Introduction to Physiological Psychology and Biopsychology
1/94
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
95 Terms
Biopsychology
Scientific study of biology's influence on behavior.
Physiological Psychology
Links behavior to brain and organ activity.
Ontogenetic
Development of structure influenced by genes and experiences.
Epigenetic
Influences of environment on gene expression.
Evolutionary Psychology
Studies evolutionary history of behavior and structures.
Functional Explanation
Describes why a behavior evolved as it did.
Neuroanatomy
Study of nervous system structure.
Neurochemistry
Chemical bases of neural activity.
Neuroendocrinology
Interactions between nervous and endocrine systems.
Neuropathology
Study of nervous system disorders.
Neuropharmacology
Effects of drugs on neural activity.
Neurophysiology
Functions and activities of the nervous system.
Experiment
Method to determine causation in research.
Quasi-experimental Study
Studies groups exposed to real-world conditions.
Case Study
In-depth analysis of a single subject.
Cartesian Dualism
Philosophy separating mind and body by Descartes.
Behavioral Neuroscience
Biological approach to psychology and behavior.
Chemical Reactions
Hormones influencing brain activity and muscle control.
Testosterone Influence
Hormone affecting songbird brain area growth.
Sensitive Period
Critical time for learning behaviors, like songs.
Songbird Behavior
Males sing to attract females and establish territory.
Cultural Influences
Societal factors affecting biological differences.
Ancestral Modifications
Evolutionary changes from ancestral species to modern forms.
Cartesian Dualism
