Autonomic Nervous System Physiology
1/60
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
61 Terms
response to…? somatics vs autonomic nervous system
somatic NS
responds to external environment
autonomic NS
responds to body’s internal environment to maintain homeostasis
effector organs: somatic vs autonomic nervous system
somatic NS
somatic muscles
autonomic NS
smooth and cardiac muscle, glands
action: somatic vs autonomic nervous system
somatic NS
voluntarily
autonomic NS
involuntarily, self-governing, autonomic
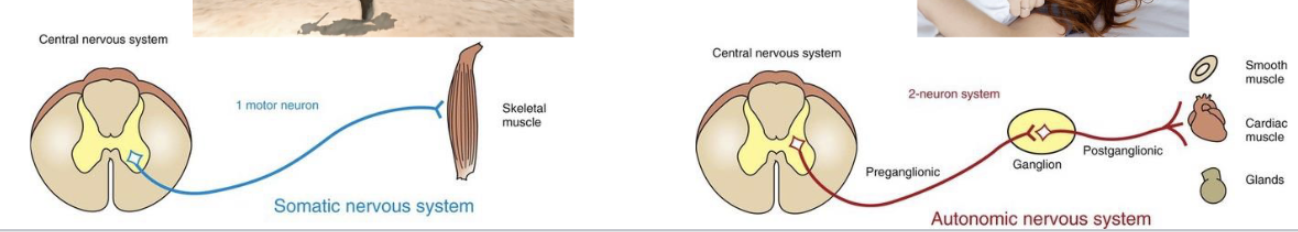
motor pathway: somatic vs autonomic nervous system
somatic NS
one neuron
autonomic NS
2-neuron chain
in somatic NS, cell bodies are located where…?
ventral horn of spinal cord OR in brainstem nuclei
in autonomic NS, cell bodies are located where…?
preganglionic neuron has cell body within CNS in brain stem or spinal cord
axons project out and terminate in ANS ganglia
post-ganglionic neuron has cell body in ganglion
axons project out to peripheral target tissue
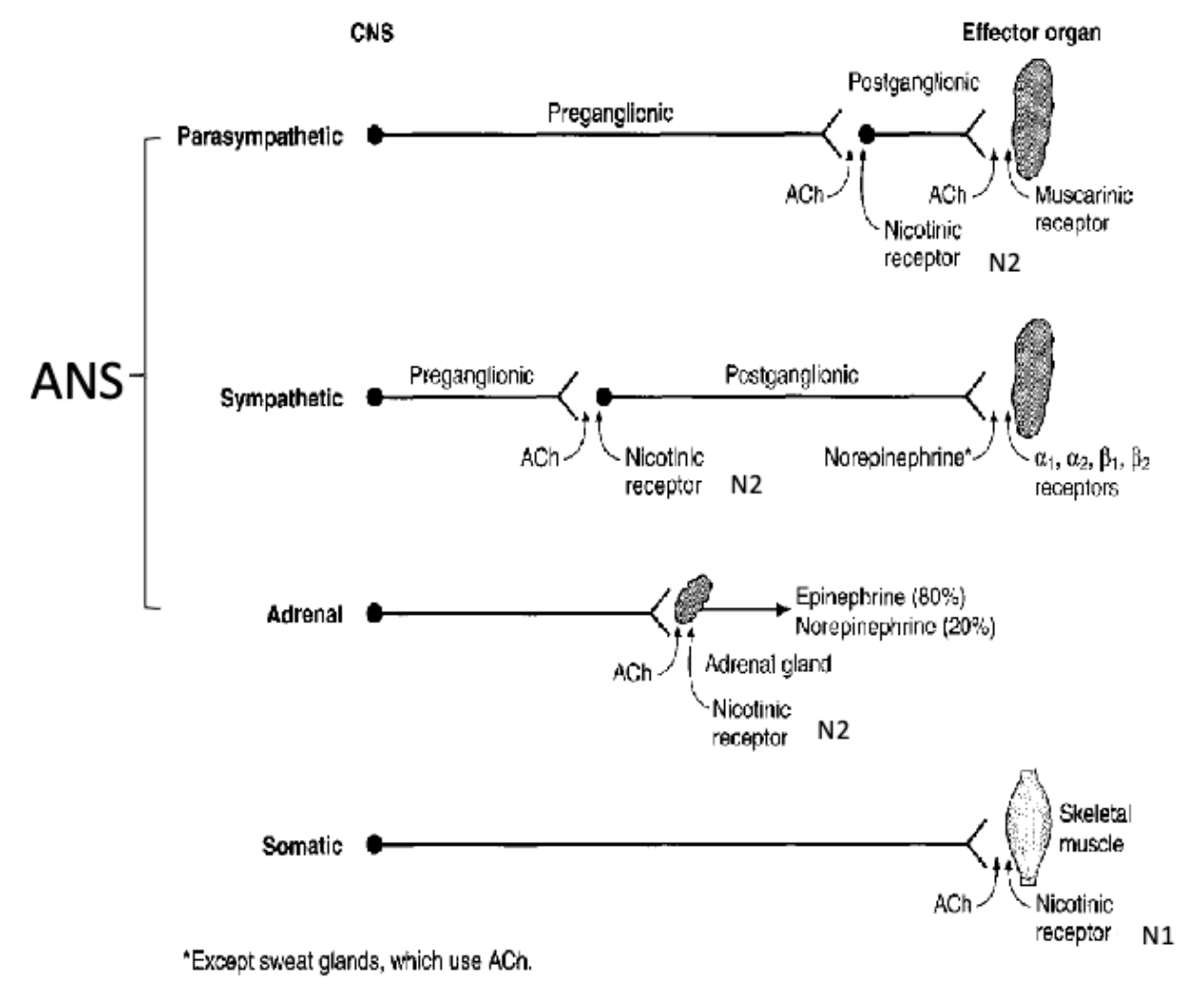
motor outputs of the autonomic NS consist of 3 divisions:
sympathetic (fight or flight)
Emergency, Excitement, Exercise
parasympathetic (rest and digest)
enteric (neruon system within GI tract)
how are the 2-neuron chains of sympathetic vs parasympathetic nervous systems different?
