Chapter 2: Synapses
1/13
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Vocabulary flashcards covering key terms related to synapses and neuronal signaling.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
14 Terms
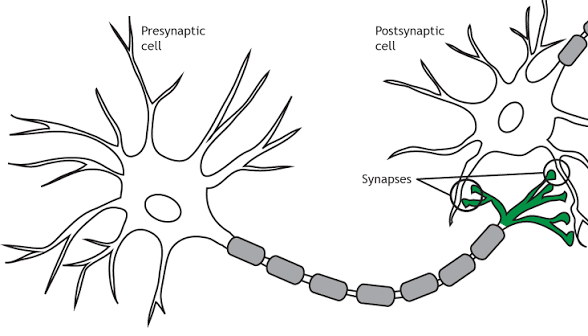
synapse
The point of communication between two neurons.
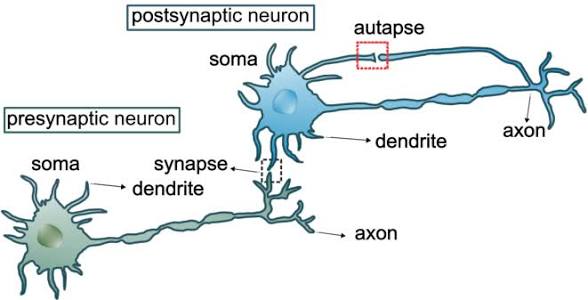
presynaptic neuron
The neuron that sends the signal across a synapse.
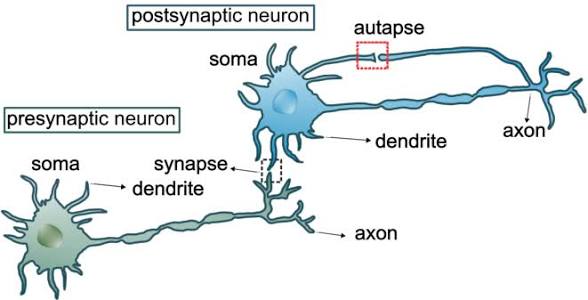
postsynaptic neuron
The neuron that receives the signal at a synapse.
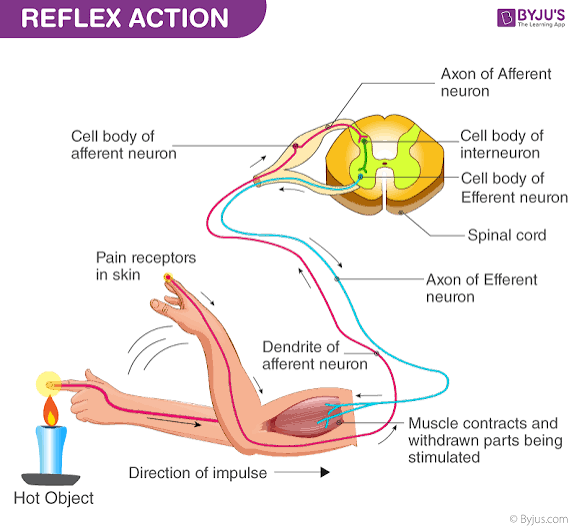
reflex arc
The neural pathway that mediates a reflex; transmission along a reflex arc is slower than along an equivalent length of axon due to synaptic delay.
reflexes
Automatic, involuntary responses to sensory stimuli mediated by neural circuits.
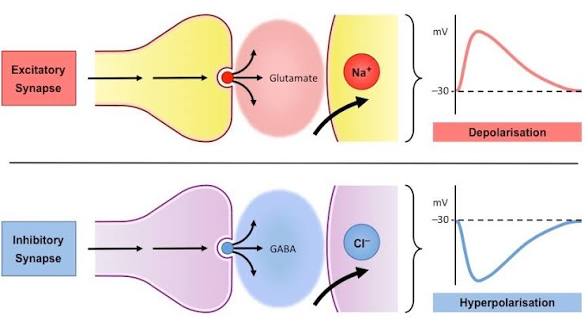
EPSP
Excitatory postsynaptic potential; a brief depolarizing graded potential produced when sodium (Na+) enters the postsynaptic neuron.
