Puberty, Menstruation, Common Menstrual Disorders
1/96
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
97 Terms
puberty
physical maturation that occurs during adolescence
adolescence
timeframe in human development of physical, cognitive, and psychosocial maturation
what is the age of puberty in males and females?
Females: 11yo (8-13yo)
Males: 12yo (9-14yo)
precocious puberty
early gonadotropin secretion from the pituitary (FSH and LH) results in signs of puberty at an age 2-3 standard deviations below the mean age (physical signs before 8)
precocious pseudopuberty
early signs of puberty from estrogen exposure in females, androgen exposure in males
delayed puberty
absence of signs of puberty at an age 2-3 standard deviations above the mean age
gonadarache
activation of the gonads stimulated by pituitary hormones
what hormones are involved in gonadarache?
follicule stimulating hormone (FSH) and luteinizing hormone (LH)
adrenarche
increase in the adrenal androgens
what hormone is involved in adrenarche?
dehydroepiandrosterone (DHEA)
thelarche
the development of breasts stimulated by ovarian hormones
what hormones are involved in thelarche? what are they each specifically responsible for?
estradiol: growth of ducts
progesterone: growth of lobules and alveoli
pubarche
the development of axillary and pubic hair stimulated by adrenal androgens
menarche
the first menstrual period stimulated by ovarian hormones
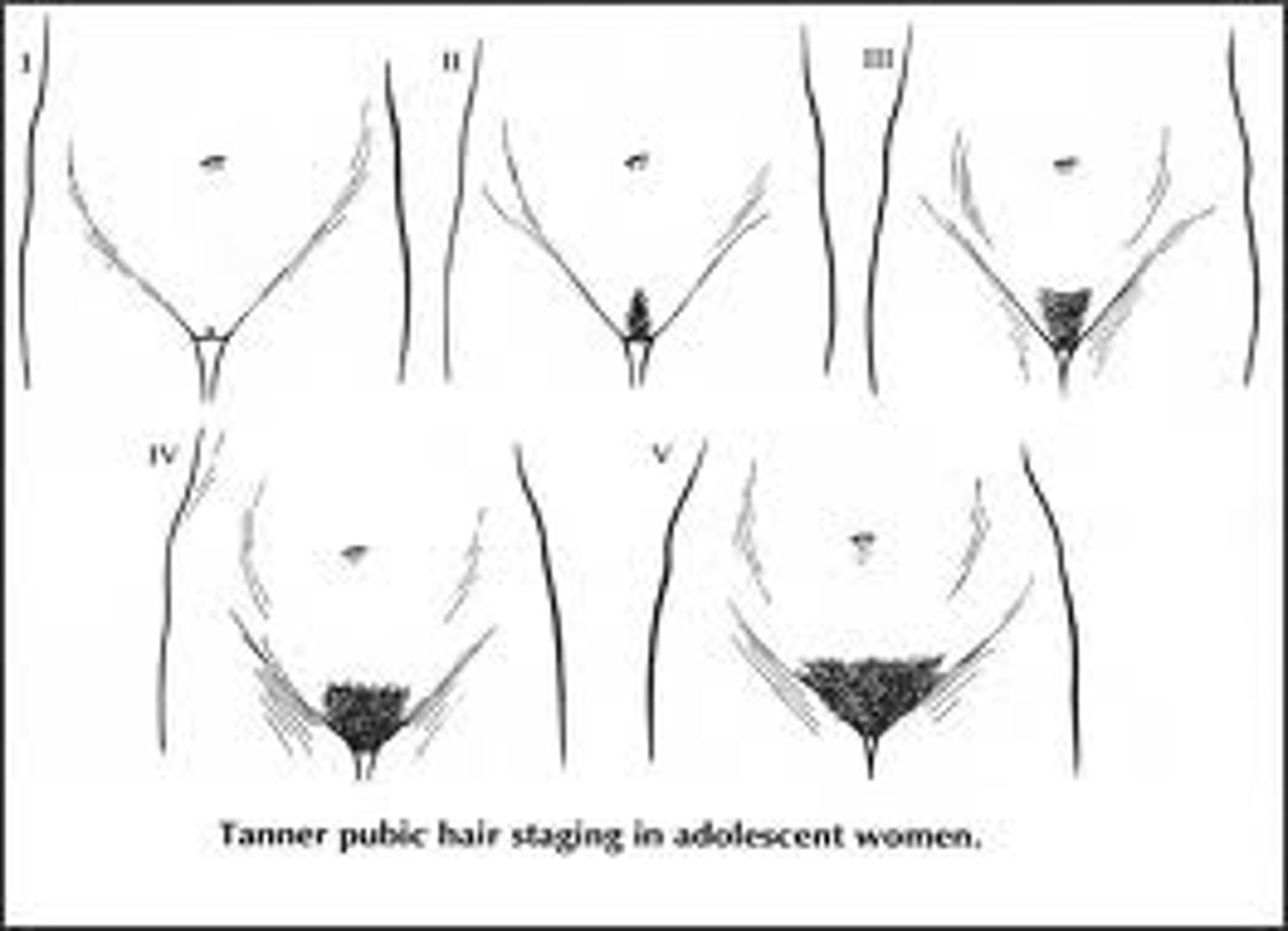
what are the 5 tanner stages for hair?
