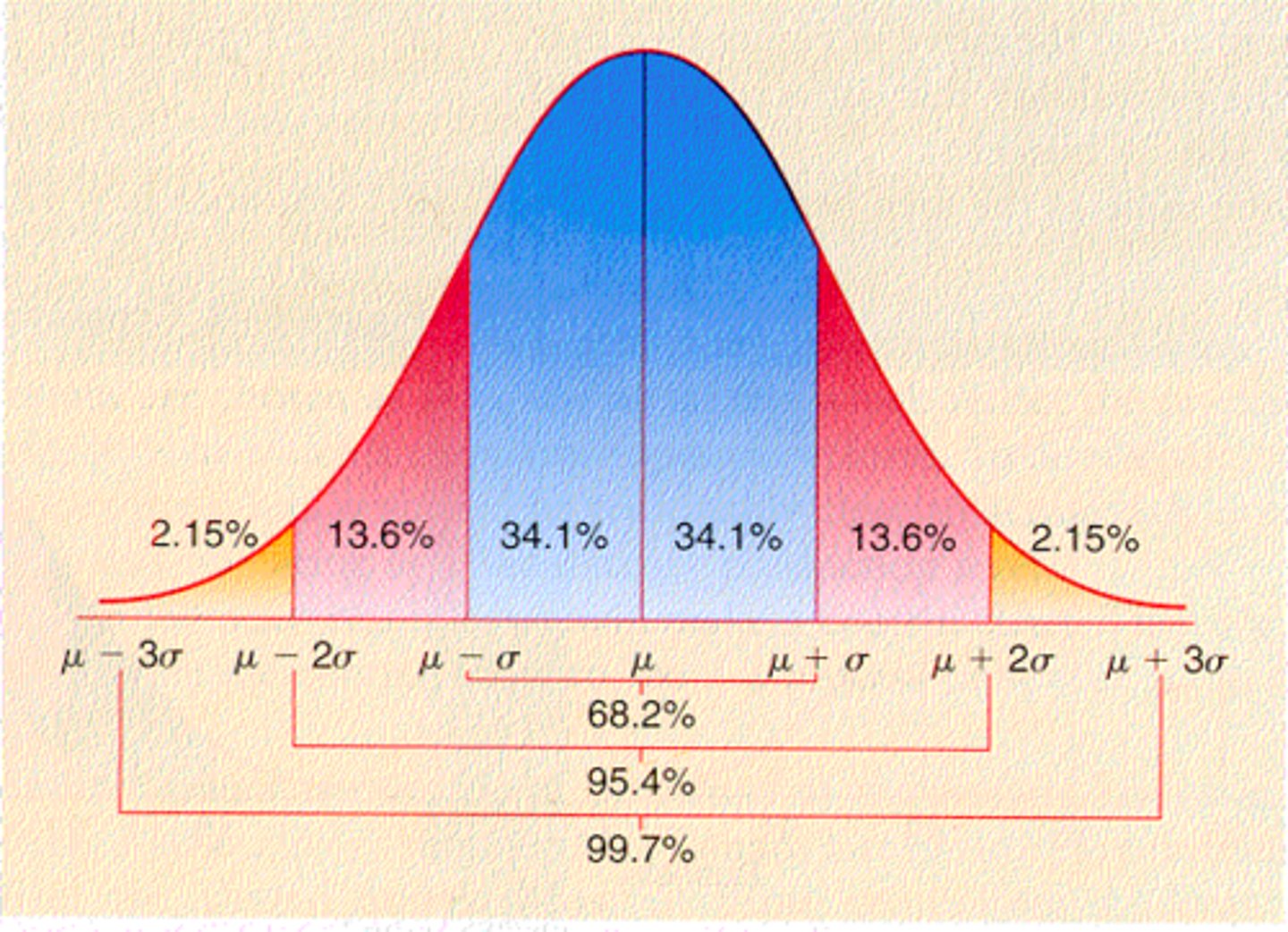
normal distribution
a symmetrical frequency distribution/bell curve where the mode mean and median are at a 0 point value.
