Physical Analysis II Exam I
1/55
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
56 Terms
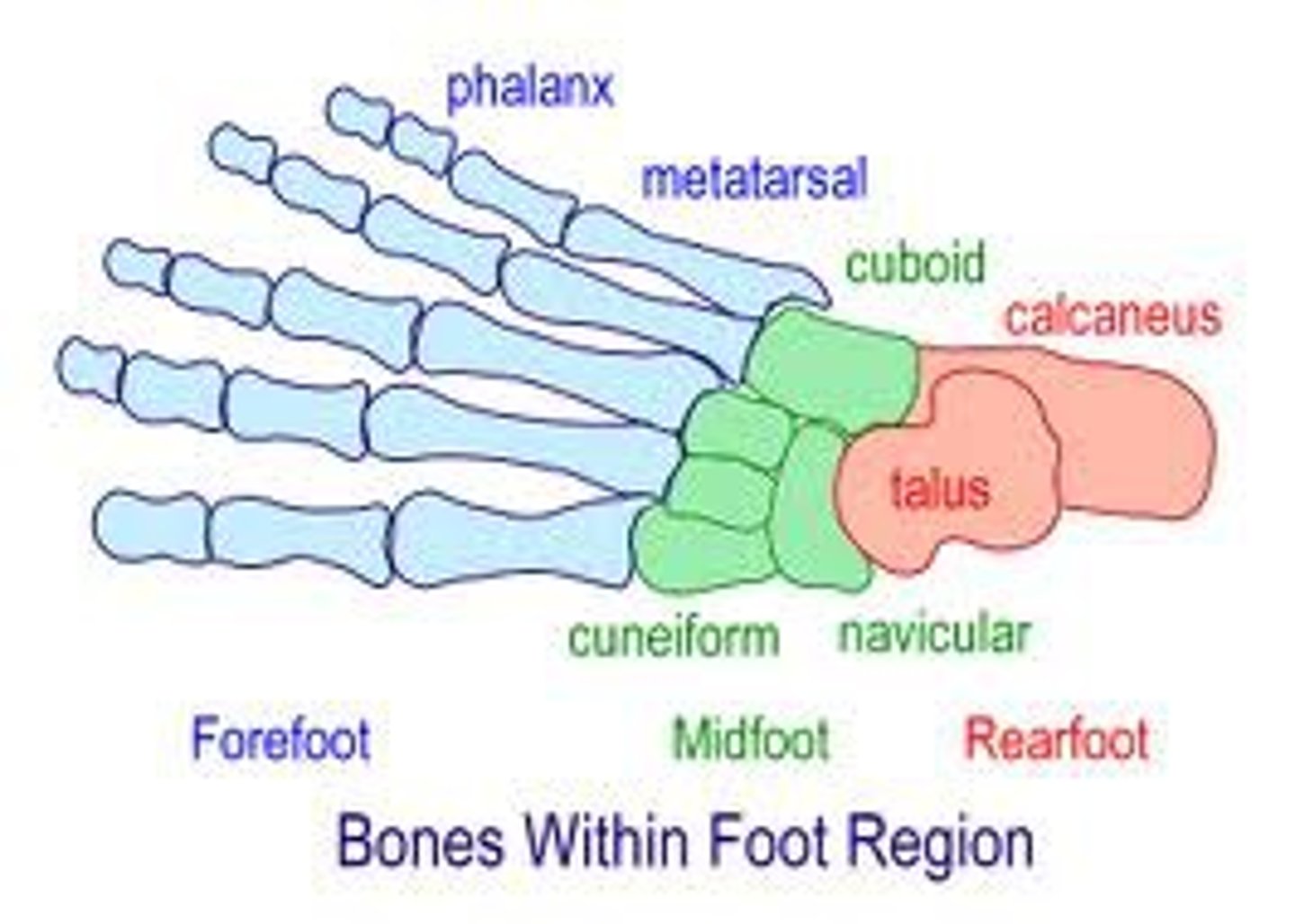
Rearfoot/Hindfoot
Includes talus and calcaneus
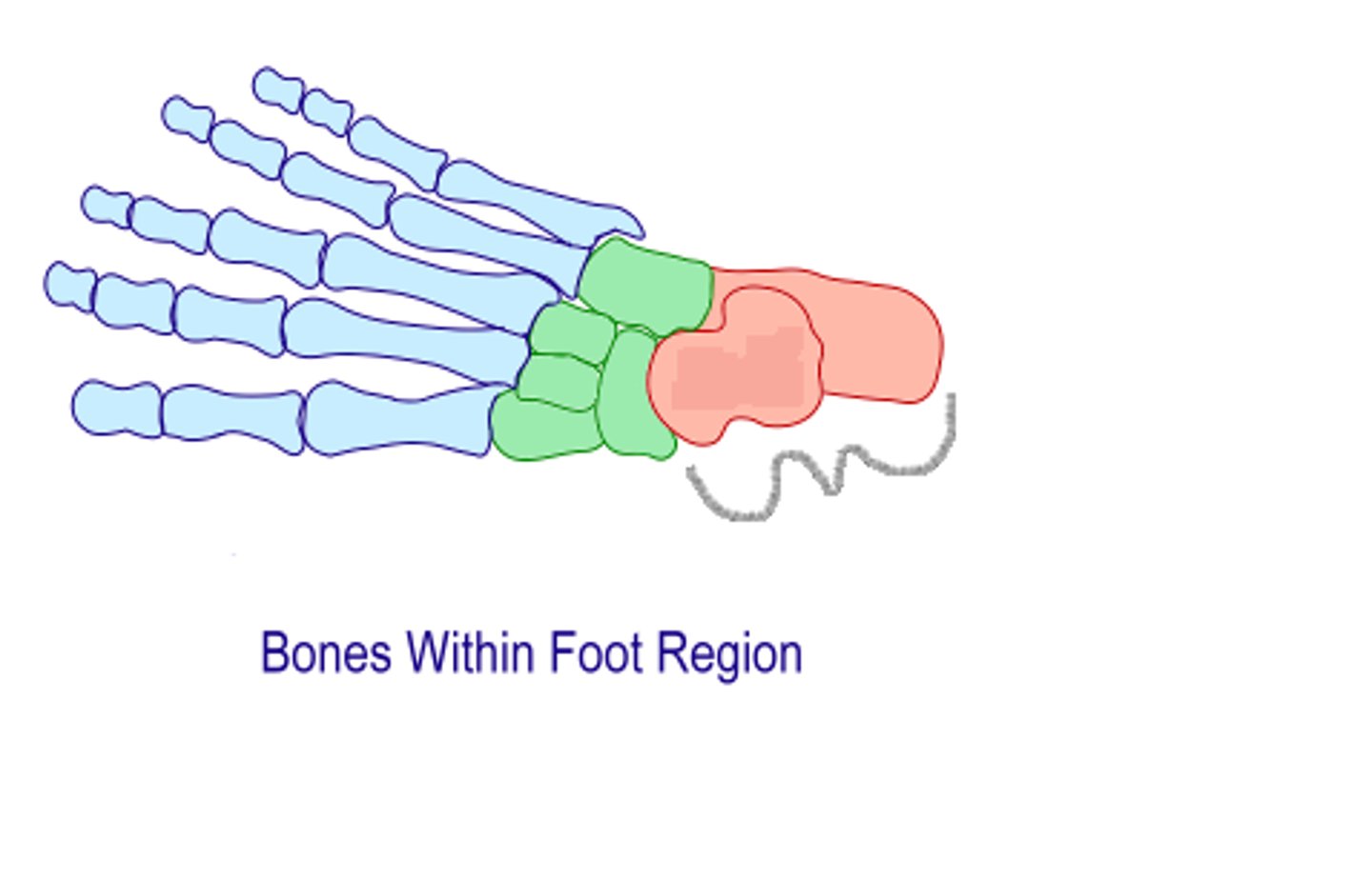
Midfoot
Includes navicular, cuboid, and cuneiforms 1, 2, & 3
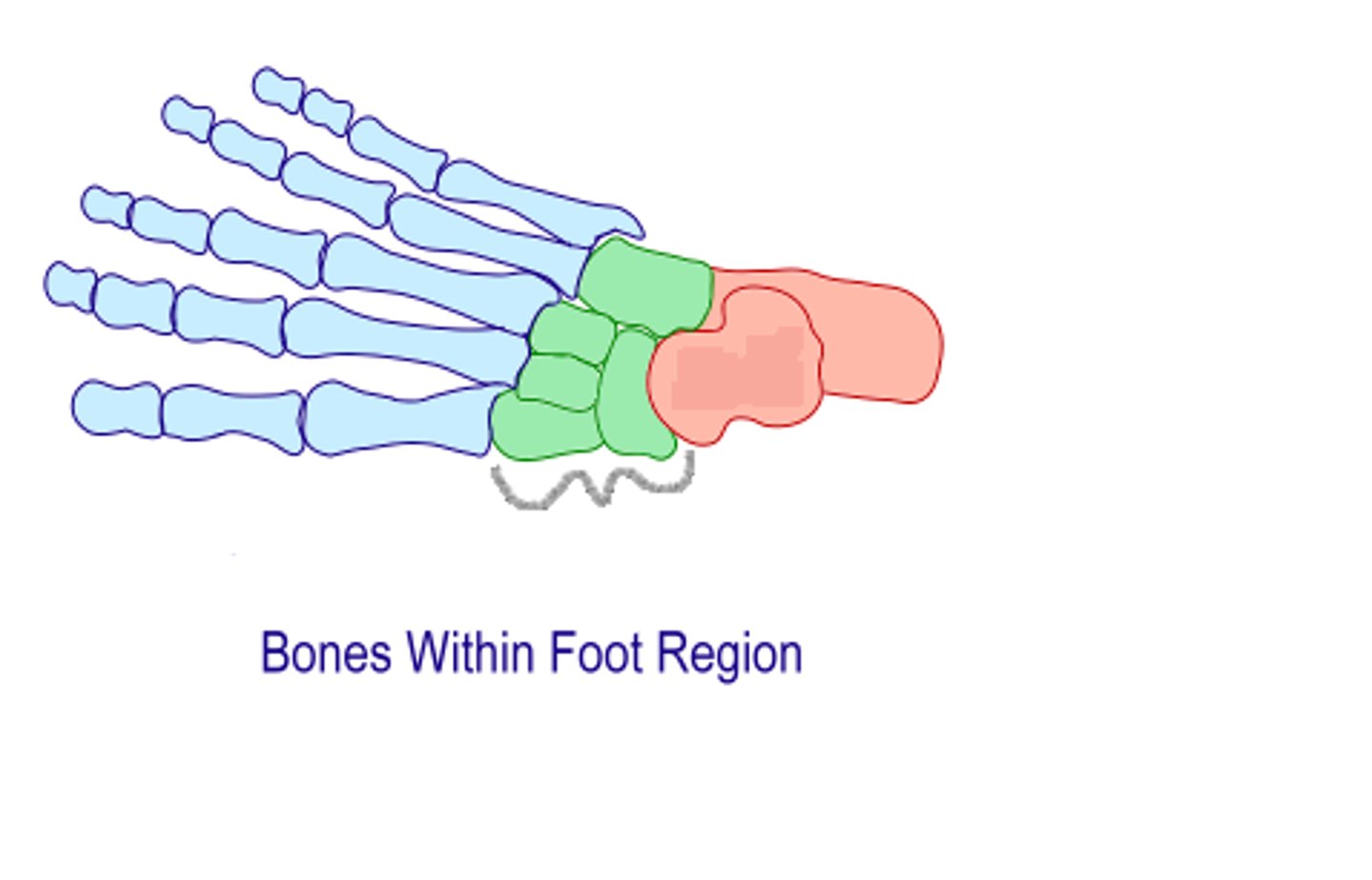
Forefoot
Includes metatarsals, phalanges, and sesamoids
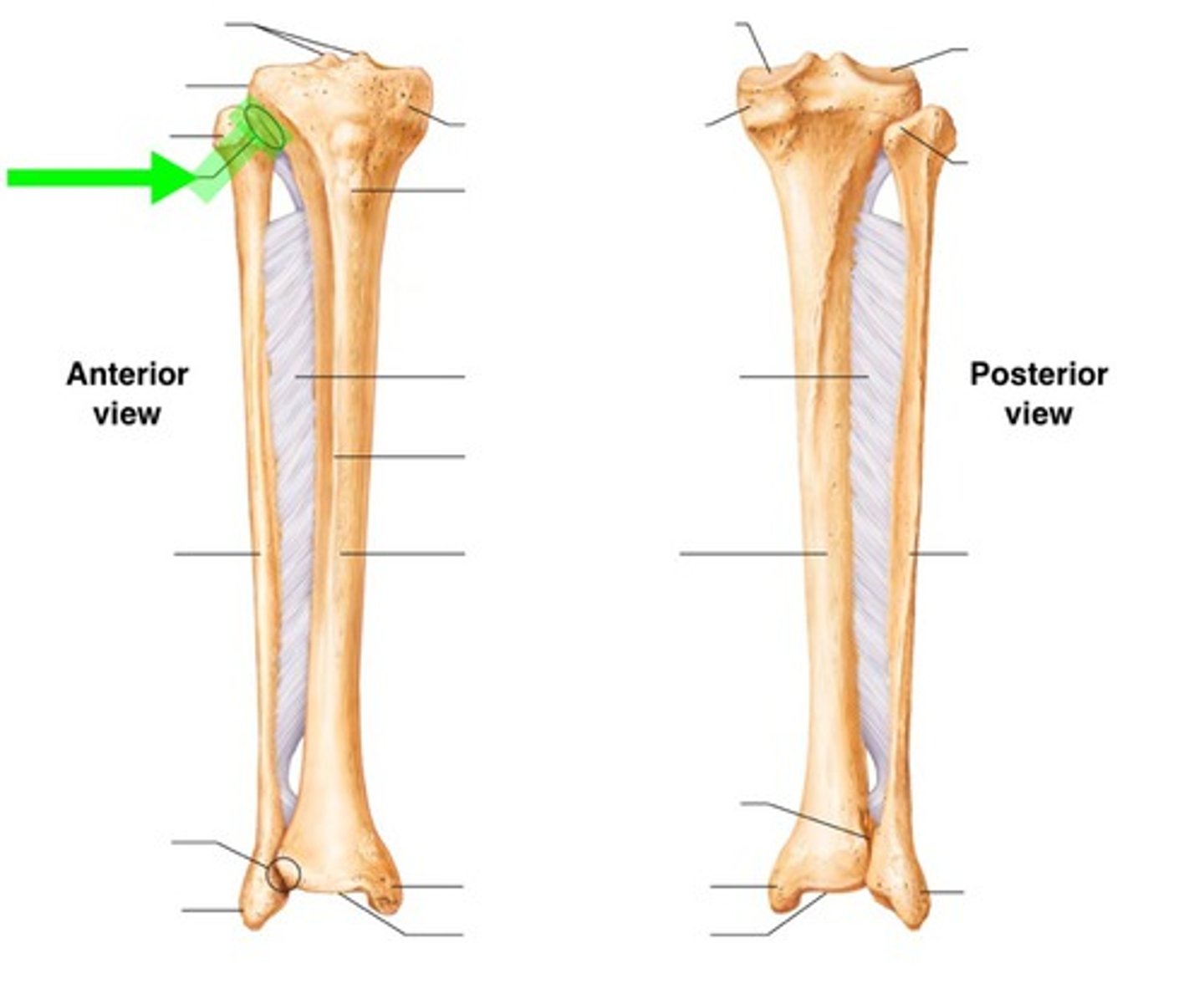
Proximal Tibiofibular Joint
Type: gliding joint
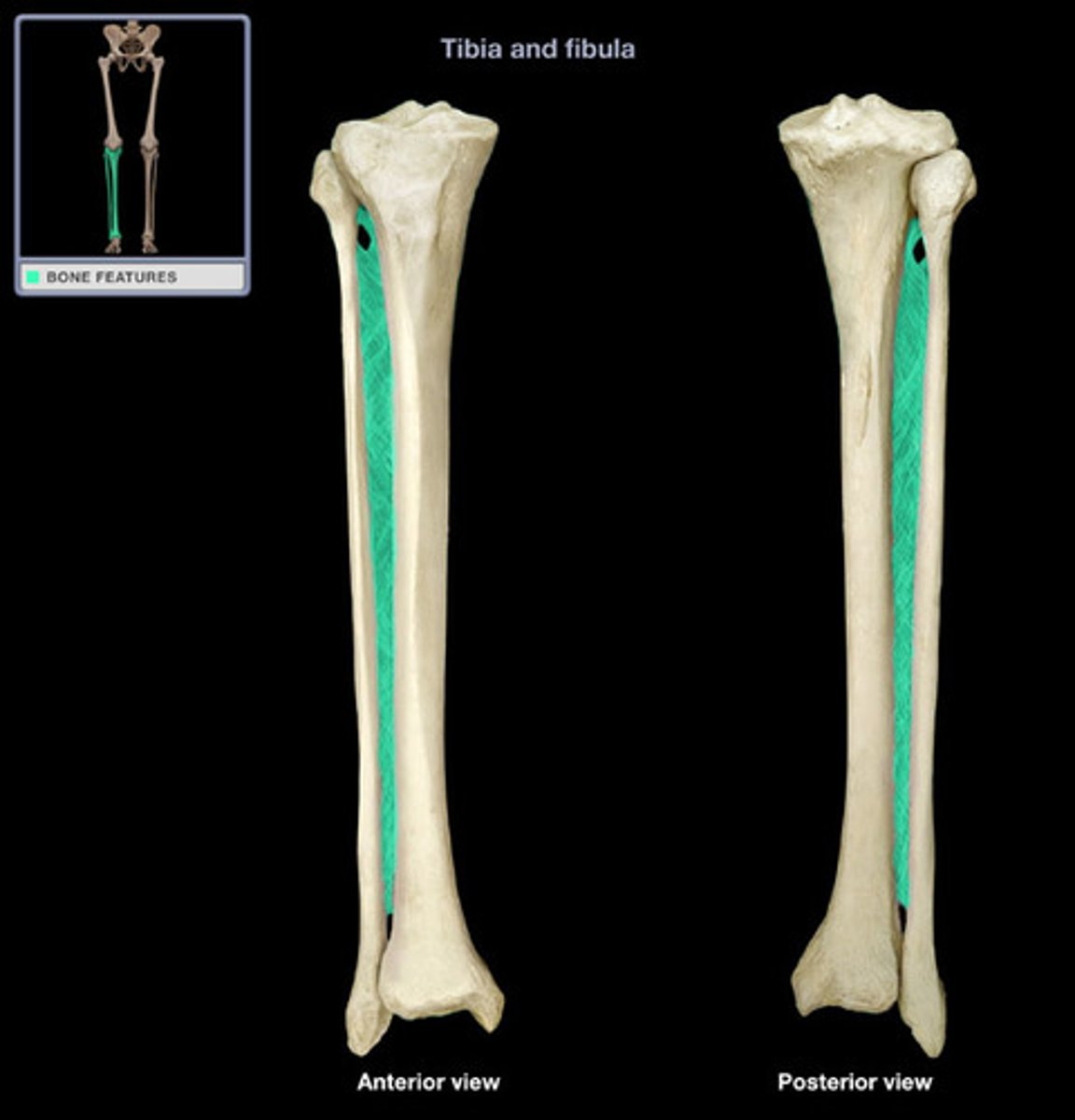
Interosseous Membrane
Connects long part of the bone; "Strong ligamentous sheet." Attachment point for muscles
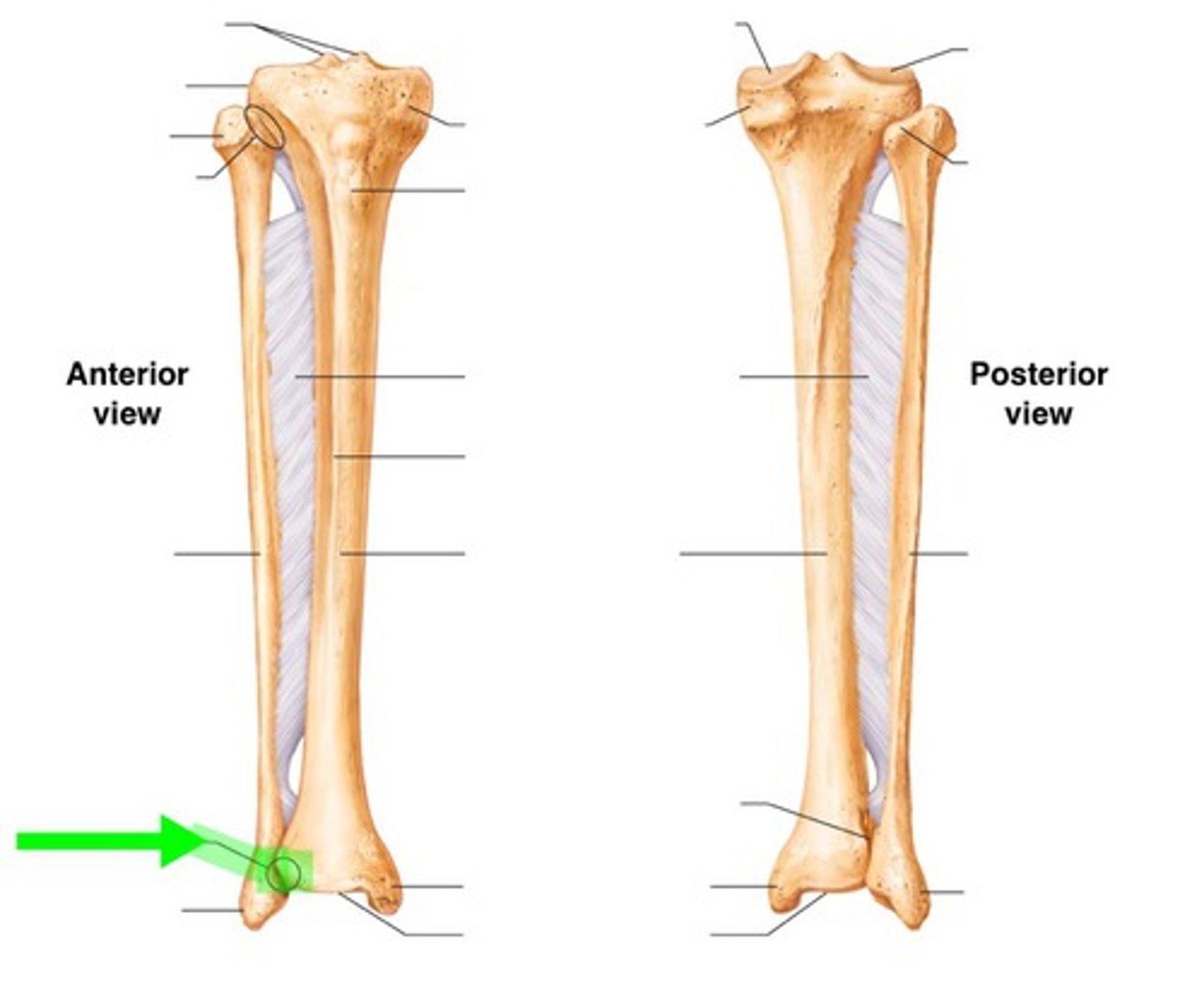
Distal Tibiofibular Joint
Type: fibrous joint, reinforced by four ligaments at the ankle
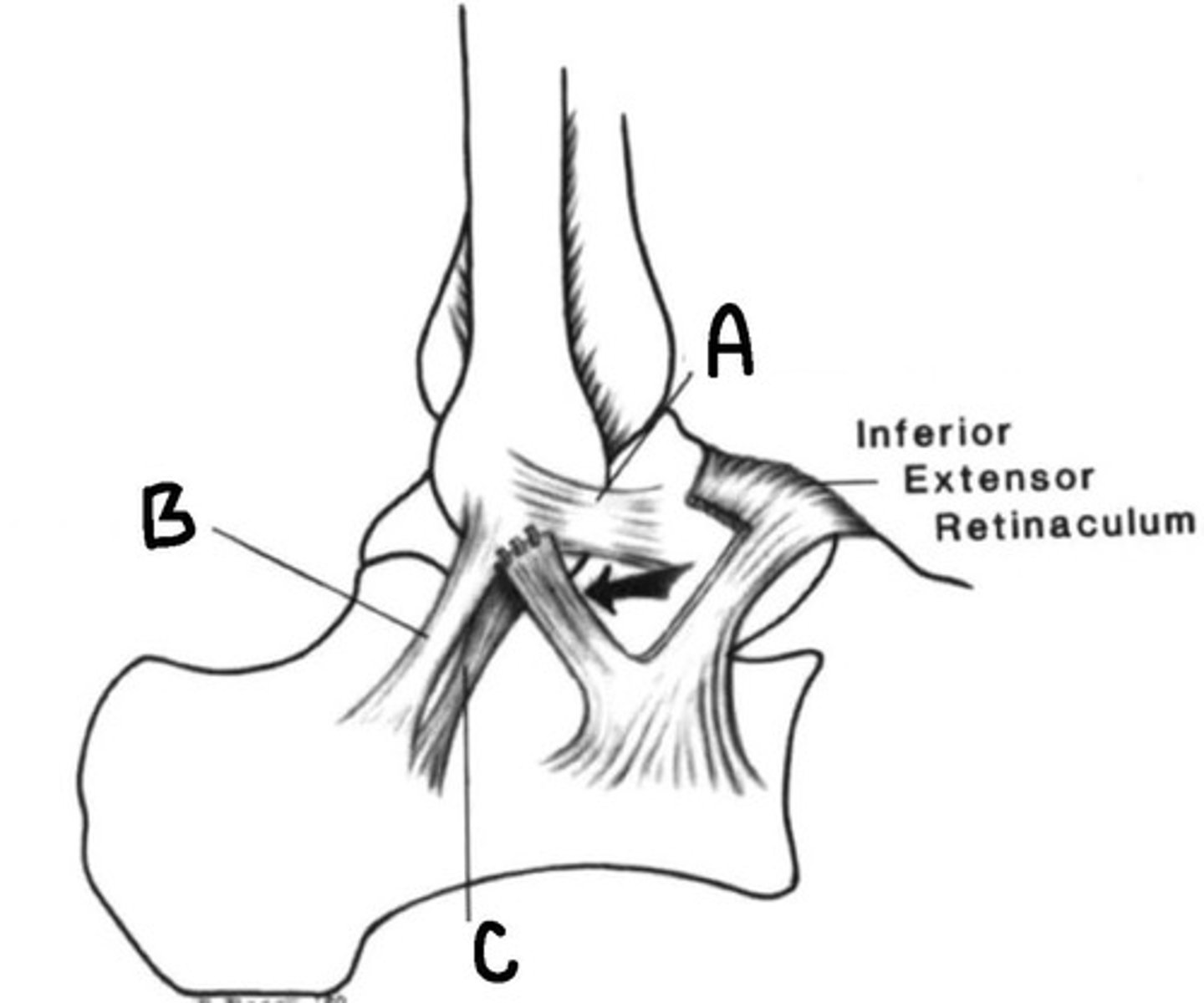
Anterior Talofibular (A), Lateral Talocalcaneal (C), and Calcaneofibular Ligaments (B),
Ligaments in an ankle sprain
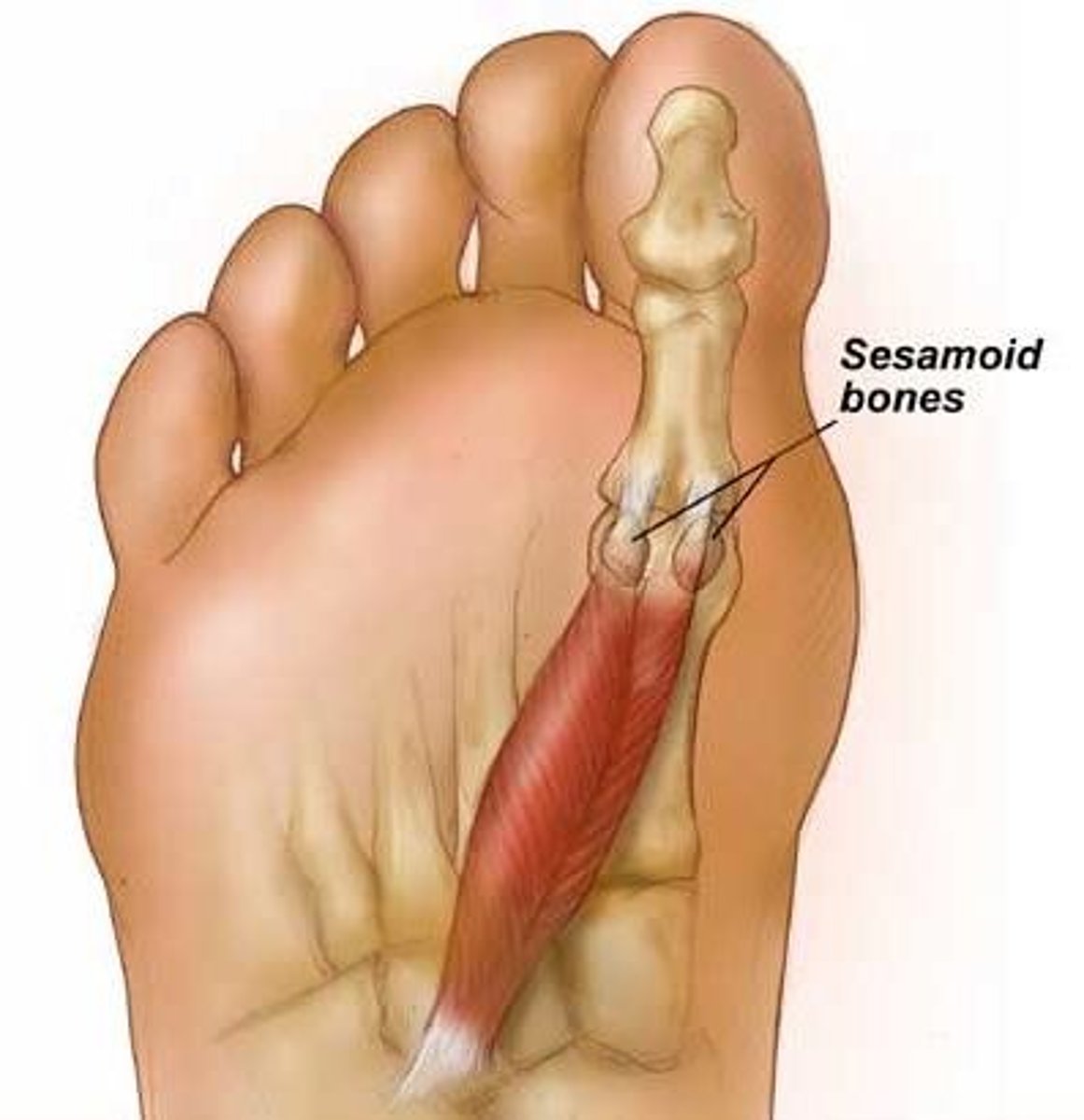
Sesamoid Bones
Two bones connected to flexor hallucis brevis; produce force for muscle
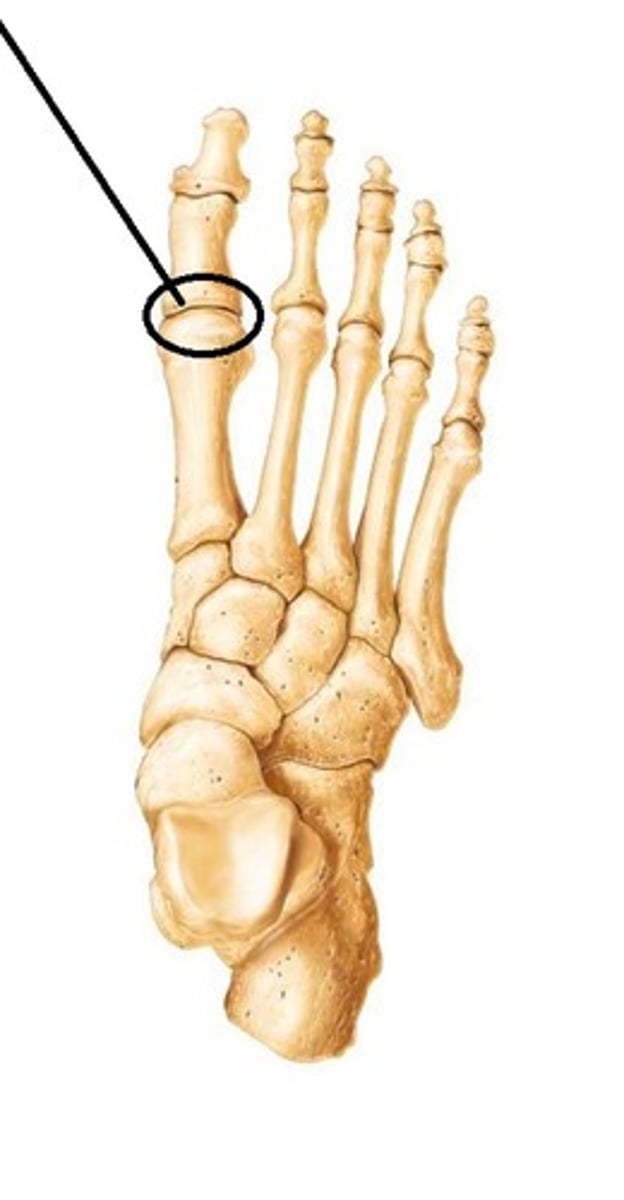
