BIOL 1113 (General Biology 2) Exam 3 Mary Susan Potts Santone
1/132
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
133 Terms
Plant
Multicellular photosynthetic eukaryotic organism
Apical meristem
Group of actively diving cells at the growing tip
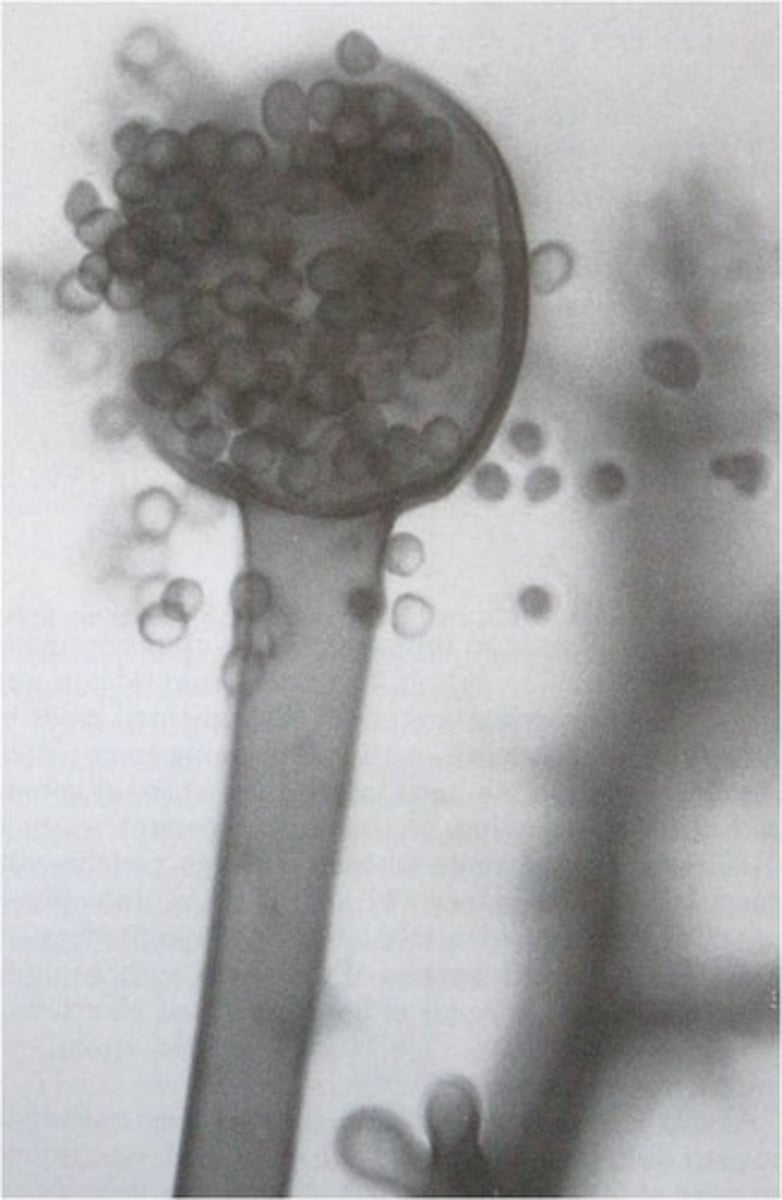
Spore
Haploid reproductive structure of plants that is dispersed into the environment and is able to grow into a plant gametophyte in suitable habitat

Nine phyla of (living) plants
Liverworts, mosses, hornworts, lycophytes, pteridophytes, cycads, ginkgos, conifers, and angiosperms (flowering plants), make up what?
Bryophytes
Liverworts, mosses and hornworts make up this group of nonvascular land plants; dominant generation is their life cycle are gametophytes;
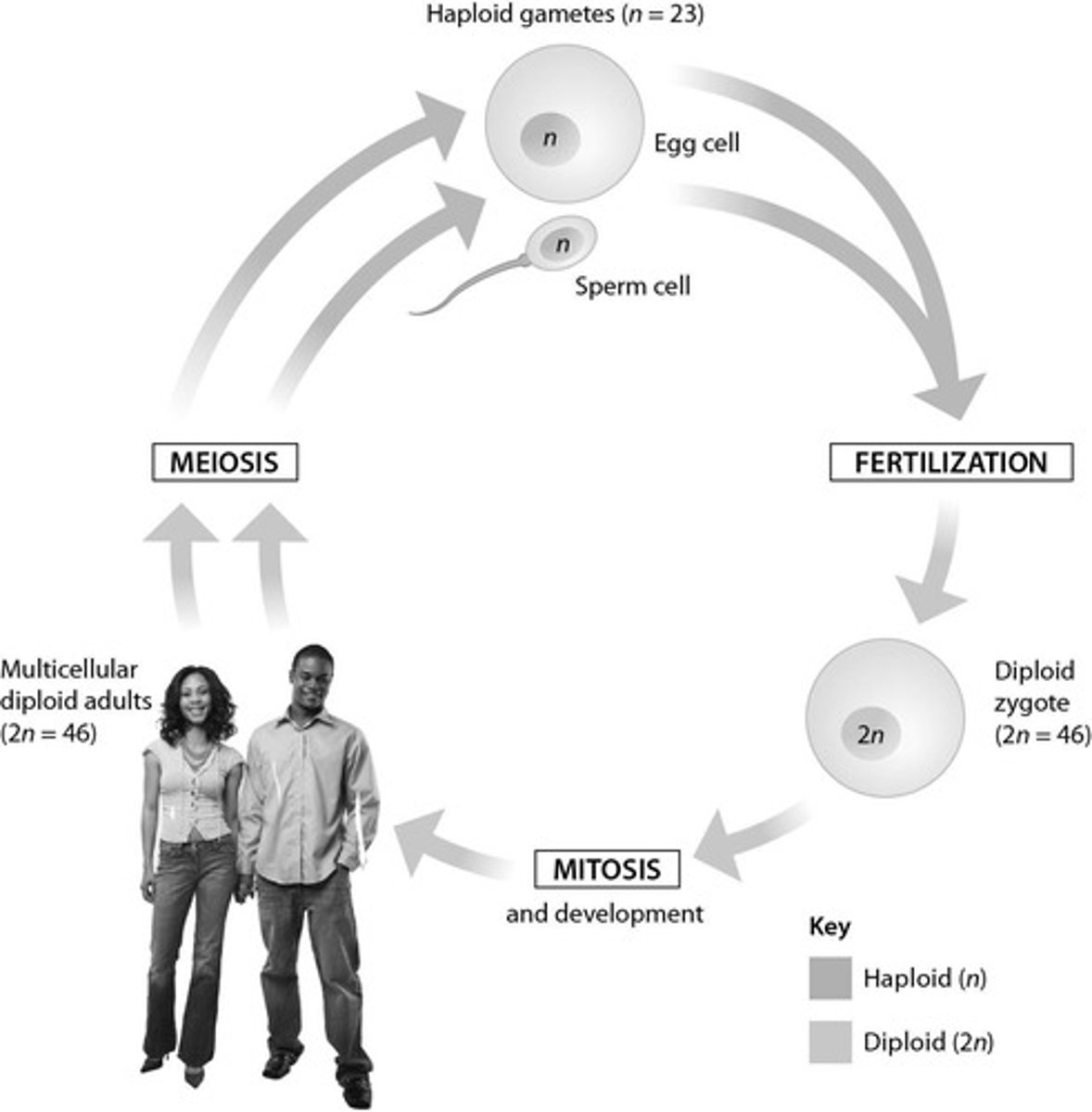
Zygotic life cycle
Life cycle where haploid cells develop into gametes then two gametes combine to form a single-celled diploid zygote; name of this life cycle comes from the observation that the zygote is the only cell that undergoes meiosis
Sporic life cycle (alteration of generations)
Life cycle for all plants where meiosis results in the formation of spores; where land plants produce two types of multicellular bodies that alternate in time: diploid spore-producing sporophyte and the haploid gamete-producing gametophyte
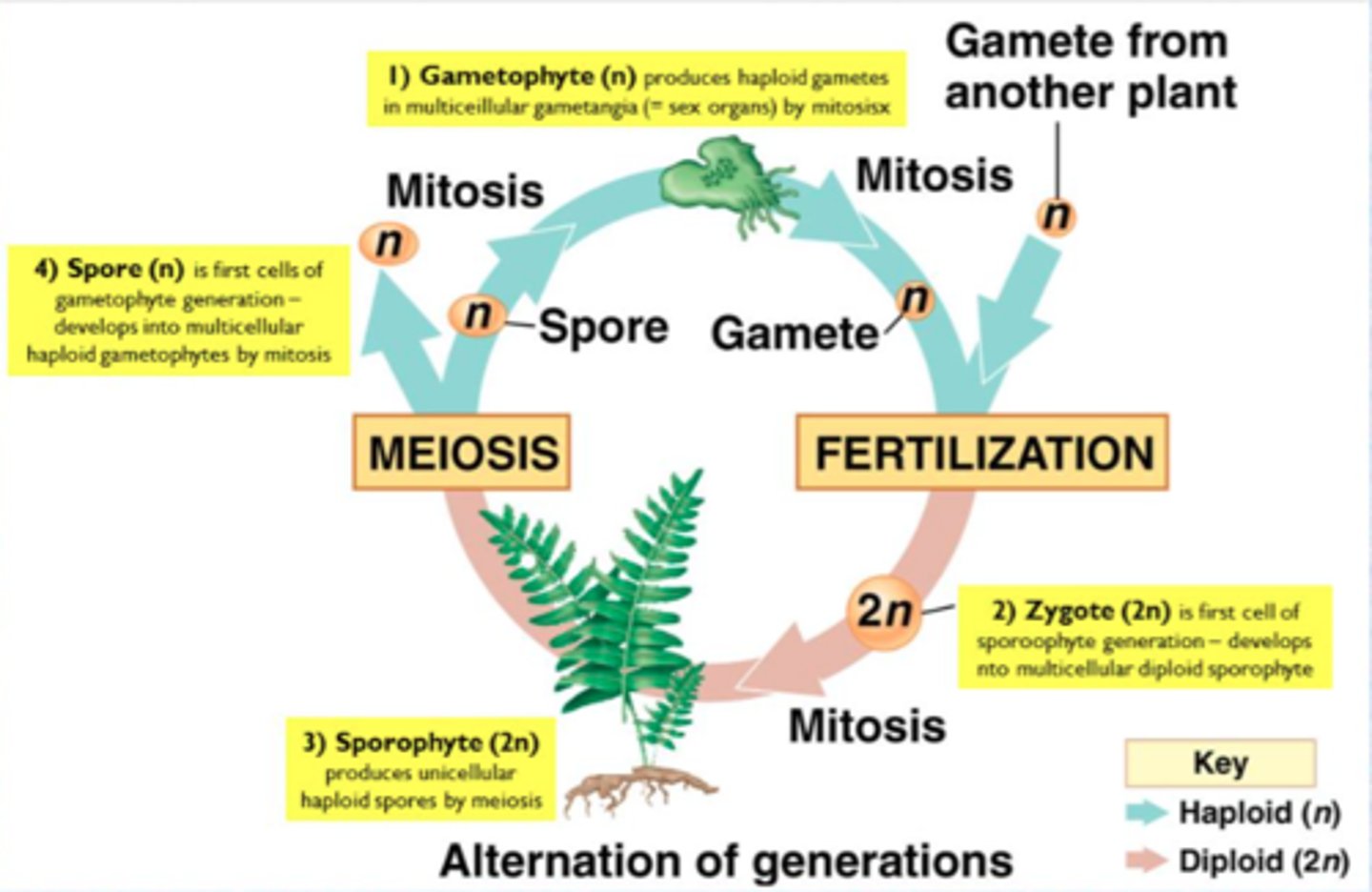
Sporophyte
Diploid generation of plants; this generation produces haploid spores by meiosis

Gametophyte
Haploid generation of plants; produces gametes by mitosis
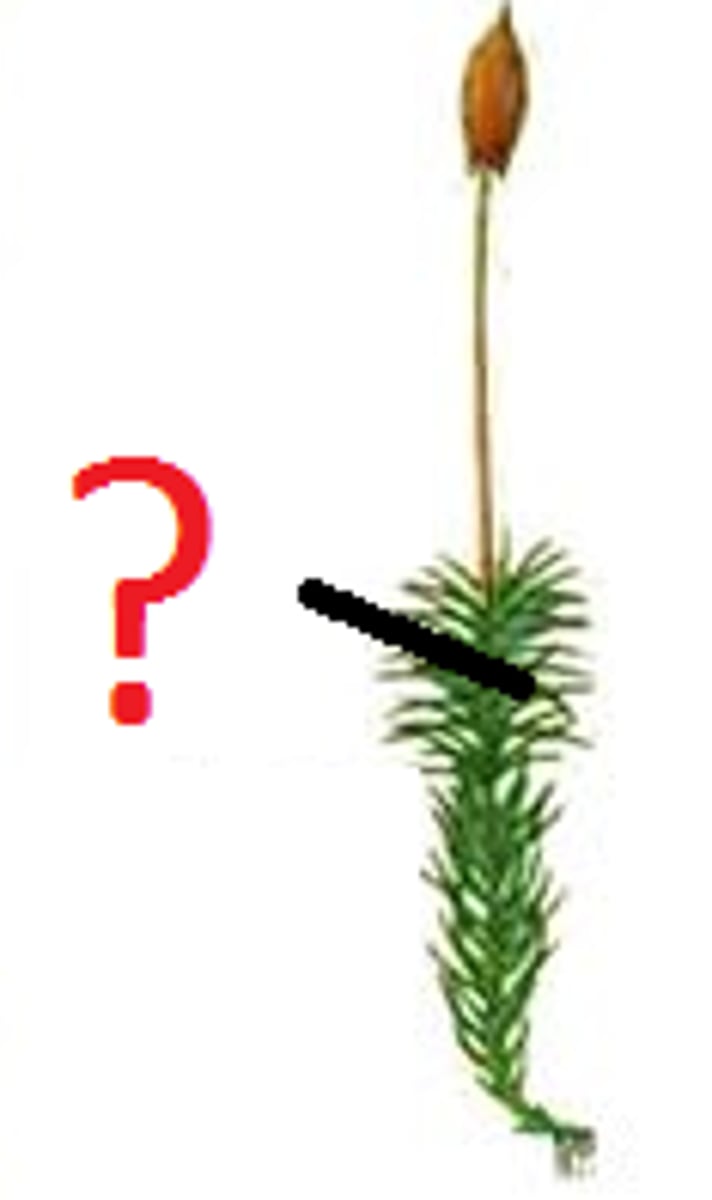

Sporangia
Enclosures that produce and disperse plant spores; tough cells walls protect spores from UV radiation and microbial attack
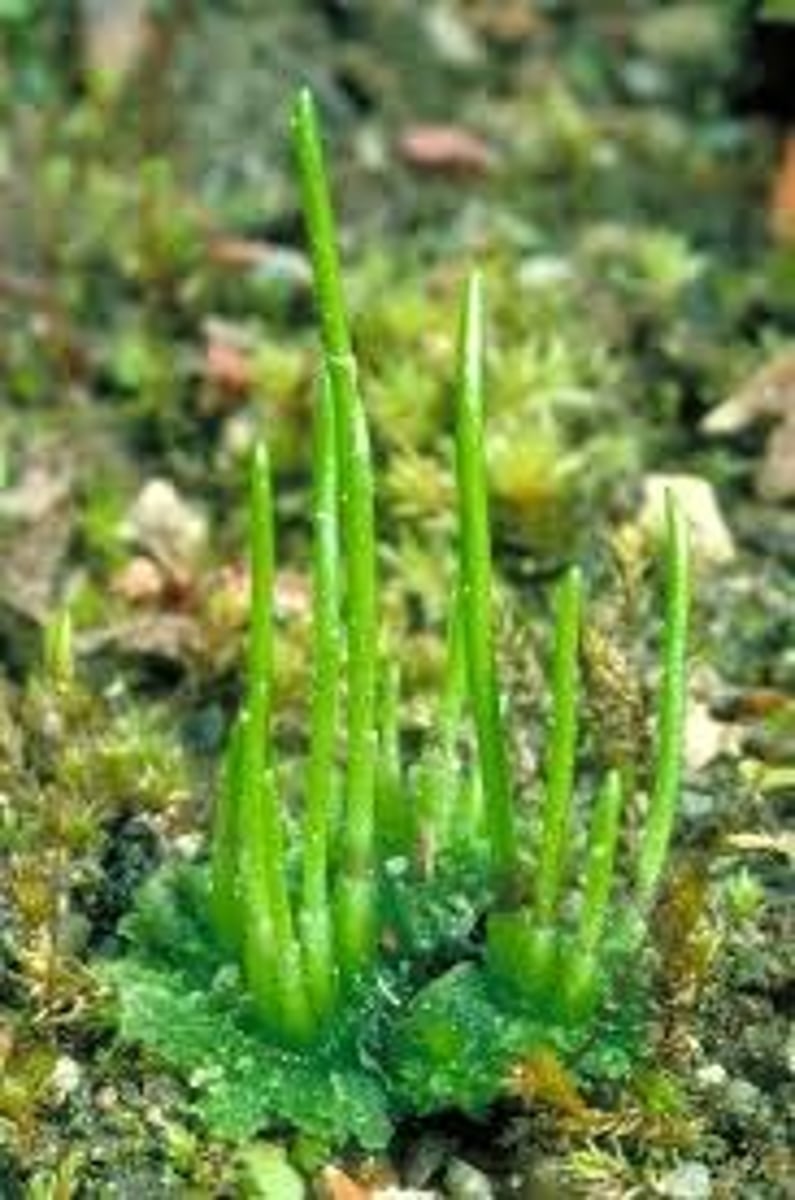
Hornwort
Phylum of bryophyta characterized by an common elongated horn-like structure, which is the sporophyte; flattened, green plant body is the gametophyte

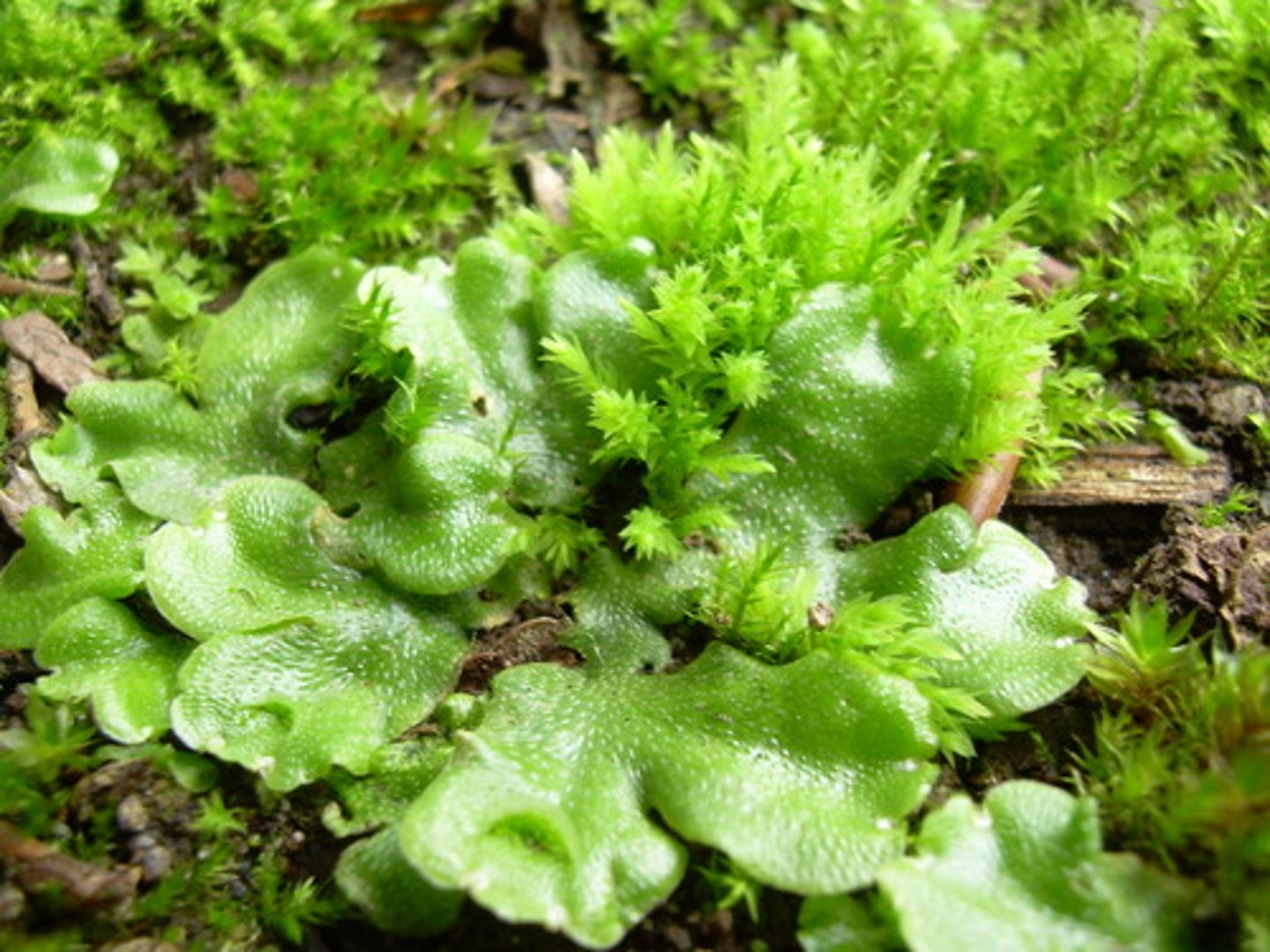
Liverwort
Phyulm of Bryophya; most species are leafy with a form very much like a flattened moss