Stage I: no hair
Stage II: sparse growth
Stage III: darker, coarser, more curled hair
Stage IV: adult type hair over a smaller area
Stage V: spread to the medial surface of the thighs
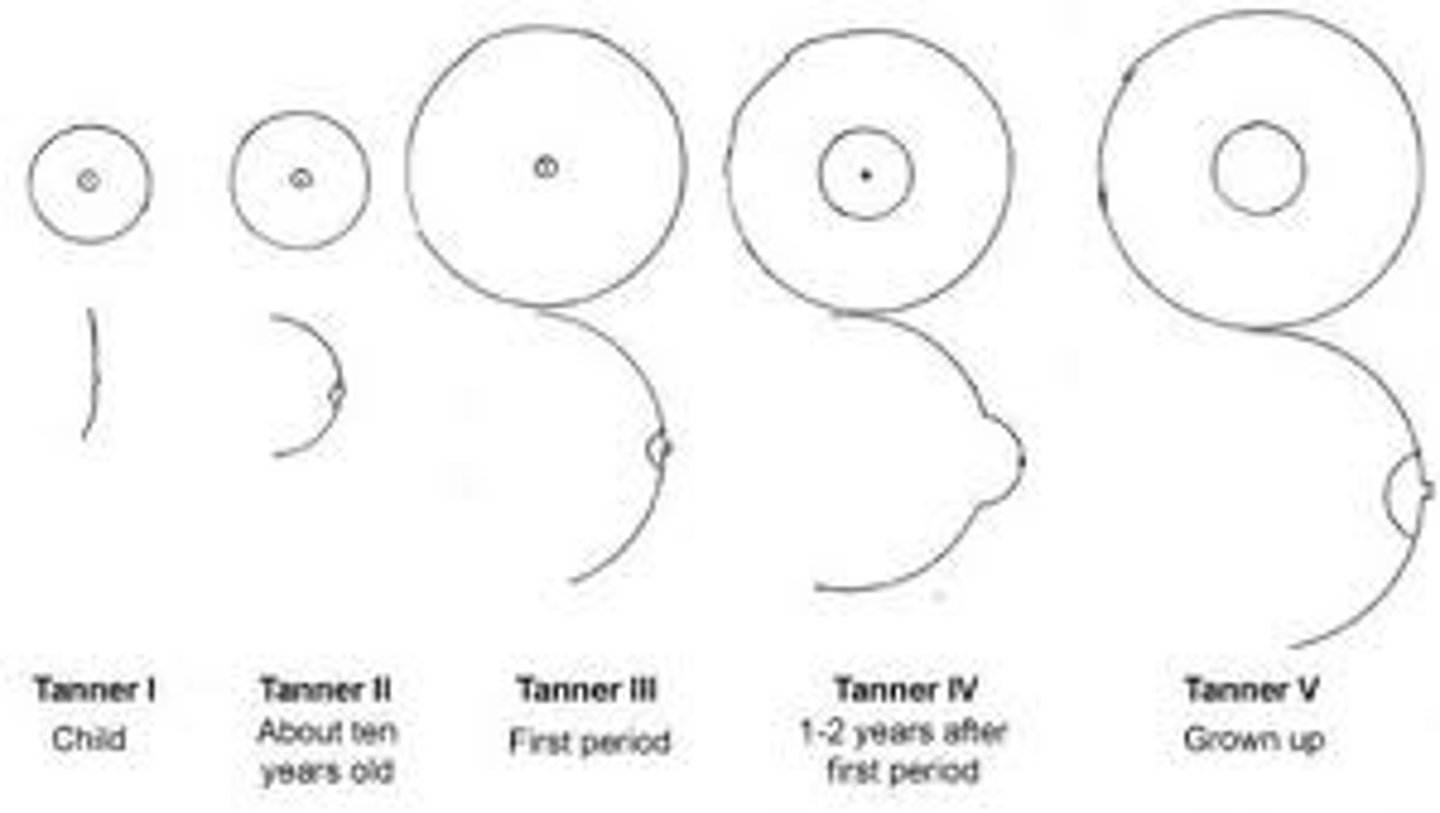
what are the 5 tanner stages for breast development?