Mind-body interaction theory by Rene Descartes.
Reflexes
Automatic responses to stimuli, coined by Descartes.
Pineal Body
Small brain organ for mind-body interaction.
Soul
Descartes' term for what we now call the mind.
Theory of Evolution
Darwin's concept explaining biological changes over time.
Natural Selection
Process favoring traits enhancing survival and reproduction.
Functionalism
Understanding biological phenomena by their useful functions.
Nature vs Nurture
Debate on genetic vs environmental influences on behavior.
Gregor Mendel
Father of Genetics; studied inheritance in pea plants.
Dichotomous Traits
Traits with two distinct forms studied by Mendel.
DNA
Double-stranded molecule with nucleotides and a phosphate backbone.
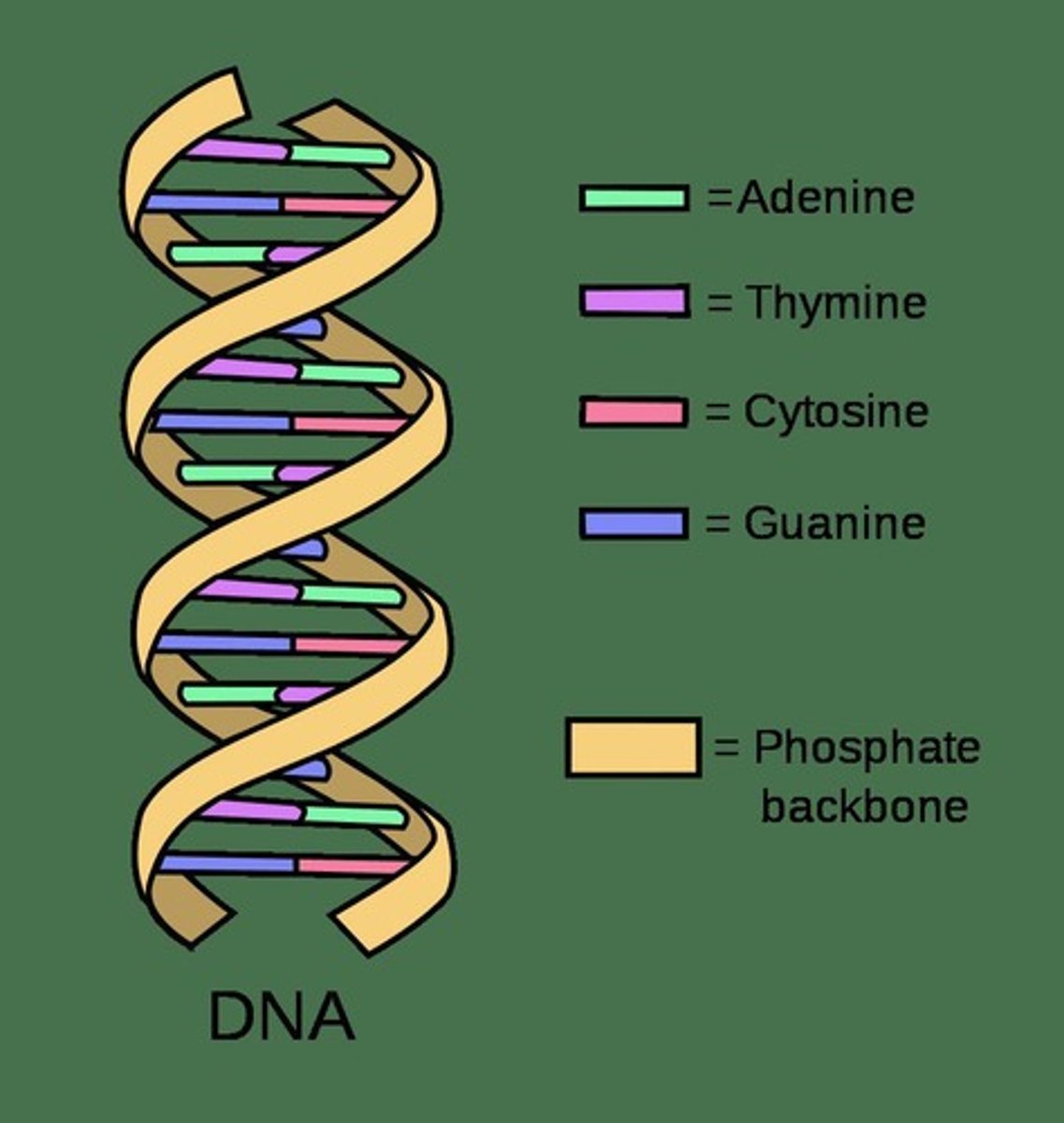
Chromosome
DNA structure in cell nucleus, tightly coiled by histones.

Mutation
Genetic alteration in an organism's make-up.
Point Mutation
Single nucleotide change in genetic code.
Frameshift Mutation
Insertion or deletion altering genetic sequence.
Chromosomal Aberration
Change in chromosome number or structure.
Evolutionary Development
Study of brain structure evolution across species.
Behavioral Capacities
Abilities linked to evolutionary changes in species.
Selective Advantage
Trait increasing likelihood of survival and reproduction.
Environmental Stimuli
External factors influencing behavior and responses.
Visual Information
Data from eyes processed by the brain.
Pressurized Fluid
Substance diverted by the pineal body to muscles.
Social Dominance
Hierarchy established within social groups.
Central Nervous System
Comprises the brain and spinal cord.