Vascular tissue
Plant tissue that provides structural support and serve in conduction of water and nutrients.
Seedless vascular plants
Lycophytes and pteridophytes are what? T his informal group diverged prior to the origin of seeds; homosporous
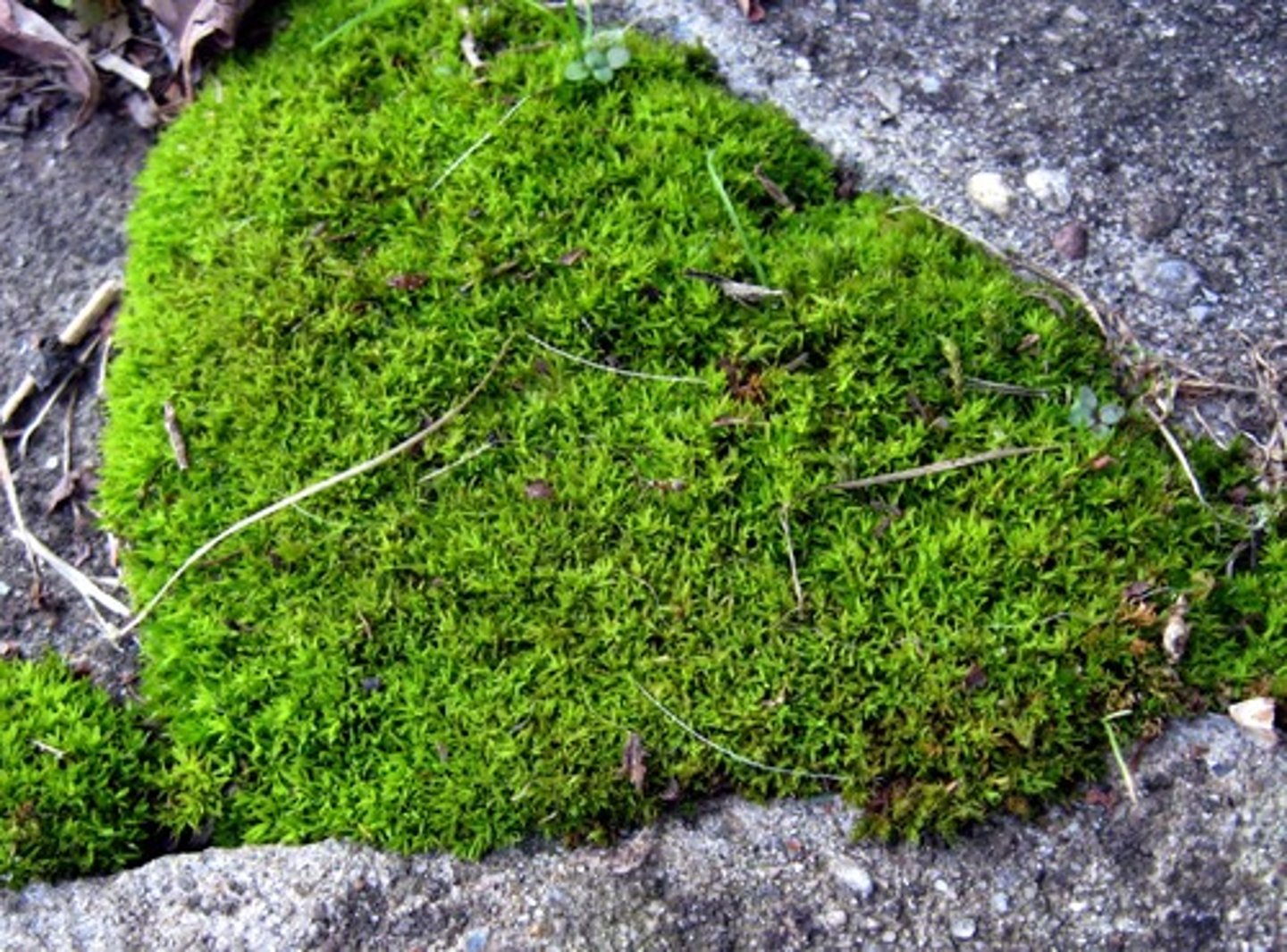
Moss
Group of Bryophyta that typically grow in dense green clumps or mats, often in damp or shade;

Stem
Branching structures that contain vascular tissue and produce leaves and sporangia
Phloem
Specialized conducting tissue in the plants stem; carries sugars and other metabolic products downward from the leaves
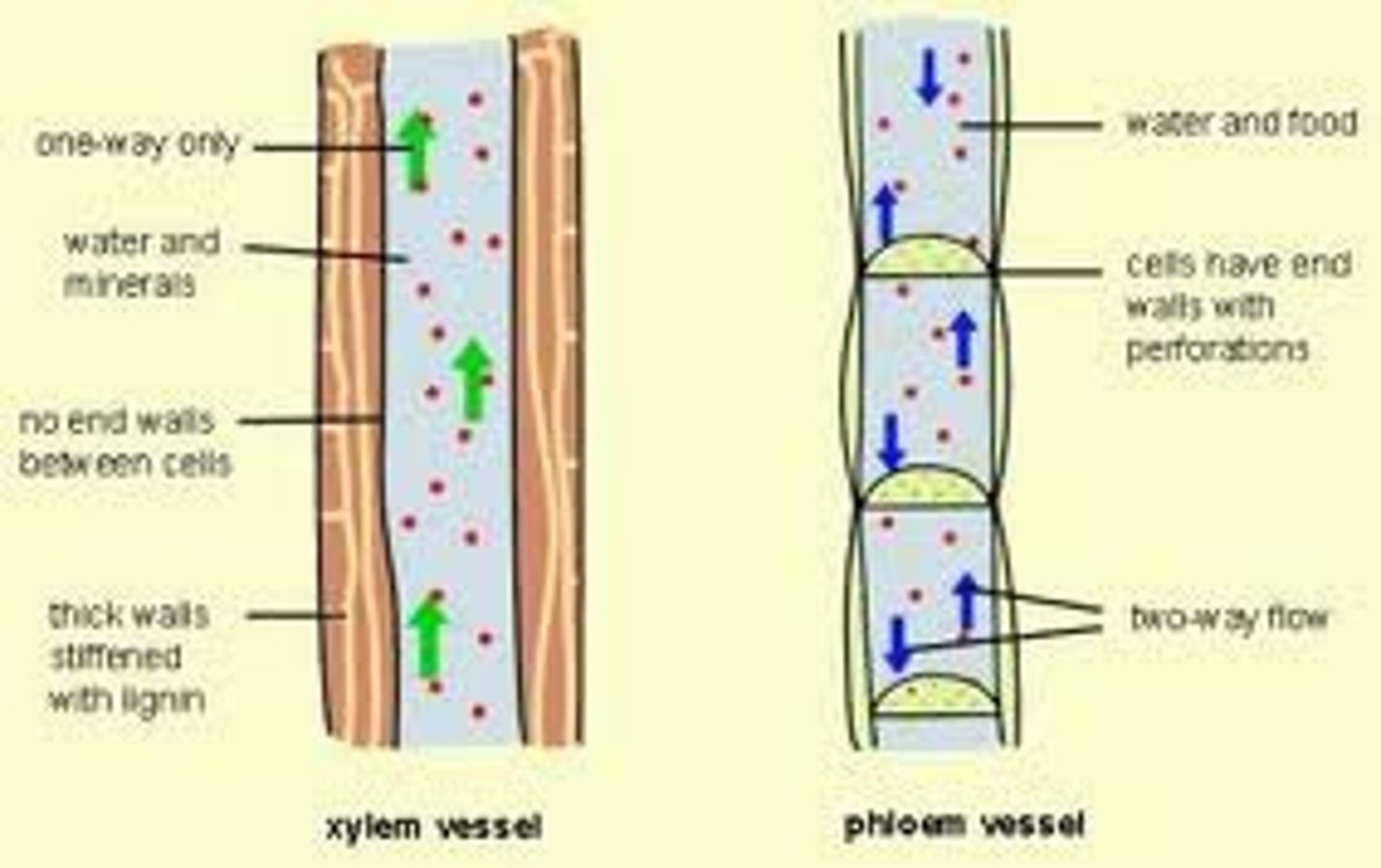
Xylem
Specialized conducting tissue in plant stem that provides structural supports; carries water and nutrients upward from the roots
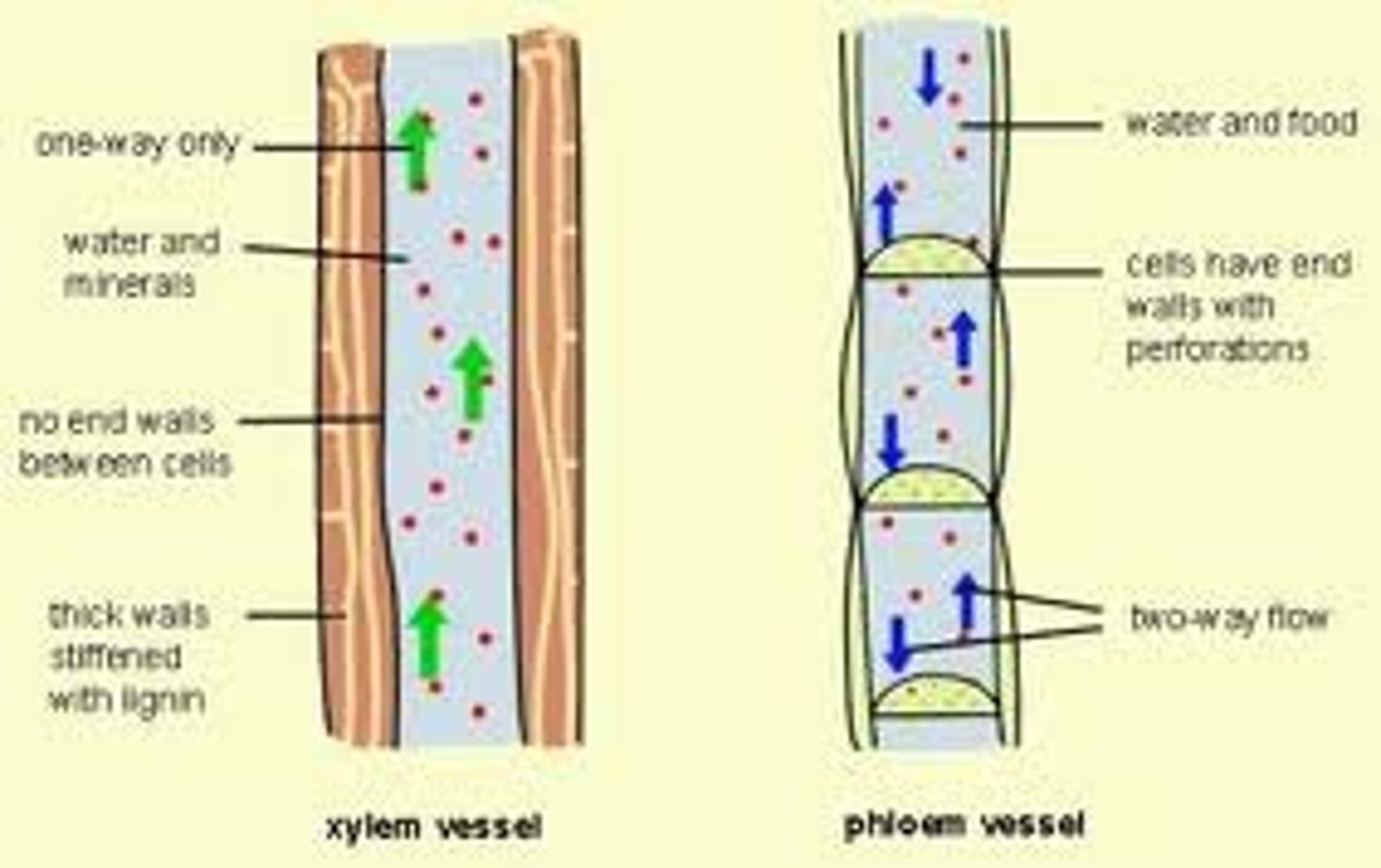
Lignin
Tough polymer that adds strength and decay resistance to the cell walls of tracheids and other types of plant cells
Roots
Plant organ that provides anchorage and is specialized for uptake of water and minerals from the soil
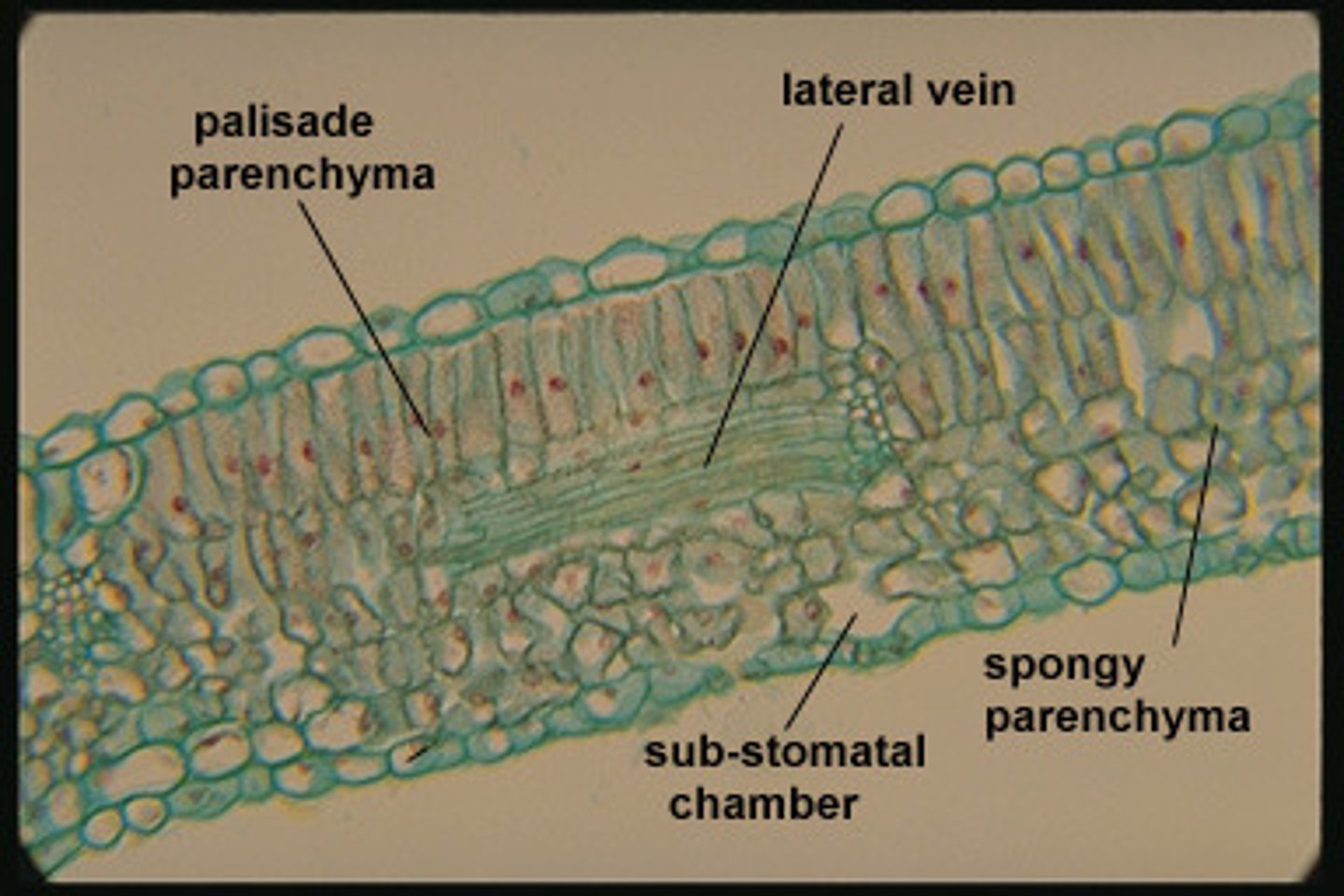
Leaves
Flattened plant organs that emerge from stems and function in photosynthesis
Cuticle
A coating of wax and cutin that helps reduce water loss from plant surfaces.
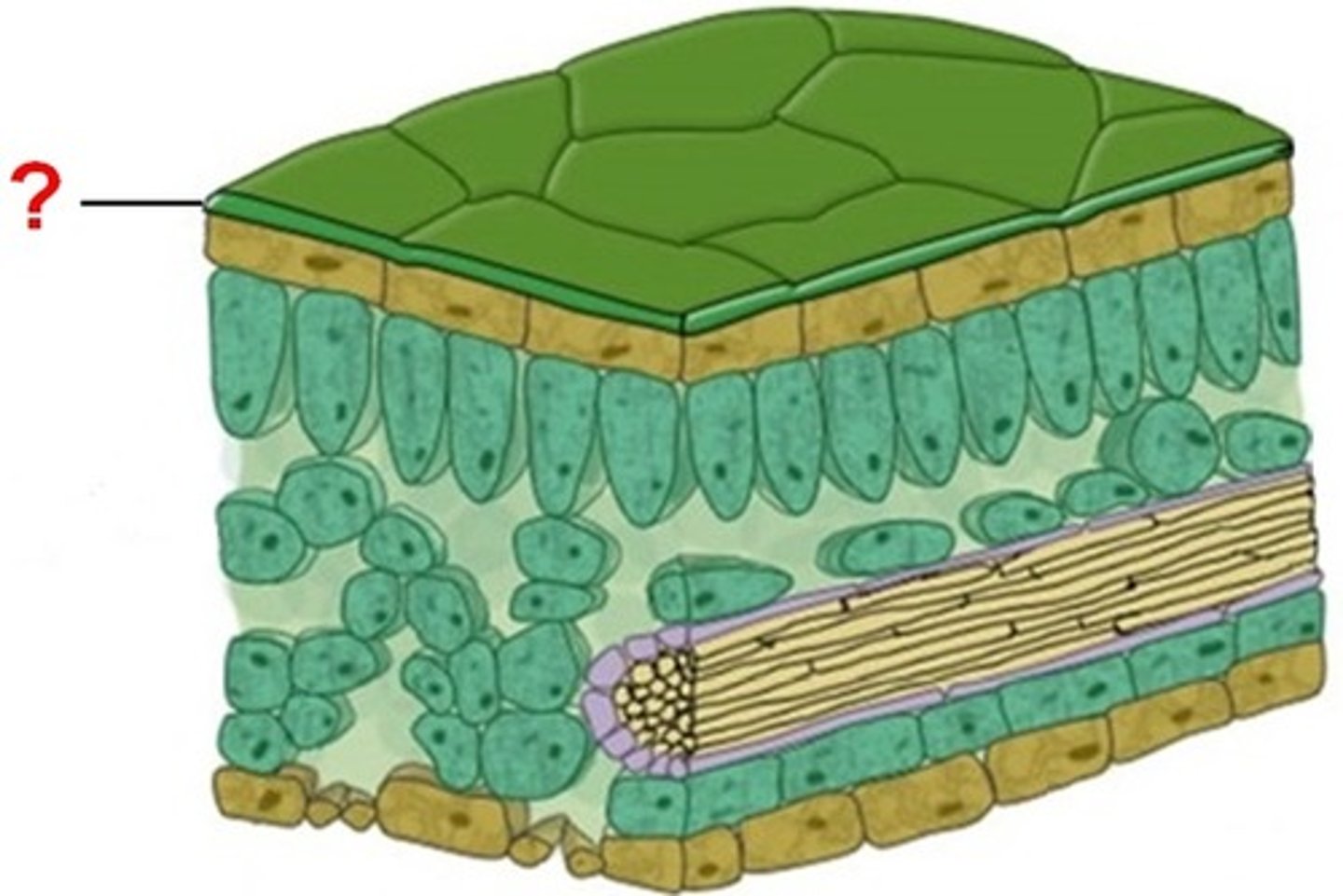
Stomata
Pores on plant surfaces that open and close to regulate gas exchange and the release of water vapor from the plant

