Lecture 9-10 Oral/Extravascular Kinetics & Absorption
1/58
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Understand the concept of 1st order absorption. Define the rate constant of absorption (ka), peak plasma concentration (Cmax), the time to the peak plasma concentration (tmax), and lag time (tlag). Estimate the rate constant of absorption (ka) using the method of residuals. Estimate the peak plasma concentration (Cmax) and the time to peak plasma concentration (tmax). 1) Identify routes of administration that require absorption 2) Define advantages and disadvantages of oral drug administration 3) Understand and describe the major physiologic factors that affect oral drug absorption 4) Understand and describe the major physiochemical factors that affect oral drug absorption.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
59 Terms
What does it mean that a drug is extravascular?
A drug that is extravascular is administered outside of the systemic circulation (IV).
Examples: oral, suppositories —> tablets, capsules
True or false: The most common route of extravascular administration is oral.
True!
Absorption is the process by which drug is moved from the _________ ______ ____ into the systemic circulation.
extravascular administration site
The rate of change of drug in the body is dependent on drug ______ and drug ______.
absorption, elimination
Match the following graph to the type of drug administration:
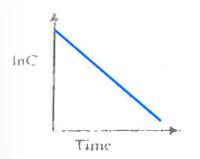
a. Extravascular
b. Intravascular
b. Intravascular
Match the following graph to the type of drug administration:
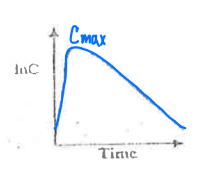
a. Extravascular
b. Intravascular
a. Extravascular
Pick the TRUE statements:
a. Most drugs are zero order processes (absorption at a constant rate).
b. An example of a drug with zero order process (absorption at a constant rate) are IV infusions.
c. Very few drugs have first order processes, since most drugs have relatively the same bioavailability (F).
d. Most drugs are first order processes (the rate of change of drug in the body is proportional to the amount of drug).
b. An example of a drug with zero order process (absorption at a constant rate) are IV infusions.
d. Most drugs are first order processes (the rate of change of drug in the body is proportional to the amount of drug).
If a drug is absorbed at a first-order rate, then the amount of drug at the absorption site will (increase/decrease).
decrease
Shown below is an equation for plasma concentration in the body at any time after an extravascular dose.
Define the variables and the assumptions the equation assumes.
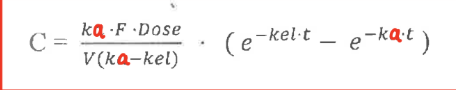
ka = first order absorption rate constant
kel = first order elimination rate constant
F = fraction of drug that is absorbed into the systemic circulation
assumes first order absorption and elimination
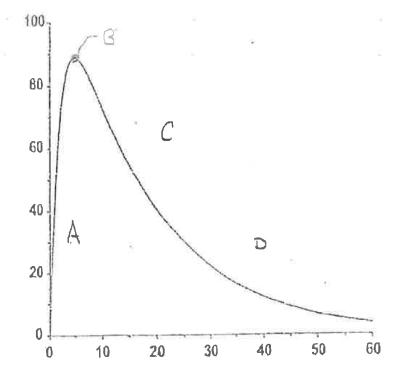
There are 4 important regions in the extravascular plasma concentration vs time curve.
Define Region A.
Initial Absorption Phase
Absorption > Elimination
rate of elimination (kel) = 0 —> no drug in the body
rate of drug absorption from absorption site = max
↑ Plasma concentration
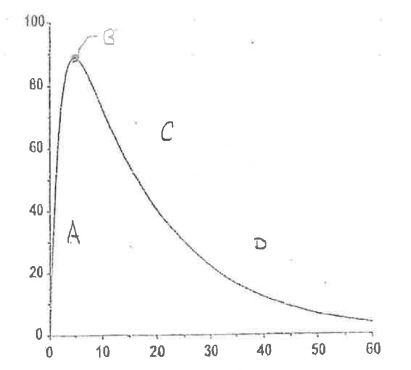
There are 4 important regions in the extravascular plasma concentration vs time curve.
