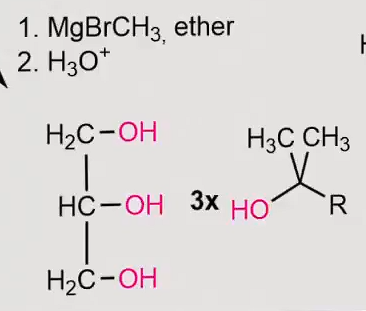
Org 2 reactant to product
1/43
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
44 Terms
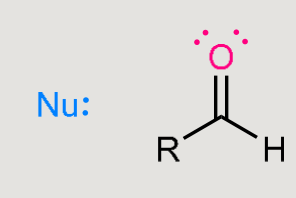
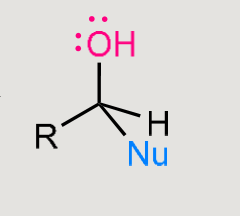
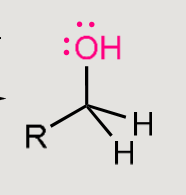
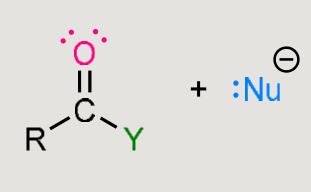
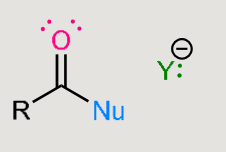
A nucleophilic addition reaction
Nucleophile adds to the carbonyl carbon.
Carbonyl is converted into an alcohol.
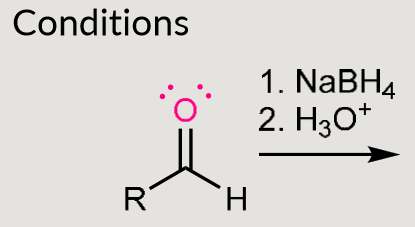
Hydride addition, what acts as H donor?
NaBH4 or LiAlH4
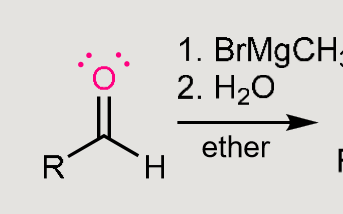
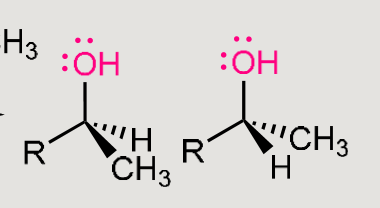
Grignard reaction
You always need H3CMgBr
which forms H3C:-and +MgBr
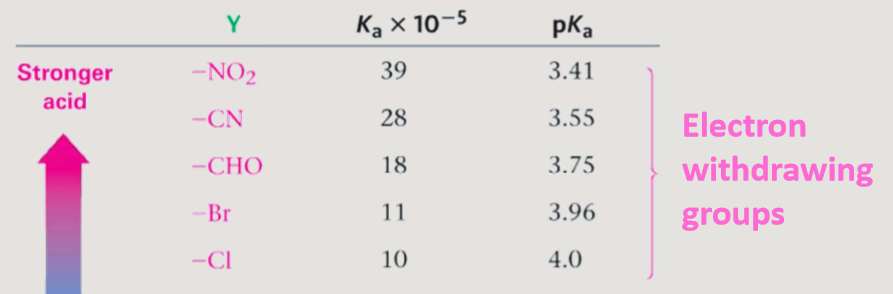
Electron withdrawing groups
pull electron density away from the carboxyl group. This increases the positive charge on the carbonyl carbon, making the molecule more electrophilic and increasing its acidity.
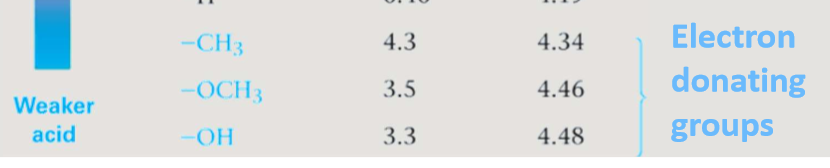
Electron donating groups
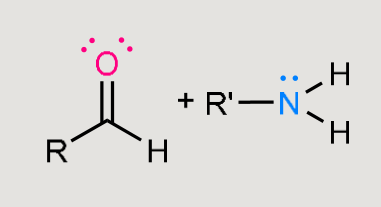
What does this form under mildly acidic conditions?
