2.4 - Nuclear Model
1/51
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
52 Terms
The theory of atomic structure is known as
The Nuclear Model
What does this model suggest?
That the atom consists of:
a very small and extremely dense region called the nucleus; and
a cloud of negative electrically charged particles surrounding the nucleus at a distance
The nucleus is _________ when compared to the rest of the whole atom
very small
What does this model also suggest?
That the atom consists of three smaller sub-atomic particles
What are these sub-atomic particles?
Protons, Neutrons and Electrons
Since these particles are extremely small and light, and therefore cannot be measured in grams, what is used instead
atomic mass units (amu)
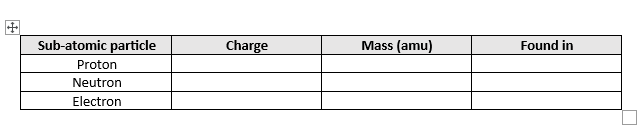
Fill in this table
In more detail, explain where and how electrons are found.
Electrons are found moving at a very high speed around the nucleus
Electrons exist in different shells; each shell has a different amount of energy, increasing moving away from the nucleus
How are the electrons held within the atom?
By an electrostatic force of attraction towards the positive charge of the protons in the nucleus
What does the atomic number of an element represent?
The number of protons
Can different elements have the same atomic number
No
Therefore…
the no. of protons in an atom (atomic no.) gives identity to the atom
Why is the no. of protons equal to the number of neutrons
because the atom is neutral and has no overall electric charge
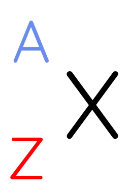
In this shorthand notation, which letter represents the atomic number
Z (Z is the symbol given for atomic number)
What is the mass number of an atom
the number of protons and neutrons in the nucleus
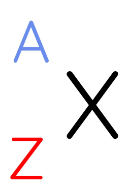
in the shorthand notation, which is the symbol for mass number
A
What is the mass number also referred to as
the nucleon number
so the mass number (A) = ….
mass number (A) = number of protons (Z) + number of neutrons (N)
So, if you have the atomic number (no of protons - Z) and you have the mass number (no of protons + neutrons - A), how do you find just the number of neutrons
you subtract the atomic number from the mass number
no of neutrons (N) = mass number (A) - atomic number (Z)
And how would you find the number of electrons in an atom?
The number of electrons is equal to the number of electrons
so whatever the atomic number is, the electron number is
Electrons are arranged in sets of ____ or ____
energy levels or shells
These shells can accept
a limited number of electrons
The first shell can take
up to 2 electrons
The second shell can take
up to 8 electrons
The third shell can take
up to 8 electrons
The way electrons are arranged in an atom is called the
electron configuration (or electron structure)
so lets take carbon as an example, its atomic number is 6 - find its electron configuration
6 protons = 6 electrons
2, 4
The horizontal rows in the periodic table are known as
periods
what does the period number tell us
the number of shells present in an atom
examples?
period 1 - hydrogen and helium = 1 electron shell
period 2 - lithium, neon.. = 2 electron shells
period 3 - sodium, argon.. = 3 electron shells
the vertical columns are known as
groups
elements in the same group have the same
number of electrons in their outer shell
explain
All elements in group 1 have 1 electron in their outermost shell
All elements in group 2 have 2 electrons in their outermost shell
….
What about noble gases
Noble gases, found in group 8 or 0 have a full outer shell (2 or 8)
Sine elements in the same group have the same number of electrons in their outer shell
they have similar chemical properties
What about hydrogen, does it share the same properties as the group 1 elements
No, it does not - ideally hydrogen should be placed on its own
What are isotopes
Isotopes are atoms of the same element with the same number of protons, but different number of neutrons
so in some elements the atoms are not identical
yes
What is the same about isotopes and what is different
Isotopes have the same chemical properties because they have the same electronic structure/ configuration
Isotopes have different physical properties (e.g. density) due to more or less neutrons
Why are some isotopes of certain atoms unstable/ said to be radioactive
because of the extra number of neutrons
How were isotopes discovered
using a mass spectrometer
What does the detector in this instrument measure
how many isotopes are present and also the percentage abundance
What is the relative abundance of an isotope
the proportion of one particular isotope in a mixture of isotopes found in nature
e.g. 75% of chlorine atoms are Cl-35 while 25% are Cl-37
The average mass of a large number of atoms of an element is called the
Relative atomic mass (RAM or Ar)
What does this quantity consider
the percentage abundance of all the isotopes of an element which exist
Define RAM
Relative atomic mass is defined as the average mass of isotopes of an element compared to
1/12 th of the mass of an atom of 12C
Formula for RAM

When actually working out the RAM, why is there no need to put the bottom part of the formula
because 1/12th of the mass of 1 carbon-12 atom = 1 amu
For compound what two terms are used
Relative molecular mass (RMM)
Relative formula mass (RFM)
Which is used for what?
Relative molecular mass (RMM) - Covalently bonded substances (non-metals)
Relative formula mass (RFM) - Ionically bonded substances (metals and non-metals)
Why do RAM, RMM and RFM have no units
because they are a comparison of masses
DO PRACTICE PROBLEMS!!
yes sir 😉