Practice Exam 4 Accounting 1 Stephen Gibbs
1/50
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
51 Terms
The quick ratio, although similar to the current ratio, is more conservative.
True
1 multiple choice option
The percent of receivables method to estimate uncollectible accounts expense is also known as the:
Balance Sheet Approach
3 multiple choice options
The Miller Company recognized $190,000 of service revenue earned on account during Year 2. There was no beginning balance in the accounts receivable and allowance accounts. During Year 2, Miller collected $136,000 of cash from accounts receivable. The company estimates that it will be unable to collect 3% of its sales on account.
The net realizable value of Miller's receivables at the end of Year 2 was:
$48,300
3 multiple choice options
Rosewood Company made a loan of $16,000 to one of the company's employees on April 1, Year 1.The one-year note carried a 6% rate of interest.
The amount of interest revenue that Rosewood would report during the years ending December 31, Year 1 and Year 2, respectively, would be:
$720 and $240
3 multiple choice options
Anton Company uses the perpetual inventory method. Anton purchased 400 units of inventory thatcost $12.00 each. At a later date the company purchased an additional 600 units of inventory that cost$16.00 each.
If Anton uses the FIFO cost flow method and sells 700 units of inventory, the amount of cost of goods sold will be:
$9,600
3 multiple choice options
Assuming Chase uses a FIFO cost flow method, the cost of goods sold for the sales transaction on January 31 is:
$1,020
3 multiple choice options

Harding Corporation acquired real estate that contained land, building and equipment. The propertycost Harding $1,900,000. Harding paid $350,000 and issued a note payable for the remainder of thecost. An appraisal of the property reported the following values: Land, $374,000; Building, $1,100,000and Equipment, $726,000.