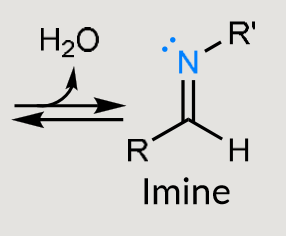
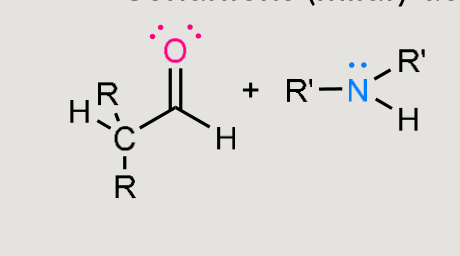
What does this form under mildly acidic conditions?
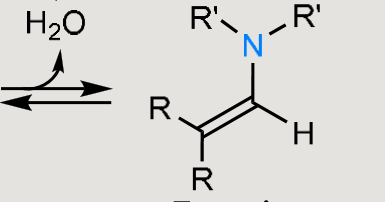
What does this form under basic or acidic conditions?
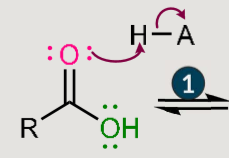
Fischer esterification: what does it reasult in? and when does it happen?
Reactants: The reaction happens when a carboxylic acid is treated with an alcohol.
• Catalyst: It requires acidic conditions to proceed
Formation: carboxylic acid + alcohol → ester
Hydrolysis: ester + water → carboxylic acid + alcohol
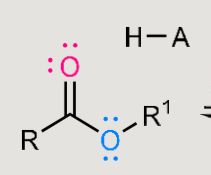
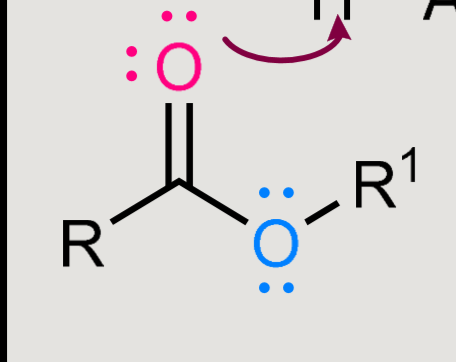
What does this form when reacted in an acidic environment?
Formation: carboxylic acid + alcohol → ester
Hydrolysis: ester + water → carboxylic acid + alcohol
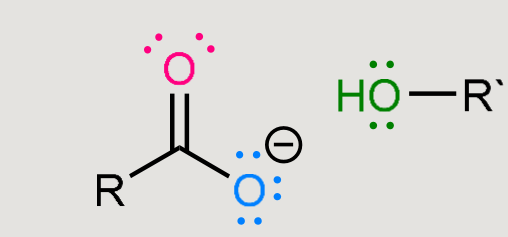
Ester hydrolysis
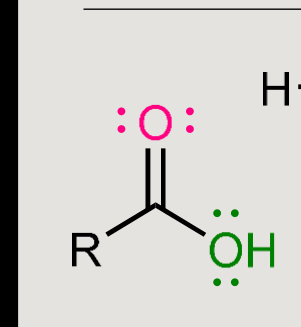
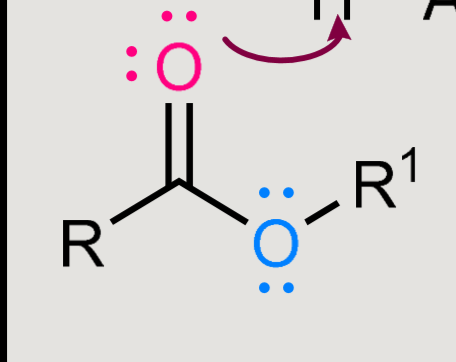
What does this form when reacted in a basic environment?
Saponification
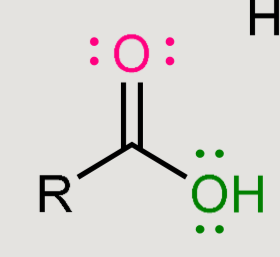
What does this form when reacted in an acidic environment?