Stage I: elevation of papilla only
Stage II: breast bud
Stage III: enlargement of breast and areola
Stage IV: projection of the areola and papilla
Stage V: recession of the areola to the contour of the breast, projection of papilla only
what are the 3 layers of the uterus?
serosa, myometrium, endometrium
serosa
outer connective tissue layer of the uterus
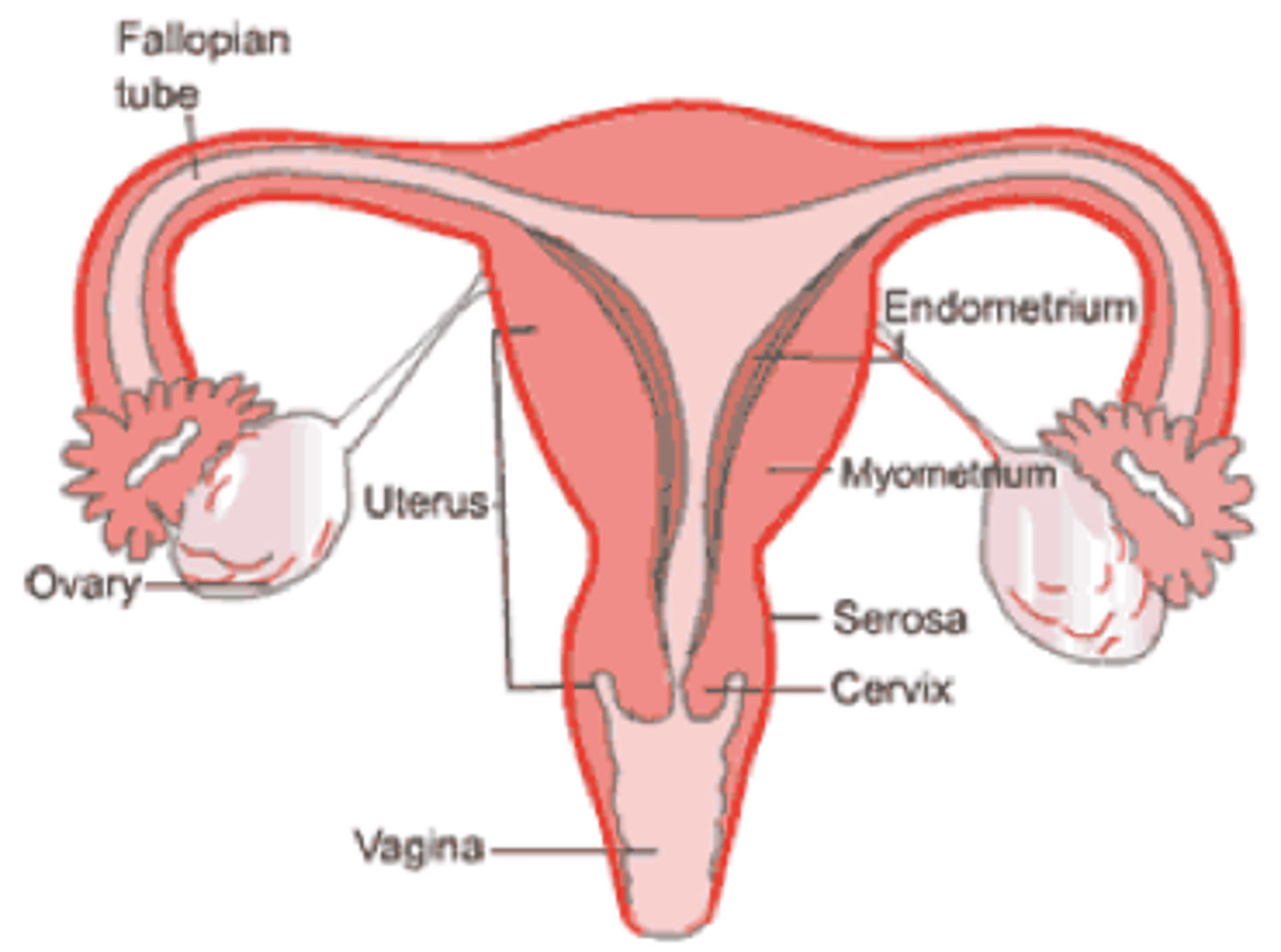
