Exam 1 (Surgery & Anesthesia)
1/240
Earn XP
Description and Tags
By Quizlet user ihateinfluenza
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
241 Terms
Cattle are sensitive to the effects of Xylazine and should be administered 1/10th of the dose _______________ receive.
Horses
Which two species are more sensitive to the effect of opioids?
Horses & Cats
Which species has a rougher recovery period after going under anesthesia?
Horses
What drugs can influence the effect of anesthetic agents?
Sympathomimetics (epi), tricyclic antidepressants (amtriptyline), MOA inhibitors (selegiline), & antihistamines
Dogs can have a behavior change after ____________________ administration
Acepromazine
Tenesmus
painful, ineffective defecation. AKA straining
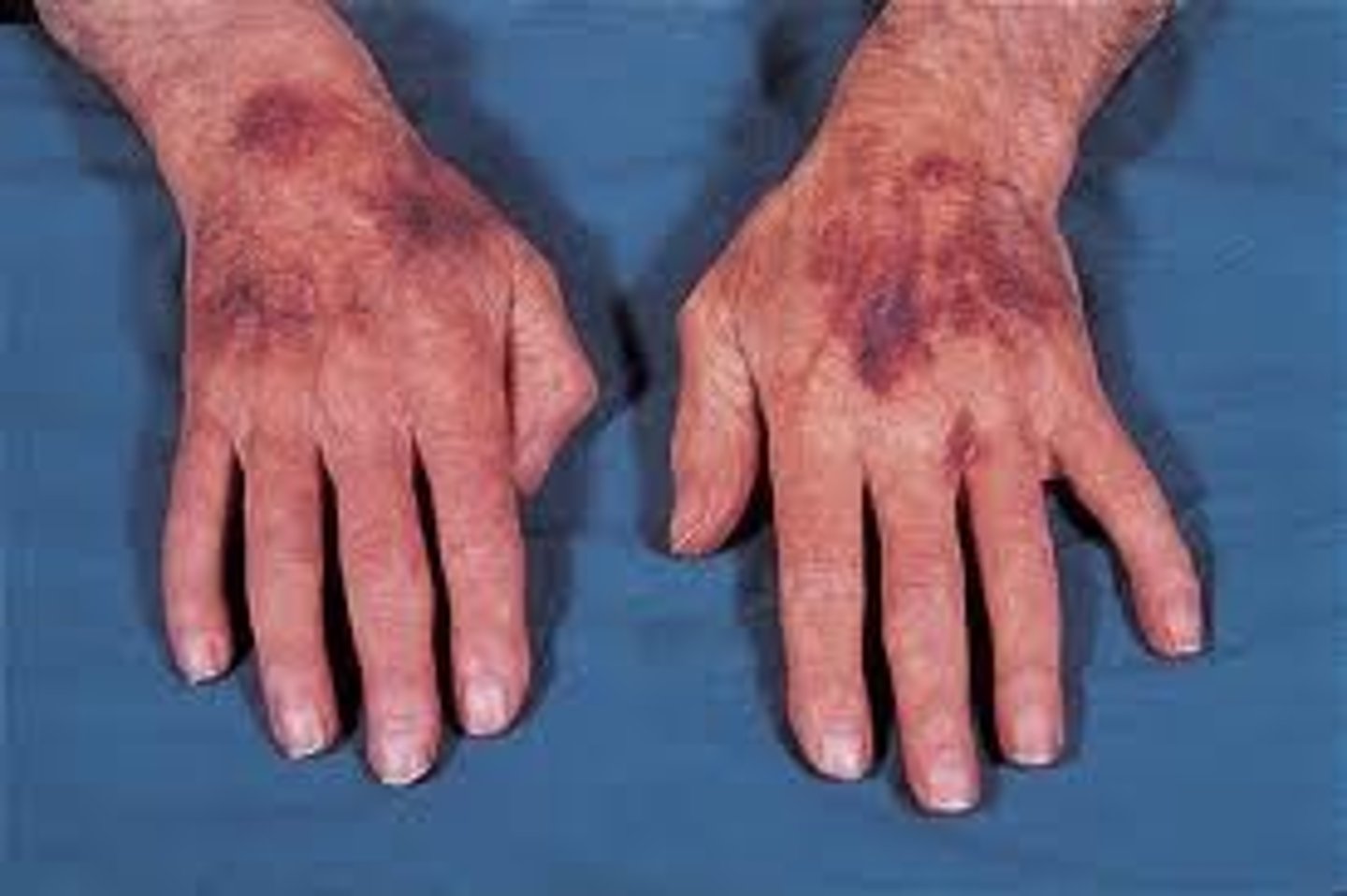
Purpura
the appearance of multiple purple discolorations on the skin caused by bleeding underneath the skin
cachexia
loss of weight and generalized wasting that occurs during a chronic disease
Box lock
This part is only on instruments that have ring handles. The box lock is the joint/hinge that absorbs the greatest amount of stress
The jaws and tips of instruments can be either:
traumatic or atraumatic
Shank/Shaft
This is the longest portion of the instrument- acts as the "body"
Ratchet
Interlocking teeth that locks the jaw into a closed position. Only found on instruments with ring handles
What are the four types of forceps?
Thumb, hemostatic, bandage, & tissue
Scissors are described as:
sharp/sharp (s/s), blunt/blunt (b/b), or sharp/blunt (s/b)
Mayo dissecting scissors
For cutting thicker, non fragile tissue (muscle, cartilage, etc). Used for the linea alba in spay surgeries. Blades can be straight or curved- commonly used in large and small animal