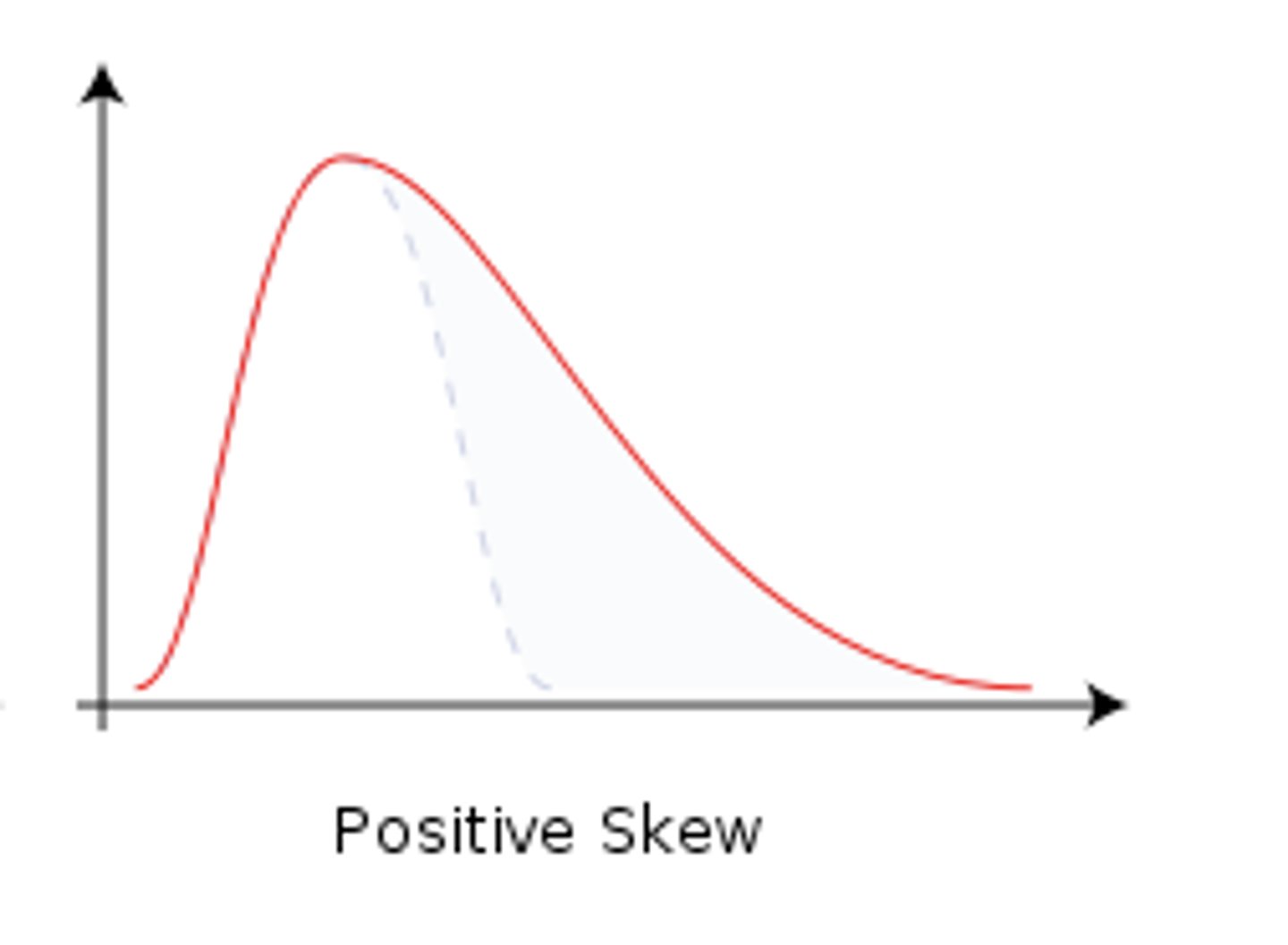
positively skewed distribution
Has a tail extending to the right (towards the larger values).This occurs when the dataset has a few unusual large values.