myometrium
the muscular layer of the uterine wall (smooth muscle)
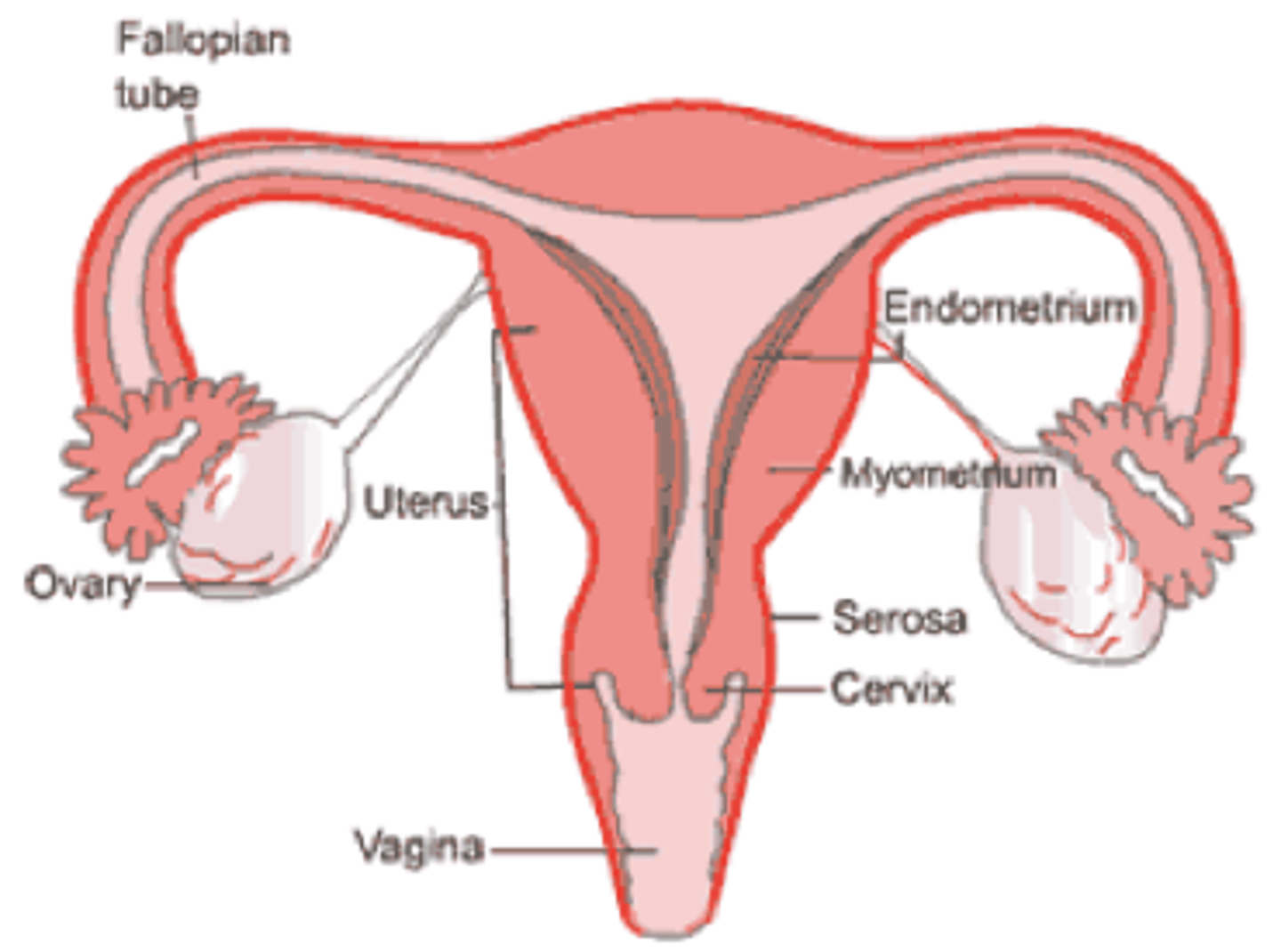
endometrium
mucous membrane lining of the uterus; provides environment for reproduction
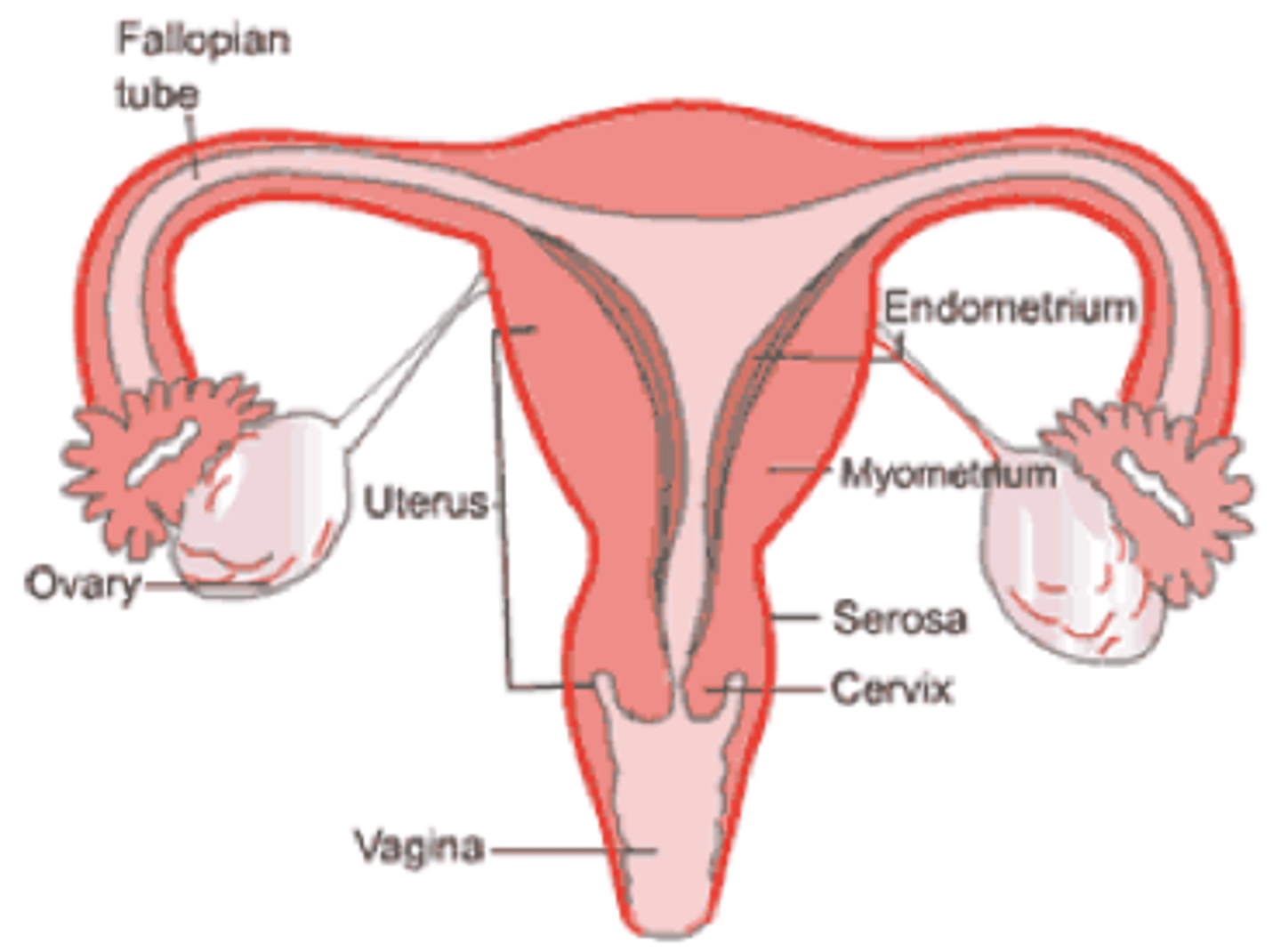
what are the 3 layers of the endometrium? what layers build and shed? what layer is the basal layer that is always there?