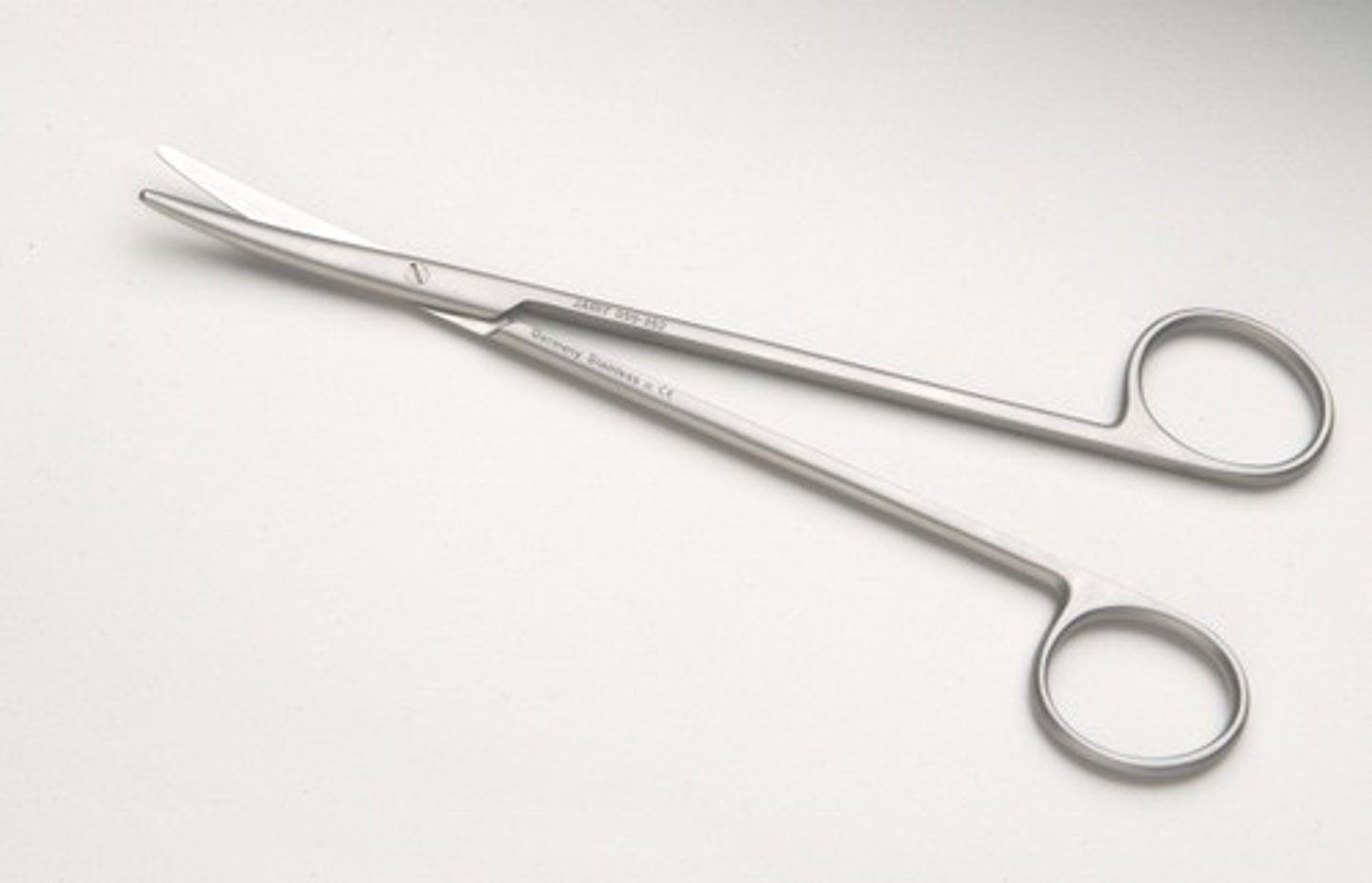
Metzenbaum scissors
Fine blades with blunt or pointed tips only used to cut soft delicate tissues that may not be as dense or fibrous. Longer handles in relation to the size of the blade. Not for cutting tough fascia/sutures- the blades are easily dulled
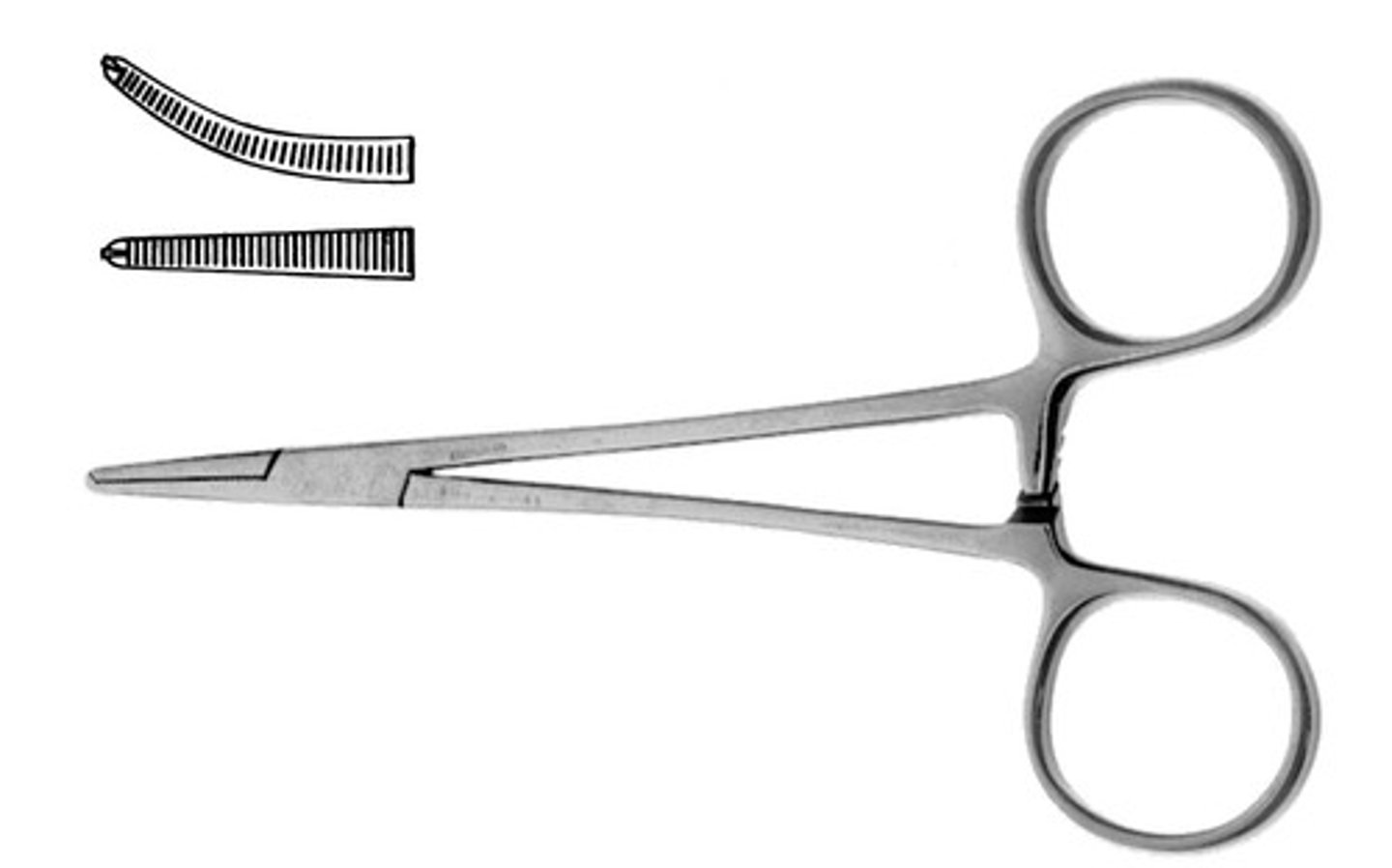
Hemostatic forceps
Surgical instruments used to control flow of blood/aid hemostasis. Jaws can be straight or curved and can have serrations that can both give grip and crush. This instrument has a ratchet/lock box
Halstead Mosquito Hemostatic Forceps
These hemostats have a small jaw with fine horizontal serrations that extend the entire length of the jaw. The jaw can be either curved or straight. This instrument is used to clamp small blood vessels
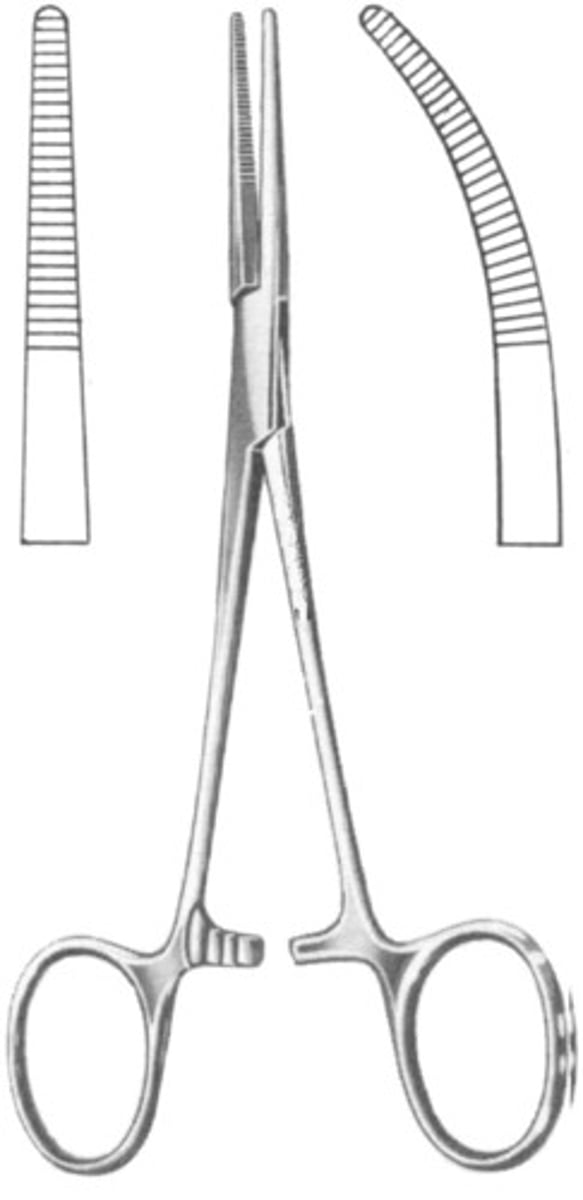
Crile hemostatic forceps
This instrument has horizontal teeth that run the entire length of the jaws. Used to occlude uterine horn vessels or small to medium sized blood vessels
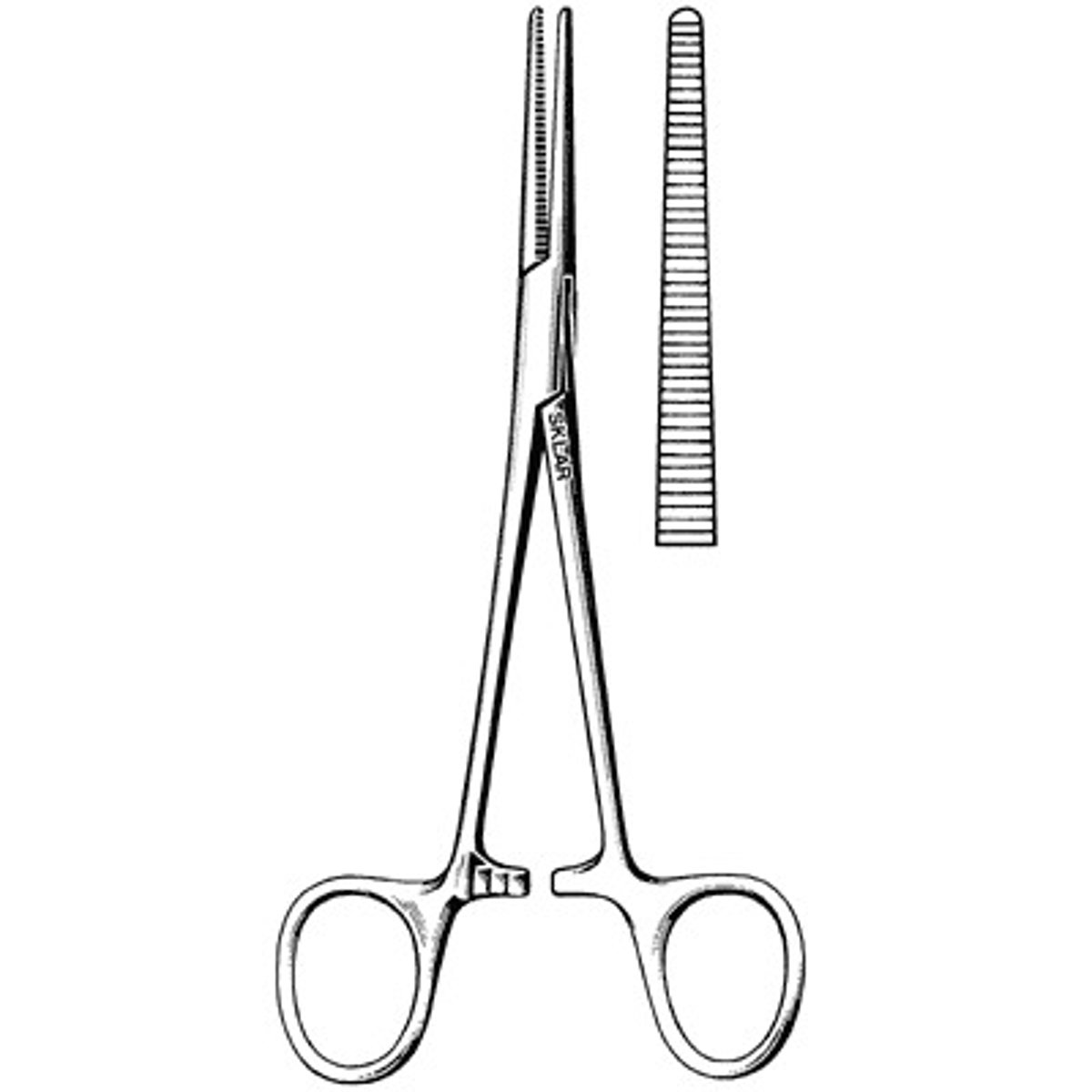
Kelly hemostatic forceps
Instrument used to occlude small to medium sized blood vessels. Serrations are on the distal half of the jaws and the proximal half (the half closest to the hinge) is smooth. The smooth area is used to clamp tubing without the risk of cutting it
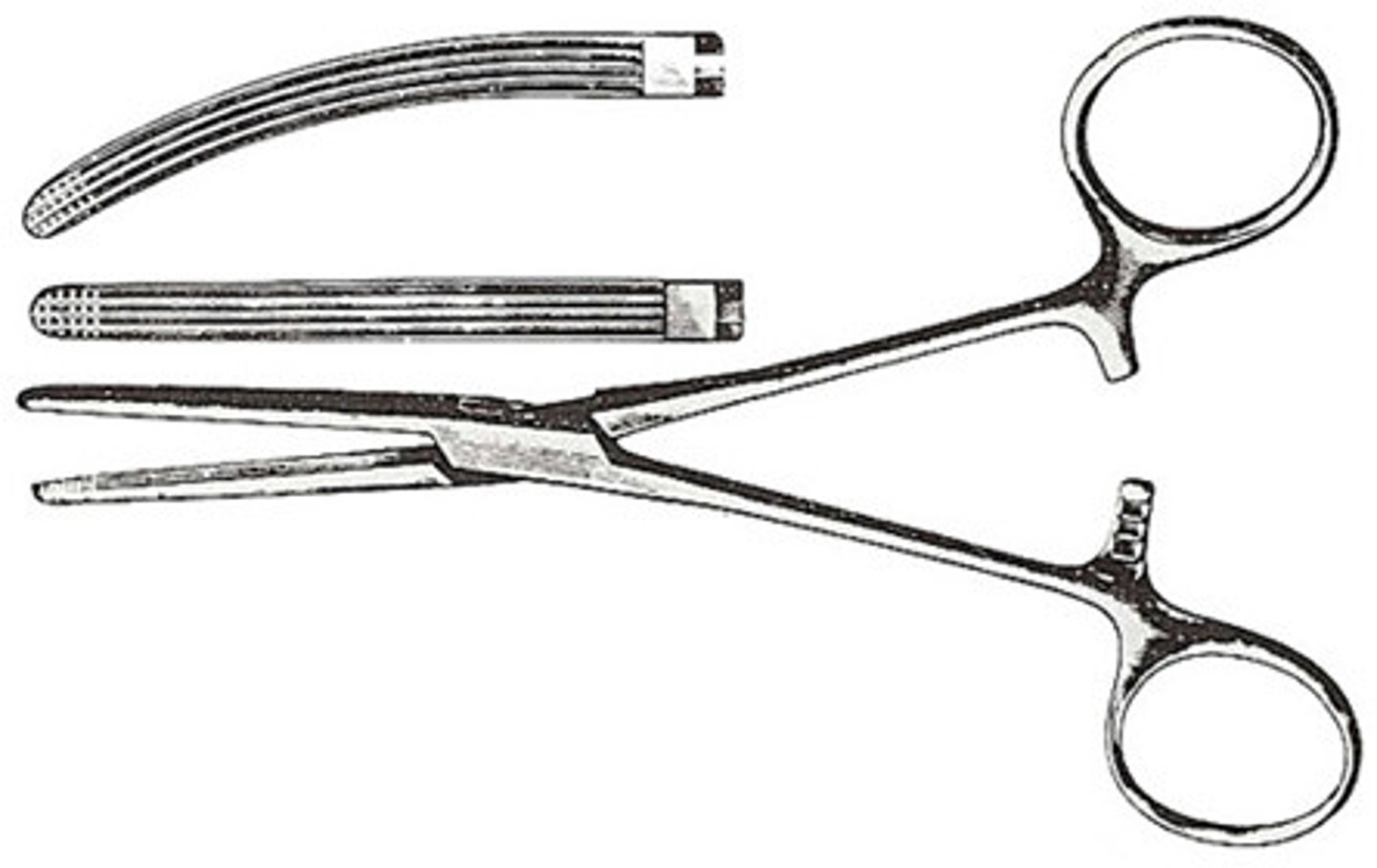
Rochester-Carmalt Hemostatic Forceps
This instrument is large (usually around 8 inches) and has both vertical and horizontal serrations/ Used to clamp larger vessels or large tissue masses
Olsen-Hegar Needle Holder
A needle holder that has scissors built into the jaw. This instrument is designed with the intent of holding metal and should only be used to attach scalpel blades onto handles or hold needles.