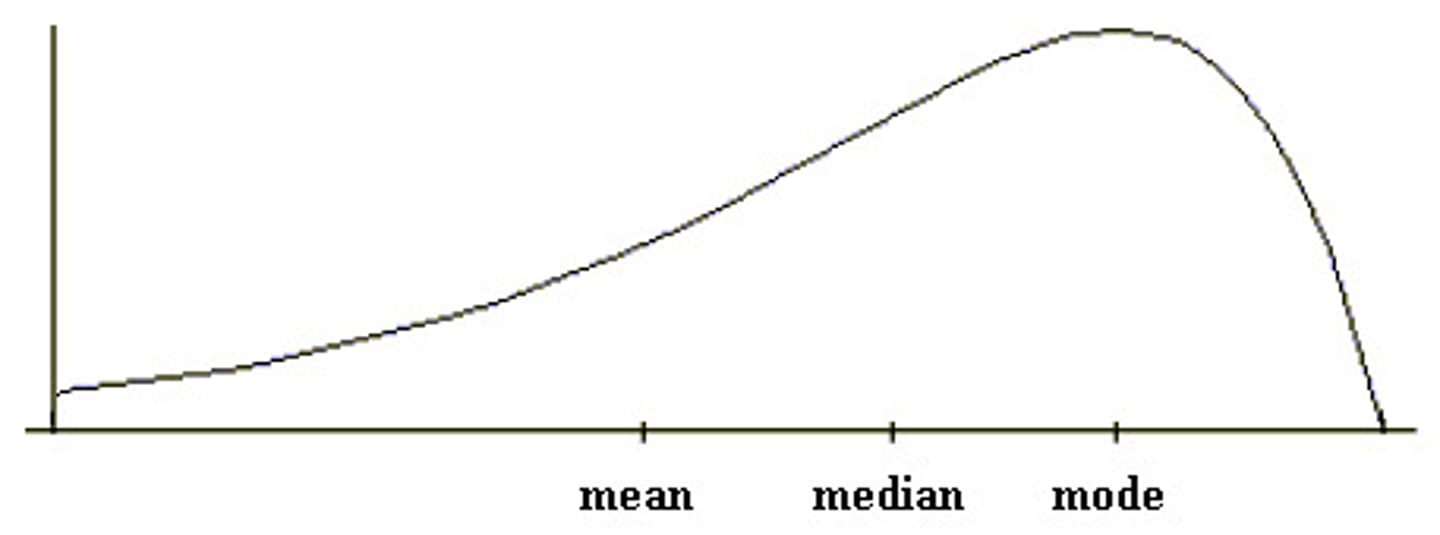
negatively skewed distribution
has a tail pointing to the left (towards the smaller values) This occurs when the dataset has a few unusual small values.
Quantitative data
numerical data
qualitative data
Information describing color, odor, shape, or some other physical characteristic
p-value
The probability level which forms basis for deciding if results are statistically significant (not due to chance).
psychometric
the scientific study of the measurement of human abilities, attitudes, and traits
Chromosomes
threadlike structures made of DNA molecules and proteins that contain the genes located inside the nucleus. Humans have 46 chromosomes (23 pairs in each cell).
Genome
the complete set of genes in a cell or organism that is a blueprint for an organisms design and function.
molecular genetics
the field of biology that studies the molecular structure and function of genes.
behavior genetics
A field of study in psychology that examines the role of genetic and environmental influences on our behavior.
DNA
deoxyribonucleic acid is a molecule that carries most of the genetic instructions used in development functioning and growth.

identical twins (monozygotic twins)
twins who develop from a single fertilized egg that splits in two, creating two genetically identical organisms
heritablity
The proportion of observed differences on a trait among individuals of a population that are due to to genetic differences.
natural selection
A process in which individuals that have certain inherited traits tend to survive and reproduce at higher rates than other individuals because of those traits.
Genes
DNA segments that serve as the key functional units in hereditary transmission.
fraternal/dizgotic twins
twins who develop from separate fertilized eggs. They are genetically no closer than brothers and sisters, but they share a fetal environment.
Mutation
change in a DNA sequence that affects genetic information that may lead to change.
Nature vs. Nurture
name for a controversy in which it is debated whether genetics or environment is responsible for driving behavior
Epigenetics
How are enviroment influences how are genes are expressed and shapes you into the person who you are.
epigenetic marks
Caused by life experiences. chemical modifications to DNA that can turn genes on or off
Charles Darwin
English natural scientist who formulated a theory of evolution by natural selection
gene expression
genes that is turned on or off in response to environmental factors which can influence personality.
