Atmospheric Layers and Weather Concepts
1/41
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Flashcards covering key vocabulary and concepts related to atmospheric layers and weather.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
42 Terms
troposphere
The atmospheric layer closest to Earth's surface; extends to altitudes between 8-15 km; where weather occurs; temperature decreases with altitude.
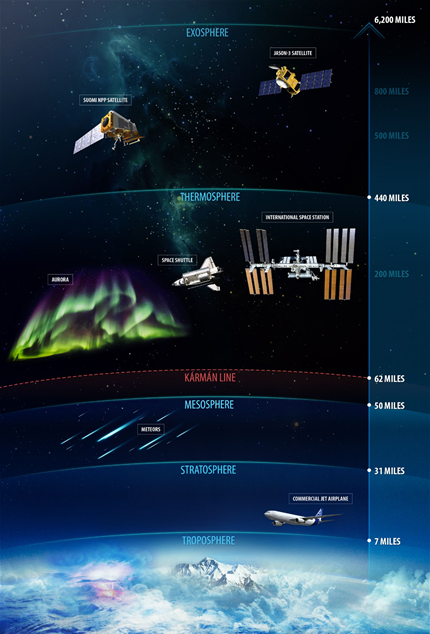
stratosphere
The second layer of the atmosphere; extends from 15 km to 50 km; location of the ozone layer; absorbs 95% of ultraviolet radiation; temperature increases with altitude.
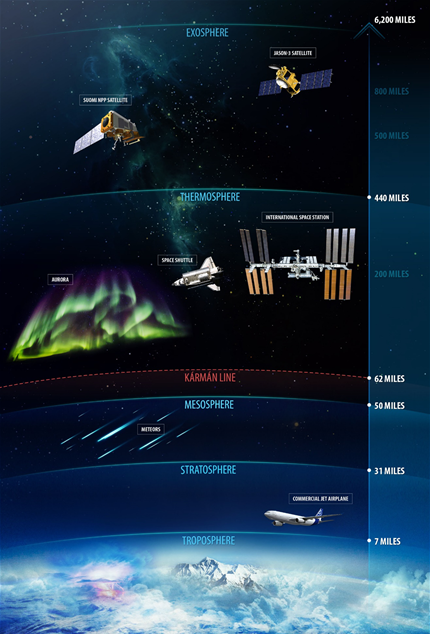
mesosphere
Extends from 50 km to 85 km; one of the two layers where most meteors burn up.
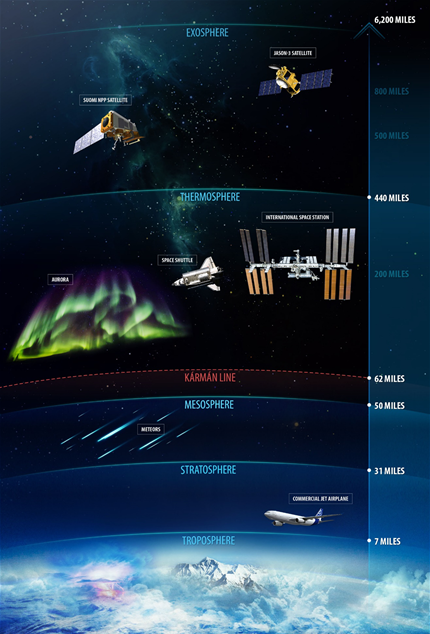
thermosphere
Extends from 85 km to 500 km; the layer where most meteors burn up.
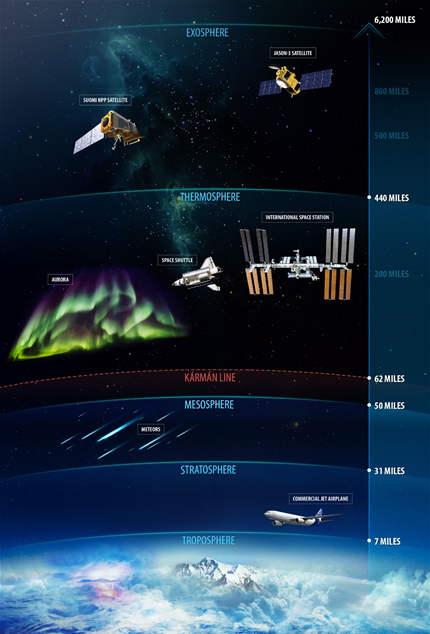
ionosphere
Region between 69 km and 500 km that contains ions which can reflect AM radio waves transmitted at ground level.
