molecular bio firestine
1/84
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
85 Terms
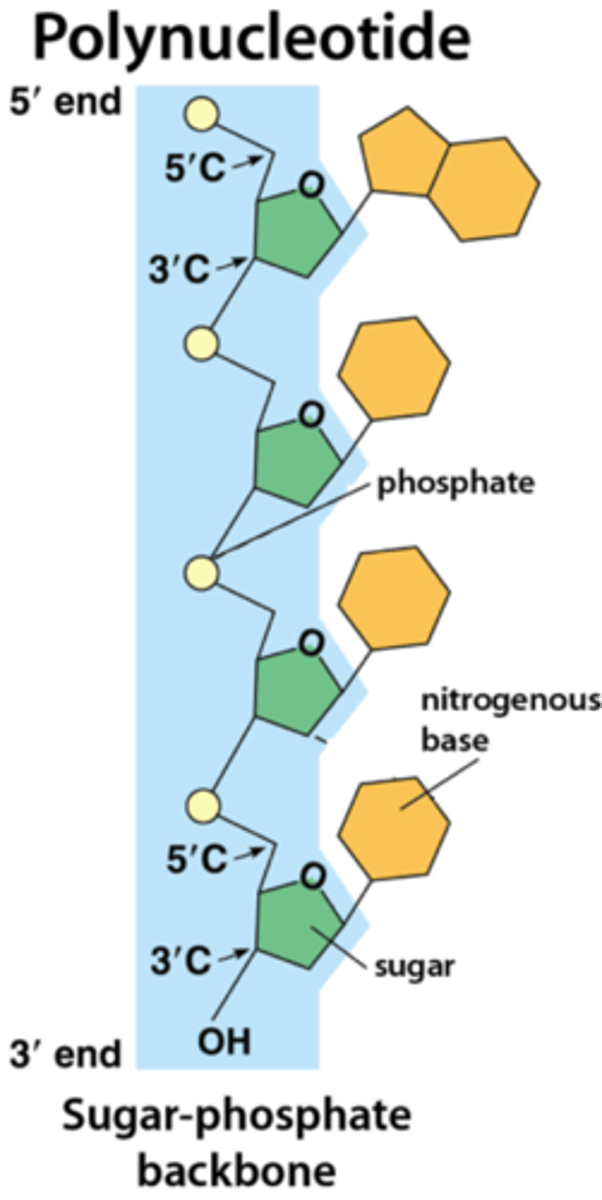
while proteins are composed of amino acids, nucleic acids are composed of __________
nucleotides
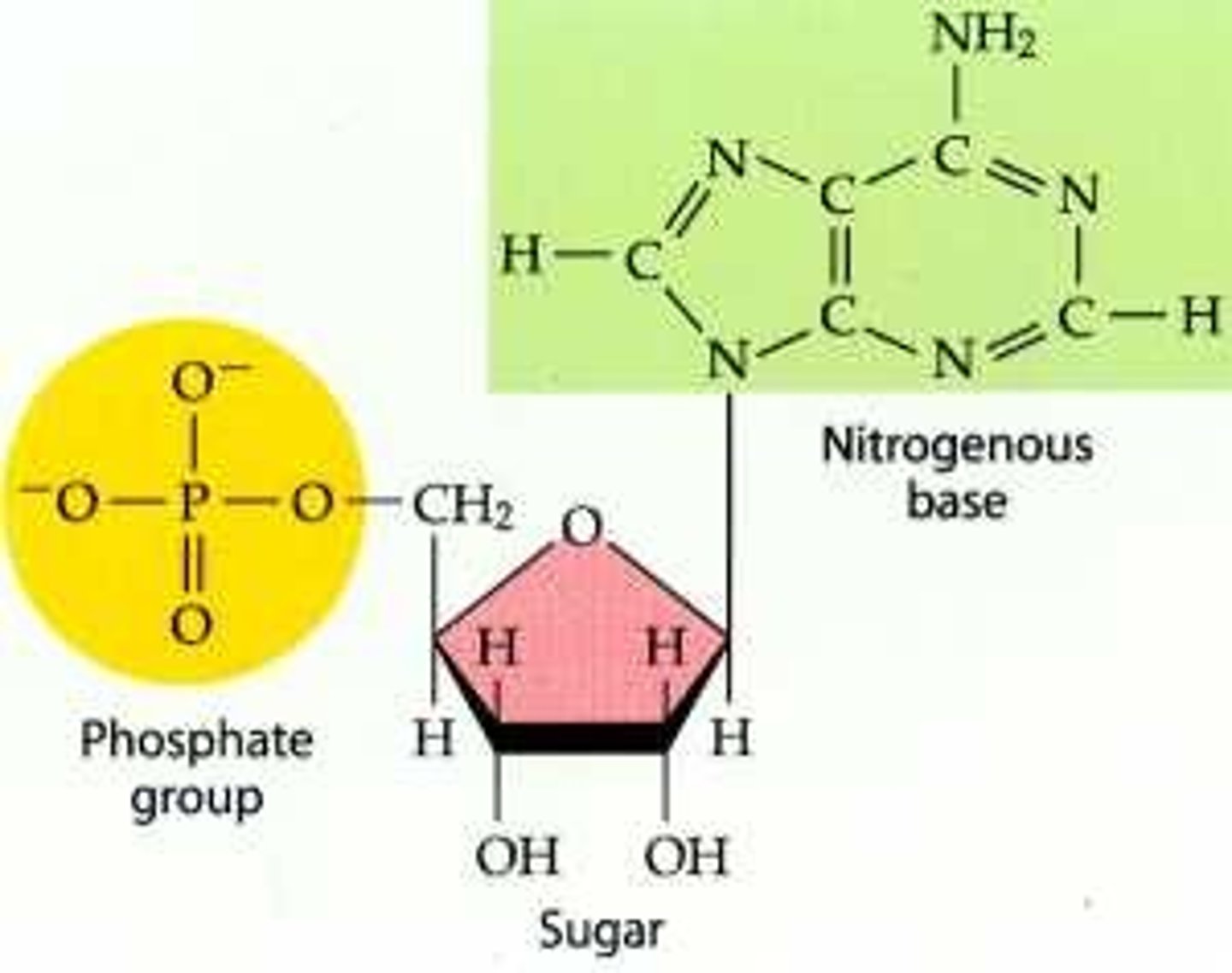
nucleotides are composed of what 3 elements
1. nitrogen containing base (purine or pyrimidine)
2. pentose sugar
3. phosphate group
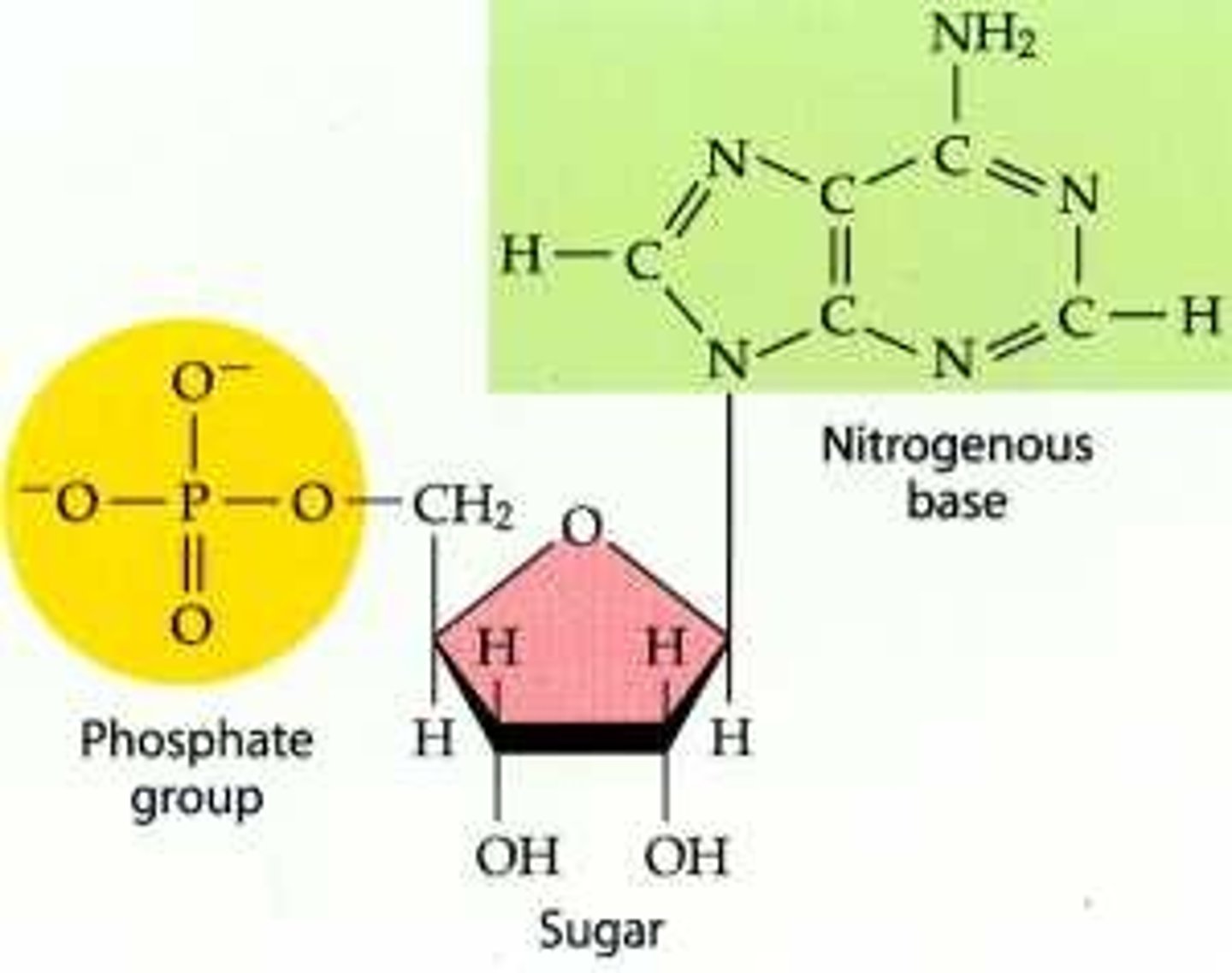
where does the phosphate group of a nucleotide attach
5' of pentose sugar
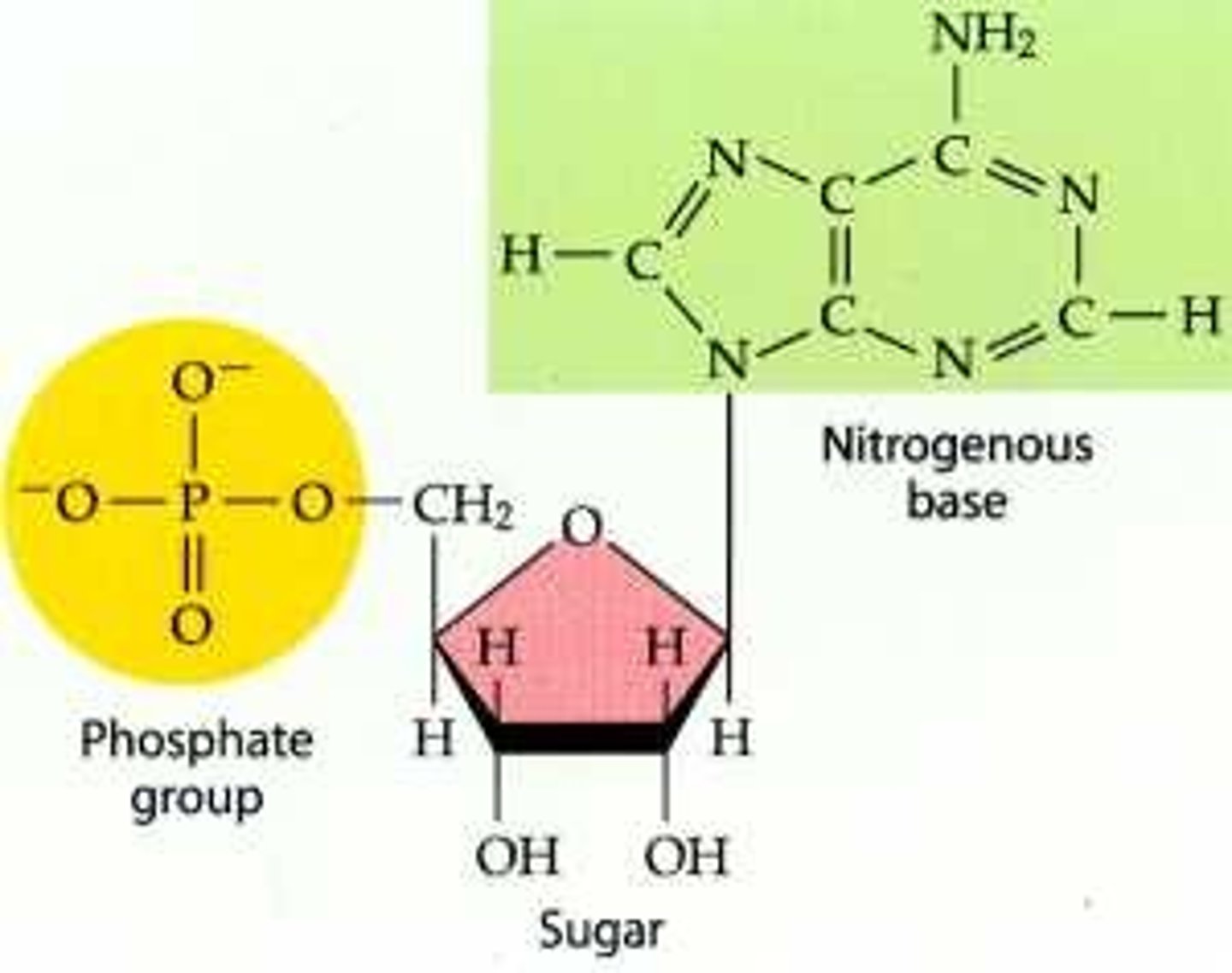
where does the N containing base of a nucleotide attach
1' of pentose sugar
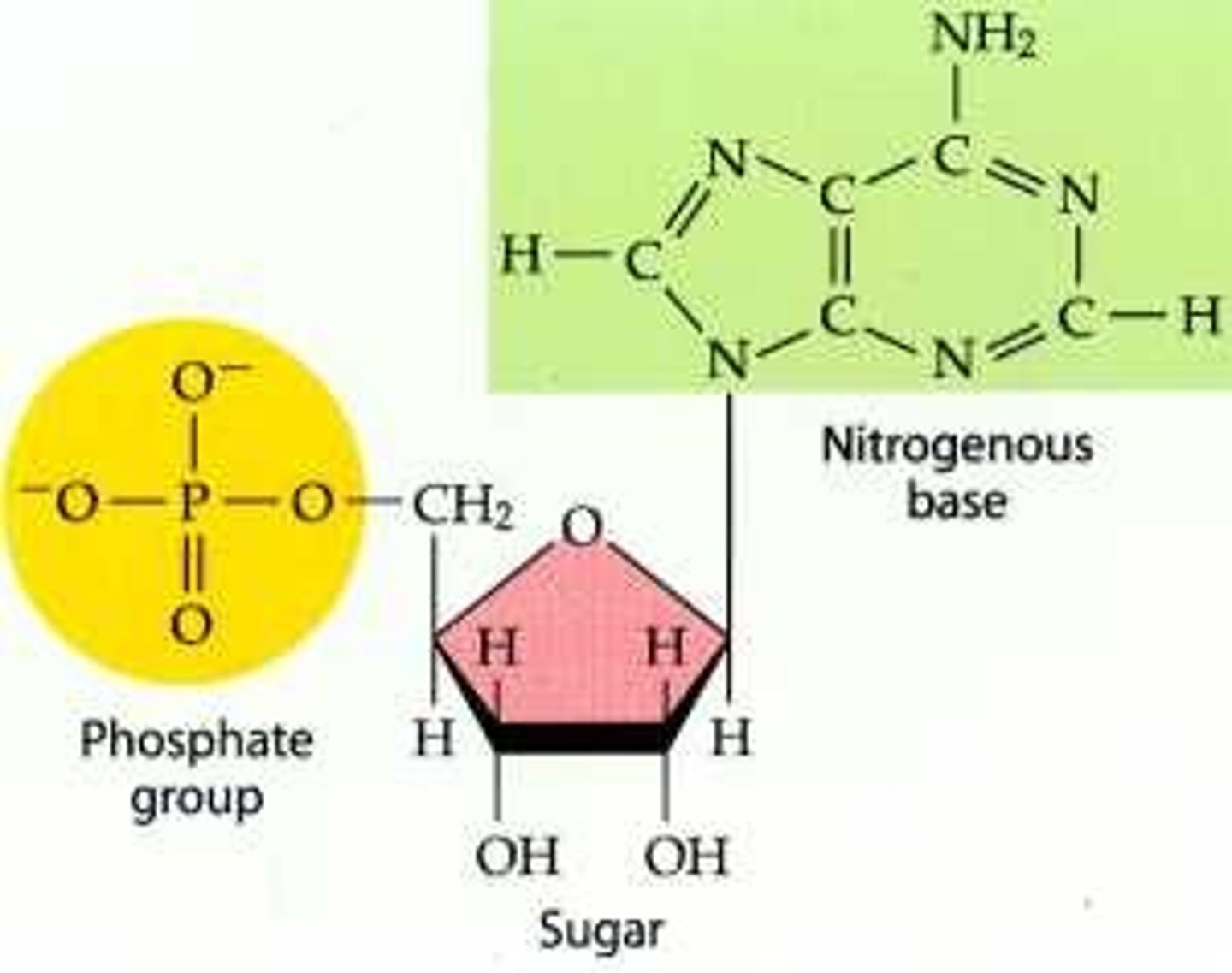
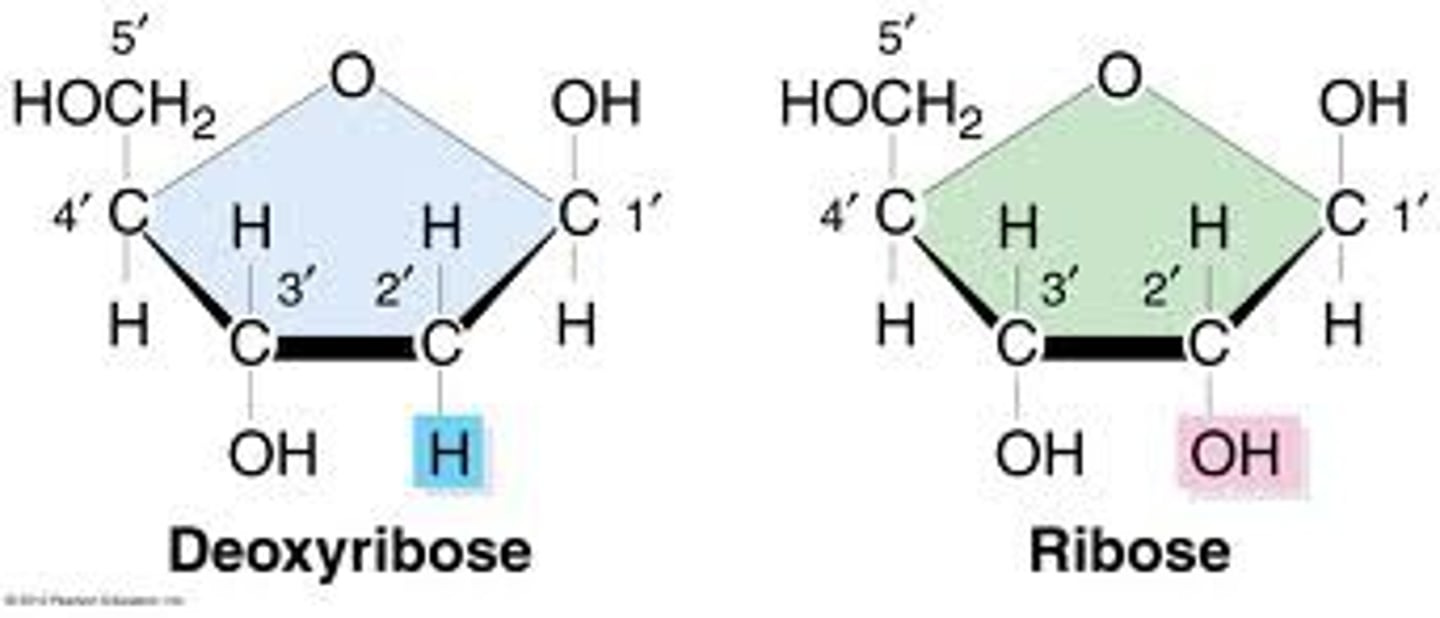
which carbon of the pentose sugar varies among DNA and RNA