Amide hydrolysis
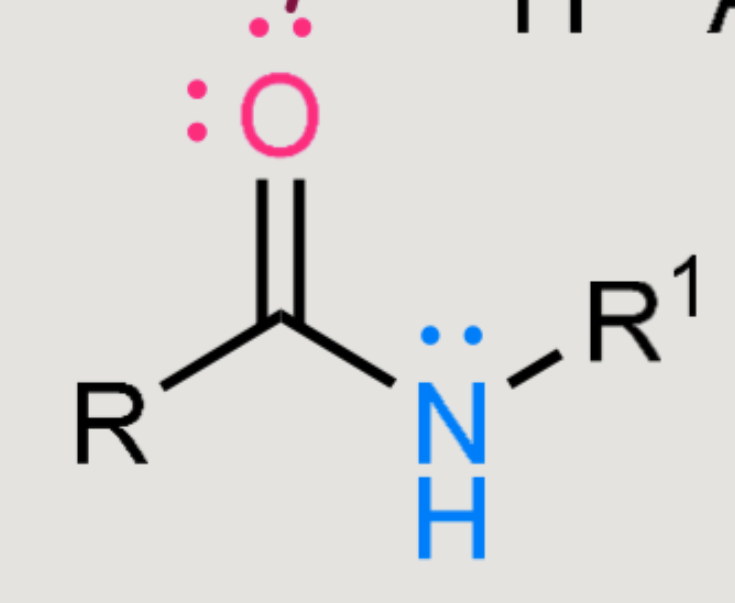
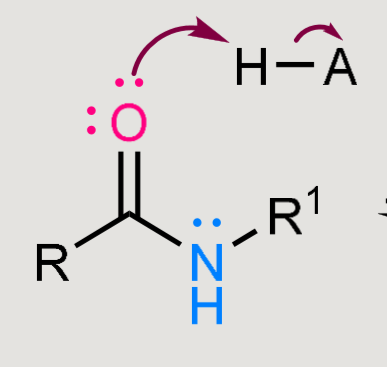
What does this form when reacted in a basic environment?
Amide hydrolysis
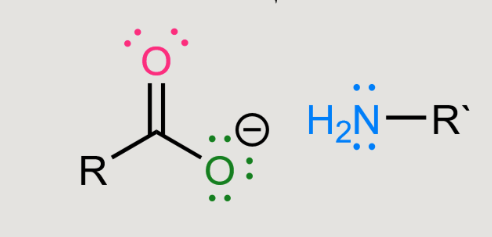
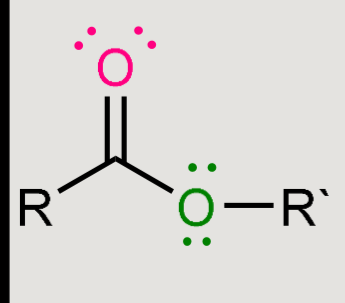
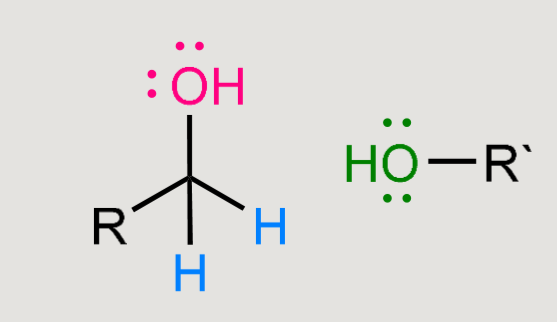
What does a reaction of this with LiAlH4 cause?
Reduction
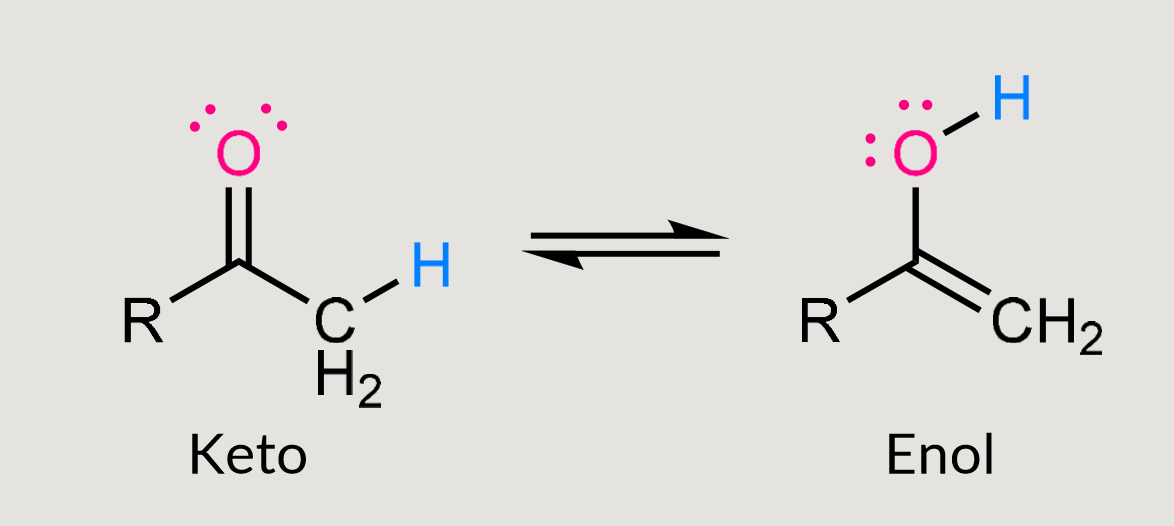
what’s keto–enol tautomerization
when a molecule switches back and forth between two forms:
the keto form (has a C=O carbonyl)
the enol form (has a C=C double bond and an –OH)
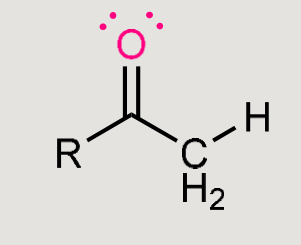
What does this form when it reacts in basic conditions?