Define Region B.
Peak Drug Concentration
Rate of elimination = Rate of absorption
NO change in amount of drug in body
Cmax = max concentration reached
tmax = time in which Cmax reached
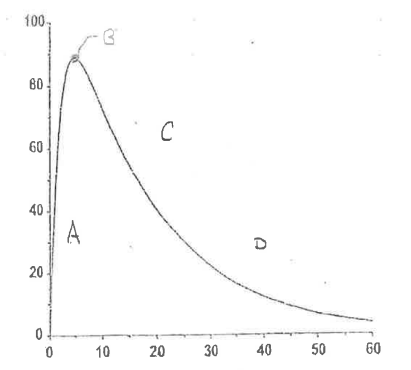
There are 4 important regions in the extravascular plasma concentration vs time curve.
Define Region C.
Post-Absorption Phase
Absorption < Elimination
drug becomes depleted at the absorption site
↓ Plasma concentration
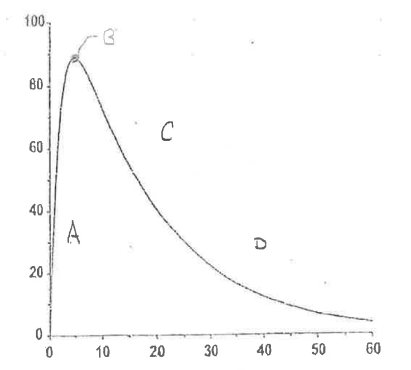

There are 4 important regions in the extravascular plasma concentration vs time curve.
Define Region D.
Elimination Phase
No drug remains at absorption site; Absorption is complete
Rate of absorption = 0
Which is true for tmax?
a. dependent of dose
b. independent of dose
c. dependent on ka and kel
d. maximum time of drug that reaches its full efficacy
b. independent of dose
c. dependent on ka and kel
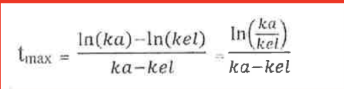
True or false: Usually, elimination is a more rapid process than absorption, so kel » ka.
False. Absorption is more rapid, so ka » kel
e-kat approaches 0 faster than e-kelt
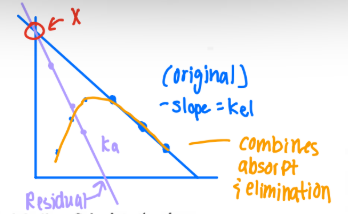
What are the steps for the Method of Residuals/Feathering?
-kel = found by taking the last 3 points on the terminal part of the ln(C) vs time curve.
Extrapolate (extend) the line to obtain the y-intercept.
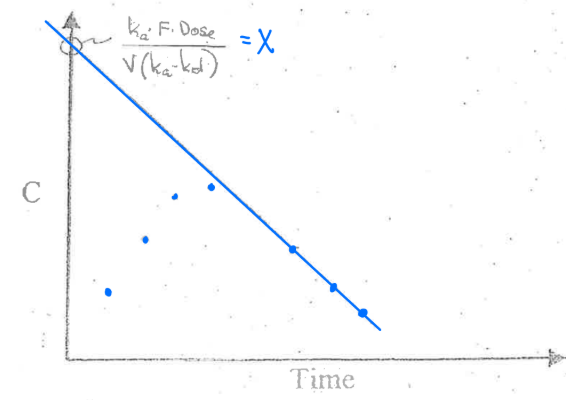
Obtain the concentrations at the first 3 points during the absorption phase from the extrapolated concentrations.