sympathetic NS
short preganglionic neruon
long postganglionic neruon
cell bodies in pre and para-vertebral ganglia
parasympathetic NS
long preganglionic neruon
short postganglionic neruon
cell bodies in regional ganglia
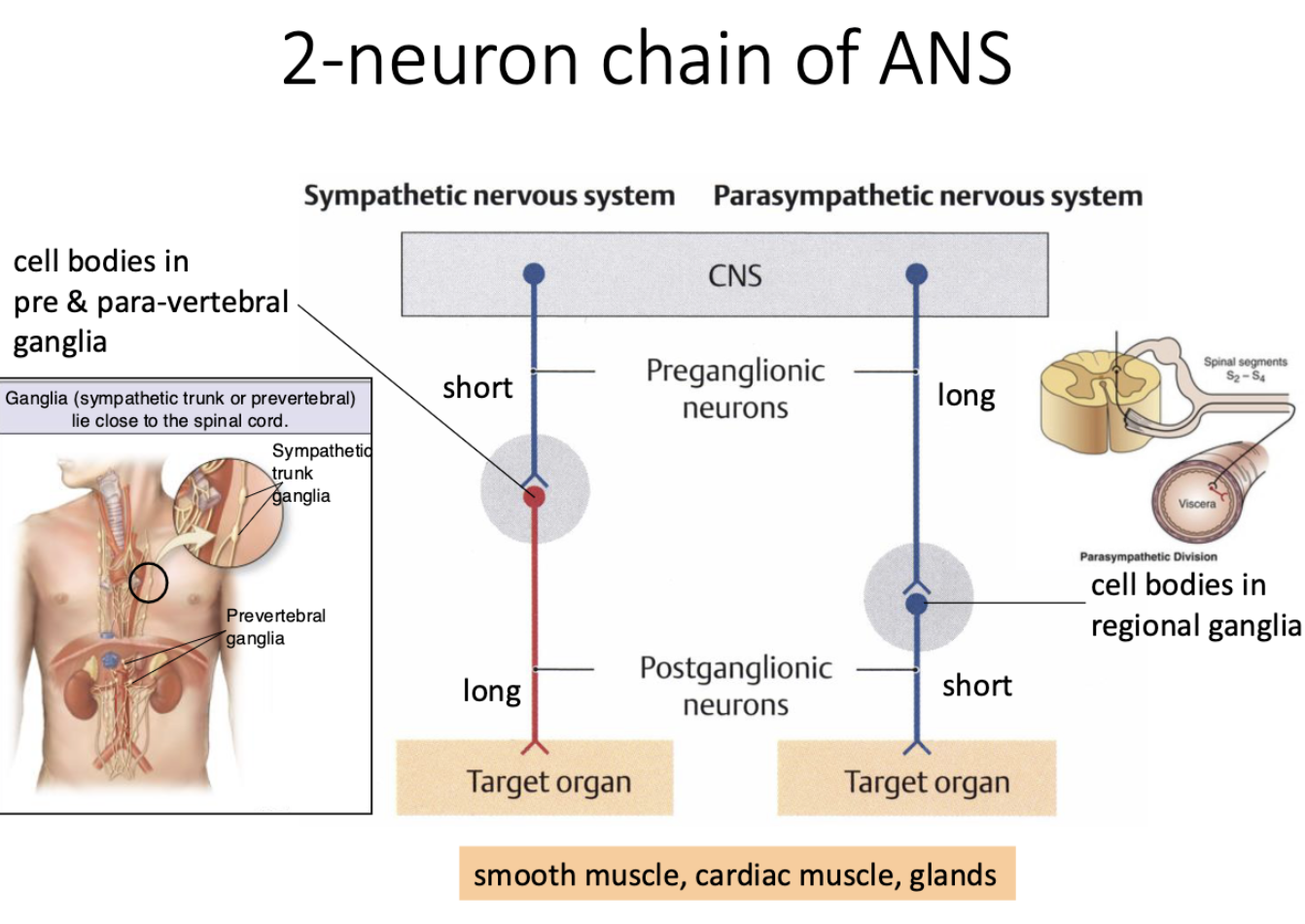
what are the target organs of both the sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous system of ANS?
smooth muscle, cardiac muscle, glands
Although the sympathetic neurons emerge only from the thoracolumbar regions of the cord, the chain ganglia extend from the _________ in the neck down to the sacral region
cervical ganglia
t/f: Each preganglionic neuron can synapse with multiple postganglionic neurons
true
what is the endocrine gland that releases epinephrine when stimulated by sympathetic preganglionic neurons?