Gymnosperm
Any plant that produces seeds that are exposed rather than enclosed in fruit; conifers, cycads, ginkgos, and gnetophytes
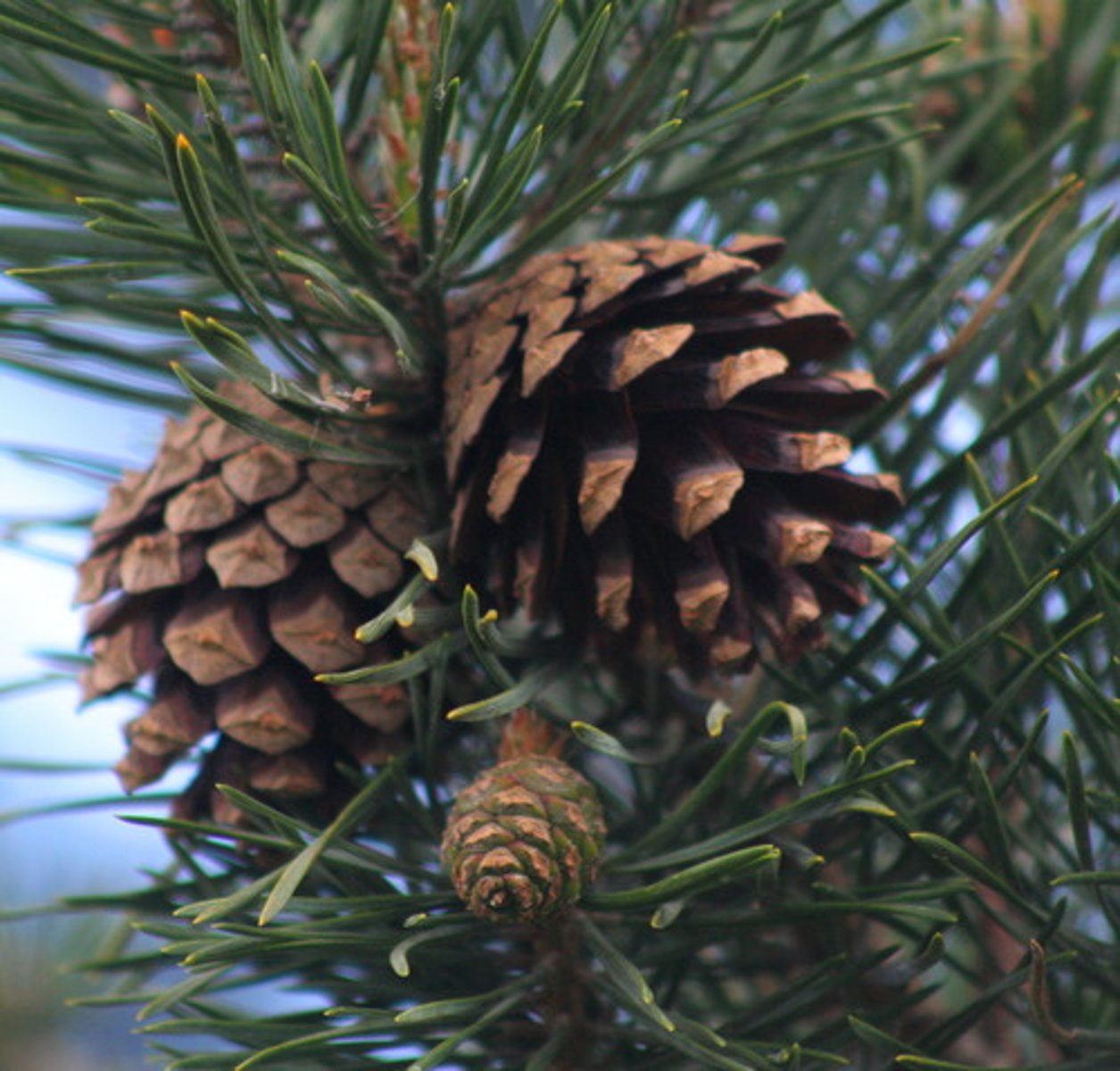

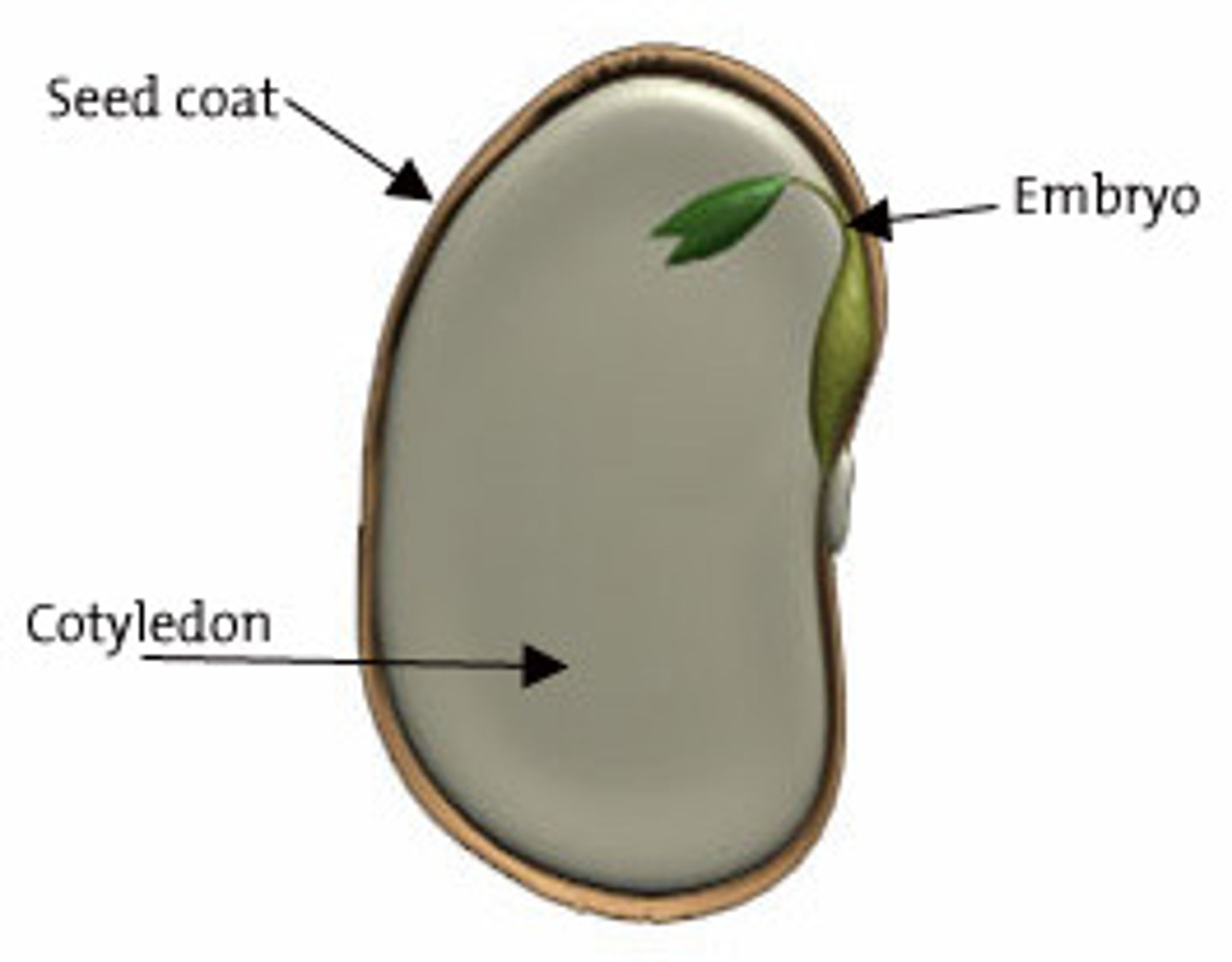
Seed
Reproductive structures with specialized structures that enclose plant embryos; produced by gymnosperms and angiosperms; components include seed coat, food reserves, and the sporophyte/embryo
Angiosperm
A flowering plant that produces seeds enclosed in fruit

Flower
A reproductive shoot; short stem that produces reproductive organs instead of leaves
Fruit
Structures that develop from flower organs, encloses seed, and fosters seed dispersal in the environment
Endosperm
A nutritive tissue that increases the efficiency with which food is stored and used in the seeds of flowering plants.
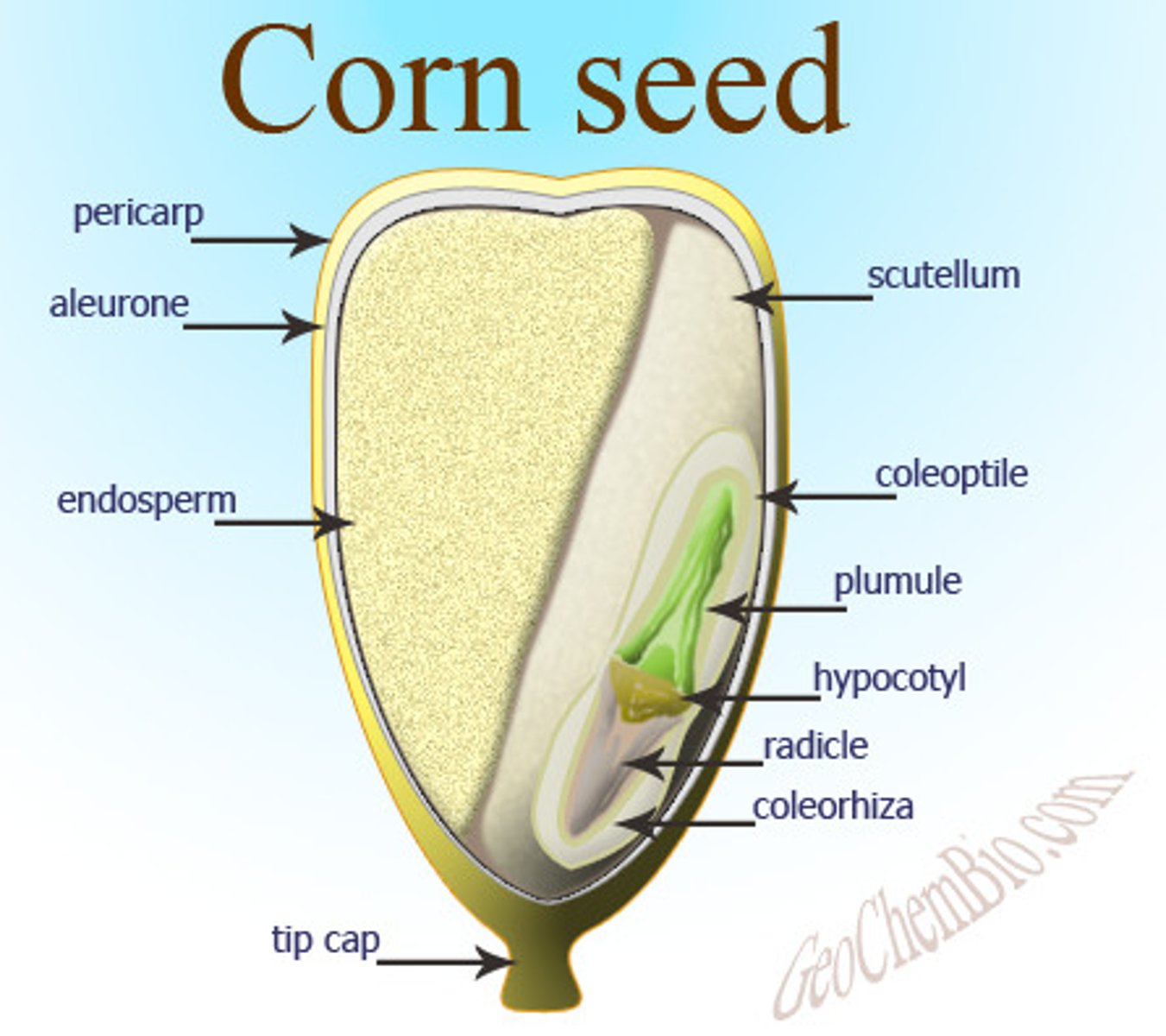
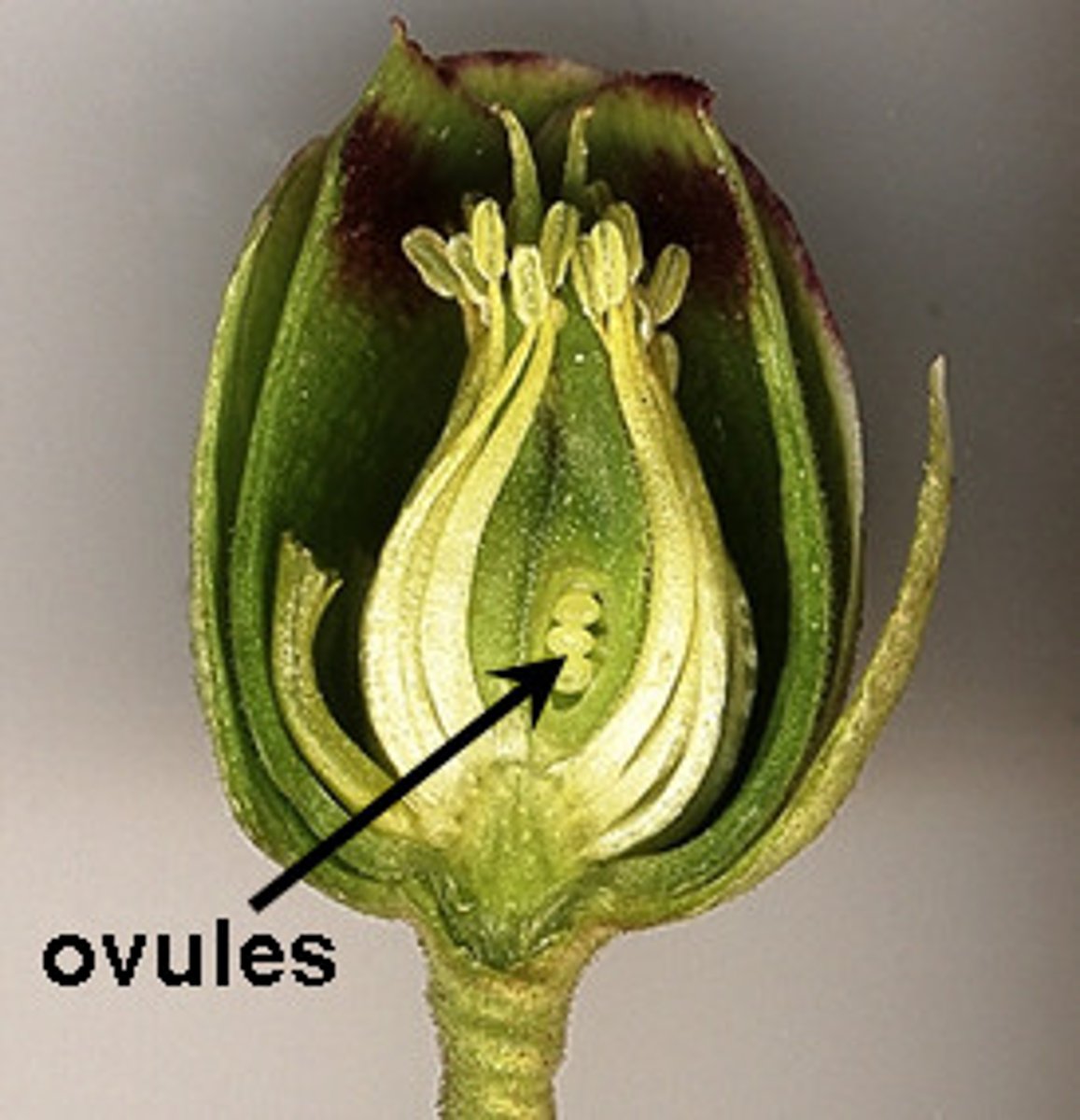
Ovule
Sporangium that typically contains only a single spore that develops into a very small egg-producing gametophyte; entire structure is enclosed by leaflike structures called integuments

Pollen
Tiny male gametophytes enclosed by protective sporopollennin walls

Pollination
Process by which pollen comes into contact with ovules
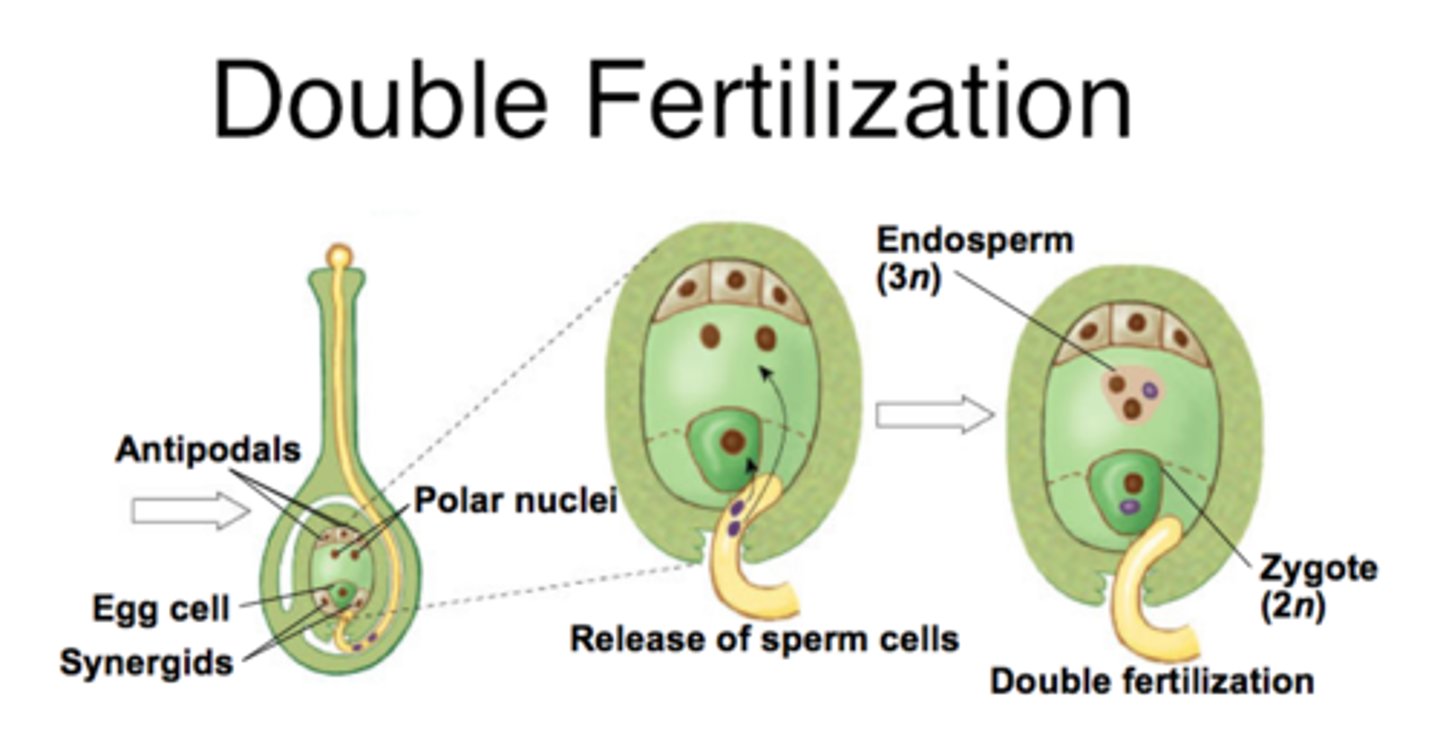
Double fertilization
Process where two different fertilization events occur; produces a zygote and a food storage tissue, the endosperm
Needle-shaped leaves
Type of leaf that reduces water loss from leaf surface
Resin
stick flammable organic substance on plants; insoluble in water; protects against pathogens and herbivores

Wood
A plant tissue composed of numerous pipe-like arrays of empty, water-conducting cells whose walls are strengthened by lignin; also called secondary xylem
Vascular cambium
Plant tissue that produces thick layers of wood and thinner layer of inner bark
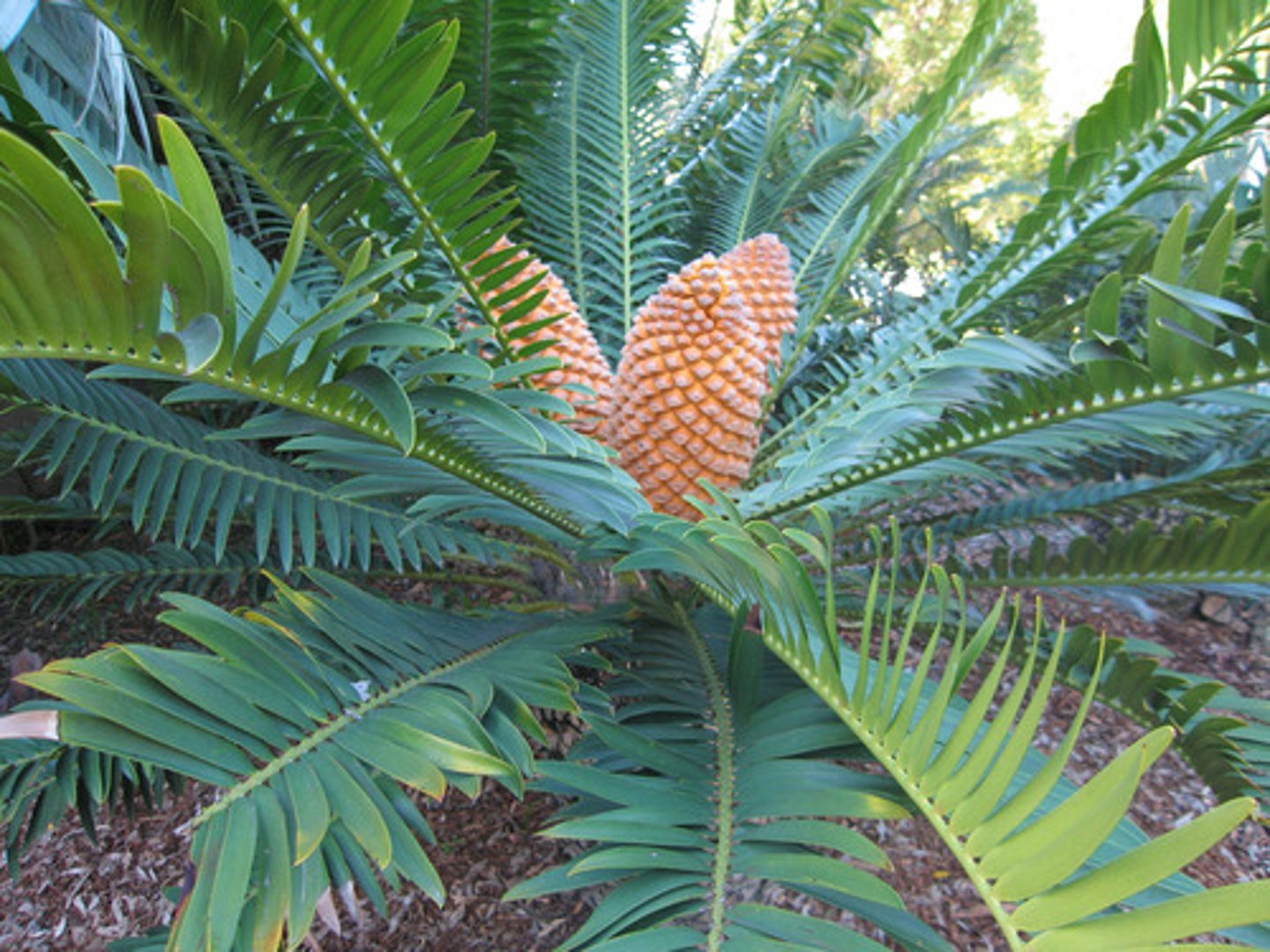
Cycad
Phylum of gymnosperms; stout unbranched trunk; large finely divided leaves that grow in cluster at top of stem; pollenated by insects; coralloid roots

