General Medicine I Exam 1
1/179
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
180 Terms
ICU Monitors
- Uses for continuous monitoring of cardiovascular and pulmonary systems
- ECG, pulse oximetry, blood pressure, respiratory rate, body temperature, advanced hemodynamics, intra-cranial pressure
Peripheral IV
- Used to deliver intravenous fluids or medications
- Placed in peripheral vein -> dorsal hand/wrist, cubital fossa, dorsal foot
Central Lines
- Used for central venous access (jugular, subclavian, femoral)
- Allows for monitoring of Central Venous Pressure (CVP) or Right Atrial Pressure (RAP)
- Route for medication delivery, fluid administration, blood sampling, TPN
- Tunneled (implanted port) = allowed for long-term access
- Peripherally Inserted Central Catheter (PICC) Line -> typically placed in upper arm
Swan-Ganz (PA) Catheter
- Pulmonary Arterial Catheter
- Placed in central vein
- Advanced to superior vena cava -> right atrium -> right ventricle -> pulmonary artery
Swan-Ganz (PA) Catheter - Measurements
- CVP (central venous pressure)
- Right atrial pressure
- Pulmonary artery pressure
- Pulmonary wedge pressure
- Cardiac output and cardiac index
- Calculation of systemic and pulmonary vascular resistance
- Temporary pacing
Arterial Line
- Placed in artery
- Allows continuous blood pressure measurement and sampling of arterial blood -> MAP and ABGs (arterial blood gases)
- Usually placed radial or femoral
- Pulling out this line can cause patient to bleed out!!
- Transducer must be AT LEVEL of right atrium to have accurate reading -> body position can change reading
Intracranial Pressure (ICP) Monitor
- Catheter placed through skull into epidural space, subarachnoid space, or directly into ventricle
- Can measure pressure and/or drain cerebral spinal fluid (CSF)
- Normal ICF < 10 mmHg
- Elevated ICP can lead to brainstem compression and reduced cerebral blood flow
- High infection risk
Chest Tubes
- Used to drain excess air or fluid from pleural space or mediastinum
- Tube connected to drainage system and collection box, usually placed on floor next to bed
- Can be placed to suction or water seal
JP Drains
- Drain fluid from body cavity or surgical site
- Consist of small collection tube draining into a collection container
- May use suction or gravity
Foley Catheter
- Indwelling catheter, inserted in urethra, sits in bladder, drains urine
- Held in place with balloon inflated in bladder
Nasogastric (NG) Tube
- Placed through nose
- Ending in stomach or small intestines
- Can be placed to suction to remove stomach contents -> common after surgery to await return of GI function
- Can also be used for nutrition
Nasal Cannula
- 1-6 L/min
- Oxygen extensor tubing to allow pt to walk around room
High Flow Nasal Cannula
- High amounts supplemental oxygen (up to 60 L/min)
- Oxygen is heated and humidified
- Larger diameter tubing
- Snug nasal prongs
- ex: optiflow, vapotherm
Noninvasive Positive Pressure Ventilation (NPPV)
- CPAP/BIPAP
- Short-term ventilatory support
- Used to prevent or wean off mechanical ventilation
- Delivered with fitted face/nose mask
Mechanical Ventilation
- Circuit includes ventilator and artificial airway to provide ventilation and oxygenation in respiratory failure
Endotracheal Tube
- Type of mechanical ventilation
Tracheostomy Tube
- Type of mechanical ventilation
- can be used longer
Goals of Early Rehab Post-Op
1) Minimize pain
2) Prevent post-op complications
3) Resume safe level of functional mobility
4) Protect surgical site - Tissue inflammation
Posterior Approach THA Contraindications
- Hip flexion > 90
- Hip adduction past neutral
- Hip IR past neutral
Spinal Surgery Precautions
- Limit excessive spine flexion/extension and rotation
- Lifting restrictions
- Log roll technique with bed mobility
- Avoid extended periods of sitting
- May require bracing
- May have HOB restrictions
Medical Research Council Sum-Score (MRC-SS)
- Diagnoses muscle weakness in critically ill patients
- Used to measure impairments in strength that influence both activity and participation restrictions