2' carbon; varies in what is attached
DNA= H
RNA= OH
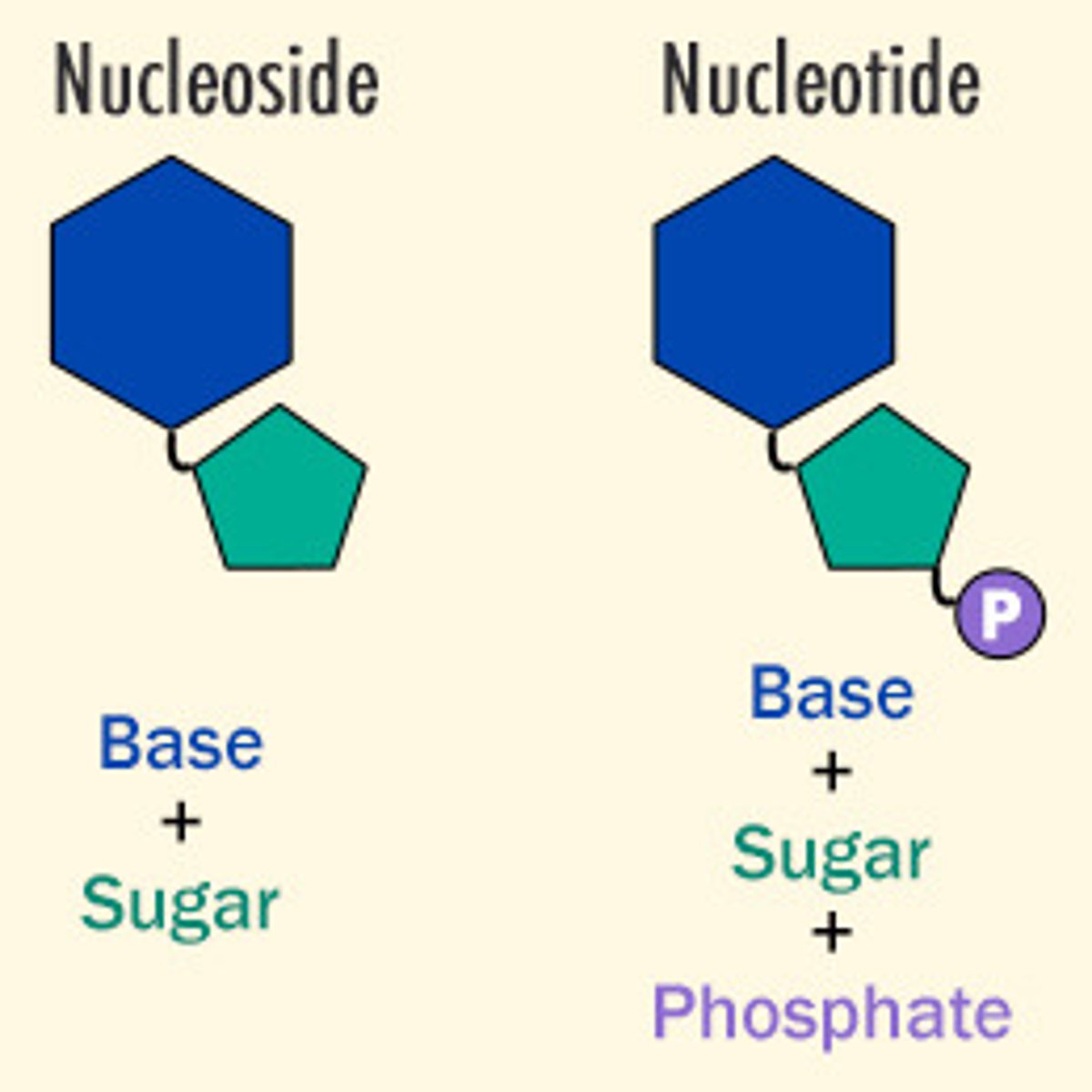
a nucleotide without a phosphate group is called
nucleoside
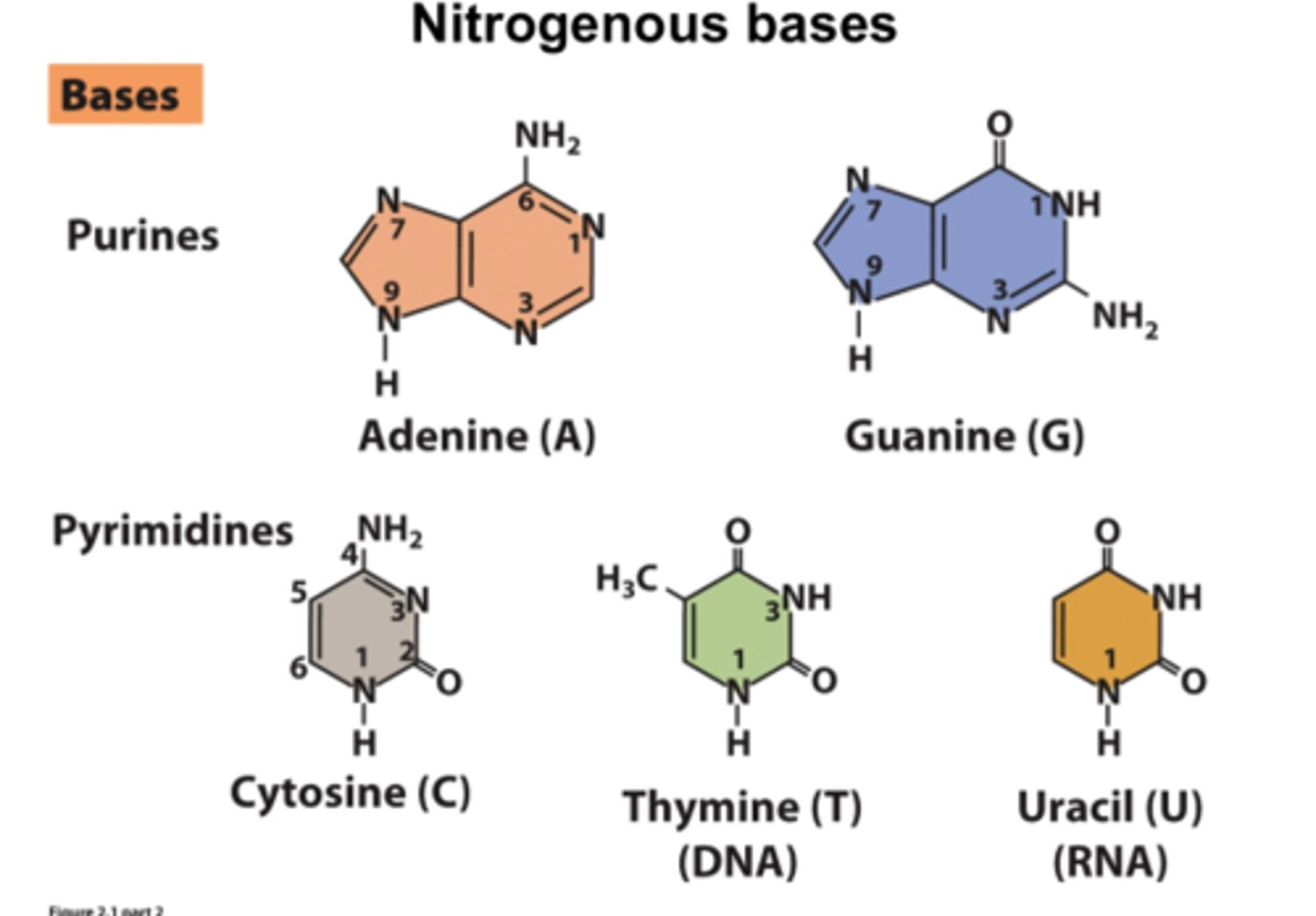
nitrogen containing bases of purines vs pyrimidines
Purines: adenine, guanine
Pyrimidines: cytosine, thymine (DNA), uracil (RNA)
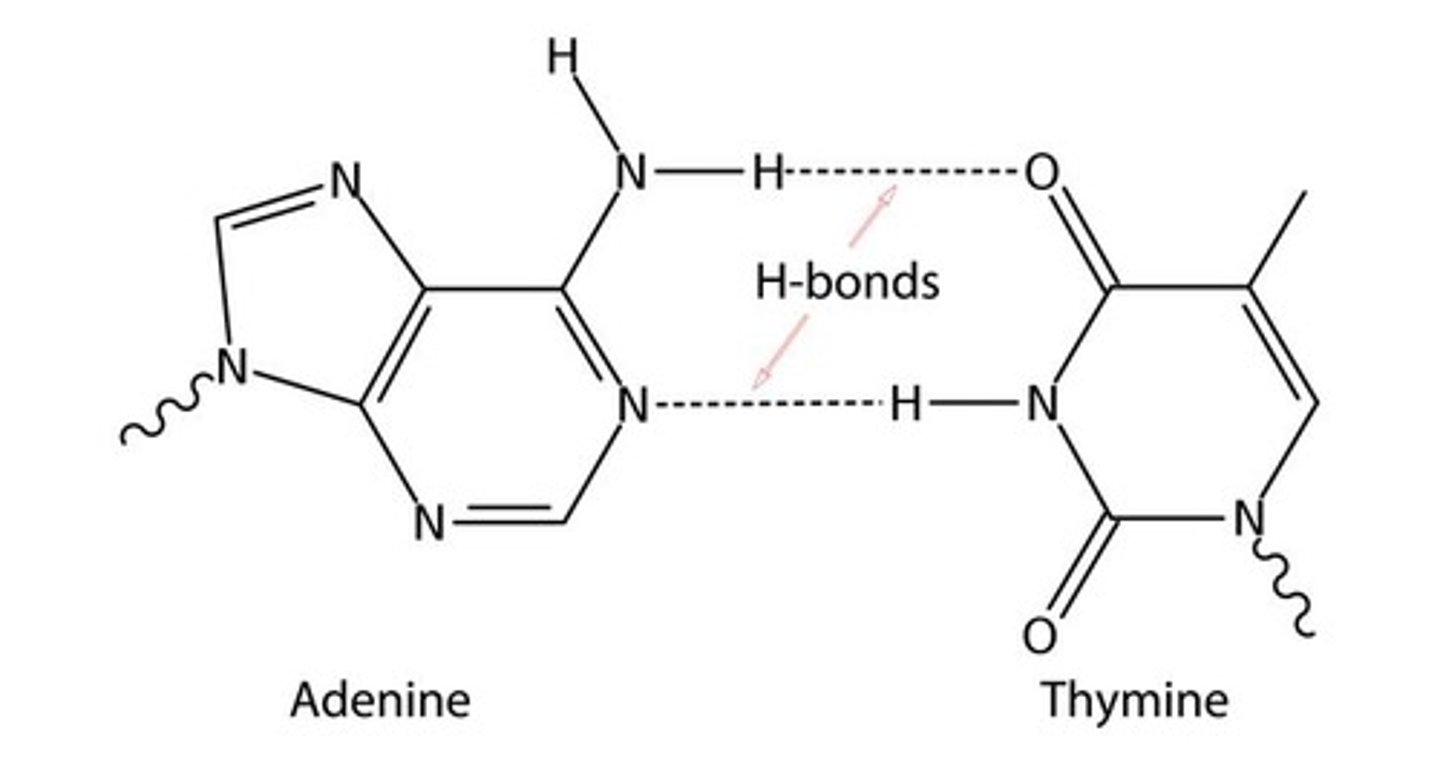
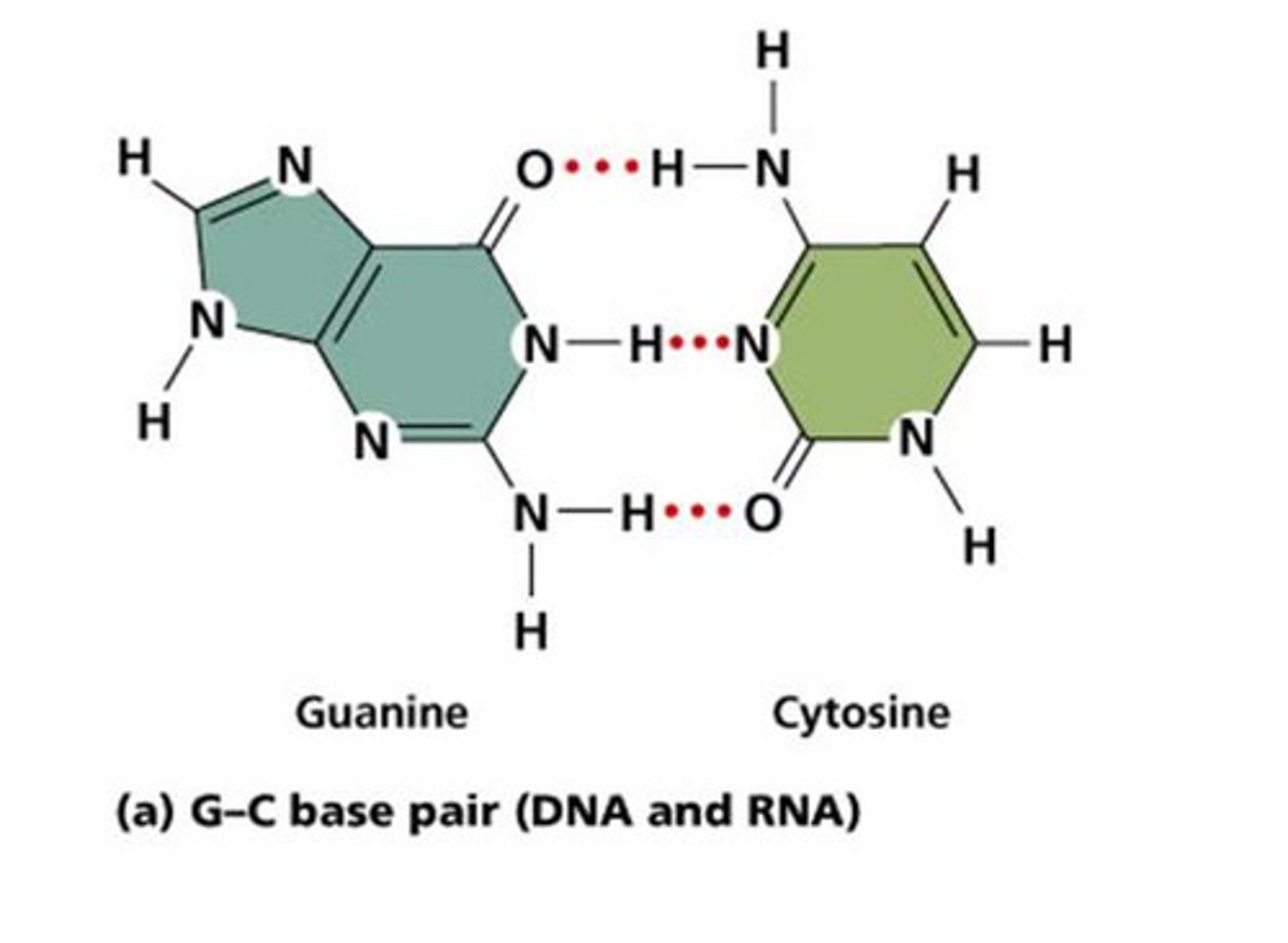
be able to draw adenine= thymine H bonds
be able to draw cytosine= guanine H bonds
2 amino acids make an amide/peptide bond, while 2 nucleotides form a _________ bond
phosphodiester
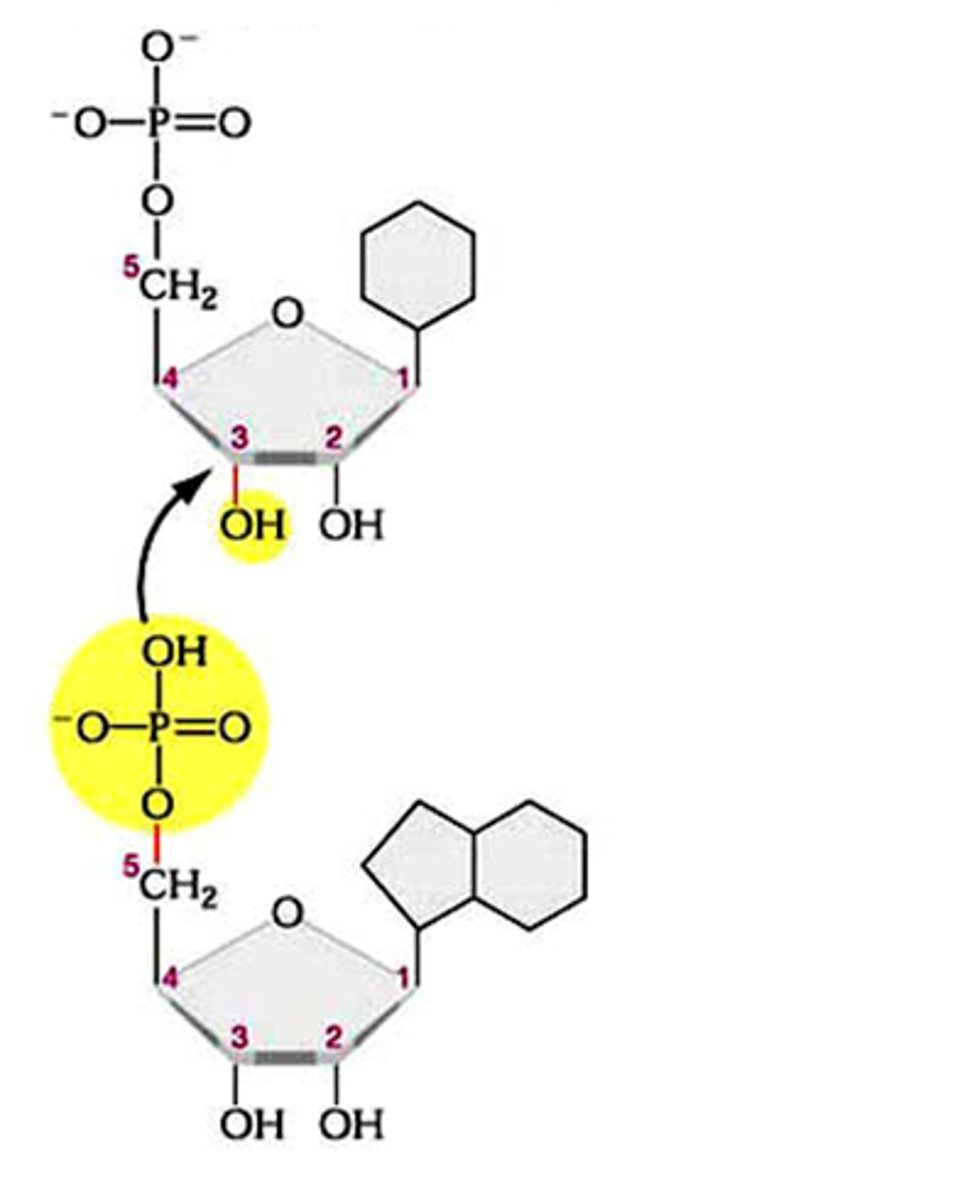
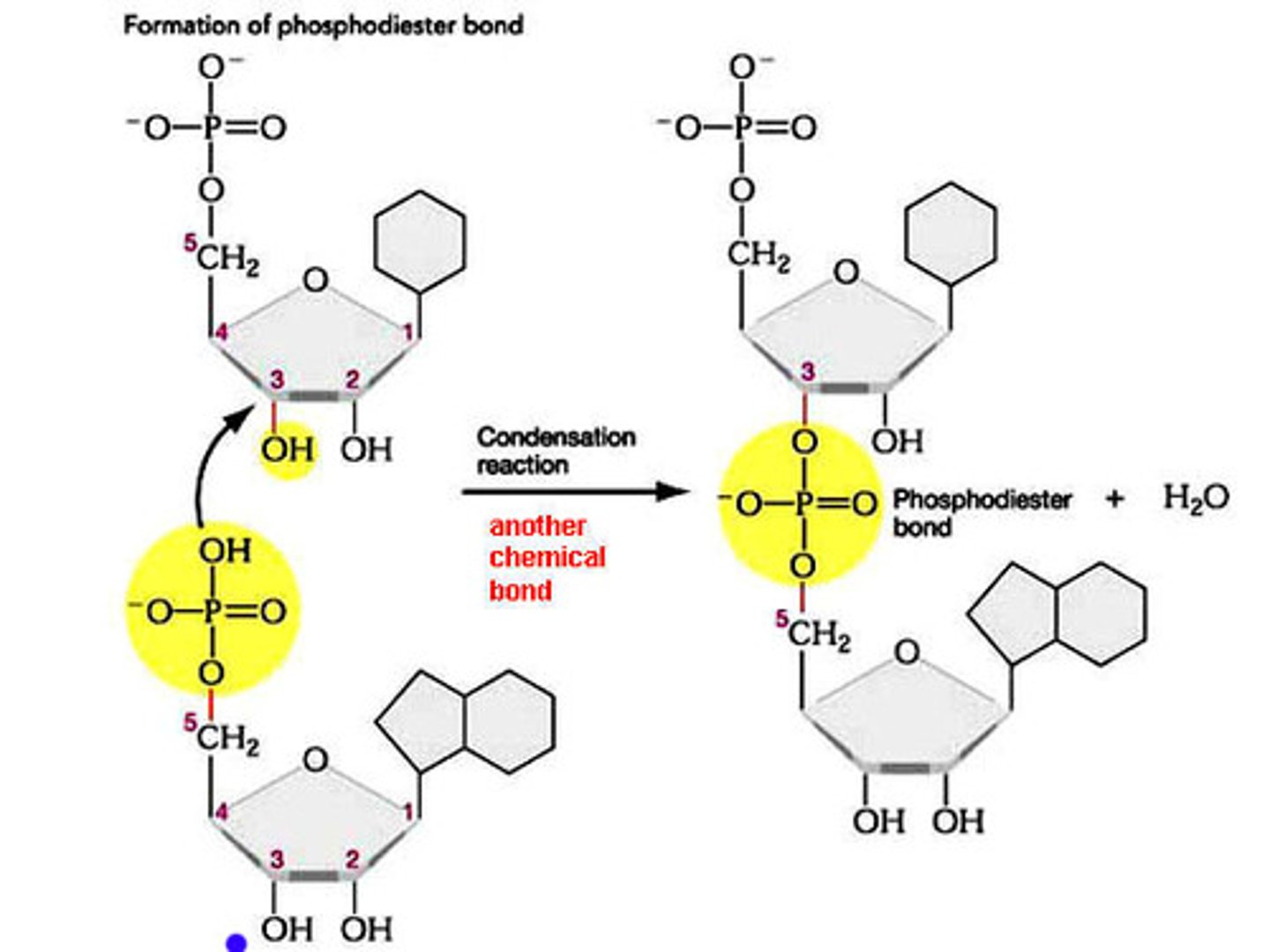
a phosphodiester bond in nucleic acids joins which regions?