stratum compactum and
stratum spongiosum (builds and sheds)
stratum basale (basal layer that is always there)
what is the average frequency of a menstrual cycle?
28-35 days
typically how long is the follicular/proliferative phase of the menstrual cycle?
14-21 days
typically how long is the luteal/secretory phase of the menstrual cycle?
14 days
what organs produce estrogen?
ovaries (estradiol), adrenal glands (estrone), and liver (estriol)
what are the functions of estrogen?
Stimulates endometrial growth
Stabilizes the endometrium
Prepares the follicle for the release of an egg
Helps create a "sperm-friendly" environment in the uterus.
what organs produce progesterone?
ovaries and adernal glands
what are the functions of progesterone?
Prepares the uterus for pregnancy
Balances estrogen to prevent over-thickening of the endometrium
Facilitates estrogen-withdrawal bleeding (menses)
what organ produces FSH?
anterior pituitary gland
what are the functions of FSH?
Stimulates follicles to ripen eggs
Stimulates the ovaries to produce estrogen
Acted on by Activin and Inhibin
what organ produces LH?
anterior pituitary gland
what are the functions of LH?
Stimulates ovulation
Stimulates the follicle to change into the corpus luteum
Stimulates secretion of estrogen and progesterone from the corpus luteum
what organ produces GnRH?
hypothalamus
what are the functions of GnRH?
Stimulates the synthesis and release of pituitary gonadotropins (FSH and LH)
Released in a pulsatile fashion
Responds differently depending on timing in the cycle
which organ produces prolactin?
anterior pituitary gland
what is prolactin affect by? what does it cause? and what does it inhbit?
Affected by environmental factors (nipple manipulation, medications and drugs, surgical and emotional stress, etc), hypothalamic regulating hormones (estrogen, progesterone, dopamine, etc.), and pituitary regulating hormones (activin, relaxin, melatonin, etc)
Causes milk secretion from the breasts during lactation
Inhibits the affects of FSH and LH, often resulting in amenorrhea and anovulation
follicular/proliferative phase
Rising FSH stimulates follicle growth; dominant follicle secretes estrogen.
Estrogen promotes the proliferation of the endometrium (thickening and repair after menstruation).
Preparation for ovulation and potential implantation.