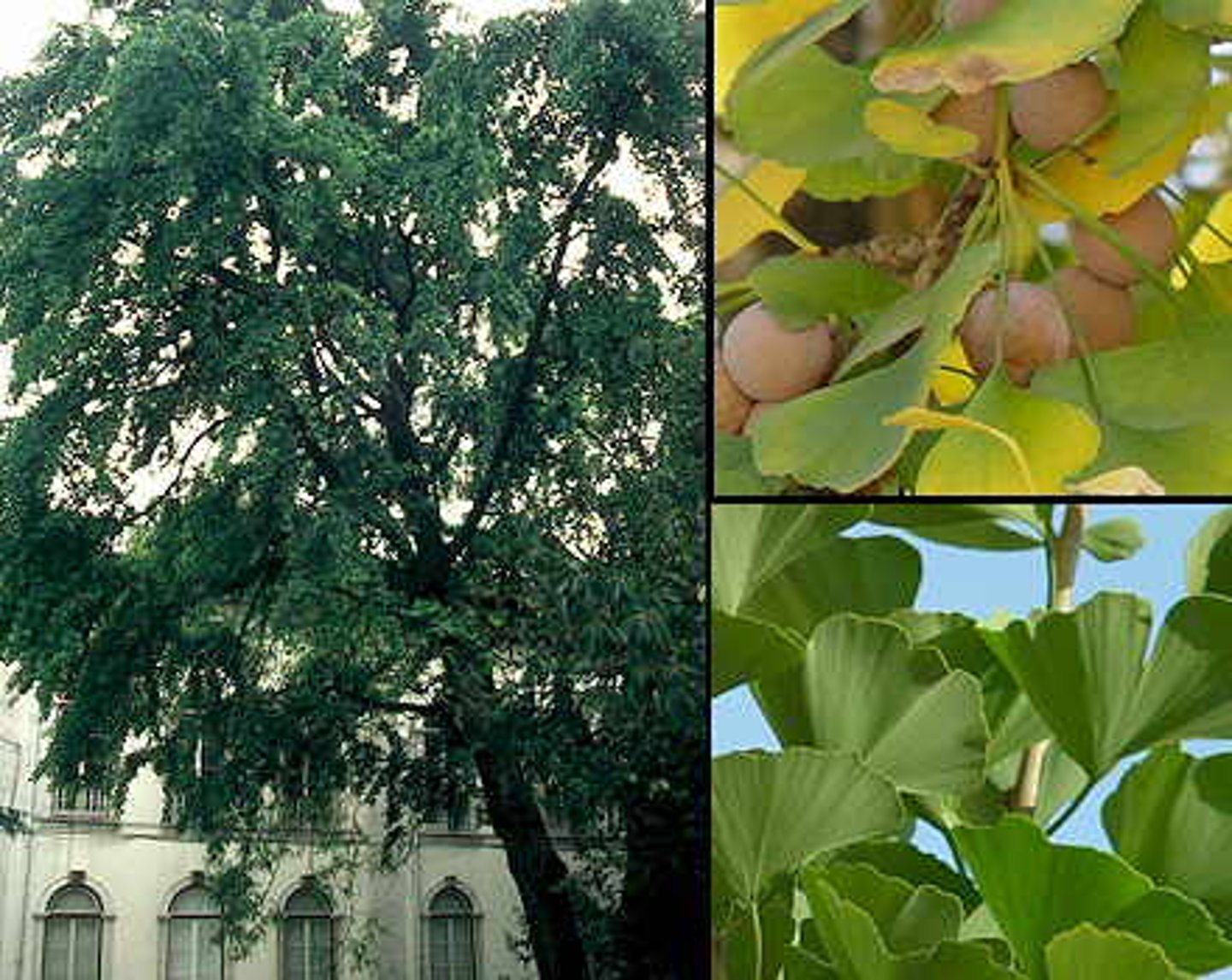
Ginkgo
Phylum of gymnosperms; Ginkgo biloba is single remaining species; characterized by two-lobed shape of leaves and "silver apricot;" trees produce either seeds or pollen based on sex chromosomes, similarly to humans

Conifer
Phylum of gymnosperms; cone-bearing trees and shrubs; tough needle-like leaves conserve water w/ thick cuticle and recessed stomata; evergreen

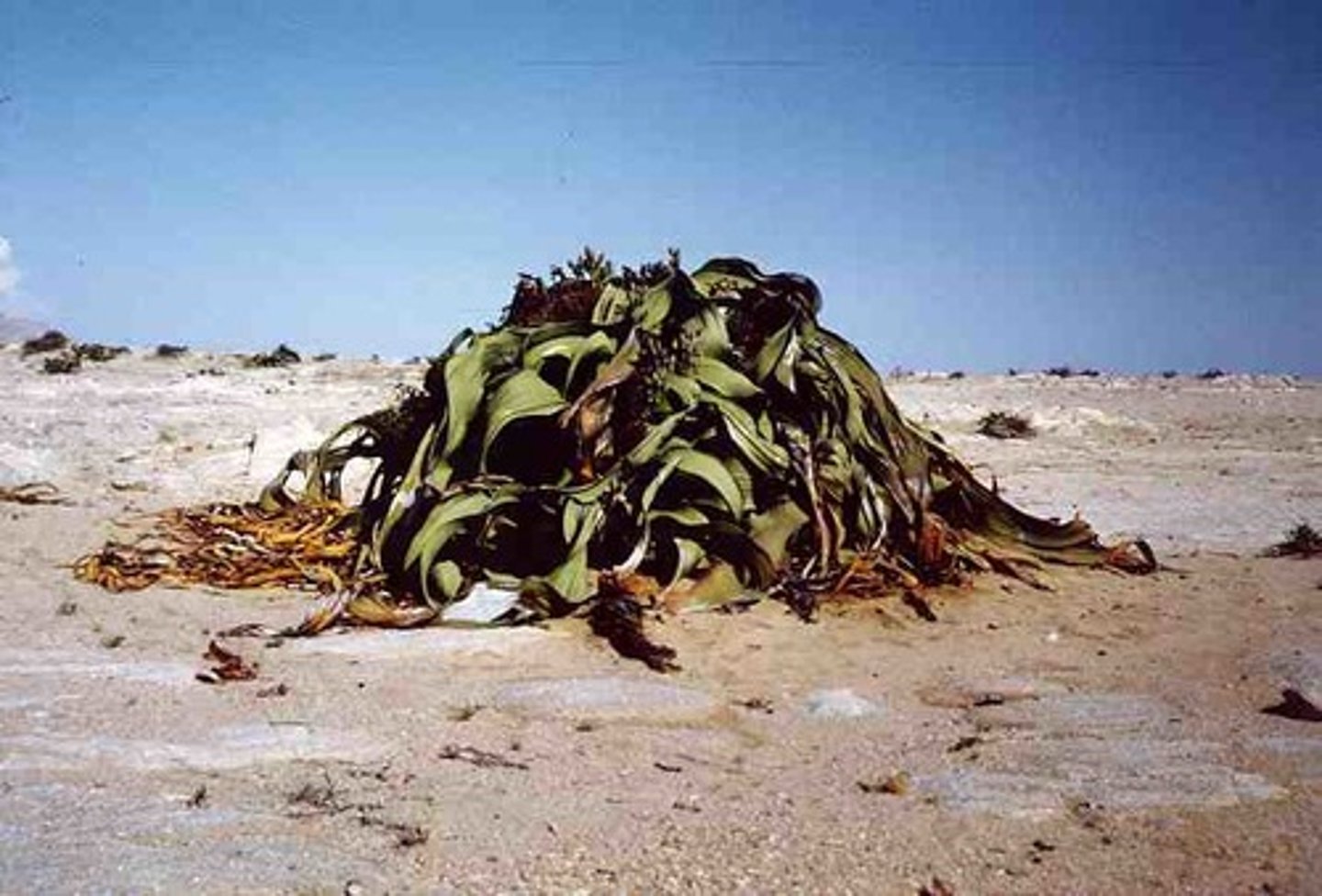
Gnetophyte
Type of gymnospore; contains vessel elements in xylem; has no archegonia (female sex organs)

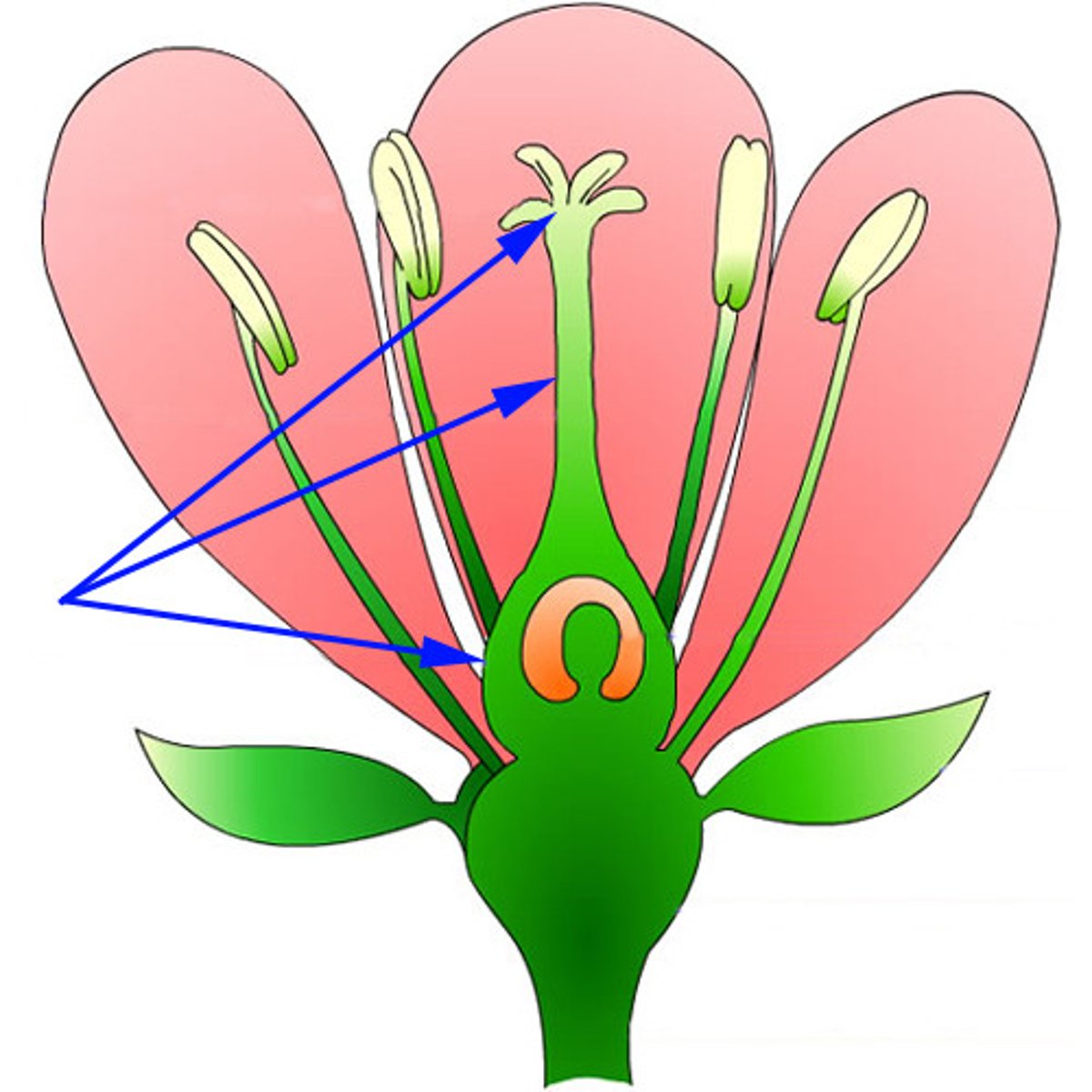
Petal
Flower organ that usually serves to attract insects or other animals for pollen transport
Stamen
Male reproductive organ of flower that produces and disperses pollen; consists of anther and filament

(Four) flower organs
Sepals, petals, stamens, and carpels are the four what?
Complete flower
Flowers that possess all four types of flower organs
Incomplete flower
Flowers that lack one or more organ types
Perfect flower
Flowers that contain both stamens and carpels
Imperfect flowers
Flowers lacking either stamens or carpels
Pistil
Flower structure of either single or compound carpels; differentiated into stigma, style, and ovary; can be multiple of these in a flower's single
carpel
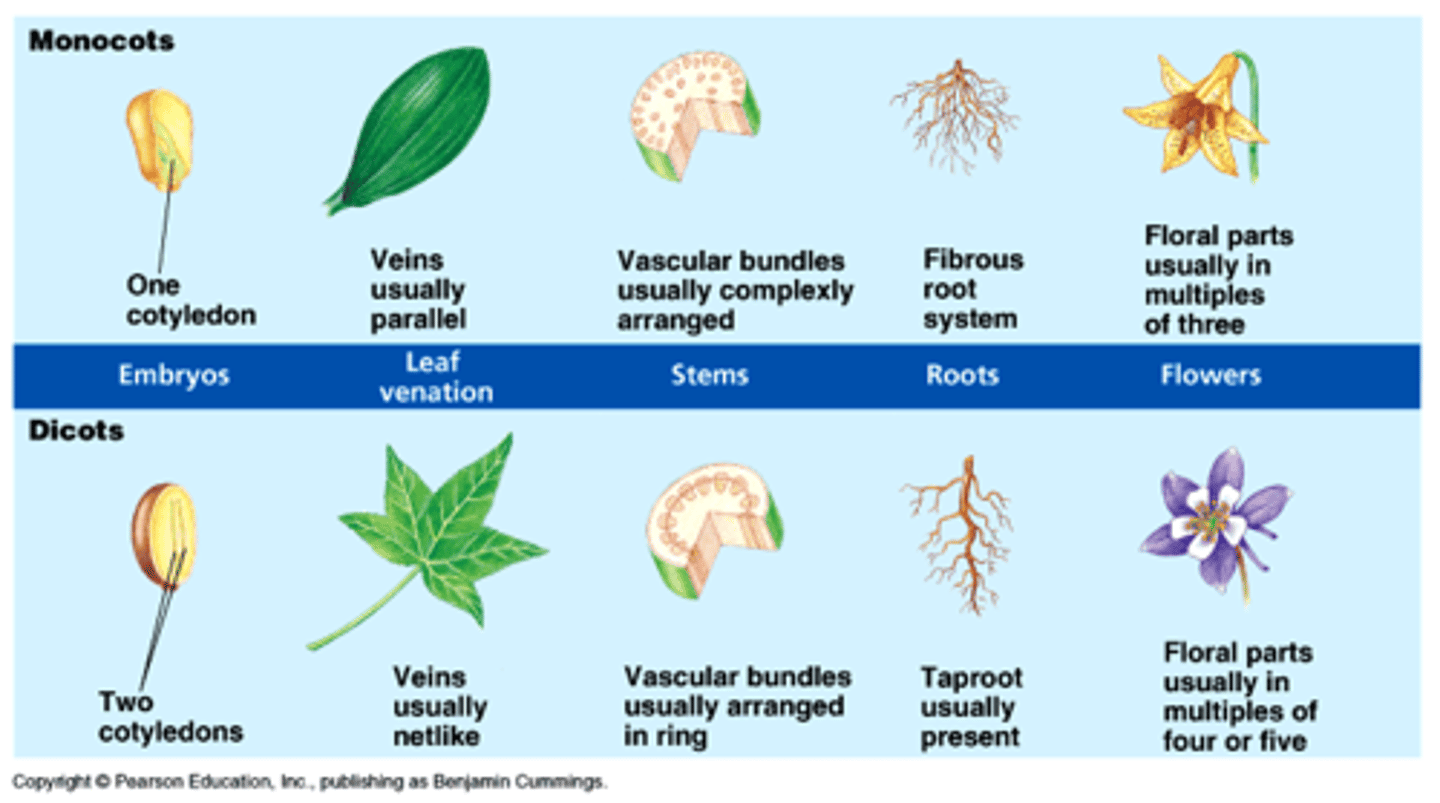
Monocot
Type of flowering plant; characterized by having one cotyledon, flower parts in multiples of 3s, with parallel venation, scattered vascular bundles and fibrous root system
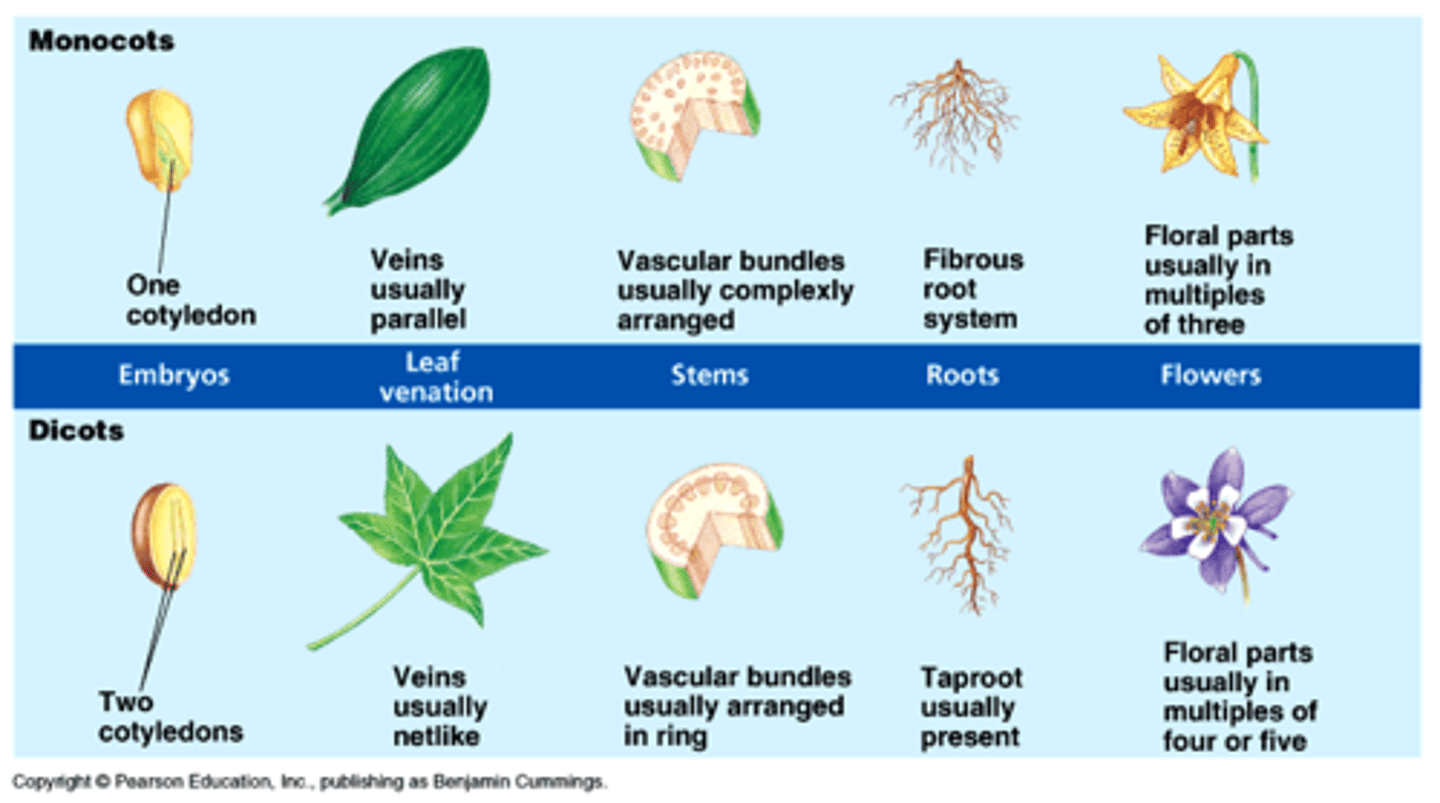
Eudicot
Type of flowering plant; characterized by having 2 cotyledons, flower parts in multiples of 4 or 5s, with net venation, ringed vascular bundles, and tap-root system
Inflorescence
Groups of flowers tightly clustered together; ie sunflower
Terpenes and Terpenoids
Secondary metabolite characterized by intense smells and colors; incl. carotenoids, steroid hormones, cinnamon, fennel, mint, TCH
Phenolics
Secondary metabolite characterized as antioxidants with intense flavors and smells; incl. flavinoids such as vanilla, chocolate, tannins and lignins
Alkaloids
Secondary metabolite characterized by bitter taste and used for defense; stimulatory: caffeine, nicotine, capsaicin, cocaine, ephedrine; inhibitory: codeine, morphine
Polyketides
Secondary metabolites used as chemical weapons; i.e. antibiotics (penicillin, streptomycin), tetrodotoxin, conotoxin
Carpel
Female reproductive organ of a flower; consists of ovary, stigma, and style

