Geography Y9
5.0(6)
Card Sorting
1/60
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 4:55 AM on 11/14/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
61 Terms
1
New cards
lithosphere
solid part of the earth’s crust, consisting of rocks and soil
2
New cards
hydrosphere
water bodies, including lakes, rivers, streams, oceans, ground water, and ice caps
3
New cards
atmosphere
layers of gas surrounding the Earth
4
New cards
biosphere
realm of living things, plants and animals
5
New cards
structure
what makes up an ecosystem, the function
6
New cards
dynamics
energy flow through system
7
New cards
ecosystem
self-sustaining system of living organisms which interact with each other and the non-living components of the environment
8
New cards
biotic factors
living components of an ecosystem
9
New cards
abiotic factors
non-living components such as air, soil, and rocks
10
New cards
autotrophs
self-feeding
11
New cards
heterotrophs
consumers
12
New cards
saprotrophs
decomposes
13
New cards
components of an ecosystem
Biotic components:
* autotrophs
* heterotrophs
* saprotrophs
abiotic:
* air, water, wind, soil, rocks, etc.
* autotrophs
* heterotrophs
* saprotrophs
abiotic:
* air, water, wind, soil, rocks, etc.
14
New cards
how do components interact?
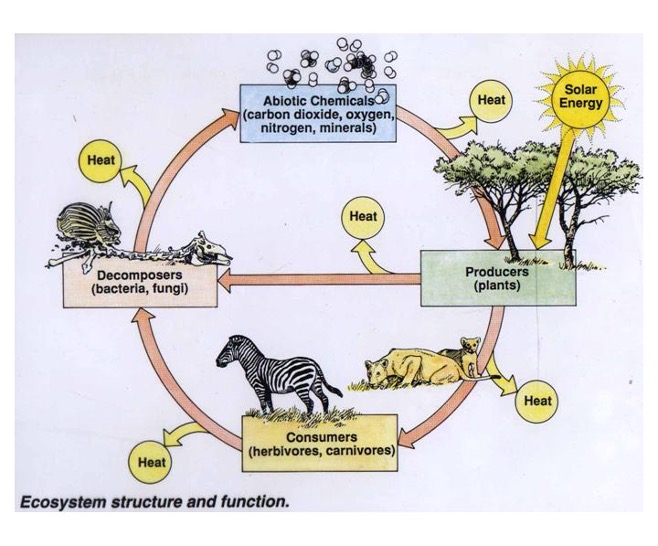
15
New cards
how do the 4 spheres interact?
energy (heat) + materials → flow through the atmosphere, lithosphere, and hydrosphere → supports the biosphere by creating the perfect conditions for life
16
New cards
aquatic
in water
17
New cards
terrestrial
on land
18
New cards
ecological balance
a state of dynamic equilibrium within a community of organisms in which genetic, species and ecosystem diversity remain relatively stable, subject to gradual changes through natural succession
19
New cards
how is ecological balance maintained?
Water cycle \n Gaseous cycle
Food chains of the ecosystem \n Environmental balance is maintained in the following ways:
* Through continuous operation of various natural cycles such as the water cycle, carbon cycle, oxygen cycle and nitrogen cycle.
* It is also maintained due to the existence of various food chains in the ecosystem. For example, if the population of pests such as grasshoppers isn't controlled by frogs or lizards that prey on them, pests start to manifest rapidly and destroy all crops, breaking the balance of the environment.
Food chains of the ecosystem \n Environmental balance is maintained in the following ways:
* Through continuous operation of various natural cycles such as the water cycle, carbon cycle, oxygen cycle and nitrogen cycle.
* It is also maintained due to the existence of various food chains in the ecosystem. For example, if the population of pests such as grasshoppers isn't controlled by frogs or lizards that prey on them, pests start to manifest rapidly and destroy all crops, breaking the balance of the environment.
20
New cards
biome
A biome is a biogeographical unit consisting of a biological community that has formed in response to the physical environment in which they are found and a shared regional climate.