MTP Joint
Allows movement of the toes in flexion and extension; important for demi-pointe and walking
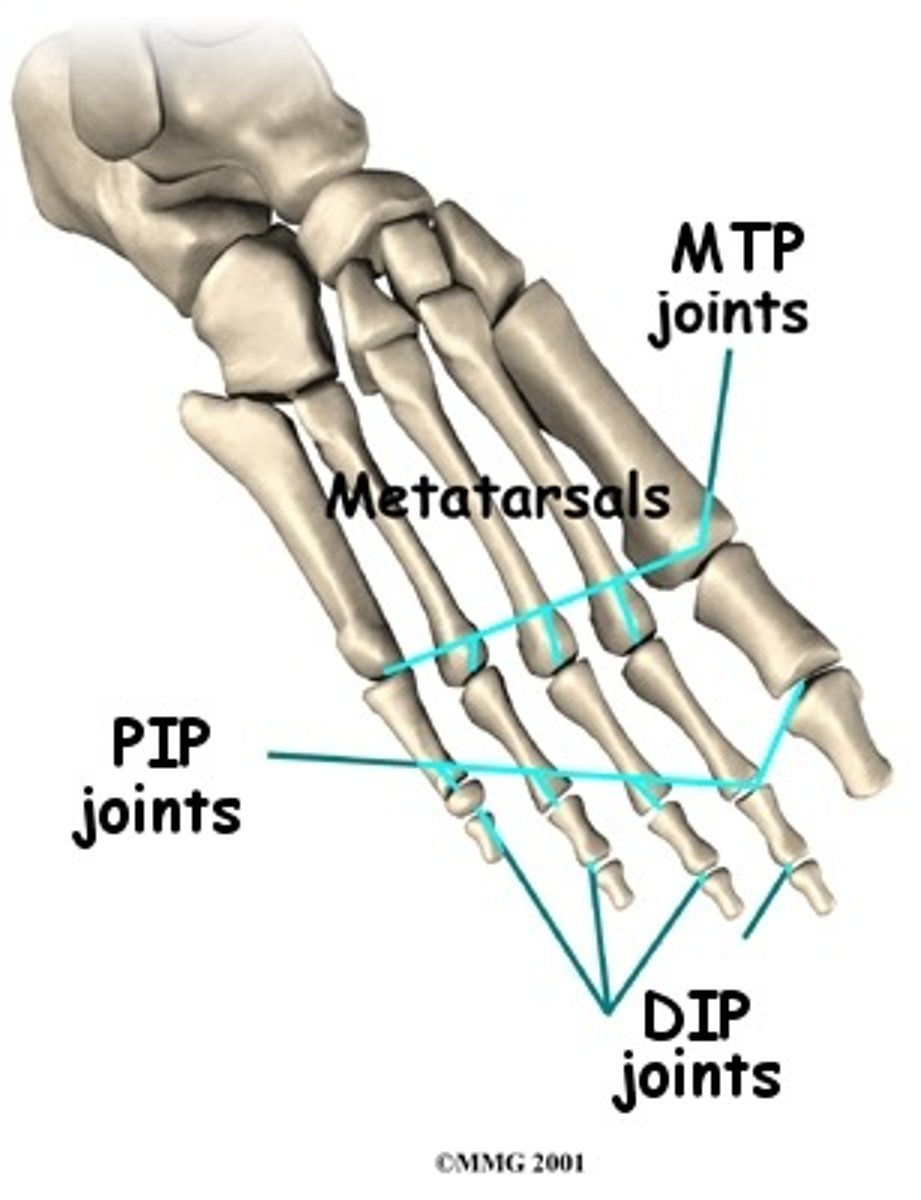
Distal and Proximal IP Joints
Hinge joints allowing flexion & extension of the smaller toes
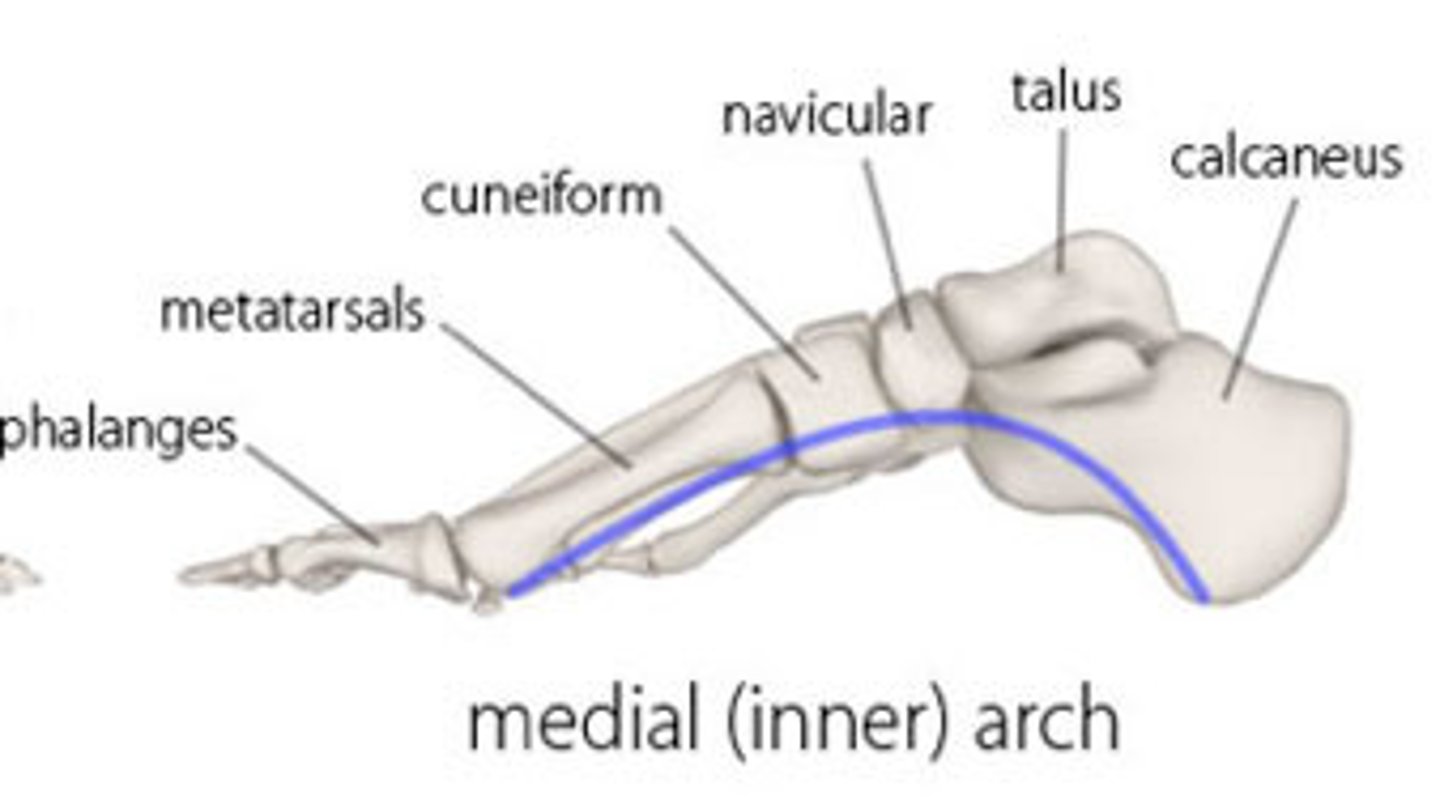
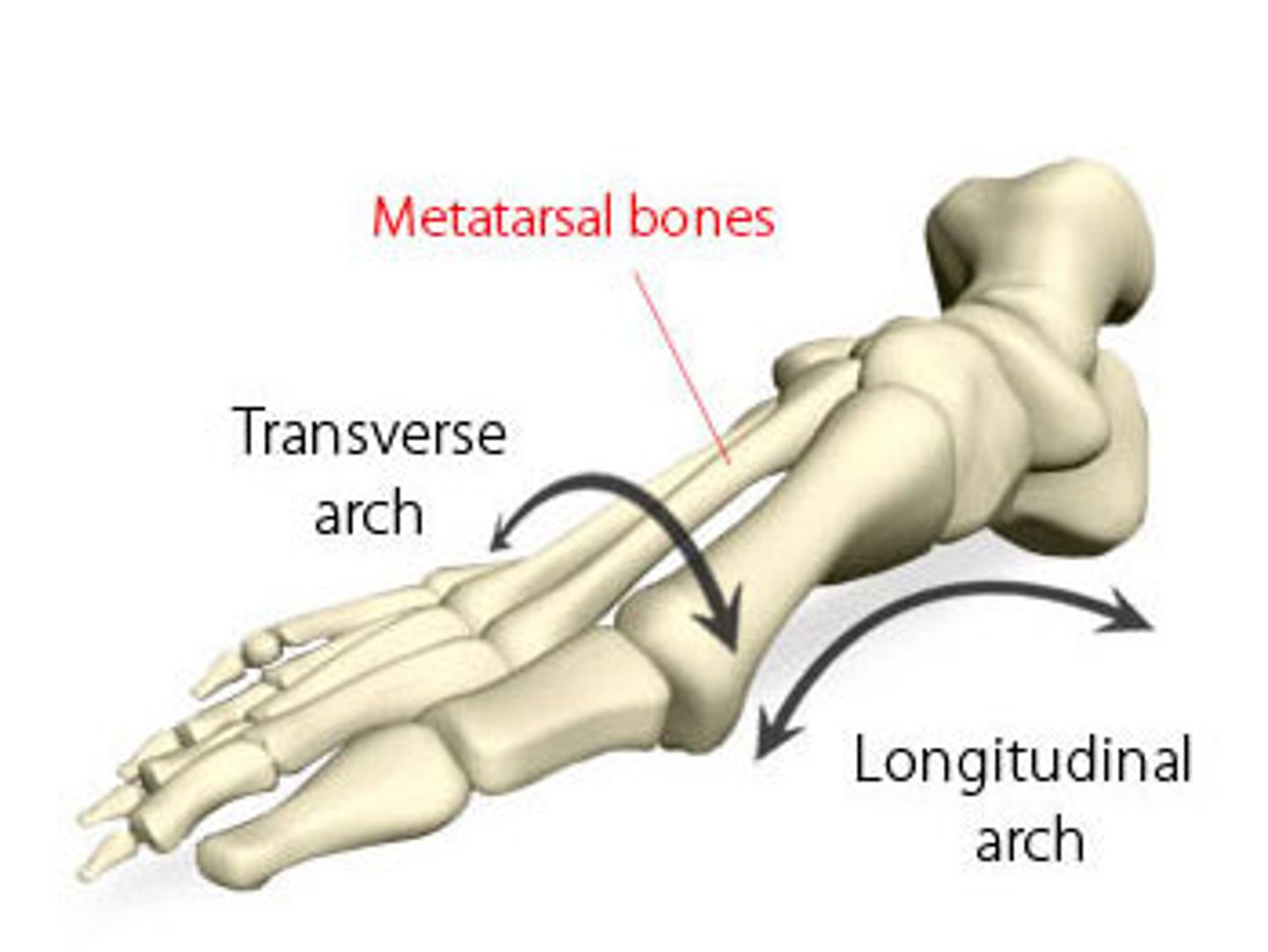
Medial Longitudinal Arch
Higher of the two arches; designed for shock absorption and uneven surfaces
Lateral Longitudinal Arch
Designed for stability and in contact with the ground while standing
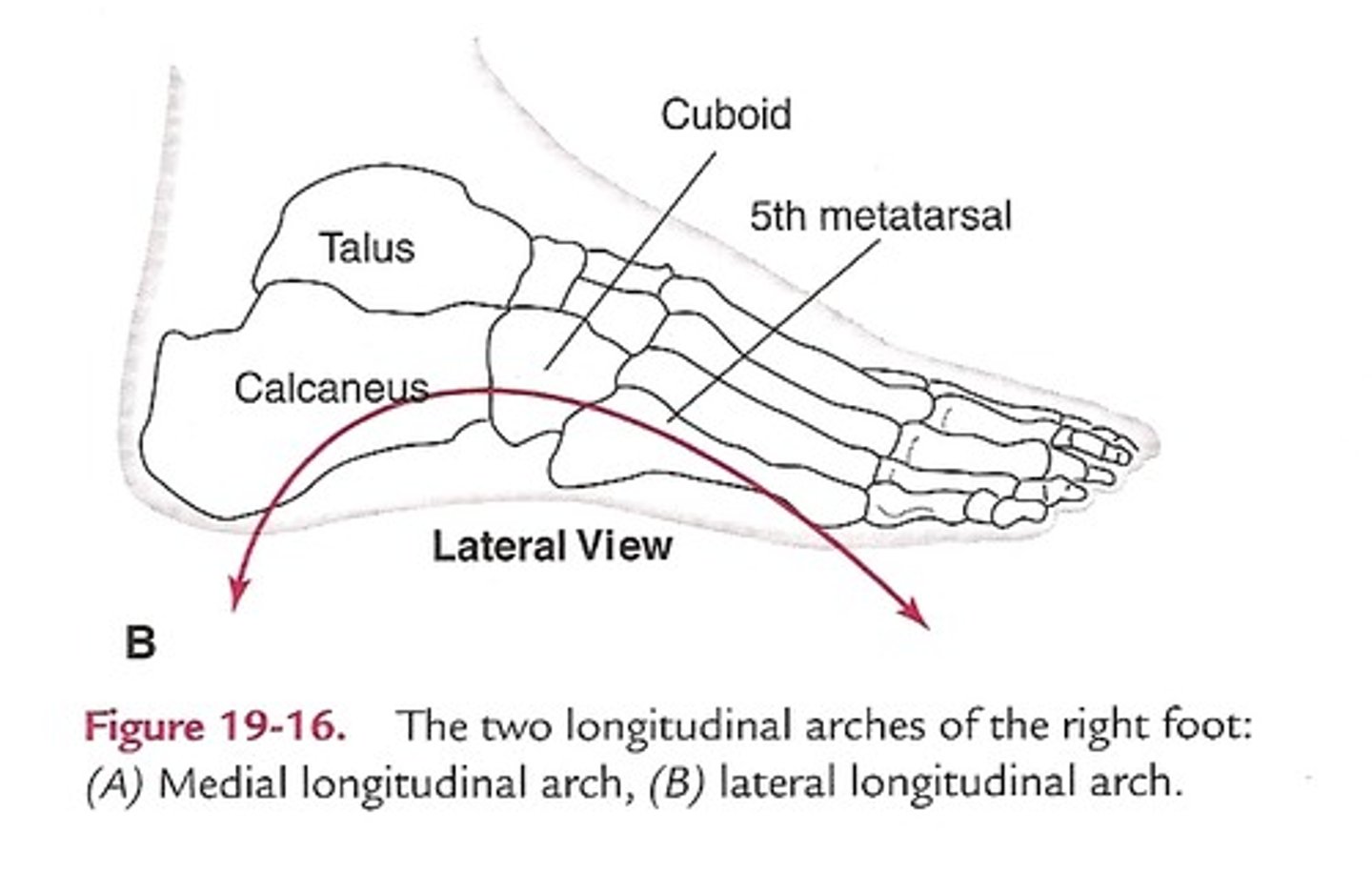
Transverse Arch
Referred to as the 'instep' or the top of the foot
Pes Planus
Flat feet
Pes Cavus
High arches
Retinaculum
Thickened bands of connective tissue holding ligaments, tendons, and muscles in place
Heel Pad
Fat pads under the calcaneus and metatarsals for shock absorption
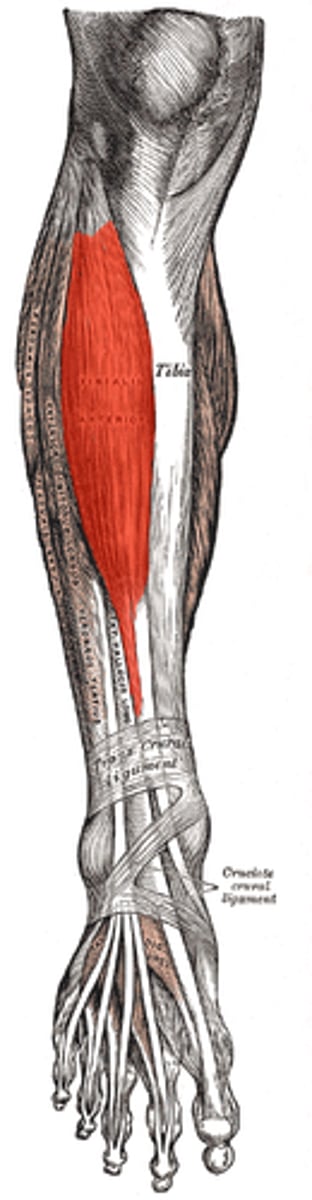
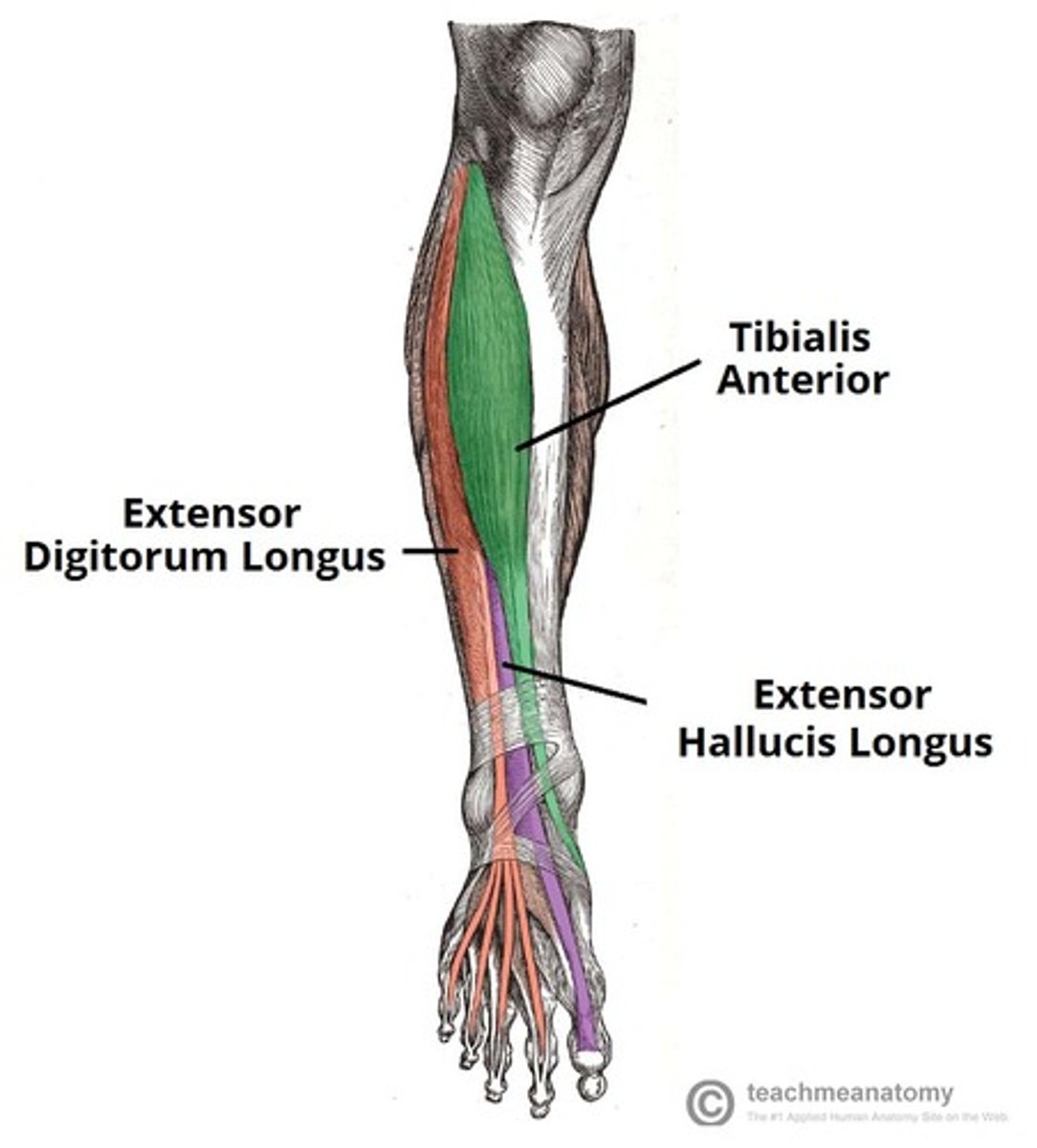
Tibialis Anterior/Anterior Tib
• Proximal Attachment: upper two-thirds of lateral tibia and interosseus membrane
• Distal attachment: plantar surfaces of the first cuneiform base of 1st metatarsal