Sepal
Part of the flower that typically functions as protection for the flower bud and supports the petals when in bloom; can consist of multiple pistils

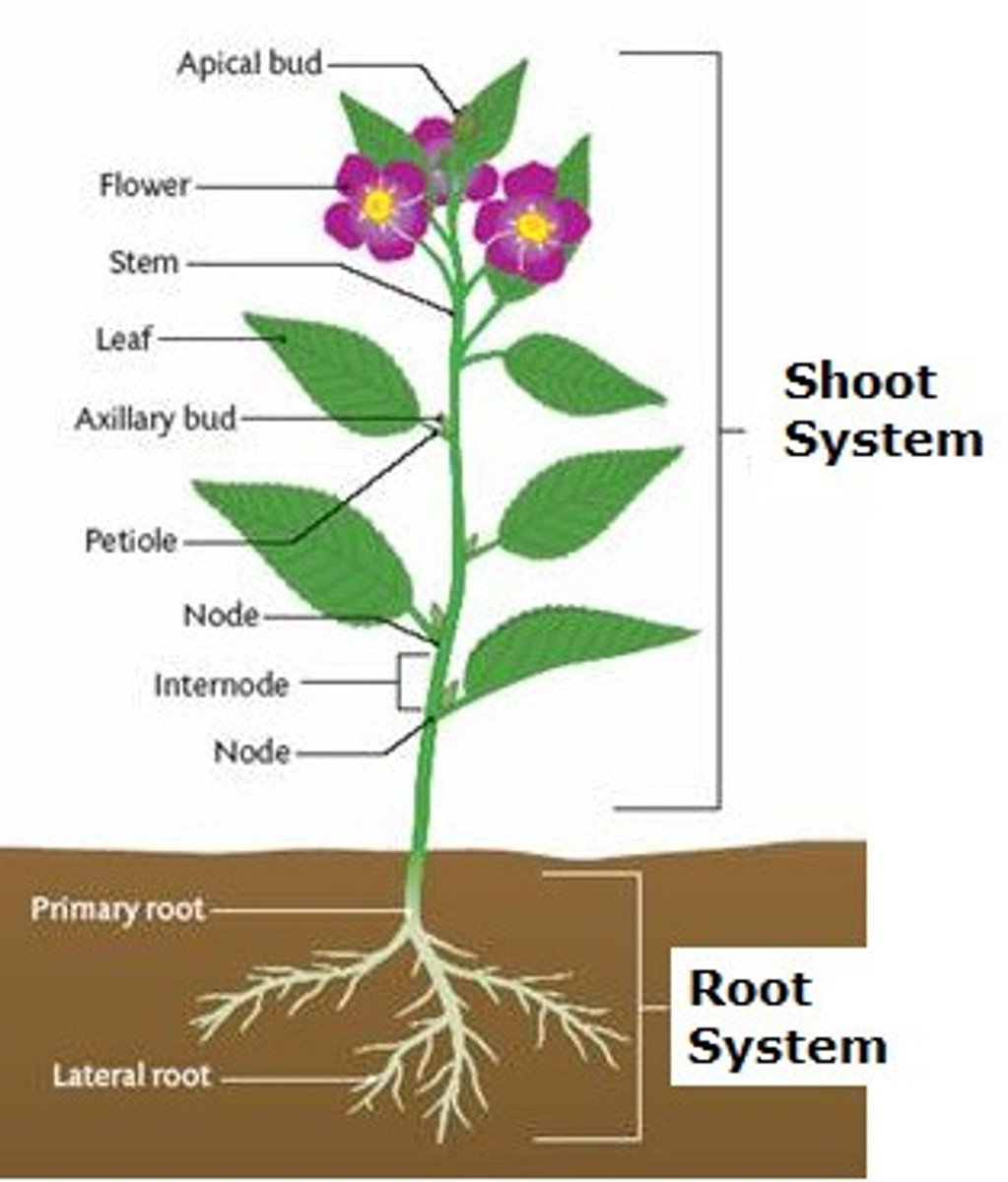
Plant body organs
Stems, leaves, and roots are the three types of what?
Shoot
The portions of a plant made of stems and leaves
Annuals
Type of plant that dies after producing seeds during their first year of life
Biennials
Type of plant that does not reproduce during the first year of life but may reproduce within the following year
Perennials
Type of plant that lives for more than 2 years, often producing seed each year after they reach reproductive maturaity
Primary meristem
Meristematic tissue that produces new organs and increases plant length
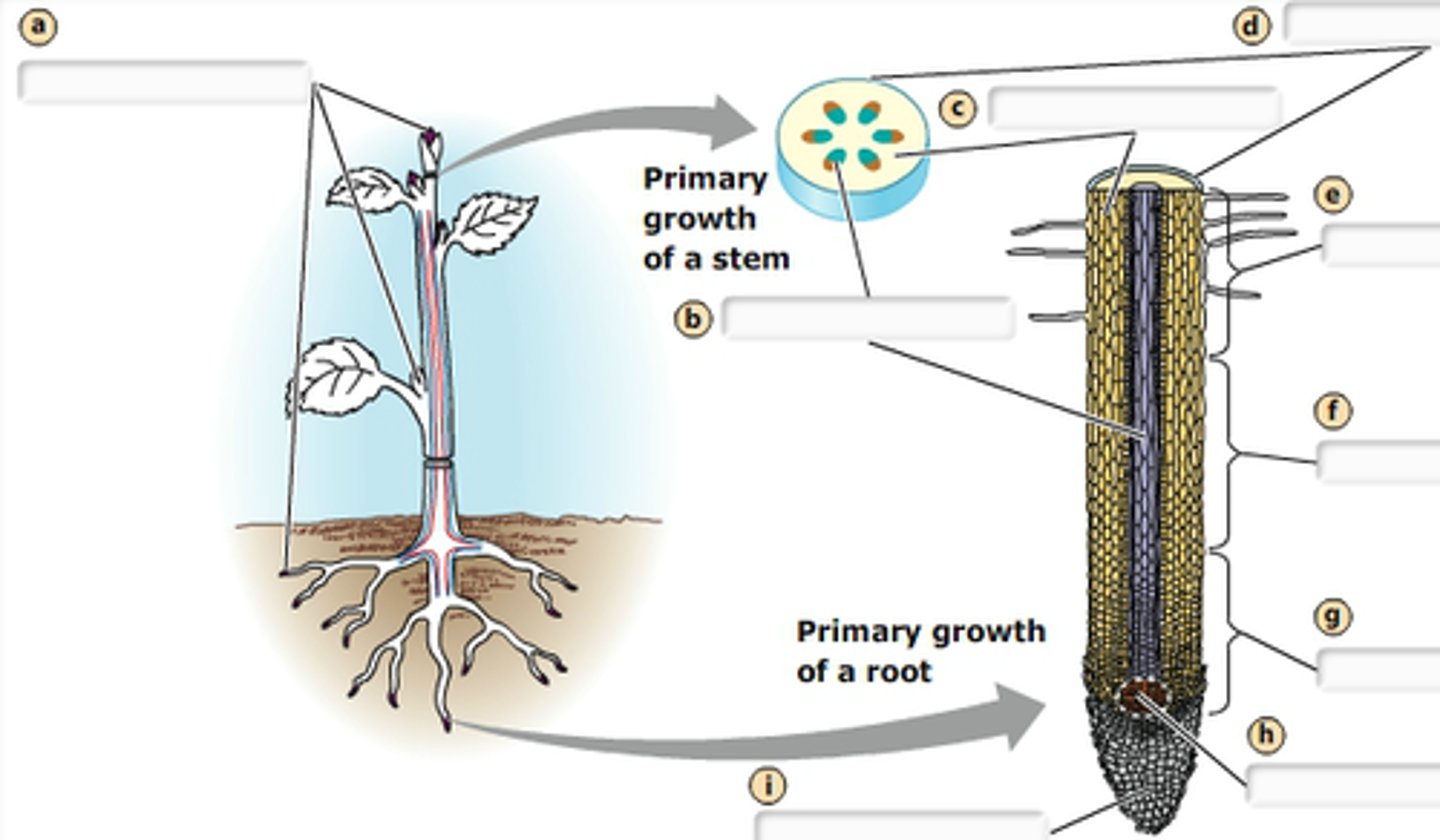
Primary growth
Plant growth that occurs from primary meristems and produces primary tissues and organs of diverse types
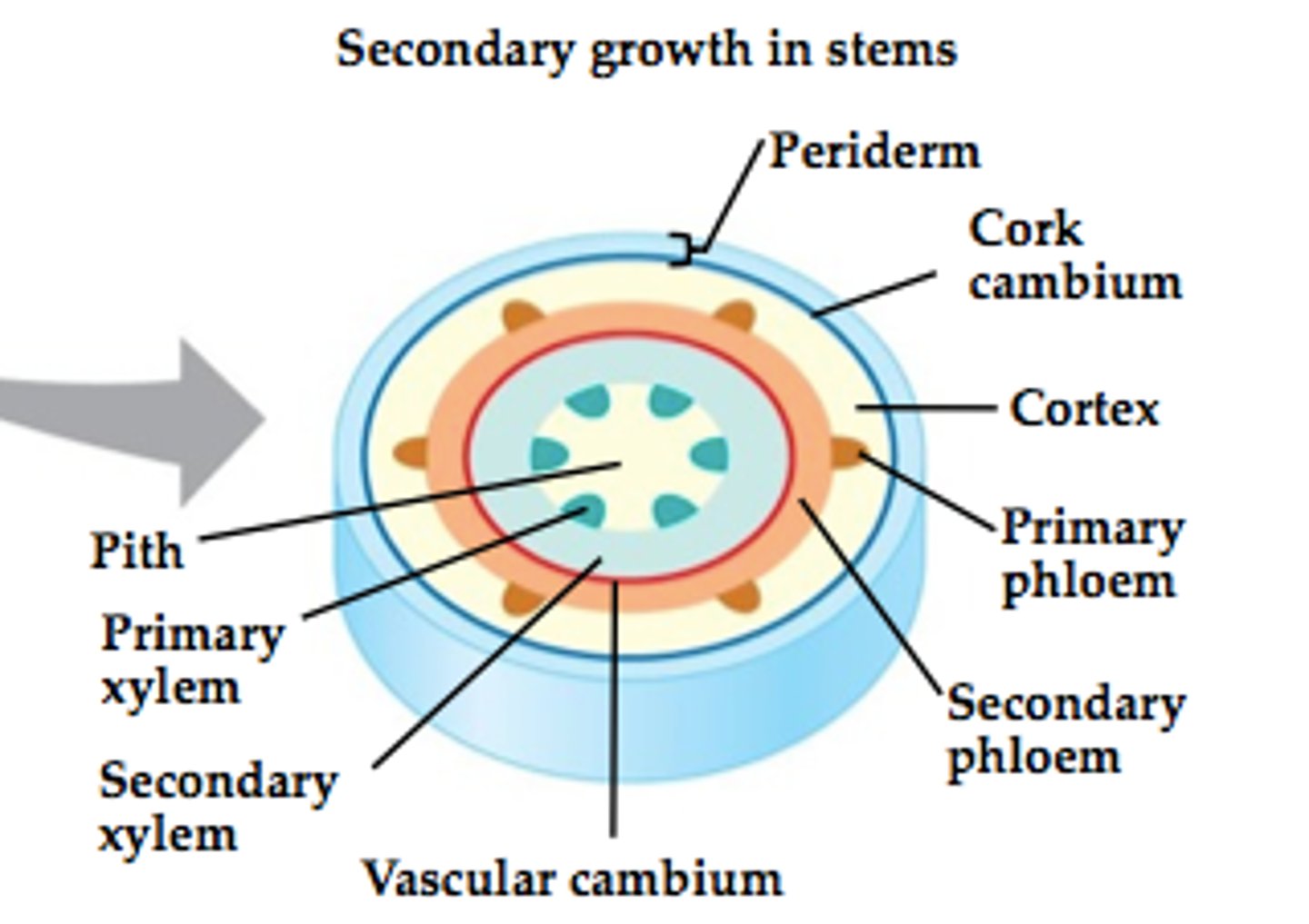
Secondary growth
Plant growth that occurs from secondary meristems and increases the girth of woody plant stems and roots by producing secondary tissues
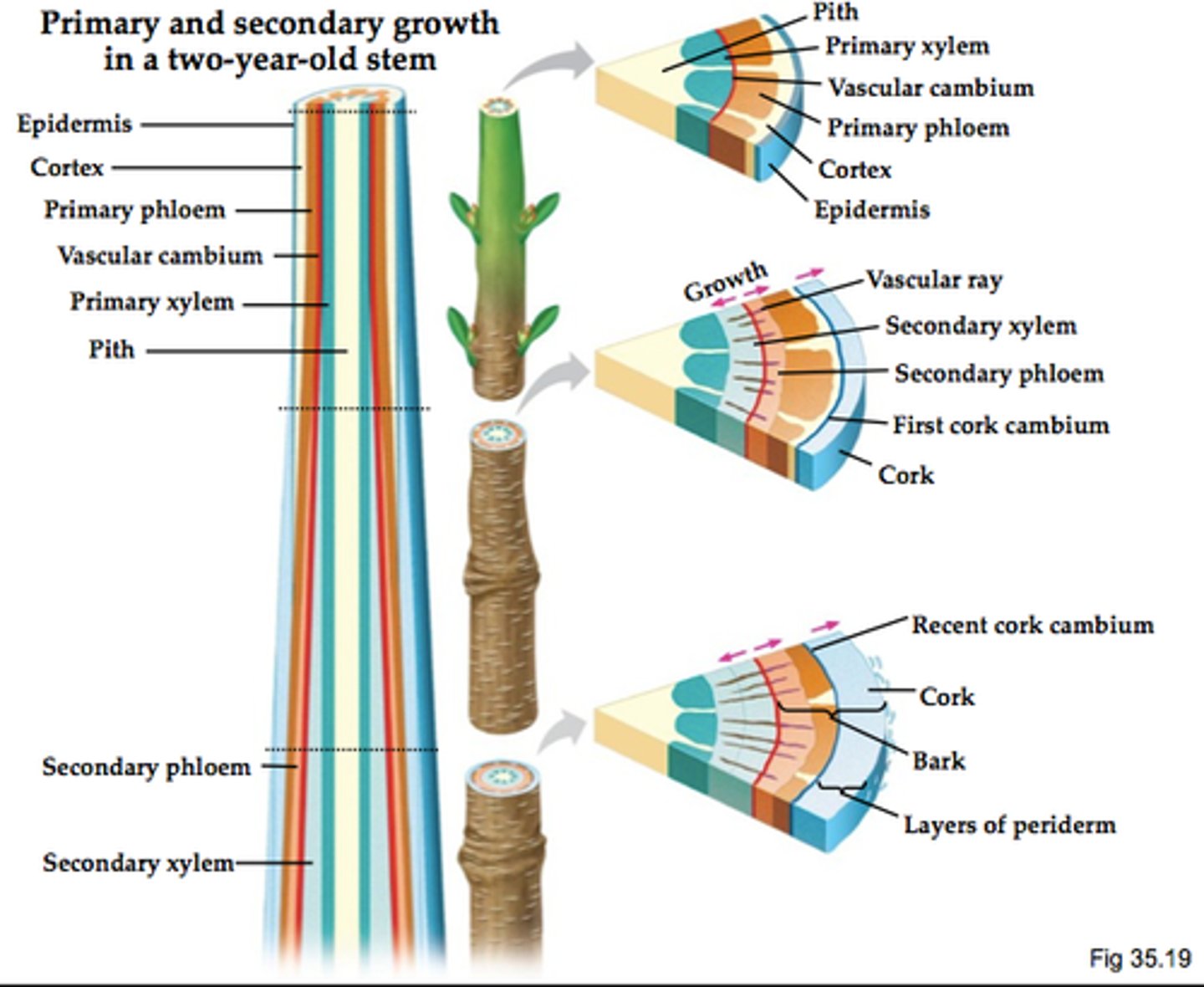
Epidermis
Outermost issue of plant that helps protect it from damage
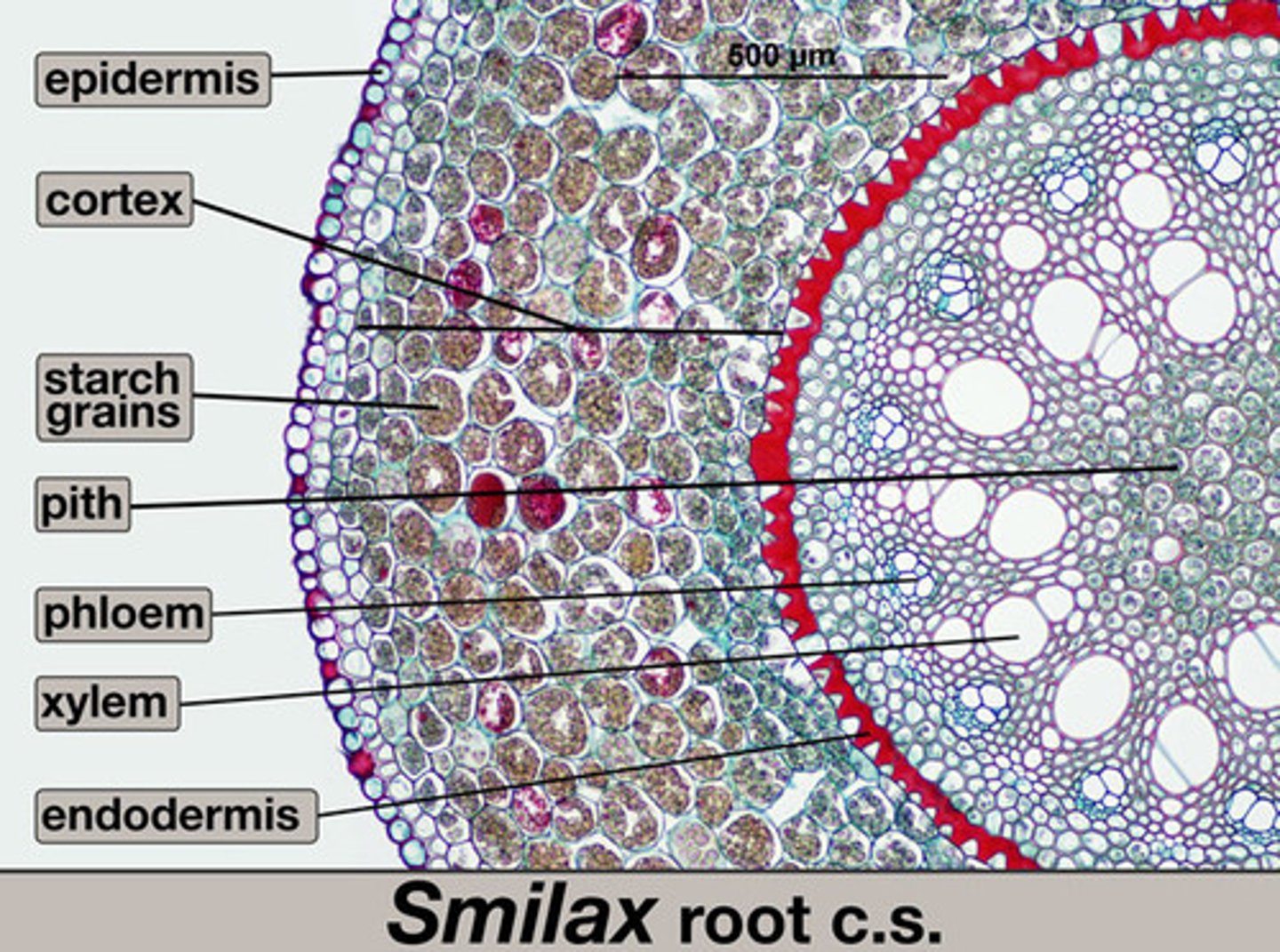
Cortex
Area of plant stem or root beneath the epidermis; largely composed of parenchyma cells