the hydroxyl group (3'-OH) on the sugar attacks the phosphate group of the next nucleotide
the ___' end has a free phosphate and the ___' end has a free hydroxyl group
5'= free phosphate
3'= free hydroxyl
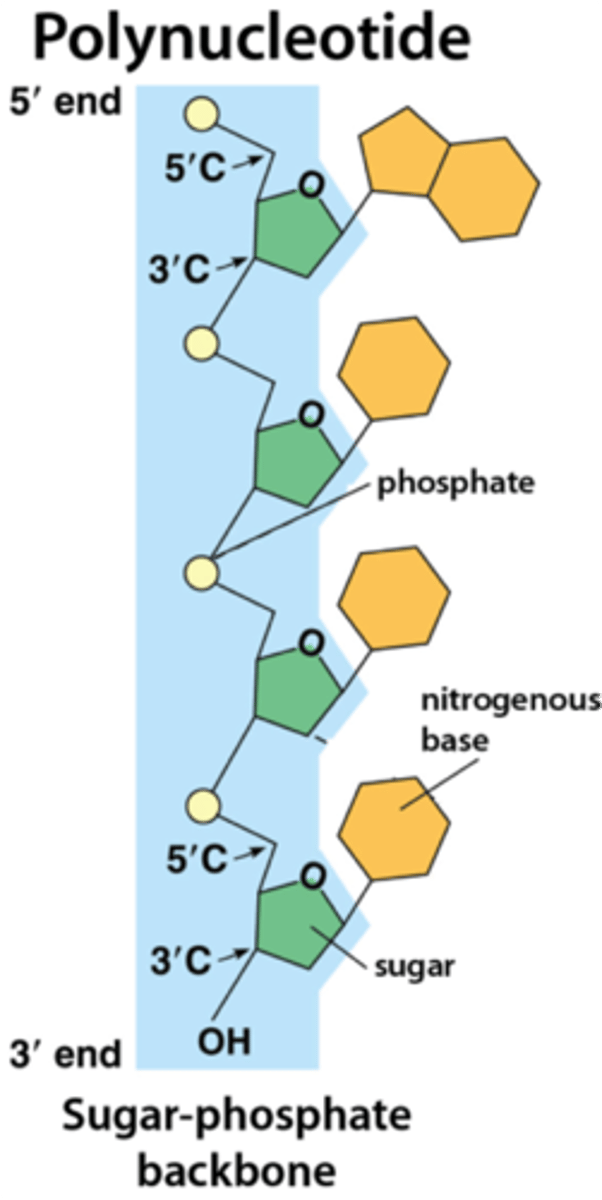
ALL nucleic acids are listed in the __________ direction
5' to 3'
what is the complementary strand of AGT
a. TCA
b. ACT
c. GAT
b. ACT because 5'ACT3' is the same as 3'TCA5' which complements AGT
*remember answer choices are listed 5->3 order
what is the single most important feature in determining the structure of nucleic acids
hydrogen bond capability
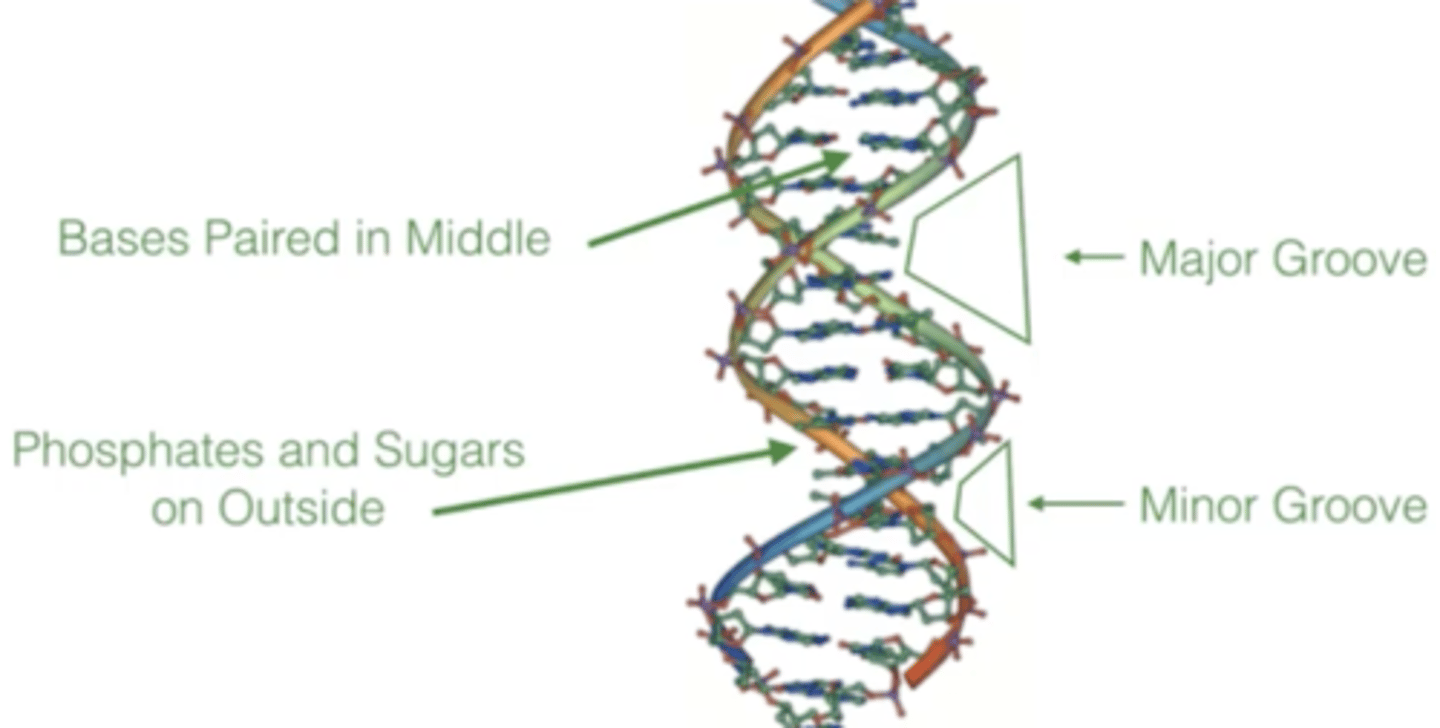
describe the DNA double helix structure
1. base pairs stacked on inside
2. hydrophilic phosphate backbone on outside
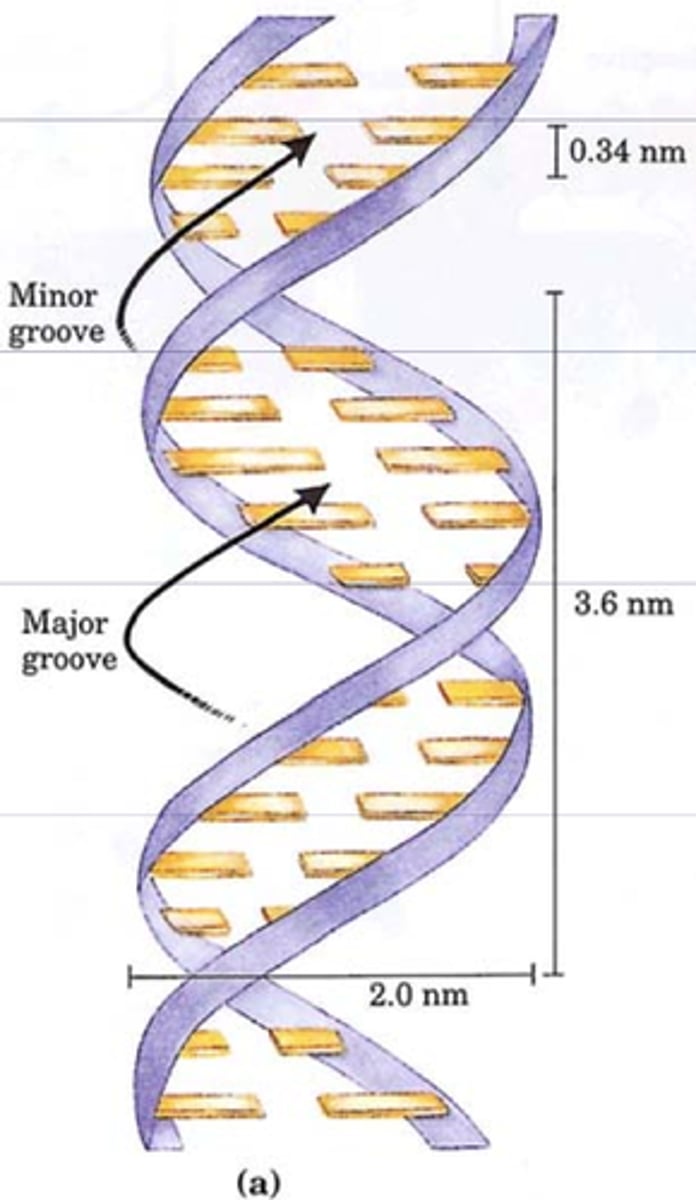
phosphate groups of DNA backbone are ______ charged, making them ________
negatively; hydrophilic
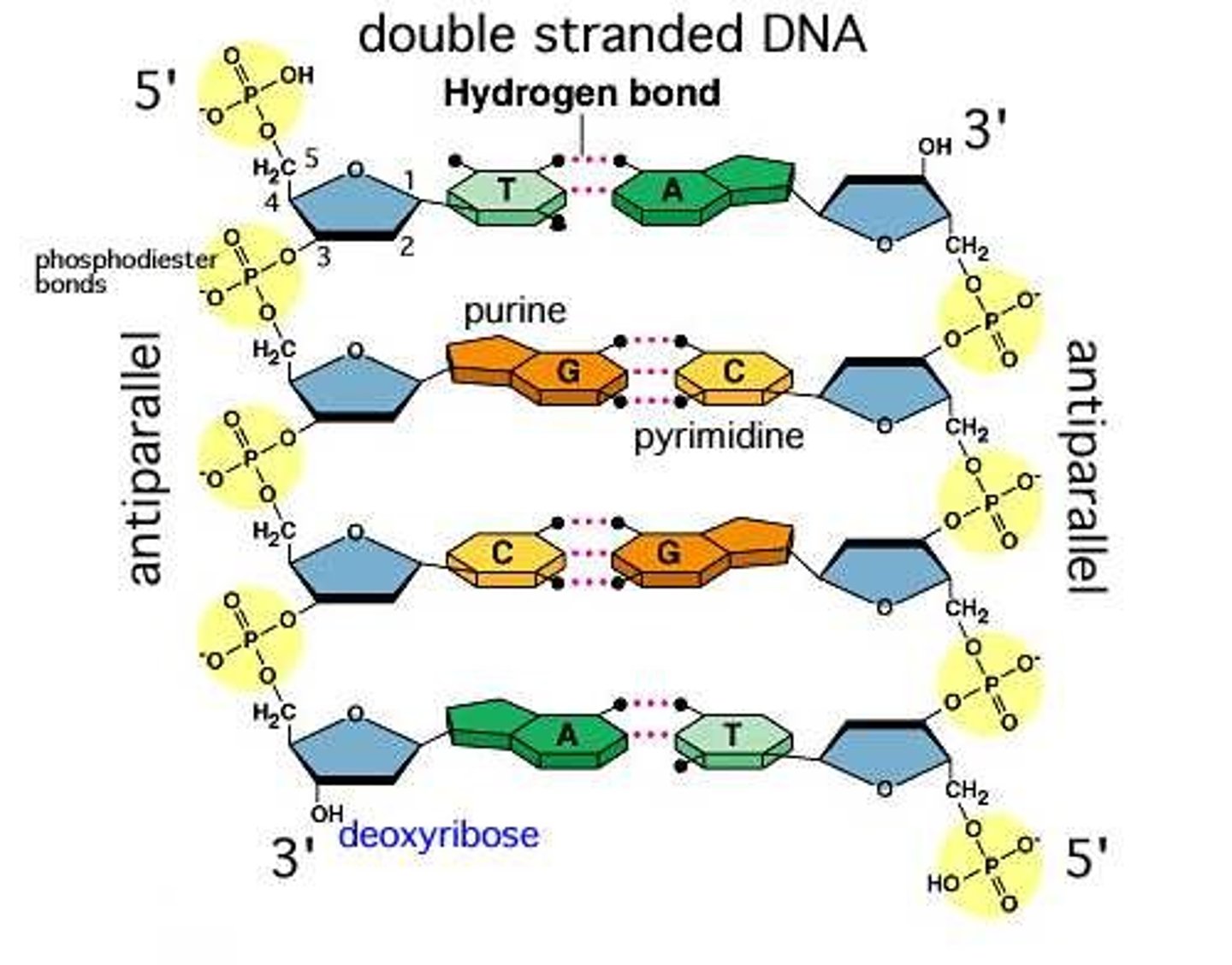
which interactions inside the DNA double helix contribute to hydrophobic regions
aromatic ring stacking among base pairs
proteins mostly bind to the ___ groove to recognize a DNA sequence
major
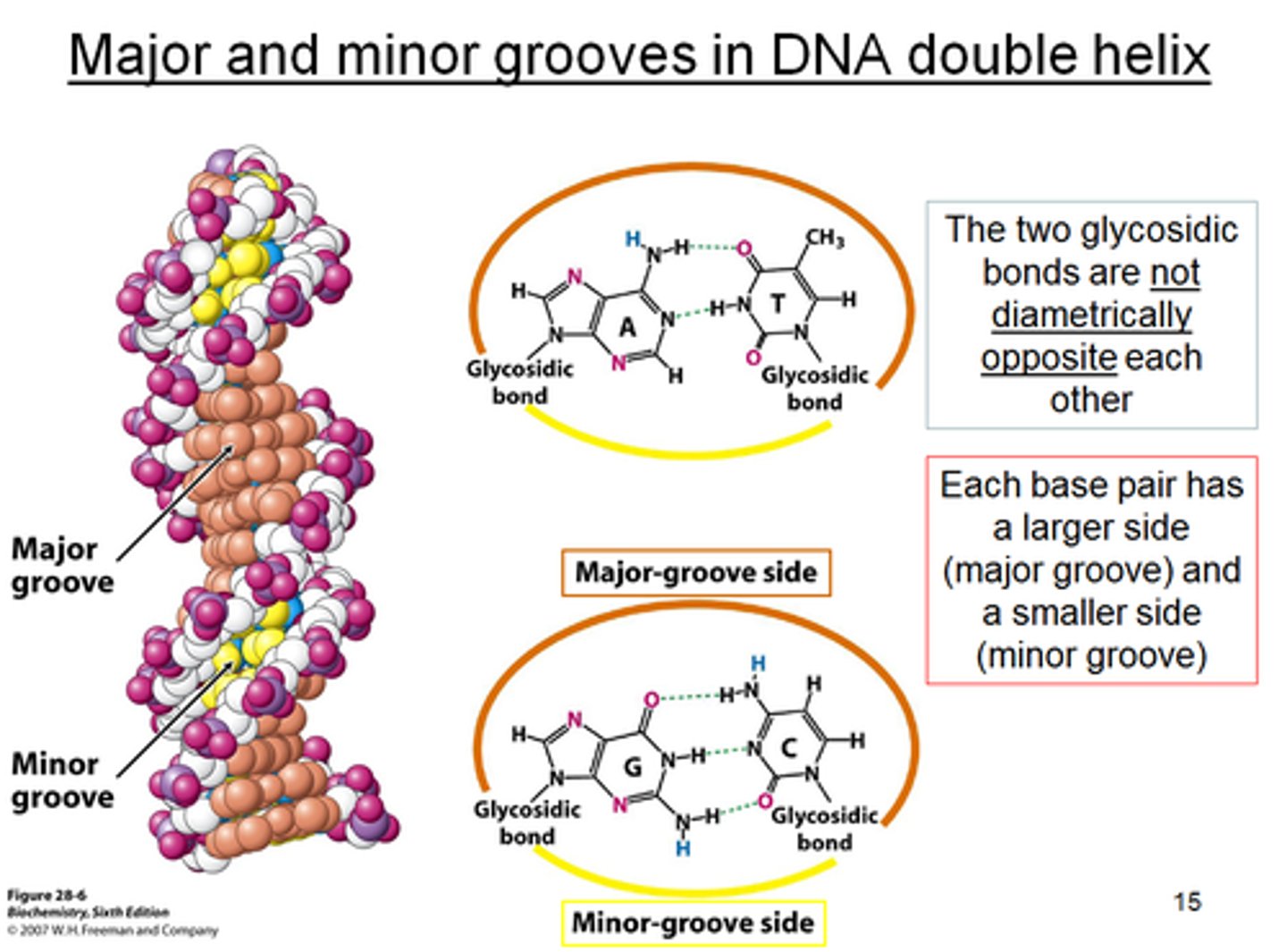
What do major and minor grooves do?