• Dorsiflexion and Inversion of the foot/leg at tarsal joints
• Irritation of this muscle is often related to shin splints
• One of the “stirrup muscles” which can lift the medial arch
• Distress of this muscle is commonly associated with splints
Extensor Digitorum Longus
• Proximal attachment: anterior aspect of upper tibia and fibula, interosseus membrane
• Distal attachment: dorsal surfaces of lesser toes
• Extends the 2nd -5th toes (Dorsiflexion); Foot eversion
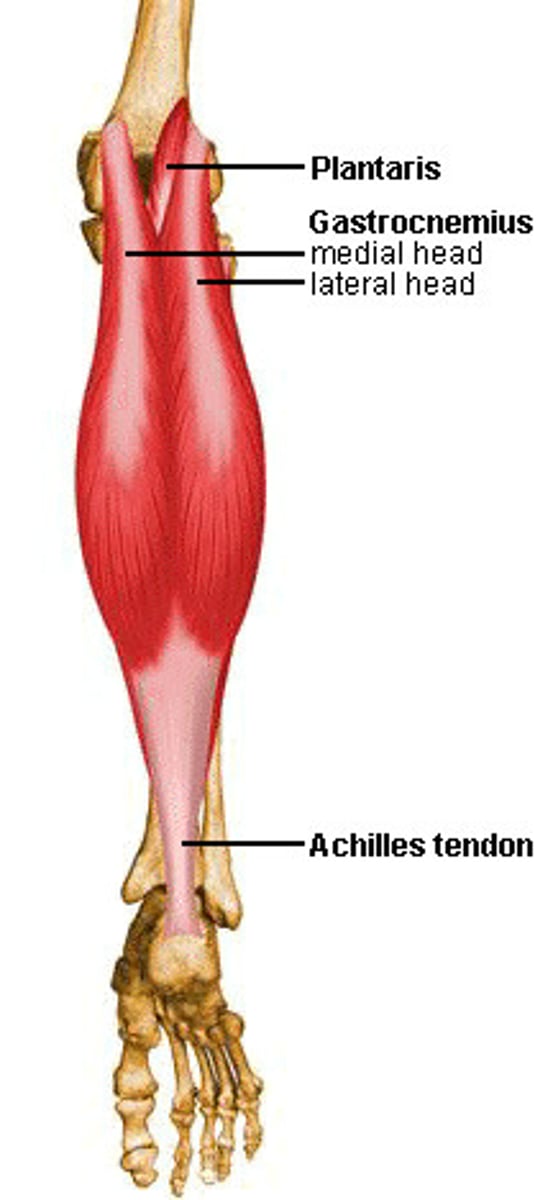
Gastrocnemius
• Proximal attachment: posterior aspect of medial and lateral condyles of the femur
• Distal attachment: posterior calcaneus via Achilles tendon
• Plantarflexion, Knee flexion
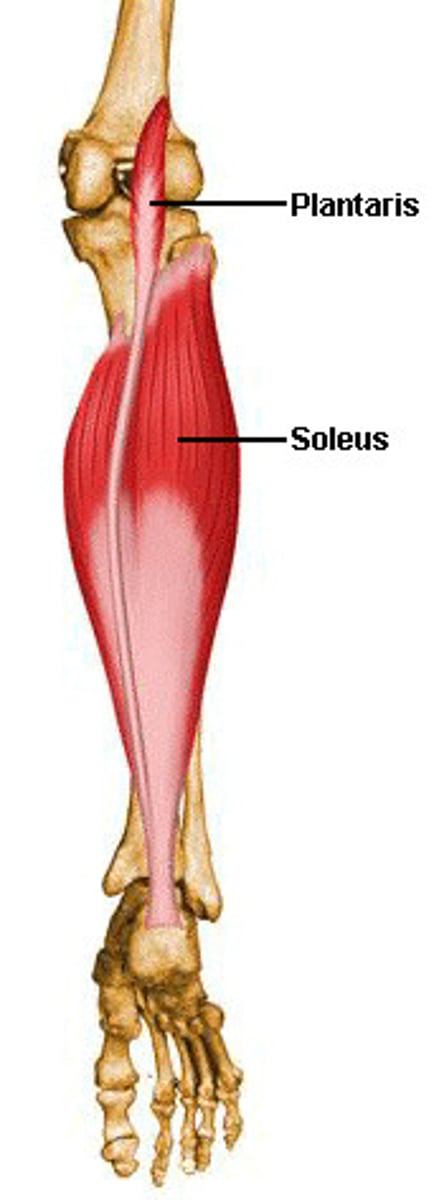
Soleus
• Proximal attachment: posterior aspect of upper tibia, fibula, and interosseus membrane
• Distal attachment: posterior calcaneus via Achilles tendon
• Deep to/under the gastroc
• “Slow twitch” - Stability and balance
• Plantarflexion
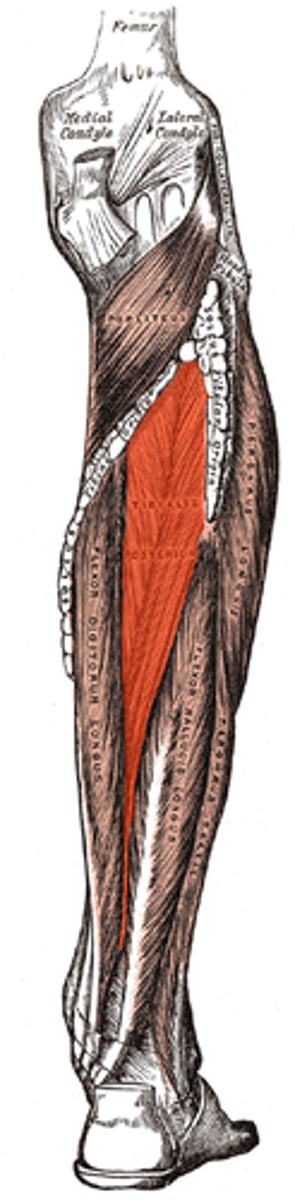
Tibialis Posterior/Posterior Tib
