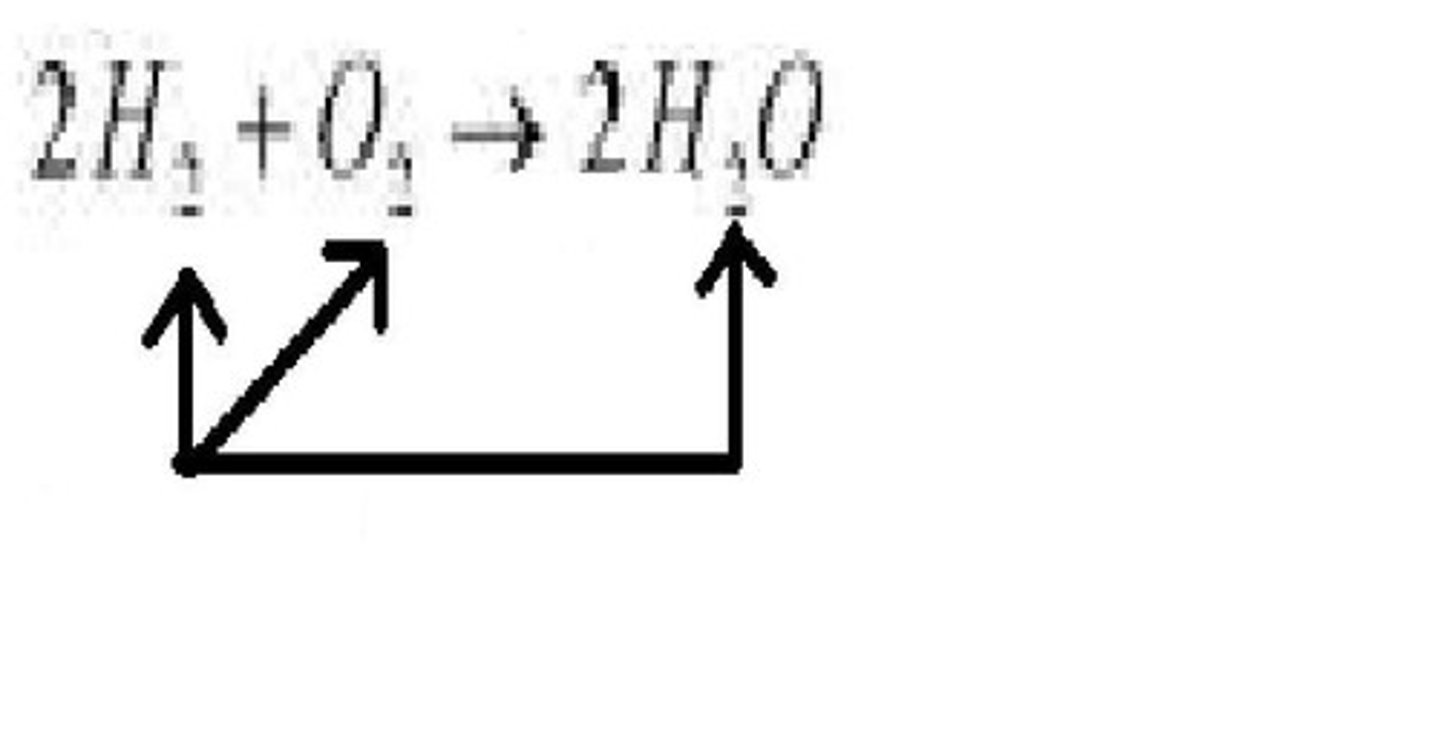
Unit 2 - Law of Conservation of Mass
1/62
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
63 Terms
Burning
Chemical Change

Spoiling Milk
Chemical change

Breaking a stick
Physical Change
Freezing
Physical change

Melting
Physical Change

Sublimation
Physical Change

Condensation
Physical Change

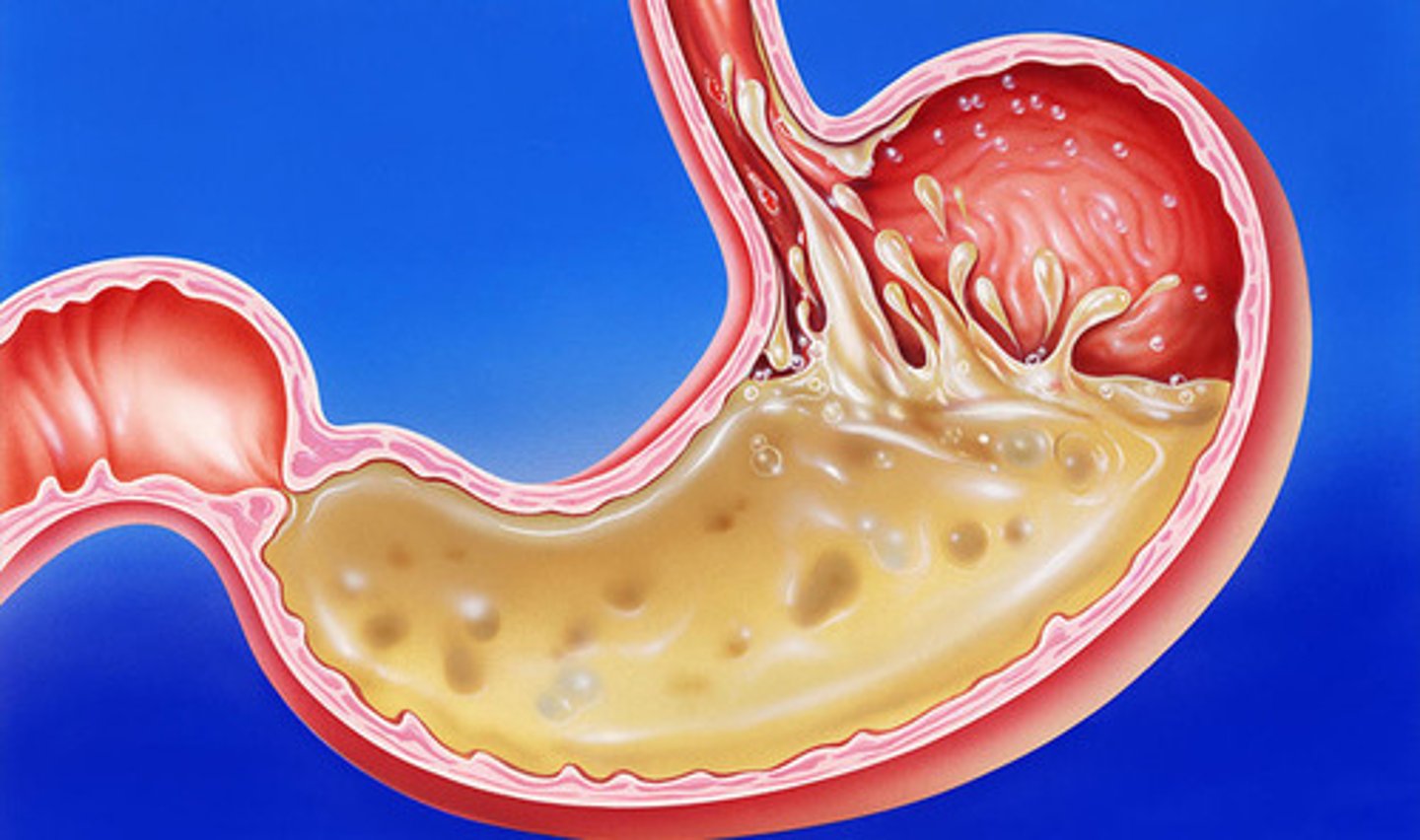
Digestion
Chemical Change
Evaporation
Physical Change

chemicals changing colors
chemical change

Leaves Changing Colors In The Fall
Chemical change

Crushing
Physical change

Chopping, Cutting, Carving
Physical change

Rusting
Chemical Change
Tarnishing
Chemical Change

Baking a Cake
Chemical Change

Braiding Hair
Physical Change

Mixing Vinegar and Baking Soda
Chemical Change

Painting your fingernails
Physical Change

Cooking scrambled eggs
Chemical Change

A change in matter that doesn't create a new substance; only the appearance changes
Physical Change
A change in matter that creates a new substance by rearranging atoms.
Chemical Change
Glow Stick Glowing
Chemical Change