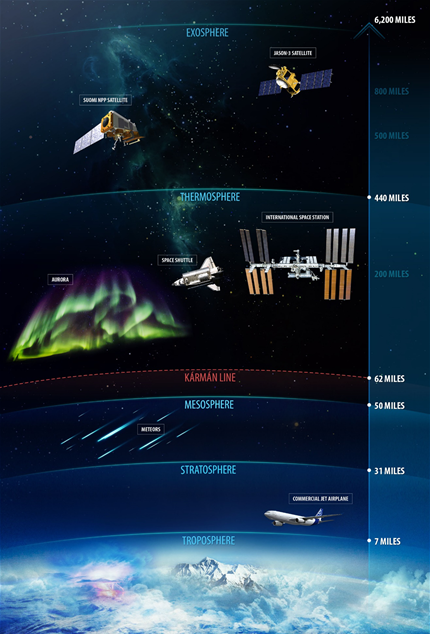
aurora
An atmospheric phenomenon that occurs when ions from the Sun strike air molecules, causing them to emit vivid colors of light.
exosphere
The outermost region of the atmosphere; molecules move at high speeds after absorbing the Sun's radiation.
air pressure
The force that a column of air applies on the air or a surface below it.
altitude
Height above sea level.
radiation
The transfer of energy by electromagnetic waves.
greenhouse effect
Natural situation in which heat is retained in Earth's atmosphere by carbon dioxide, methane, and other gases.
conduction
The transfer of thermal energy by collisions between particles of matter.
convection
The transfer of thermal energy by the movement of particles within matter.
temperature inversion
Atmospheric condition in the troposphere in which warm air traps cooler air near the earth's surface.
wind
The movement of air from areas of high pressure to areas of low pressure created by unequal heating of the Earth's surface.
trade winds
Prevailing winds that blow from east to west from 30 degrees latitude to the equator in both hemispheres.
westerlies
Prevailing winds that blow from west to east between 30-60 degrees latitude in both hemispheres.
polar easterlies
Prevailing winds that blow from east to west between 60-90 degrees latitude in both hemispheres.
Coriolis effect
Earth's rotation causes moving air and water to appear to move to the right in the northern hemisphere and to the left in the southern hemisphere.
jet stream
A narrow band of high winds near the top of the troposphere; moves cold air from the poles toward the tropics.
sea breeze
Wind that blows from the sea to the land due to local temperature and pressure differences.
land breeze
Wind that blows from the land to the sea due to local temperature and pressure differences.
weather
The atmospheric conditions and short-term changes of a certain place at a certain time.
climate
The average weather conditions in an area over a long period of time.
weather variables
Factors that include temperature, precipitation, air pressure, wind speed and direction, humidity, and cloud cover.
humidity
The amount of water vapor in the air.
relative humidity
The amount of water vapor present in the air compared to the maximum amount the air could contain at that temperature.
dew point
The temperature at which air is saturated and condensation of water vapor can occur.
condensation
The change from a gas to a liquid.
cloud
A collection of small water droplets or ice crystals suspended in the air.
stratus clouds
Flat, white, and layered clouds at altitudes up to 2,000 m.
cumulus clouds
Fluffy, heaped clouds at altitudes of 2,000 - 6,000 m.
cirrus clouds
Wispy clouds found above 6,000 m of altitude.
fog
A near surface cloud.
nimbus clouds
Clouds that produce precipitation that reaches the ground.
high-pressure system
A large body of circulating air with high pressure at its center and lower pressure outside of the system.
low-pressure system
A large body of circulating air with low pressure at its center and higher pressure outside of the system.
front
A boundary between two air masses.
cold front
Dense cold air pushes under warm air mass; can bring thunderstorms followed by cool weather.
warm front
Moist, warm air slides up and over cold air mass, bringing gentle rain or light snow.
stationary front
Warm and cold air meet and stand still, possibly bringing clouds and prolonged precipitation.
occluded front
Forms when a warm air mass gets caught between two cold air masses.