allow proteins to recognize a certain DNA sequence (base pairs)
each base pair is ____A apart up to down
3.4A
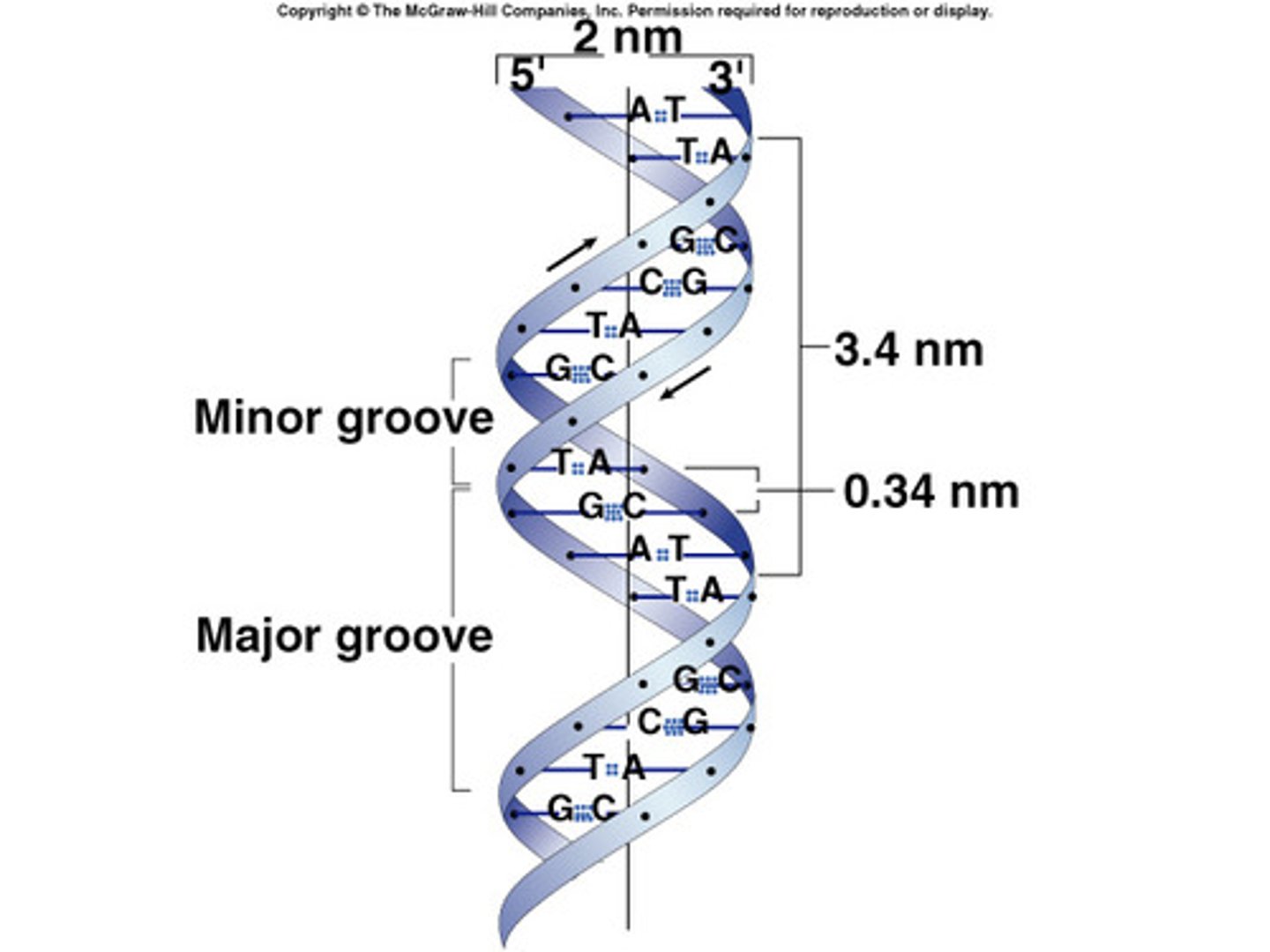
how many base pairs in one helical turn
10.5bp
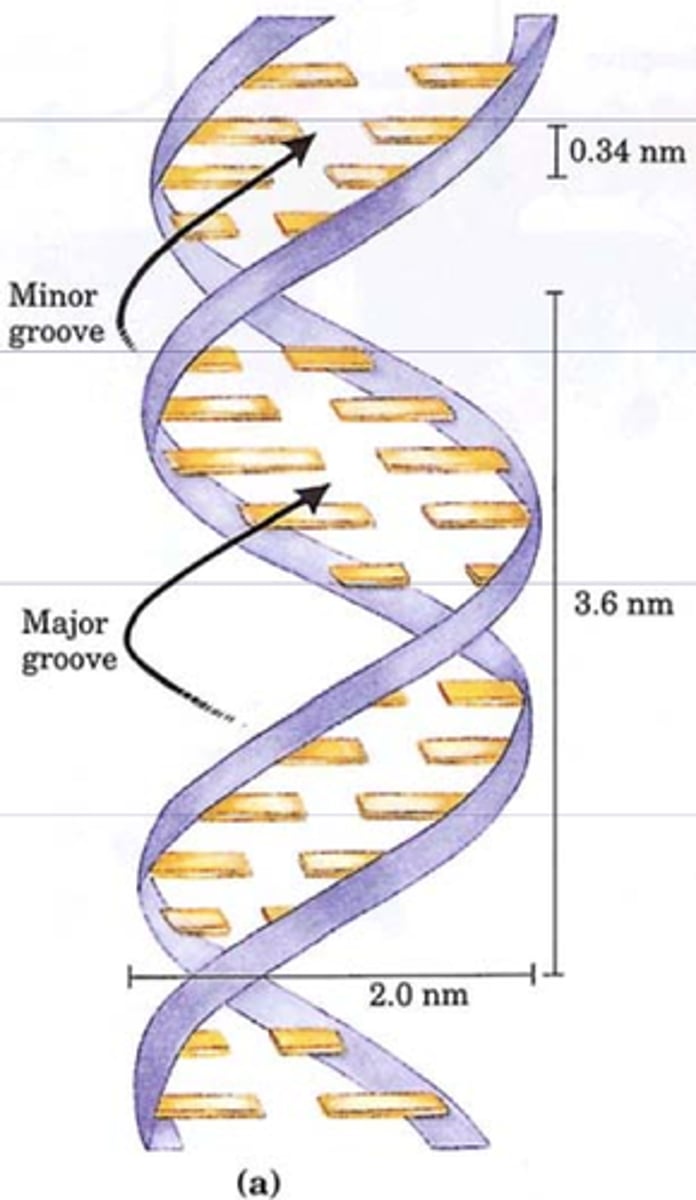
2 major forces used to stabilize DNA sequence
1. hydrogen bonds between base pairs
2. base pair stacking
3 types of cloning
1. organism ("carbon copy")
2. transgenic (ex:GMOs)
3. DNA (ex: recombinant)
DNA cloning methods were developed by
Berg, Boyer, Cohen
5 general steps of DNA cloning
1. cut DNA at precise locations
2. select DNA for self replication
3. join DNA together
4. move DNA into host
5. select hosts that have desired DNA
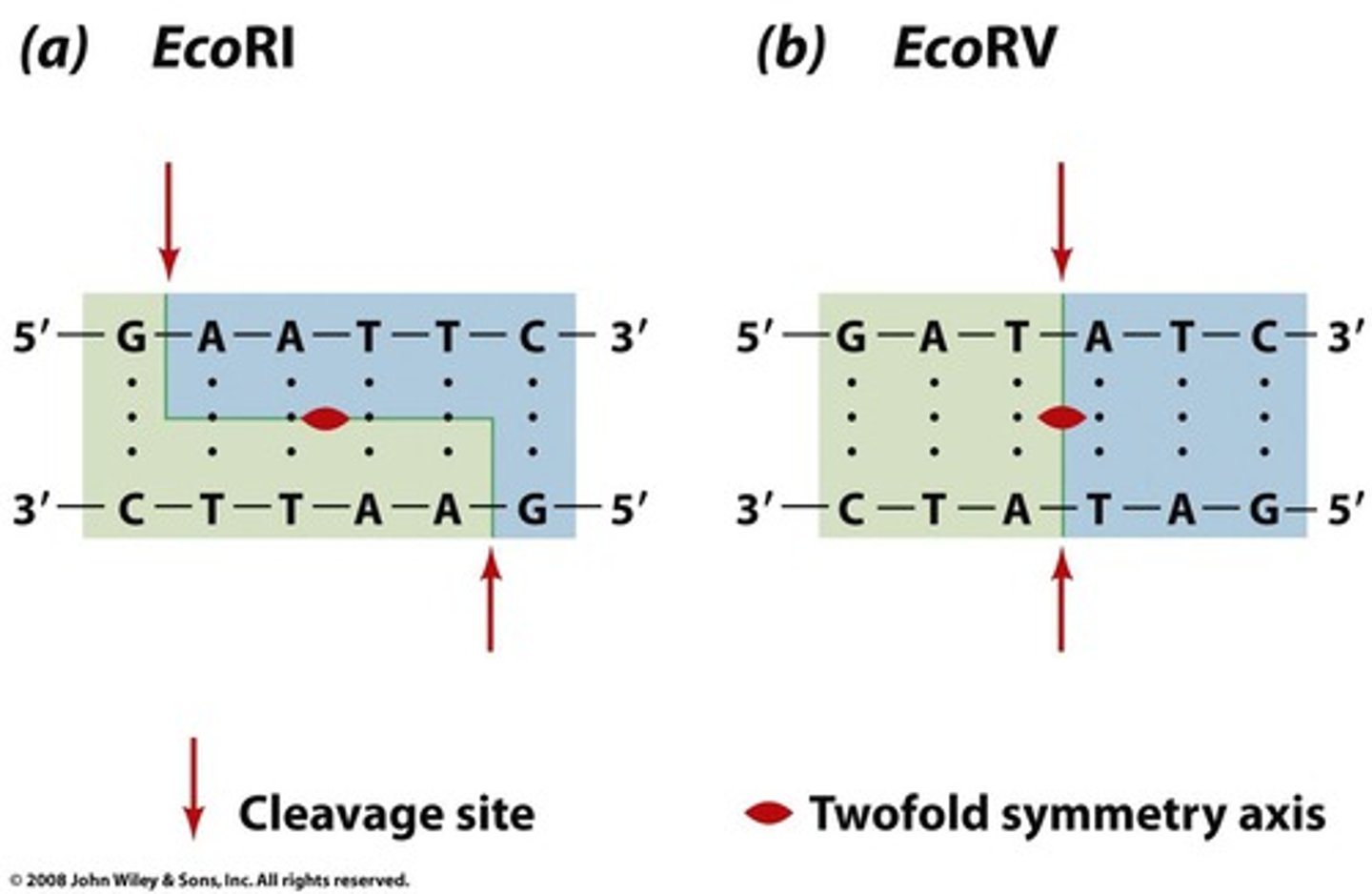
what cleaves DNA at a specific base sequence
type 2 restriction endonucleases
which enzyme joins 2 DNA molecules
DNA ligase
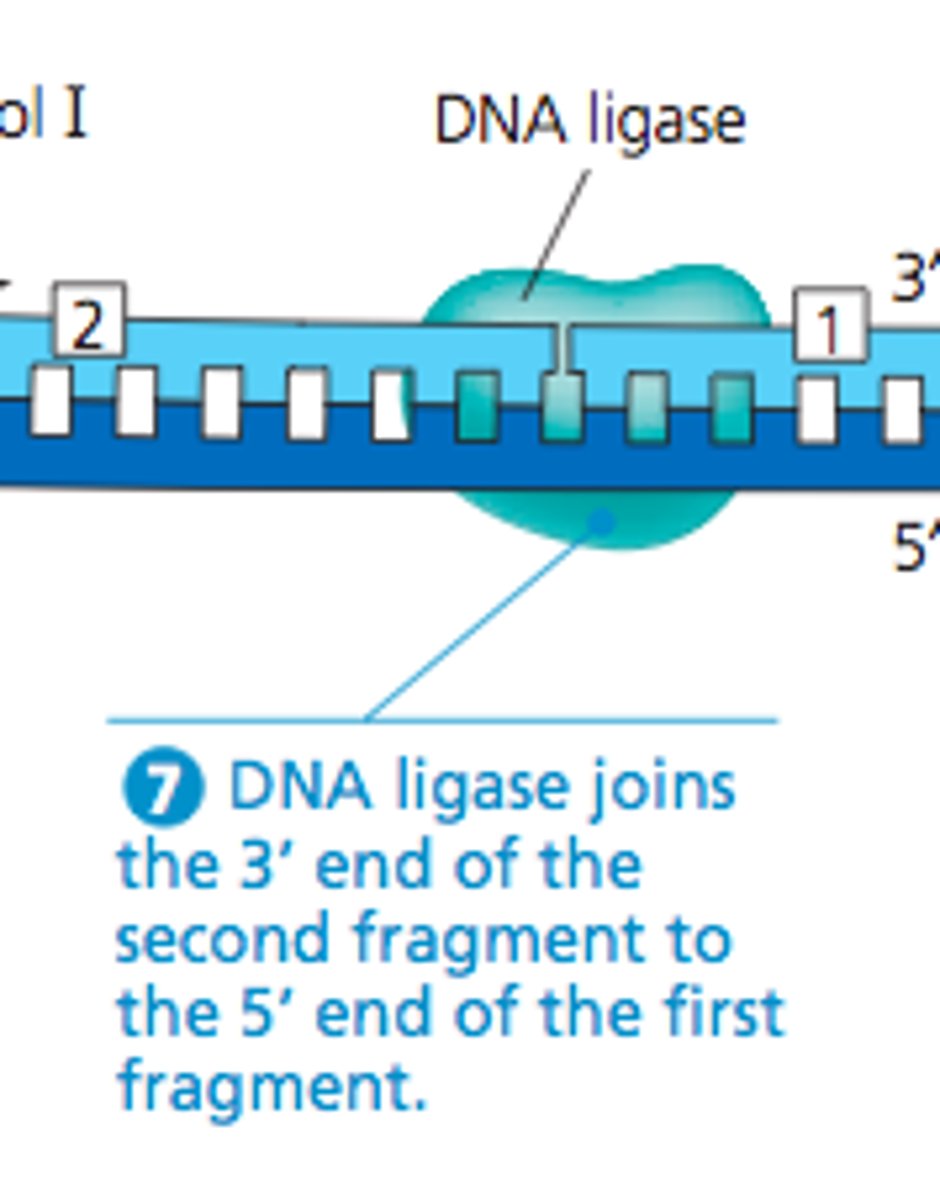
which enzyme fills gaps in DNA via addition of nucleotides
DNA polymerase 1
which enzyme makes a DNA copy of an RNA molecule
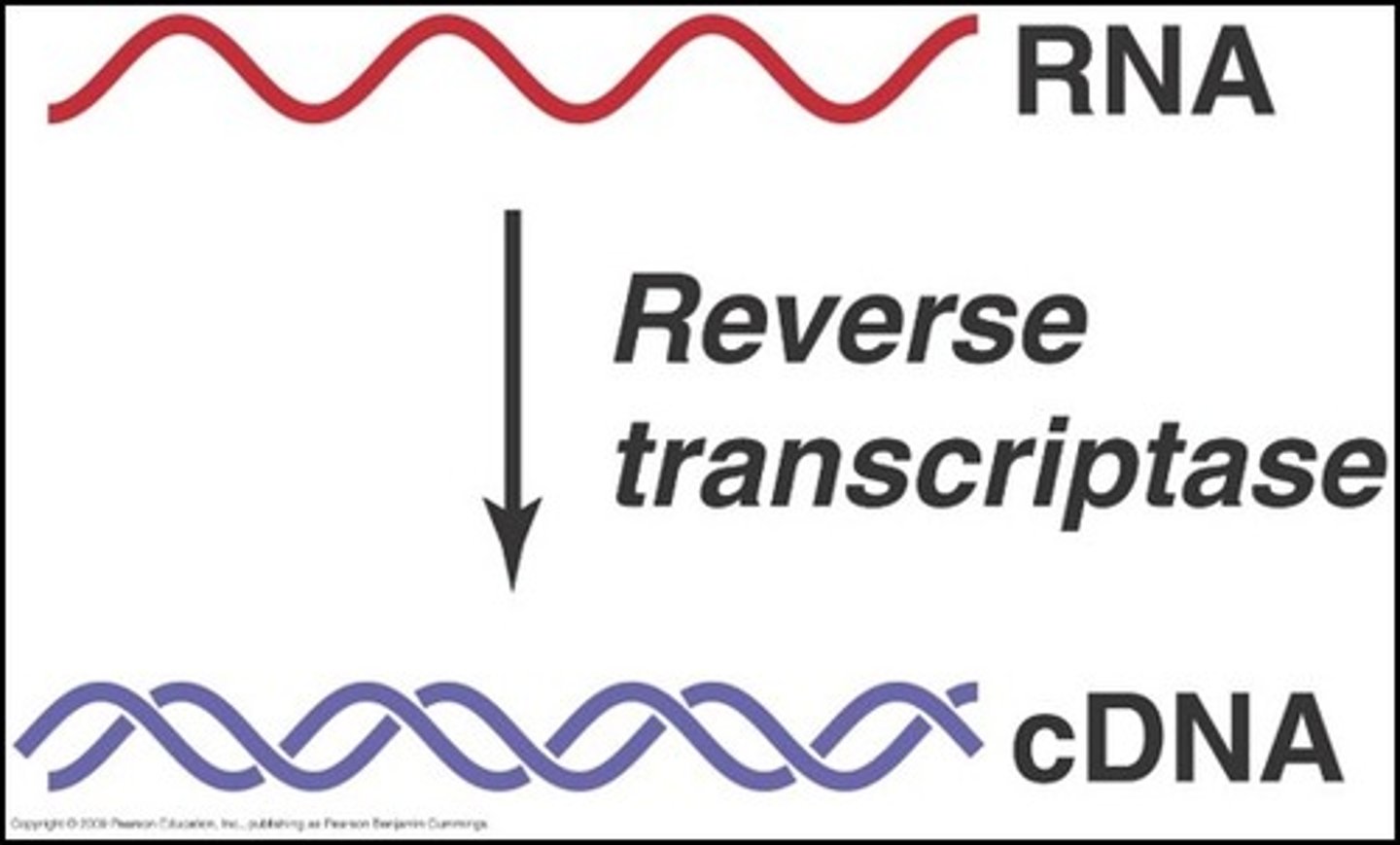
reverse transcriptase
of the 3 types of restriction endonucleases, which one is used the most?