Parenchyma (cells)
Unspecialized thin-walled plant cells that serve in food storage and cell division for healing
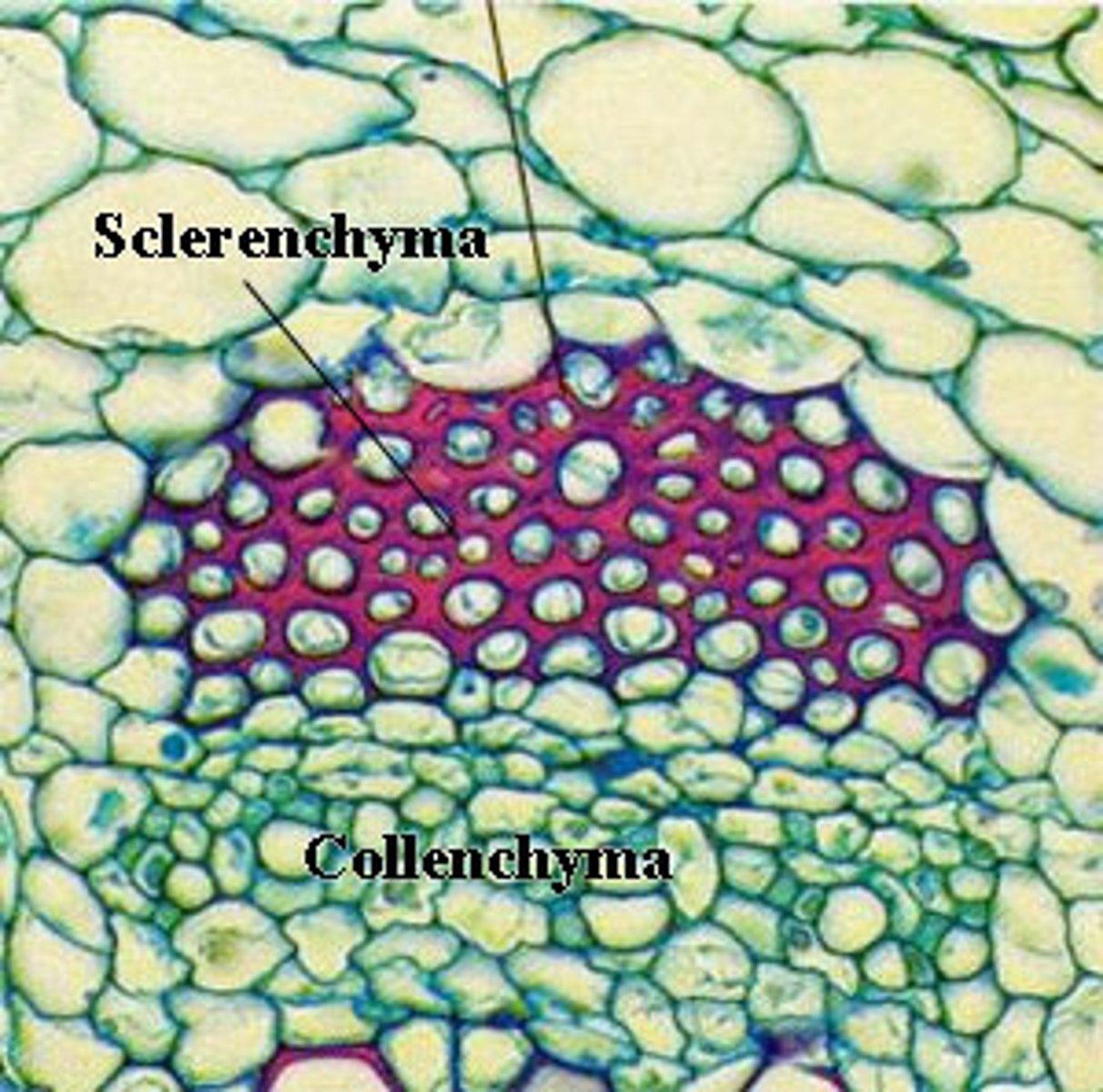
Collenchyma (cells)
Flexible cells that have provide support to plant organs; found in bundles under epidermis
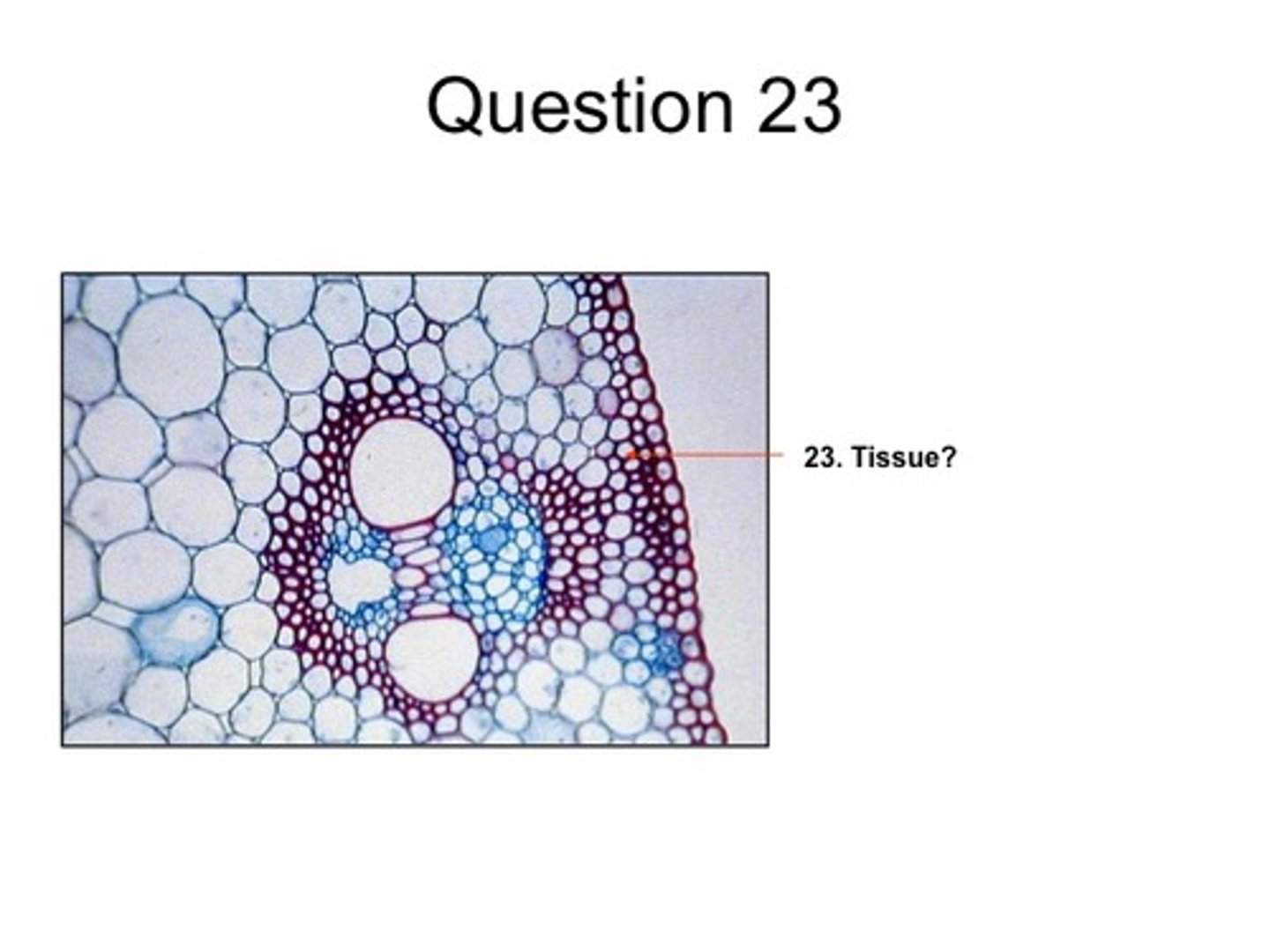
Sclerenchyma (cells)
Rigid plant cells with walls that contain lignin; nonliving; used in support and protection
Phytomere
Modular unit of a plant shoot; consists of four parts: stem node, internode, leaf, and axillary meristem or bud
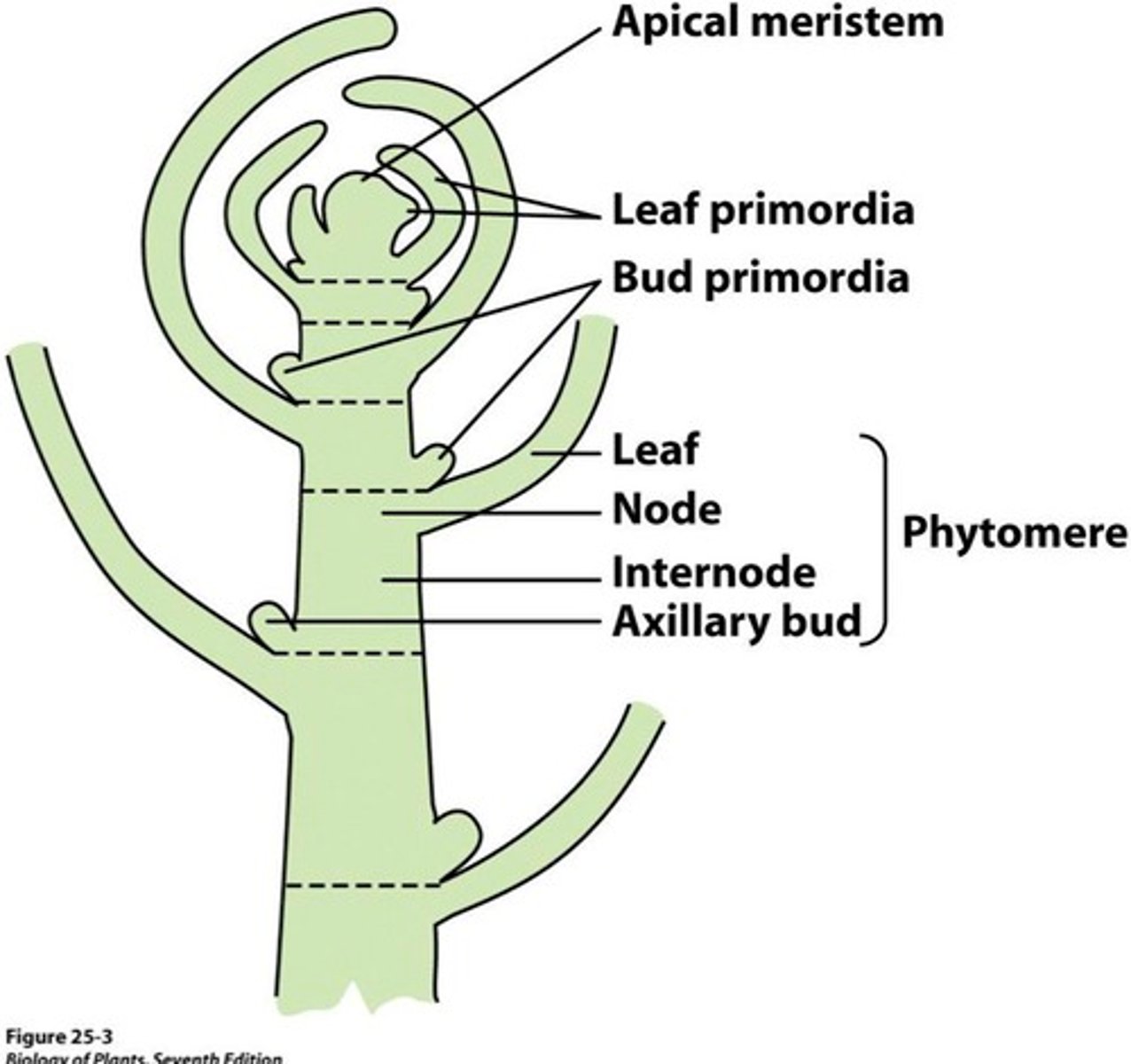
Stem node
Stem region from which one or more leaves emerge