•Proximal attachment: posterior upper half of interosseus membrane and adjacent tibia/fibula
•Distal attachment: plantar surface of navicular
•Foot inversion, Plantarflexion
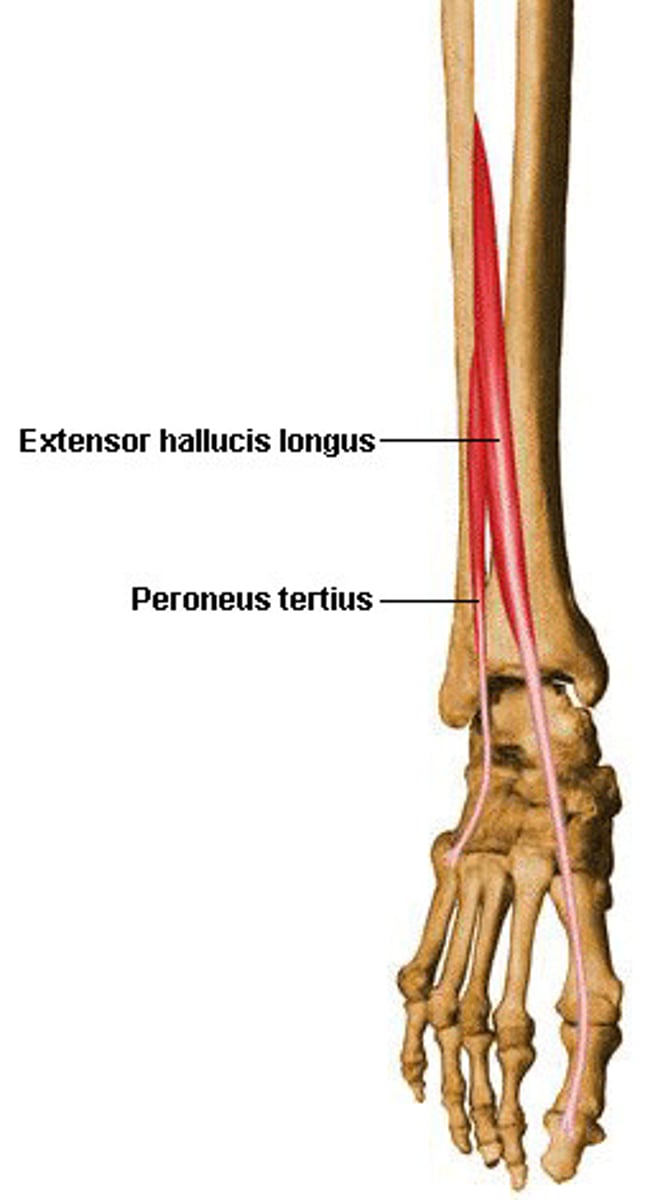
Extensor Hallucis Longus
• Proximal attachment: middle portion of anterior fibular and interosseus membrane
• Distal attachment: dorsal surface of big toe
• Extends the big toe, dorsiflexion, inversion
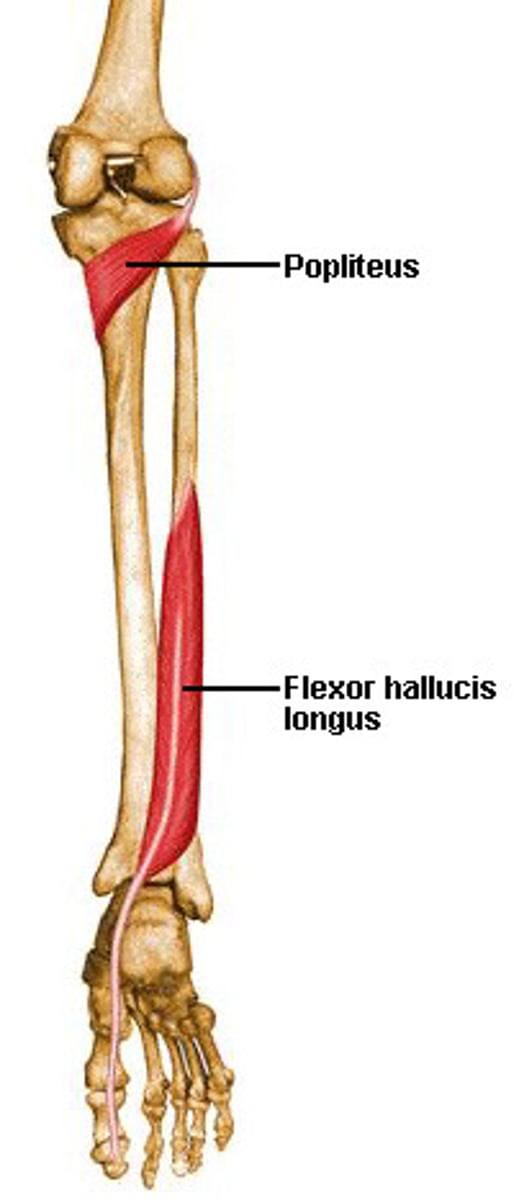
Flexor Hallucis Longus
• Proximal Attachment: posterior aspect of lower fibula, interosseous membrane
• Plantar surface of base of distal big toe
• Big toe flexion, plantar flexion, foot inversion
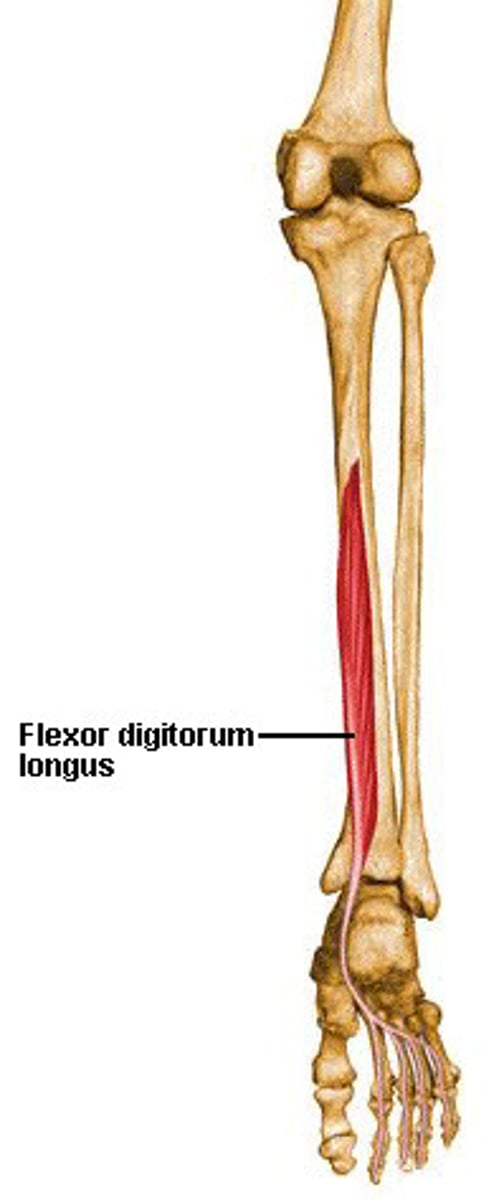
Flexor Digitorum Longus
•Proximal attachment: posterior surface of tibia and tibialis posterior fascia
•Distal attachment: plantar surface of lesser toes
•Plantarflexion of lesser toes, foot inversion
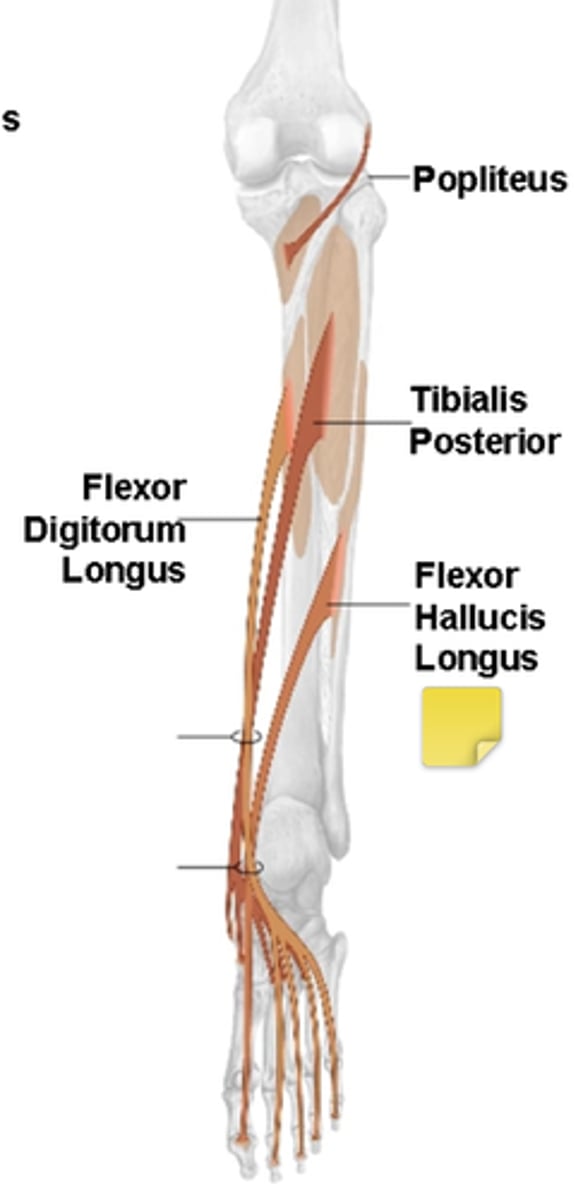
Tom, Dick, & Harry - muscle insertions
Tibialis Posterior, Flexor Digitorum Longus, Flexor Hallucis Longus
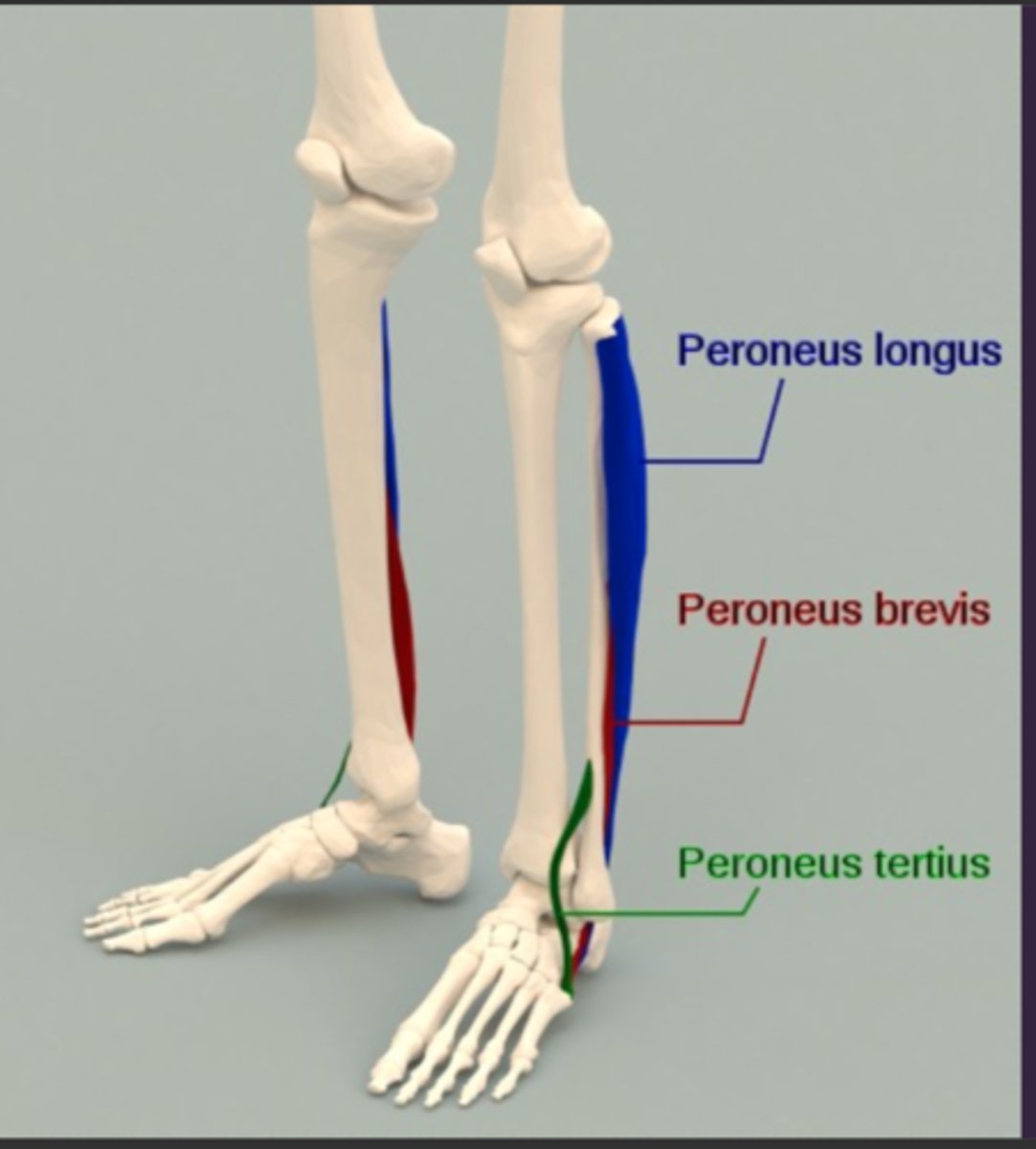