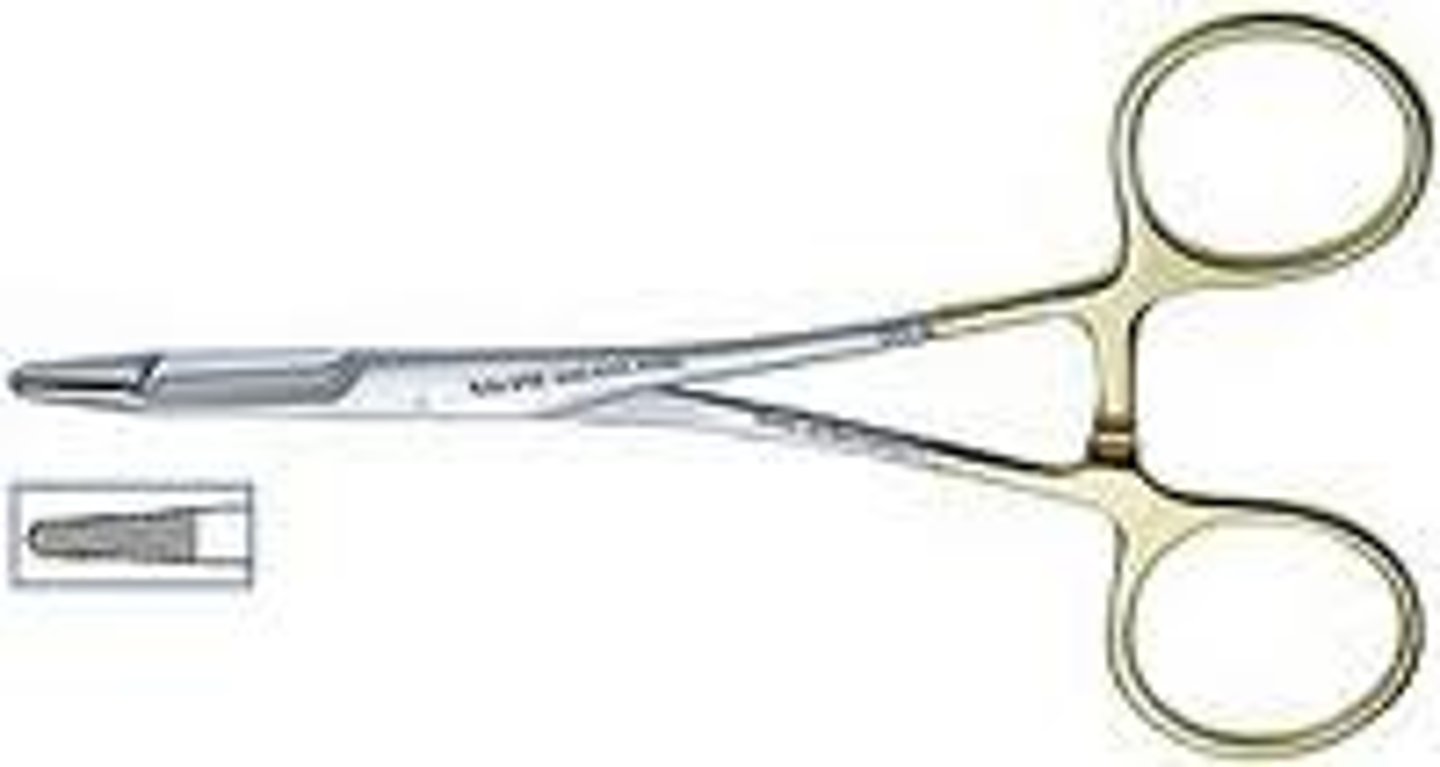

Mayo-Hegar Needle Holder
This instrument is available in a variety of sizes. These needle holders do not have scissors built in.
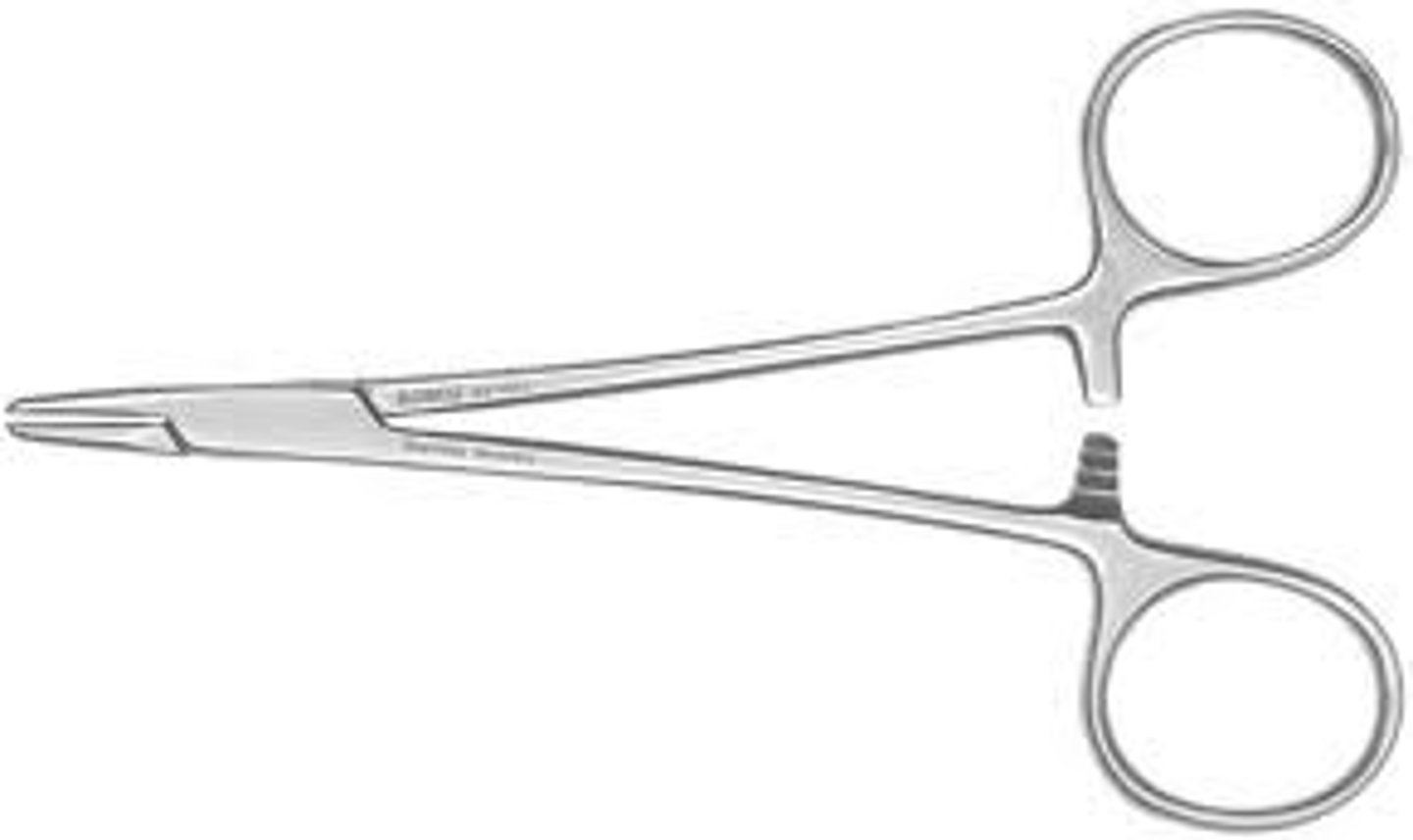

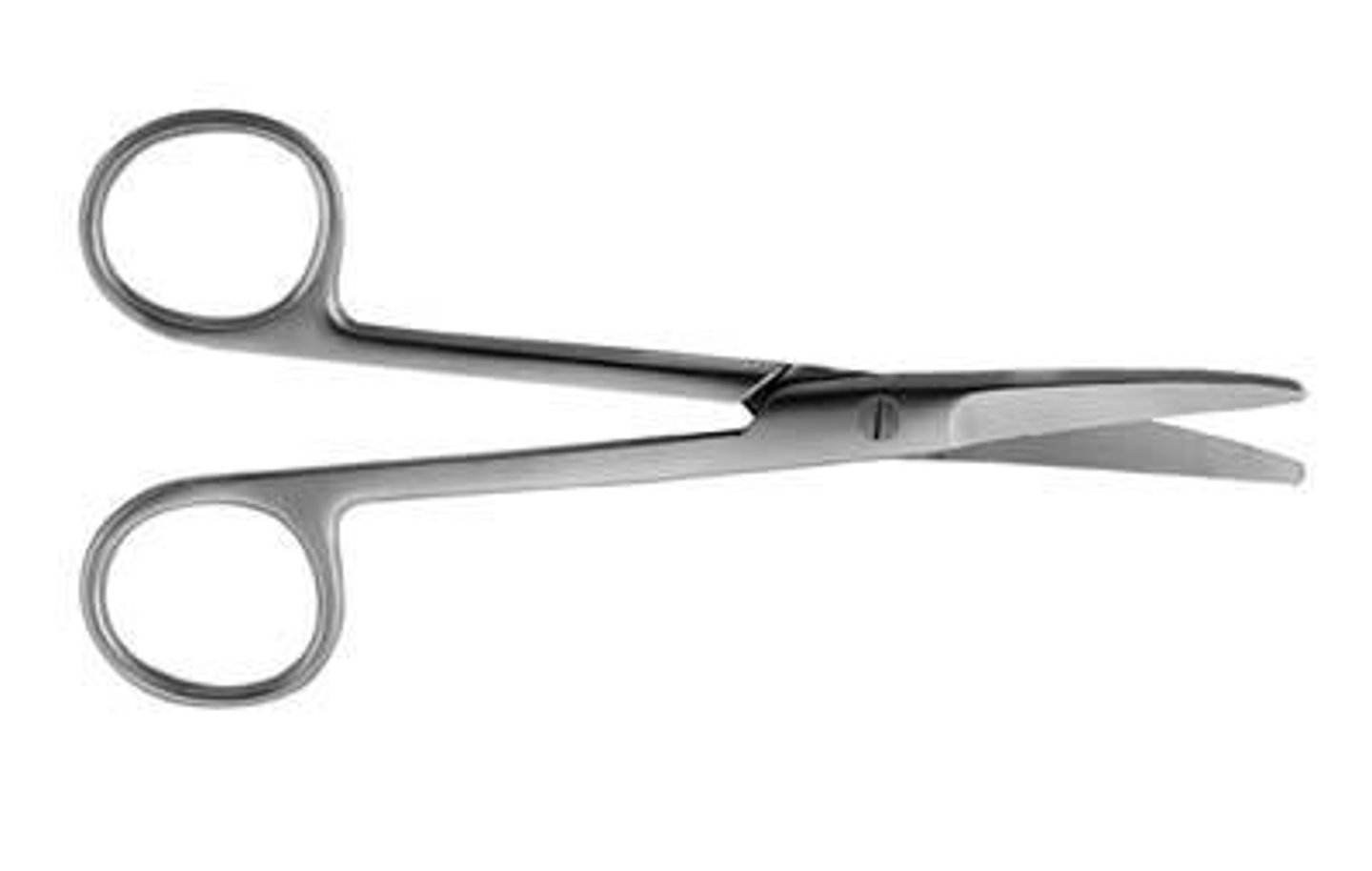
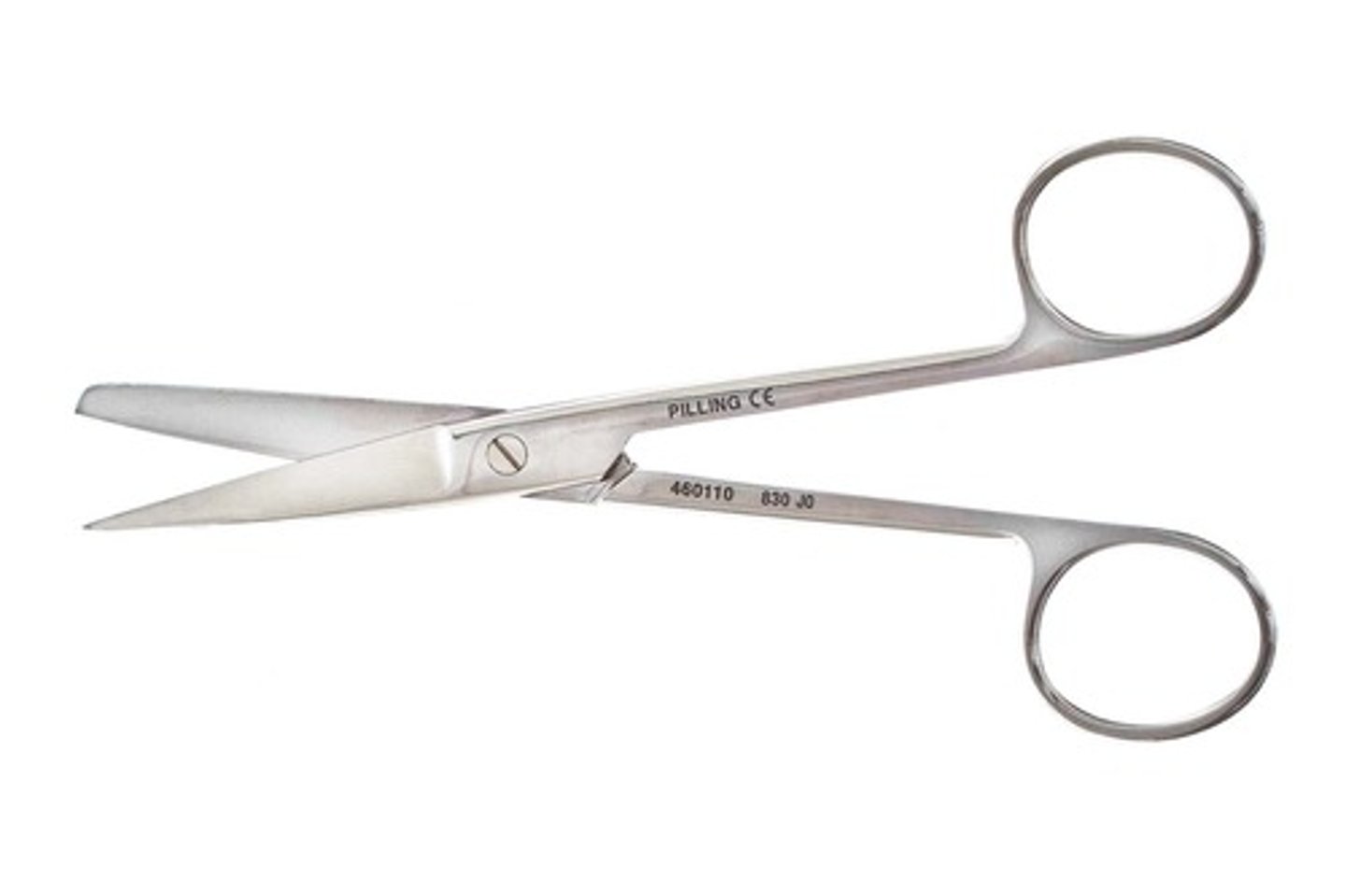
Operating scissors
This instrument can be straight or curved with sharp or blunt blades. The intended use is to cut inanimate objects (sutures, paper drapes, and sponges).