type 2 restriction endonuclease
which enzyme breaks phosphodiester bonds of DNA at exact locations
restriction endonucleases
type 2 restriction enzymes usually recognize _______bp DNA sequence that is ________
4-6bp; palindromic
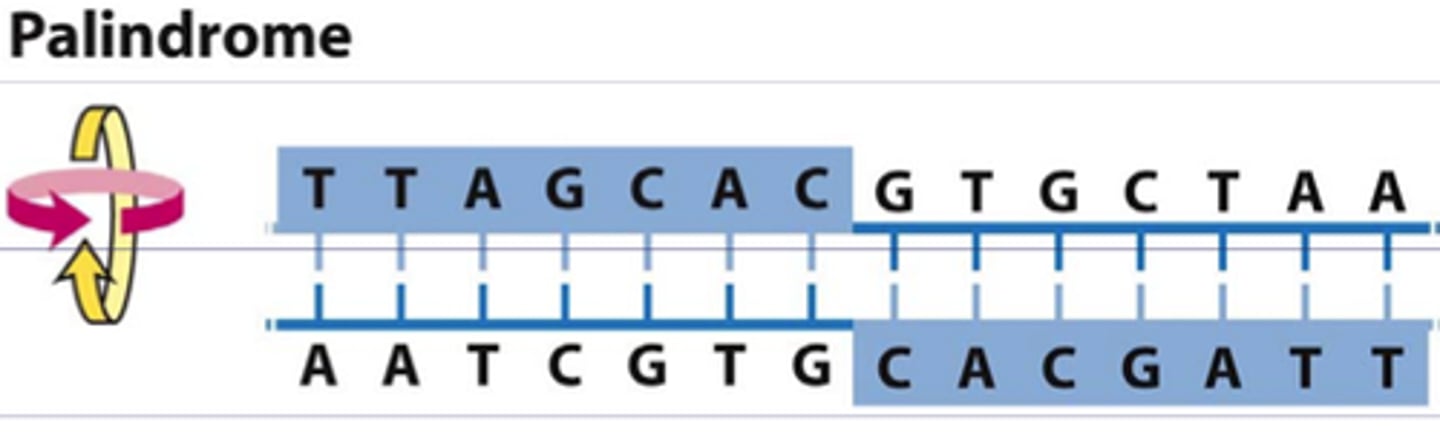
what does it mean that restriction endonucleases only work on "palindromic" sequences
reads the same on both strands when read in the 5' to 3' direction.
ex :
5'-GAATTC-3'
3'-CTTAAG-5'
sticky ends vs blunt ends
Sticky Ends - Staggered ends on a DNA molecule with short, single-stranded overhangs. ** require same restriction endonuclease
Blunt Ends - A straight cut, down through the DNA that results in a flat pair of bases on the ends of the DNA.
t/f: you must cut 2 pieces of DNA with the SAME restriction endonuclease to join at same spot if STICKY ENDS are formed
true. if different enzymes are used then sticky ends wont match
t/f: you must use the SAME restriction endonuclease for an enzyme that forms BLUNT ends on DNA
false. blunt ends can be ligated to any other end, so the same restriction enzyme is not necessary (unlike sticky ends)
t/f: blunt ends are usually less efficient than sticky ends
true
___________ can be used to "fill in" sticky ends created by restriction enzymes to make a blunt end
DNA polymerase
DNA polymerase can only add on to
3' OH (needs primer)
DNA polymerase reads in the _________ direction and synthesizes in the __________ direction
reads: 3->5
synthesizes: 5->3
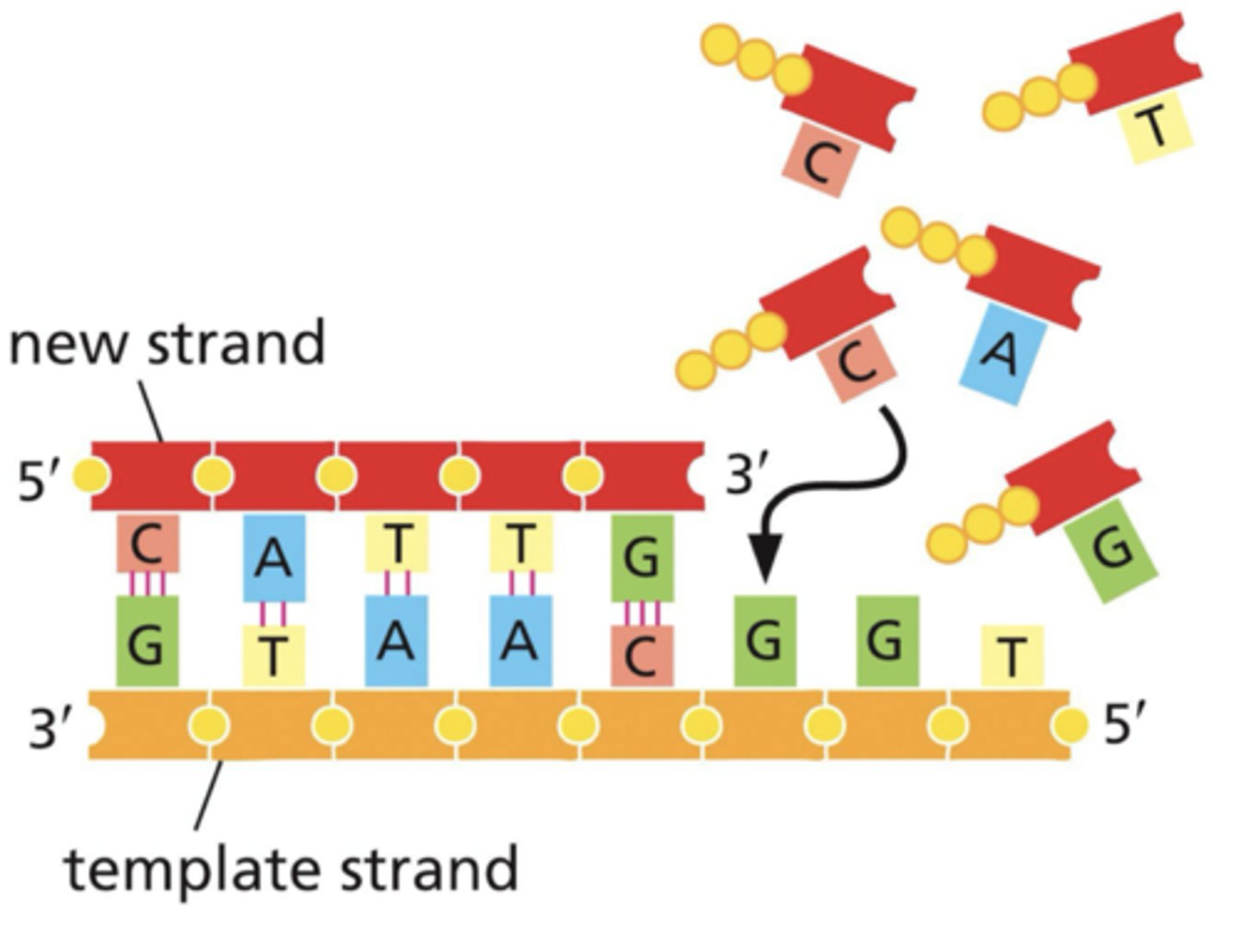
what 2 things does DNA polymerase need in PCR
1. template strand
2. 2 primer strands (with free 3' OH)
how does ligase form a phosphodiester bond
3'OH group links to 5' phosphate of DNA
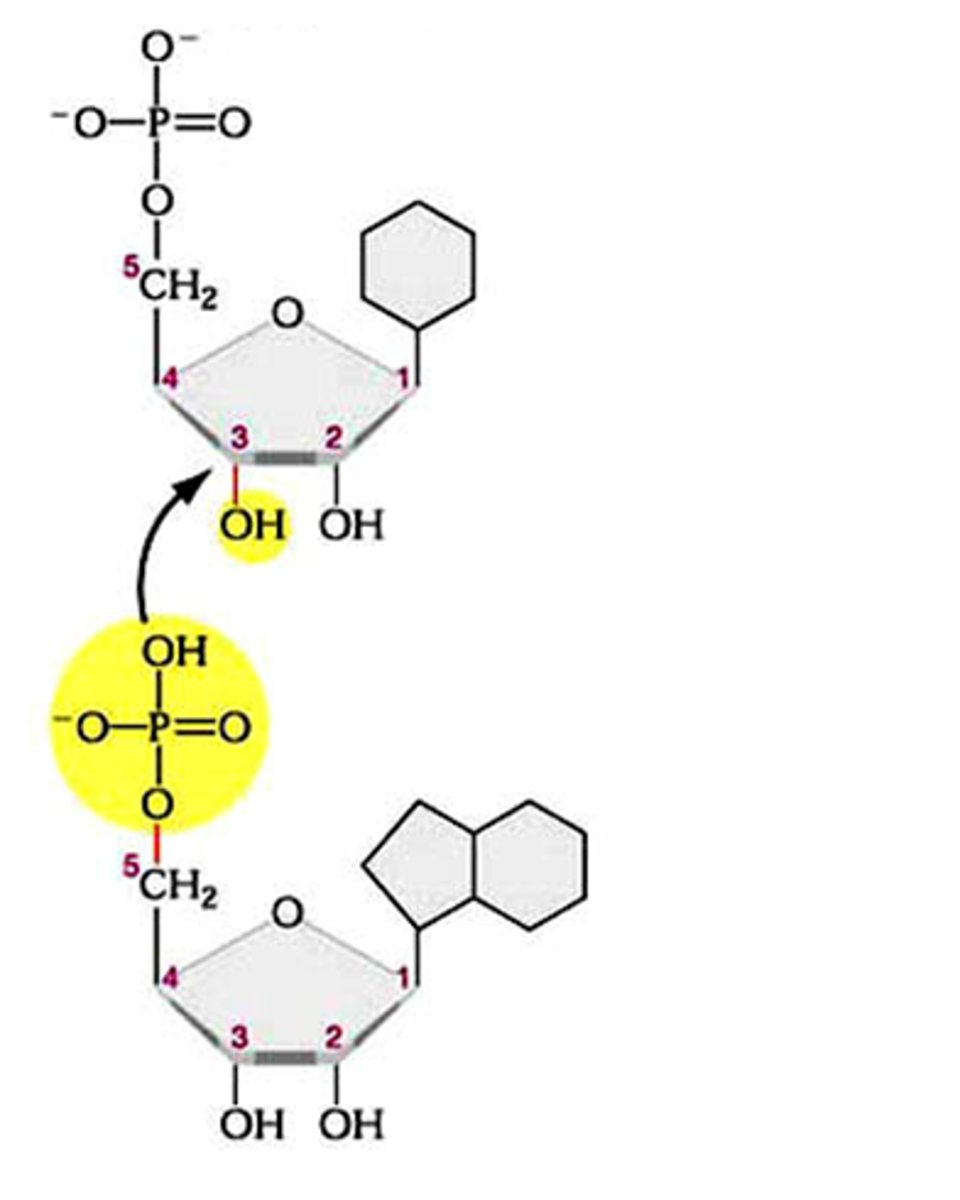
dna ligase forms a __________ bond
phosphodiester
which enzyme is used to make complementary DNA (cDNA)
reverse transcriptase