21
New cards
biome vs. ecosystem
* biomes are bigger
* biomes are characterised by dominant vegetation while ecosystem is by interaction of different species
* biomes are characterised by dominant vegetation while ecosystem is by interaction of different species
22
New cards
tundra (15)
* north of the equator
* low temperatures
* high wind
* permafrost
* 150 - 250 ml of rain a year
* 18 to -40 degrees
* scarce vegetation
* animals have many adaptations to climate
* mainly mamals
* birds are migratory
* little insects
* hibernation, thick pelts, large body mass
* soil frozen due to permafrost
* low nutrients
* example - Russia
* low temperatures
* high wind
* permafrost
* 150 - 250 ml of rain a year
* 18 to -40 degrees
* scarce vegetation
* animals have many adaptations to climate
* mainly mamals
* birds are migratory
* little insects
* hibernation, thick pelts, large body mass
* soil frozen due to permafrost
* low nutrients
* example - Russia
23
New cards
tropical forest (11)
* dominant vegetation trees
* tall trees form canopy
* despite high sun and wind
* lower level forest has smaller trees and moss
* around equator
* example amazon
* 21 - 30 degrees, can get higher
* 750 - 1500 ml of rain a year
* soils are infertile due to frequent rain leaching nutrients deeper
* decomposing plants are used as nutrients
* many animals due to large amounts of flora
* primary adaptation is camouflage
* tall trees form canopy
* despite high sun and wind
* lower level forest has smaller trees and moss
* around equator
* example amazon
* 21 - 30 degrees, can get higher
* 750 - 1500 ml of rain a year
* soils are infertile due to frequent rain leaching nutrients deeper
* decomposing plants are used as nutrients
* many animals due to large amounts of flora
* primary adaptation is camouflage
24
New cards
temperate forest (12)
* 4 seasons
* 30 to - 30 degrees
* 10 degrees average
* continous canopy of broad leaved trees
* such as oak, maple, chestnut
* high biodiversity
* 750 - 1500 ml of rain a year
* shallow with hard rock near the surface
* small plants on the floor
* grow in spring
* thick bark on trees to survive winter
* example: pacific temperate forests
* 30 to - 30 degrees
* 10 degrees average
* continous canopy of broad leaved trees
* such as oak, maple, chestnut
* high biodiversity
* 750 - 1500 ml of rain a year
* shallow with hard rock near the surface
* small plants on the floor
* grow in spring
* thick bark on trees to survive winter
* example: pacific temperate forests
25
New cards
savannah grasslands
* Animals including elephants, giraffes, lions and cheetahs make their homes in the savanna
* . Due to its open environment, camouflage and mimicry are essential for animal survival in the savanna.
* Savannas have extreme wet seasons and dry seasons.
* Due to this lack of precipitation, it is very difficult for large plants like trees to grow in savannas.
* While savannas are located on six of the seven continents, the largest are found in equatorial Africa.
* key vegetation is small shrubs and trees
* . Due to its open environment, camouflage and mimicry are essential for animal survival in the savanna.
* Savannas have extreme wet seasons and dry seasons.
* Due to this lack of precipitation, it is very difficult for large plants like trees to grow in savannas.
* While savannas are located on six of the seven continents, the largest are found in equatorial Africa.
* key vegetation is small shrubs and trees
26
New cards
temperate grasslands
* 500 to 900 millimeters
* generally open and continuous, fairly flat areas of grass
* The height of grass correlates with the amount of rainfall it receives
* average temperatures are about -20°C to 30°C
* Temperate grasslands have cold winters and warm summers with some rain
* The grasses die back to their roots annually and the soil and the sod protect the roots and the new buds from the cold of winter or dry conditions.
* A few trees may be found in this biome along the streams, but not many due to the lack of rainfall.
* generally open and continuous, fairly flat areas of grass
* The height of grass correlates with the amount of rainfall it receives
* average temperatures are about -20°C to 30°C
* Temperate grasslands have cold winters and warm summers with some rain
* The grasses die back to their roots annually and the soil and the sod protect the roots and the new buds from the cold of winter or dry conditions.
* A few trees may be found in this biome along the streams, but not many due to the lack of rainfall.
27
New cards
desert
* a layer of soil that can either be sandy, gravelly, or stony
* at most 50 centimeters (20 inches) of rainfall a year
* organisms that live in deserts are adapted to this extremely dry climate.
* Plants in deserts have adaptations to conserve water.
* at most 50 centimeters (20 inches) of rainfall a year
* organisms that live in deserts are adapted to this extremely dry climate.
* Plants in deserts have adaptations to conserve water.
28
New cards
alpine
* ecosystem that doesn’t contain trees due to its high altitude.