What are the types of Adson tissue forceps?
Adson dressing, Adson-Brown, & Adson 1x2
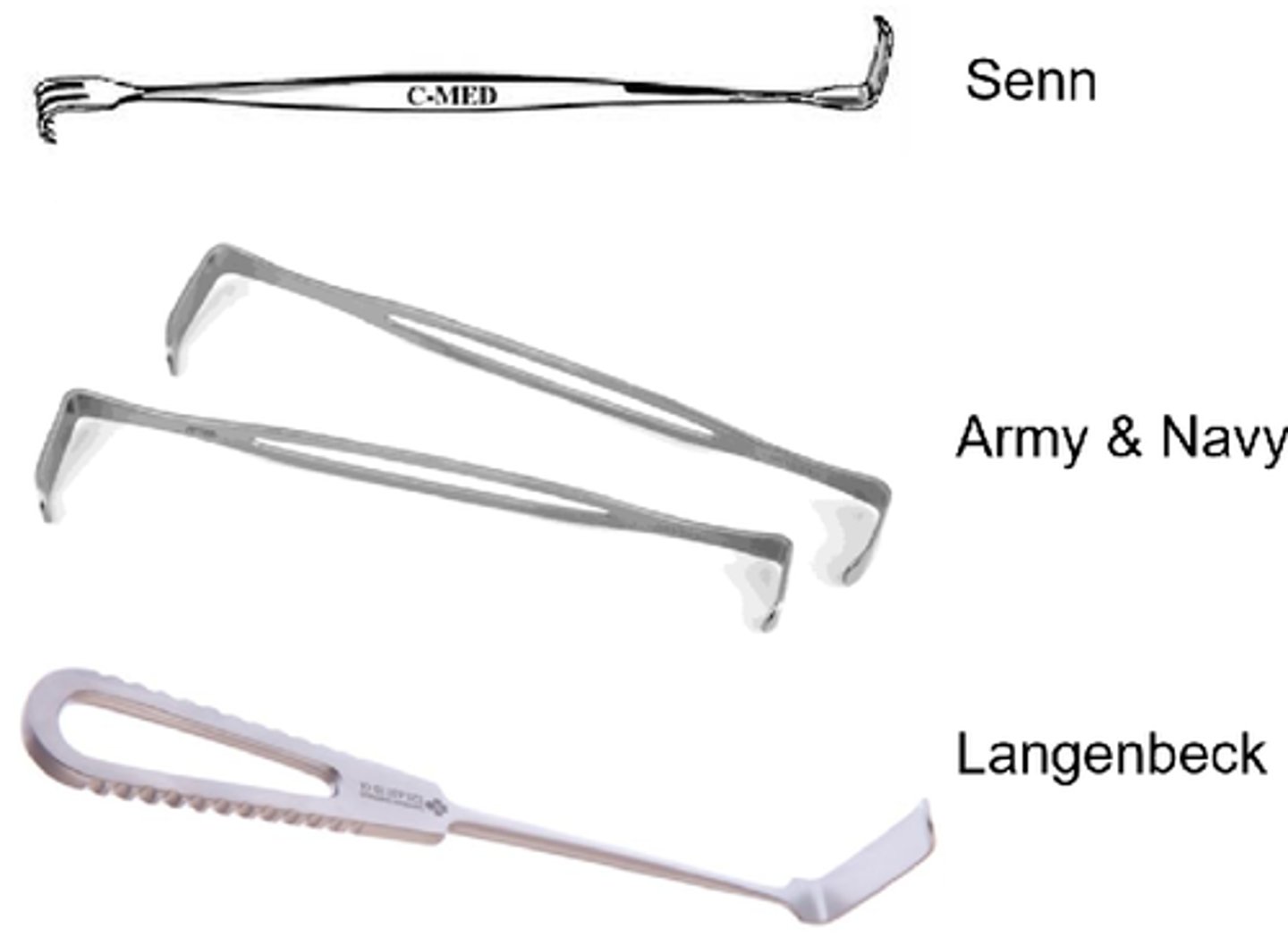
Handheld retractors
U.S Army & Senn
Gelpi Self-Retaining Retractor
This retractor has single, sharp pointed tips and is considered fairly traumatic. Limited use in soft tissue surgery- more common in orthopedic and neuro surgery
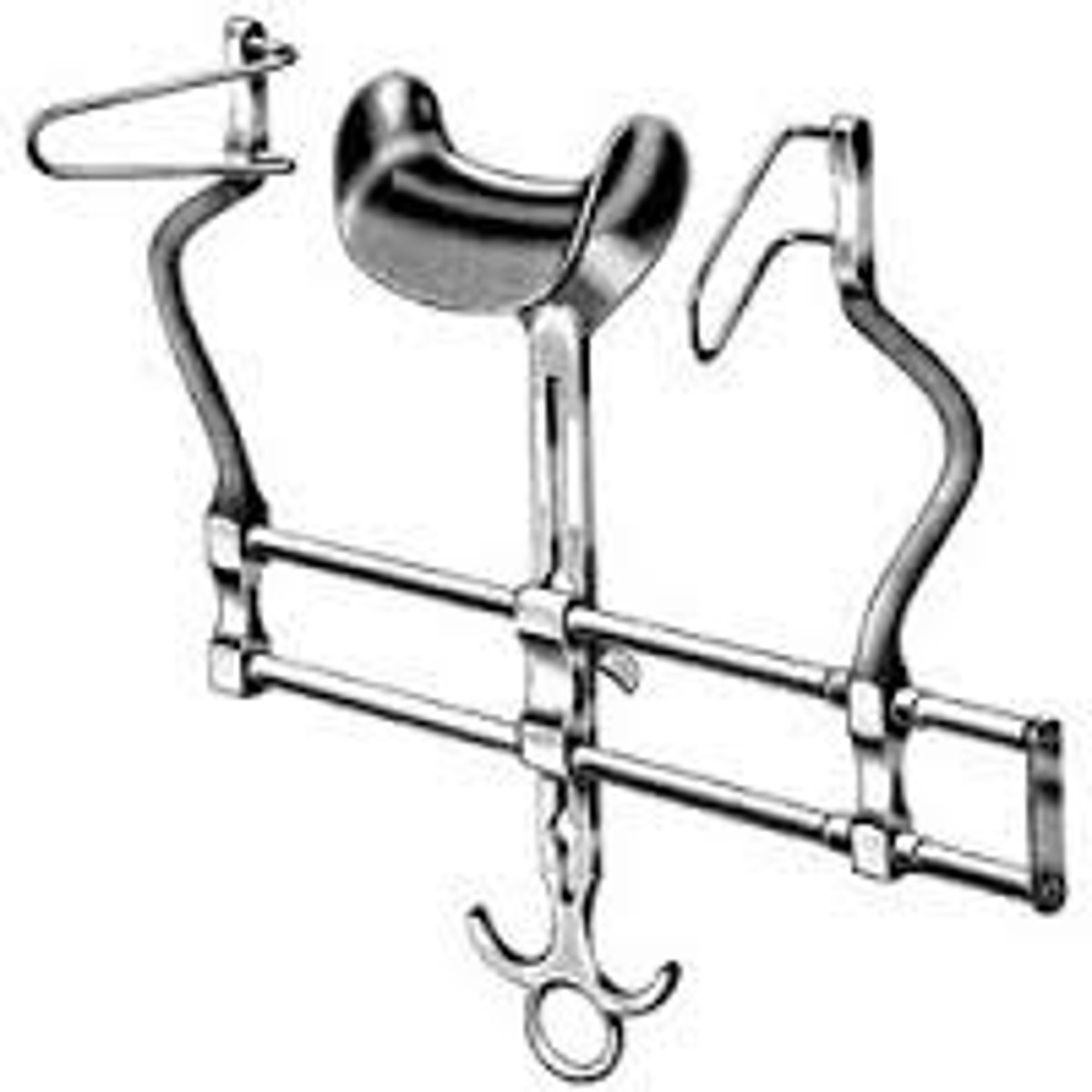
Balfour retractor
This instrument is a self-retaining retractor that has three blades and provides greater visualization of the abdominal cavity