adrenal medulla
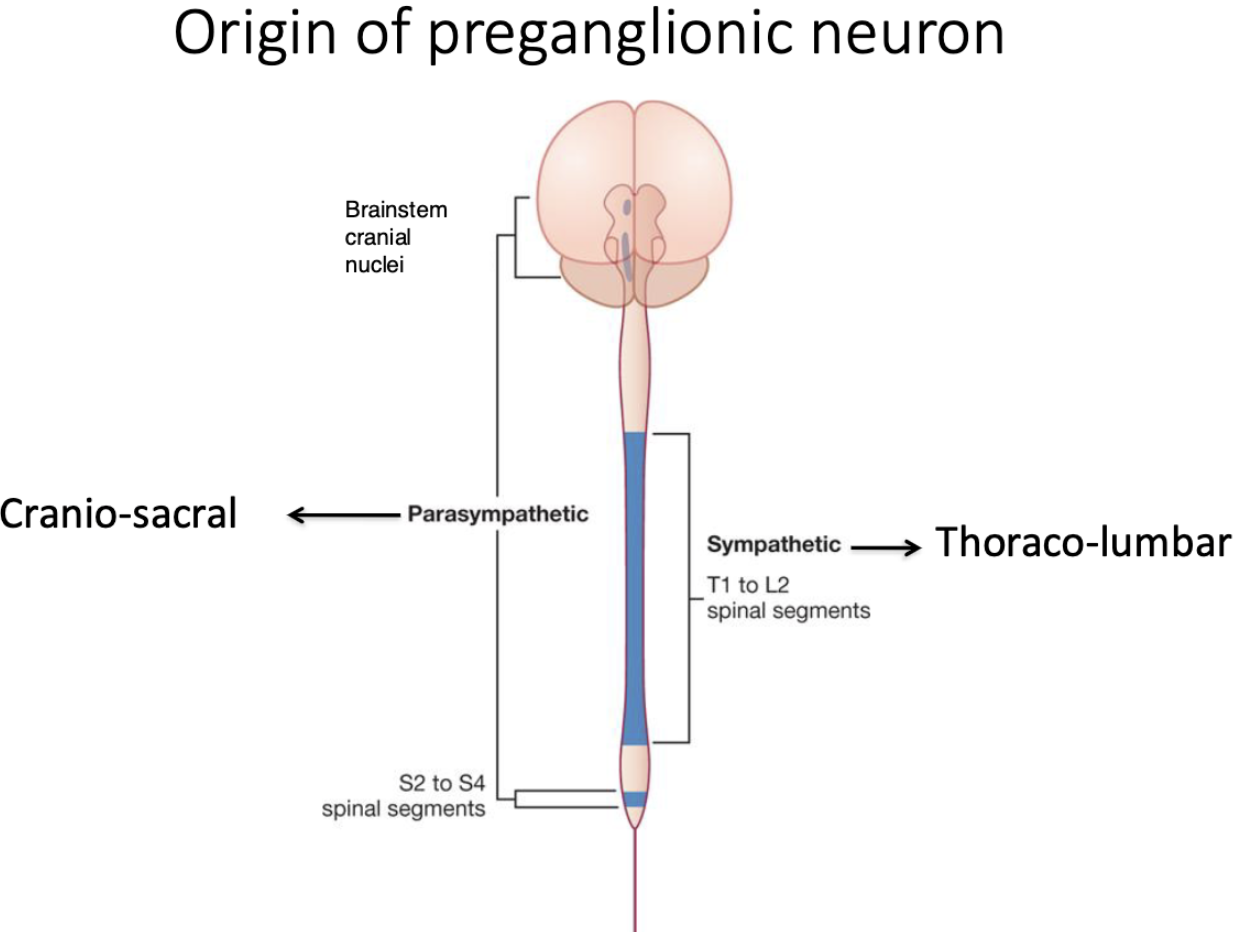
where does the parasympathetic system orginate from?