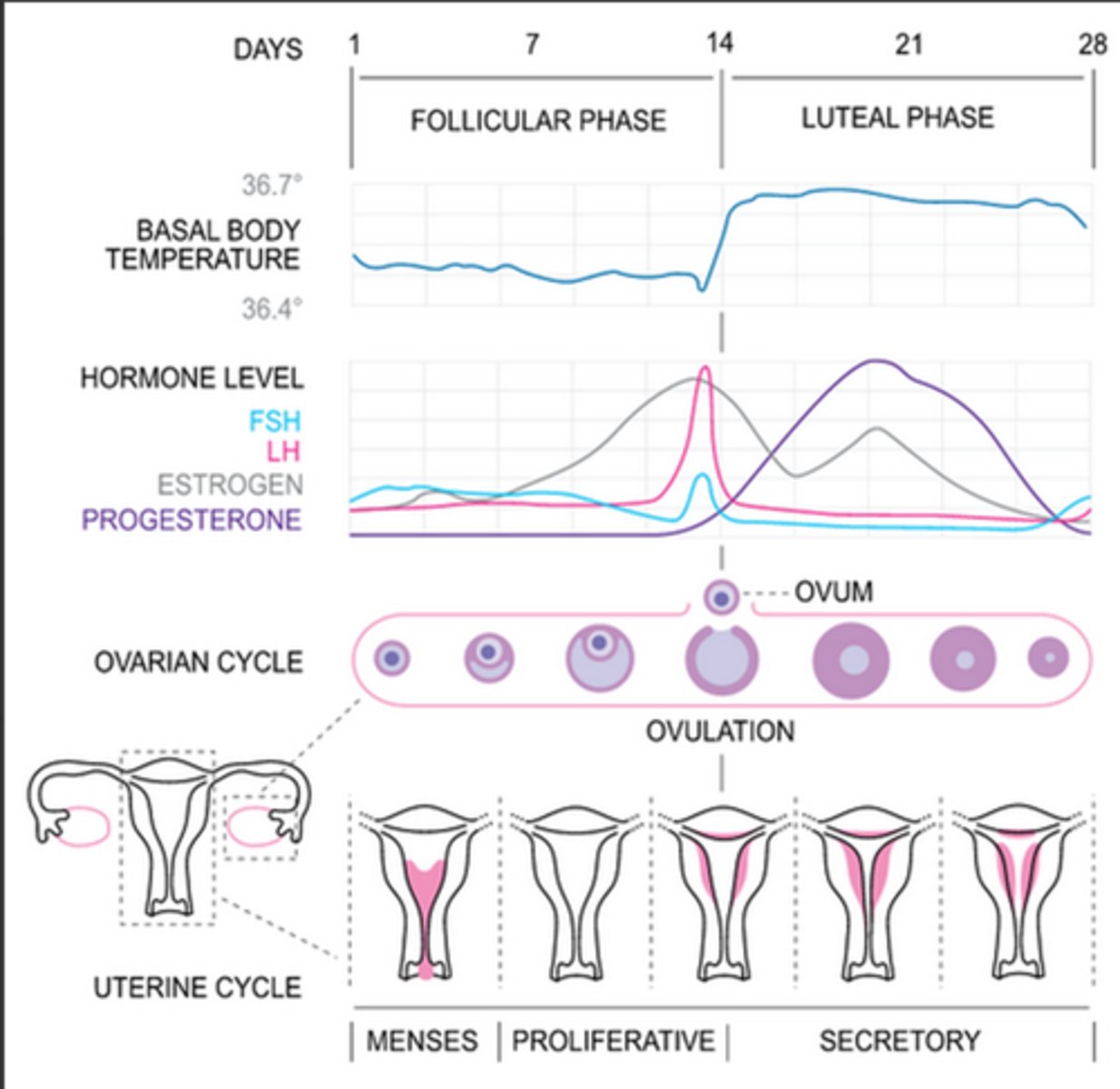
what is activin?
a protein hormone produced in the ovaries that stimulates the follicular/proliferative phase by acting on the anterior pituitary to release FSH
what is inhibin?
a protein hormone produced in the ovaries that is stimulate by high estrogen levels during the follicular/proliferative phase that suppresses FSH secretion from the anterior pituitary gland, acting as a negative feedback regulator
what is the LH surge?
peak estrogen levels cause an increase of the frequency of GnRH pulsation which causes a rapid increase of LH which then leads to ovulation
what is the corpus hemorrhagicum?
the ruptured follicle that fills with blood after ovulation
mittelschmerz
pain that occurs in the lower abdomen during ovulation from minor bleeding from the corpus hemorrhagicum
how is the corpus luteum formed and what does it produce?
clotted blood in the follicle degrades and is replaced with luteal cells; progesterone in increasing amounts as well as estrogen in lesser amounts
luteal/secretory phase
Progesterone (from the corpus luteum) stimulates the endometrium to become more glandular and vascular, preparing for implantation of a fertilized egg.
High progesterone and estrogen suppress FSH and LH secretion to prevent new follicle development.
If fertilization occurs: The corpus luteum is maintained by hCG from the developing embryo.
