Chapter 15: Genes and How They Work
1/37
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
38 Terms
Transcription
The genetic sequence is copied from DNA to mRNA
Translation
mRNA travels out the nucleus to a ribosome to become a protein
mRNA (messenger)
The RNA that copies DNA and brings it to rRNA for protein synthesis
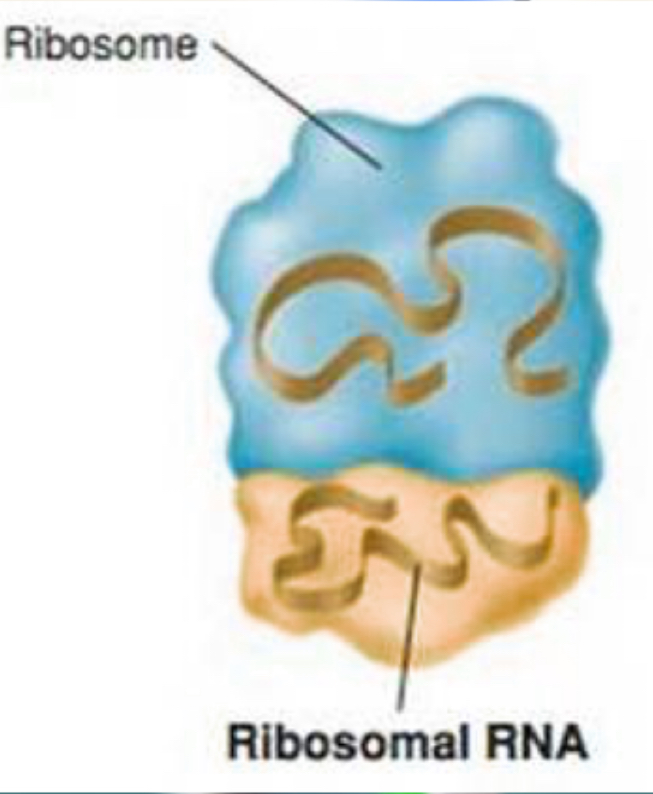
rRNA
Type of RNA that makes up ribosomes, helps catalyze the formation of peptide bonds
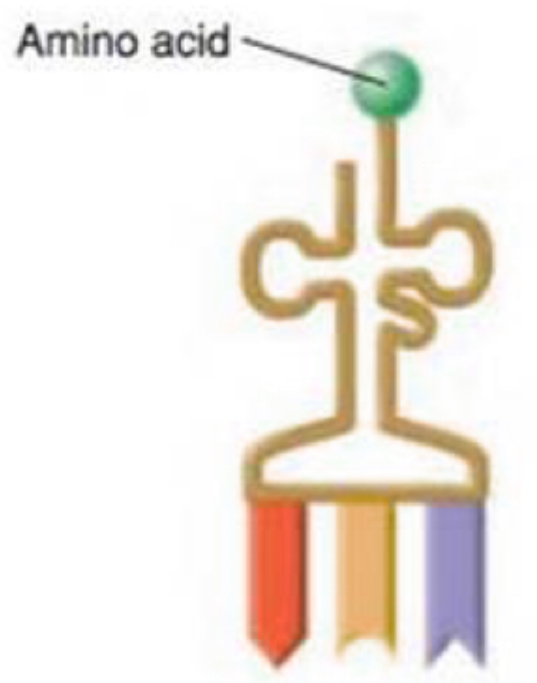