What value will be recorded for the building?
$950,000
3 multiple choice options
Which of the following would most likely not be expensed using the straight-line method?
A timber stand
3 multiple choice options
On March 1, Bartholomew Company purchased a new stamping machine with a list price of $34,000.The company paid cash for the machine; therefore, it was allowed a 5% discount. Other costs associated with the machine were: transportation costs, $550; sales tax paid, $1,360; installation costs,$450; routine maintenance during the first month of operation, $500.
The cost recorded for the machine was:
$34,660
3 multiple choice options
On January 1, Year 1, Mike Moving Company paid $27,000 to purchase a truck. The truck was expected to have a four-year useful life and $3,000 salvage value.
If Mike uses the straight-line method, the Year 3 depreciation and Year 3 book value would be:
Depreciation $6,000, Net Book Value $9,000
3 multiple choice options
Emir depreciates its assets under the straight-line method. The amount of depreciation expense shown on the Year 4 income statement and accumulated depreciation on the 12/31/Year 4 balance sheet would be:
$17,000 and $68,000
3 multiple choice options

Issuing a note payable is a(n):
asset source transaction.
3 multiple choice options
If a bond is sold at 101, its stated rate of interest would be:
Higher than the market rate.
3 multiple choice options
Madison Company issued an interest-bearing note payable with a face amount of $24,000 and a stated interest rate of 8% to the Metropolitan Bank on August 1, Year 1. The note carried a one-year term.
The amount of cash flow from operating activities on the Year 1 statement of cash flows would be:
Zero
3 multiple choice options
Which of the following items is not classified as a current asset?