what does reverse transcriptase do
makes DNA from RNA
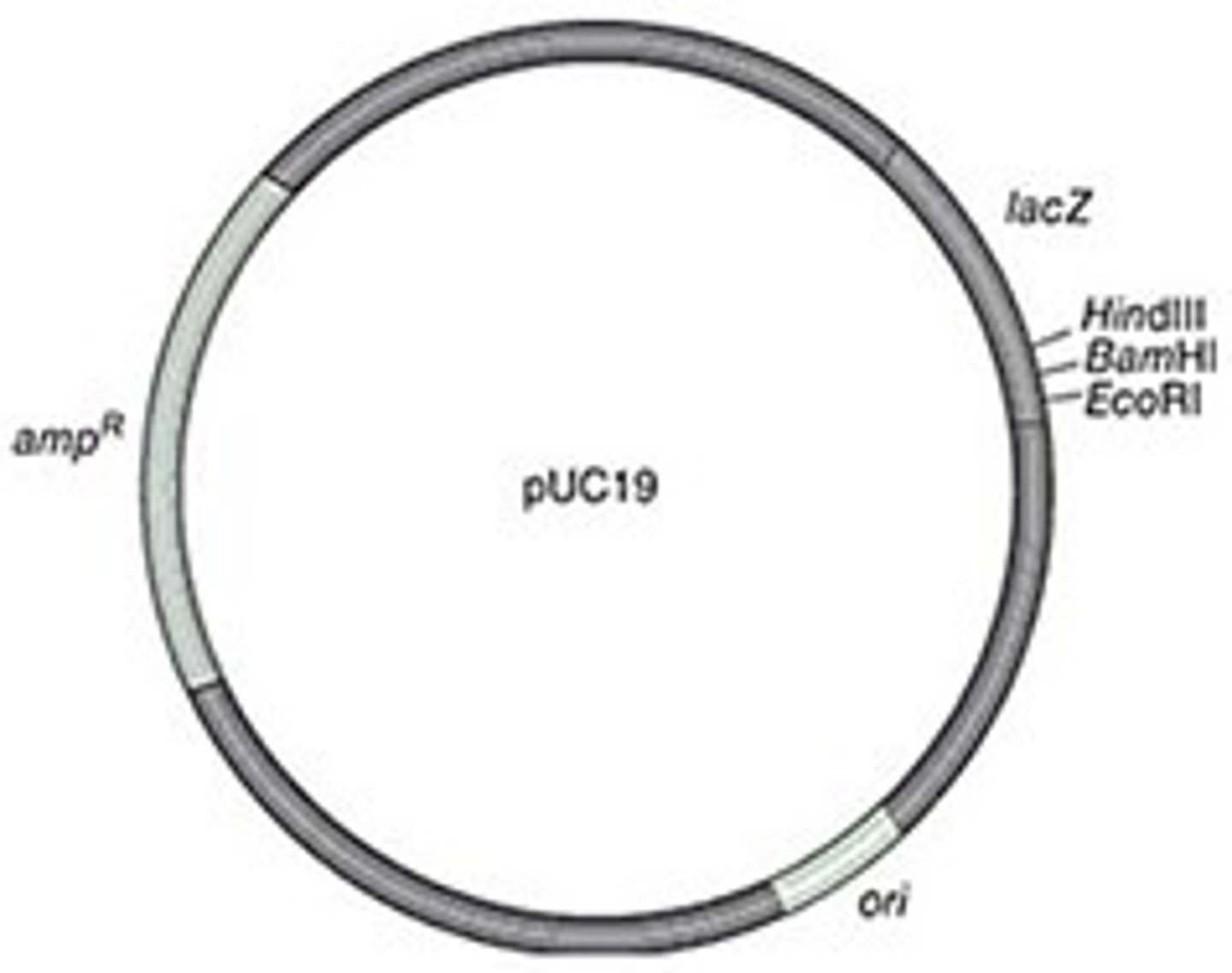
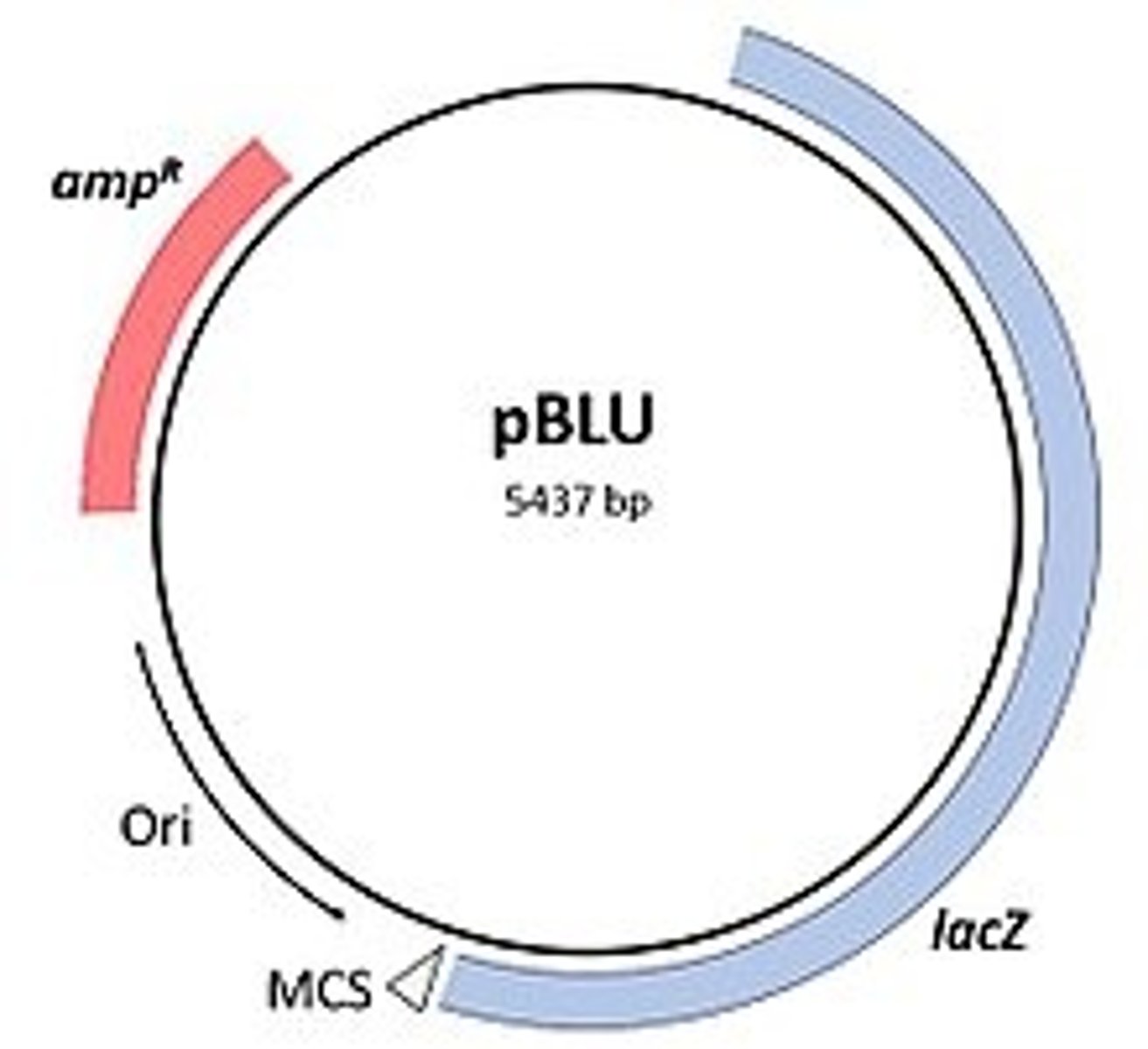
most plasmids/vectors are small and average _________ bp
5000
t/f: plasmids do not occur naturally and are synthesized in lab
false. they occur naturally in bacteria
what is present in all plasmids that allows for replication
ori= origin of replication
introducing foreign DNA into a host is called
transformation
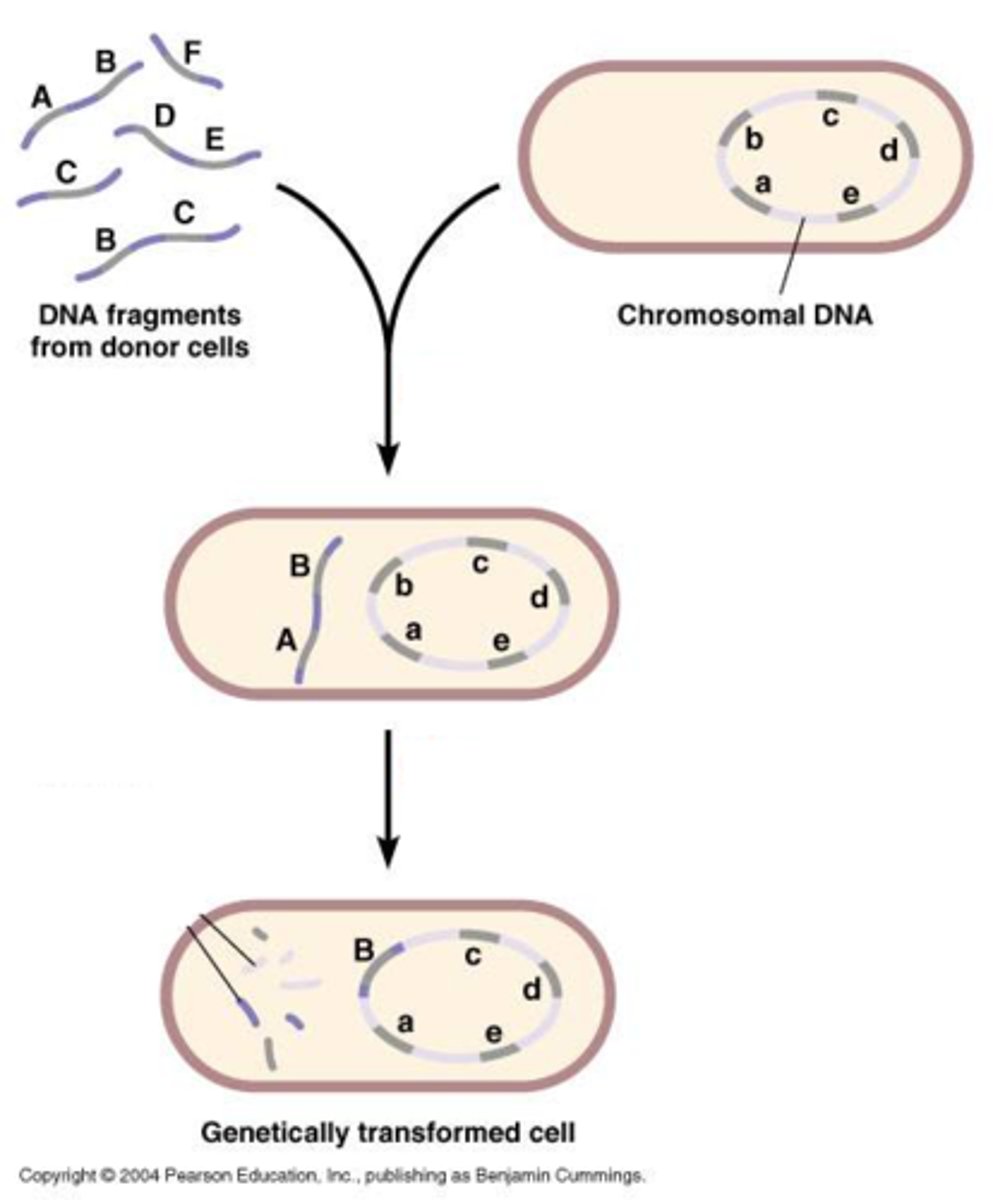
what allows for identification of organisms that have accepted the plasmid
selectable markers (ex: amp resistant genes)
a technique used to transport DNA into a host cell via high-voltage charge
electroporation
explain how selective markers are used to determine if an organism has accepted a plasmid
a plasmid has selective markers like amp or tetra resistance. if an organism picks up this plasmid, they will become resistant and grow in amp. those that did not will die
explain how selective markers are used to select for hosts that have the desired plasmid DNA sequence
1. foreign DNA is introduced in the midst of a selective marker (ex: amp)
2. if the host picked up the plasmid with the foreign DNA, then they will NOT be amp resistant since thats where the DNA is
3. if the host did not pick up the plasmid they will still be amp resistant
separation of DNA in electrophoresis uses what 2 principles
1. electrical charge
2. size of DNA
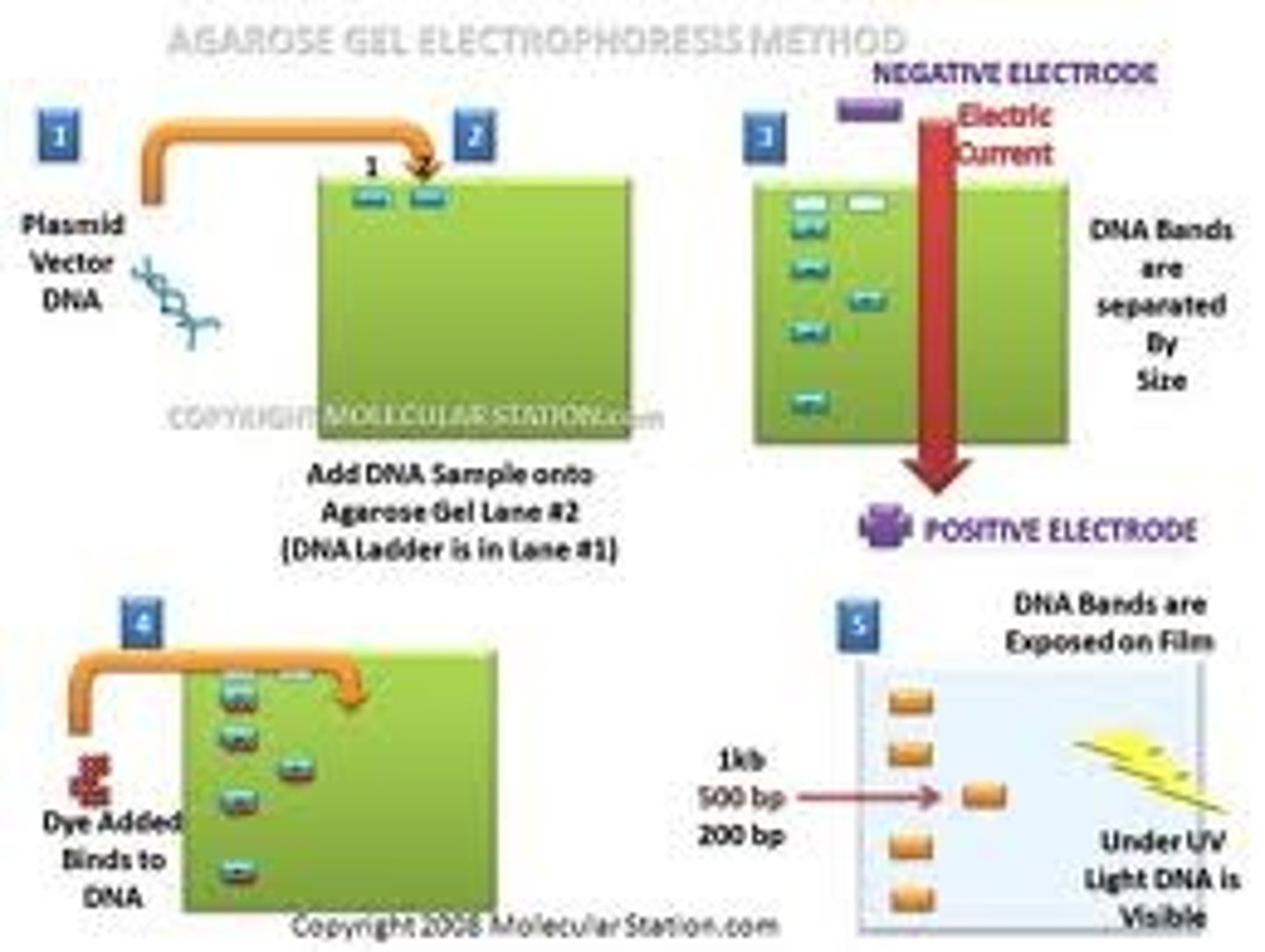
DNA has a _______ charge, allowing it to travel to the _______ end in electrophoresis
DNA= negative
travels to positive end
_________ DNA would travel further in electrophoresis
small
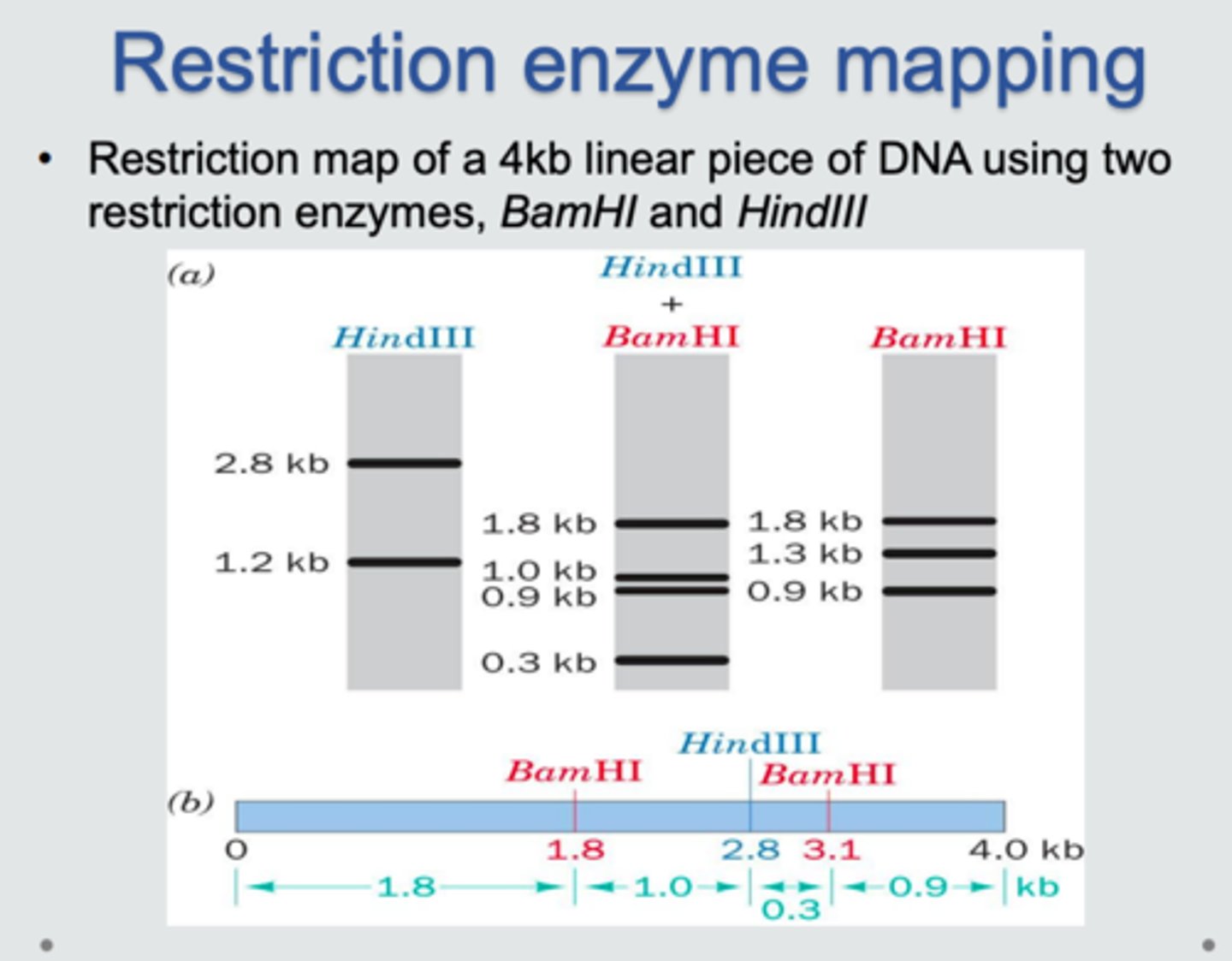
restriction mapping
technique used to determine the locations of restriction enzyme cleavage sites in DNA by analyzing the sizes of resulting fragments after digestion and electrophoresis