- Determines and tracks if patient develops ICU acquired weakness
Short Physical Performance Battery (SPPB)
- Assesses lower extremity function (strength, balance, and mobility)
- Identifies individuals who may be at risk of functional decline, disability, or falls
- Provides a good snapshot of physical performance
Confusion Assessment Method (CAM-ICU)
- Assesses delirium in patients who are critically ill, at risk for dementia, and/or on a mechanical ventilator in the ICU
Physical Function ICU Test (PFIT)
- Evaluates pt's strength, endurance, and mobility to predict functional outcomes after being discharged from the ICU
- A standardized tool for assessing baseline function, tracking progress, and predicting long-term outcomes
Shuttle Walk Test/Modified Shuttle Walk Test
- Assesses a person's aerobic fitness, walking ability, and endurance
- Used for patient's with chronic conditions (ex: COPD)
Richmond Agitation Sedation Scale (RASS)
- A scale used to categorize a patient's alertness and distressed behavior
- 6 levels on scale for alertness, 4 levels on scale for agitation/aggression
Seated Step Test
- Measures a patient's sitting balance while weight shifting, aerobic capacity, and motor control of the lower extremity
- Typically used post-stroke
- Also can be used in deconditioned patients to determine their aerobic capacity and exercise tolerance
2 Minute Step Test
- Used to assess aerobic capacity and functional mobility
- Demonstrates level of physical activity and exercise tolerance
Activity Measure for Post Acute Care (AM-PAC)
- Measures activity limitations related to ADLs, cognition, and functional mobility through patient-reported outcomes
John Hopkins Highest Level of Mobility (JH-HLM)
- Evaluates the highest level of mobility possible
De Morton Mobility Index (DEMMI)
- Measures mobility in elderly patients who have been hospitalized
Functional Status Score for the Intensive Care Unit (FSS-ICU)
- Measures patient's ability to complete various transfers in ICU
- Rolling, supine <> sit, sitting at edge of bed, sit <> stand, walking
Acute Care
- Health Systems that treat "sick" patients that would get worse without care
Biggest Roles of Acute Care PT
- Mobility assessment
- Discharge planning
Review of Active Orders
- PT Order -> can't break this!!
- Activity -> bedrest, OOB, ambulate, etc.
- Restrictions -> WBAT, no ROM, etc.
- Precautions -> cardiac, seizure, fall, etc.
- Diet -> NPO, fluid restrictions, etc.
- Code status -> DNR, full, etc.
Arousal and Attention
- Patient consciousness can vary from awake and alert to comatose
- If patient is not awake and alert, document what stimulus was used to arouse them, how the patient responded to that stimulus, and how long the patient was able to maintain arousal
Cognition Assessment
- Can't typically do this unless patient is awake and alert
- Can test multiple aspects of cognitive function including orientation, following commands, attention, memory, etc.
PT Evaluation
- Diagnosis
- Prognosis
- Plan of Care
Diagnosis
- PT, not medical
- Based on clinical findings or problems
- Includes impact on functional limitations and disability
Prognosis
- Predicted optimal level of improvement in function and amount of time needed to reach that level
Plan of Care
- Short-term and long-term goals
- Interventions to be used
- Criteria for discharge
Goals
- Should reflect discharge destination
- Focus on functional tasks!!
Discharge Planning in Acute Care
- Starts at or before admission
- Patients are ready for discharge once medically stable (typically in a few days)
- Need a plan in place for transition
- PTs play a vital role in discharge planning!
- Options = home, SNF, IRF, LTAC
Home Discharge
- Without further therapy services
- With outpatient PT, or home health PT
- Patient may require patient and/or family education, HEP, DME, etc.
Skilled Nursing Facility (SNF)
- Must be medically stable
- Can have RN needs and/or therapy needs
- PT/OT/Speech available
- Length of stay can be days-months
- Can be stand-alone or within a retirement community
- TEMPORARY!!!