cranio-sacral regions
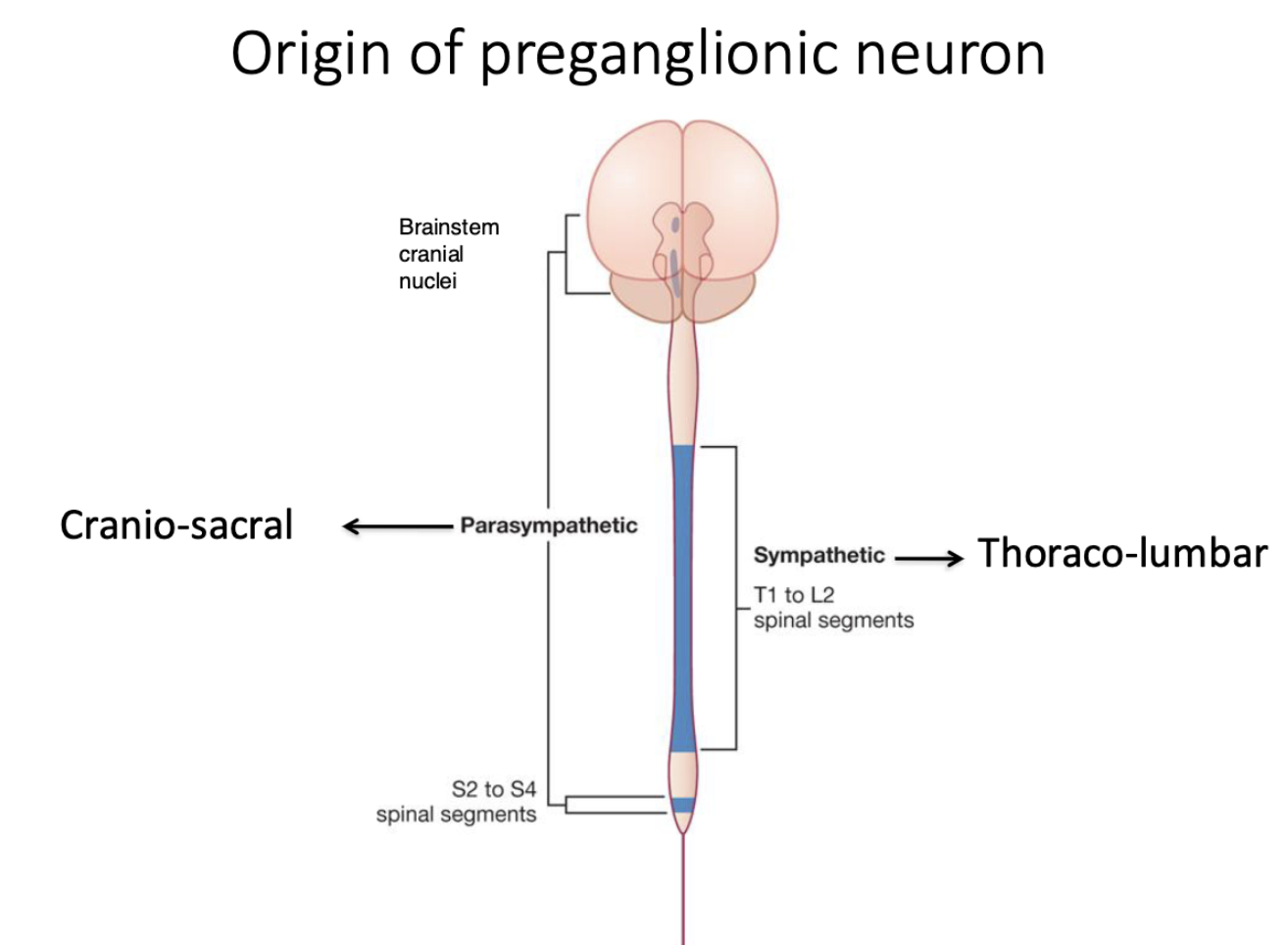
where does the sympathetic system orginate from?
thoraco-lumbar regions
what is ganglionic transmission?
Both sympathetic and parasympathetic preganglionic nerves release acetyl choline (ACh) which binds to cholinergic receptors in the ganglia
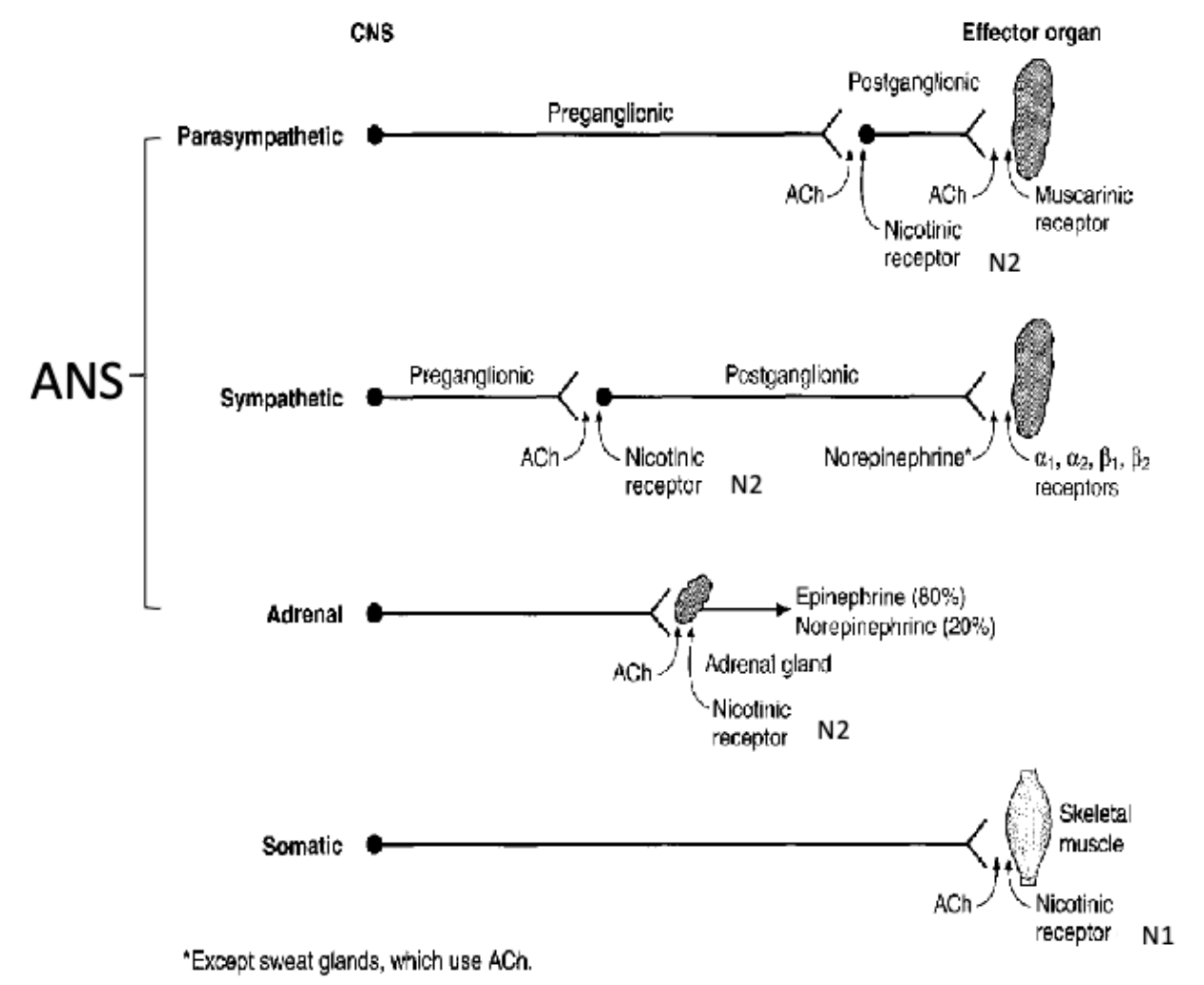
Both sympathetic and parasympathetic preganglionic nerves release ________ which binds to cholinergic receptors in the ganglia.