Backhaus Towel Clamps
The most common style of towel clamp- this instrument has penetrating tips and comes in 3.5 inch or 5.5 inch sizes
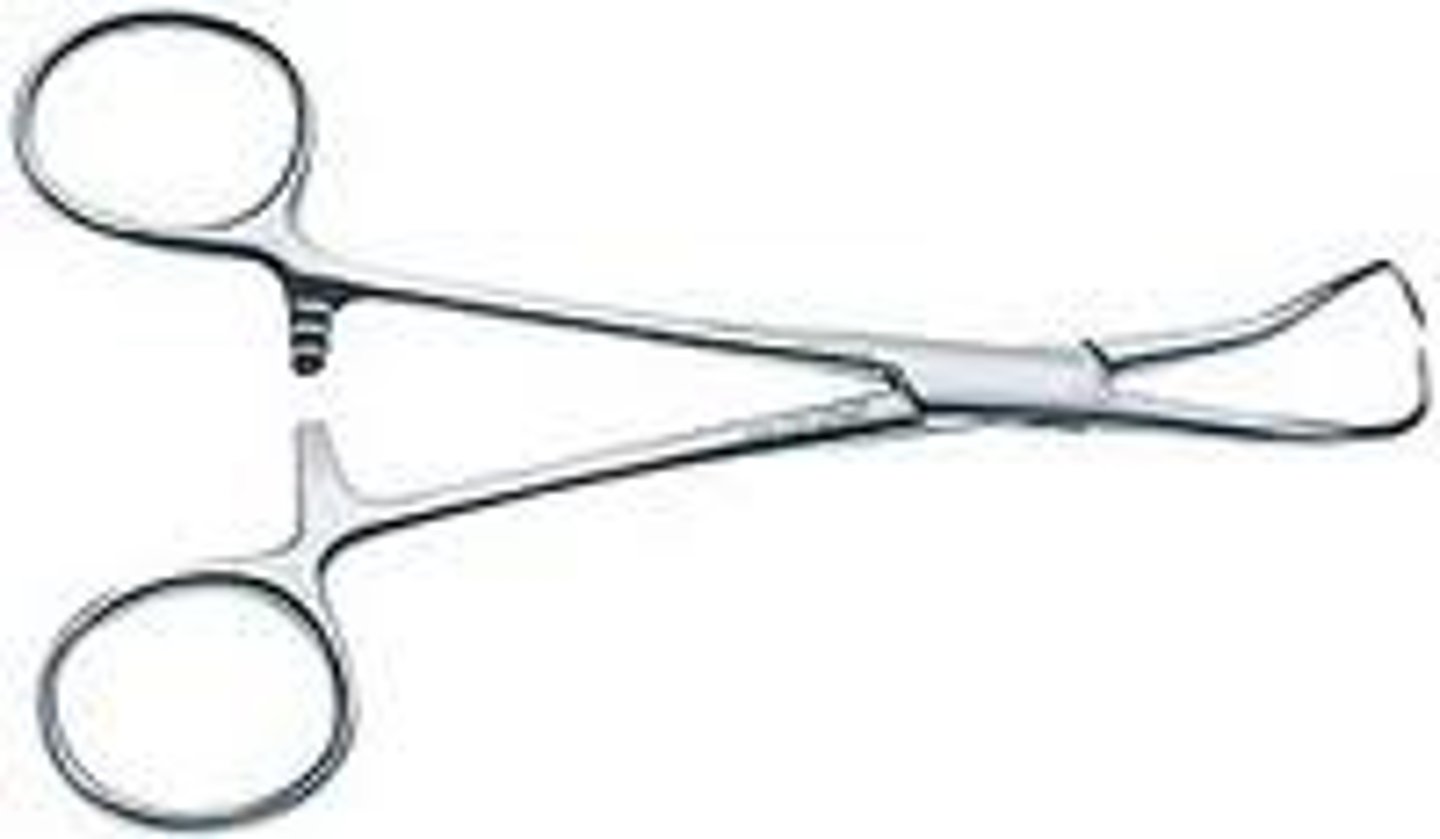
The rachet on a surgical instrument is responsible for:
Clamping the instrument closed
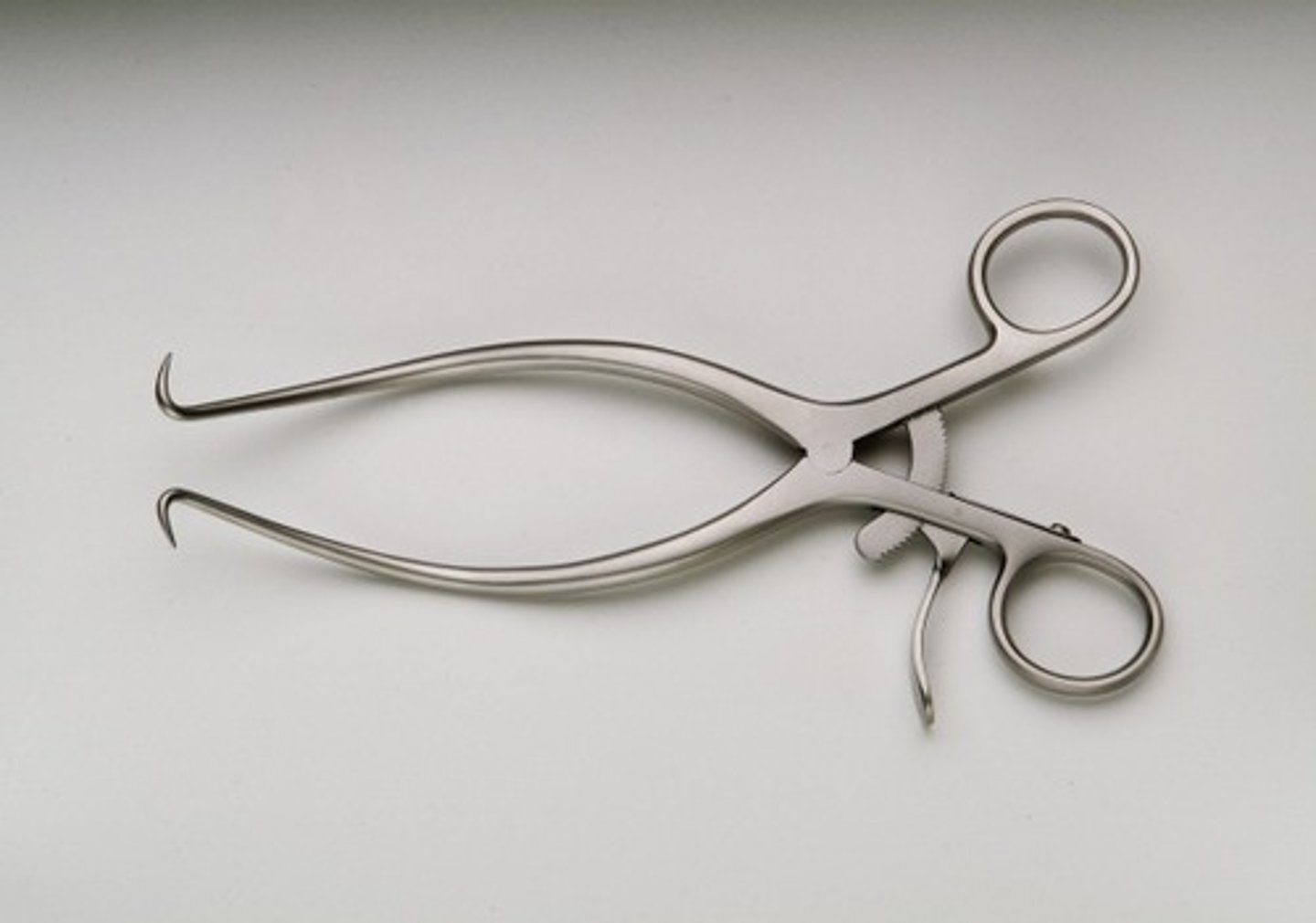
Snook Spay Hook
Instrument designed to retrieve the uterine horn from the body during spays. Available in smaller or larger sizes.