tRNA
A type of RNA that carries specific amino acids to the ribosomes and matches them to codons on mRNA
Exon
A segment of a gene that codes for protein
Intron
A segment of a gene that doesn’t code
Poly A Cap
A chain of adenine nucleotides added to the 3’ end of mRNA
One Gene One Enzyme Hypothesis
Each gene directs the synthesis of a single enzyme
Archibald Garrod
First to suggest genes dictate phenotypes through enzymes that catalyze specific reactions in cells; coined the term “inborn errors of metabolism”
Alkaptonuria
Lack of enzymes to break down the acid alkapton; causes black urine, acne, tendonitis, kidney stones, and hunchback
George Beadle and Edward Tatum
Showed that genes specify enzymes
The Central Dogma (Crick)
The fundamental flow of genetic information in living cells: DNA→RNA→Protein
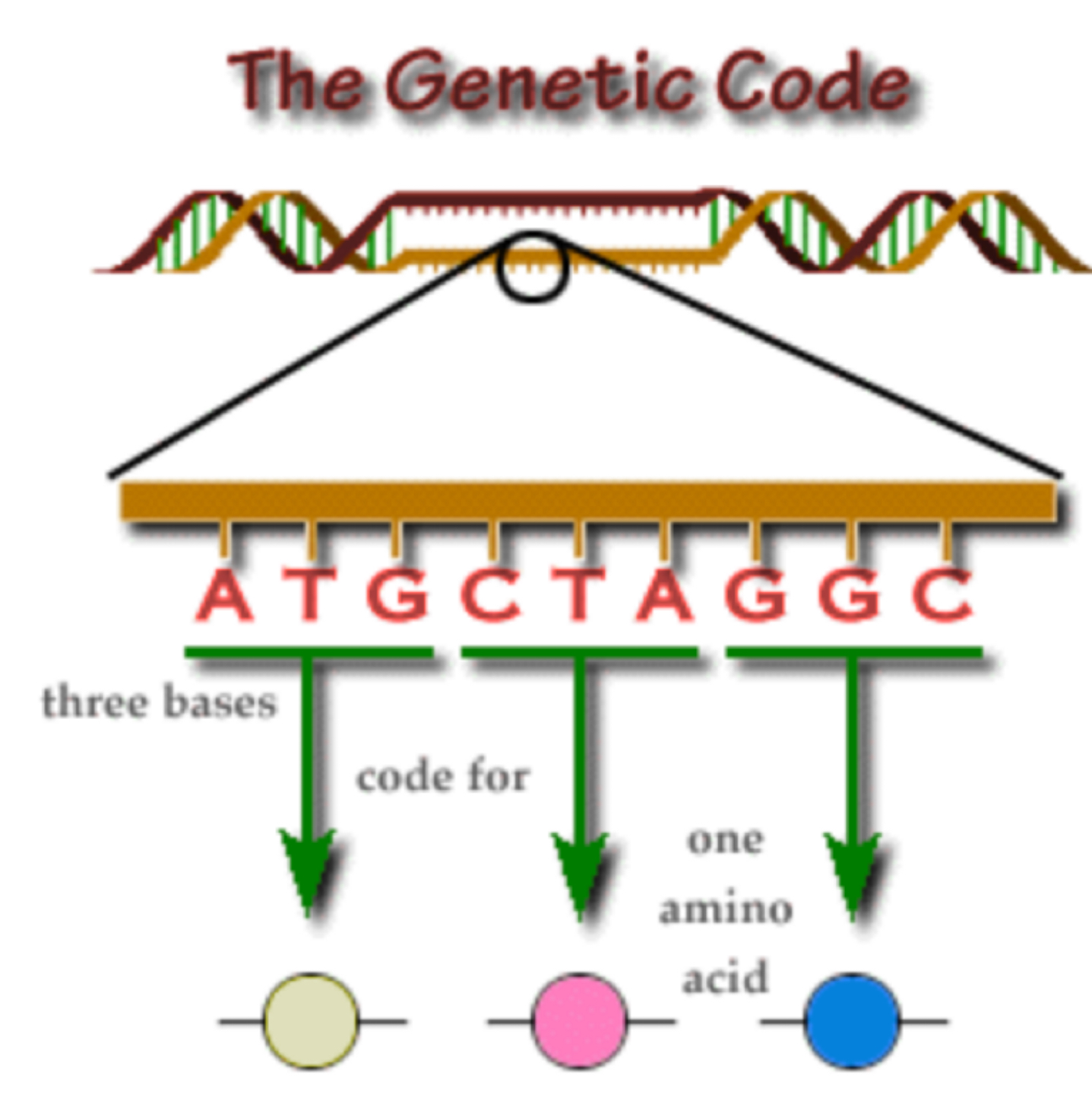
The Genetic Code (Crick and Brenner)
Three bases(one codon) code for one amino acid
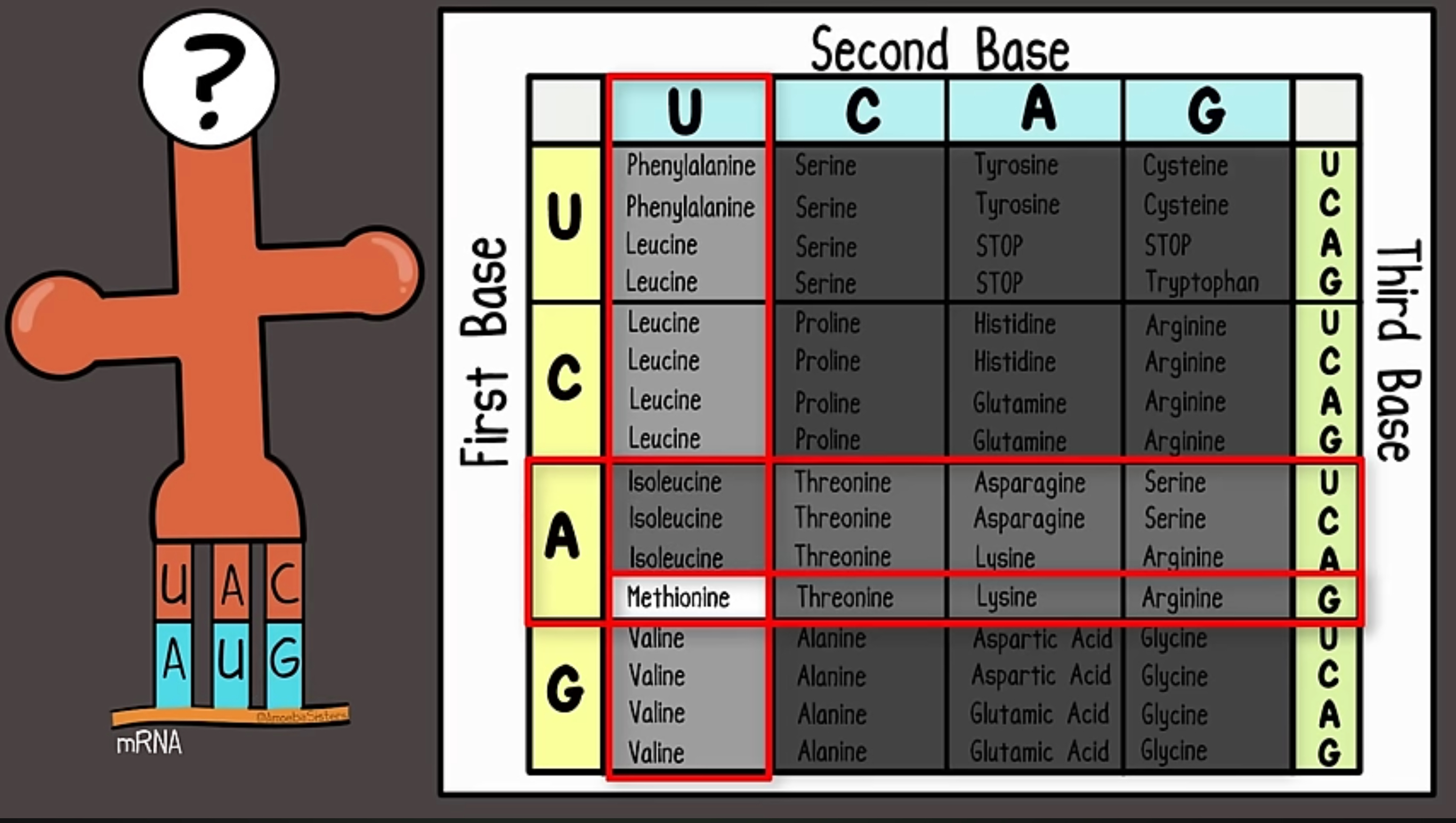