t/f: PCR can both amplify and change a DNA sequence
true
t/f: DNA polymerase is able to make a copy of the template strand
FALSE. it makes a copy of the complementary strand
t/f: DNA polymerase reads in the 3-> 5 direction and makes a copy in the 5-> 3 direction
true
what 4 things does PCR require
1. Taq polymerase
2. Template DNA strand
3. Primer (20-30bp)
4. deoxynucleotide triphosphates
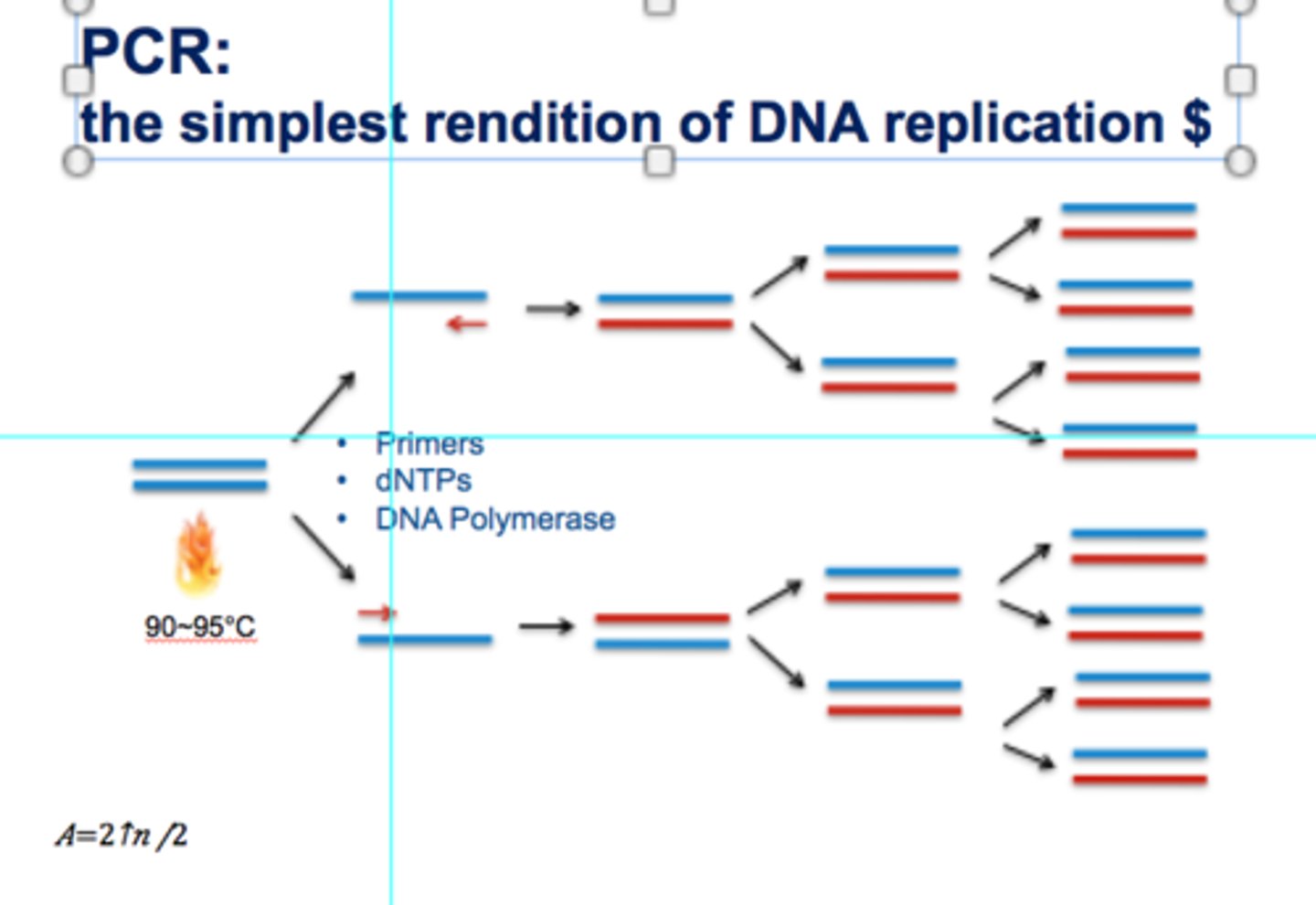
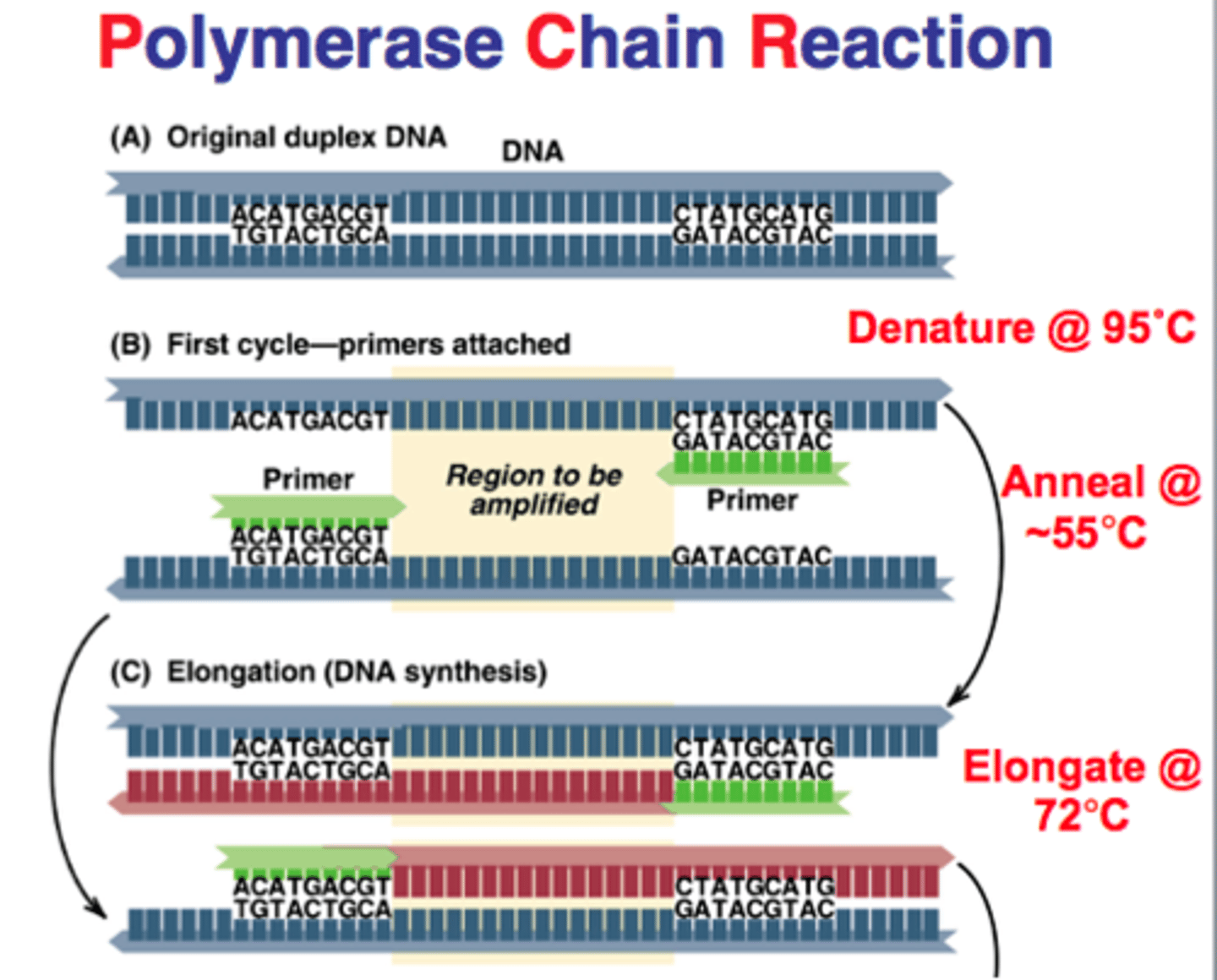
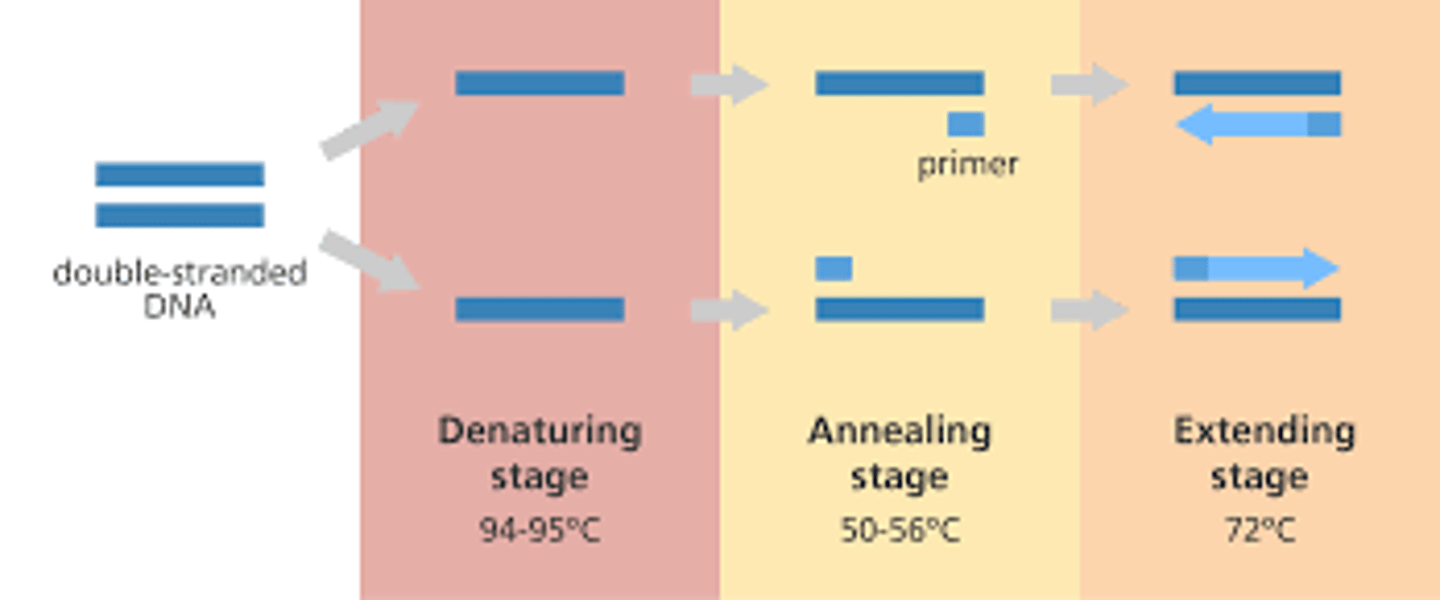
3 steps of PCR
1. Denaturation
2. Annealing
3. Extension
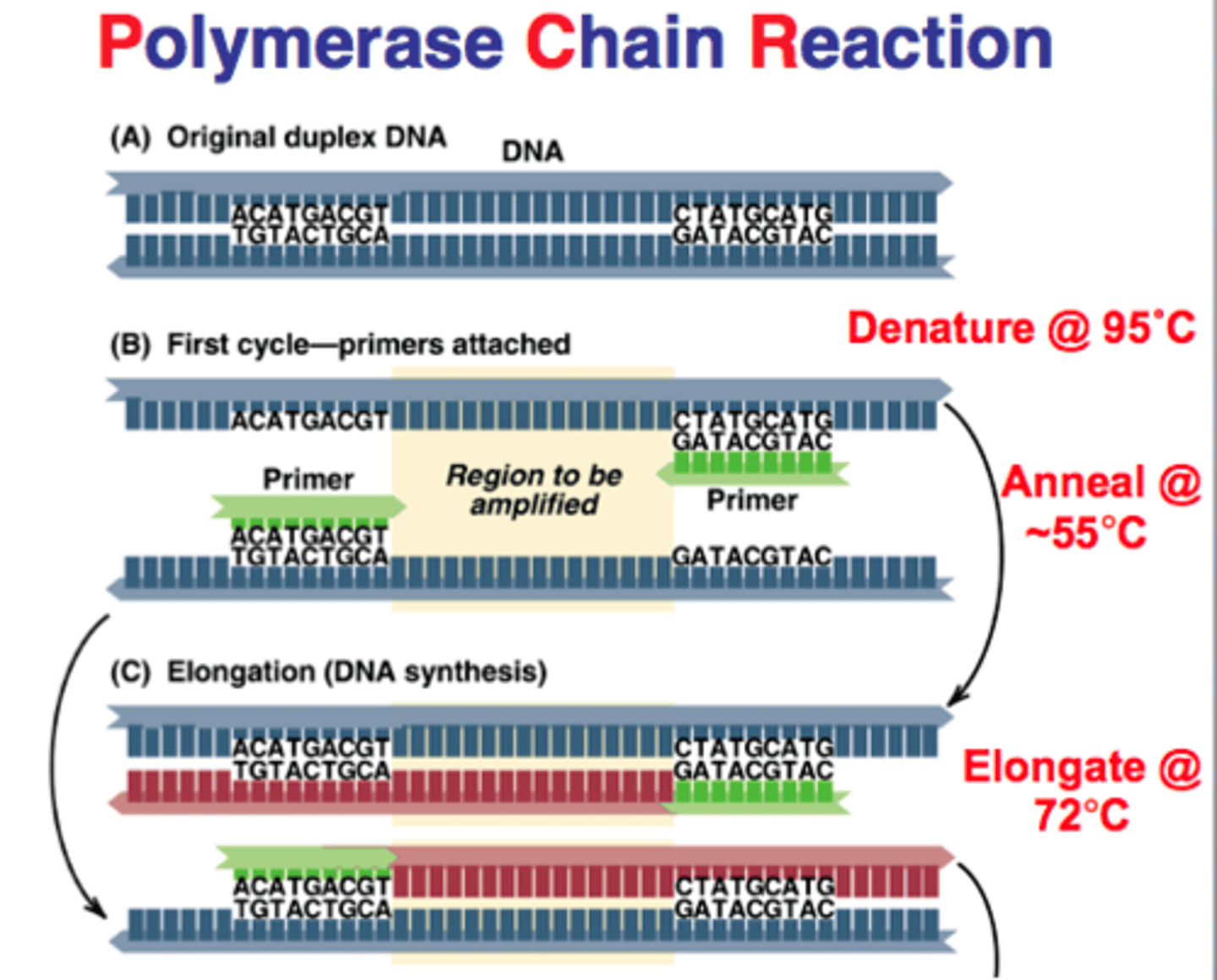
describe what happens during denaturation and annealing in PCR
denaturation= hydrogen bonds btwn 2 dna strands are broken
annealing= formation of hydrogen bonds btwn 2 single strands of DNA
what does Tm represent in PCR
the temp at which half of DNA is annealed (double stranded) and half is denatured (single stranded)
the _________ the Tm, the stronger the 2 pieces of DNA bind to each other
higher
the ________ the Tm, the weaker the 2 pieces of DNA interact with each other
lower
what can contribute to a lower Tm?
1. mismatch between base pairs
2. AT bonds (bc have 2 H bonds while CG have 3)
would DNA with more AT base pairs have a higher or lower Tm than DNA with more CG base pairs
lower Tm bc A:T only has 2 hydrogen bonds= weaker= takes less heat to melt
t/f: in PCR, 2 primers are needed for both strands of DNA
true, 2 primers on 5' ends
why is Taq polymerase used in PCR
it is stable at high temperatures
summarize the PCR process
1. denaturation: heat DNA to separate strands
2. add 2 primers (ssDNA) to 5' end (cool and anneal)
3. Taq polymerase reads 3->5 and makes a strand in the 5->3 direction
repeat
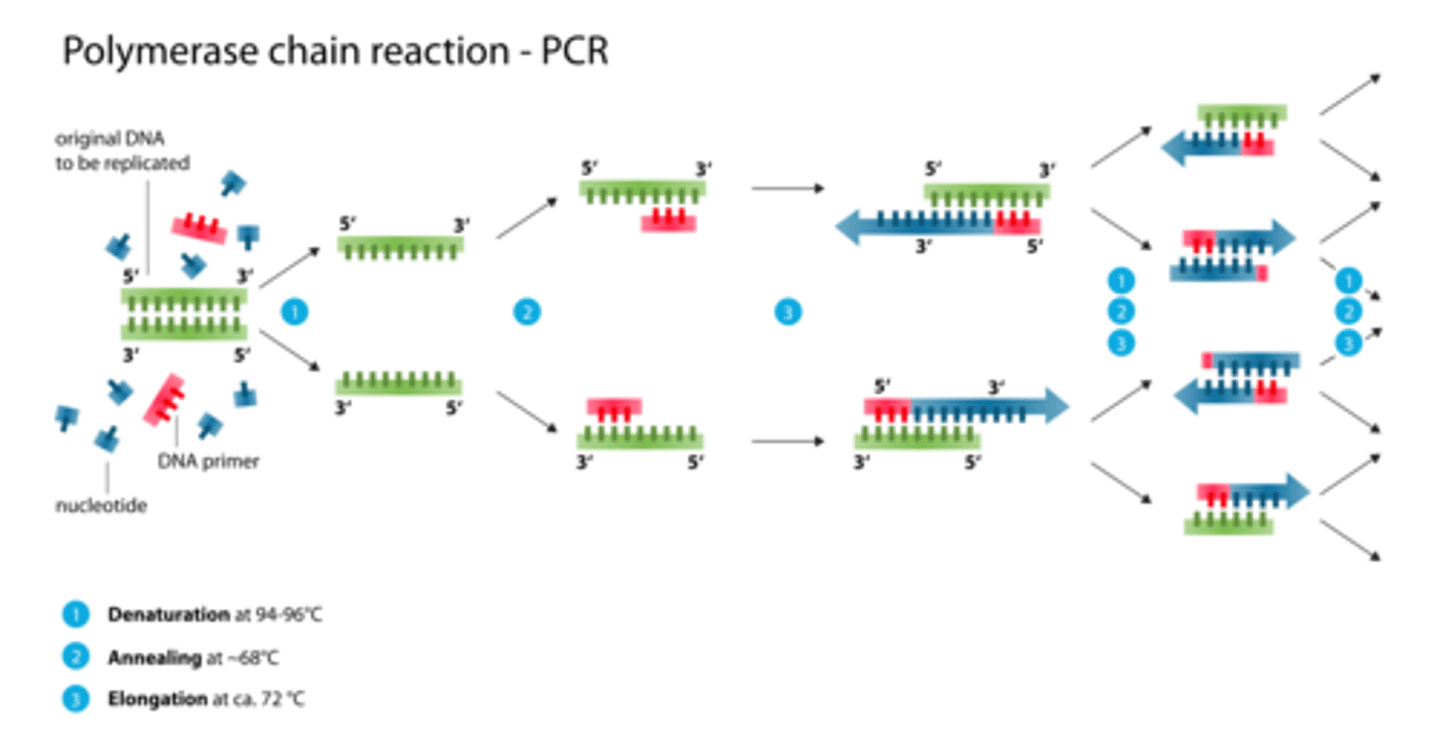
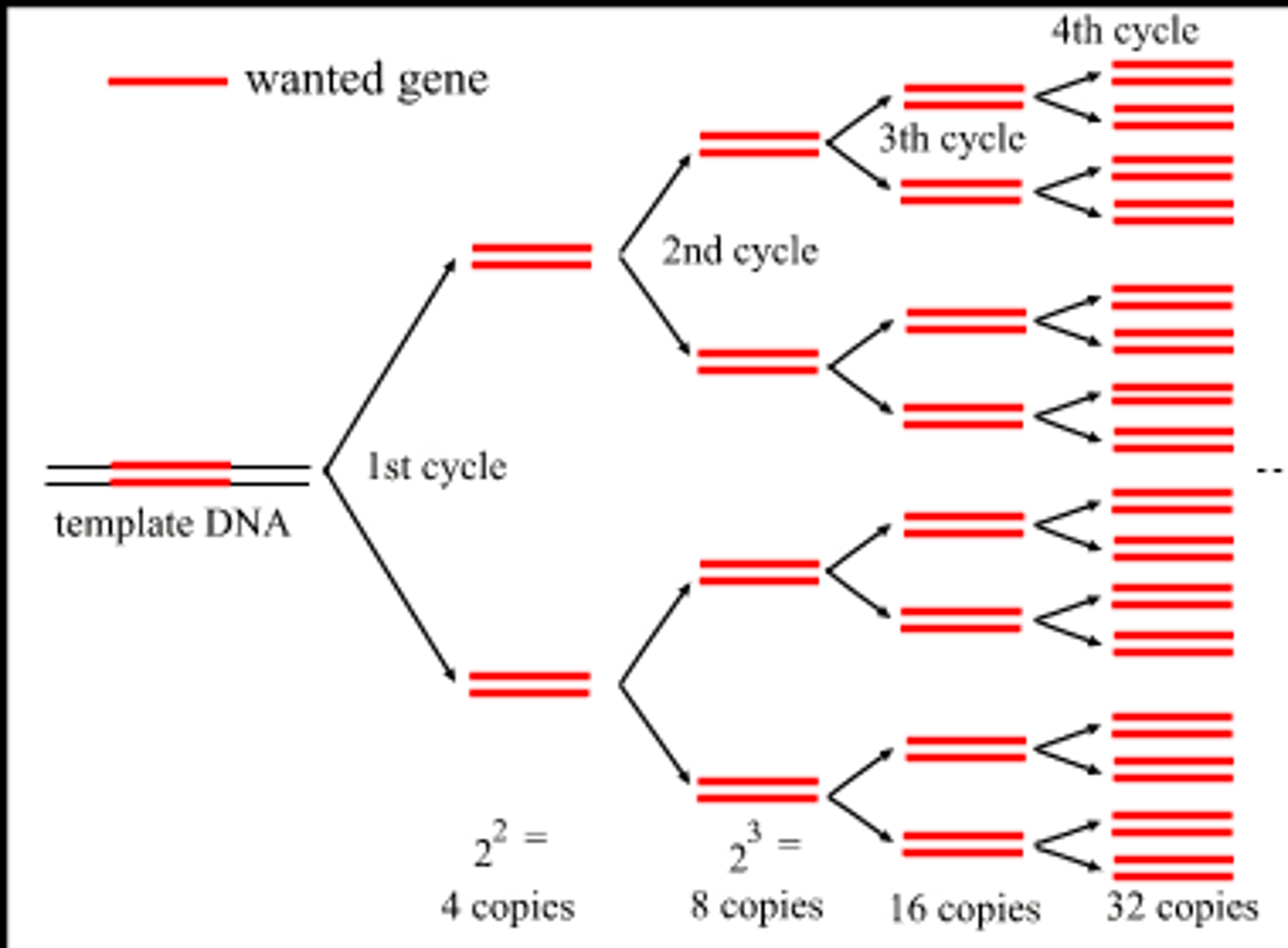
after 20 cycles of PCR, how many copies of target DNA are there?