Name the 3 Peroneals/Fibularis and their function
Longus, Brevis, Tertius
Muscles for foot eversion and plantarflexion; 'winging' muscles
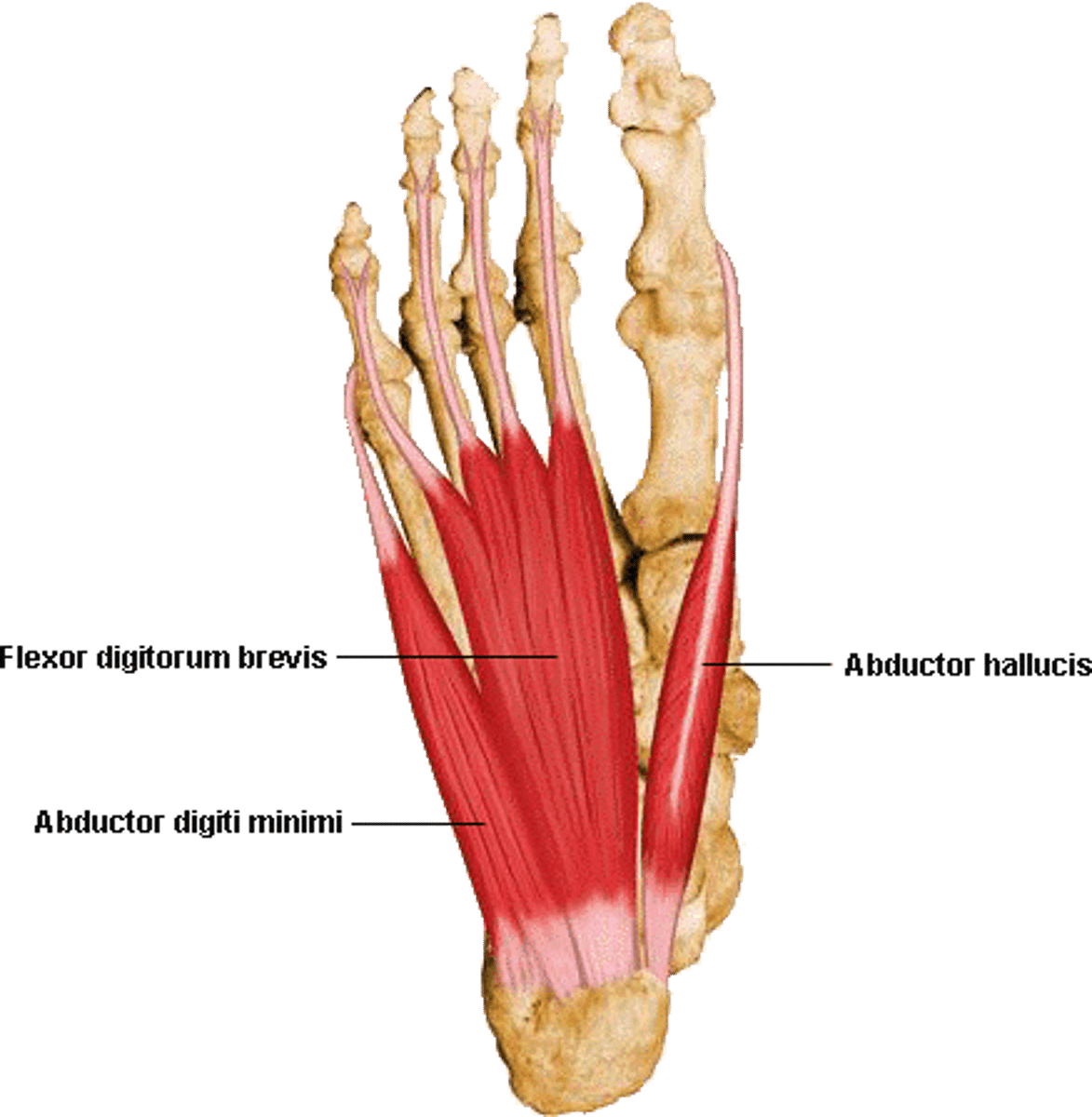
Layer 1 of Plantar Foot
Includes flexor digitorum brevis, abductor digiti minimi (abducts 5th toe) , and abductor hallucis
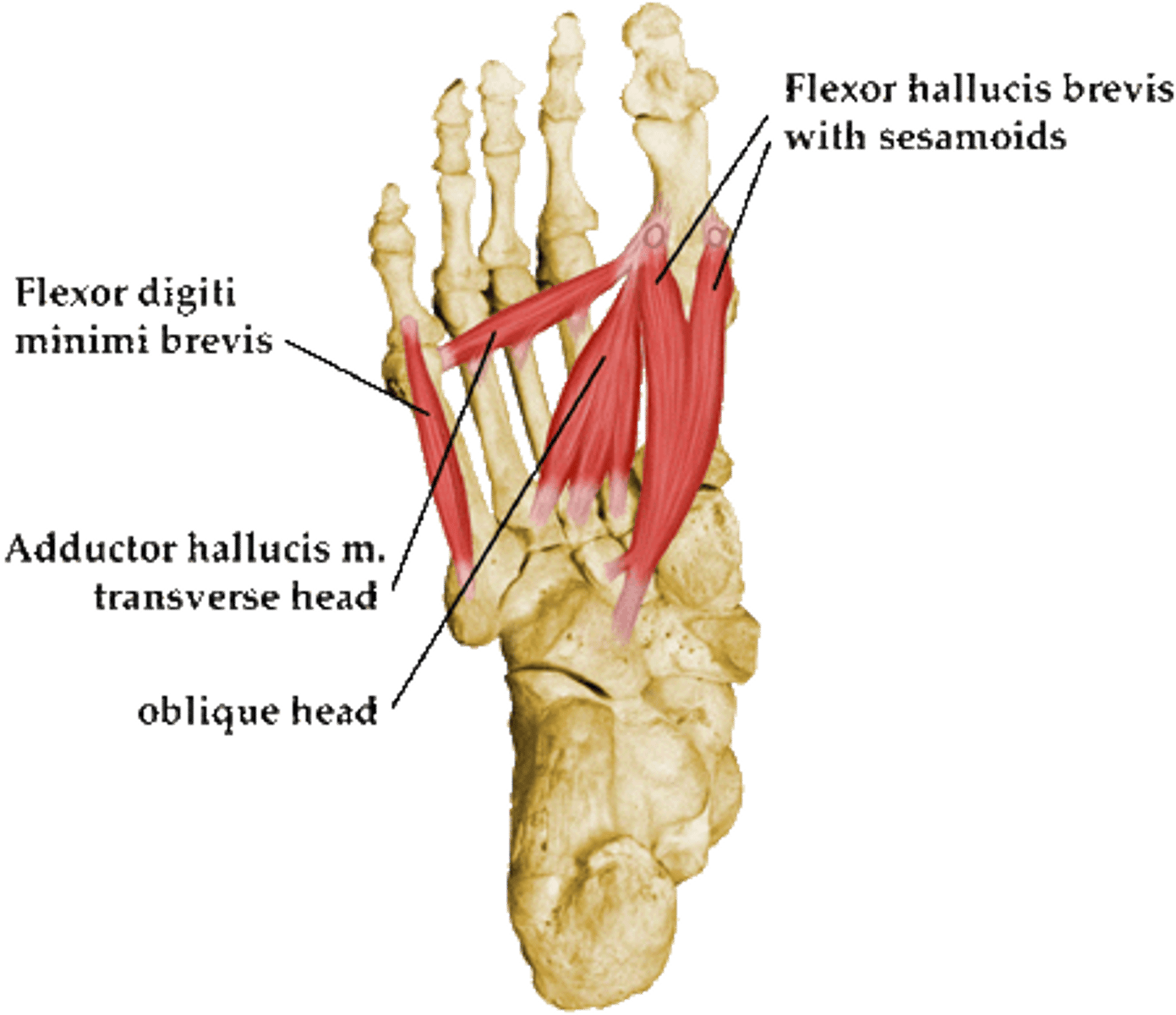
Layer 3 of Plantar Foot
Includes Flexor hallucis brevis: plantarflexes the big toe, connects to sesamoid
(flexor hallucis longus FHL runs through this)
Shin Splints
Tenderness on the anterior and/or medial tibia;
muscles involved: Tibialis Anterior, Tibialis Posterior, Flexor Hallucis Longus, Soleus
AKA: Tibial Stress Syndrome
Treatment: controlling foot pronation with taping, arch supports, orthotics in street shoes, and strengthening/stretching the muscles involved in shin splints
Bunions (Hallux Valgus)
Bony bump at the MTP joint; caused by big toe pushing against the second toe
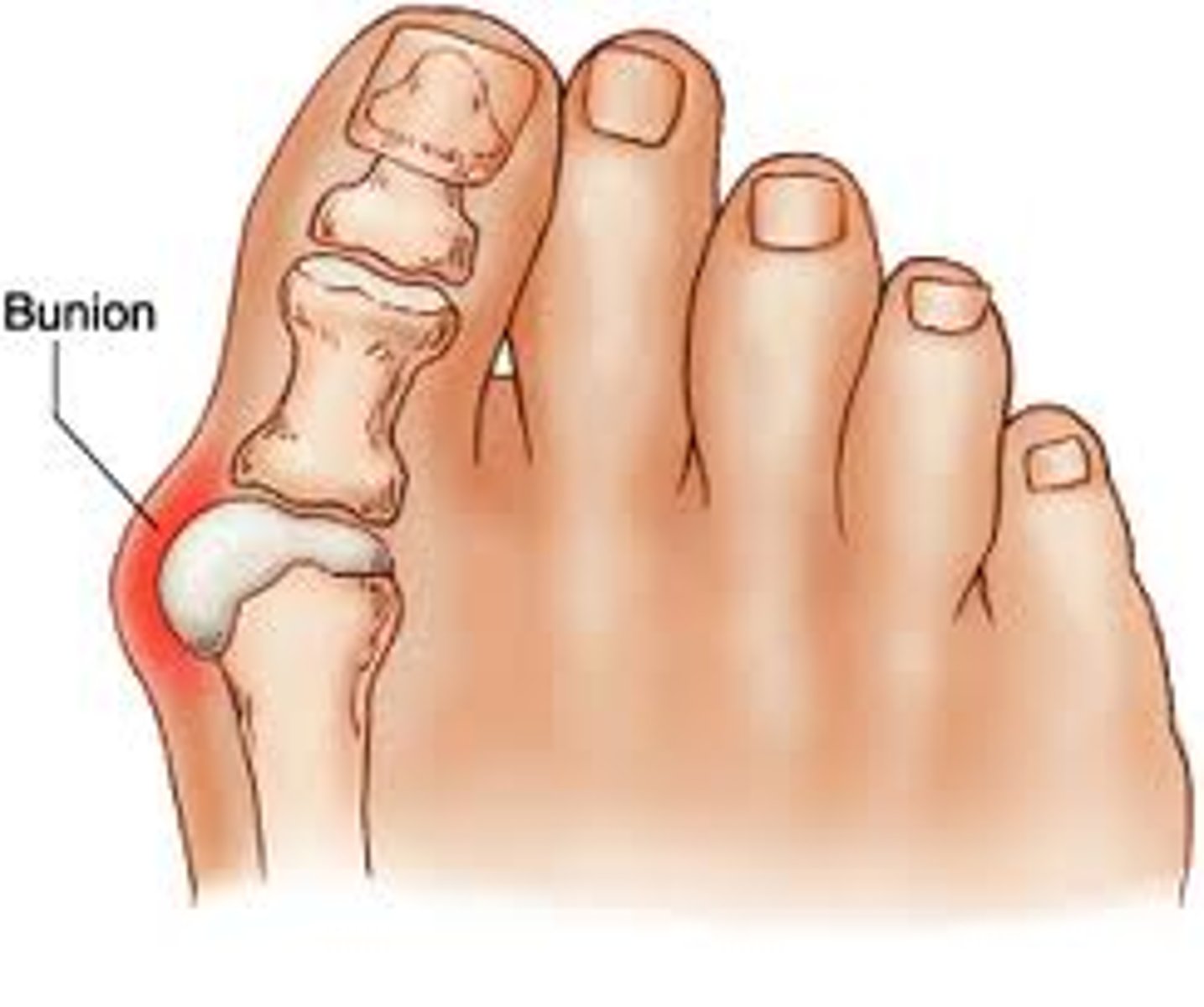
Bunion Prevention
Preventing Bunions
• Wear wider shoes
• Use a toe separator