The Codon Table (Nirenberg and Khorana)
Read using the 3 bases on the mRNA(right to left): first base on the left, second base on the top, third base on the right
Nucleotide Bases in RNA
Adenine=Uracil, Guanine=Cytosine
The Steps of Both Transcription and Translation
Initiation, Elongation, and Termination
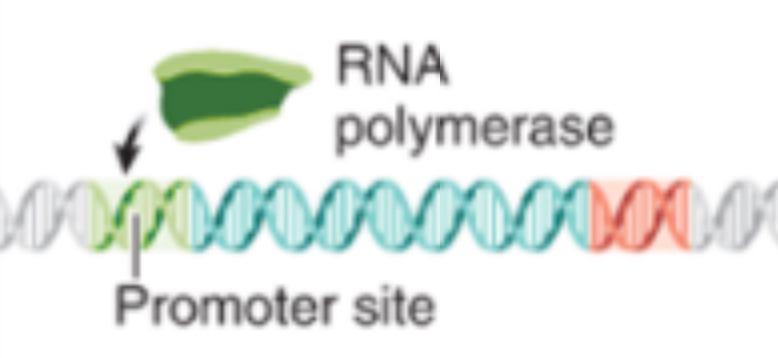
Recognition
RNA polymerase recognizes a promoter sequence in DNA, binds to the strand, and begins reading the gene’s message
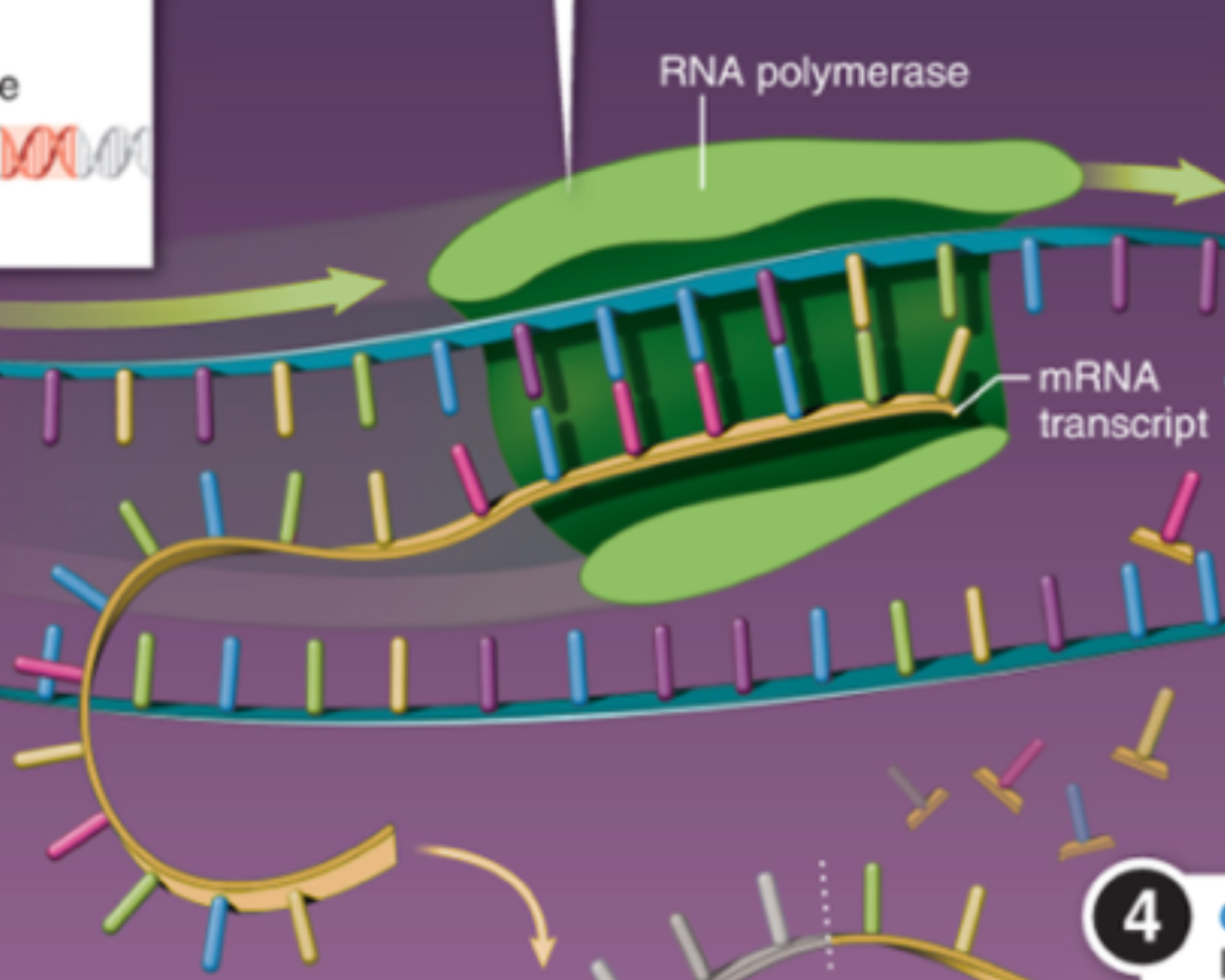