* found in mountainous regions across the globe. Their elevation normally ranges between 10,000 feet (3,000 meters) and the area where a mountain’s snow line begins.
* only about 200 plant species, as their dynamic conditions are not favorable for plant growth
* characterized by cold and windy conditions, as well as harsh sunlight
* extreme temperatures and low humidity.
* high elevation and low precipitation
* temperatures can typically drop from warm to freezing within a day.
* 30 cm) of precipitation annually. Nevertheless, snow may remain on the ground for an extended period, thanks to the consistently low temperatures.
* The soil found in alpine biomes is usually nutrient-poor and acidic. It is mainly made up of rocks and minerals that have been broken down by bacteria. In the winter months, the soil freezes and becomes covered in a layer of frost.
* characterized by small groundcover plants
* \
* found in mountainous regions across the globe. Their elevation normally ranges between 10,000 feet (3,000 meters) and the area where a mountain’s snow line begins.
* only about 200 plant species, as their dynamic conditions are not favorable for plant growth
* characterized by cold and windy conditions, as well as harsh sunlight
* extreme temperatures and low humidity.
* high elevation and low precipitation
* temperatures can typically drop from warm to freezing within a day.
* 30 cm) of precipitation annually. Nevertheless, snow may remain on the ground for an extended period, thanks to the consistently low temperatures.
* The soil found in alpine biomes is usually nutrient-poor and acidic. It is mainly made up of rocks and minerals that have been broken down by bacteria. In the winter months, the soil freezes and becomes covered in a layer of frost.
* characterized by small groundcover plants
* \
29
New cards
spatial distribution
spatial distribution is the arrangement of a phenomenon across the Earth's surface
30
New cards
spatial distribution of biomes
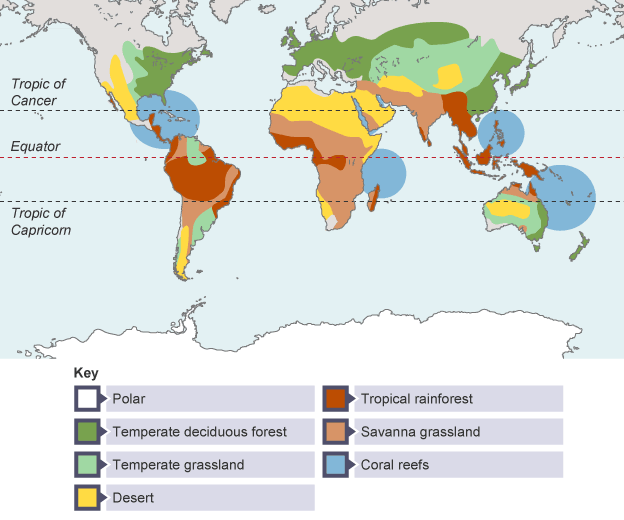
31
New cards
climate
Climate refers to the average weather conditions of a specific location over an extended period of time. A location’s climate consists of:
The temperature of an area.
The amount of precipitation of an area
32
New cards
biome
a biome is a large area/landmass with similar flora and fauna and a common climate.
33
New cards
weather
Weather refers to the short-term conditions of the atmosphere, i.e. the specific weather conditions being experienced at one moment in time
34
New cards
distribution of biomes
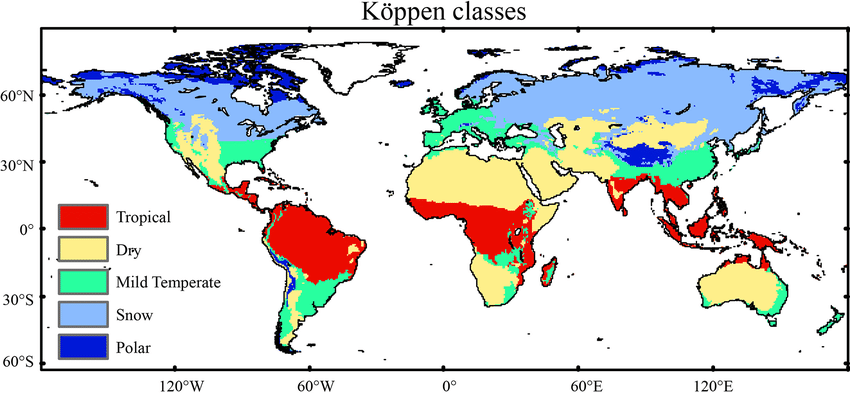
35
New cards
koppen system of classification
divides climates into five main climate groups, with each group being divided based on patterns of seasonal precipitation and temperature.