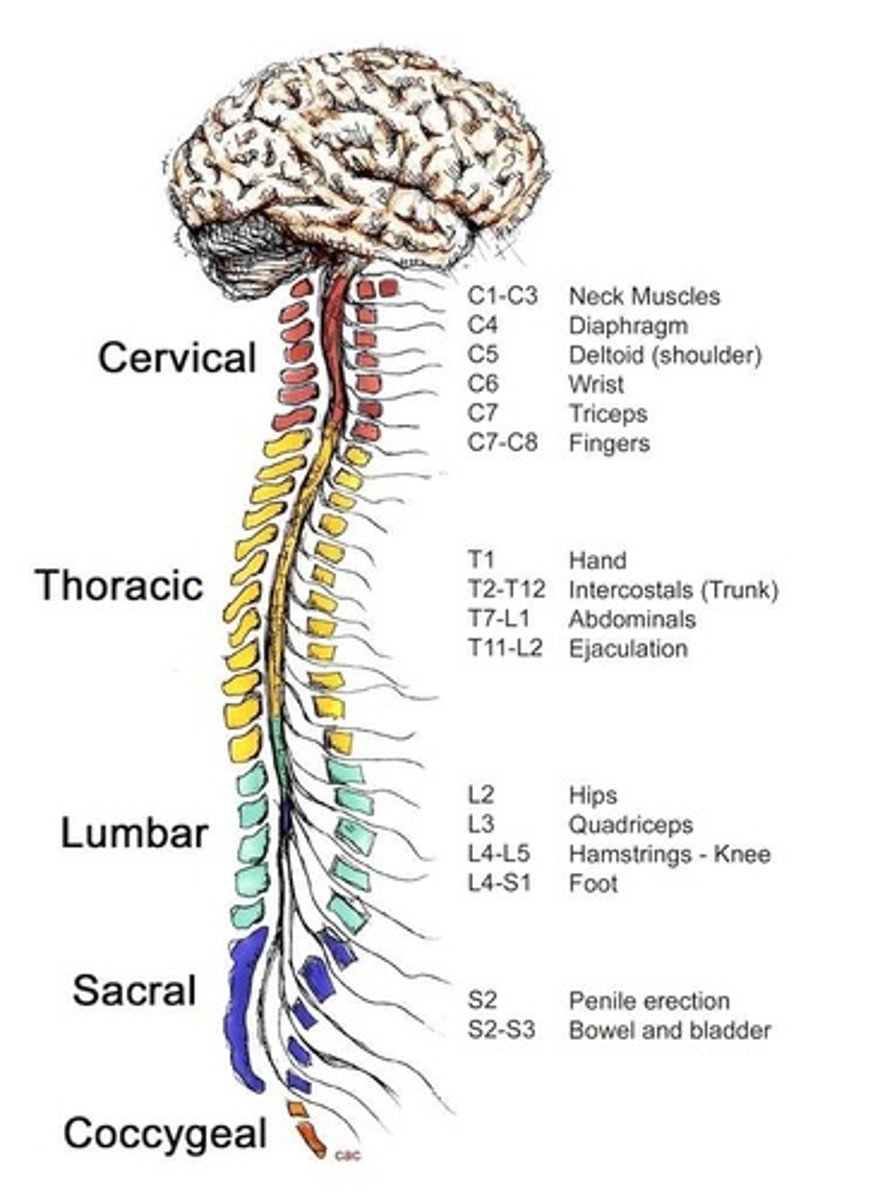
Peripheral Nervous System
Includes cranial and spinal nerves.
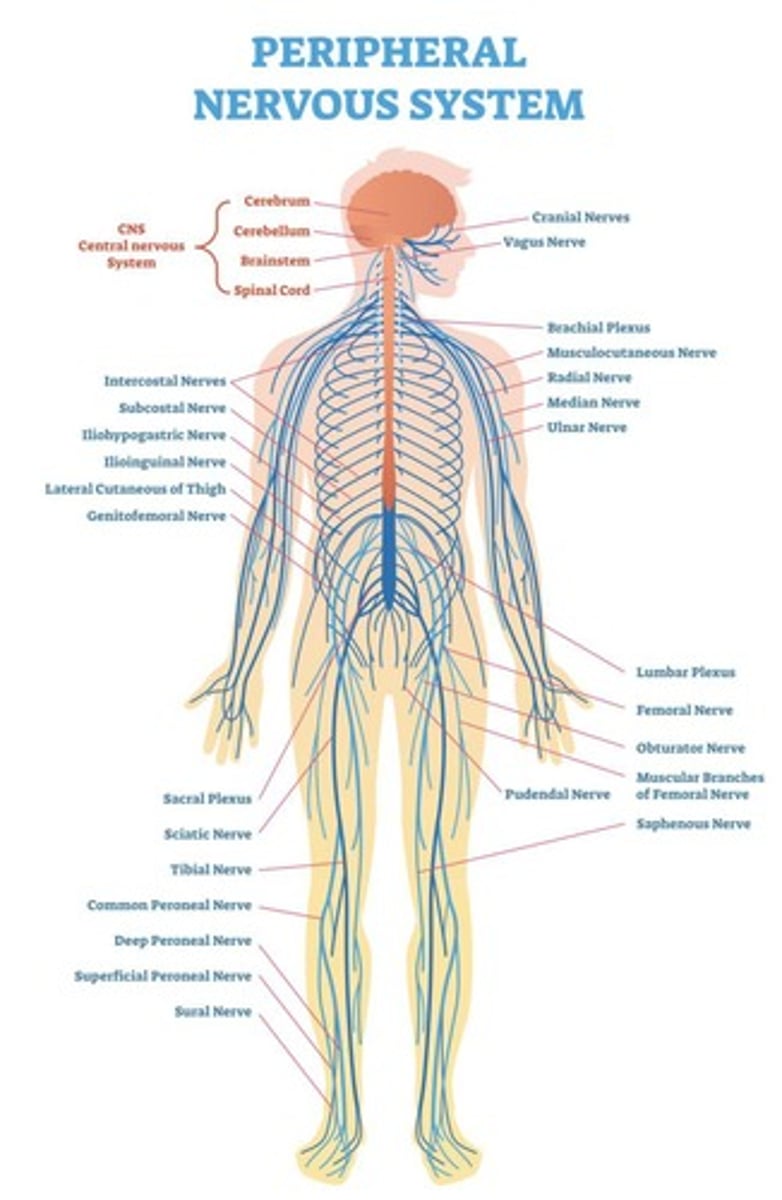
Somatic Nervous System
Controls voluntary movements via skeletal muscles.
Autonomic Nervous System
Regulates involuntary bodily functions.
Afferent Nerves
Transmit sensory information to the CNS.
Efferent Nerves
Carry motor commands from the CNS.
Sympathetic Division
Prepares body for 'fight or flight' response.
Parasympathetic Division
Promotes 'rest and digest' activities.
Meninges
Protective layers covering the brain and spinal cord.
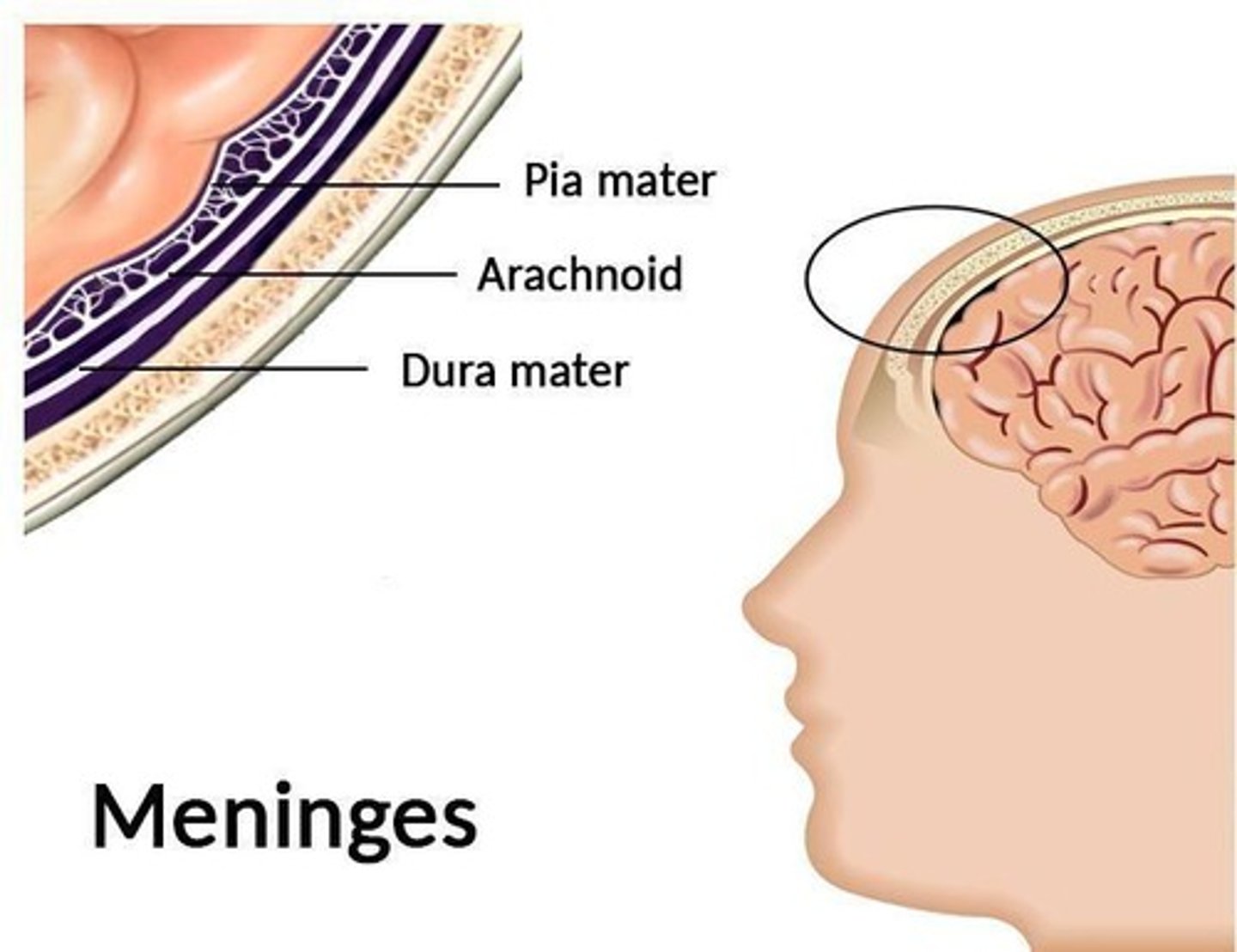