Mowing the grass
Physical Change

Boiling water
Physical Change

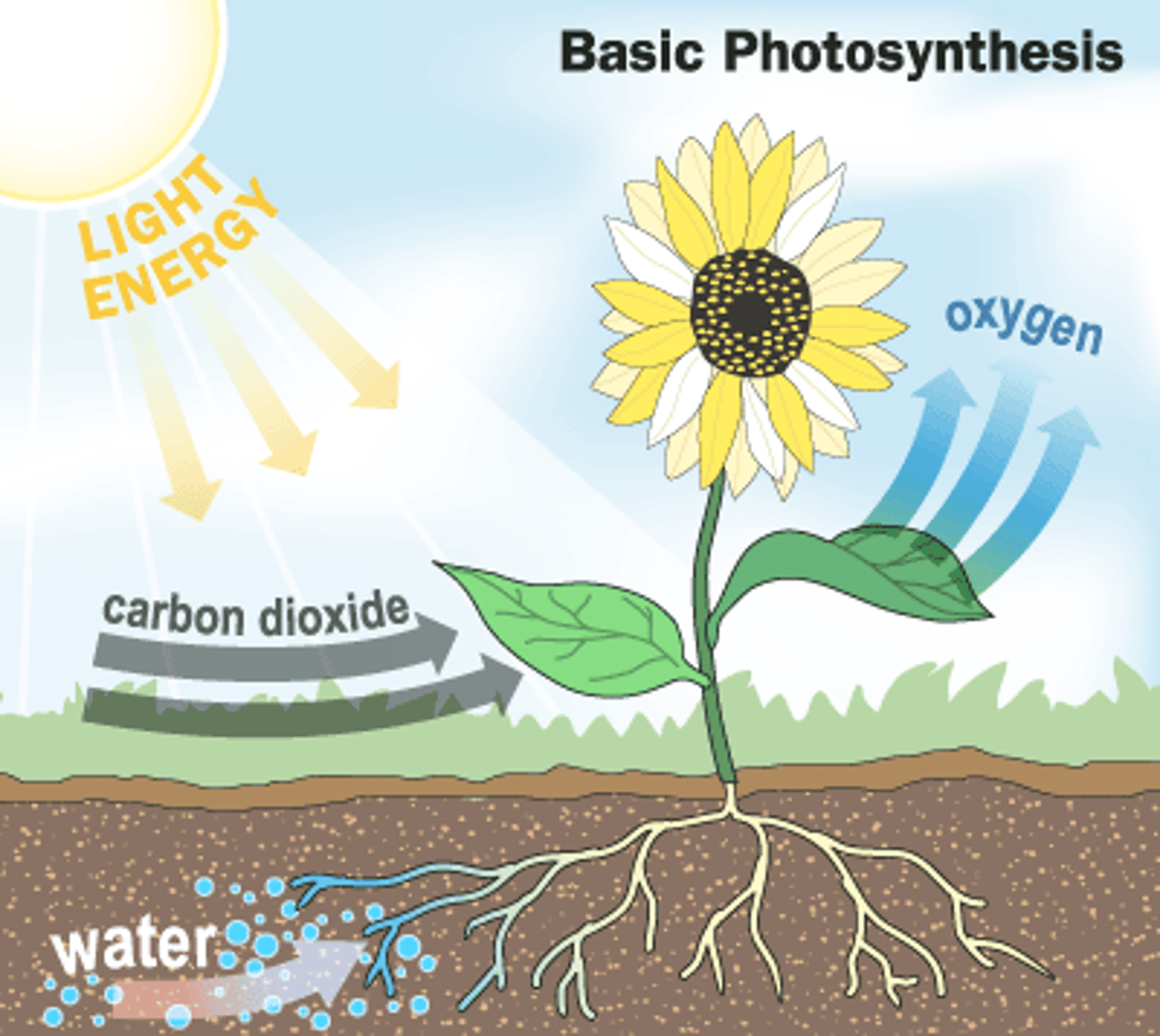
Photosynthesis
Chemical Change
Folding laundry
Physical Change