Calculate the residual concentration (Extrapolated concentration — Observed concentrations)
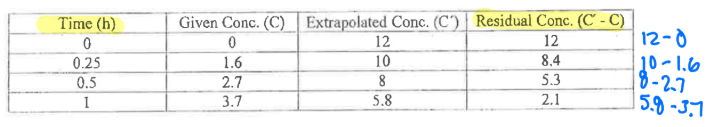
Plot the residuals vs time. Slope = -ka
Final graph (all together)
A minimum of ____ points should be used to define any straight line. Calculate the slope using points ____ the line of best fit.
3,on
kel is determined in the ____ part of the curve after _____ is complete. Data points occurring after tmax should/should not be used because drug adsorption is continuing at this point.
terminal, absorption, should not
ka is determined in the ____ part of the curve when the major process occurring is ____. Data points occurring after tmax should/should not be used because drug absorption is not the major process occurring.
early, absorption, should not
What is lag time?
The time delay between the administration of a single extravascular dose and the beginning of absorption.
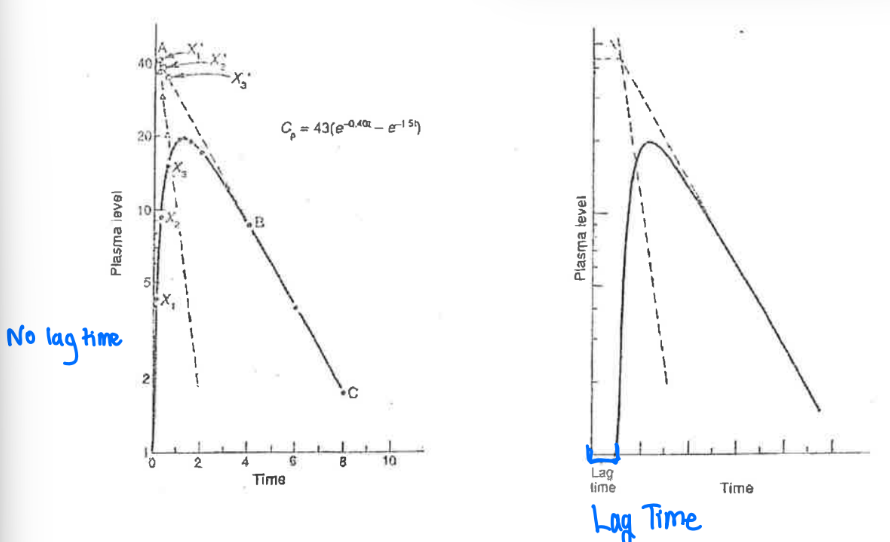
What are the factors that contribute to the lag time after oral drug administration and how do you identify lag time?
formulation (i.e. enteric coated tablets —> delayed)
stomach emptying (i.e. if stomach is empty or full)
How to identify:
C = 0 at a time after time = 0
Method of residuals = the extrapolated and residual line intersect at a point after time = 0.
True or false: The concentration gradient between blood and site of drug administration encourages absorption.
True. Concentration gradient encourages absorption.
Define Parenteral as a route of drug administration.
It is the administration of a drug outside the GI tract.
Examples: IV, Intra-arterial, IM, SQ, Intrathecal, Transdermal, Intranasal
Which systemic route does absorption avoid or occur at the side of administration?
a. Enteral
b. Parenteral
b. Parenteral
Which systemic route does absorption occur throughout the intestinal tract?
a. Enteral
b. Parenteral
a. Enteral
Define Enteral as a route of drug administration.
The administration of drug inside the gastrointestinal tract.