Internode
Stem regions between adjacent nodes
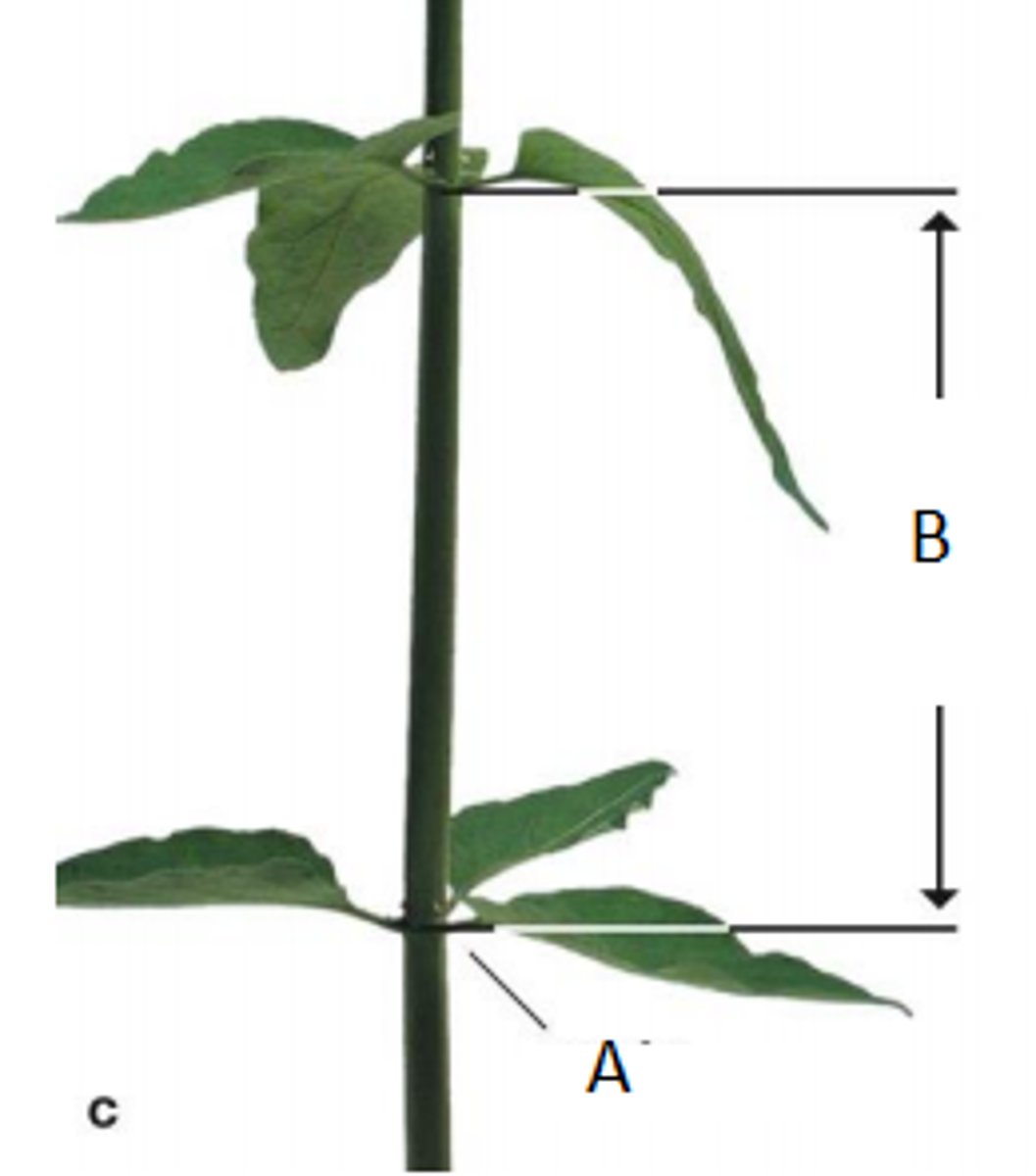
Axillary bud
Bud that occurs in the axil, the upper angle where a twig or leaf emerges from the stem
Herbaceous plant
Type of plants that produce mostly only vascular tissues
Woody plant
Type of plant that produces both primary and secondary vascular tissues
Primary vascular tissues
Plant tissues composed of primary xylem and phloem
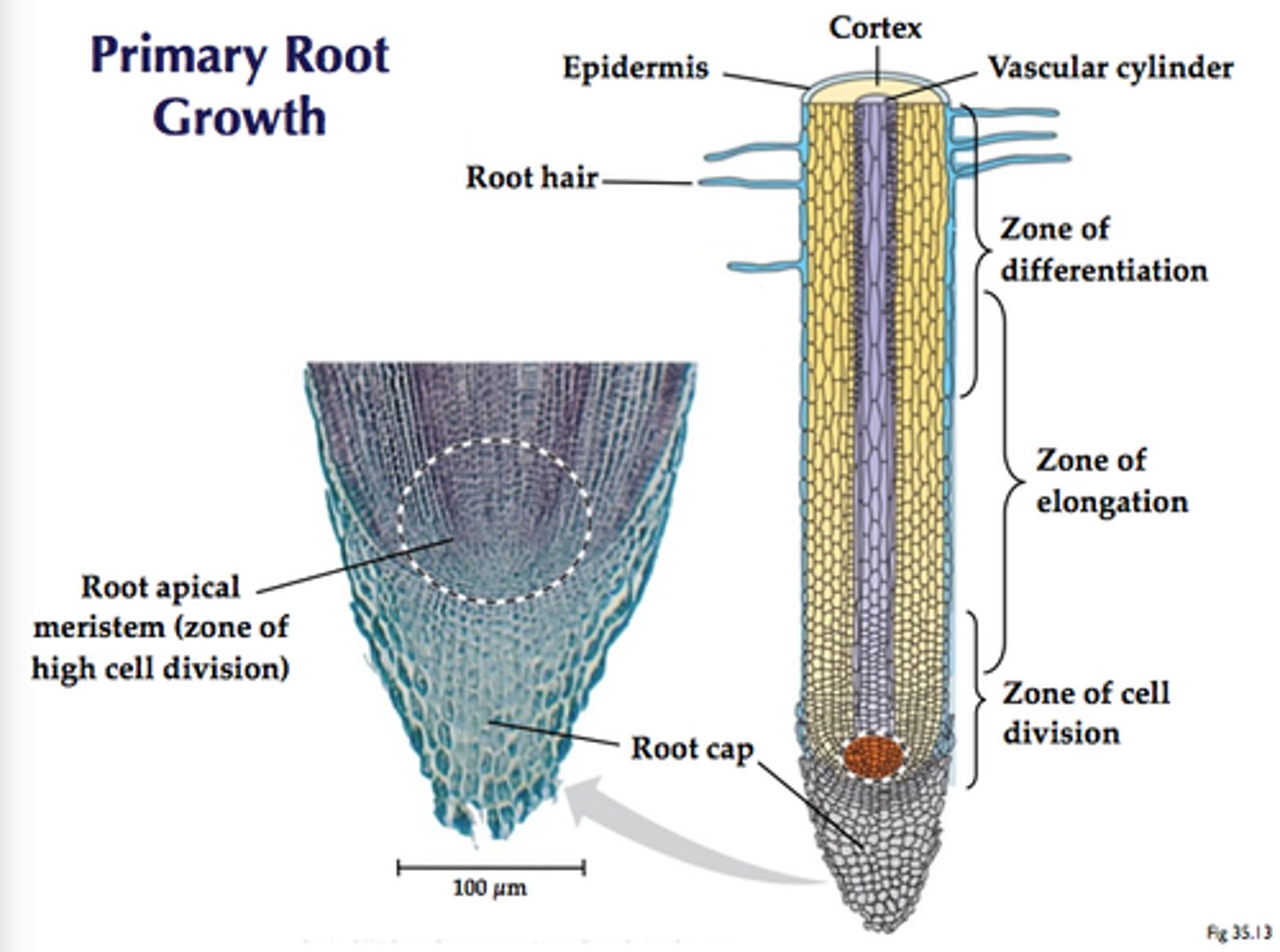
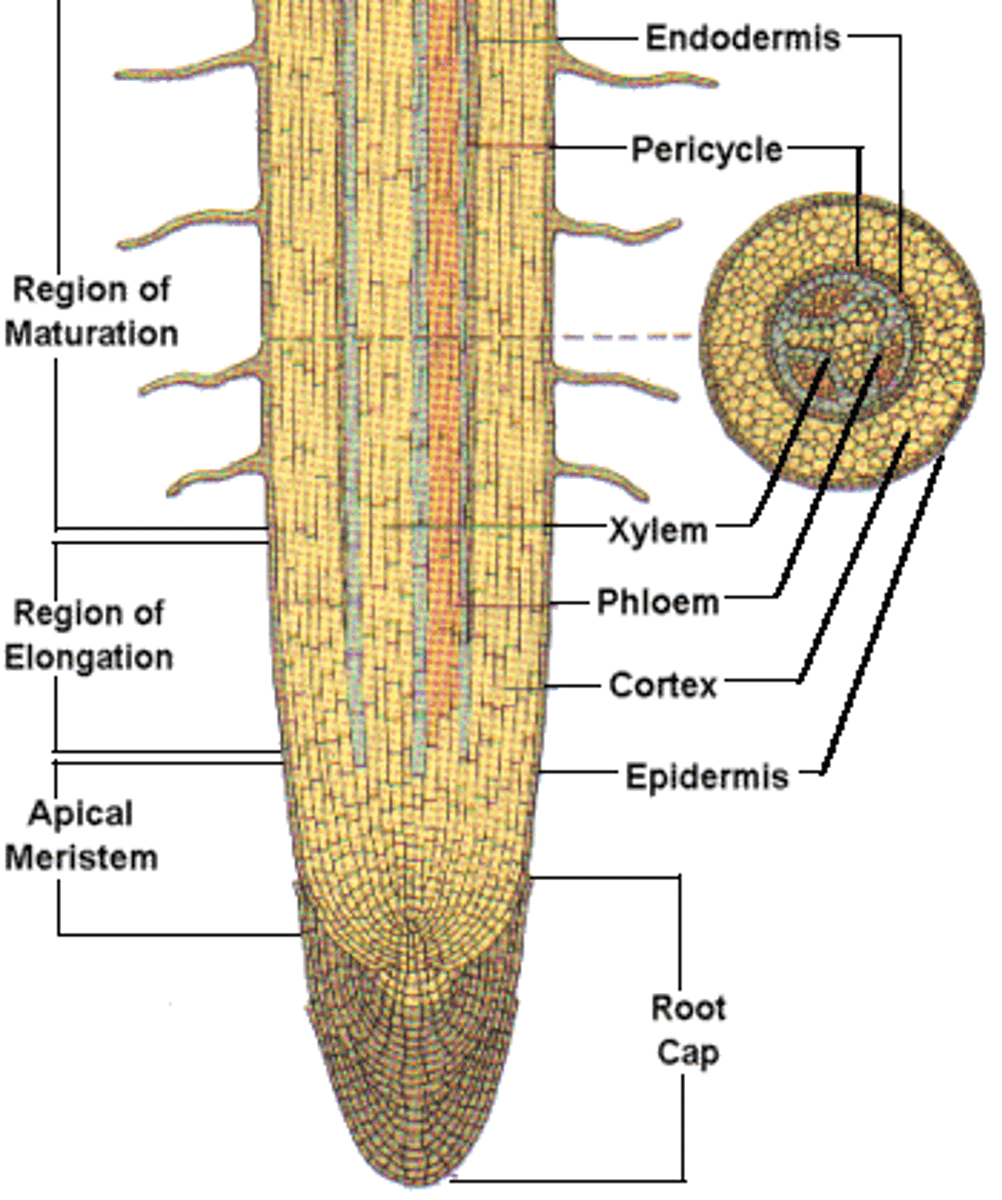
(Three zones of) root growth
The root apical meristem region, zone of elongation, and zone of maturation are the three major zones of what ?
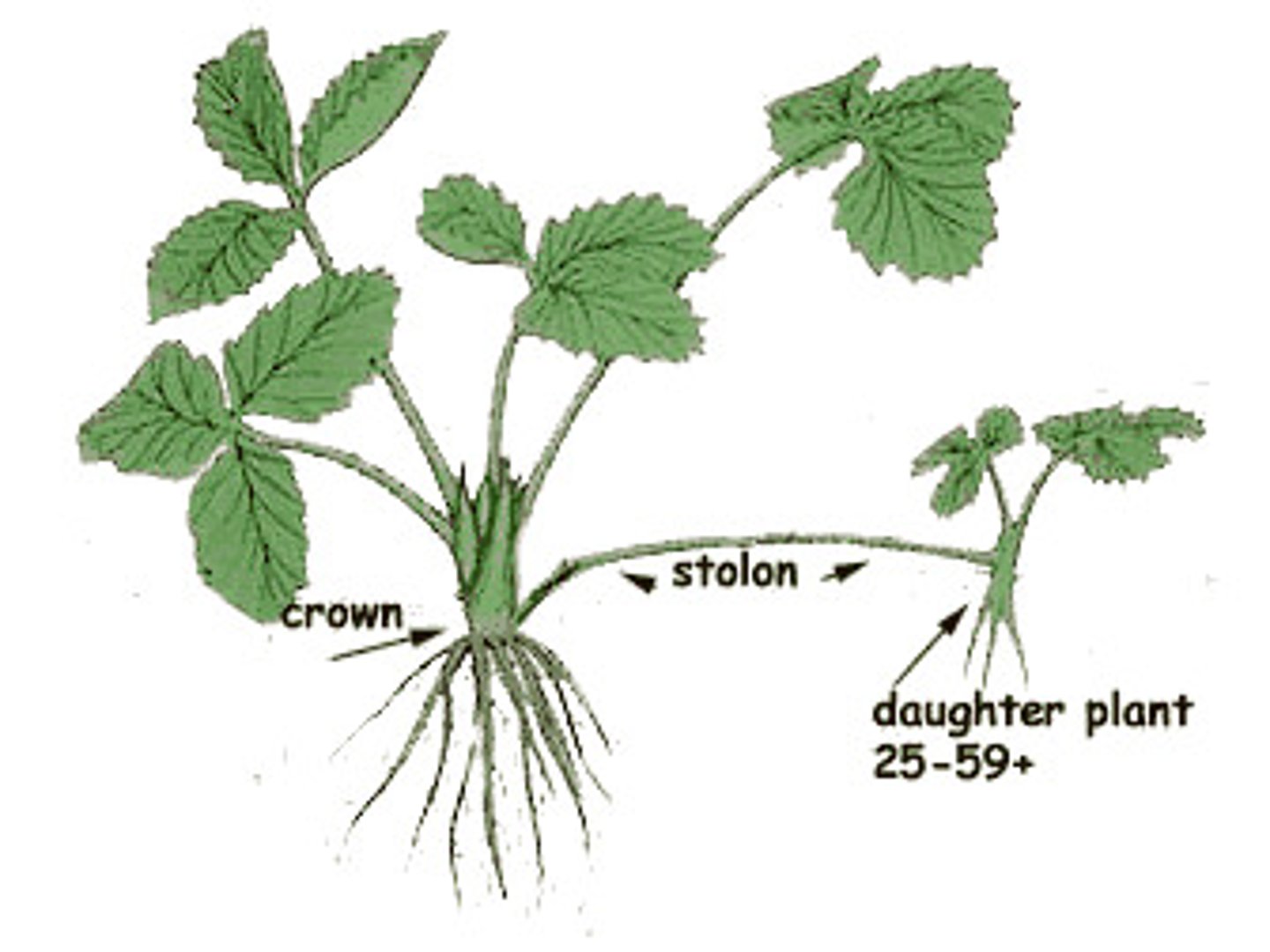
Stolon
Above ground horizontal stem; produce new plants when nodes touch the ground
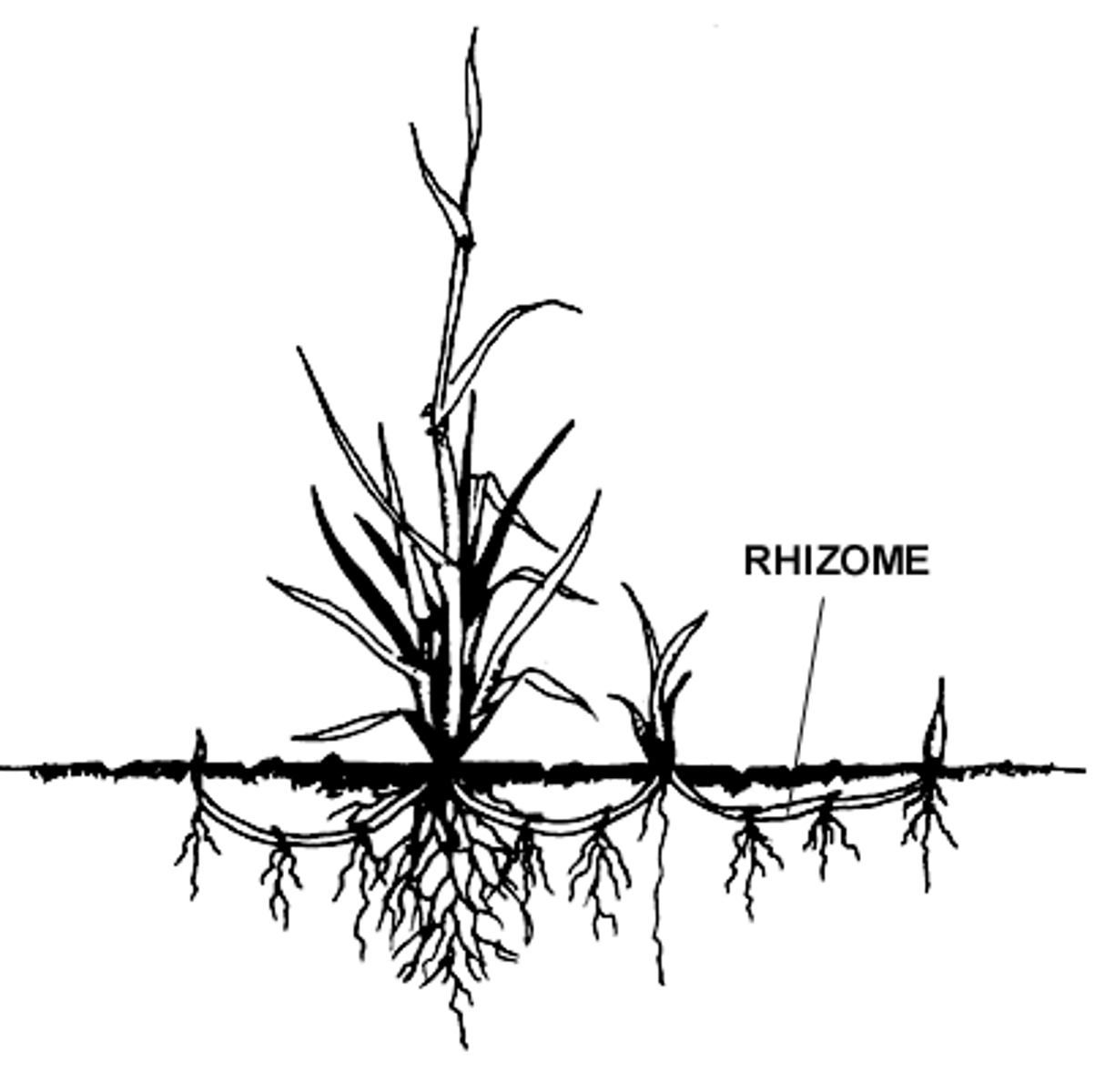
Rhizome
Underground horizontal stem; contribute to asexual reproduction
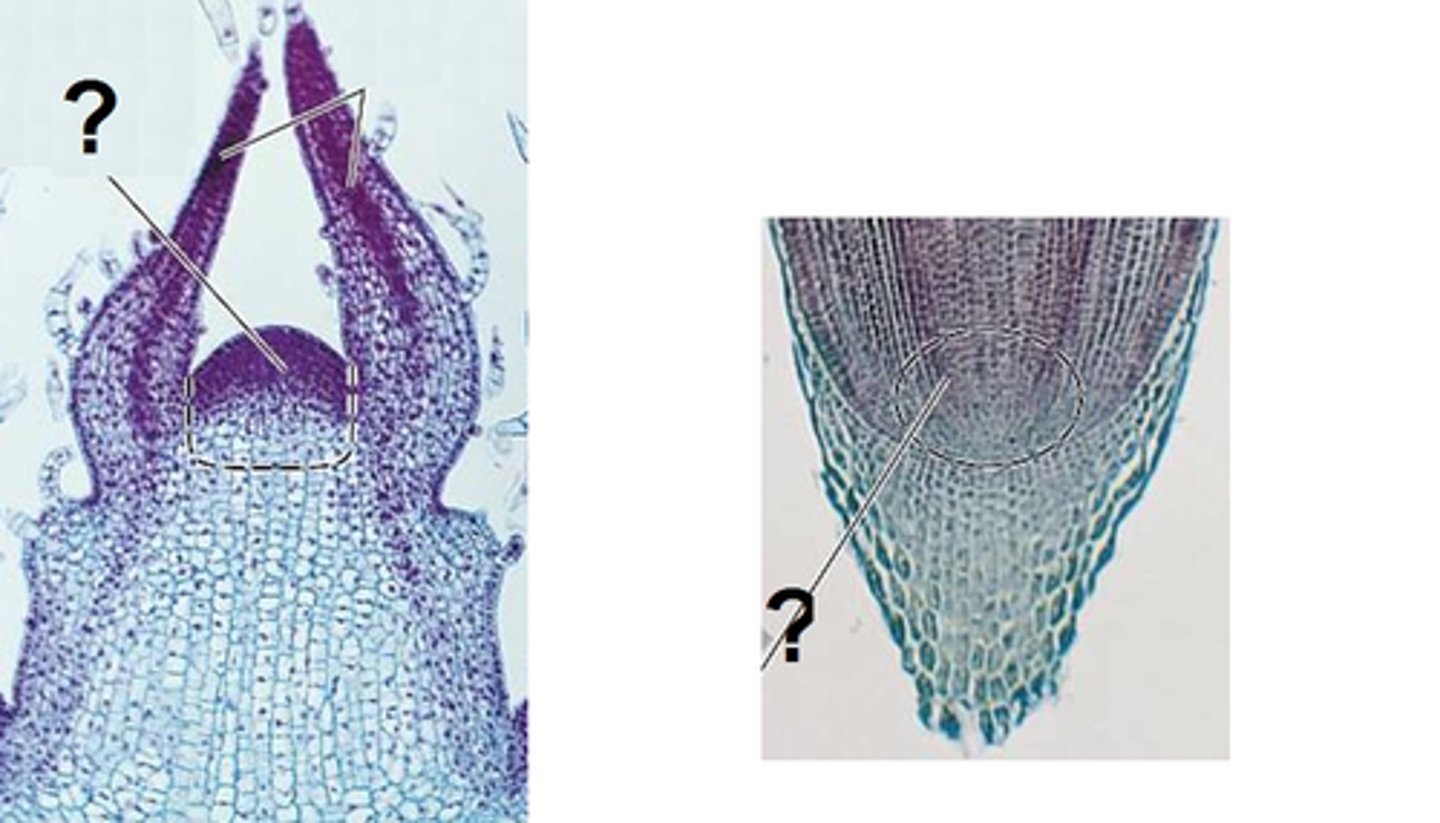
(Root) apical meristem
Region within the growing root containing meristematic (stem) cells
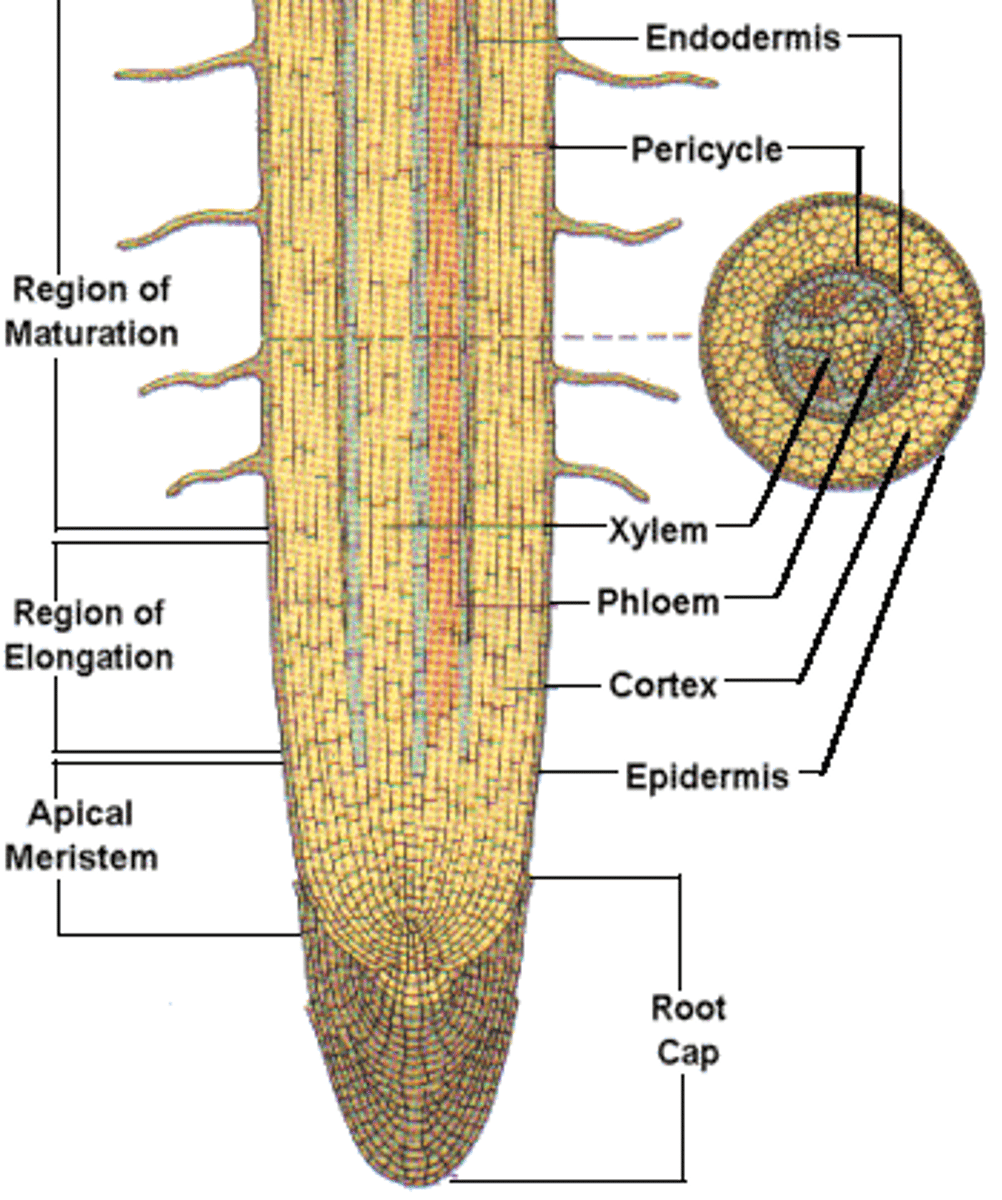
Zone of maturation
Area above the zone of elongation in a plant root where most root cell differentiation and tissue specialization occur; differentiated areas include root hairs, cortex, and endodermis
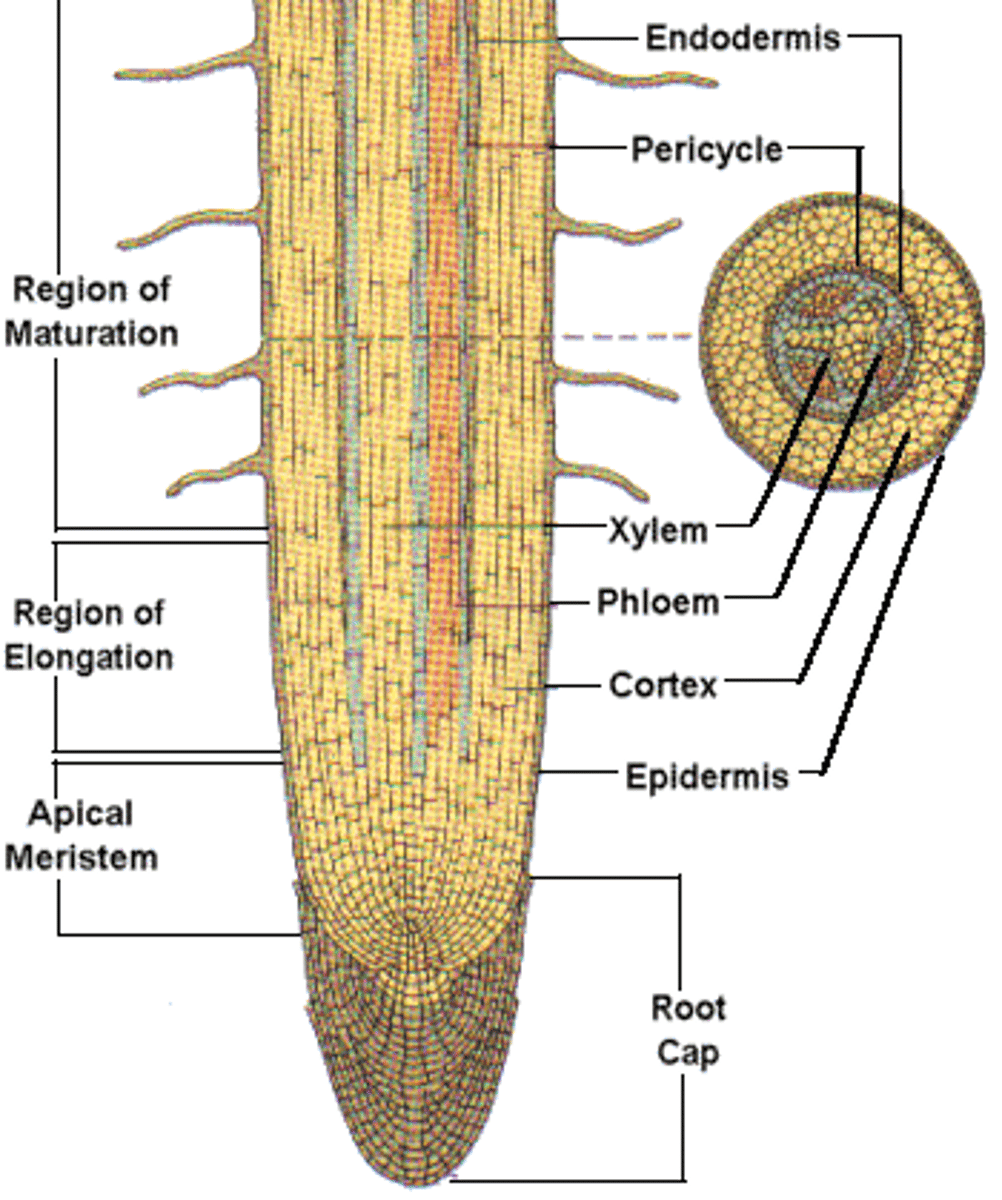
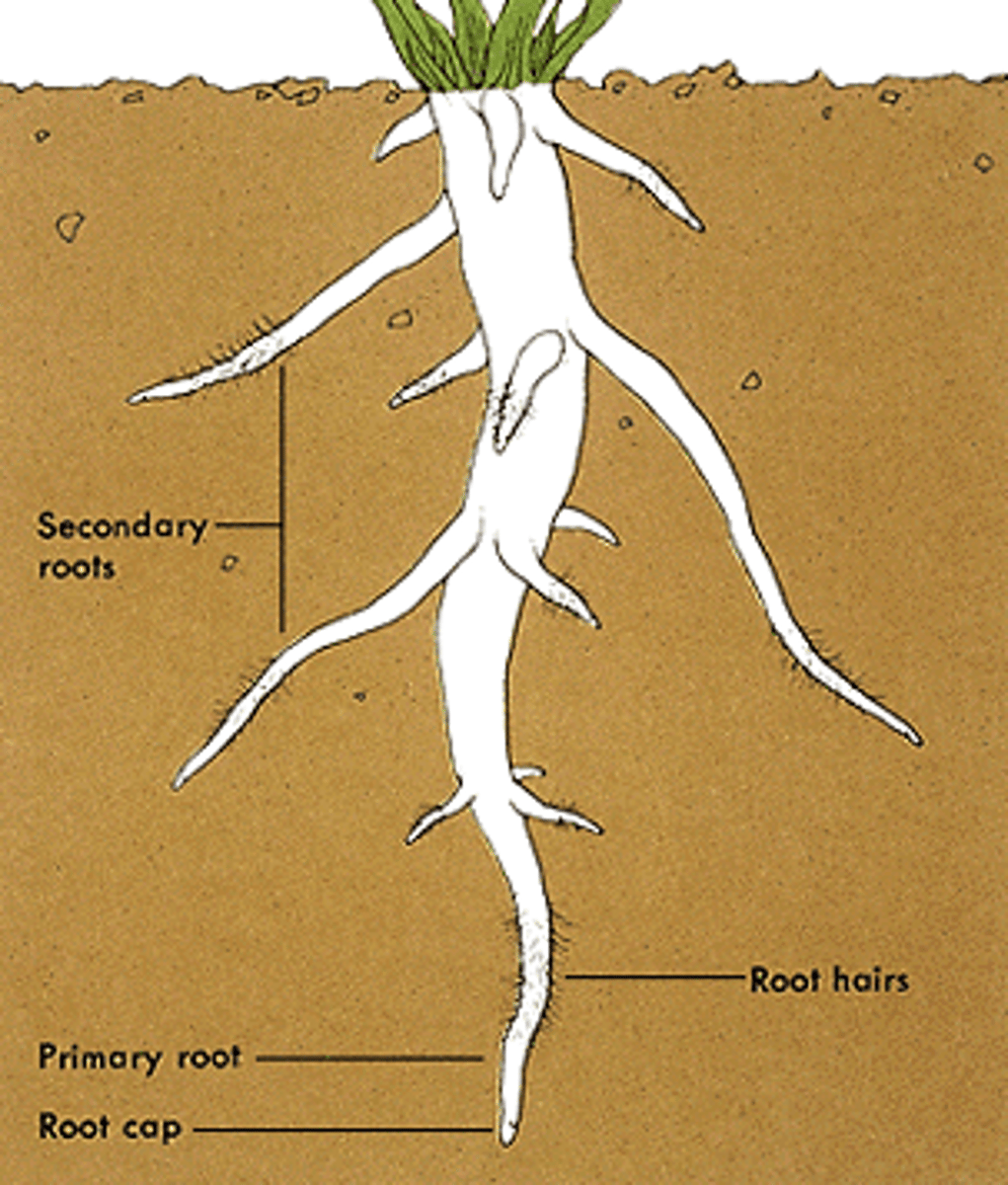
Root hair
Specialized epidermal cells that functions to absorb water and minerals
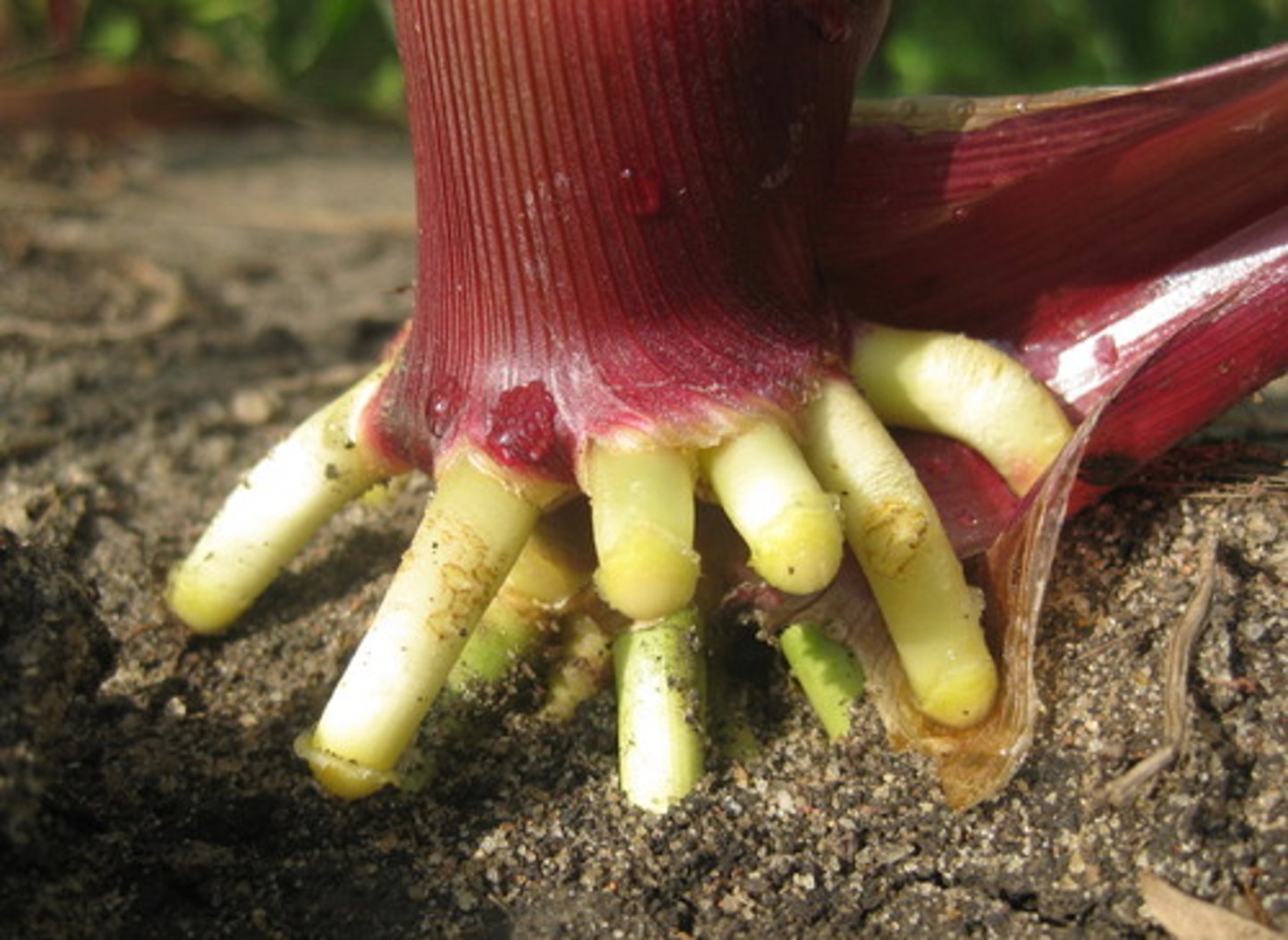
Primary root (taproot)
Root system of eudicots consisting of one main root with many branching roots
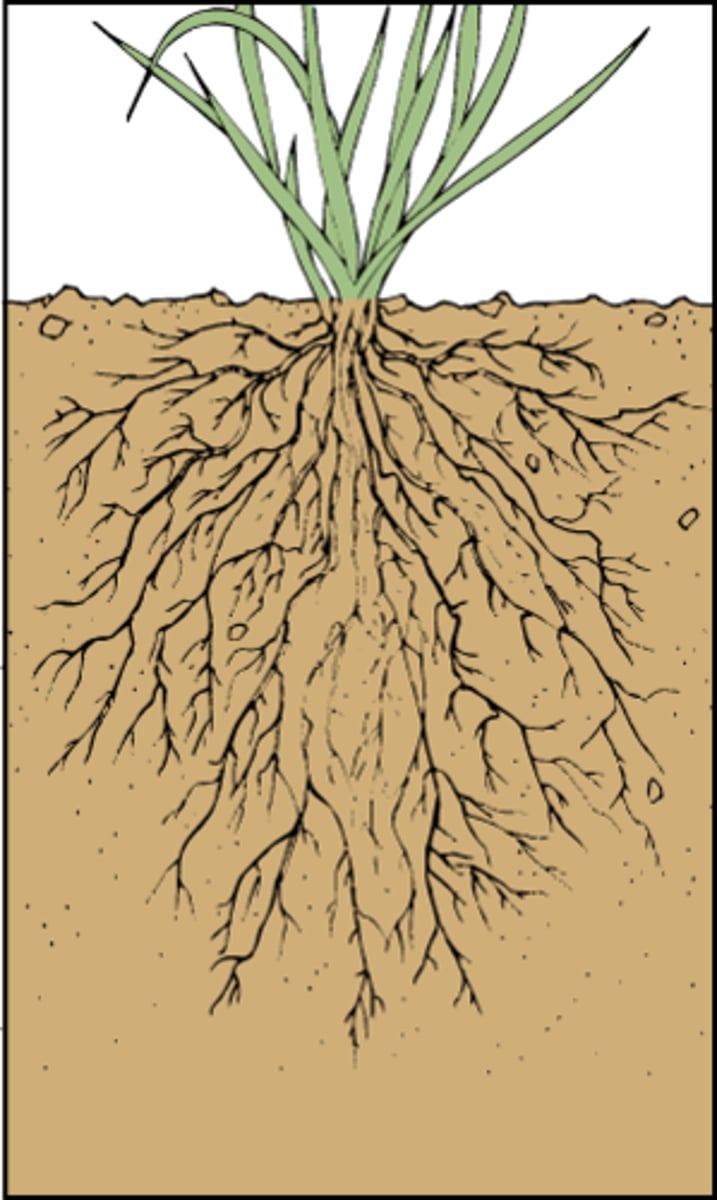
Fibrous root
Root system of monocots consisting of multiple adventitious roots that grow from the stem base
Adventitious root
A root that is produced on the surface of stems (and sometimes leaves) of vascular plants; roots that develop at the basis of stem cuttings