Fireworks
Chemical Change

Tearing paper
Physical Change

Making Kool-aid
Physical Change

salt dissolving in water
Physical change

Ice cream melting
physical change

Blending a smoothie
Physical change

rotting food
chemical change

Clouds forming (condensation)
Physical Change
Coefficient
A number in front of a chemical formula in an equation that indicates how many molecules of each reactant and product are involved in a reaction.
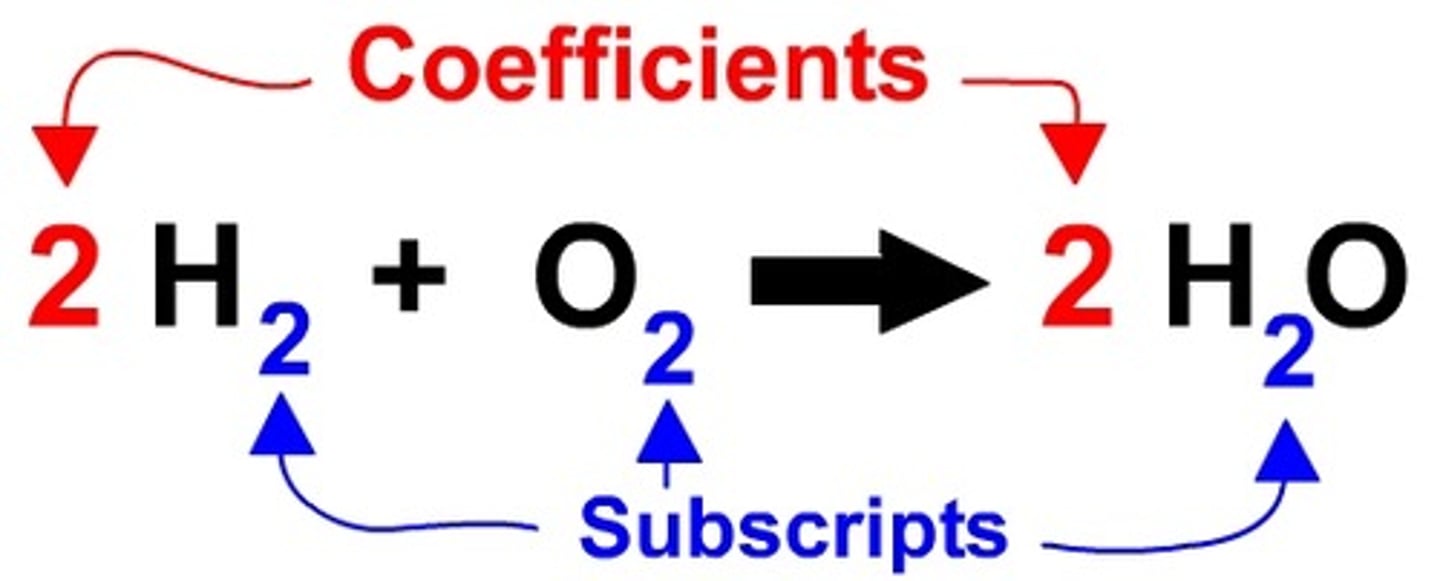
Subscript
A number in a chemical formula that tells the number of atoms in a molecule or the ratio of elements in a compound