Examples: Buccal, sublingual, Oral (PO), Rectal
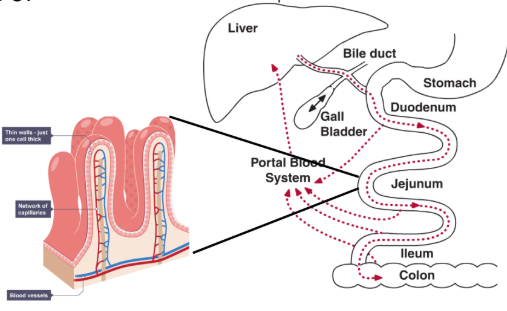
____ is the major site of drug absorption.
a. stomach
b. small intestine
c. kidney
d. liver
e. large intestine
b. small intestine
Especially the jejunum:↑ Surface area ↑ Permeability ↑ Blood flow
Which routes of administration do not require absorption?
a. IM (intramuscular)
b. SQ (subcutaneous)
c. IV (Intravenous)
d. Intrathecal
e. Buccal
f. Intraarterial
c. IV (Intravenous)
d. Intrathecal
f. Intraarterial
What is Oral Bioavailability (F)?
The fraction of the drug that gets to the blood after oral administration.
The amount of drug that escapes the intestine and avoids the first-pass effect.
Define the factors involved in the equation for Oral Bioavailability (F).
F = FF * FG * FH
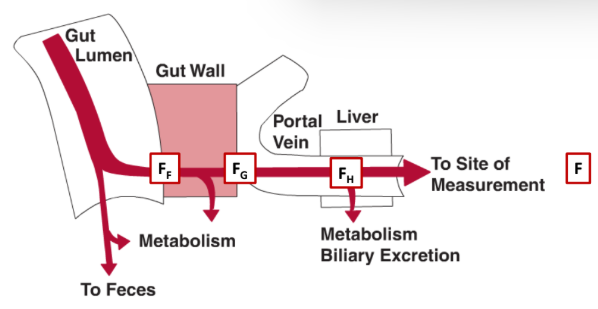
FF = fraction of drug absorbed (escapes intestine)
FG = fraction that escapes intestine wall
FH = fraction that escapes liver
What patient related factors affect oral absorption physiologically? (2)
Gastric emptying time
Intestinal transit time
What drug-related factors affect oral absorption physiochemically?
Solubility/Dissolution
Molecule size
Lipophilicity
How does gastric emptying affect oral absorption? What increases or delays drug effect?
The time for drug to pass from the stomach to intestine.
Impacts the peak and speed of drug effect within the first few hours of dosing.
Increases drug effect: Liquids, Prokinetic drugs (i.e. metoclopramide)
Decreases drug effect: Foot (high fat), diabetic gastroparesis, anticholinergic drugs, opioids
How does intestinal transit time affect oral absorption? What accelerates and delays drug effect?
The time for drug to proceed through the intestine
Impact overall absorption (especially for poorly absorbed drugs) and has impact thru longer period of time
Increases drug effect: Diarrhea, Prokeinetic drugs (i.e. meoclopramide)
Decreases drug effect: Constipation, Anticholinergic drugs, opioids
True or false: High-fat foods significantly alter transit time in small intestine and passage of solids into intestine.
False. High-fat foods only alter the speed in which solids pass into the intestine, not the transit time in the small intestine.
Intestinal transit time impacts what kind of drugs more?
a. poorly absorbed/sustained-release products
b. rapidly absorbed compounds
a. poorly absorbed/sustained-release products
more impactful in absorption
rapidly absorbed compounds are impacted by the changes with the Cmax and Tmax
Why might you recommend for a patient to take a drug on an empty stomach? (4)
Faster onset of drug action
Reduce exposure to stomach acid (drugs may be degraded)
More consistent absorption (diff meals = diff effect on transit time)
No interactions with food components (i.e. chelation w/ cations)
Why might you recommend for a patient to take a drug with food? (2)
To reduce side effects
To improve drug dissolution (increase stomach pH)

What pharmacokinetic profile would we expect if we administered acetaminophen with metoclopramide (a prokinetic agent)?

A. Line A
B. Line B (unchanged)
C. Line C
A. Line A
Which of the following increases absorption based on molecular size?
a. decrease molecular size
b. larger molecular size
a. decrease molecular size
smaller molecules diffuse faster through intestinal membrane
True or false: Drugs that are high in lipophilicity pass better through phospholipid bilayer.