acetyl choline (ACh)
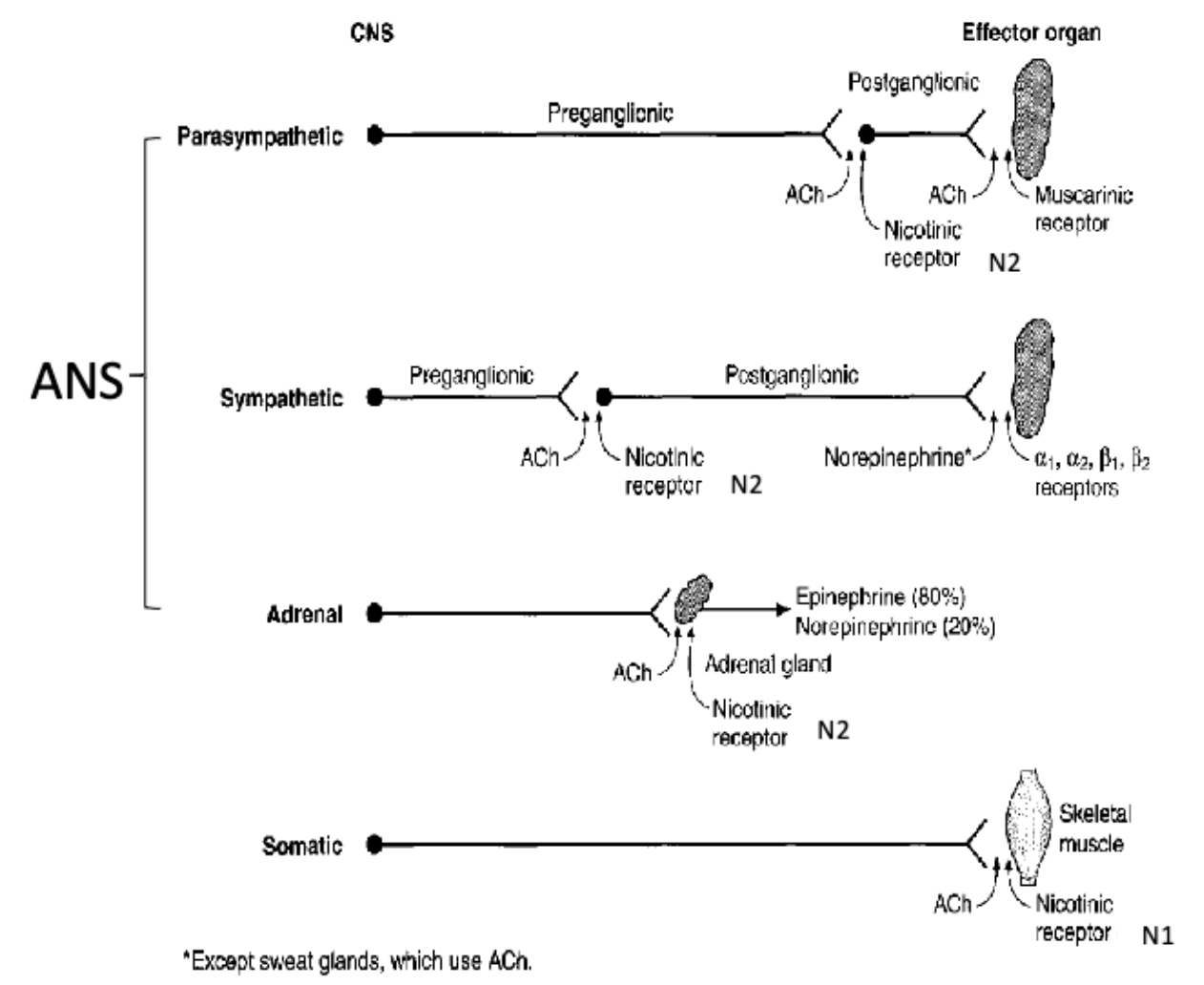
cholinergic receptors in the ganglia are also known as…?