Inpatient Rehabilitation Facility (IRF)
- Patient must be medically stable
- Must have qualifying medical diagnoses
- Can have skilled nursing needs (dialysis, wounds, IV meds, ventilator)
- MUST have therapy needs: PT/OT/Speech (need 2/3)
- Therapy will be 3 hours a day and patient must be able to tolerate it
- Expected length of stay = 2-8 weeks
- Must have a reasonable final discharge destination
Long-Term Acute Care Facility (LTAC)
- Patient needs to have continued MEDICAL needs to qualify
- Length of stay can be weeks-months
- PT/OT/Speech available
Discharge Decision-Making
- Medical team, patient/healthcare power of attorney must approve facility
- Insurance must approve facility
- Facility must accept patient
- Patient is discharged from hospital and admitted to next facility
Pre-Participation Health Screening
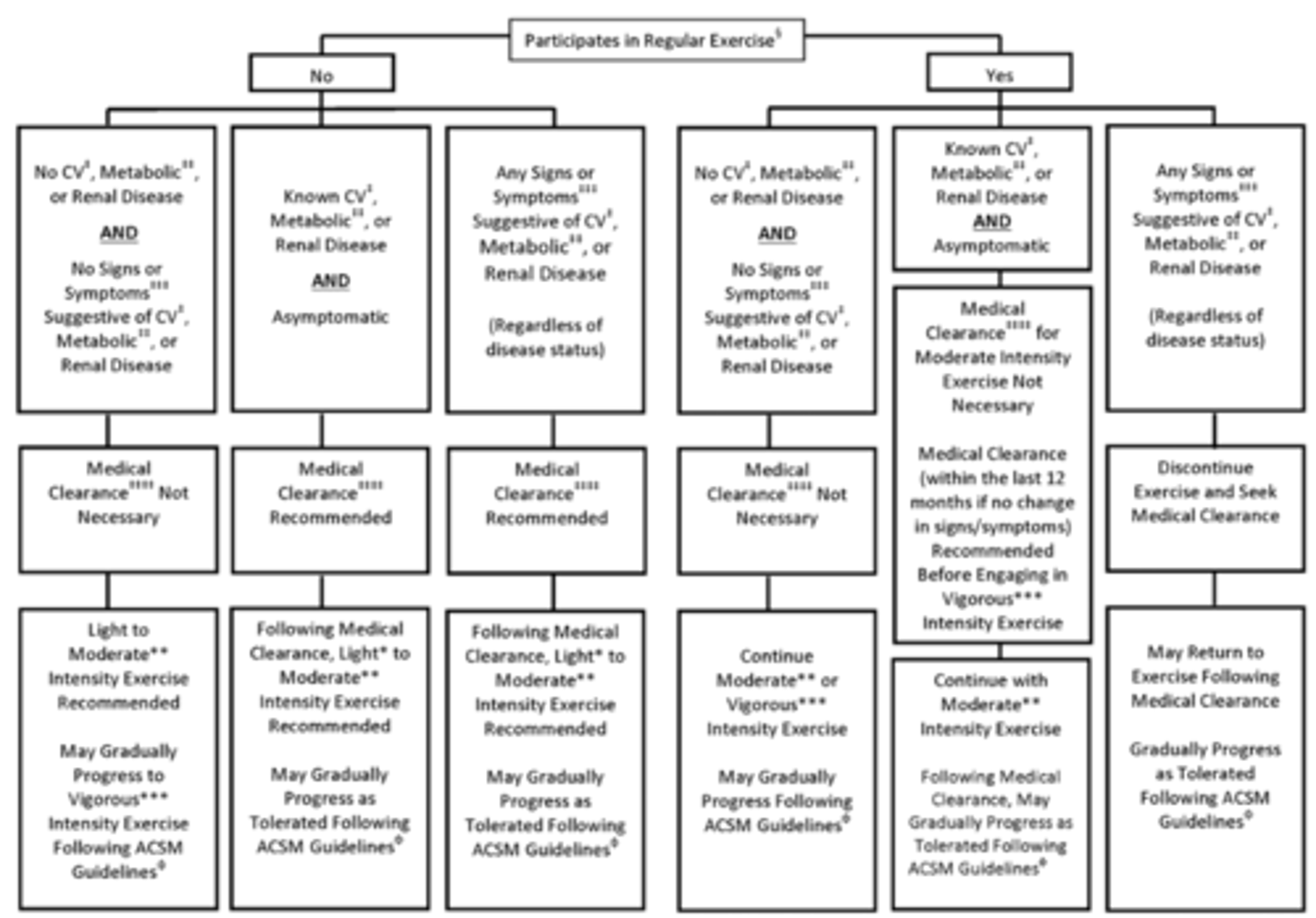
Physical Activity Recommendations
- 150 min/wk of moderate intensity physical activity
CV Risk Assessment
- PAR-Q+
- Framingham Risk Score
- ACC/AHA Risk Factor Profile
Non-Modifiable CV Risk Factors
- Age
- Gender
- Family History
Modifiable CV Risk Factors
- Blood lipid abnormalities (total cholesterol, LDL, triglycerides, HDL)
- Hypertension
- Smoking
- Physical inactivity
- Hyperglycemia/DM
- Obesity
- Stress
- Diet
Emerging CV Risk Factors
- C-reactive protein
- Homocysteine
- Kidney disease
- Environmental factors, infection, abnormal sleep, etc.
- Gender, racial, and ethnic disparities
CV Disease
- Affects > 80 million Americans