Transcription Process (makes mRNA)
As a DNA strand (3’→5’) passes through RNA polymerase, the RNA polymerase builds a single-stranded RNA copy of the gene (mRNA)
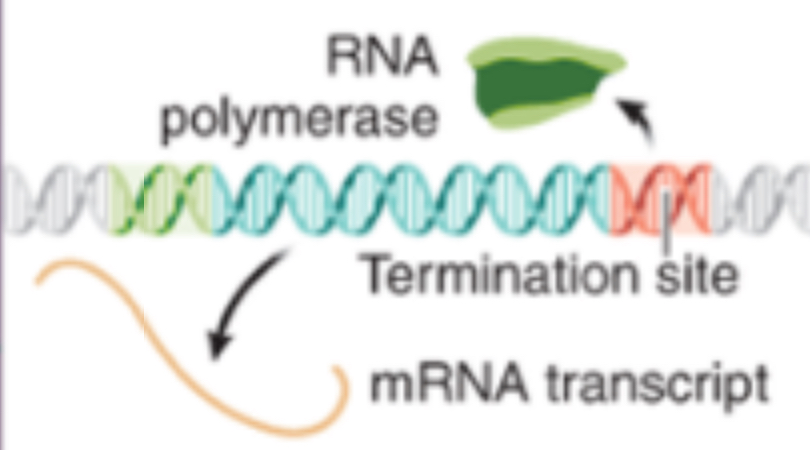
Termination of Transcription
The RNA polymerase will encounter a code signaling the end of the gene, releasing the mRNA transcript
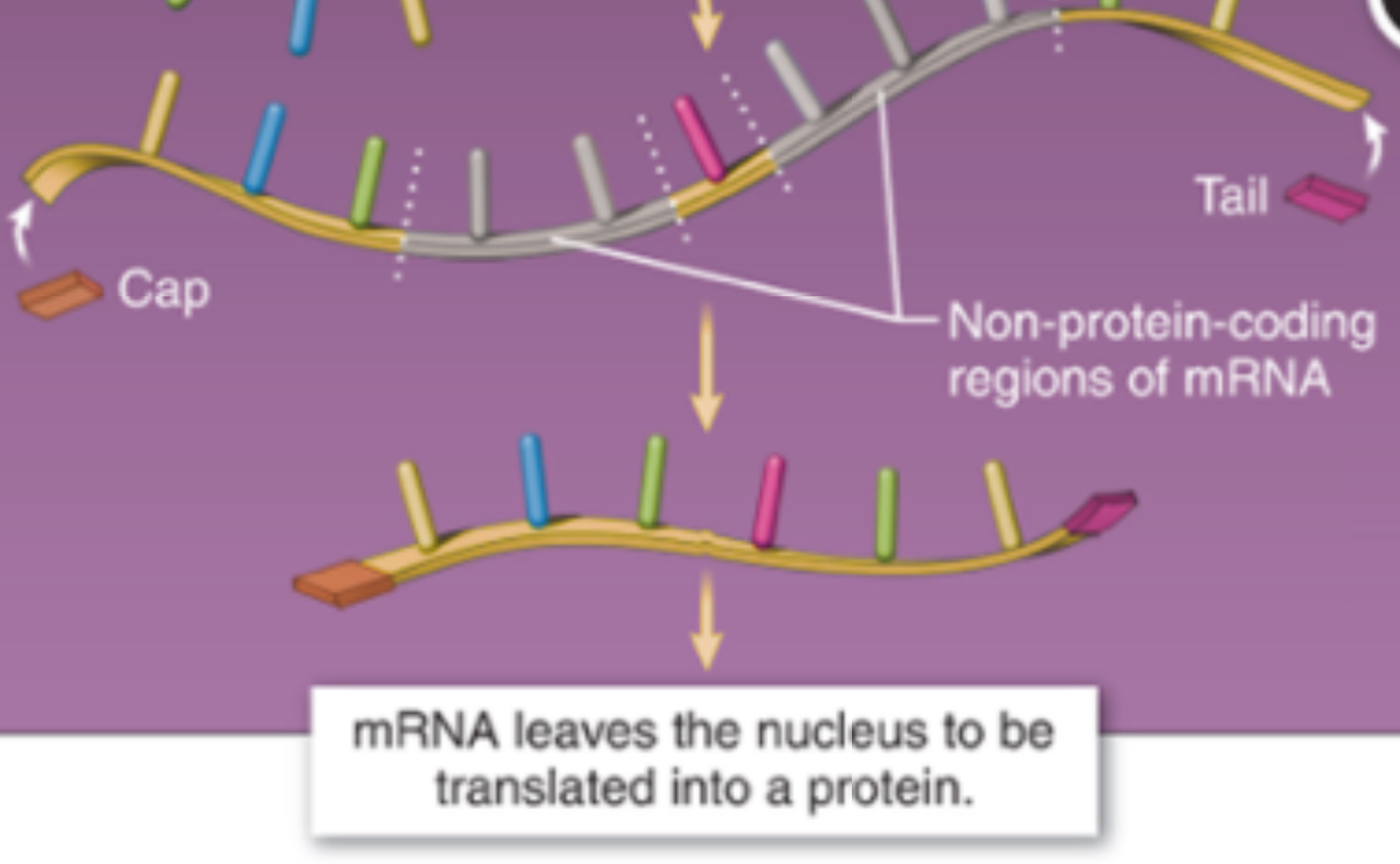
Capped and Processed mRNA
mRNA receives a cap and tail after transcription, for protection, recognition, and noncoding sections are removed