Aldol product
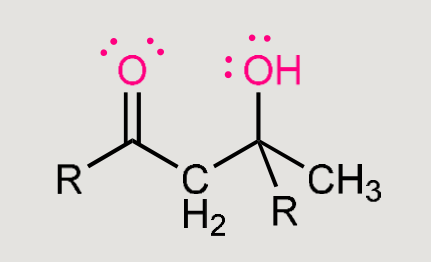
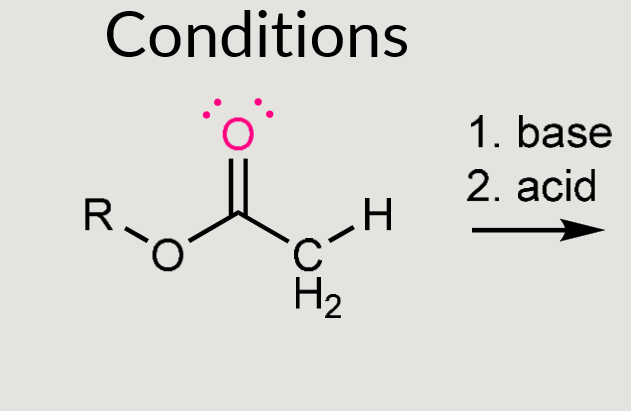
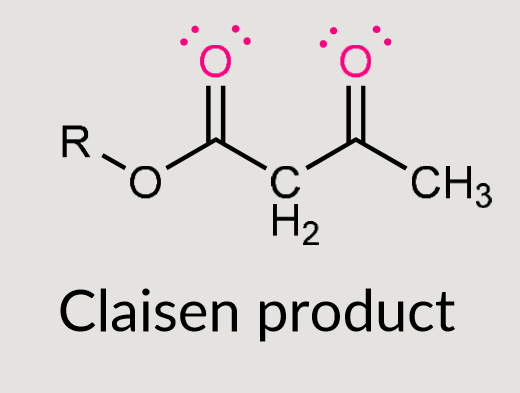
What does this reaction form?
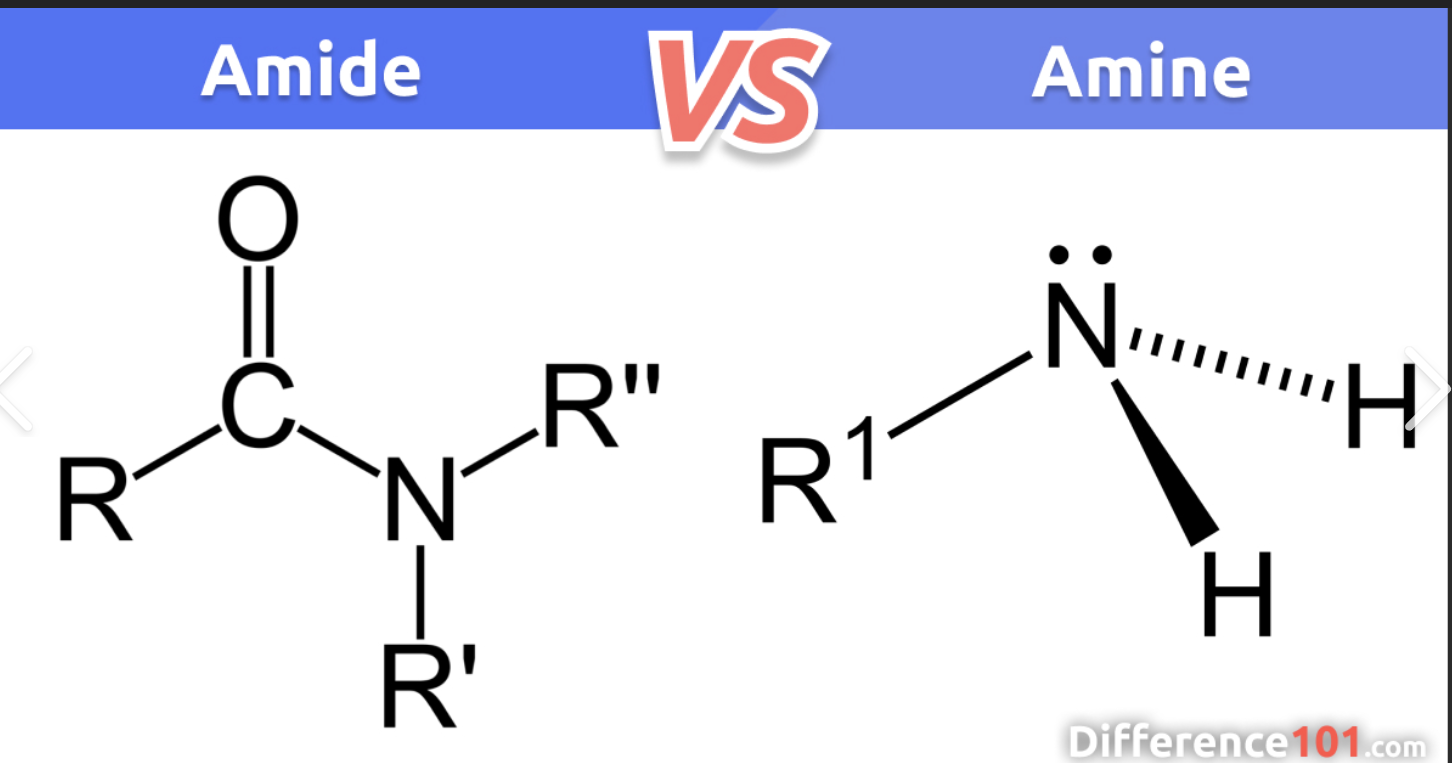