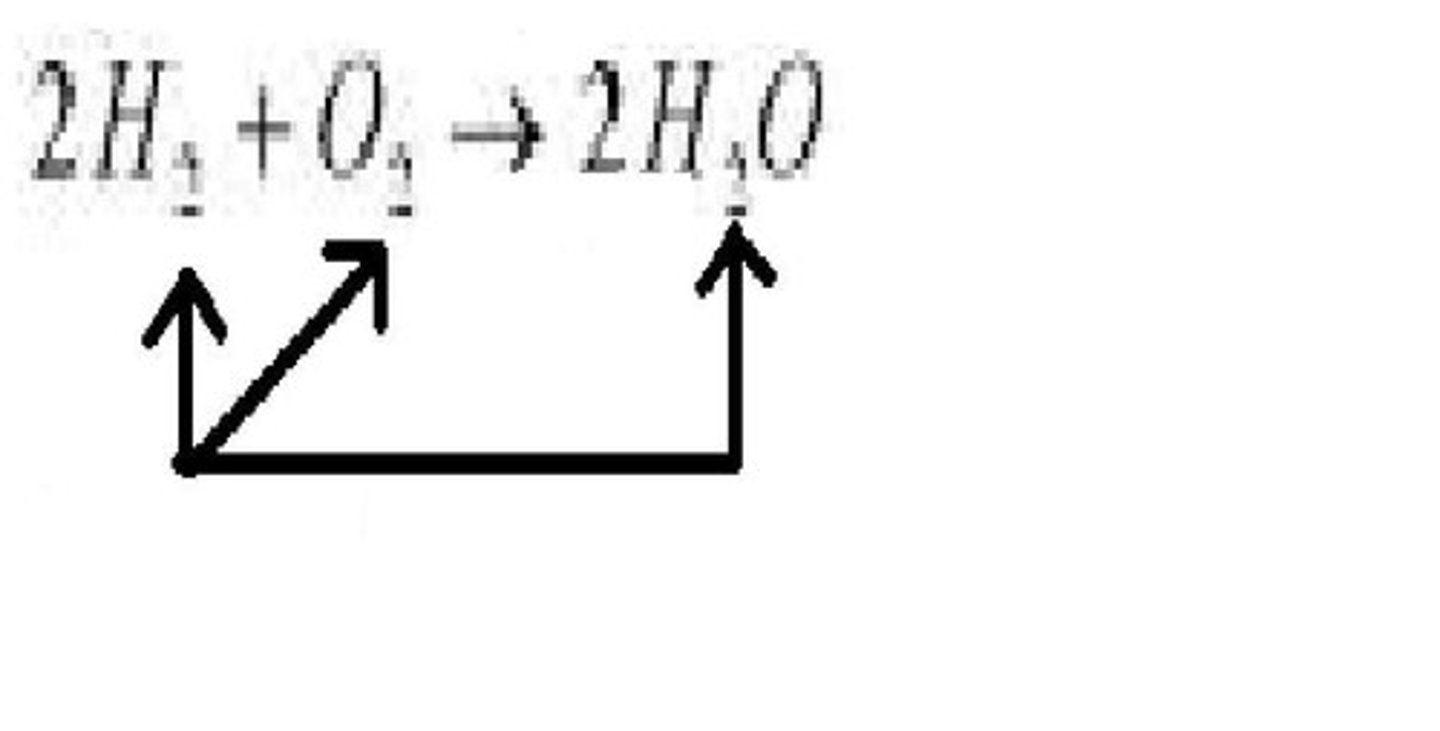
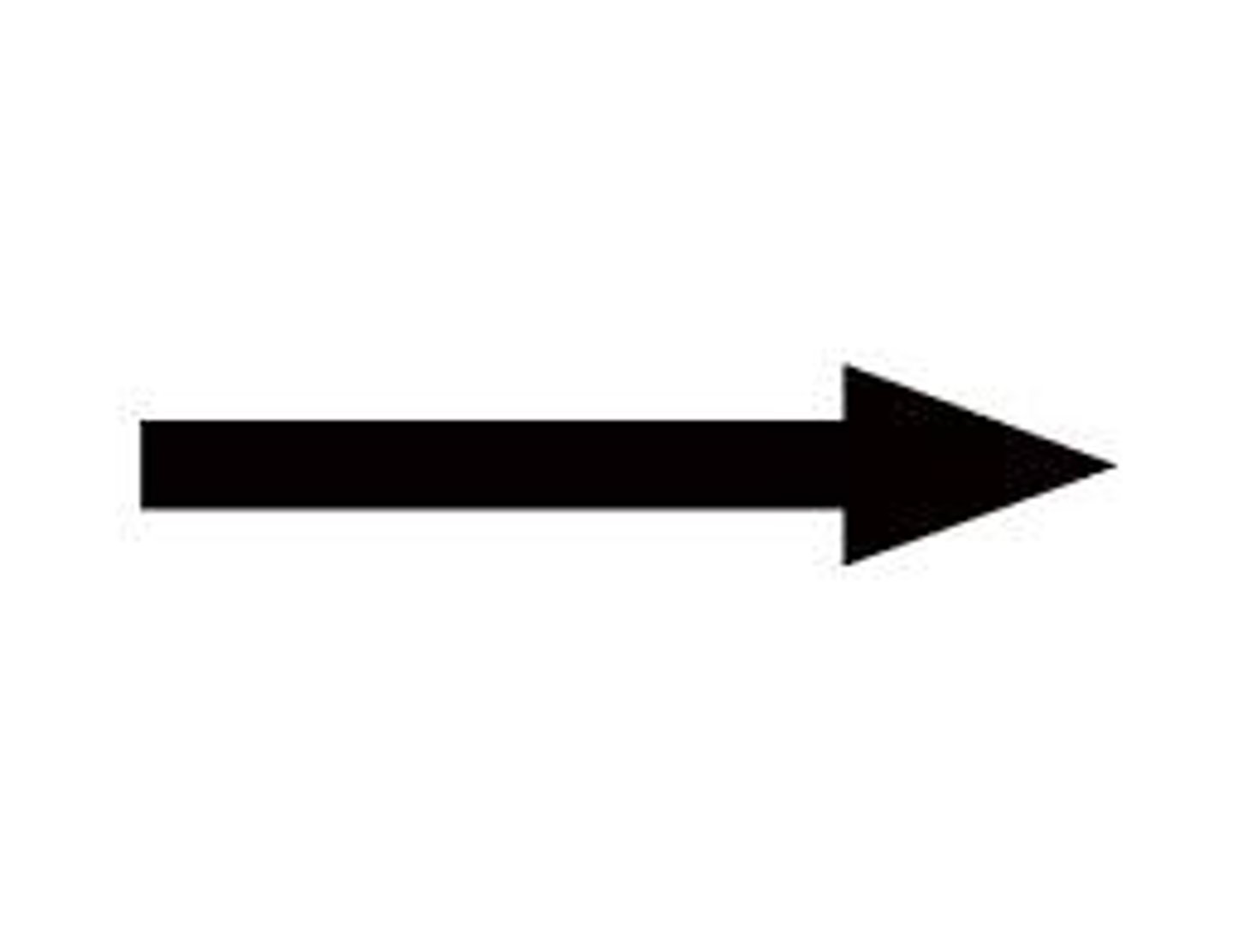
arrow
yields or produces; indicates a chemical reaction
chemical formula
A combination of chemical symbols and numbers to represent a substance
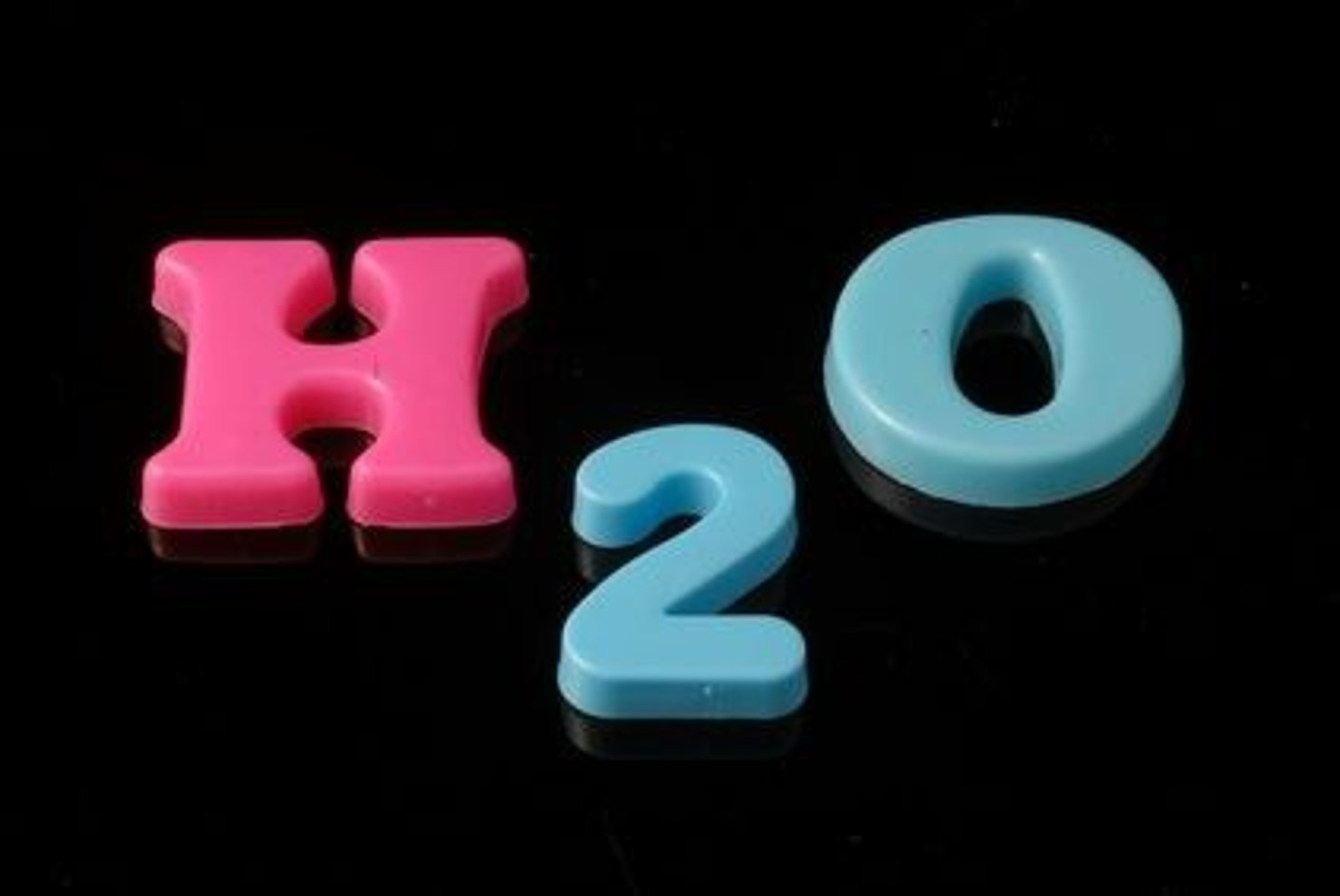
Chemical equation
a way to describe a chemical reaction using chemical formulas and other symbols
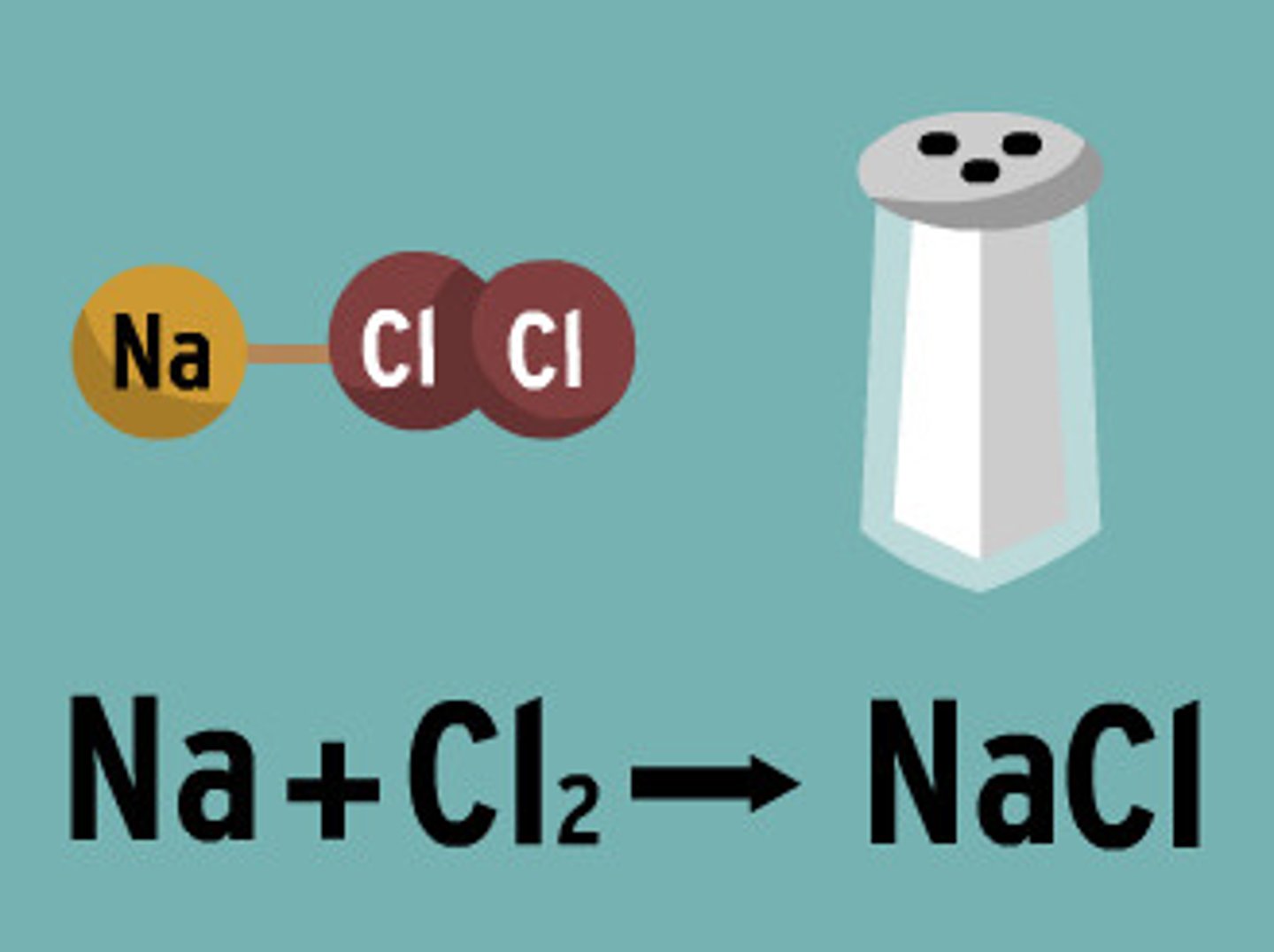
Reactants
A starting material in a chemical reaction
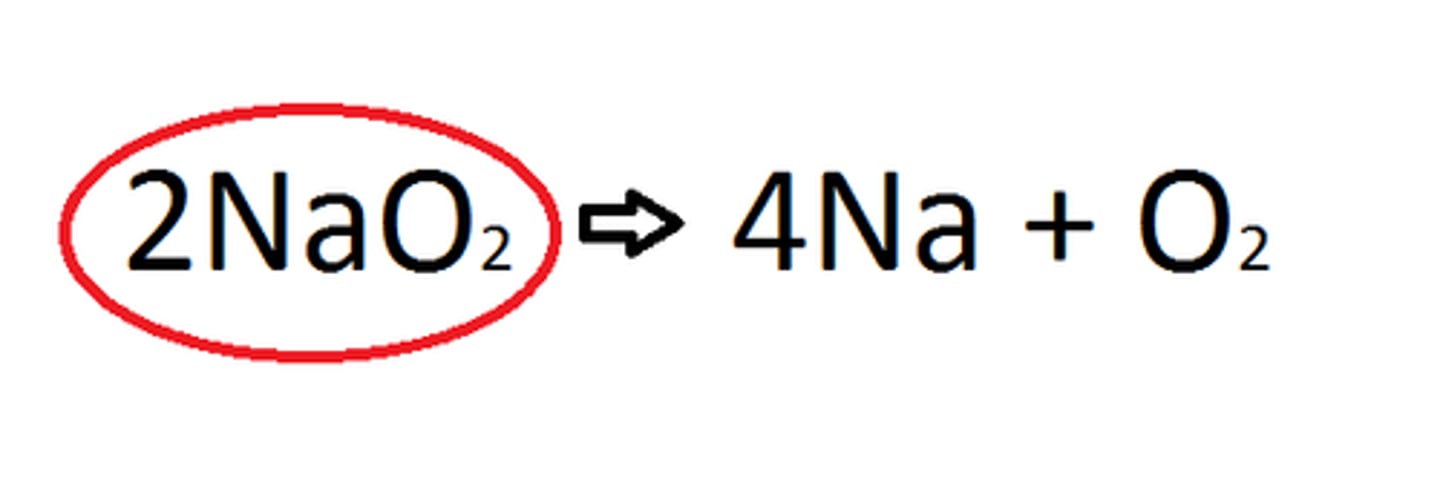
Products
Ending materials in a chemical reaction.