Transcription Occurs In
The Nucleus
Promotor Sequence in DNA
TATA Box
Spliceosome
Enzyme that does the editing of the mRNA after transcription
Translation Occurs In
The cytoplasm (in a ribosome)
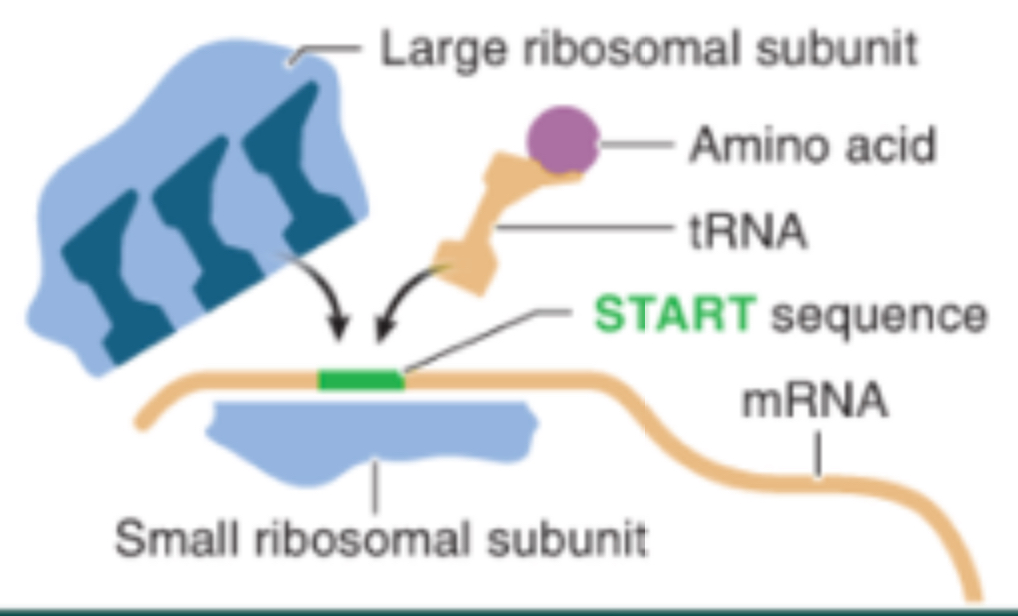
Initiation in Translation
The “START” sequence AUG in mRNA is recognized by a corresponding tRNA molecule and two ribosomal subunits
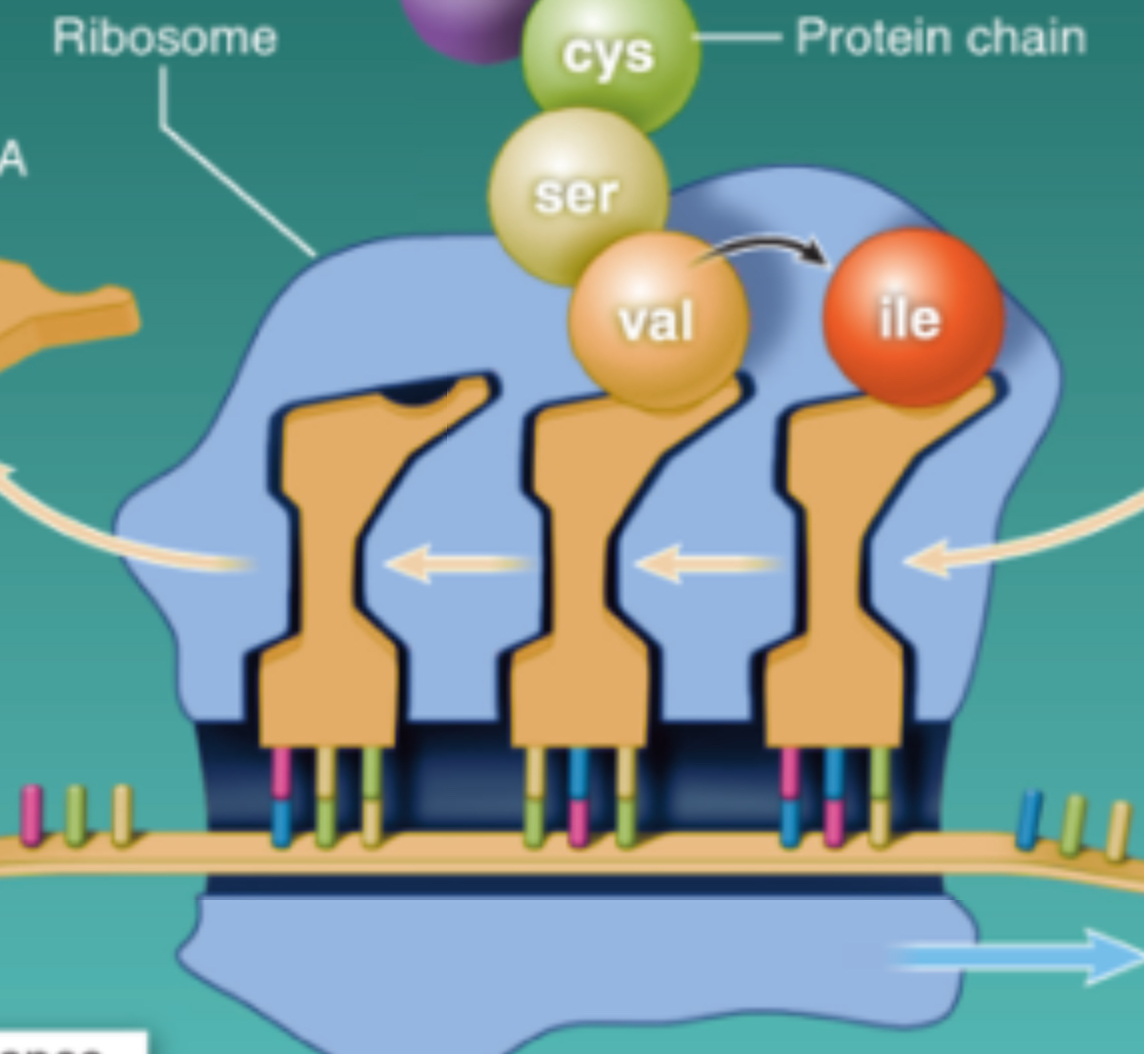
Elongation in Translation (makes protein)