- Leading cause of death in US
- Coronary heart disease, heart failure, cerebrovascular disease, peripheral arterial disease, congenital heart defects
Myocardial Ischemia
- Occurs when blood flow/oxygen supply to myocardial cells is inadequate to meet demands of the myocardium
Atherosclerosis
- Progressive inflammatory disease
- Plaque made up of cholesterol and inflammatory response material
- Plaque is sensitive and cascade can be triggered by plaque being scratched
- Patient typically asymptomatic until vessel is stretched by 70%!!
- Common in LE!! -> LE pain while walking
- Causes stroke and MI
- Can be an embolus or thrombus
Thrombus
- Plaque that breaks off but remains at site of build-up
Embolus
- Plaque which breaks off and flows along artery to another site
Stable Angina
- Chronic exertional angina precipitated by stress or activity, usually at set level of myocardial oxygen demand
- Blood supply to the heart is insufficient to meat metabolic demand
- Pattern is predictable
- Relieved by rest or nitroglycerin
Unstable Angina
- UNPREDICTABLE!!
- Not necessarily provoked by an increase in myocardial oxygen demand
- New onset or more severe and prolonged
- MEDICAL EMERGENCY!!!
Nonanginal Discomfort
- Nitroglycerin generally has no effect
- Occurs any time; lasts for hours
- Muscle soreness, joint soreness, evoked by palpation or deep breaths
- Minimal additional symptoms
- No ST-segment depression
Myocardial Infarction (MI)
- Single largest killer of men and women!!