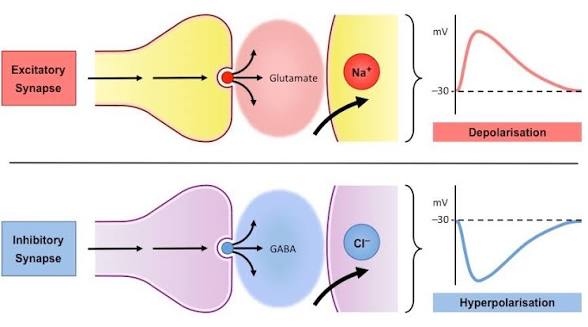
IPSP
Inhibitory postsynaptic potential; a brief hyperpolarizing graded potential produced when potassium (K+) leaves or chloride (Cl−) enters the postsynaptic neuron.
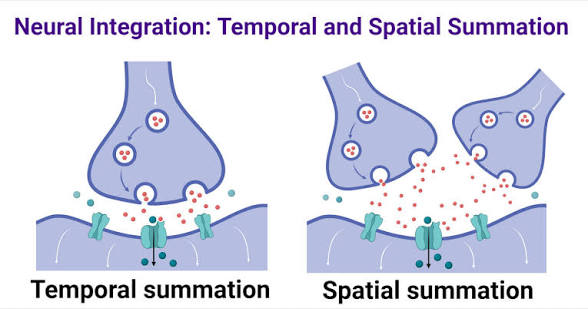
temporal summation
combines multiple signals over time, occurring when a single neuron fires repeatedly in rapid succession
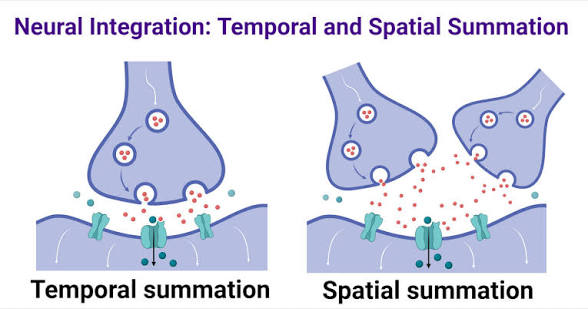
spatial summation
The summation of graded potentials arriving from different locations on the neuron.
inhibition
An active brake that suppresses excitation; as important as excitation for proper nervous system function.
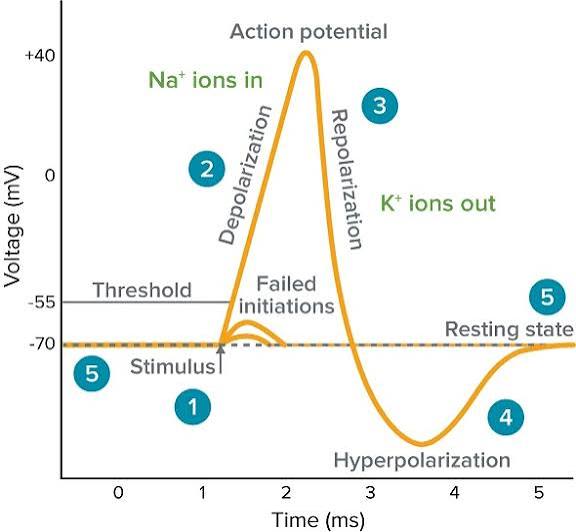
depolarization
A decrease in membrane negativity (less negative), often due to Na+ entry during an EPSP.
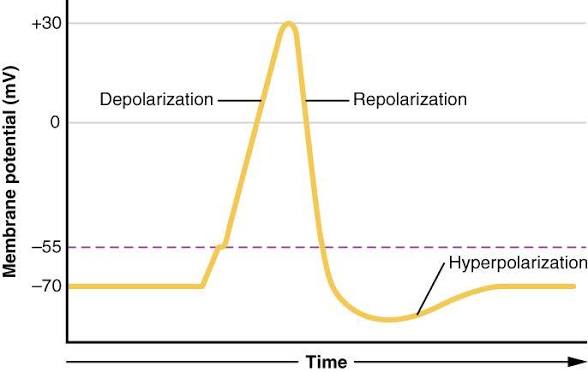
hyperpolarization
An increase in membrane negativity (more negative), often due to K+ leaving or Cl− entering during an IPSP.
graded potential
A brief, local change in membrane potential that can summate to influence whether an action potential fires.
spontaneous firing rate
The baseline firing rate of a neuron in the absence of stimulation.