2^20 = 1 million
do the 2 primers that are added to PCR have the same sequence
no
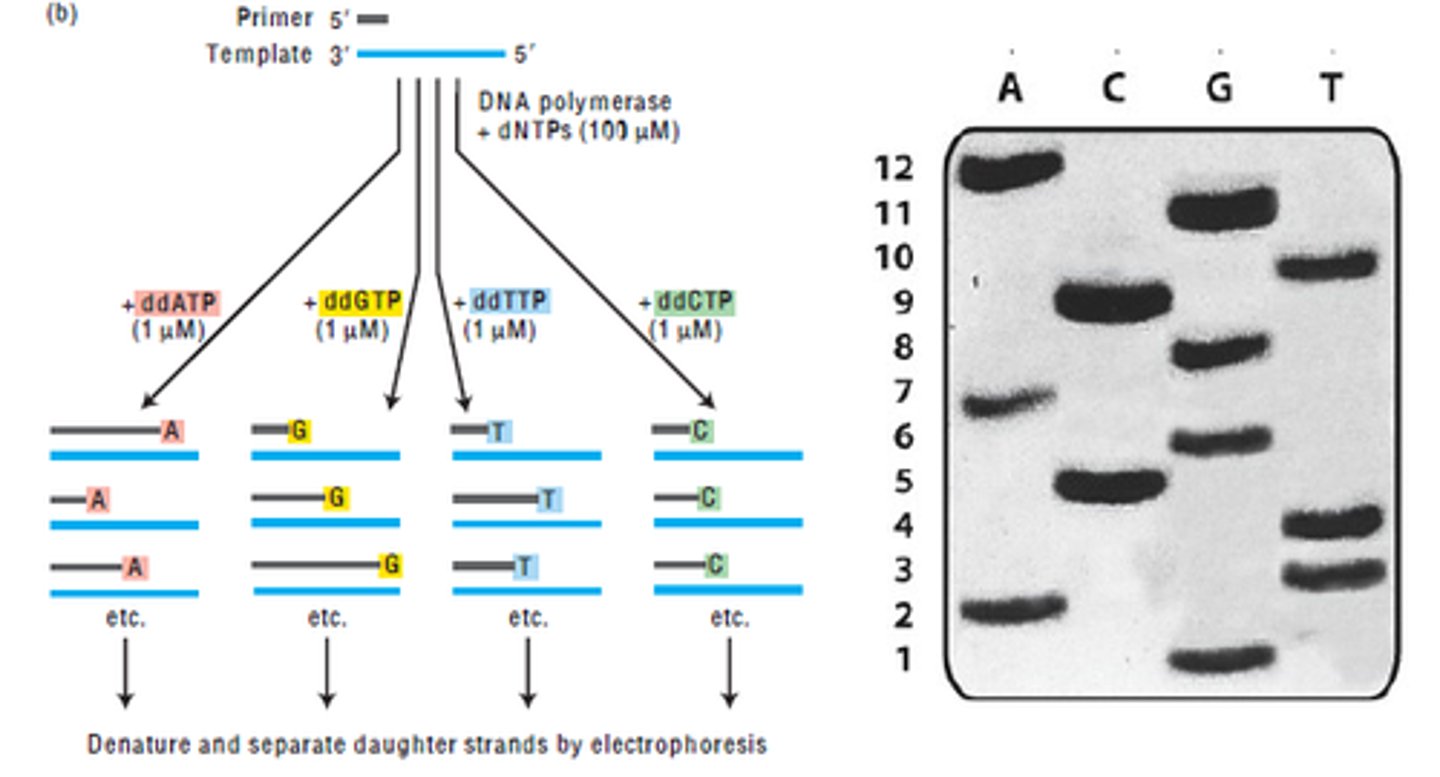
what nucleotide is used in DNA sequencing
dideoxy nucleotides (ddNTP)
4 other uses of PCR besides amplification
1. introduce restriction enzyme sites into DNA
2. quantitate the amount of DNA
3. mutate DNA
4. screen material for desired gene
why are dideoxy nucleotides used in DNA sequencing
they lack a hydroxyl group at the 3' position, therefore they cannot bond to form nucleic acid (they
mark end)
what happens when ddNTP is added in place of a nucleotide in DNA sequencing
it acts as a cap and no further nucleotides are added (synthesis stops)
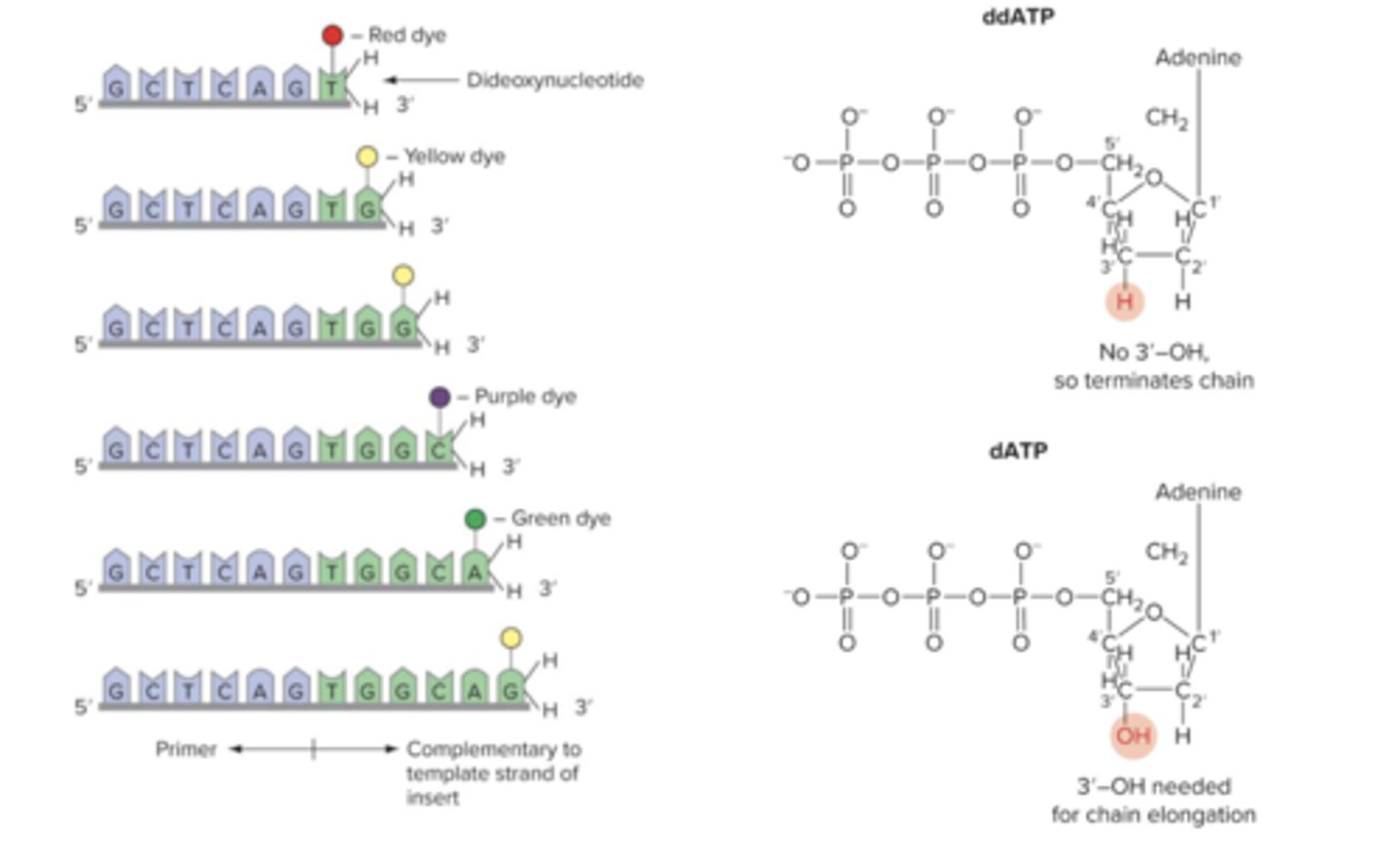
what will happen if some ddNTP is added along with all other nucleotides?
a full DNA strand is produced and a partial strand with the ddNTP cap is produced
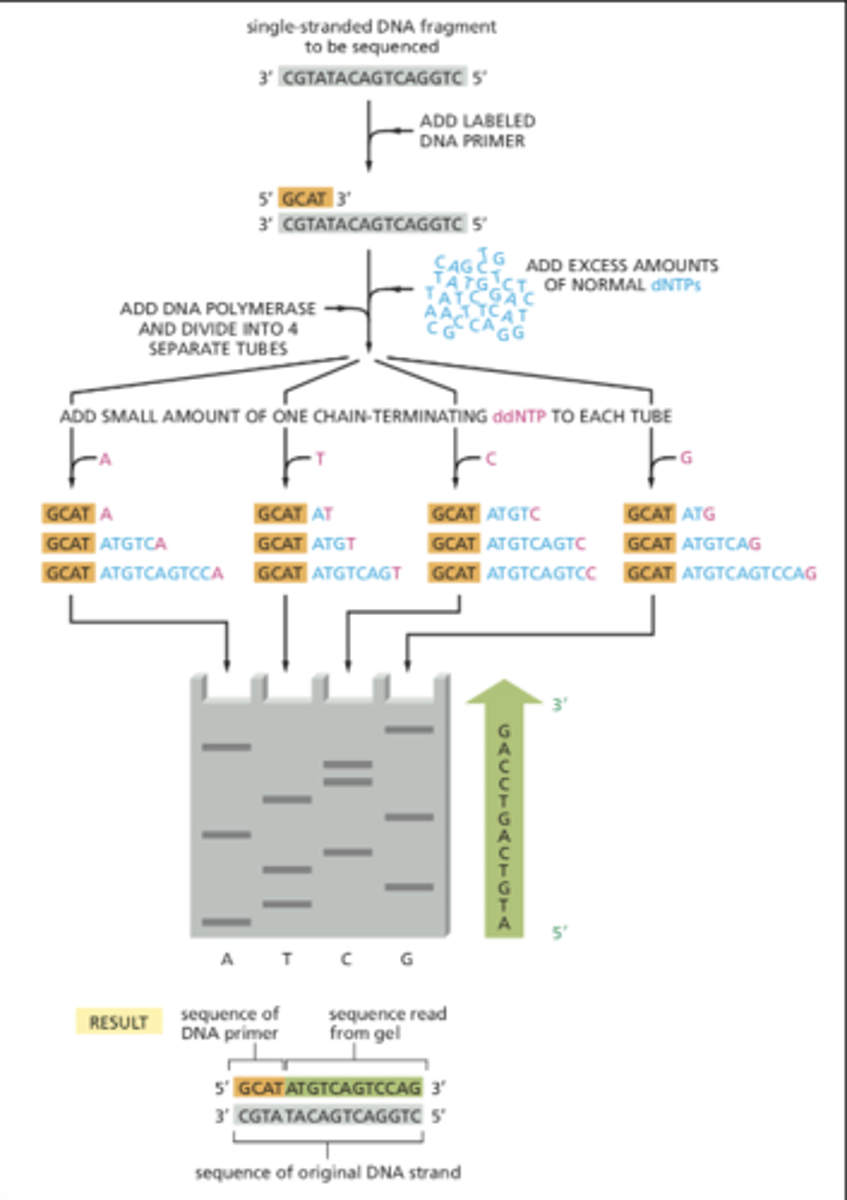
t/f: in dna sequencing, the strand that ddNTP caps is the template strand
false. that is complement. electrophoresis will give sequence of complementary strand (must be converted to get template)
in dna sequencing, electrophoresis will have _________ at the bottom
5' end (bc it is shortest, travels furthest)
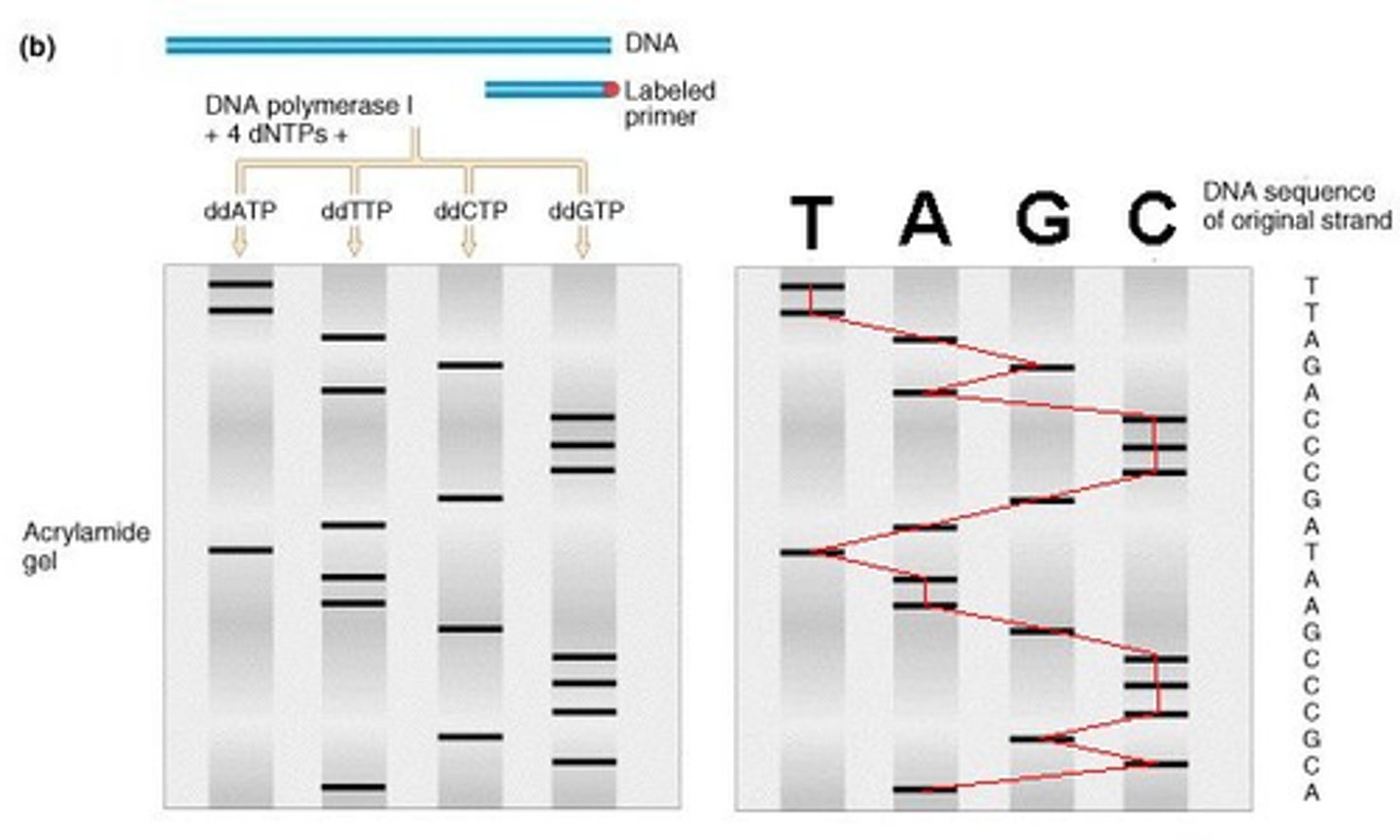
is the nucleotide sequence produced in electrophoresis the template or complement strand (in dna sequencing)
complement! it must be converted to get og template strand
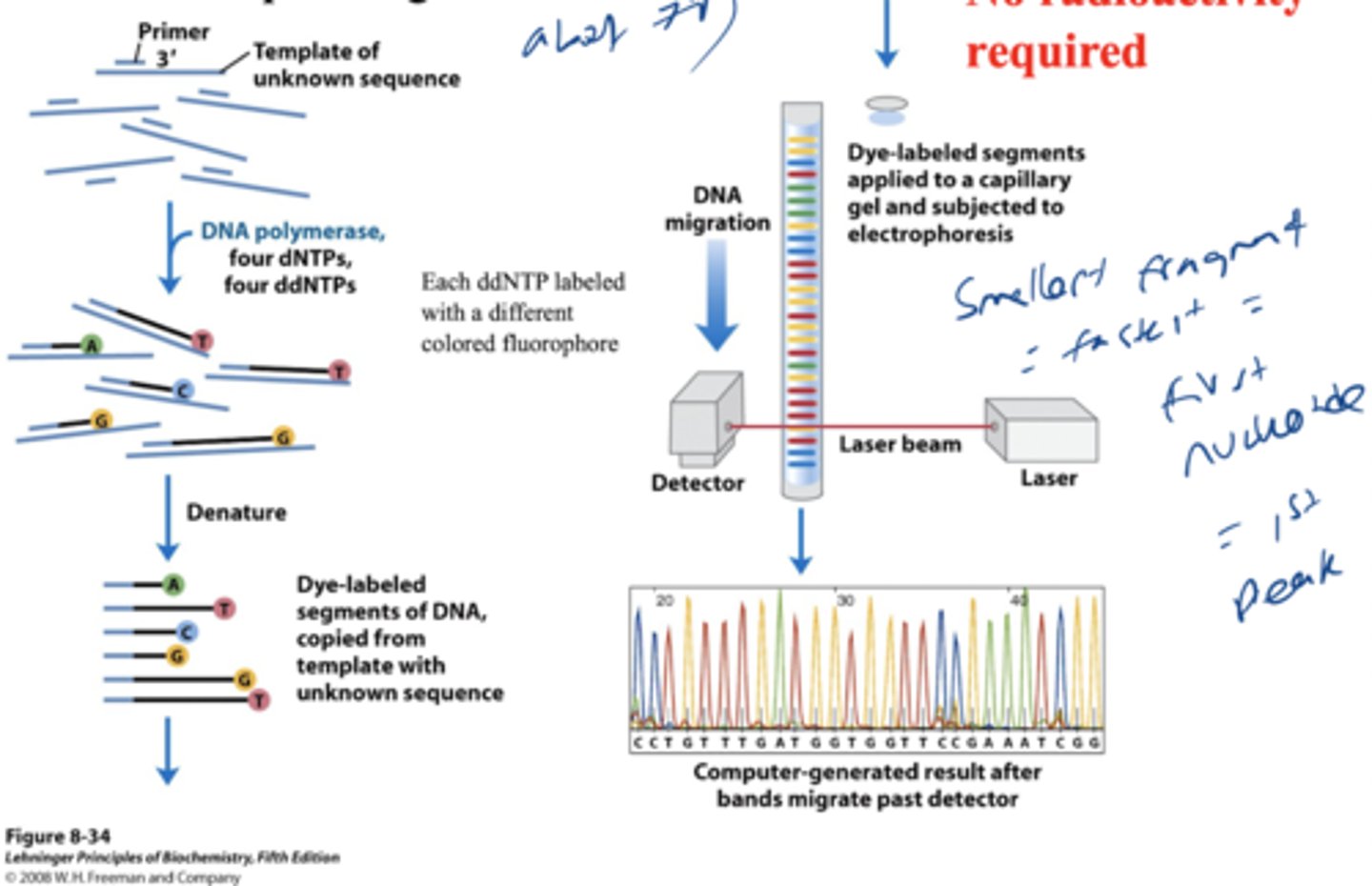
describe modern DNA sequencing
each ddNTP is color coded and run in electrophoresis
explain how to calculate melting temp of a DNA strand
A:T pair = 2 degrees celsius
G:C pair= 4 degrees celsius
count total pairs in sequence
ex: calculate the Tm of the following strand: ATGGC
AT pair= 2C
CG pair= 4C
ATGGC= 2+2+4+4+4= 16 degrees celsius