If no fertilization: The corpus luteum degenerates, hormone levels drop, and the endometrial lining sheds (menstruation)
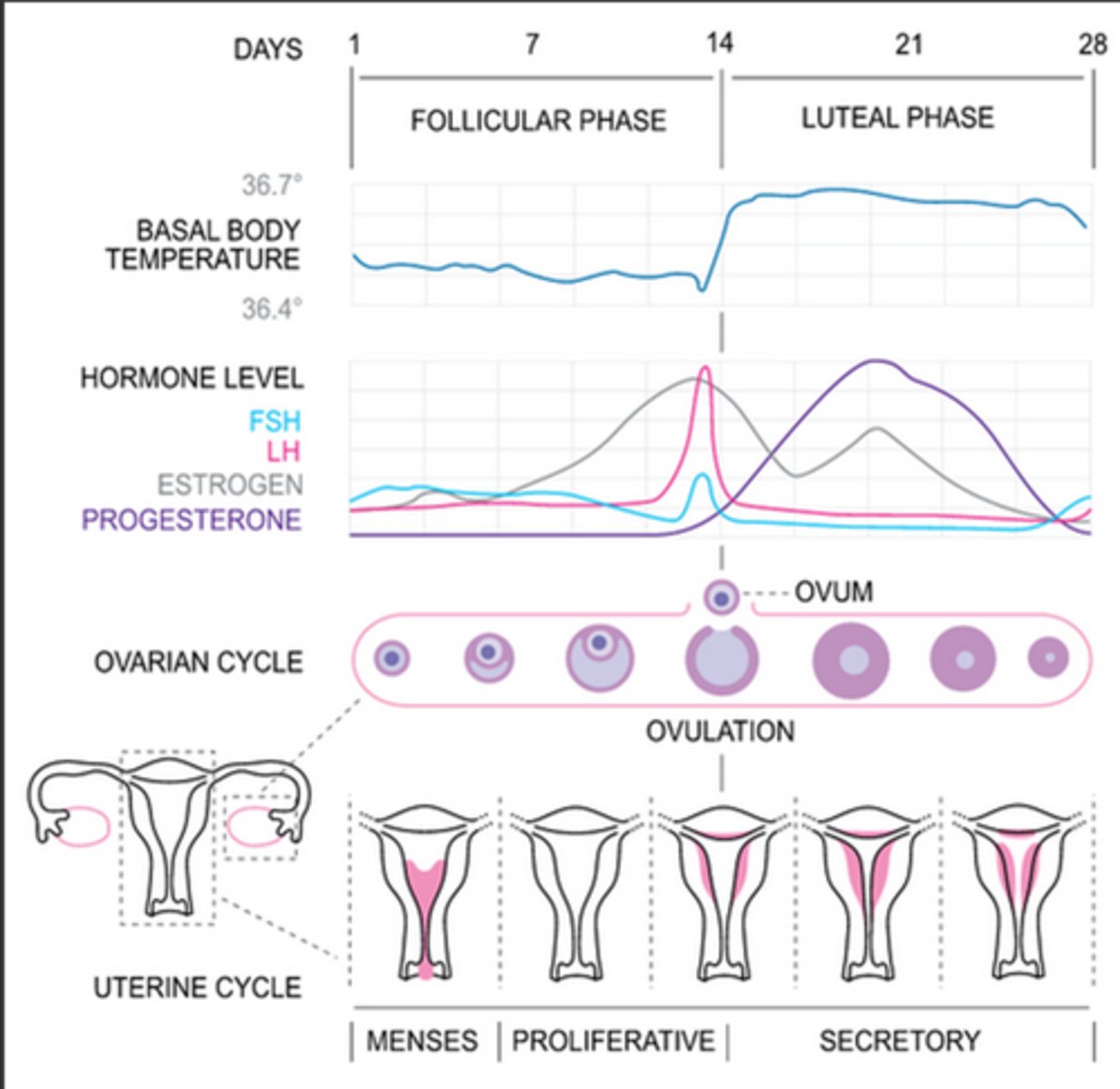
what is the corpus albicans?
fibrous tissue left behind by corpus luteum
what effects does estrogen and progesterone have on the cervix?
Estrogen: Makes the cervical mucous thinner and alkaline, facilitating sperm transport
Progesterone: Thickens cervical mucous
what effects does estrogen and progesterone have on the vagina?
Estrogen: Increases cornified epithelial cells
Progesterone: Promotes proliferation of vaginal epithelium
what effects does estrogen and progesterone have on the breasts?
Estrogen: Causes breast enlargement, pigmentation of the areola, and proliferation of mammary ducts
Progesterone: Causes growth of lobules, alveoli, and areola, supports lactation
what effects does estrogen and progesterone have on the MSK system?
Estrogen: Causes epiphyseal plate closure, decreases bone resorption, influences secondary sexual characteristics
Progesterone: Increases bone formation
what effects does estrogen and progesterone have on neuro?
Estrogen: Increases libido, regulates body temperature, delays memory loss
Progesterone: Enhances cognitive function, decreases anxiety
what effects does estrogen and progesterone have on the endocrine system?
Estrogen: Increases pituitary size, libido, angiotensin, and thyroid binding globulin
Progesterone: Promotes metabolism of fat and thyroid function
what effects does estrogen and progesterone have on parts of the body (other than the ones previously mentioned)?
Estrogen: Inhibits comodones and acne, promotes thrombosis, regulates cholesterol production, reduces abdominal fat
Progesterone: Promotes hair growth, regulates blood pressure and blood sugar, dilates blood vessels, prevents constipation
anovulatory cycles
menstrual cycles without ovulation; common close to menarche and menopause; no corpus luteum
what are 4 ways to predict ovulation?
map cycles, detect change in cervical mucous, ovulation predictor kits, basal body temperature
what is "fertile time"?
~2 days before ovulation through 1-2 days after ovulation
dysmenorrhea
painful menstruation that limits activity and requires OTC or Rx medication
what is primary and secondary dysmenorrhea?
Primary- idiopathic
Secondary- pathological cause
what is the main etiology of dysmenorrhea?
Prostaglandin release from endometrial sloughing
what is the typically clinical presentation including symptoms of dysmenorrhea?
Pain typically occurs with the onset of menses
Nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, headache
what are management options for dysmenorrhea?
Conservative therapies
Antiprostaglandins (NSAIDs, Cox 2 inhibitors)
Combination oral contraceptive pills (cOCPs)
amenorrhea
absence of menstruation
what is primary and secondary amenorrhea?