Office equipment
3 multiple choice options
Bonds payable are usually classified on the balance sheet as:
Long-term liabilities.
3 multiple choice options
All of the following are considered to be measures of a company's short-term debt-paying ability except:
Earnings per Share
3 multiple choice options
Which of the following statements is generally incorrect from an investor's perspective?
A 1:1 current ratio is generally preferred over a 1.5:1 current ratio.
3 multiple choice options
Accrual accounting requires the use of many estimates, including:
All of these answers are correct.
3 multiple choice options
Harding Corporation acquired real estate that contained land, building and equipment. The propertycost Harding $2,850,000. Harding paid $875,000 and issued a note payable for the remainder of thecost. An appraisal of the property reported the following values: Land, $627,920; Building, $3,047,080and Equipment, $806,000.
What value will be recorded for the building?
$1,938,000
3 multiple choice options
The Cost of Goods Sold using LIFO is:
$10,210
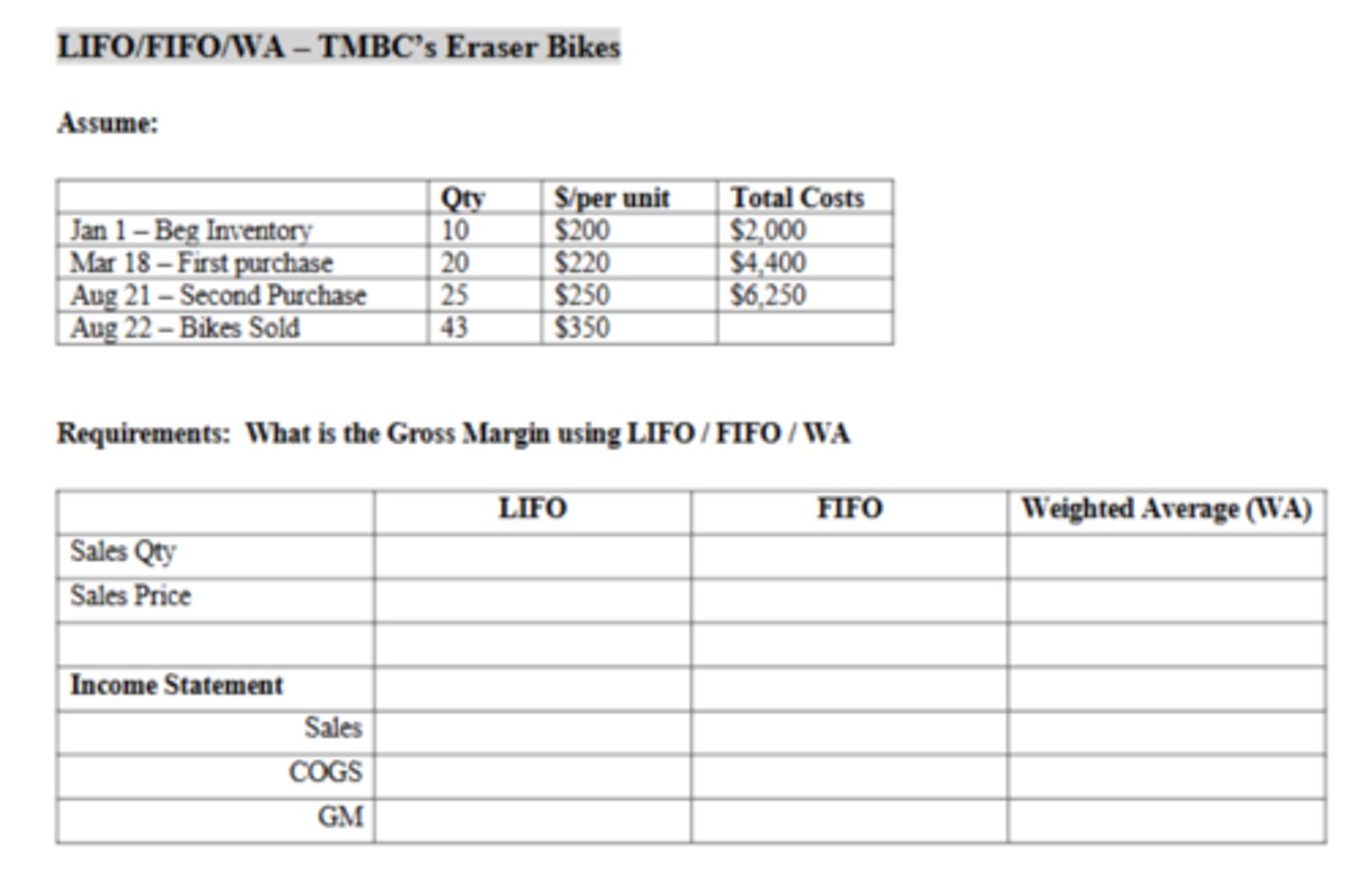
The Cost of Goods Sold using FIFO is:
$9,650
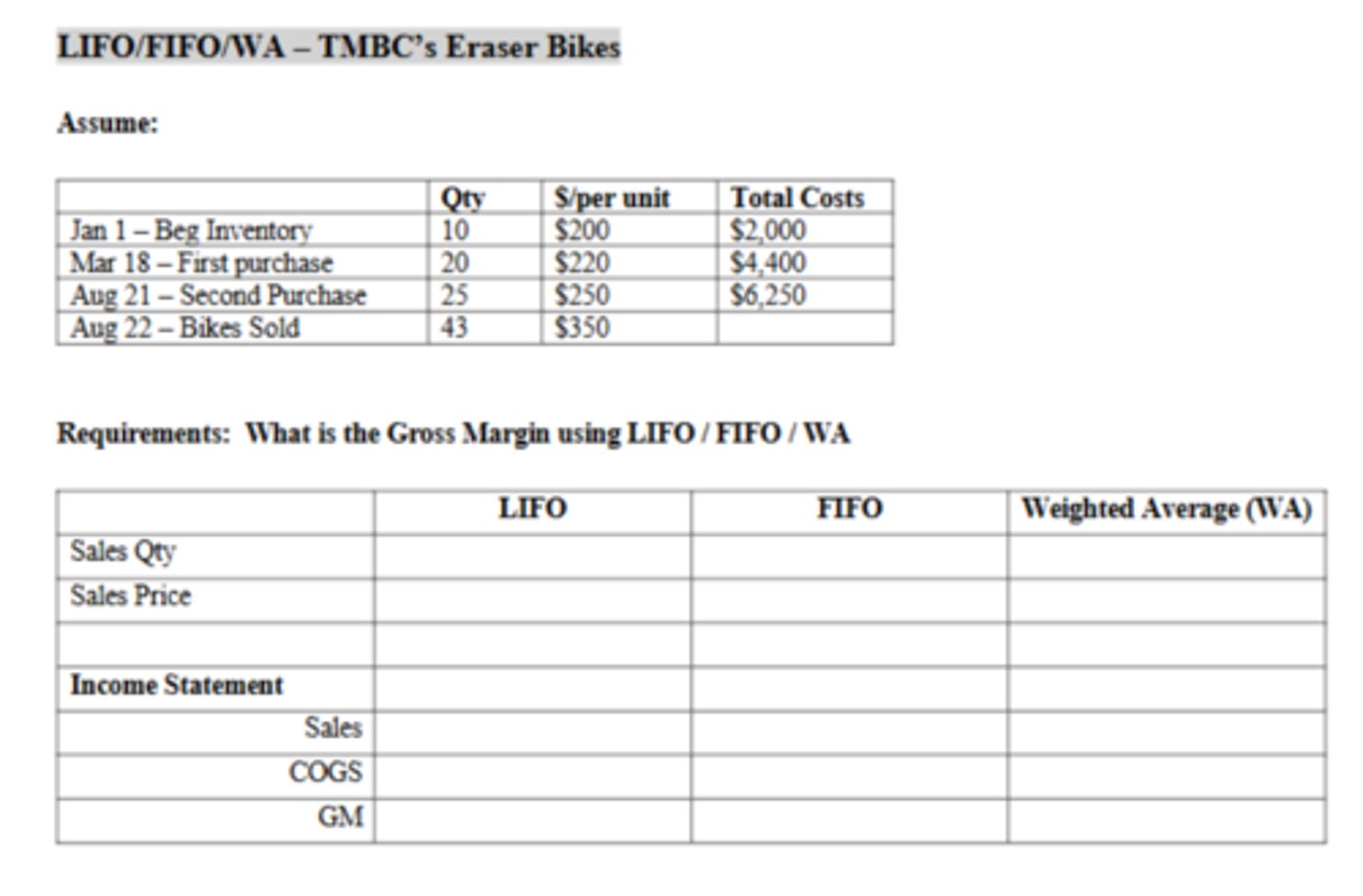
The Cost of Goods Sold using WA is:
$9,939.13
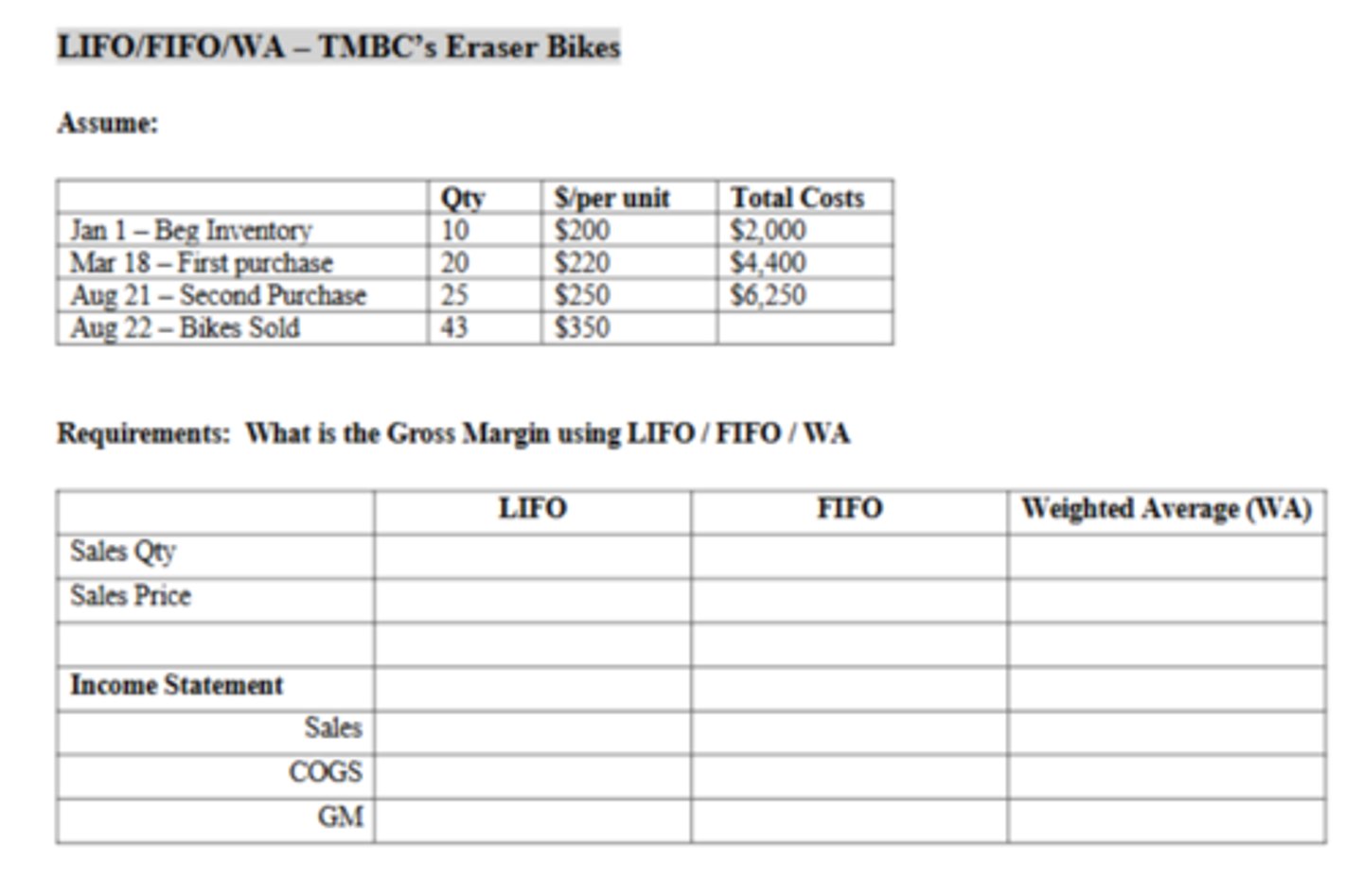
The Weighted Average cost of a bike is:
$230.91
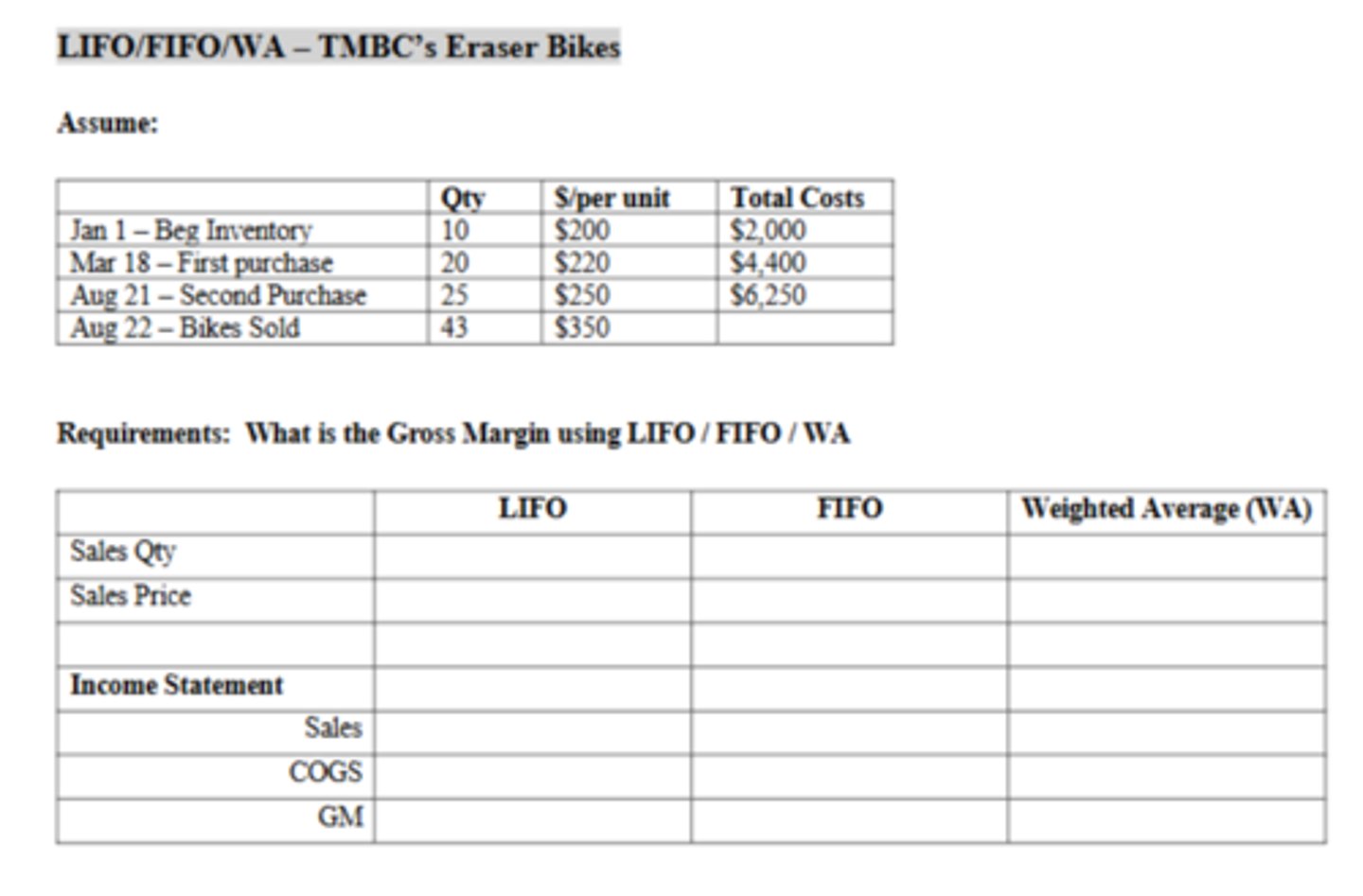
Which inventory method produced the highest gross margin?
FIFO
2 multiple choice options
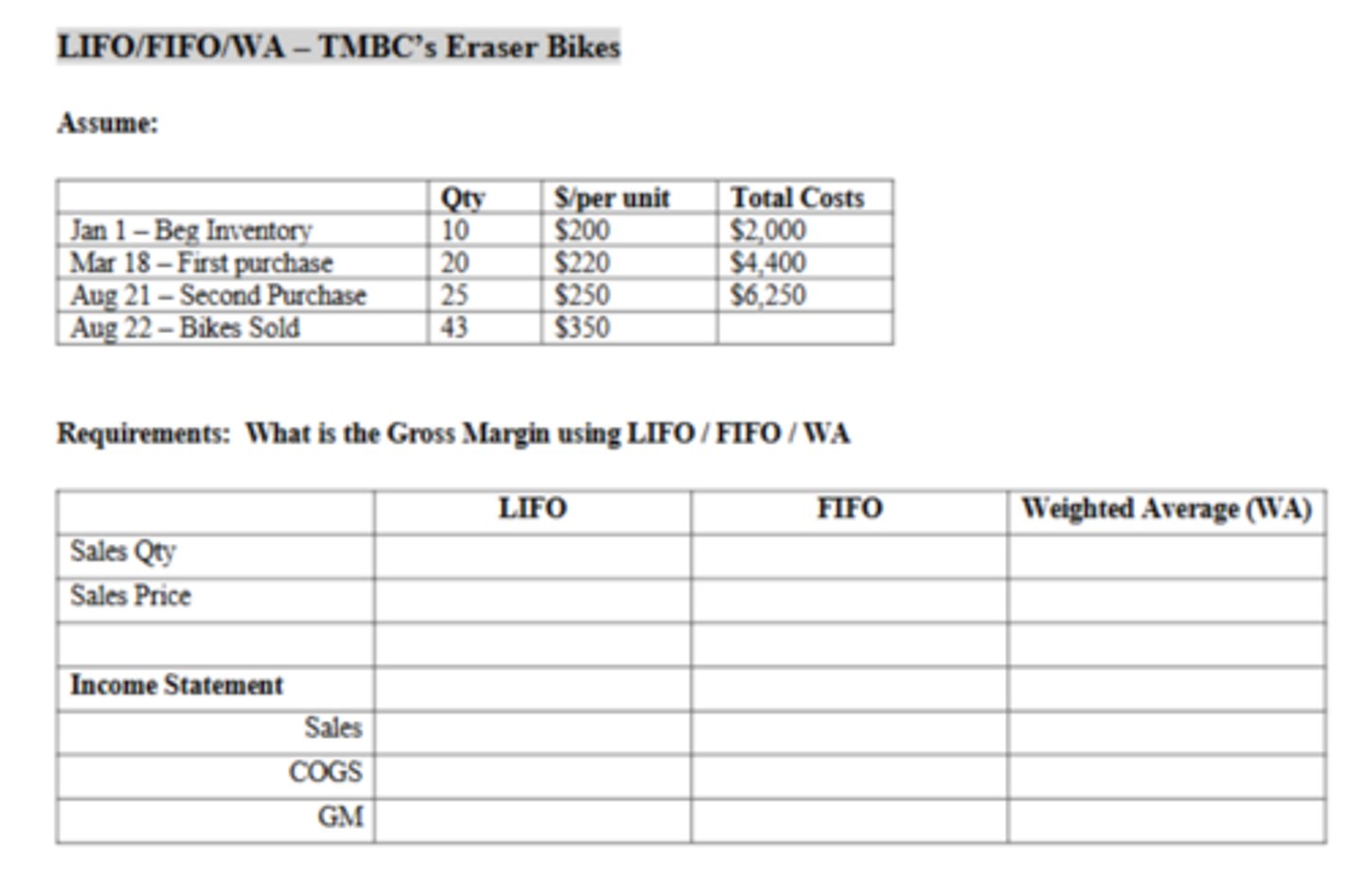
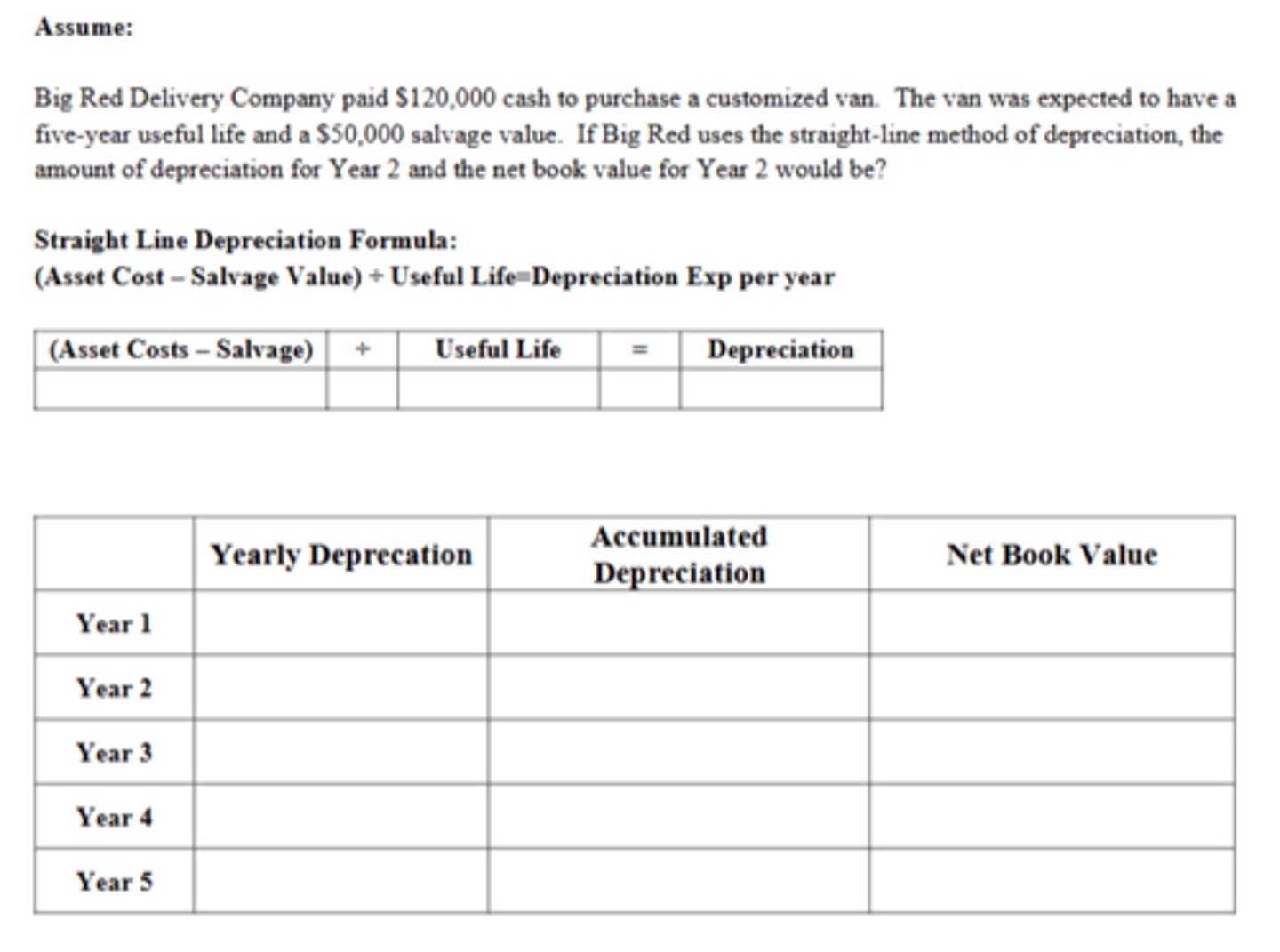
How much is the net book value of the van at the end of five years?
$50,000
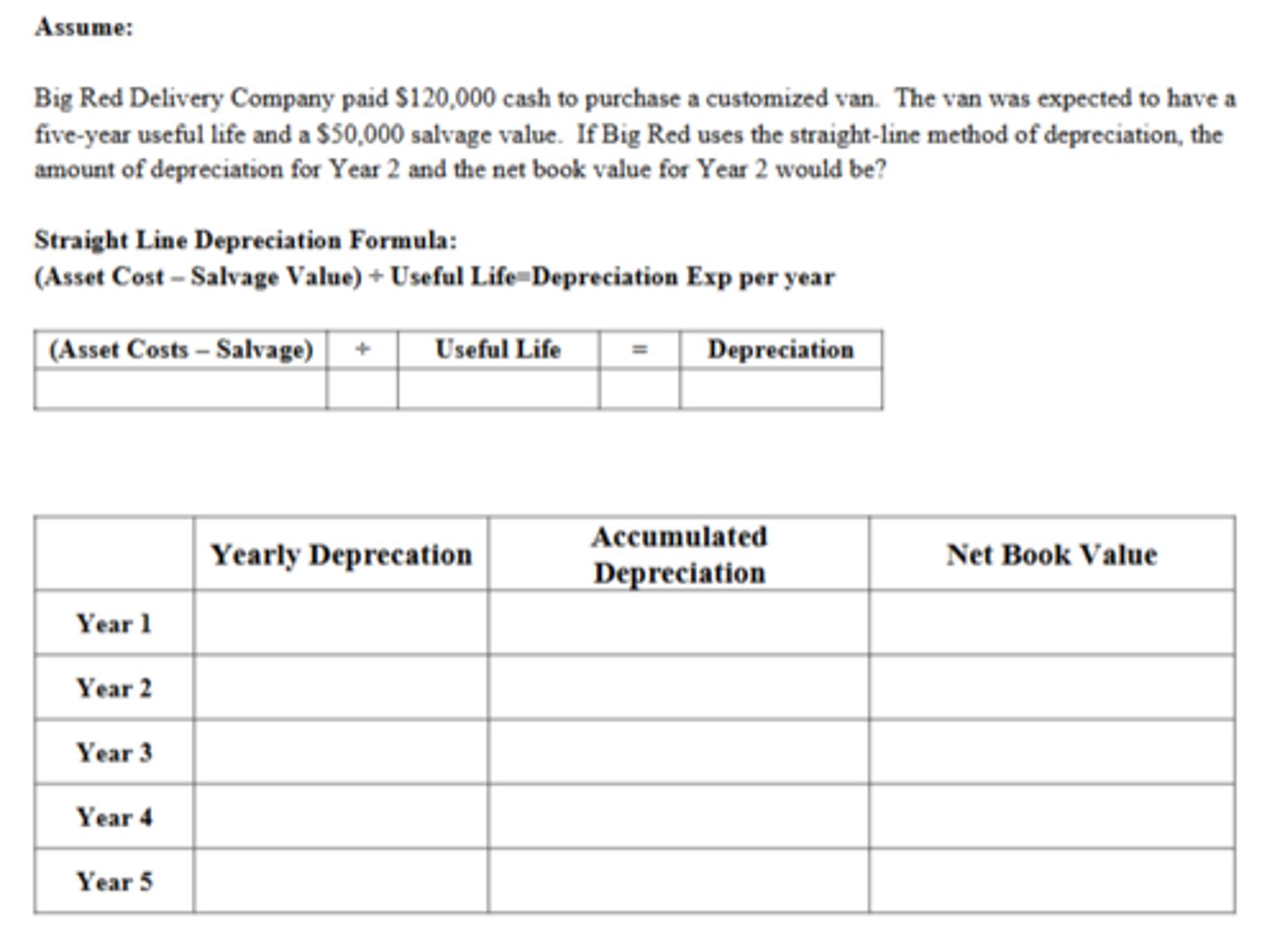
The Depreciation in Year 2 is:
$14,000
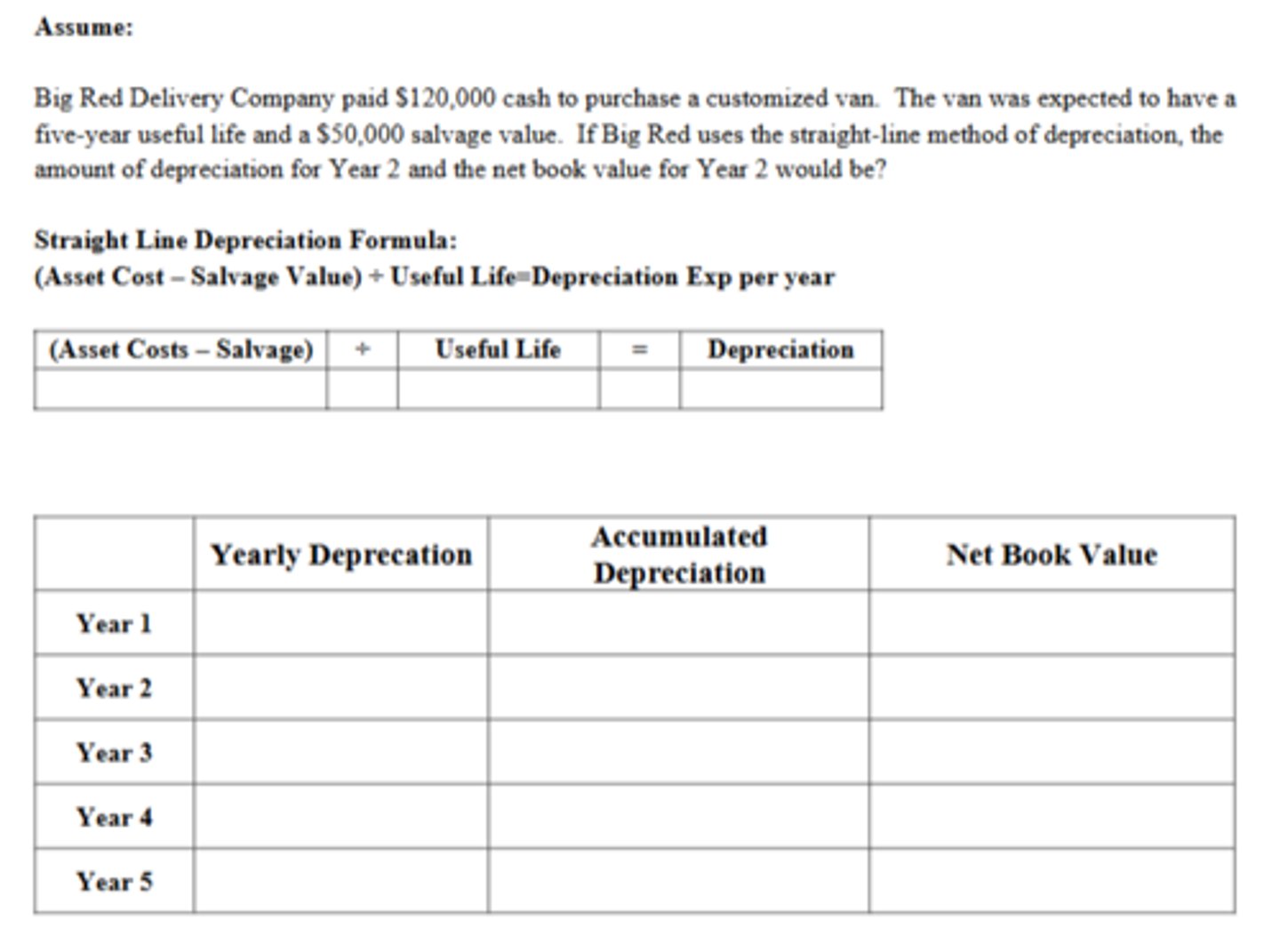
The Net Book Value at the End of Year 2 is:
$92,000
How much accrued interest expense would LRR recognize in Year 1?