nicotinic receptors (because they also bind to nicotine, acetyl choline binds to same receptor)
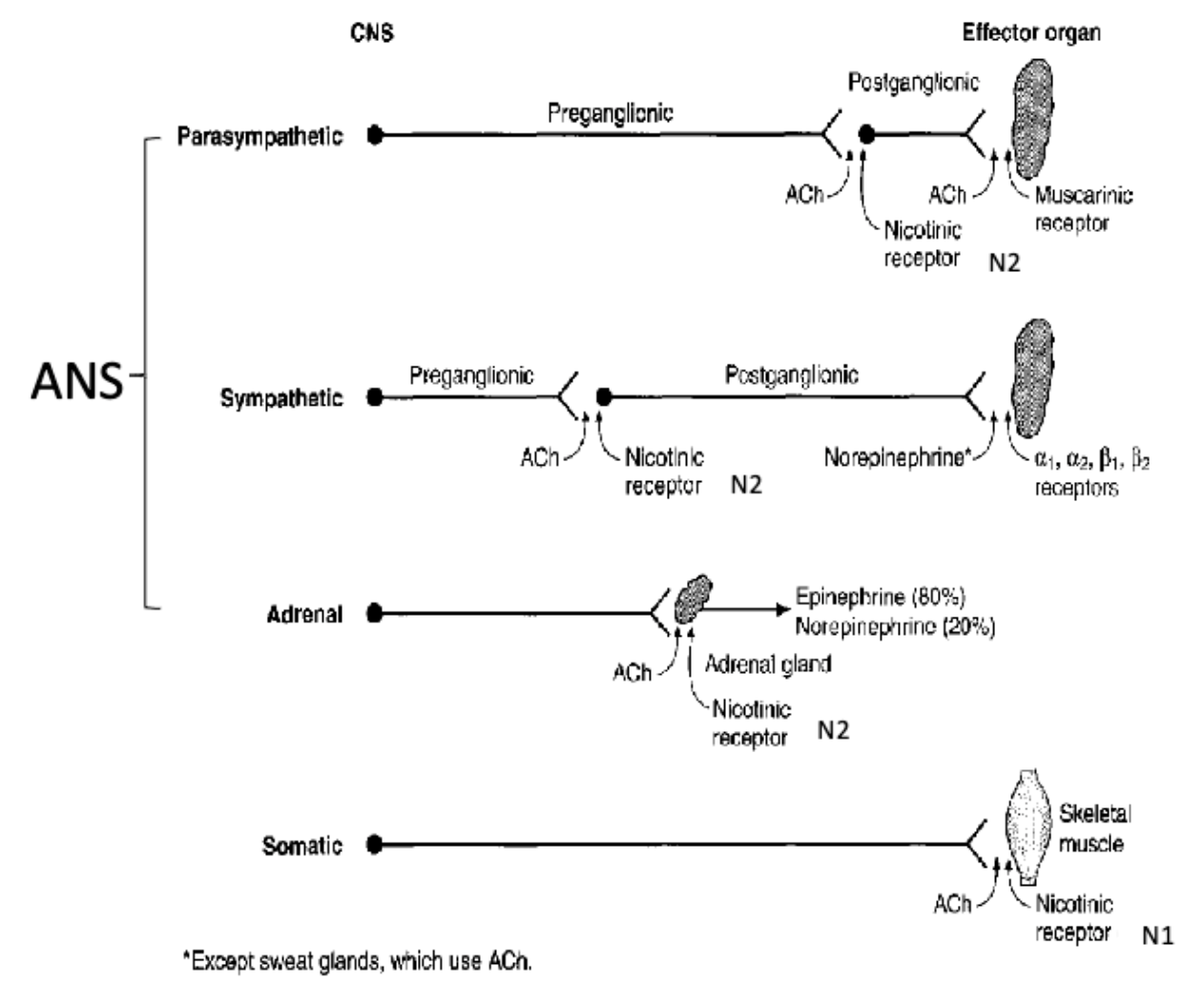
what are the 2 major subtypes of nicotinic receptors?