Cerebrospinal Fluid
Fluid cushioning the brain and spinal cord.
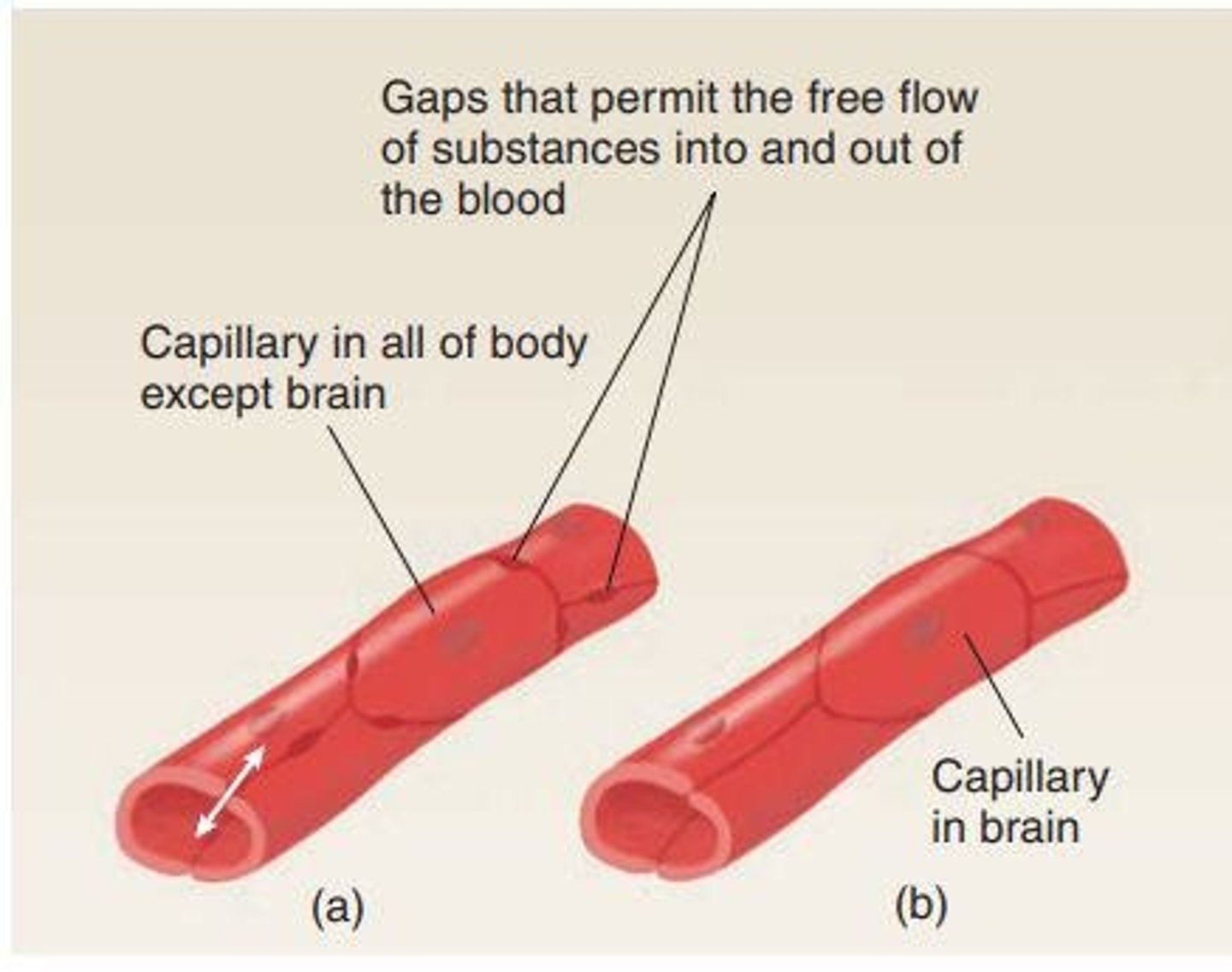
Blood-brain Barrier
Protects the brain from harmful substances.
Neuron
Information-processing and transmitting cell of the nervous system.
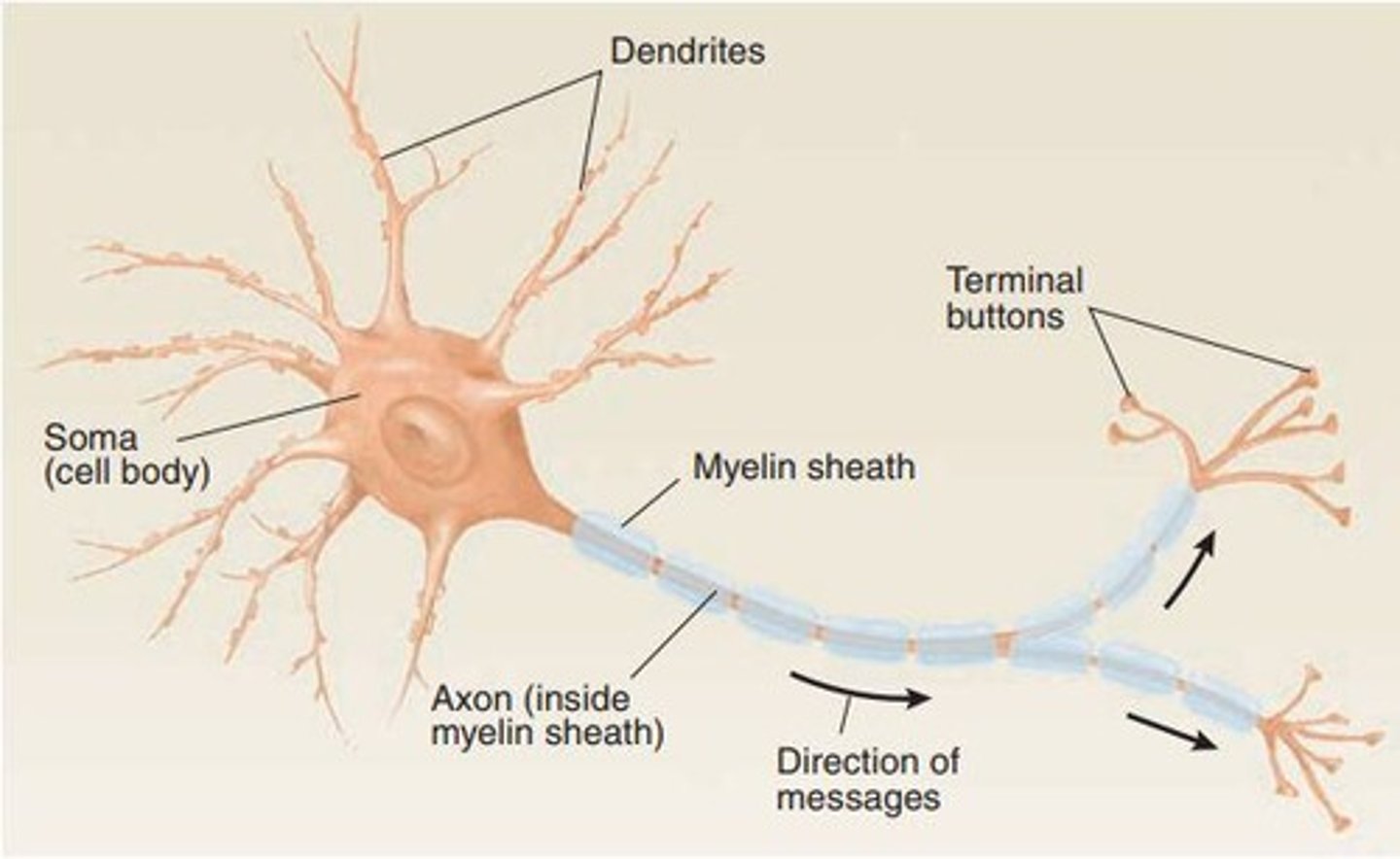
Dendrites
Receive signals from other neurons.
Cell Body
Contains nucleus and organelles of the neuron.
Axon
Transmits action potentials away from the cell body.
Terminal Buttons
Release neurotransmitters to communicate with other neurons.
Glial Cells
Support and protect neurons in the nervous system.
Astrocytes
Maintain blood-brain barrier and nutrient supply.