$5,333.33
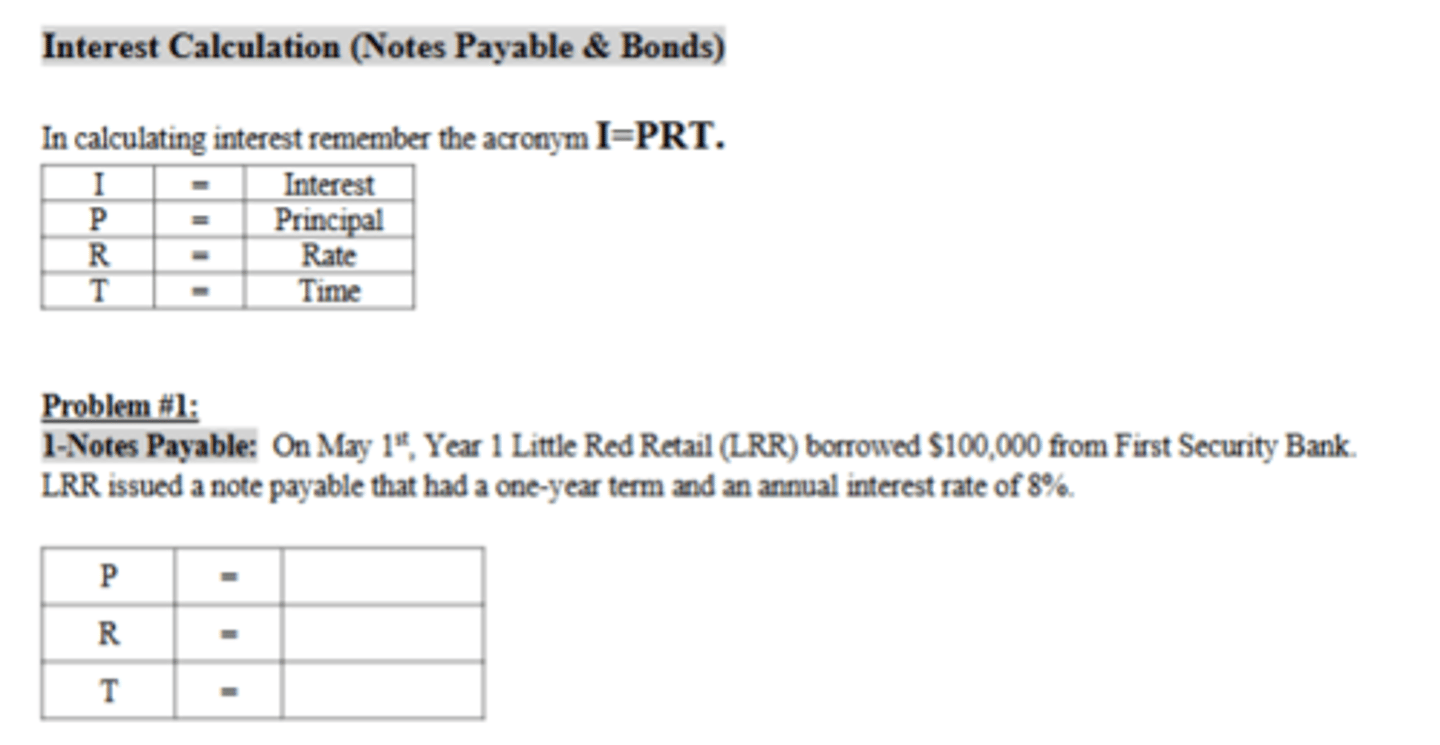
How much accrued interest expense would LRR recognize in Year 2?
$2,666.67
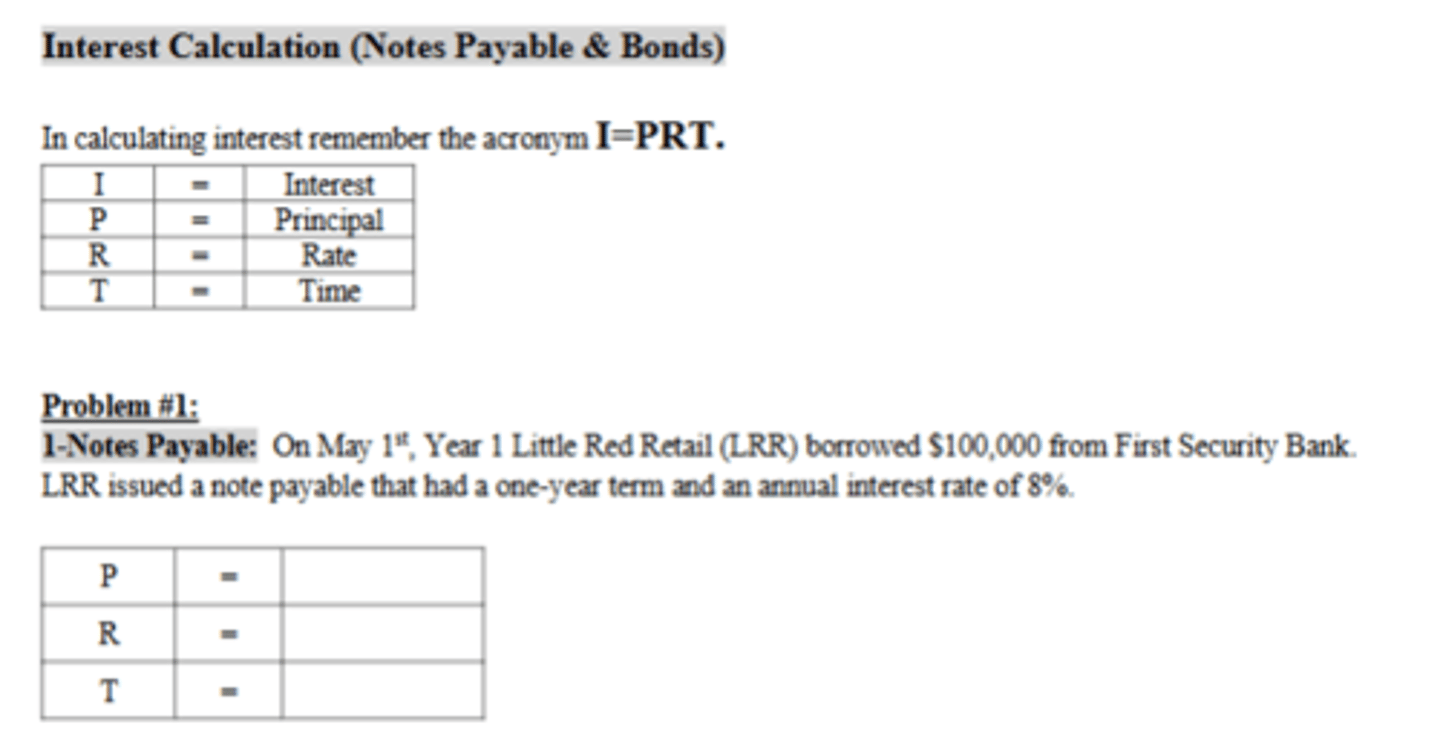
How much total interest expense will LRR recognize for the term of the note payable?