36
New cards
5 categories of biomes (according to KSC scheme 1)
A - tropical
B - arid
C - temperate
D - continental
E - polar
B - arid
C - temperate
D - continental
E - polar
37
New cards
subcategories according to KSC
each letter (apart from E) is assigned a subcategory based on precipitation and temperature
38
New cards
scheme 2 of KSC
w - dry winter
f - no dry season
s - dry summer (can apply to anything but polar)
f - no dry season
s - dry summer (can apply to anything but polar)
39
New cards
scheme 3 of KSC
h (Hot) (only dry)
k (Cold) (only dry)
a (Hot summer)
b (Warm summer)
c (Cold summer)
d (Very cold winter) (only temperate or continental)
\
T (Tundra) (only polar)
F (Ice cap) (only polar)
no TROPICAL
k (Cold) (only dry)
a (Hot summer)
b (Warm summer)
c (Cold summer)
d (Very cold winter) (only temperate or continental)
\
T (Tundra) (only polar)
F (Ice cap) (only polar)
no TROPICAL
40
New cards
climate graph
* displays yearly temperature and precipitation statistics for a particular location
* Temperature (C) is measured using the numbers on the left hand side of the chart.
* The average temperature for each month is plotted on the graph with a red dot and the dots are then connected in a smooth, red line.
* precipitation is shown as a bar graph with the amount of precipitation each month
* precipitation - blue
* temperature - red
* x axis is time over a year
* y axis is number / amount
* Temperature (C) is measured using the numbers on the left hand side of the chart.
* The average temperature for each month is plotted on the graph with a red dot and the dots are then connected in a smooth, red line.
* precipitation is shown as a bar graph with the amount of precipitation each month
* precipitation - blue
* temperature - red
* x axis is time over a year
* y axis is number / amount
41
New cards
climate graph purpose
to illustrate the average temperature and rainfall experienced at a particular place over the course of a year.
42
New cards
example of a climate graph
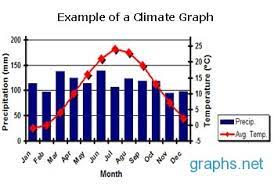
43
New cards
6 factors that influence climate
L - latitude
A - altitude
P - prevailing winds
D - distance from sea
O - ocean currents
G - geographic barriers
A - altitude
P - prevailing winds
D - distance from sea
O - ocean currents
G - geographic barriers
44
New cards
acronym for things that influence climate
LAPDOG
45
New cards
Latitude
* measure of distance of equator
* degrees north or south of equator
* latitude does not necessarily impact climate but determines it
* closer to equator, warmer climate
* further from equator, colder climate
* this is because of the solar energy from the sun, equator is closer therefore it gets more sunlight, polar regions are colder as it receives less energy
* this is caused by the different angles at which the suns rays hit the earth
* affects temperature more
* degrees north or south of equator
* latitude does not necessarily impact climate but determines it
* closer to equator, warmer climate
* further from equator, colder climate
* this is because of the solar energy from the sun, equator is closer therefore it gets more sunlight, polar regions are colder as it receives less energy
* this is caused by the different angles at which the suns rays hit the earth
* affects temperature more
46
New cards
altitude
* measure of height above sea level
* the higher above, the lower the temperature
* this is because of decreased air pressure, which means particles are further apart, and because of that heat energy is lost
* 1000 metres above sea level - falls 6.5 degrees
* the higher above, the lower the temperature
* this is because of decreased air pressure, which means particles are further apart, and because of that heat energy is lost
* 1000 metres above sea level - falls 6.5 degrees
47
New cards
prevailing winds
* wind patterns over specific region
* carry climate of area they came from
* two patterns are
* prevailing trade winds (tropical)
* prevailing westerlies (subpolar)
* winds from cooler places = cooler climate
* winds from warm places = warmer climate
* carry climate of area they came from
* two patterns are
* prevailing trade winds (tropical)
* prevailing westerlies (subpolar)
* winds from cooler places = cooler climate
* winds from warm places = warmer climate
48
New cards
distance from ocean
* ocean has more consistent temperature than land, as it takes longer to change temperature
* coastal locations have more temperate season climates
* less temperature fluctuation between day and night
* coastal locations have more temperate season climates
* less temperature fluctuation between day and night
49
New cards
ocean currents