Amide vs amine, what is the difference between them?
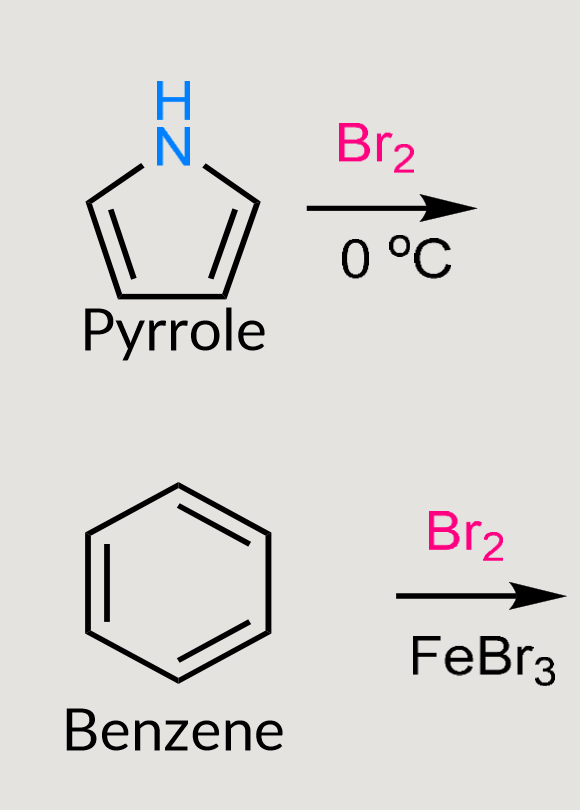
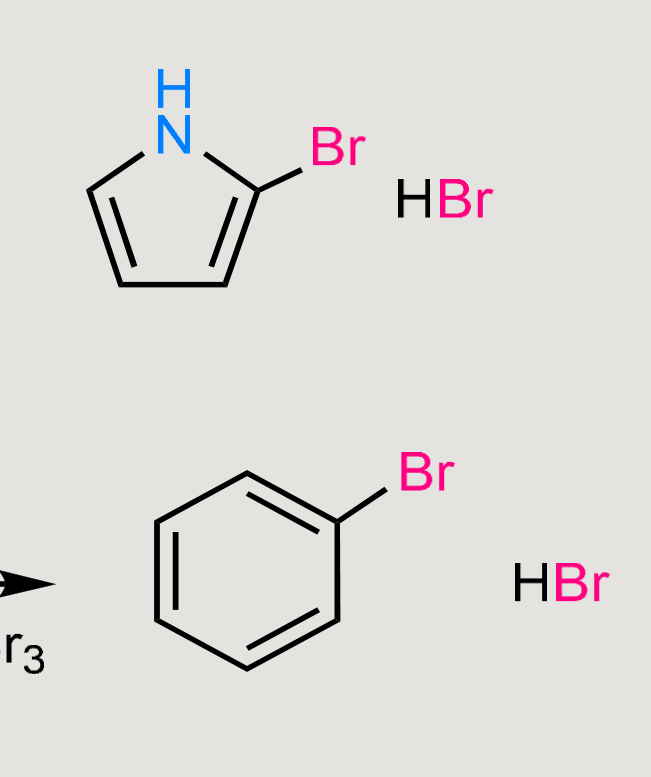
What would these reactions form?