precipitate
A solid that forms from a solution during a chemical reaction.

physical change
A change in a substance that does not change its identity

chemical change
A change in matter that produces one or more new substances
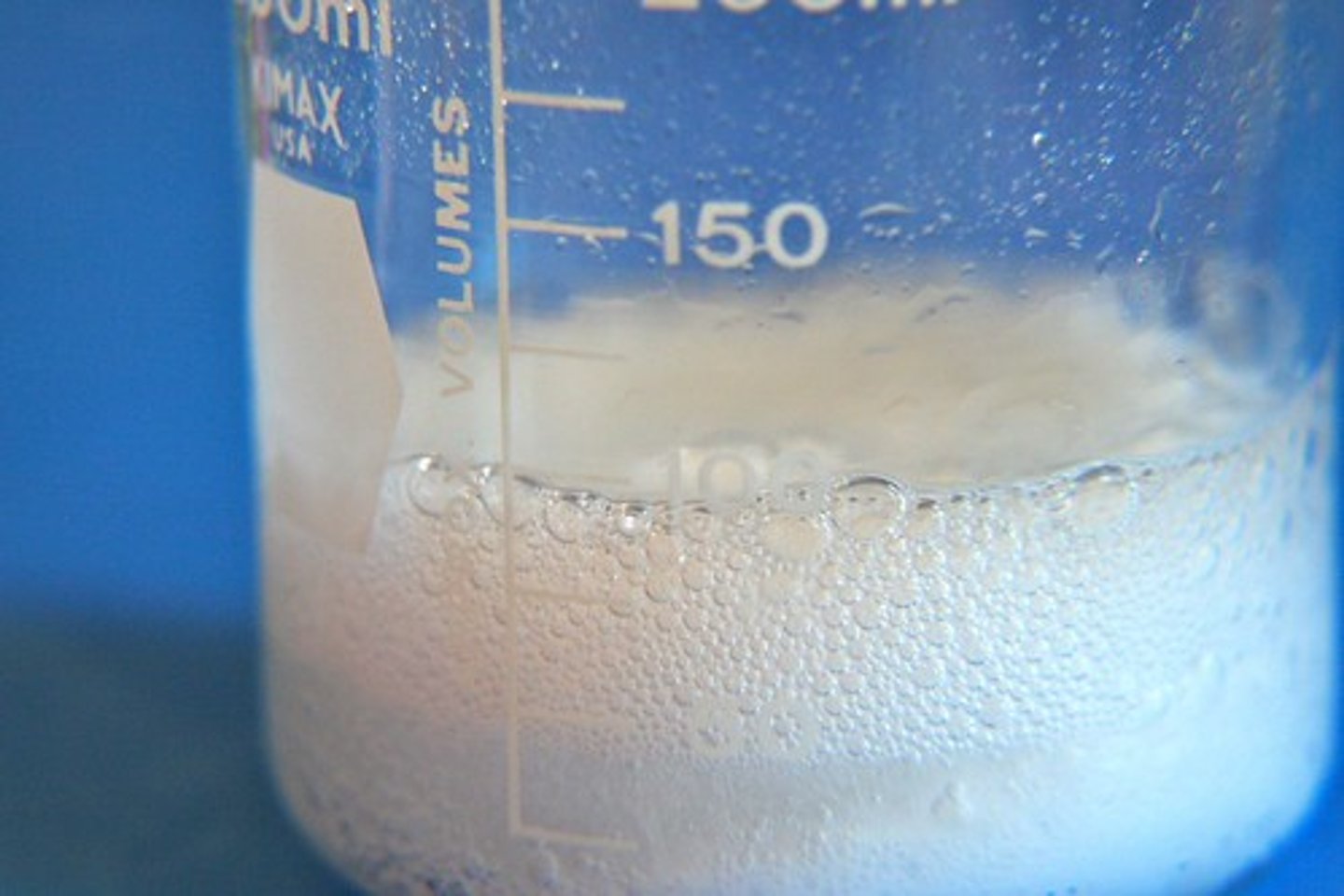