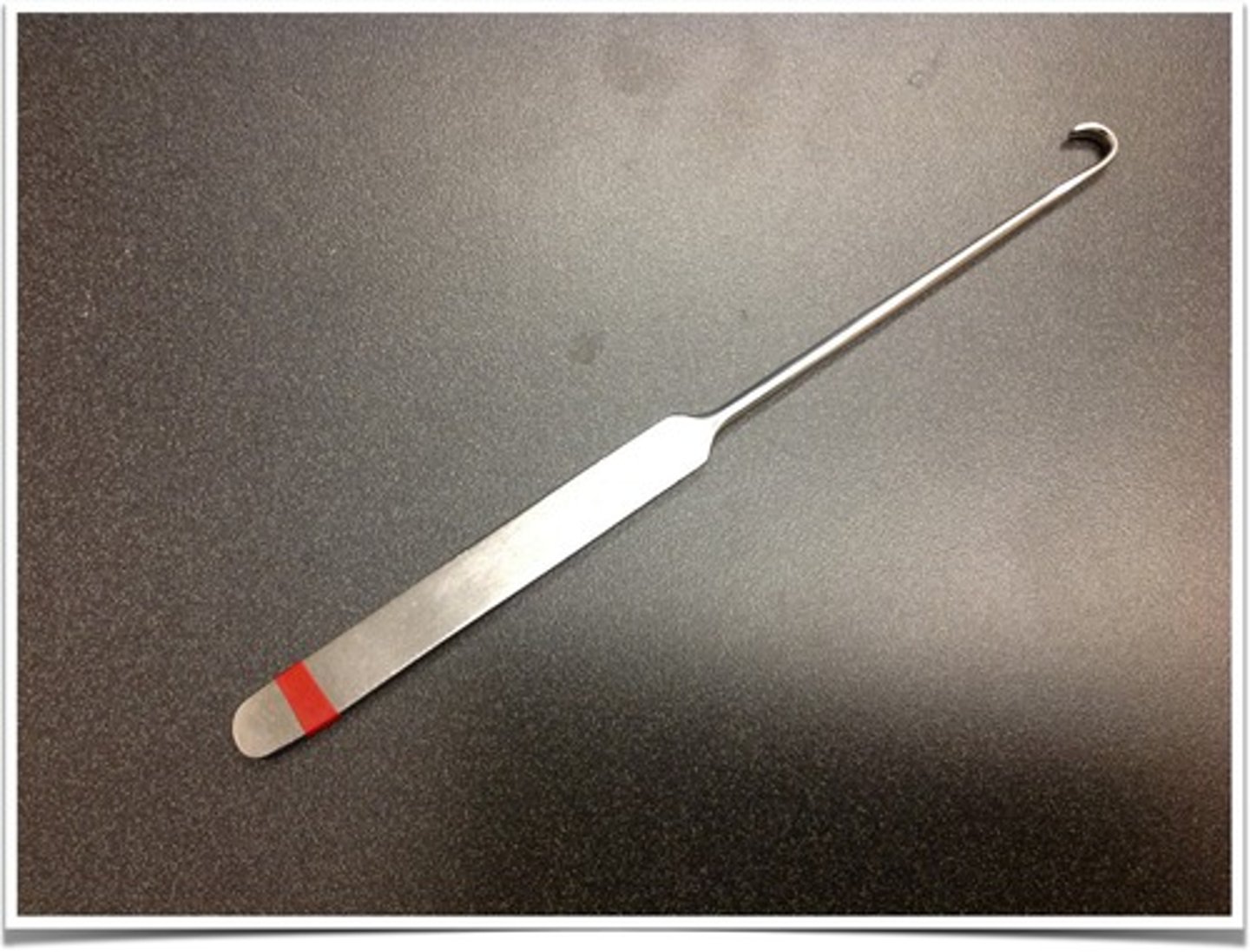
Allis Tissue Forceps
This instrument is neither a hemostat or a thumb tissue forecep- it's designed to grasp tissue in a traumatic way- teeth can be either 3x4 or 4x5 style. This instrument is used to grasp tougher tissues or tissues being removed from the patient (ex: tumor, skin).
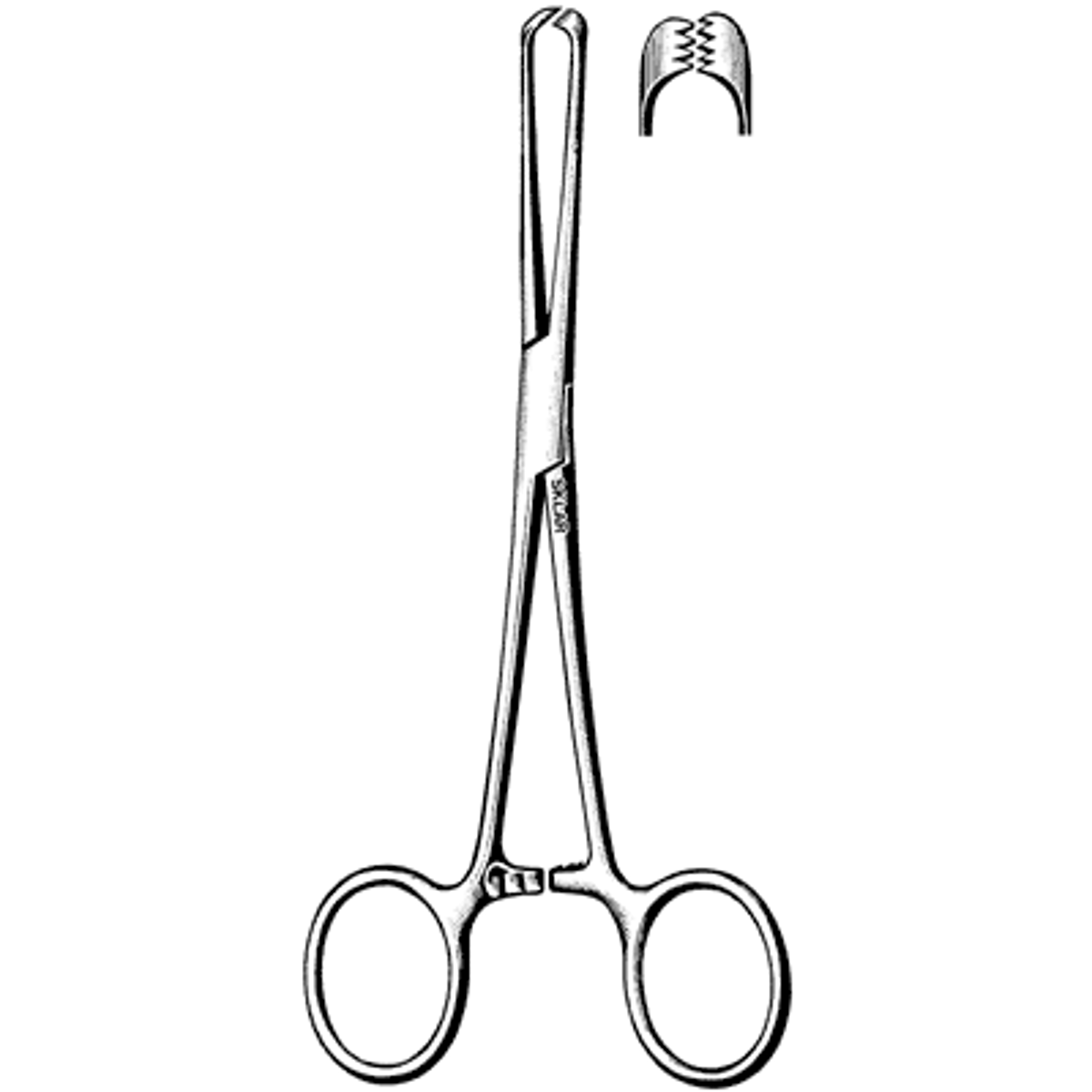
U.S. Army Handheld Retractor
Double-ended retractor with different lengths of blades on either end, with no teeth. Causes minimal tissue trauma other than pressure damage if used roughly
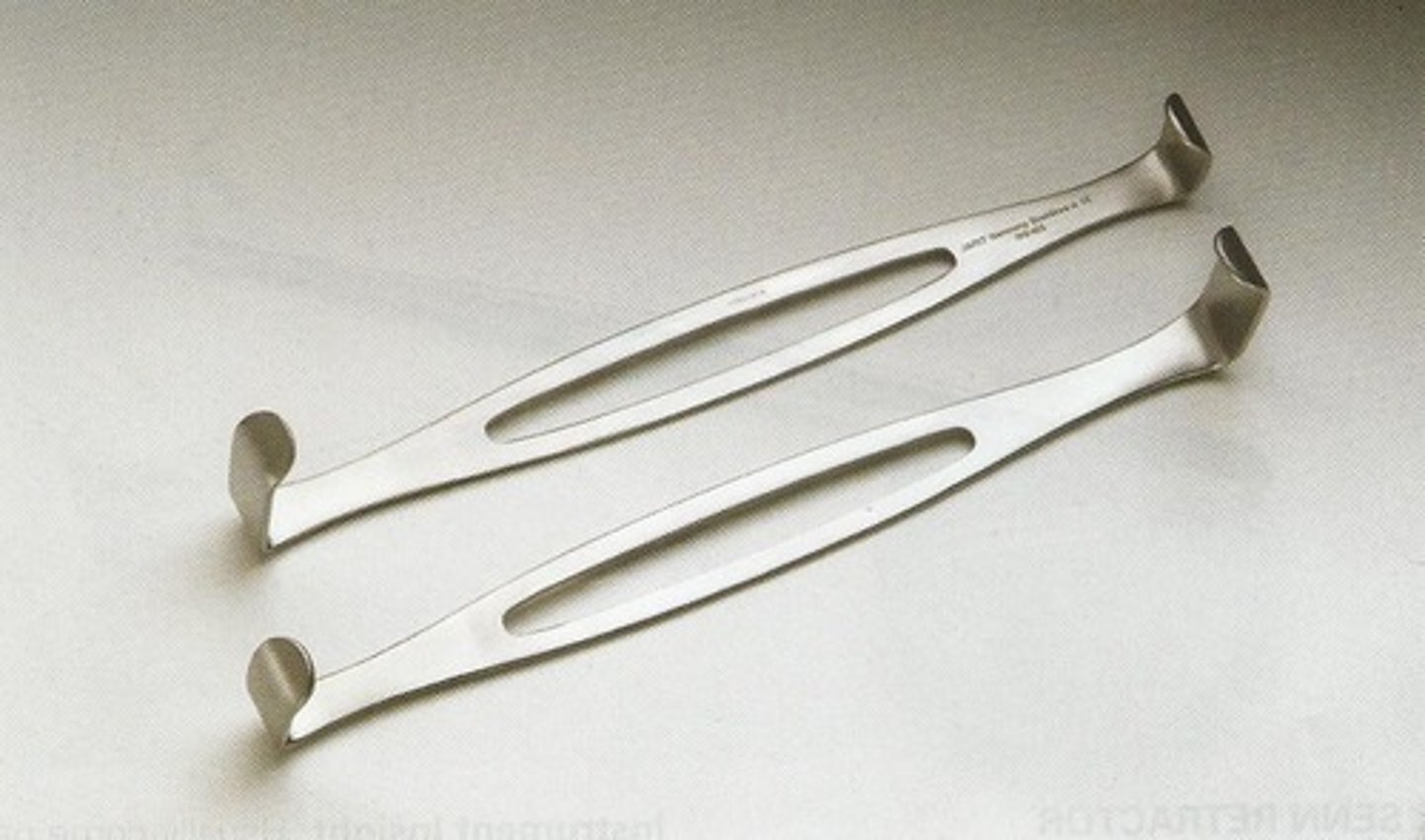

Weitlaner Self-Retaining Retractor
This instrument is used for retracting tissues to gain access to deeper tissues or structures. It can have blunt or sharp teeth.