Electrophilic substitution
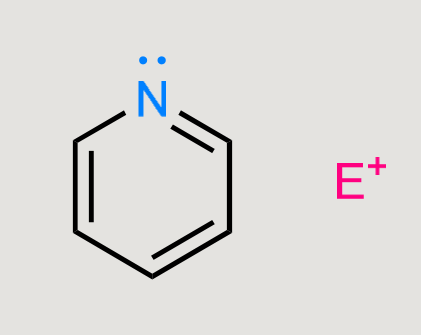
What would this form?
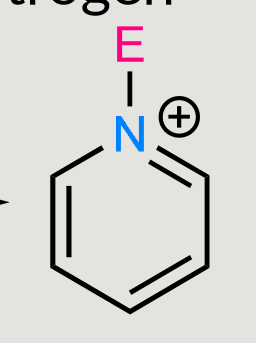
Substitution on nitrogen
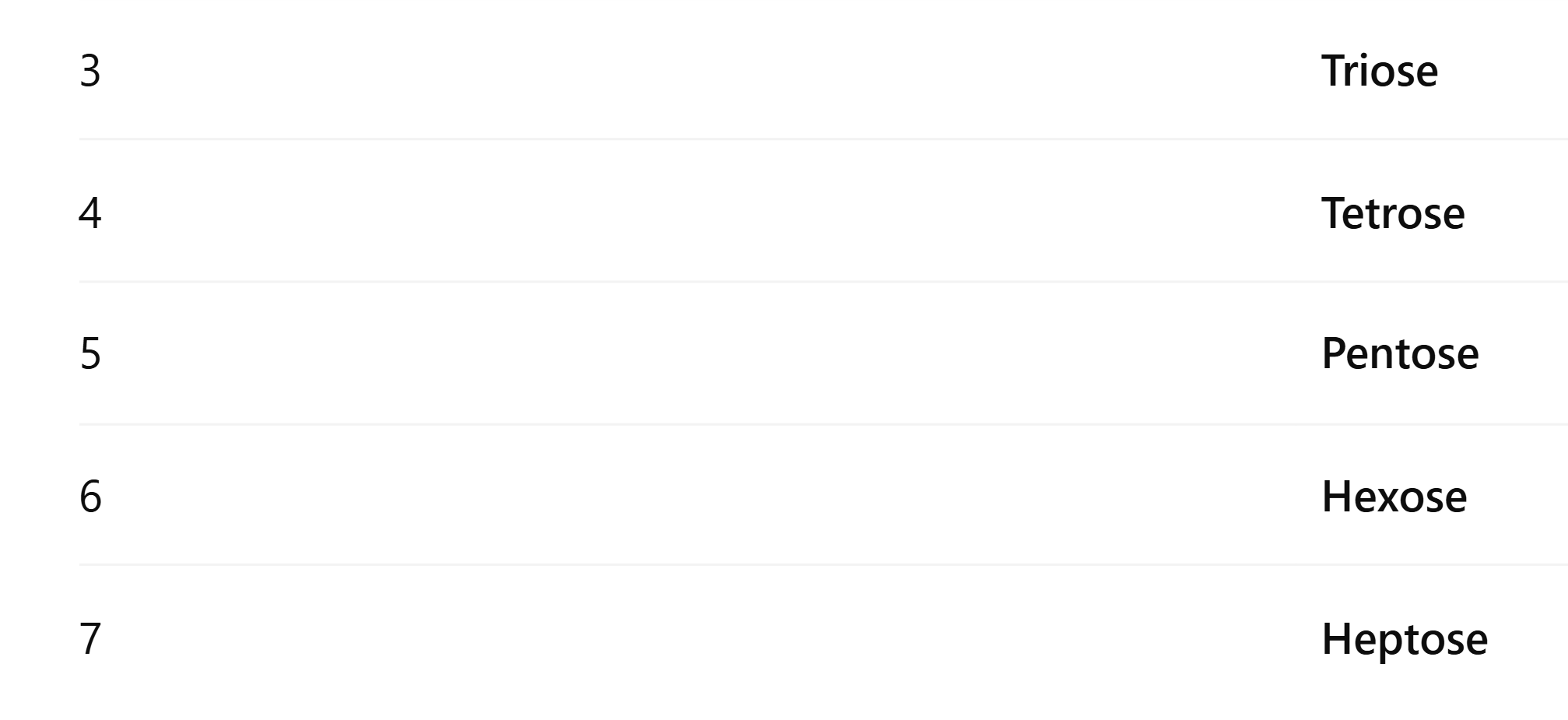
Monosaccharides naming system through how many carbon atoms they have
epimers
types of diastereomers that differ at only one chirality centre
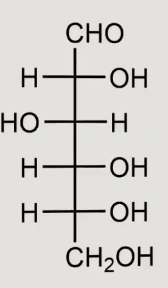
what structure is this:
D-glucose
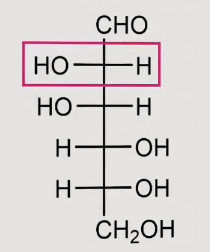
What structure is this
D-mannose
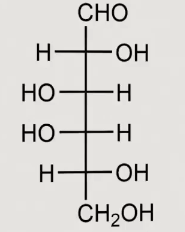
What structure is this
D-galactose
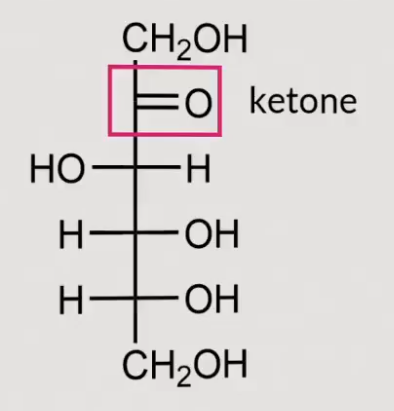
What structure is this:
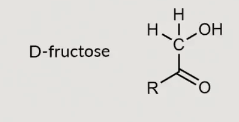
D-fructose
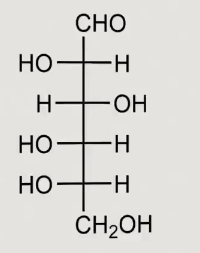
What structure is this