N1 → found in somatic nervous system in neuromuscular junctions
N2 → found in ANS ganglia
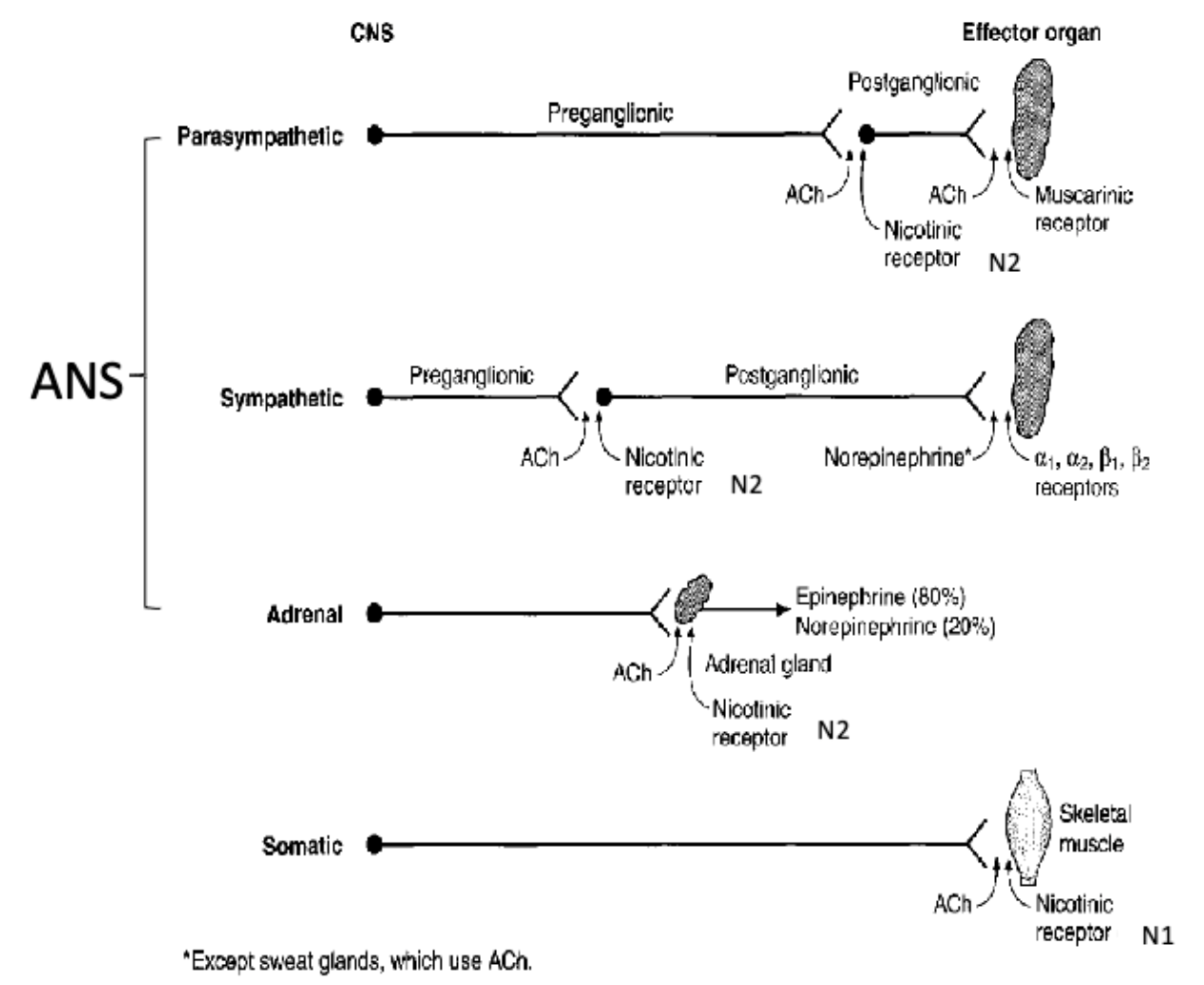
how do nicotinic receptors work?
ligand-gated channels that open when ACh binds
rapid depolarization of cell = ionotropic
where are N1 receptors located? N2?
N1 = skeletal muscle
N2 = autonomic ganglia
If a drug blocks the receptors in a ganglion, but not the receptors in neuromuscular junction, it would be a ___ receptor antagonist, blocking ___ receptor.
N2
If a drug blocks the receptors in neuromuscular junction, but not the receptors in ganglion, it would be a ___ antagonist, blocking ___ receptor.
N1
the neurotransmitter of the parasympathetic postganglionic neurons is __
ACh (same as ANS nurotransmitter)
parasympathetic postganglionic receptors are _______ instead of nicotinic
muscarinic
activation of muscarinic receptors does what?
activate G-proteins to:
- activate PLC to ➙ increase [Ca++]i and PKC
- inhibit adenylyl cyclase to decrease cAMP
- open or close K+ channels
what does it mean that muscarinic receptors are metabotropic?
Muscarinic receptor responses are slow compared to nicotinic
Muscarinic receptor responses are slow/fast compared to nicotinic
slow
what is the transmitter of postganglionic sympathetic neurons?
Norepinephrine
In adrenal medullary chromaffin cells, the major product is
epinephrine (adrenaline)
Norepinephrine and epinephrine are both called
catecholamines
All sympathetic target cells contain ________ receptors which are G-protein coupled
adrenergic (slow effect, metabotropic)
what are the 2 major subtypes of adrenergic receptors?
alpha
alpha-1: blood vessels (vasoconstriction)
alpha-2: presynaptic terminals (transmitter release), GI walls (movement/secretion of GI)
beta
beta-1: heart (increased heart rate and contracility)
beta-2: bronchial muscle (bronchodilation)
beta-3: fat cells (lipolysis)
which receptors are responsible for relaxing bronchi?
beta-2
which receptors are responsible for accelerating heartbeat ?
beta-1
which receptors are responsible for constricting blood vessels on skin/GI ?
alpha-1
which receptors are responsible for inhibiting peristalsis and secretion ?
alpha-2
which receptors are responsible for stimulating lipolysis ?