True. Less lipophilic drugs pass slower through phospholipid bilayer.
Which of the following increases the absorption of drug? (Select all that apply)
a. unionized drug
b. ionized drug
c. extended-release formulation
d. small particle size formulation
e. use salt formation
b. ionized drug
d. small particle size formulation
e. use salt formation
True or false: Most common drugs are either strong acids or strong bases.
False. They are either weak acids or weak bases —> helps balance solubility & lipophilicity
If pH=pKa, drug is 50% ____ and 50%_____.
ionized (highly soluble), unionized (easily passes thru cell membranes)
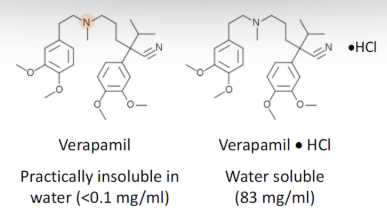
Why is a salt form of a drug preferable for drug absorption?
Salt form improves “Wetting of a drug”
More ionic = more hydrophilic = more water soluble
Dissolution rate is calculated by the Noyes-Whitney Equation.
Define the terms in the equation:
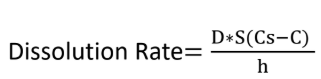
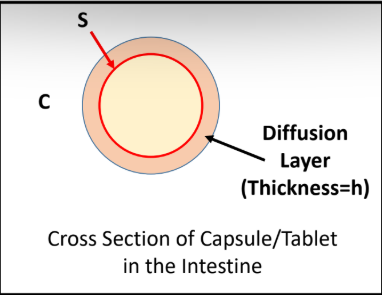
D = diffusion coefficient
S = surface area
Cs = Drug Solubility (saturation conc.)
C = concentration of drug in intestines
h = thickness of diffusion layer

Which of the following variables causes an increased dissolution rate if the variable is increased?
a. D = diffusion coefficient
b. S = surface area
c. Cs = Drug Solubility (saturation conc.)
d. C = concentration of drug in intestines
e. h = thickness of diffusion layer
a. D = diffusion coefficient
b. S = surface area
c. Cs = Drug Solubility (saturation conc.)
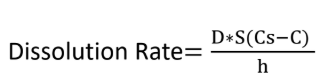
Which of the following variables causes a increased dissolution rate if the variable is decreased?
a. D = diffusion coefficient
b. S = surface area
c. Cs = Drug Solubility (saturation conc.)
d. C = concentration of drug in intestines
e. h = thickness of diffusion layer
d. C = concentration of drug in intestines
e. h = thickness of diffusion layer
Which is the correct order for dissolution rate?
a. Solutions > Tablet > Extended Release Tablet > Capsule
b. Solutions > Capsule > Tablet > Extended Release Tablet
c. Extended Release Tablet > Capsule > Tablet > Solutions
d. Capsule > Solutions > Tablet > Extended Release Tablet
b. Solutions > Capsule > Tablet > Extended Release Tablet
Which of the following drug formulation alterations would help extend the release of your newly developed compound to provide prolonged exposure? Select all that apply.
A. Increase surface area (S)
B. Decrease surface area (S)
C. Increase thickness of diffusion layer (h)
D. Decrease thickness of diffusion layer (h)
B. Decrease surface area (S)
C. Increase thickness of diffusion layer (h)

What is the goal for molecular size for a drug to be absorbed orally through the membrane?
Goal: molecular mass < 500 daltons
*Lipinski’s Rule of 5: rule of thumb that describes features typical of orally bioactive compounds
<5 hydrogen bond donors
<10 hydrogen bond acceptors
<500 dalton molecular mass
LogP < 5
What is the goal for a drug to have in terms of its lipophilicity?
must balance permeability (lipophlicity) and solubility/dissolution (hydrophilicity)
Goal: Log P < 5 (according to Lipinski’s Rule of 5)
Log P of 1-3 = balanced permeability/dissolution
Aminoglycosides have log P values of about -3. Which of the following regarding aminoglycosides is correct?