L-glucose
Hoes does the naming of D and L work?
Dependent on the 5th carbon
If OH points to the right its a D
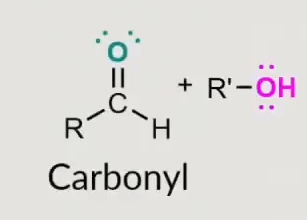
What does this form?
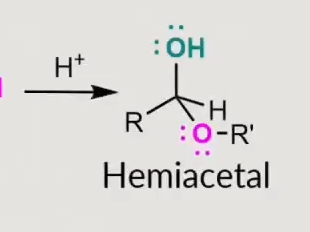
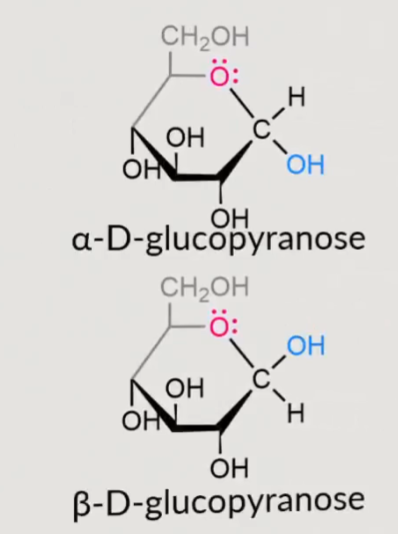
how to identify if its an alpha or beta sugar?
a on the bottom for alpha and b on the bottom for beta
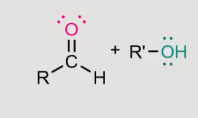
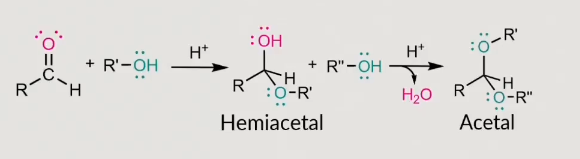
how does this to an acetyl form?
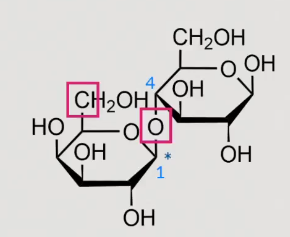
What is this?
lactose
beta 1,4 linkage
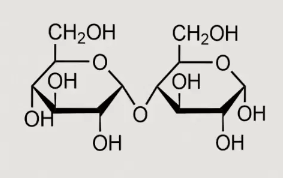
What is this?
Maltose alpha 1,4 linkage
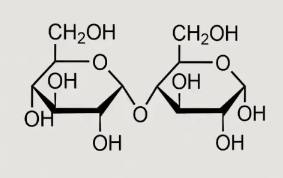
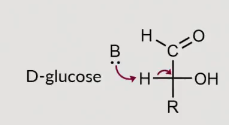
What can this reaction form?