As the ribosome moves along the mRNA, amino-acid carring tRNA molecules bind to the next three bases on mRNA, and the tRNA detaches once the corresponding bases are added
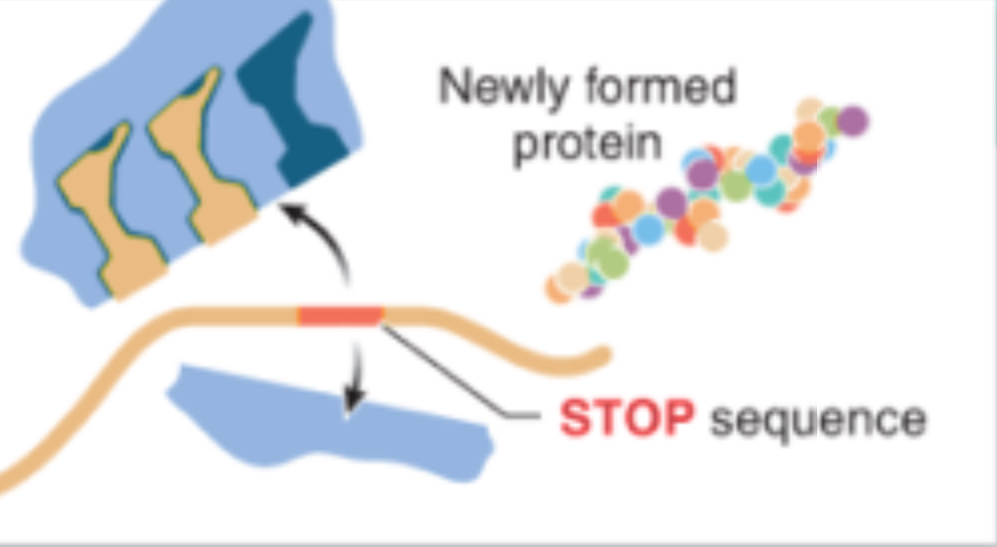
Termination in Translation
The ribosome encounters a “STOP” sequence which means the protein assembly is complete, mRNA and protein are released
RNA Start Codon
AUG
RNA Stop Codons
UAG, UAA, UGA
E Site (rRNA)
Where the empty tRNA EXITS
P Site (rRNA)
Holds the tRNA with the growing POLYPEPTIDE chain
A Site (rRNA)
Where tRNA carrying an animo acid ARRIVES
Triplet
A group of 3 DNA nucleotide bases that corresponds to one amino acid
Missense Mutation
A base is changed to another, coding for a different amino acid
Silent Mutation
A base is changed, but it codes for the same amino acid
Frameshift Mutation
A nucleotide is inserted or deleted, which causes a shift in the reading frame
Nonsense mutation
A change in bases that creates a premature stop codon (UAA, UAG, UGA