Oligodendrocytes
Form myelin sheath in the CNS.
Schwann Cells
Form myelin sheath in the PNS.
Gray Matter
Contains neuron cell bodies and synapses.
White Matter
Contains myelinated axons for signal transmission.
Telencephalon
Largest brain division, includes cerebral hemispheres.
Cerebral Cortex
Outer layer of the brain, involved in complex functions.
Primary Motor Cortex
Controls voluntary muscle movements.
Hippocampus
Involved in spatial memory and learning.
Diencephalon
Located between Telencephalon and Mesencephalon.
Thalamus
Relay station for sensory information.
Hypothalamus
Regulates autonomic functions and homeostasis.
Mesencephalon
Midbrain involved in vision and movement.
Tectum
Responsible for visual reflexes in mammals.
Tegmentum
Prevents unwanted movements.
Metencephalon
Includes cerebellum and pons.
Cerebellum
Controls balance and movement; 'little brain'.
Pons
Regulates sleep-wake cycle and breathing.
Myelencephalon
Contains medulla oblongata, vital for autonomic processes.
Medulla Oblongata
Key conduit for nerve signals; controls heartbeat.
Limbic System
Involved in motivation and emotion.
Hippocampus
Critical for learning and memory.
Amygdala
Processes emotions and emotional memories.
Synaptic Transmission
Communication of neurons via neurotransmitters.
Neurotransmitters
Chemicals that transmit signals across synapses.
Resting Potential
Neuron at -70mV, stable state before activation.
Electrochemical Gradient
Difference in ion concentration and charge.
Sodium-Potassium Pump
Moves sodium out, potassium in; energy-intensive.
Action Potential
Rapid change in membrane potential during impulse.
Depolarization
Decrease in resting membrane potential, e.g., -70 to -67 mV.
Hyperpolarization
Increase in resting membrane potential, e.g., -70 to -72 mV.
Threshold
Critical point for action potential initiation, -50mV.