- Results from prolonged myocardial ischemia
- Early reperfusion can prevent necrosis from developing
- Irreversible changes begin within 20-30 minutes
- Some recovery possible if reperfusion within 3-6 hours
MI Sign and Symptoms
- Severe chest pain, pressure, squeezing, or heaviness
- Pain radiating down arms, throat, jaw, back, stomach
- Prolonged angina unrelieved by rest or NTG
- Nausea, pallor, SOB, diaphoresis, dizziness, lightheadedness
- Indigestion
- Weakness, fatigue, anxiety
MI Causes
- Thrombus at site of atherosclerotic plaque
- Prolonged vasospasm, aortic stenosis, arrythmia, vasculitis, coronary artery dissection, hypotension, drugs (i.e. cocaine)
Myocardial Necrosis
- Related to length of time of ischemia, myocardial oxygen consumption, and collateral blood flow
STEMI MI
- Complete blockage of coronary artery
- Associated with ST elevation on ECG
- Develops a Q wave on ECG in subsequent 24-48 hours (transmural infarction)
Non-STEMI MI
- Partial blockage of coronary artery
- Associated with ST depression, T wave changes on ECG
- Does not develop a Q wave on ECG (nontransmural or subendocardial region infarction)
Myocardial Remodeling
- Dependent on size and location of infarction, ventricular load, and blood supply to the area
- Scar formation restores structural integrity, but not function
Uncomplicated MI
- Lower morbidity and mortality rates
Complicated MI
- When another event occurs during the acute post MI period (24-48 hours)
- Ventricular tachycardia and fibrillation
- Atrial flutter or fibrillation
- 2nd or 3rd degree heart block
- Persistent sinus tachycardia or hypotension
- Pulmonary edema
- Cardiogenic shock
- Persistent angina or extension of infarction
Ejection Fraction (EF)
- Proportion of blood pumped out of the left ventricle with each beat
- Useful index of cardiac pump function!!
- EF = SV/EDV
- Averages 60% at rest
MI Labs
- LDH, CK-MB, Troponin, myoglobin will be in bloodstream
- These enzymes should usually only be in the heart, but the tissue death caused by MI makes them enter bloodstream
MI Diagnosis
- Chest x-ray
- Angiography
- Echocardiography
- Stress testing
- imaging modalities -> PET, CET, MRI, etc
MI Medical Treatment
- Reduce myocardial demand -> beta-blockers, nitrates, ca2+ channel blockers
- Increase myocardial oxygen supply -> thrombolytics, antiplatelet/anticoagulants, Ca2+ blockers, supplemental O2
- Prevent arrythmias -> pacemaker, anti-arrythmias
- Pain relief -> opiods
MI Surgical Treatment
- Angioplasty
- Stent placement
- CABG
- IABP (internal mammary artery graft)
Troponin Lab Values
- Rising levels of troponin = Active MI
- When troponin levels start decreasing = MI is resolving
- Takes several days for troponin values to return to normal
Cardiac Enzyme Labs
- Typically performed in sets of 3
- One set done every ~ 8 hrs
- Complete set of 3 gives a 24-hr view of heart
- Should not do PT until all 3 sets have been done
BNP Lab Values
- This value will be present in patient with congestive heart failure
- The higher the BNP value, the more progressed the heart failure is
Heart Failure
- A clinical syndrome in which structural or functional abnormality of the heart impairs adequate filling or ejection of blood from the ventricle
- Decreased CO
- Can be right or left sided, or both
- Leads to fluid retention -> dyspnea, orthopnea, paroxysmal nocturnal dyspnea, liver congestion, and peripheral edema
- Causes fatigue and weakness
Left-Sided Heart Failure
- Increased back pressure to the lungs resulting in excessive fluids in the alveolar spaces -> pulmonary edema
- SOB, peripheral swelling
Right-Sided Heart Failure
- Increased back pressure to the peripheral venous system leading to peripheral edema and liver congestion
Stroke Volume (SV)
- Blood pumped out by ventricles/beat
- Changes based on contractility, pre-load, and afterload
Frank-Starling Relationship
- SV is related to ventricular end diastolic volume
- The greater the volume, the higher the SV
- If EDV is too high, SV goes down
Frank-Starling and CHF
- The Frank-Starling is shifted to the right during CHF, causing higher back pressures to the lungs and periphery
- heart doesn't have physiological strength to keep up during CHF
Cardiac Output and CHF
- CHF decreases CO
- To compensate, there is an increase in sympathetic hormones, activation of renin-angiotensin system, and natriuretic system
- Increase in SNS hormones and RAA system -> increased volume retention which increases back pressure -> pulmonary and peripheral edema
- Increassed NE increases after-load -> coronary ischemia
What hormones do you want to block when treating CHF?