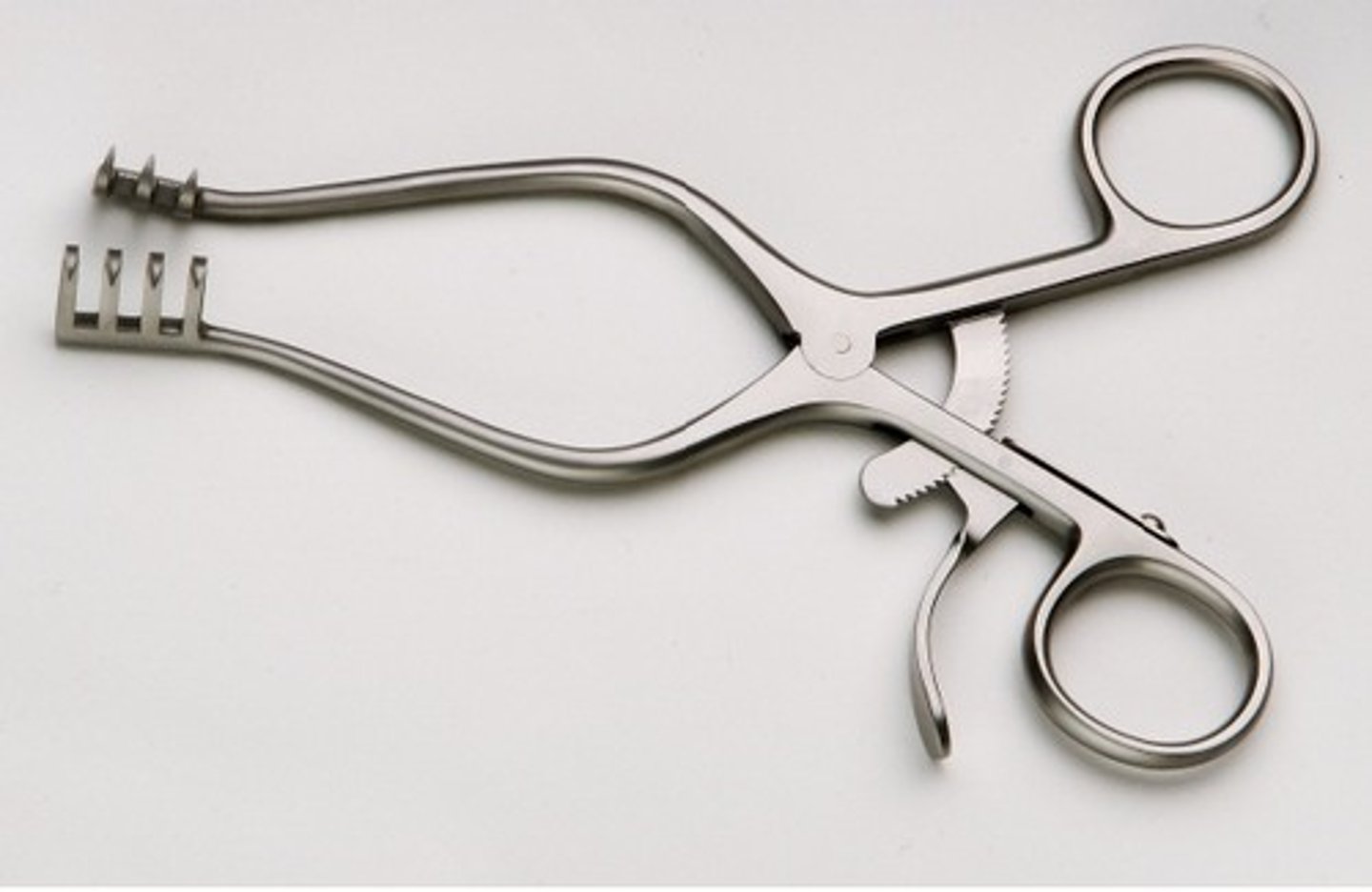
Finochietto Retractor
Retractor of choice for thoracic surgery. This instrument is designed to retract the thoracic wall and has adjustable blades
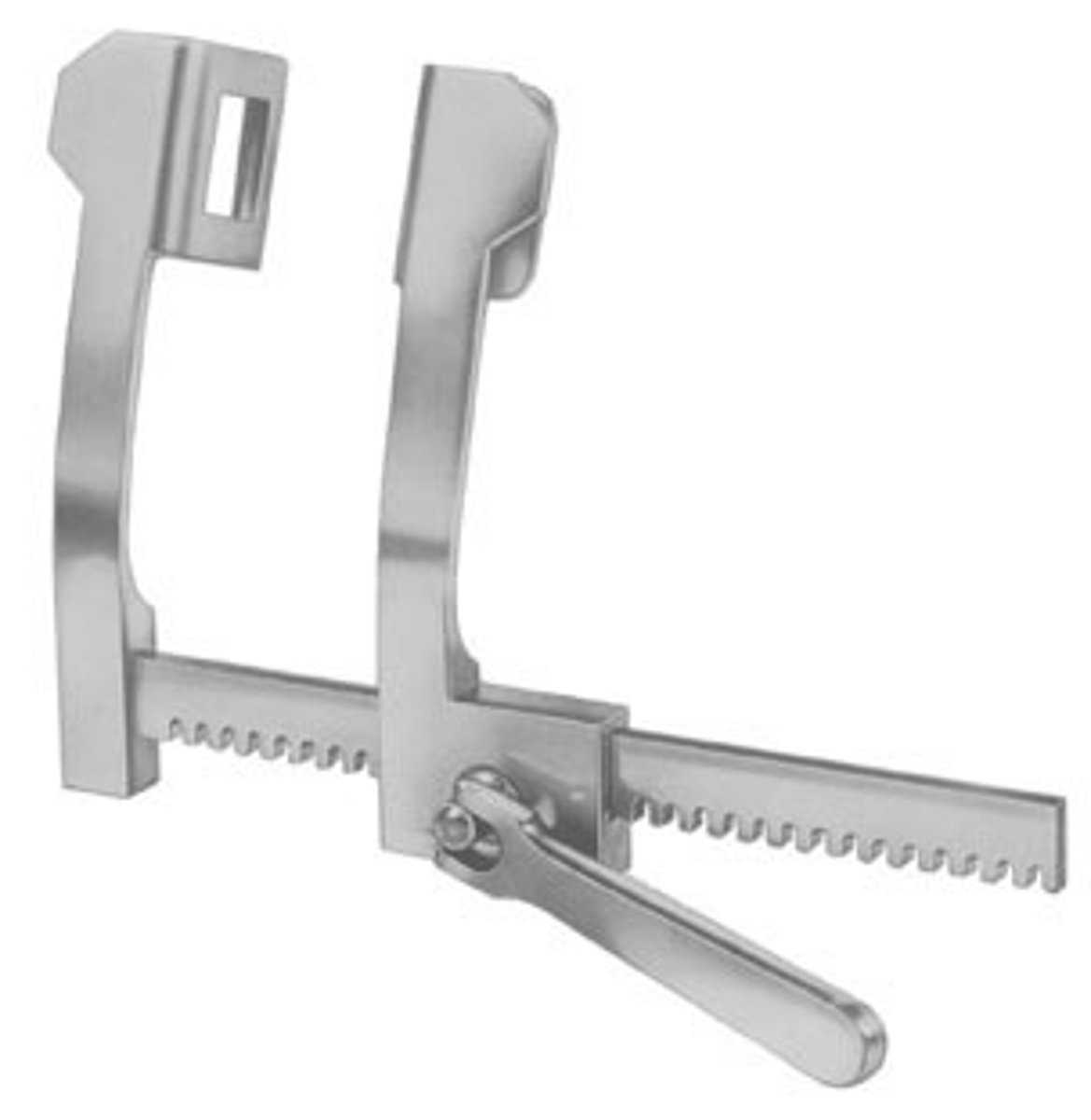

Bone Roungers
This instrument has a cupped tip with sharp edges. Used to break up bits and pieces of bone for grafting purposes & to remove pieces of unnecessary bone
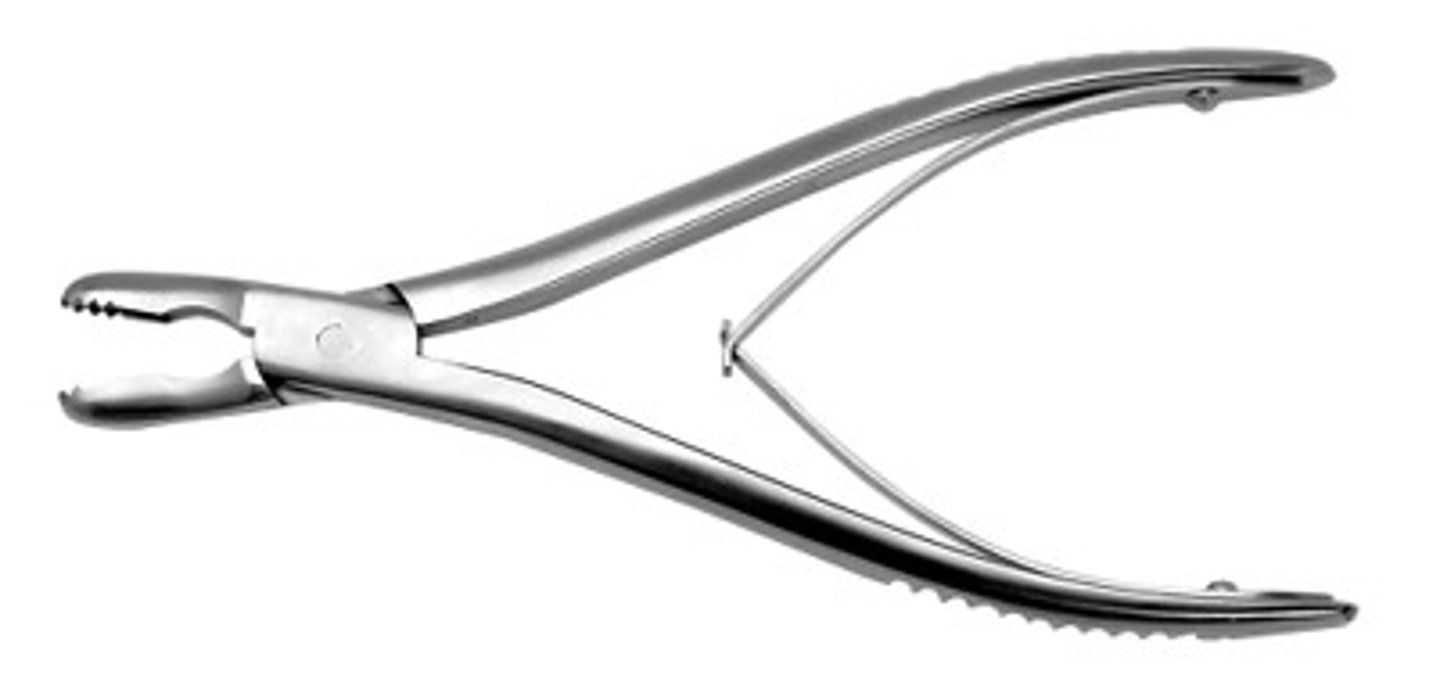

Bone Curettes
Single handed surgical instrument that has a cupped tip with sharp edges. Used to harvest bone graft material or to shape/scrape bony surfaces
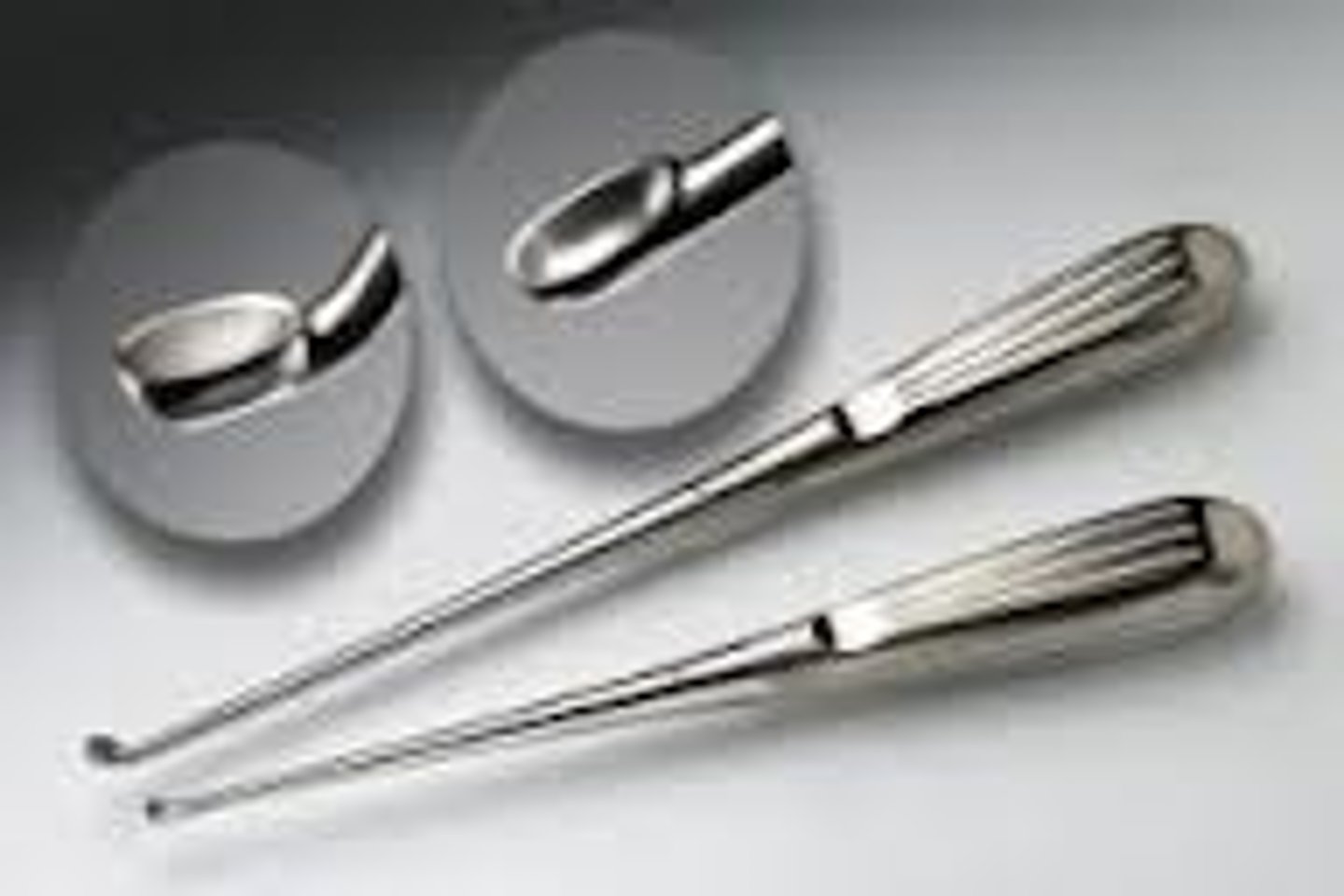

Lacrimal cannulas
Straight or curved- used to flush lacrimal ducts. One end is adapted to accept a syringe and the other end is bumb/blunt shaped

Patients less than 3kg require a ______________ circut and patients weighing more than 3kg require a ______________ circut
Non-rebreathing, rebreathing
Why do drugs used in neonates chosen carefully?
The liver pathways of neonates aren't fully developed and cannot metabolize drugs effectively
What dog breeds are prone to hereditary coagulation issues?
Doberman pinschers, Rottweilers, and Scottish Terriers
A patient with a PS1 status is a:
normal, healthy patient
PS2 Status
Low risk patient with a mild systemic disease (obesity, mild dehydration, low grade heart murmur)
A ECG is recommended for patients with:
Known or suspected heart disease, chest trauma, GDV, splenic dz, electrolyte imbalances, or in patients taking drugs that can alter cardiac rhythm
What type of fluids are used in healthy or sick patients that have normal PCV values?
Crystalloid- Isotonic is first choice. Pts have to have a PCV over 20% and a PP value of >3.5 g/dl
_________________ are prone to bloat under anesthesia.
Ruminants
Which species are prone to airway blockage because of excess airway secretions?
Cats and ruminants
Which dog breed may become hyperkalemic when undergoing general anesthesia?
Greyhounds
Cats, small dogs, and small animal pediatric patients are prone to ___________ and _____________ caused by mechanical dead space
Hypoxemia and hypercarbia
You should administer all IV anesthetic agents _____ ___________ unless told otherwise
to effect (the minimum dose required to reach the desired level of anesthesia)
All syringes containing injectable agents should be labeled with:
Patient identification, drug name, and drug concentration
TIVA boluses are administered every:
three to eight minutes
What is the most common method of inducing and maintaining general anesthesia in small animals?
IV induction and maintenance with a inhalant agent
Isoflurane should be administered at _____ to _____% by mask or chamber, while Sevoflurane should be administered at _____ to _____%.
3-5%, 4-5%
For mask based induction of anesthesia, _______ oxygen flow rates are required than when a ET tube is used
higher
What is the "goal" stage of anesthesia?
Stage 3. Anything more is too deep and risks death
How long does IM anesthesia induction take for the patient to enter stage 3?
Usually 10-20 minutes
Mask or chamber induction usually takes at least _____ to _______ minutes for the patient to enter stage three anesthesia.
5 to 10
What is a disadvantage of inhalant based anesthesia induction?
Fear in stage one and excitement in stage two can cause epinephrine release. Epinephrine predisposes the heart to arrhythmias, hypotension, etc.
What does administering a anesthetic agent to effect mean?
The minimum amount required to produce unconsciousness was administered instead of the entire calculated dose
What species has a sensitive larynx and may require numbing to intubate?
Cats
A patient under anesthesia that is "too light" might express what clinical signs?
Increased HR and RR, blinking eyelids, eyes that look straight ahead, and rigid front limbs
A patient that is under deep anesthesia might express what clinical signs?
Eyes facing forward without blinking, decreased respiratory effort, flaccid limbs, and decreased HR/BP.
Stage Two of Anesthesia
The period after loss of consciousness. Patients may be delirious or vocalizing
Stage One of Anesthesia
The period between administration of a anesthetic agent and loss of consciousness.
What kind of drugs are used as pre-medication before surgical procedures?
Alpha 2 Agonists (Xylazine, Medetomidine), Opioids (Hydromorphone), Dissociates (Ketamine), Anticholinergics, and Antiemetics