Primary Amenorrhea: failure of menarche by age 15yo or 13yo with no development
Secondary Amenorrhea: absence of menses for more than three cycles or six months in women who were previously menstruating
Mullerian dysgenesis
(primary amenorrhea) congenital absence of the uterus and the upper vagina
vaginal agenesis
(primary amenorrhea) failure of the vagina to develop; will get signs of period and normal development but no bleeding
transverse vaginal septum
(primary amenorrhea) tissue barrier across the vagina causing a blockage
imperforate hymen
(primary amenorrhea) membrane covering the vaginal opeing
Asherman's syndrome
(secondary amenorrhea) development of scar tissue as a result of surgery, difficult birth, or some type of trauma
name 3 possible causes of amenorrhea from hypothalamic dysfunction
Interference with GnRH transport or GnRH pulse discharge
Congenital absence of GnRH
Kallmans Syndrome Pituitary Dysfunction
what would be an example of primary pituitary dysfunction causing amenorrhea?
Congenital absence of the pituitary (rare and lethal)
name 5 examples of acquired pituitary dysfunction causing amenorrhea
Sheehan's syndrome
Ablation or irradiation of the pituitary
Fe+ deposits in the pituitary
Prolactinoma
Hypothyroidism
Sheehan's syndrome
postpartum pituitary necrosis
what is a sex chromosome disorder that causes amenorrhea and is when the ovaries do not develop or do not fully develop?
Turner's syndrome
what are examples of primary and secondary ovarian failure causing amenorrhea?
primary: premature ovarian failure and ovarian resistance
secondary: PCOS
how do you diagnosis primary amenorrhea?
Laboratory work-up (FSH, testosterone, prolactin, 17-hydroxyprogesterone, ACTH stimulation test, electrolytes)
Pelvic exam
Pelvic ultrasound
Genetic testing/Karyotype
how do you diagnosis secondary amenorrhea?
Laboratory Work-up (HCG, prolactin, testosterone, thyroid stimulating hormone, T3, T4, FSH, LH, estradiol)
Pelvic exam
Pelvic ultrasound
Progestin-challenge test
how do you treat amenorrhea?
treat underlying cause
stimulate menses/protect the endometrium
premenstrual syndrome (PMS)
the cyclical occurrence of symptoms that interfere with certain aspects of daily life, have a predictable relationship with menses
premenstrual dysphoric disorder (PMDD)
PMS with significant interference with daily life and predominantly mood symptoms
the cause of PMS/PMDD is multifactorial like?
Estrogen-progesterone imbalance
Excessive aldosterone
Hypoglycemia
Hyperprolactinemia
Serotonin dysfunction
Physiological ovarian function
name some somatic symptoms of PMS/PMDD
Headache/migraine (with or without aura)
Mastalgia
Pelvic pain
Bloating
Clumsiness
Fatigue
Edema
Sleep changes
Change in appetite
name some affective symptoms of PMS/PMDD
Social withdrawal
Increase in crying
Depression
Irritability
Anxiety
Decreased libido
how is PMS diagnosed?
Patient must exhibit at least 1 somatic symptom and 1 affective symptom occurring during the 5 days before menses in each of the three prior menstrual cycles
how is PMDD diagnosed?
Meeting criteria for PMS with occurrence of more severe affective symptoms
how do you manage PMS/PMDD?
lifestyle modifications, OTC remedies, Rx remedies
cOCPs containing _______ are FDA approved for treatment of PMDD
Drosperinone
abnormal uterine bleeding (AUB)
uterine bleeding in a nonpregnant female that is abnormal in volume, frequency, duration, and/or regularity
what is diagnosed when all possible pathological causes of AUB have been ruled out?
dysfunctional uterine bleeding (DUB)
which of the following is considered AUB?
prolonged uterine bleeding
heavy menstrual bleeding
midcycle bleeding/break through bleeding
all of the above
all of the above
3 multiple choice options
what is the FIBO classification system for AUB?
PALM COEIN
Structural causes -PALM
Polyp
Adenomyosis
Leiomyoma
Malignancy and hyperplasia
Nonstructural causes - COEIN
Coagulopathy
Ovarian dysfunction
Endometrium
Iatrogenic
Not otherwise classified
what is the second most common cause of AUB in adolescence?
blood dycrasias
when does most DUB occur?
in the years around menarche or in perimenopause
DUB is associated with what 90% of the time?
anovulatory or oligoovulatory cycles
DUB only results from a low estrogen state t/f
false, can be low or high
what is the first thing you need to do when diagnosing DUB?
rule out other etiologies, particularly cancer
what are possible medical and surgical treatments for DUB?
Medical: Low dose combination OCPs
Medroxyprogesterone acetate (Provera)
Depo Medroxyprogesterone acetate (Depo Provera or DMPA)
Levonorgestrel IUD
NSAIDS
Antifibrinolytic agent
Surgical: D&C, endometrial abaltion, hysrerectomy
postmenopausal bleeding (PMB)
Uterine bleeding that occurs after a full year of amenorrhea due to menopause