A. Aminoglycosides are lipophilic
B. Rapid dissolution will directly lead to good oral absorption
C. Poor oral absorption is expected due to poor diffusion through
lipid bilayer
D. All of the above
C. Poor oral absorption is expected due to poor diffusion through
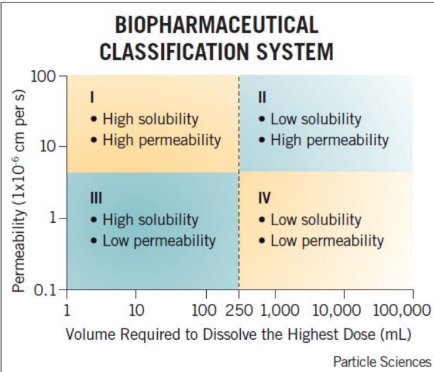
Which drug class is not typically used in oral formulation?
a. Class I
b. Class II
c. Class III
d. Class IV
d. Class IV
For each classification system, the ____ phase (dissolution or permeability) is the rate limiting step and determines the absorption rate.
Slowest
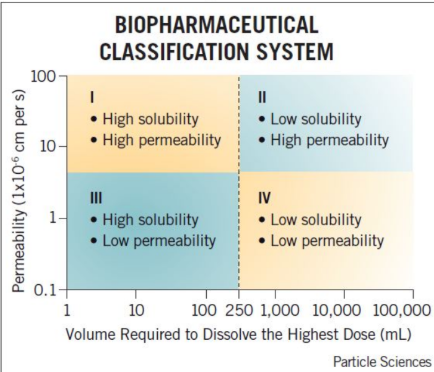
Match the rate limiting step for each class.
Rapid absorption, no apparent rate limiting step
a. Class I
b. Class II
c. Class III
a. Class I
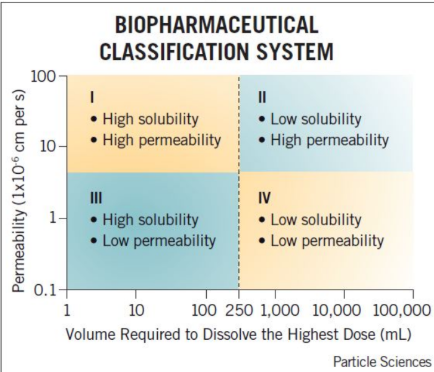
Match the rate limiting step for each class.
Rate limiting step = dissolution
a. Class I
b. Class II
c. Class III
b. Class II
Drug is absorbed as soon as it dissolves
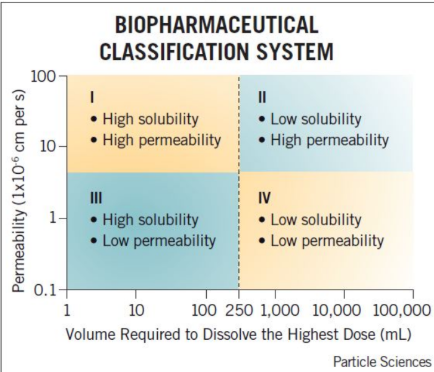
Match the rate limiting step for each class.
Rate limiting step = Permeability
a. Class I
b. Class II
c. Class III
c. Class III
Drug is in solution waiting to be absorbed
Cimetidine is a Biopharmaceutical Classification System class III compound (high solubility and low permeability). Which of the following best describes cimetidine’s absorption?
A. Slow dissolution is expected from an oral dosage form
B. Membrane permeability rate will determine absorption rate
C. Very high oral absorption is expected
D. None of the above
B. Membrane permeability rate will determine absorption rate