• Tape the big toe (Ask your PT)
• Control pronation
• Strengthen the arch muscles
• Strengthen Abductor Hallucus
Ankle Sprains
Grade 1-3 tearing of ligament(s); prevention includes thera-band exercises and relevés for strength
Ligaments do not return to their original length when overstretched
Os Trigonum
Impingement causing pain in relevé under the Achilles tendon
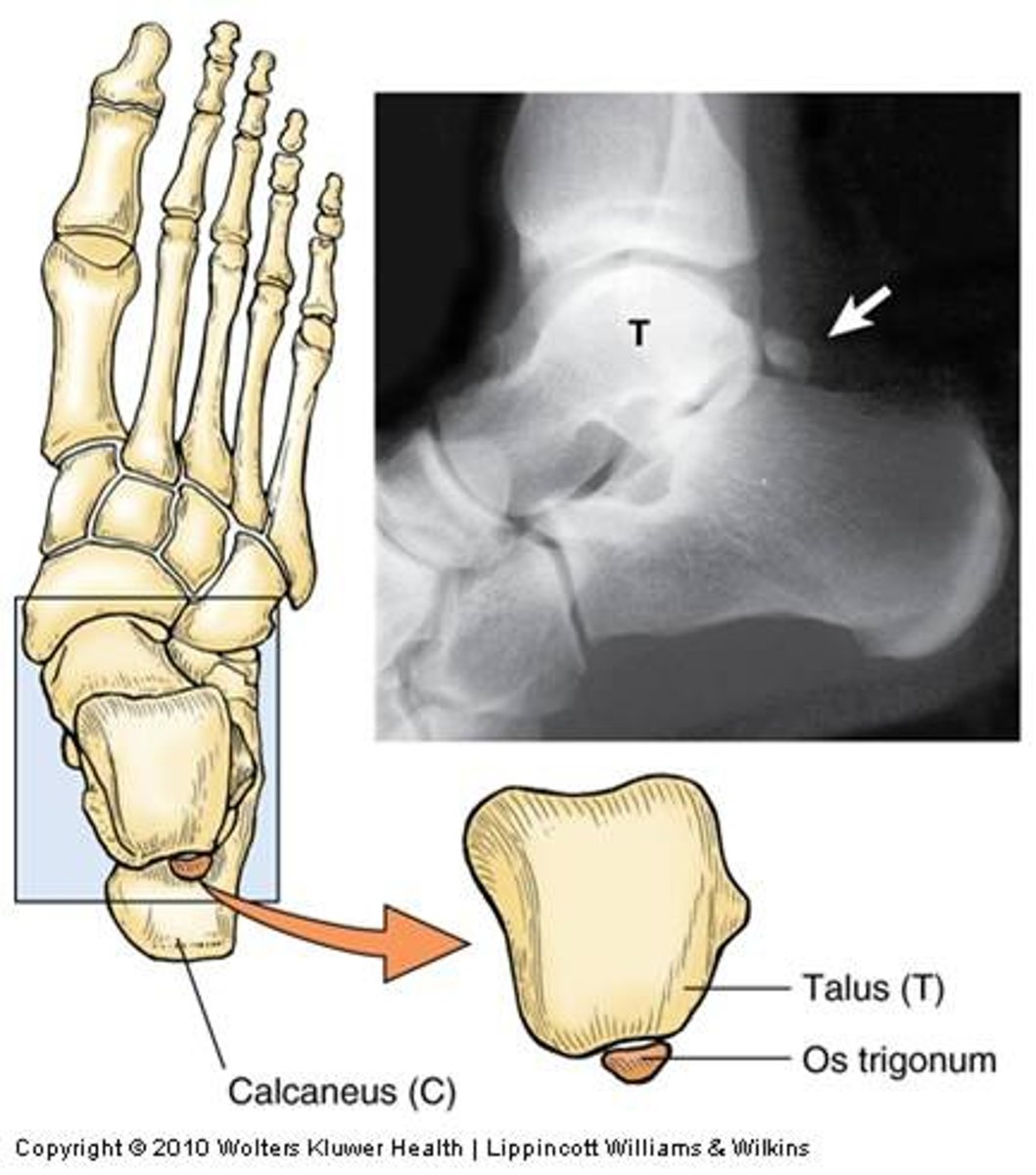
Bone Spurs
Calcification or breaking off of bone causing sharp pain in the joint; RICE and surgery for treatment
Tendinitis
Inflammation causing burning sensation, tenderness, and swelling; worsens with cold and movement
Corns
Hard, soft, and seed types caused by:
• Sandals or other shoes that are tight-fitting
• Shoes that are the wrong shape or size
• Wearing a different design of shoe than you typically do
• Hammertoes, bunions, or other foot issues
• Aging can cause the skin to thin, which can increase the risk of corn formation
Ingrown Toenails
Sharp edge of toenail irritates surrounding skin;
Prevention: cut toenails straight across, not rounded. Don’t cut them too short.