$8,000
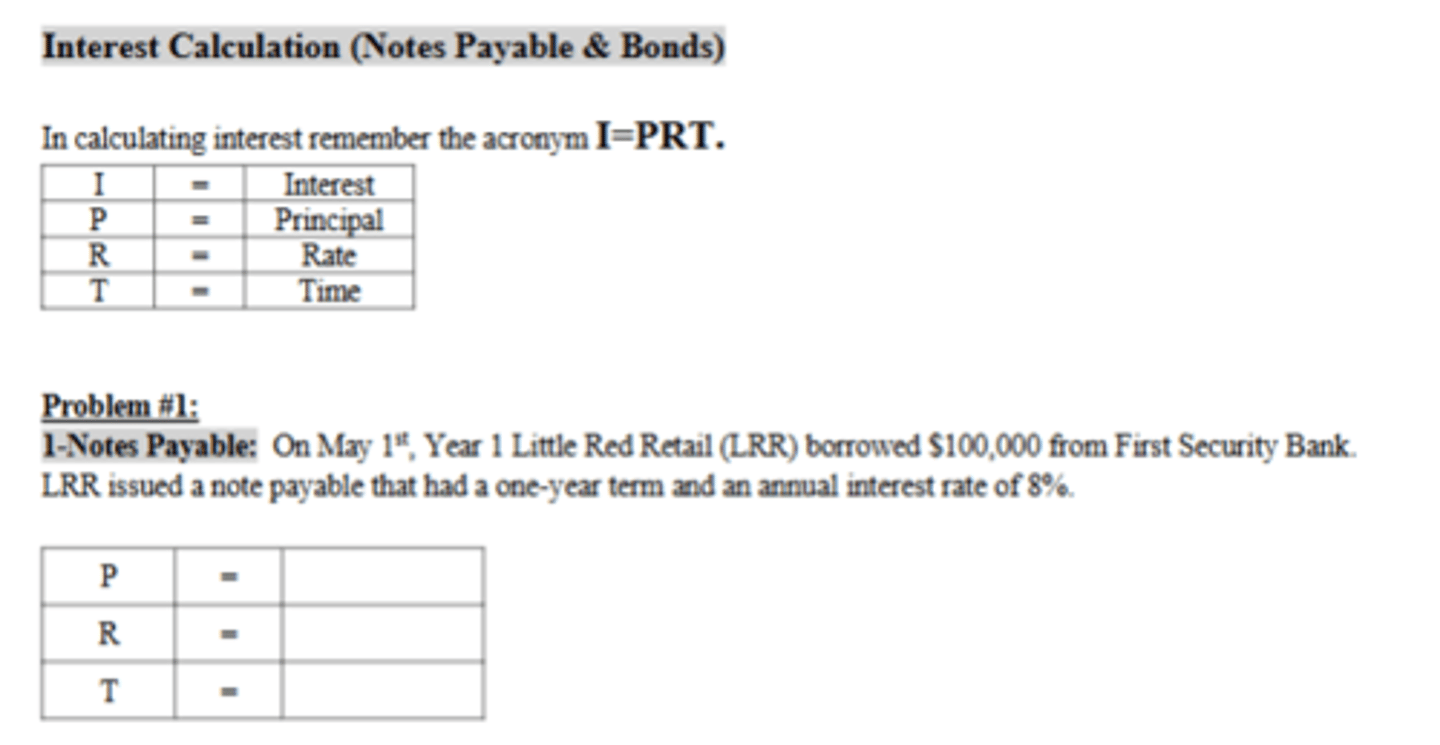
How much accrued interest expense would LRR recognize in Year 1?
$1,200

How much accrued interest expense would LRR recognize in Year 2?
$6,000

How much total interest expense will LRR recognize for the term of the note payable?
$7,200

How much interest expense would LRR recognize in Year 1?
$7,000

How much interest expense would LRR recognize in Year 2?
$7,000

How much interest expense would LRR recognize in Year 1?
$2,333.33

How much interest expense would LRR recognize in Year 2?
$7,000

If the available market rate of interest is 8% on the day LRR sells the bonds, then LRR will most likely sell those bonds at a:
Discount

If the available market rate of interest is 4% on the day LRR sells the bonds, then LRR will most likely sell those bonds at a:
Premium

Working Capital
Current Assets - Current Liabilities
Current Ratio
Current Assets ÷ Current Liabilities
Quick Ratio
(Current Assets - Inventory - Prepaids) ÷ Current Liabilities
Accounts Receivable
Turnover Net credit sales ÷ Average Receivables
Average Days to Collect Receivables
365 ÷ Accounts Receivable Turnover
Inventory Turnover
Cost of goods sold ÷ Average Inventory
Average days to sell inventory
365 ÷ Inventory Turnover
Debt -to- assets ratio
Total Liabilities ÷ Total Assets
Debt -to-equity ratio
Total Liabilities ÷ Total Stockholder's Equity
Number of times interest is earned
Earnings before interest and taxes ÷Interest Expense
Plant assts to long-term liabilities
Net Plant Assets ÷ Long-term liabilities