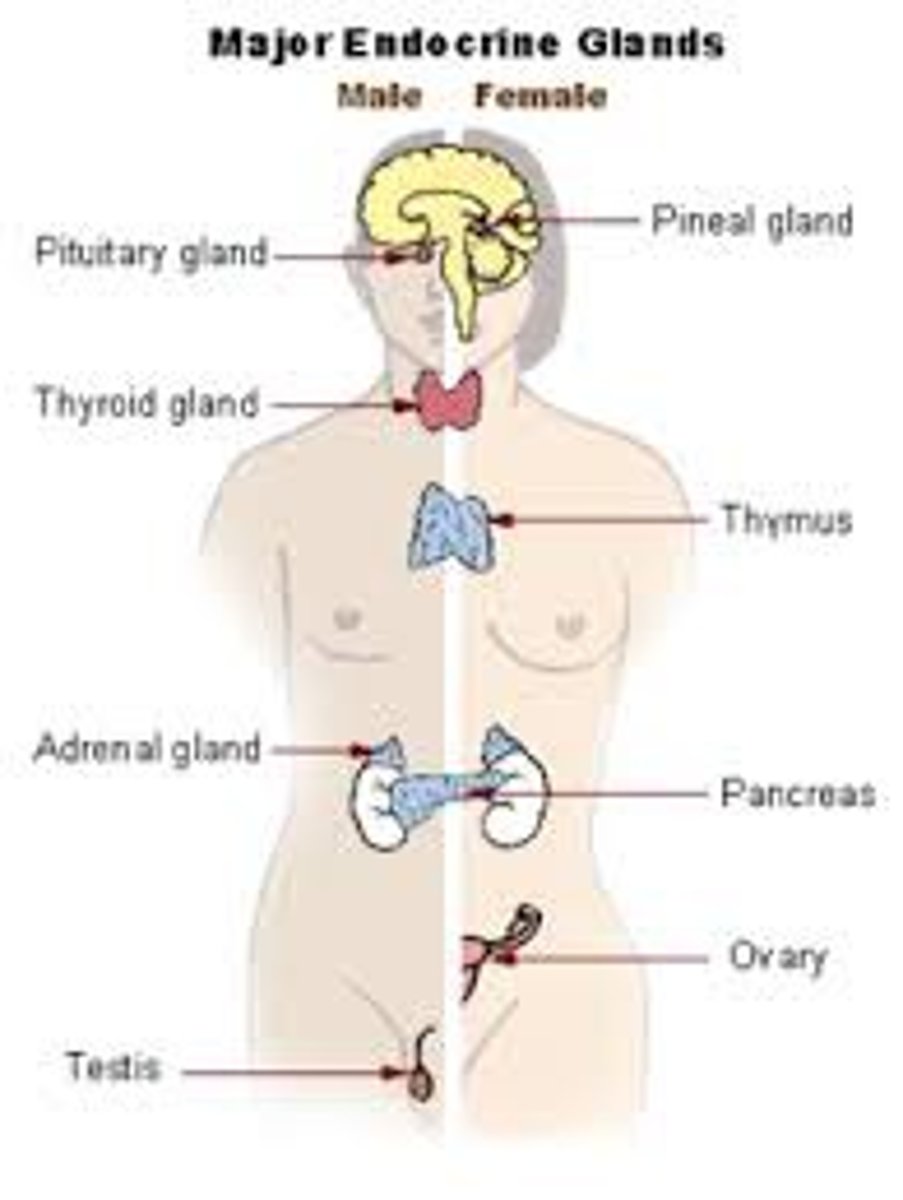
endocrine system
Our body's chemical communication system. It is a network of glands in the body that produce hormones to regulate bodily functions.
Hormones
chemical messengers that are manufactured by the endocrine glands, travel through the bloodstream that control and regulate the activity of certain cells and organs.
adrenal glands
a pair of endocrine glands that sit just above the kidneys and secrete hormones that help arouse the body in times of stress. trigger our flight or fight responses and release adreniline and norepinphrine.
pineal gland
Produces melatonin and regulates circadian rhythm.
pituitary gland
Important gland that is small pea-sized known as the master gland that controls growth and produceshormones such as oxytocin, which promotes pair bonding and social trust.
Hypothalamus
Important gland located in limic system that controls the pituitary gland. and communicates with adrenal gland. It releases and has a lot to do with the "4 Fs:" Fighting, Fleeing, Feeding, Mating.
thyroid gland
Located in neck.produces hormones that regulate metabolism, body heat, and bone growth
parathyroids
Located in neck. help regulate the level of calcium in the blood
Pancreas
Organ in stomach that regulates blood sugar and releases insulin and helps digestion.
Testies and ovaries
male/female reproductive organs that release sex hormones. Ovaries produce estrogen and testies produce testosterone.