* continuous and directed movement of ocean water through the earth
* carry hot or cold water from one area of the world, which affects the climate of those regions
* warm ocean currents:
* increase temperature
* increase rainfall
* cold ocean currents:
* lower temperature
* lower rainfall
* example: cities in america/europe along the same latitude can have varying temperatures due to different ocean currents
* carry hot or cold water from one area of the world, which affects the climate of those regions
* warm ocean currents:
* increase temperature
* increase rainfall
* cold ocean currents:
* lower temperature
* lower rainfall
* example: cities in america/europe along the same latitude can have varying temperatures due to different ocean currents
50
New cards
geographic barriers
* mountains can affect rainfall by creating barriers for passing clouds and rainfall
* force moist air to rise, which causes air to cool and condense, creating rain
* windward side of the mountain receives most of the rainfall, and other side receives less rainfall (dry and hot)p
* force moist air to rise, which causes air to cool and condense, creating rain
* windward side of the mountain receives most of the rainfall, and other side receives less rainfall (dry and hot)p
51
New cards
perth climate
* temperate mediterranean climate characterised by hot, dry summers and cool, wet winters
* receive around 700 mm of rainfall a year
* temperature ranges from 7 - 32 (winter summer)
* 30 degrees south
* located south of the tropic of capricorn, outside tropical belt
* creates temperate climate between tropical and subpolar (mild temperature and rainfall)
* at sea level no mountain ranges
* no significant altitude based temperature range
* higher rainfall levels at the foot of the darling ranges
* flat apart from DR, rainfall spread evenly
* prevailing winds in perth are seasonal
* strong westerlies during winter bring antarctic air
* dry air comes from inland
* every day in summer, breeze from the ocean called Fremantle Doctor cools perth by upto 10 degrees
* occurs because of the pressure difference between land and sea
* receives cool ocean currents from antarctica (WA Current)
* keeps climate mild in summer and wet during winter, and a dry weather climate rather than humid
* receive around 700 mm of rainfall a year
* temperature ranges from 7 - 32 (winter summer)
* 30 degrees south
* located south of the tropic of capricorn, outside tropical belt
* creates temperate climate between tropical and subpolar (mild temperature and rainfall)
* at sea level no mountain ranges
* no significant altitude based temperature range
* higher rainfall levels at the foot of the darling ranges
* flat apart from DR, rainfall spread evenly
* prevailing winds in perth are seasonal
* strong westerlies during winter bring antarctic air
* dry air comes from inland
* every day in summer, breeze from the ocean called Fremantle Doctor cools perth by upto 10 degrees
* occurs because of the pressure difference between land and sea
* receives cool ocean currents from antarctica (WA Current)
* keeps climate mild in summer and wet during winter, and a dry weather climate rather than humid
52
New cards
4 categories nature support humanity
supporting
provisioning
regulating
cultural
provisioning
regulating
cultural
53
New cards
supporting
* breakdown organic waste
* water purification
* soil formation
* nutrient cycling
* primary production
* water purification
* soil formation
* nutrient cycling
* primary production
54
New cards
provisioning
* edible goods
* timber
* medicine
* timber
* medicine
55
New cards
regulating
* floods, droughts
* moderate water, climate, soil
* reduce disease
* moderate water, climate, soil
* reduce disease
56
New cards
cultural
* religious, spiritual, educational, aesthetic, tourist, and recreational benefits of ecosystems
57
New cards
A
tropical
* significant rainfall
* avg temp a month remains above 18 the entire year
* significant rainfall
* avg temp a month remains above 18 the entire year
58
New cards
B
arid
* little rainfall
* little rainfall
59
New cards
C
temperate
* at least one month with average temperature between 0 and 18
* at least one month with average temperature over 10
* at least one month with average temperature between 0 and 18
* at least one month with average temperature over 10
60
New cards
D
continental
* at least one month with average temperature below 0
* one month with average temperature above 10
* at least one month with average temperature below 0
* one month with average temperature above 10
61
New cards
E
polar
* average temperature remains below 10
* average temperature remains below 10