Tropism
Any growth response that depends on a stimulus that occurs in a particular direction
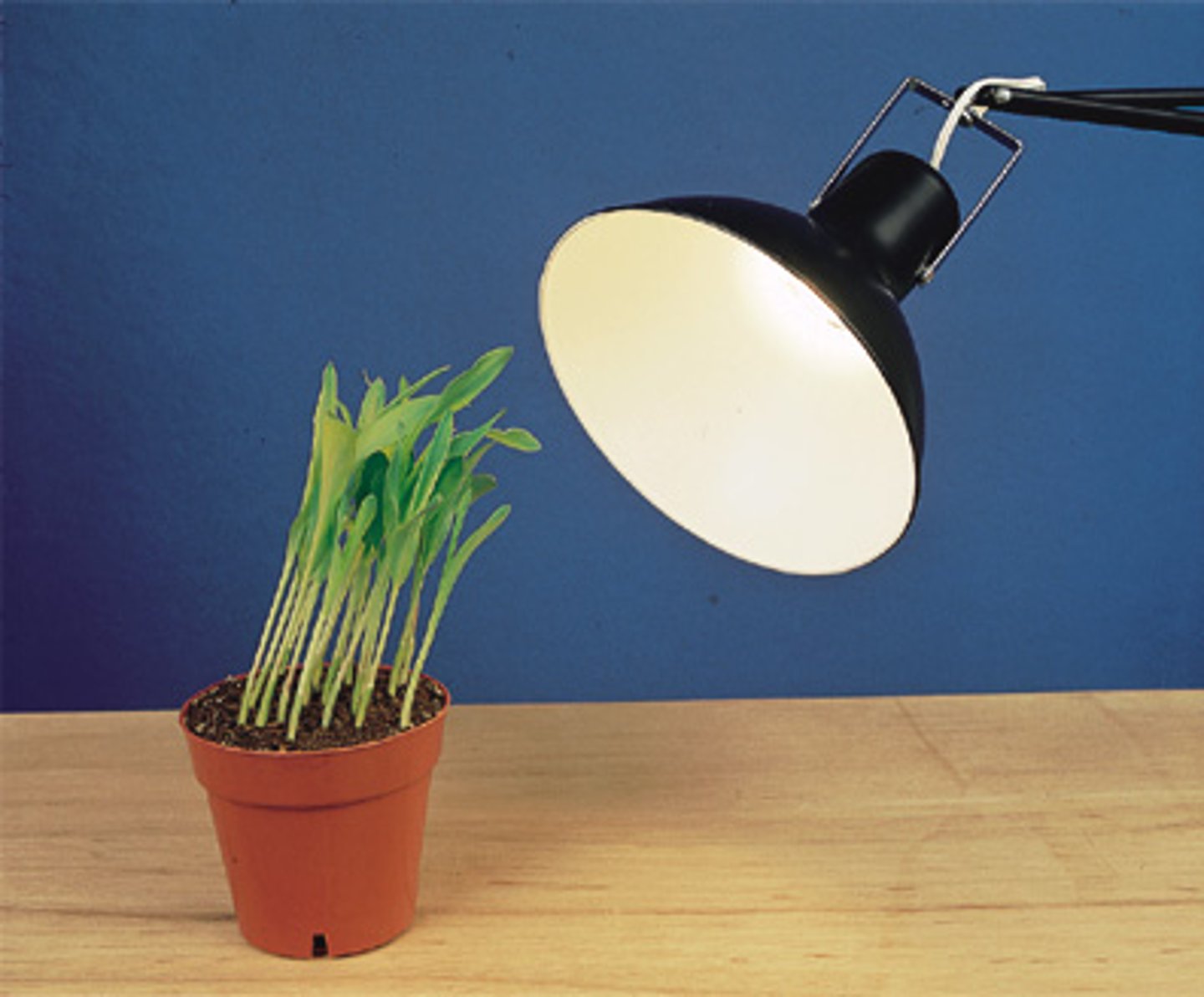
Phototropism
The tendency of plants to grow toward a light source

Auxins
Type of plant hormone that influences structure, development, and behavior of plants; produced in shoot apical meristem and is found in young leaves, flowers, and fruits
Cytokinins
Type of plant hormone that promotes cell division; derivative of adenine; made primarily in root tips; senescence:
Gibberellins
Type of plant hormone that promotes cell division and cell elongation; dormancy: retards leaf and fruit aging
Ethylene
Type of plant hormone that is involved in abscission (natural detachment of parts in plants); also coordinating plant development and stress responces; only hormone that comes in gas form
Abscisic Acid
Plant hormone involved with stopping or slowing plant metabolism when growing conditions are poor; seed and bud dormancy, closure of stomata
Brassinosteroids
Type of plant hormone that promotes cell elongation and division, stimulates xylem development, retards leaf drop; can be applied to protect plants from heat, cold, high salinity, herbicide injury, and disease; chemically related to animal steroid hormoes
Photoperiodism
Plant's ability to measure and respond to the amount of light and day length
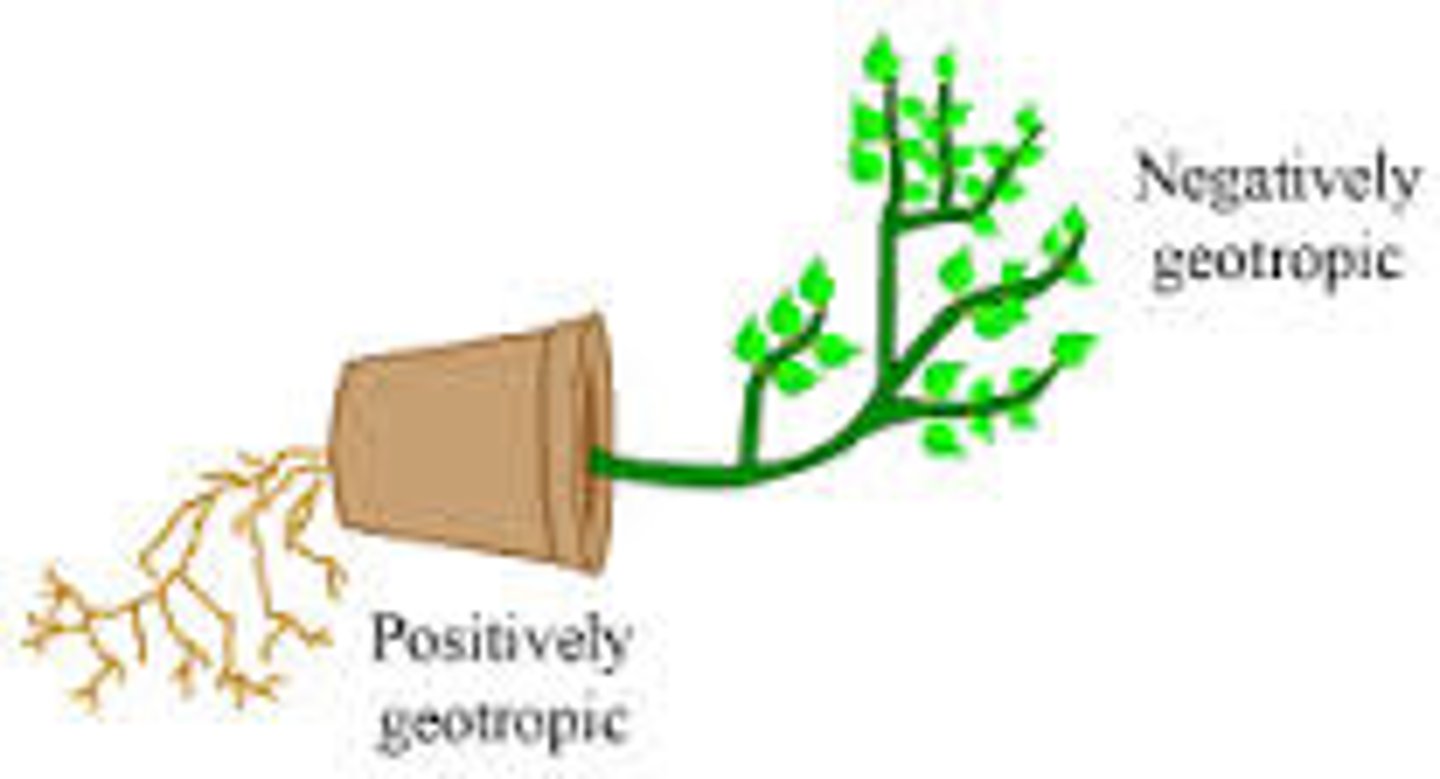
Gravitropism
Plant growth in response to the force of gravity; both roots and shoots detect gravity by means of starch-heavy plastids called statoliths

Thigmotropism
Unusual growth of plants due to contact with solid objects
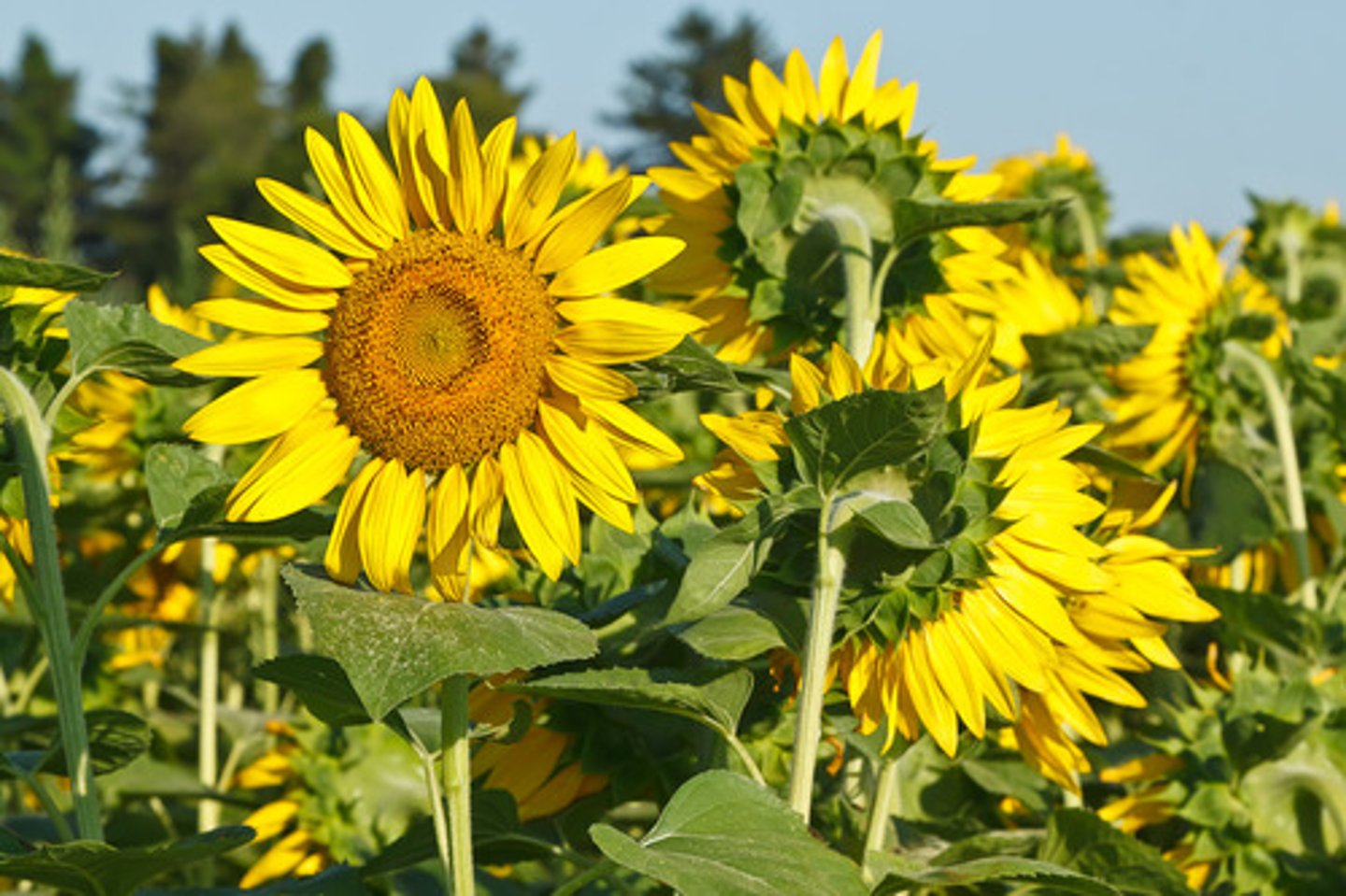
Heliotropism
Diurnal motion of plant parts in response to the direction of the sun

Nastic movements
Plant movements that occur in response to stimuli, but the direction of movement is not dependent on the direction of the stimulus