D fructose
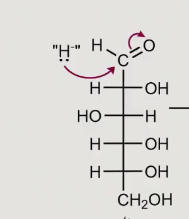
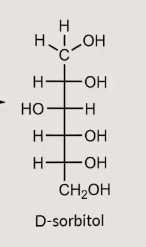
What does reduction of a sugar form?
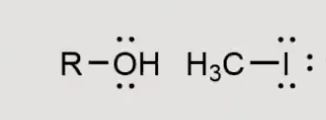
What will this form? with silver as a reaction
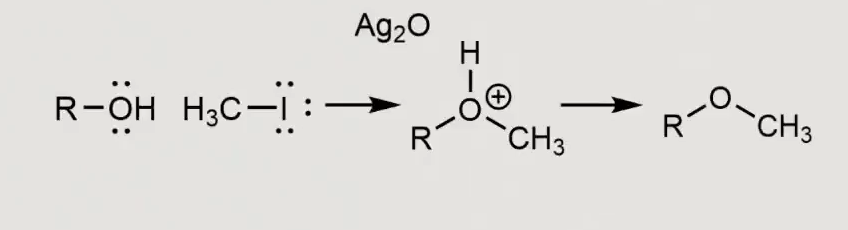
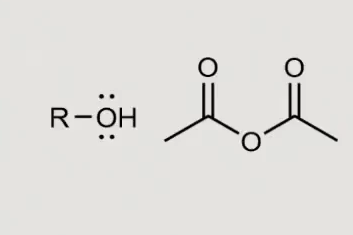
what would this form in the presence of a pyradine?
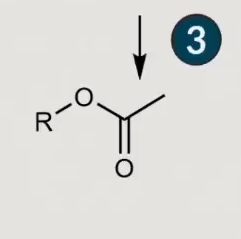
What is a lipid?
Everything that dissolves in a non polar solvent
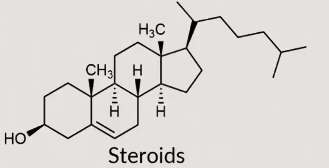
Steroids
Large complex molecules built from multiple cyclic hydrocarbon chains
functions as signaling molecules
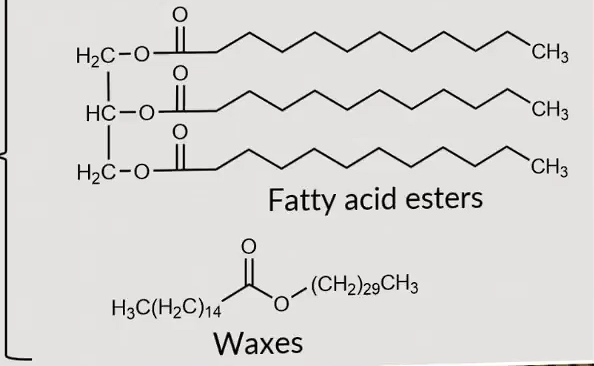
Waxes vs fatty acids?
waxes only have one ester functionality with long carbon chains on both sides where as fatty acid chains have 3 ester bonds and 3 long hydrocarbon chains (eve numbered)
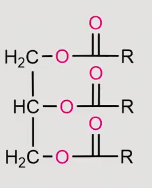
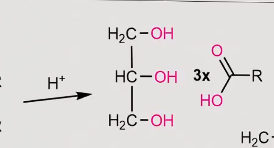
reaction of a fatty acid under acidic conditions
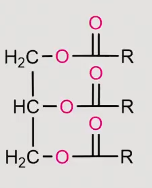
reaction of a fatty acid under basic conditions
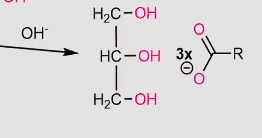
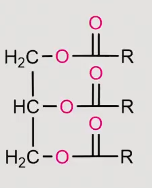
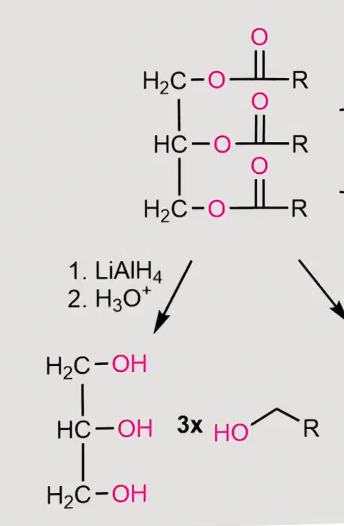
reaction of a fatty acid when reacted with reducing agents
S
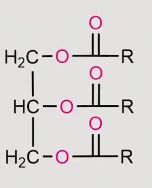
reaction of a fatty acid with Grignard reagents