Treatment methods: cut the corners of the toenails as they grow out, place cotton underneath the corner of the toenail to relieve pressure, and/or have ingrown toenail surgery. Warm Epsom salt baths help with the pain.
Plantar Warts
Prevention by avoiding touching warts
Arthritis in the Foot
Symptoms: Trouble moving, walking, or putting weight on it. Joint stiffness, warmth, or swelling. More pain and swelling after you rest, such as sitting or sleeping. Loss of range of motion. Achy, even during rest.
Diagnosis: X-ray to determine bone health and alignment
Treatment: warmth, joint supplements, and supportive shoes
Supplements for Joint Health
Osteo Bi-Flex, Fish Oil, MSM, Glucosamine Chondroitin; some with calcium
Plantar Fascia
Inelastic band of connective tissue supporting the medial longitudinal arch
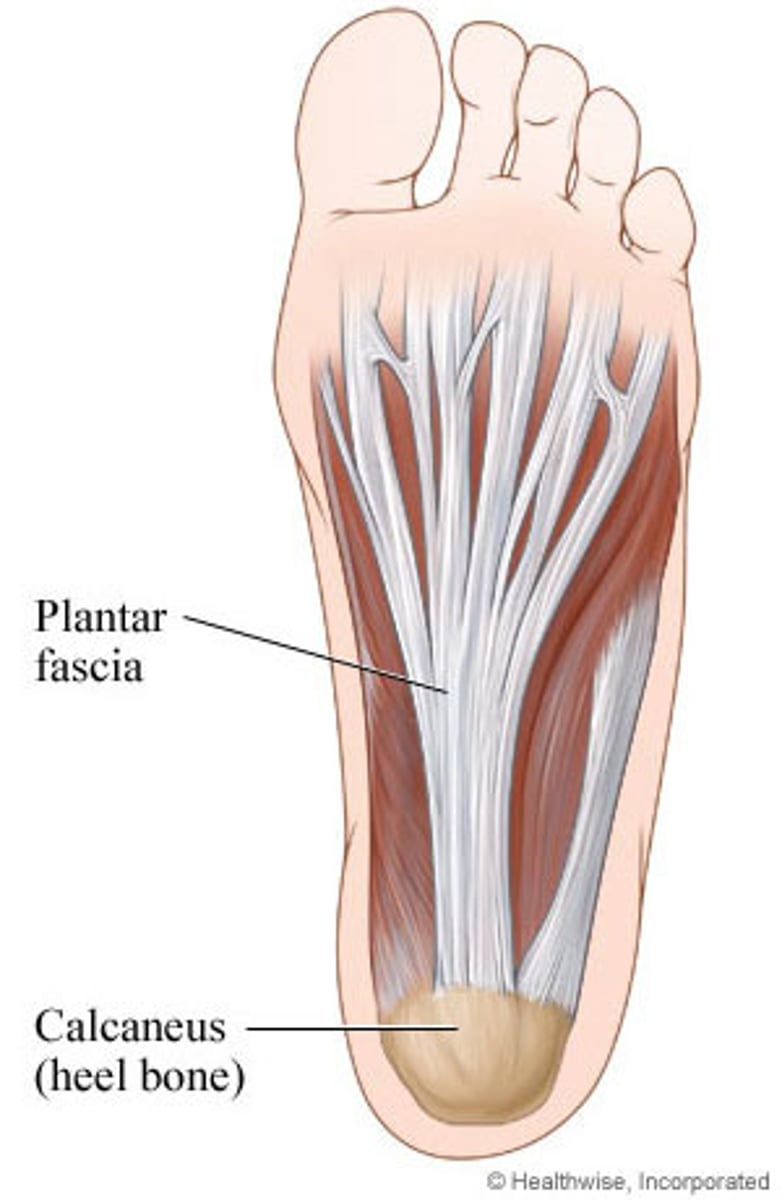
Plantar Fasciitis
Pain/inflammation under the calcaneus; worsens in the morning and with dorsiflexion
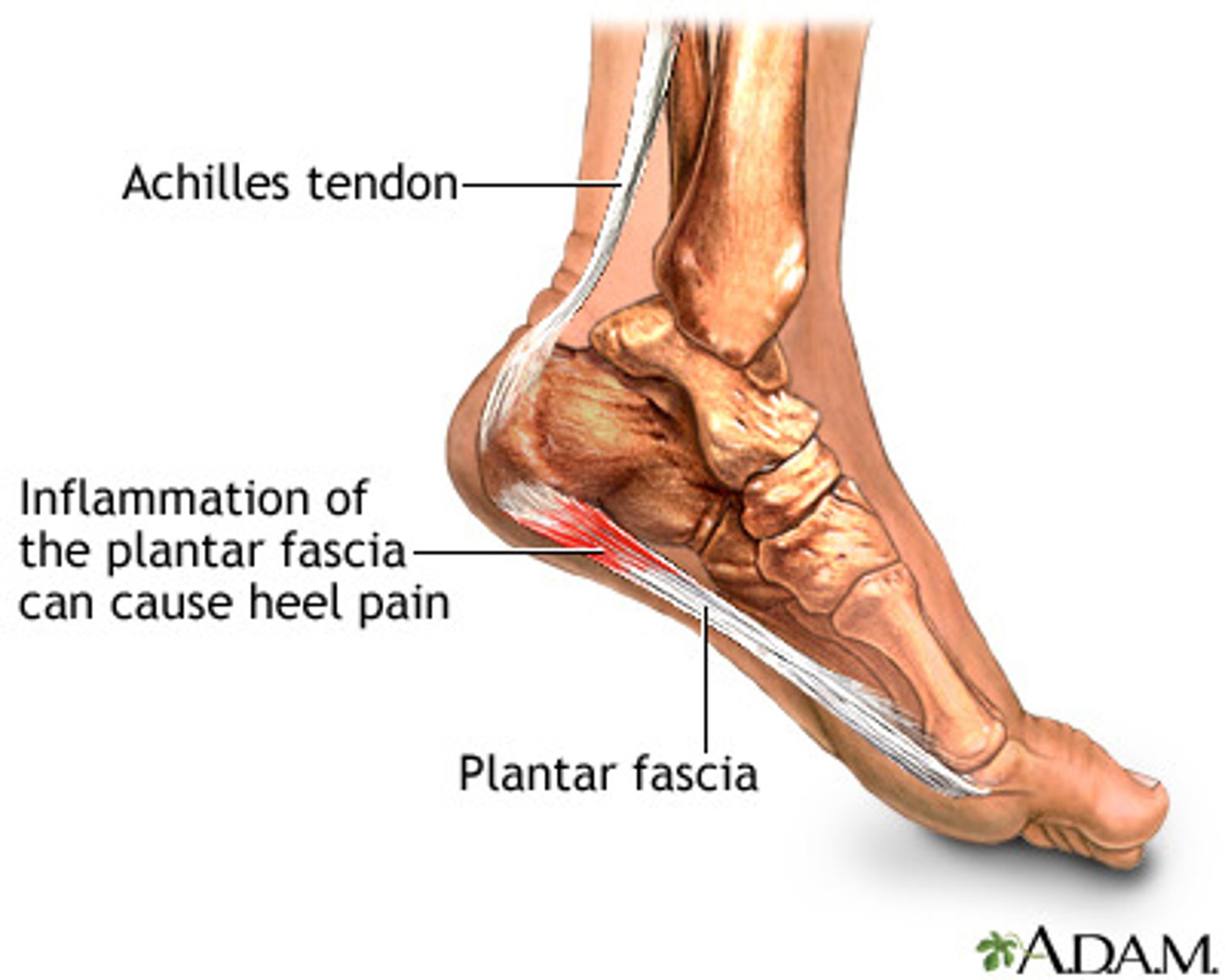
Causes, treatment, and prevention of Plantar Fasciitis
Causes of Plantar Fasciitis
• Hard floors
• Cold temperatures
• Unsupportive footwear/badly-fitted pointe shoes
• Tying pointe shoe ribbons too tightly
• Tight lower leg muscles
• Not warming up fully
• Too much pronation/supination of the foot
• Overuse
Treatment of Plantar Fasciitis
• Rest
• Stretch calves (gastrocnemius and soleus)
• Hanging your heels off the back of a stair
• Downward dog
• Stretching the peroneal muscles of the lower lateral leg
• Massage
• Ice
Prevention of Plantar Fasciitis
• Only dancing on hard floors when necessary