- Catecholamines, angiotensin II, aldosterone
- These hormones promote myocyte apoptosis (heart cell death) -> hypertrophy, loss of myocytes, fibrosis
- Use of beta-blockers, ace inhibitors, aldosterone blockers
4 Types of Heart Failure
- Left Ventricular Failure with reduced Ejection Fraction (HFrEF)
- Left Ventricular Failure with preserved Ejection Fraction (HFpEF)
- Right ventricular failure
- High output Heart Failure
Heart Failure Functional Class I
- Patient has no physical activity limitations
- Activity does not cause fatigue, dyspnea, or palpitation
Heart Failure Functional Class II
- Slight physical activity limitations
- Activity causes fatigue, palpitation, dyspnea, angina
Heart Failure Functional Class III
- Marked physical activity limitations
- Patient comfortable at rest, but activity will lead to symptoms
Heart Failure Functional Class IV
- Inability to carry on physical activity without discomfort
- Symptoms present at rest, but activity increases discomfort/symptoms
Heart Failure with reduced Ejection Fraction
- Systolic Dysfunction
- Diminished ability to pump blood/weak pump requiring increasing filling pressures (increasing back pressure) to meet demands of metabolic tissues like muscle
- Left-sided symptoms -> peripheral edema, pulmonary edema, SOB, weakness, fatigue
- Peripheral edema due to decreased RAA system
- Can lead to right-sided failure
- S3 on heart exam, rales (crackles) on lung exam, and peripheral edema
- Labs may show hyponatremia and elevated BNP
- ECHO shows reduced EF
Heart Failure with reduced Ejection Fraction Causes
- Coronary (ischemic) heart disease
- Dilated cardiomyopathy
- Hypertension
- Valvular disease (aortic stenosis, mitral regurgitation)
Heart Failure with reduced Ejection Fraction Treatment
- HTN -> beta blockers, ace inhibitors, ARBs, and mineralocorticoid antagonists
**No beta blockers if acute, uncompensated CHF!!
- Loop diuretics, hydralazine, and Ca2+ channel blockers
- Cease smoking and alcohol consumption, reduce Na2+ and control LDL
- Improved symptoms = ACE inhibitors, diuretics, beta blockers, ARBs, hydralazine/nitrates, digoxin, and aldosterone antagonists
- Improved survival = ACE inhibitors, beta blockers, hydralazine/nitrates, and aldosterone antagonists
Heart Failure with preserved Ejection Fraction
- Diastolic Dysfunction
- Normal ejection fractions, but ventricle is stiff and doesn't relax properly during diastole
- Increased LV filling pressures at rest and during exercise -> increased back pressure to the pulmonary vasculature -> dyspnea, orthopnea, PND, and pulmonary edema
- Normal EDV, but at an increased pressure due to increased LV wall thickness/mass
- S3 and S4 heart sounds, rales lung sounds, and peripheral edema
- Chest x-ray may show pulmonary edema, low sodium, and BMP elevated
Heart Failure with preserved Ejection Fraction Causes
- Systolic hypotension
- Aging
- Coronary artery disease
- Diabetes mellitus
- Sleep disordered breathing
- Obesity
- Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy
- Restrictive cardiomyopathy
- Kidney disease
Heart Failure with preserved Ejection Fraction Treatment
- Diuretics -> to treat volume overload
- Aldosterone antagonists -> BP control
- ACE inhibitors and beta-blockers not as beneficial!!
Right Ventricular Heart Failure
- Cor pulmonale
- Pulmonary hypertension leading to hypertrophy or dilation of the right ventricle
** From lung problems!! -> COPD, asthma, etcs
- Hepatic congestion, ascites, and peripheral edema may occur
- Jugular distension, right sided S3, liver enlargement, ascites, peripheral edema
Right Ventricular Heart Failure Causes
- Idiopathic pulmonary hypertension
- Hereditary
- COPD
- Interstitial lung disease
- thromboembolic disease
- Sleep disordered breathing