Evidence for a chemical change
production of gas (bubbles), formation of a precipitate, unexpected temperature change, color change, fire, a new product.
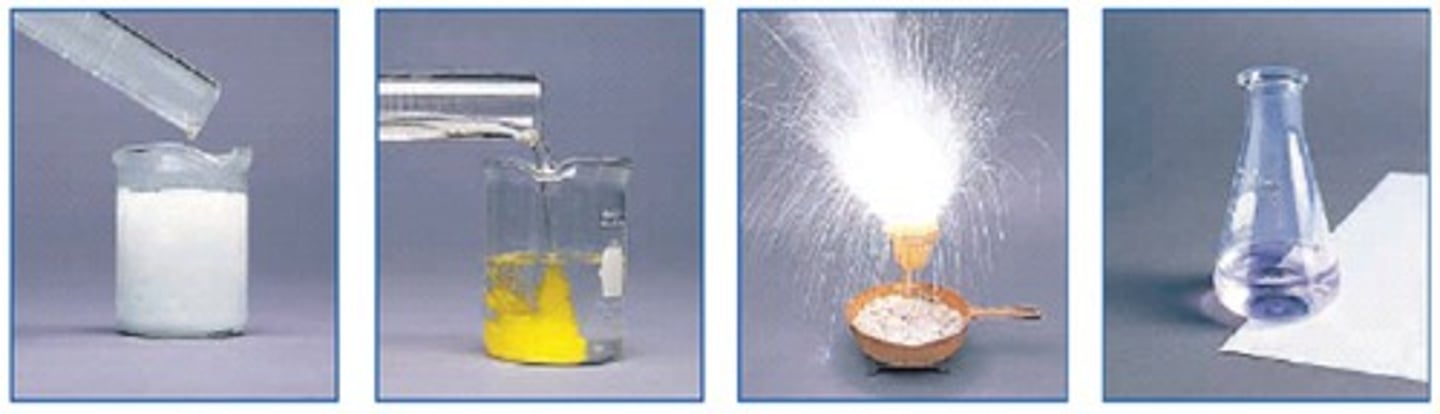

open system
A system in which matter can enter from or escape to the surroundings.
closed system
A system in which no matter is allowed to enter or leave
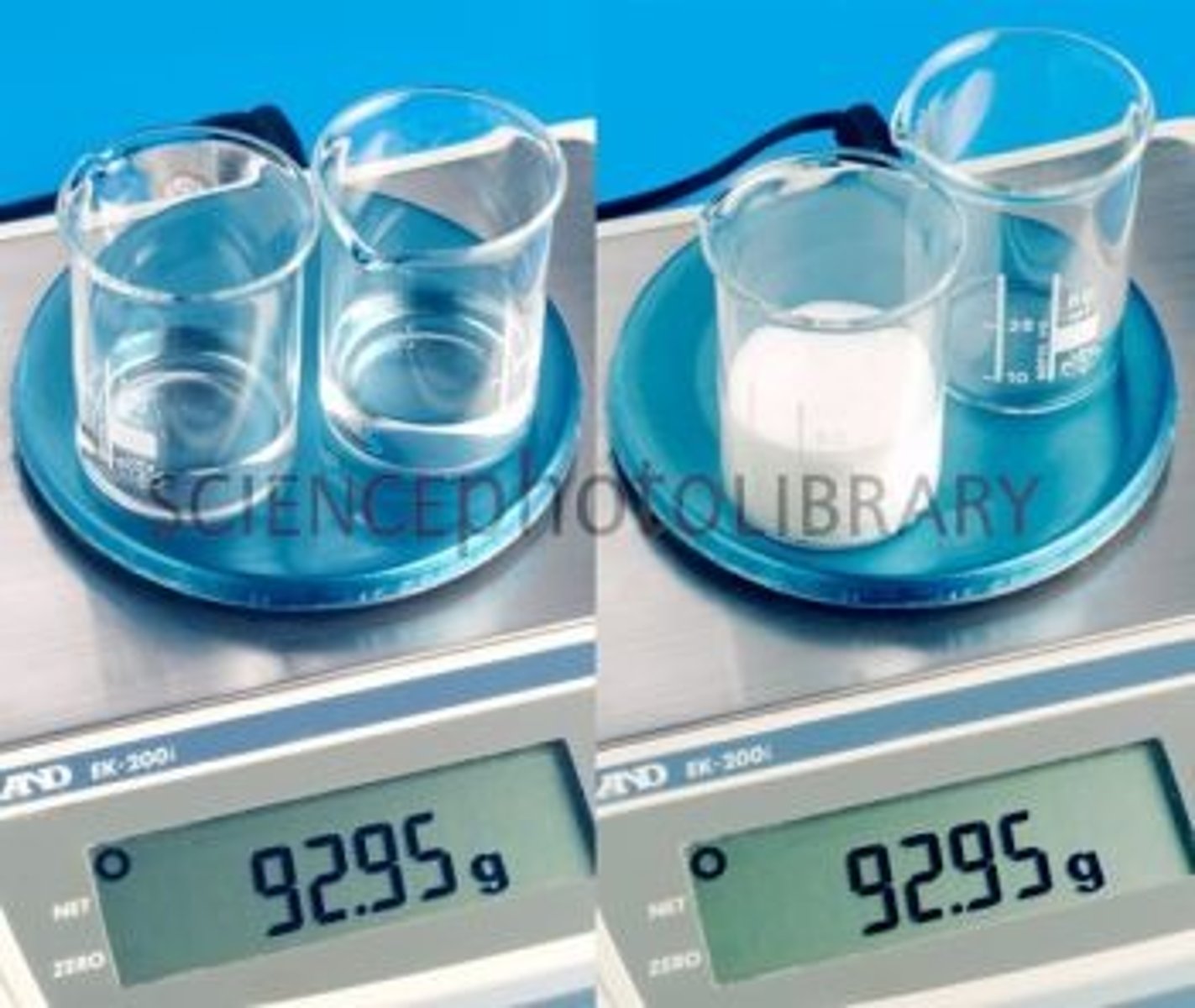
Law of Conservation of Mass
Matter is not created nor destroyed in any chemical or physical change

Solution
A solution is basically two substances
that are evenly mixed together. One
dissolves into the other.
Suspension
A mixture that has a variety of particle sizes in it that will settle on the bottom when not mixed.

Colloid
A mixture that has intermediate sized particles that don't settle at the bottom and scatter light like.

Mixture
A physical combination of two or more substances.

Solute
The substance that gets dissolved in a solution like sugar or salt.

Solvent
The substance that does the dissolving in a solution, commonly water.

Soluble
The substance is able to dissolve in the solution. It appears to have disappeared but it is still there.
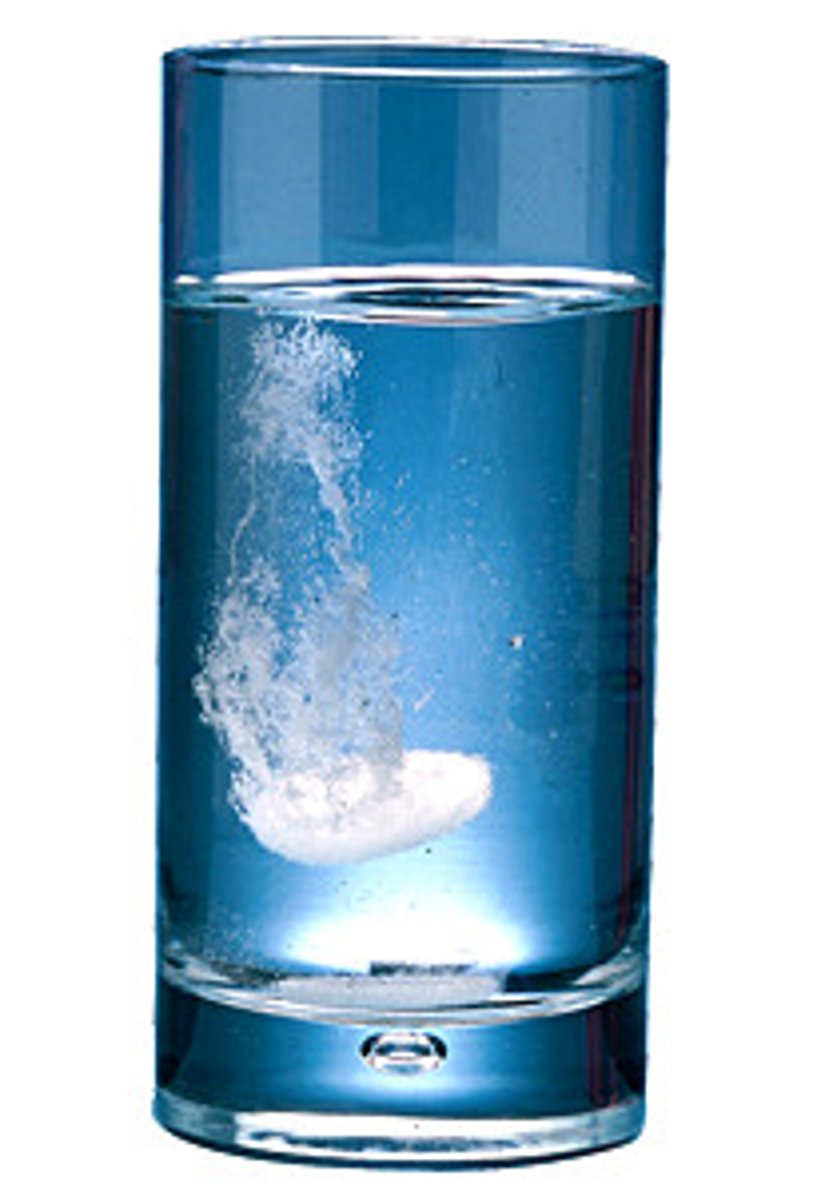