• Take time to warm up the entire body properly, but also focusing on warming up the ankles/feet
• If you don’t like your pointe shoes, get fitted again
• Loosen your pointe shoe ribbons or buy elastic ribbons
• Retrain any bad habits from the hip down
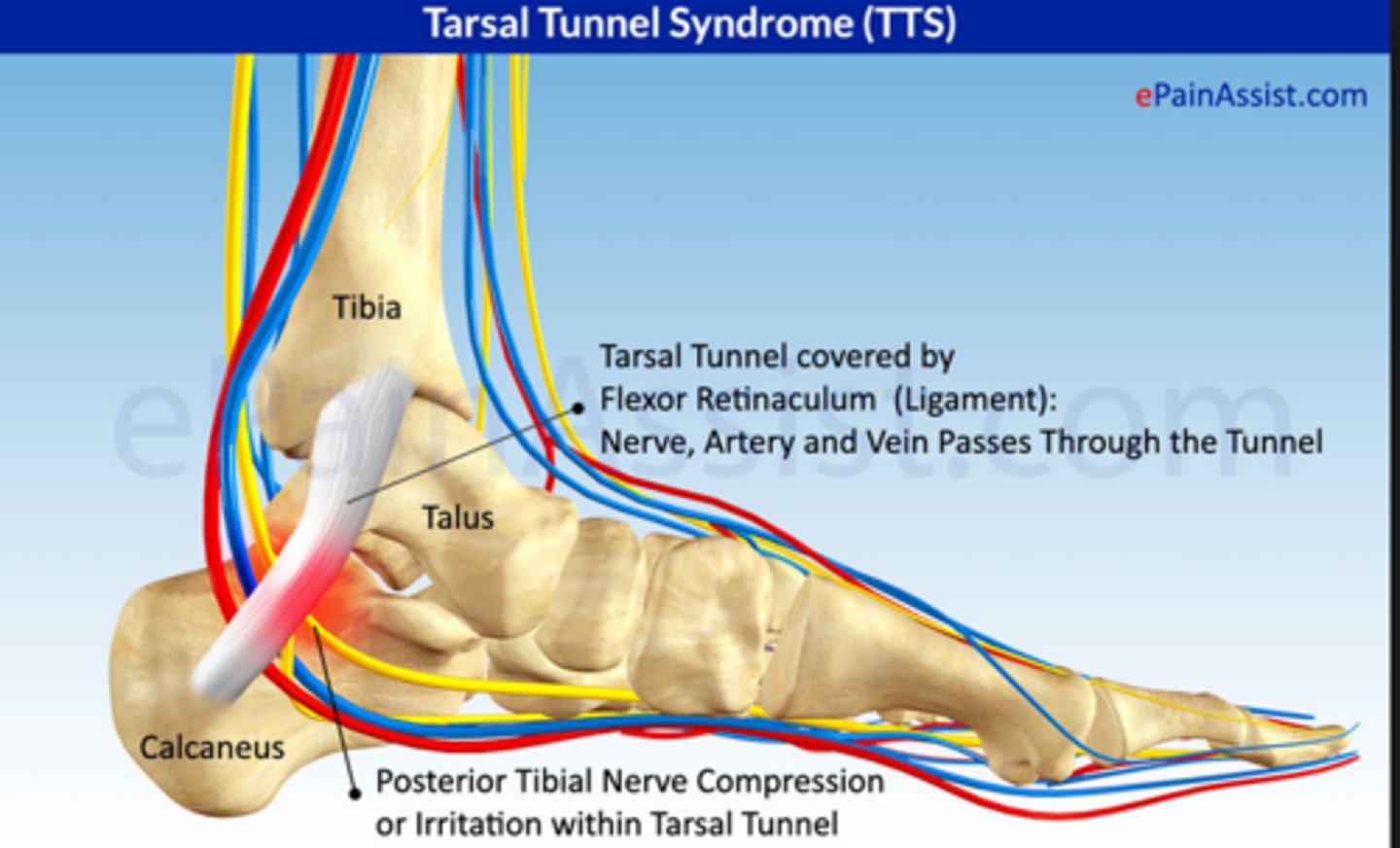
Tarsal Tunnel Syndrome
Ankle pain due to compressed tibial nerve;
Symptoms: burning pain at the sole of the foot that worsens with standing for long periods; numbness/tingling sensation at the base of the foot
Treatment: RICE, wearing orthotics in shoes, steroid shots to reduce inflammation
Signs for Pointe Work
Indications of readiness including age, training, stability, engagement, and maturity
Growth Plates
Tissue at the end of long bones determining future bone length and shape; weaker and vulnerable to injury in children and teens
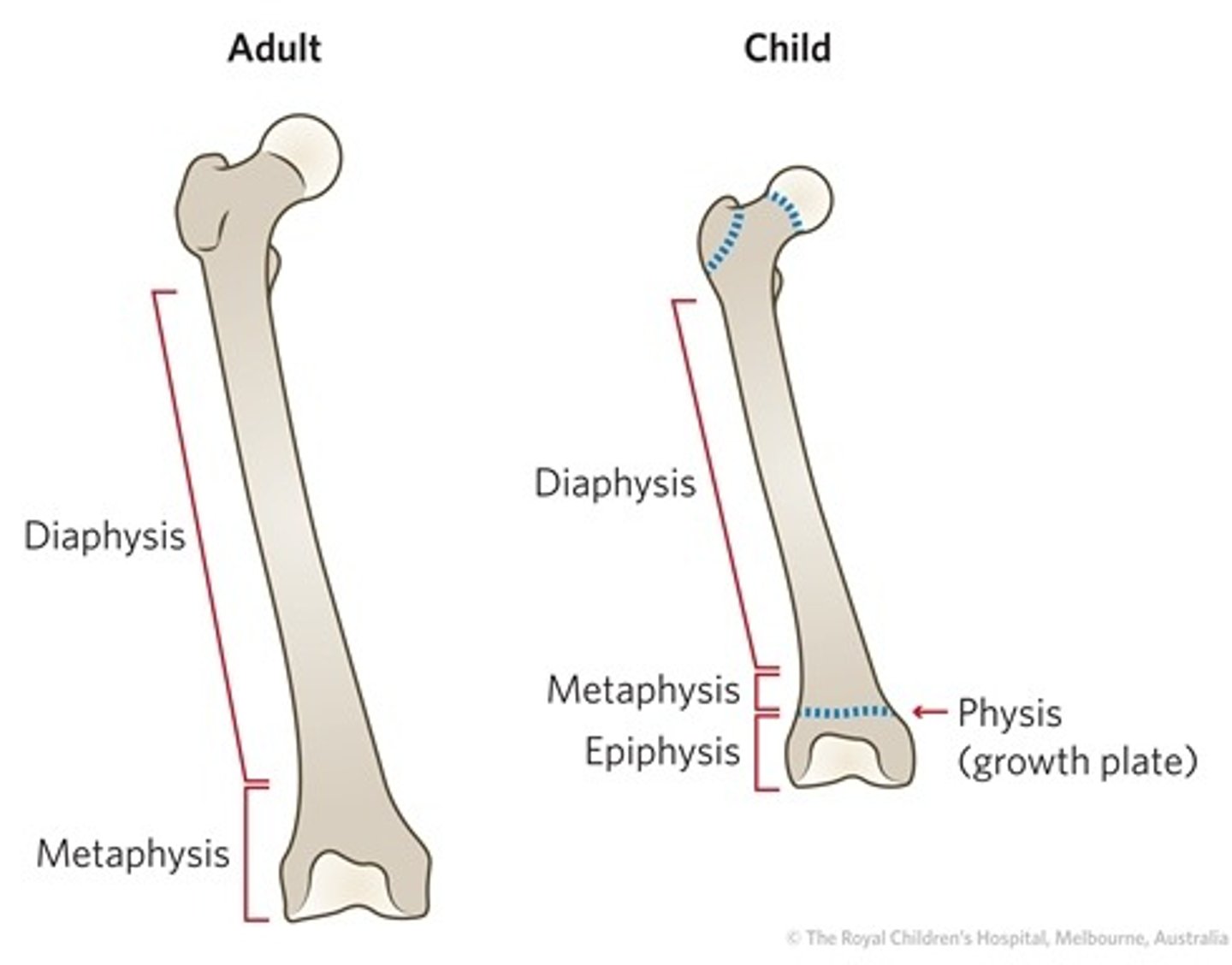
Growth Plate Injuries
• Persistent pain and tenderness after a sudden or overuse injury
• Change in shape
• Warmth and/or swelling at the end of the bone
• Changes mechanics of the limb
• Inability to move, put pressure on, or bear weight because of pain
Extrinsic Muscles
Muscles crossing the ankle joint
Intrinsic Muscles
Muscles not crossing the ankle joint
Hallucis
Indicates 'big toe'
Digitorum
Indicates the smaller four toes
Extensors of the Foot (location)
Located anteriorly (top of foot)
Flexors of the Foot (location)
Located posteriorly (bottom of foot)
Talocrural Joint
Anatomical term for 'ankle joint'
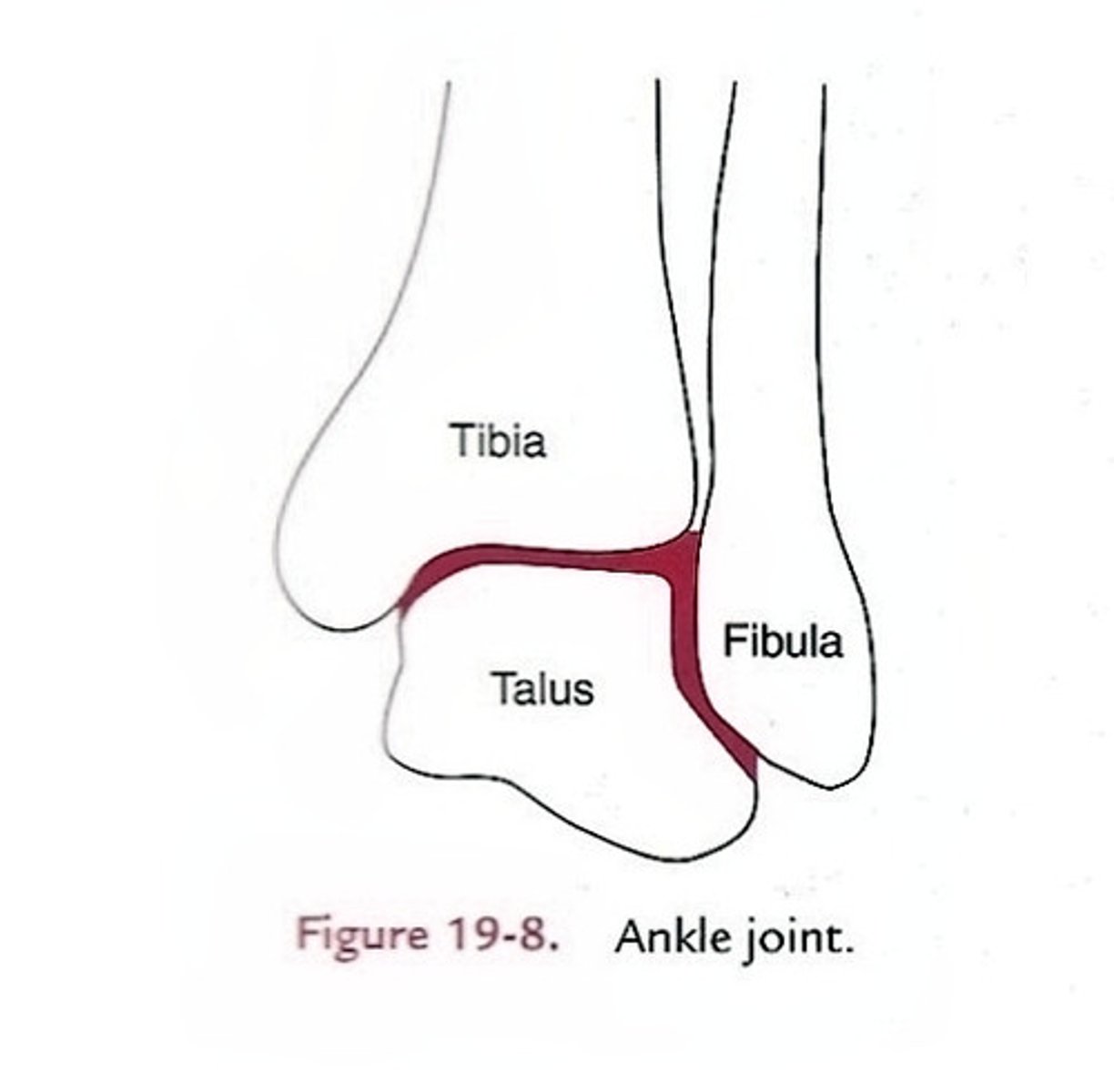
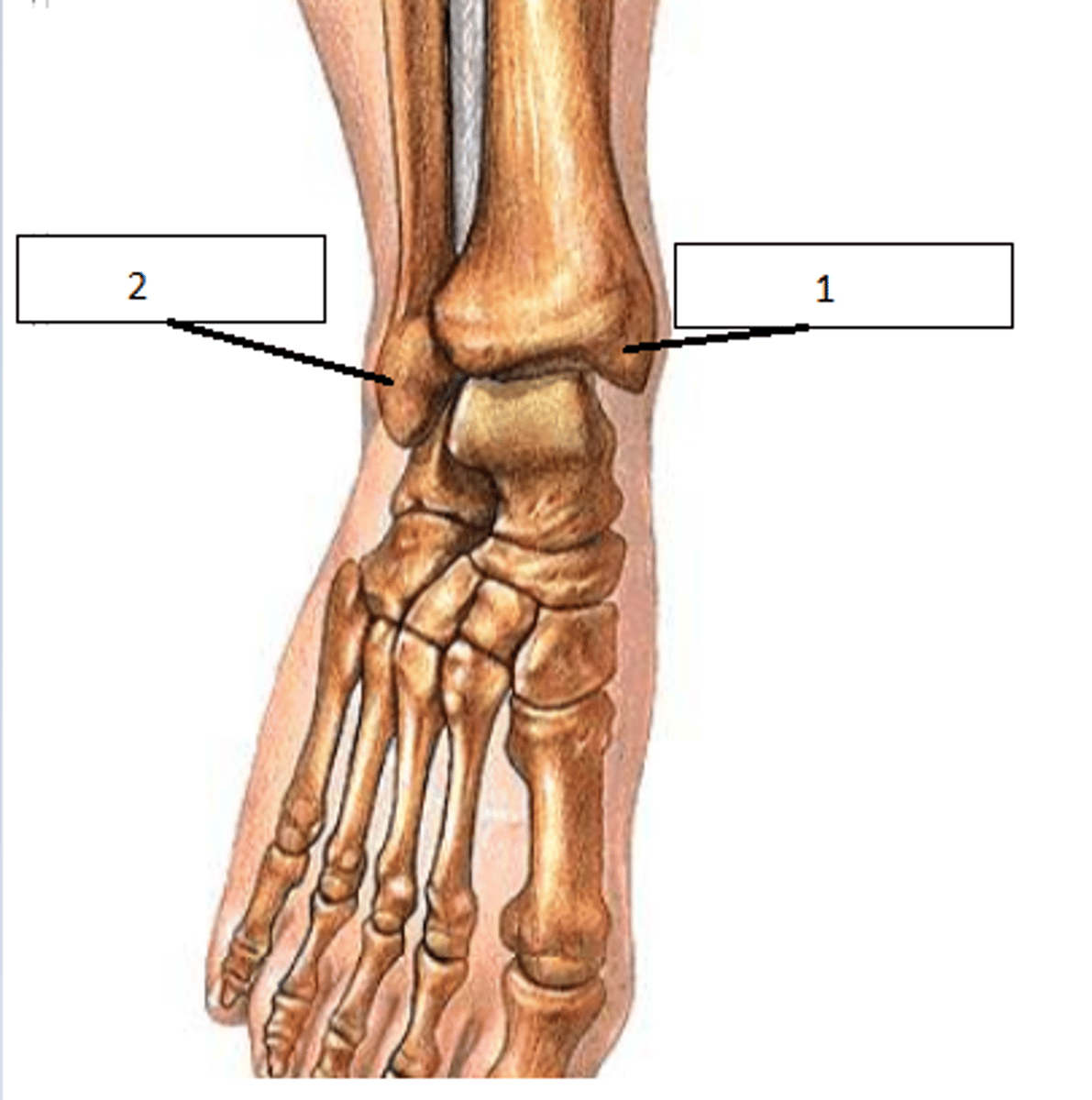
Medial (1) and Lateral (2) Malleolus
Anatomical term for 'inside and outside ankle bone'