What is a anesthesia protocol?
A list of the anesthetics and adjuncts prescribed for a patient. Includes dosages, routes, and order of administration.
When preparing to intubate a patient you should grab at least _____ differently sized ET tubes
Three
A ET tube should extend from the ___________ to the __________ ___________
(tip of the) Nose, thoracic inlet
What techniques can be used to confirm proper ET tube placement?
Watch the resivoir bag expand/contract, feel for air movement from the tube connecter, watch the tube fog with consensation on exhale, check that the motion of valves coincide w/ breathing, & capnography
What clinical sign indicates a misplaced ET tube?
The ability to vocalize (growl, whine, etc). Vocal chords have to vibrate together to make sound- this isn't possible if the tube is in the right spot
What does inflating the cuff of a endotracheal tube do?
Inflating the cuff prevents leakage of anesthetic gases and the inhalation of room air
When inflating the cuff of a ET tube in a canine patient you should use a _____ or _____ mL syringe filled with air to slowly inflate the cuff until leaking ceases around _____-_____ cm H20 but resumes at higher pressures
6 or 12 mL syringe, 18-20 cm H2O
When should extubation occur?
When the swallowing reflex returns
Supraglottic Airway Device
A device used to maintain an open airway in an anesthetized patient that connects with the opening of the glottis, but unlike an ET tube, does not enter the trachea. Commonly used in rabbits
Any time a intubated patient is turned over, the ET tube should be:
disconnected from the anesthetic circuit to avoid tracheal damage or tube collapse
If a anesthetized patient has a diseased lung, the patient should be positioned with the ____________ side down.
diseased
Anesthetic recovery period
The time between the anesthetic being discontinued and the patient being able to stand and walk
Patients recovering from ketamine may exhibit which clinical signs?
Clawing at their faces or chewing at paws
Why is delayed extubation not recommended in cats?
It can predispose the pt to laryngospasms
A recovering patient should be turned every 10 to 15 minutes to prevent:
Hypostatic congestion
Why should electric heating pads be avoided in anesthetized patients?
There's a great risk of burns and rapid rewarming can cause dilation of cutaneous vessels & lead to a hypotension and afterdrop
Pharmacokinetics
what the body does to the drug (eg. metabolism)
Pharmacodynamics
what the drug does to the body
Which anesthetic agent ISN'T water soluble?
Diazepam
Schedule II drugs have to be ordered with which form?
Form 222
What should you do in the event of unexpected significant loss or suspected theft of controlled substances?
Complete Form 106 and notify the DEA within one business day
Commonly used anesthetics are _______________ compounds
Halogenated
Halogenated compounds are ___________ at room temperature and are stored inside the ____________ of the anesthetic machine
liquid, vaporizer
To maintain surgical anesthesia the vaporizer should be set at about:
1.5 x MAC
What is the rate of diffusion of anesthetic into the bloodstream controlled by?
the concentration gradient between the alveolus and bloodstream
How are inhalation anesthetics primarily eliminated from the body?
Through the lungs
How can a anesthetist hasten the elimination of anesthetic?
By periodically bagging the animal w/ 100% oxygen
Carbon monoxide causes:
Hypoxemia. CO2 binds to spots that O2 normally would and starves the lungs of oxygen
What clinical signs suggest carbon monoxide exposure?
The presence of cherry red blood and brick red mucus membranes
Vapor pressure
The measure of a tendency of a liquid anesthetic to evaporate. Depends on the temp and the agent used. The VP determines how fast the agent will evaporate in the vaporizer
How often should corneal lubricant or tears be applied to the eyes of a anesthetized patient in surgery?
Every 2-4 hours
Antiseptic
A chemical that inhibits or prevents the growth of microbes on living tissue
Disinfectant
Chemical used to inhibit or prevent the growth of microbes on inanimate objects
Phenol based disinfectants
EX: Lysol & Pine Sol. These products work in the presence of organic material and are relatively safe but can cause skin irritation. Risk for toxicity in cats- use with caution