Insoluble
The substance cannot be dissolved in the solution. You can still see it.
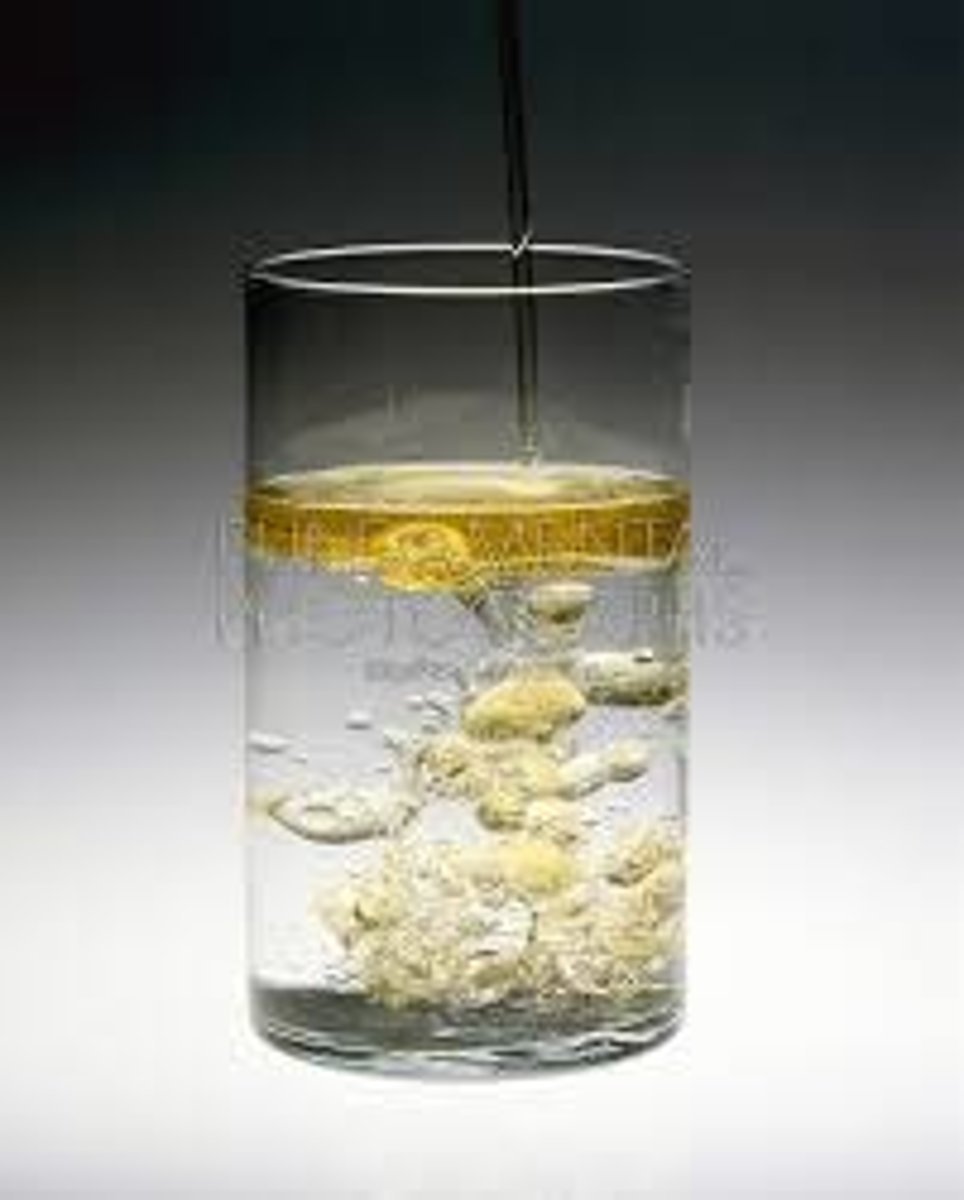

homogeneous mixture
A mixture in which substances are evenly distributed throughout the mixture
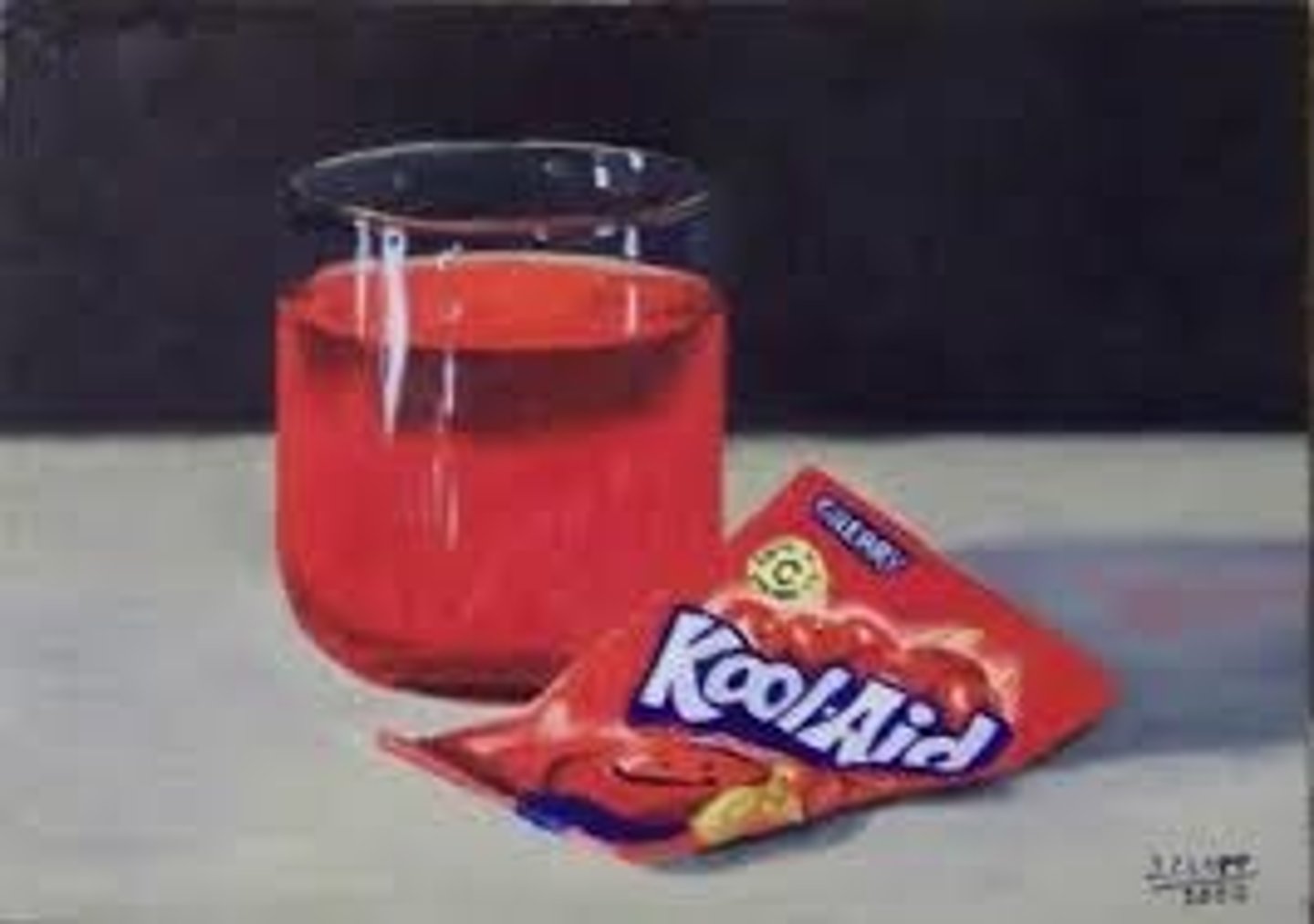

heterogeneous mixture
A mixture in which different materials can be distinguished easily
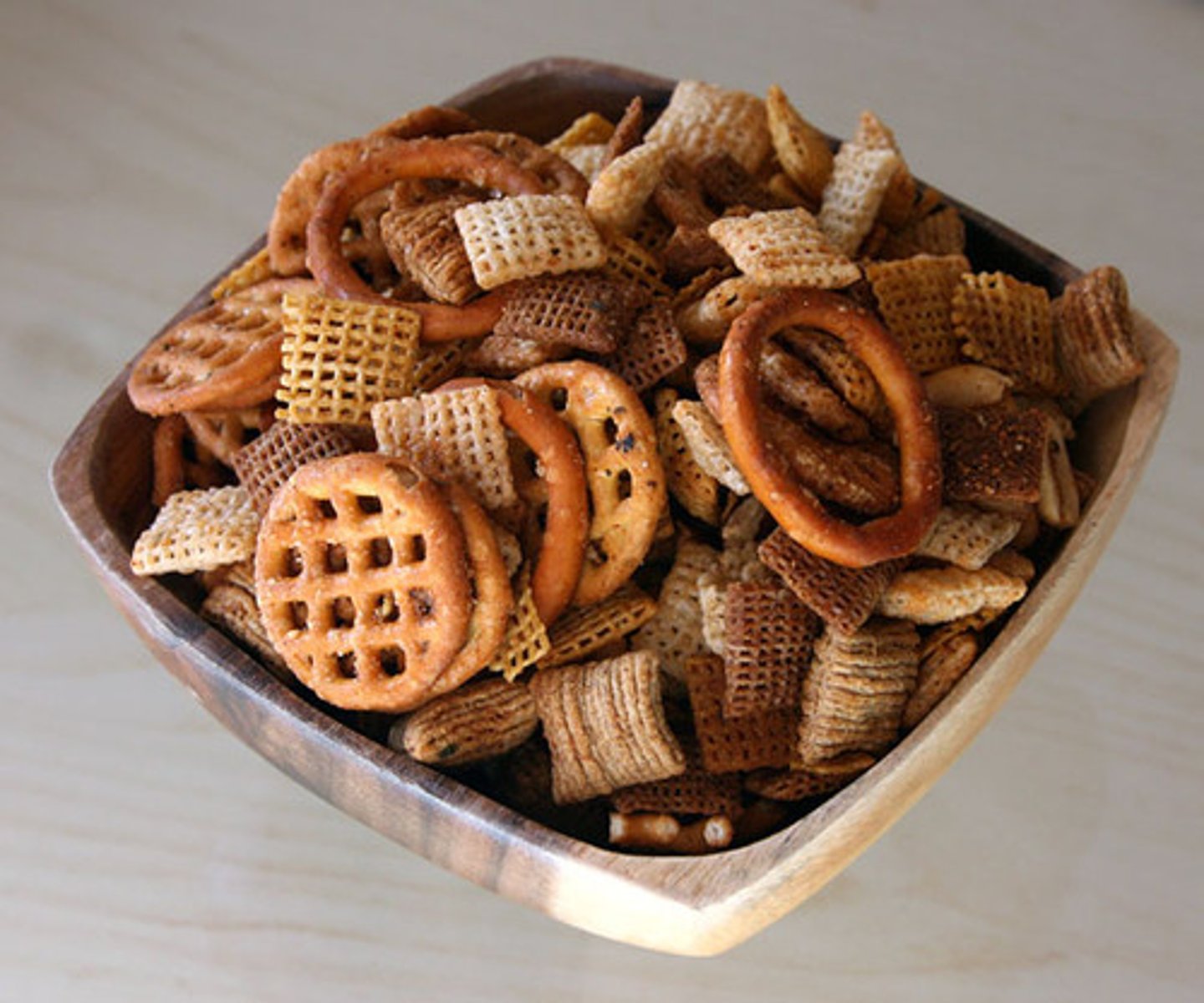

product
a substance that forms in a chemical reaction
Reactant
A chemical substance that is present at the start of a chemical reaction
Coefficient
A number in front of a chemical formula in an equation that indicates how many molecules or atoms of each reactant and product are involved in a reaction.
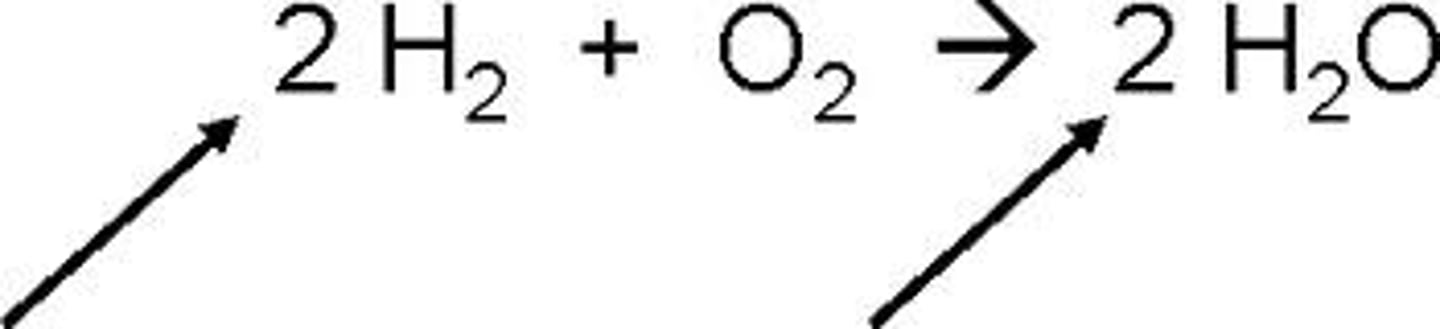
Subscript
A number in a chemical formula that tells the number of atoms in a molecule or the ratio of elements in a compound