beta-3
origin of preganglionic neuron: sympathetic vs parasympathetic
sympathetic
thoracolumbar → nuclei of spinal cord segments (T1-L2)
parasympathetic
craniosacral → Nuclei of cranial nerves III, VII,IX, X in brain stem, spinal cord segments S2-S4
length of preganglionic neuron axon: sympathetic vs parasympathetic
sympathetic
short
parasympathetic
long
length of postganglionic neuron axon: sympathetic vs parasympathetic
sympathetic
long
parasympathetic
short
effector organs: sympathetic vs parasympathetic
both → smooth and cardiac muscle, glands
neurotransmitter in ganglion: sympathetic vs parasympathetic
both → Ach
receptor type in ganglion: sympathetic vs parasympathetic
both → nicotinic
neurotransmitter in effector organs: sympathetic vs parasympathetic
sympathetic
norepinephrine (except sweat glands use Ach)
parasympathetic
Ach
receptor types in effector organs: sympathetic vs parasympathetic
sympathetic
alpha 1//2
beta 1/2/3
parasympathetic
muscarinic M1-5
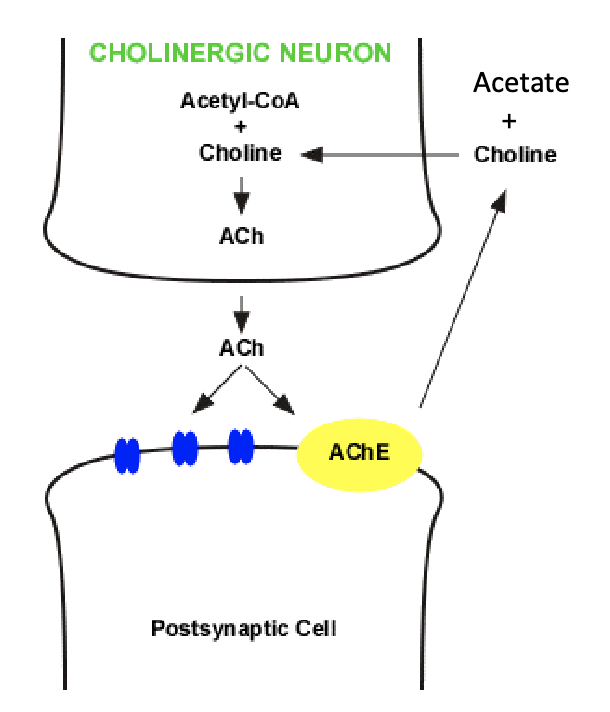
what does acetyl cholinesterase do?
present in ganglia and target tissues
splits the ester bond connecting the choline to acetate
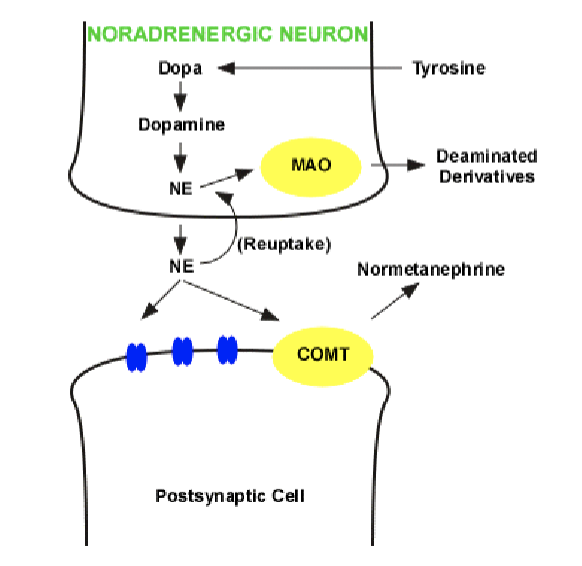
which enzymes are involved in reducing epinephrine and norepinephrine to vanillylmandelic acid (VMA)?
monoamine oxidase (MAO)
catecholamine-O-methyl transferase (COMT)
what do monoamine oxidase (MAO) and catecholamine-O-methyl transferase (COMT) do?
together reduce epinephrine and norepinephrine to vanillylmandelic acid (VMA) which is eliminated by the kidneys
what is the major route for inactivation of catecholamines?
reuptake into adrenergic nerve terminals by active transport
visceral afferents are responsible for what bodily functions?
blood pressure
distension of bladder
somatic afferents are responsible for what bodily functions?
pressure and pain
special senses afferents are responsible for what bodily functions?
vision, hearing, taste, and smell
what are the afferent inputs to the ANS?
visceral
somatic
special senses
ANS reflexes are unconscious automatic responses and can involve what structures:
spinal levels
medullar oblongata
hypothalamus
thalamus and cortex (higher centers)
How do the PNS and SNS produce opposite effects on their target organs?
Mechanism 1: opposing muscles can be innervated separately by the two systems: e.g. pupil
Mechanism 2: Both PNS and SNS neurons activate the same target cells which express different receptors for each transmitters and different second messenger systems: e.g. the sinoatrial node of the heart
one mechanism of how PNS and SNS can produce opposite effects on their target organs involve having opposing muscles innervated separately by the 2 systems.
what does the PS neuron activate? what does the S neuron activate?
• Parasympathetic neurons activate sphincter pupillae to constrict the pupil
• Sympathetic neurons activate dilator pupillae to dilate the pupil
another mechanism of how PNS and SNS can produce opposite effects on their target organs involve activating the same target cells expressed by different receptors for each transmitters and different second messenger systems.
what does the PS neuron stimulate? what does the S neuron stimulate?
Parasympathetic neurons stimulate muscarinic receptors (M2) to activate Gi protein which:
- decreases resting membrane potential
- decreases heart rate
Sympathetic neurons stimulate beta-1 adrenergic receptors which activate Gs protein to:
- increase heart rate
- increase cardiac contractility
what ANS reflexes involve spinal levels?
sweating
GI
urination before potty training
(No. 4)
what ANS reflexes involve the medulla oblongata?
blood pressure control
respiratory control
(No. 3)
what ANS reflexes involve the hypothalamus?
major integration center for the ANS controls many functions
Thermal regulation
metabolism
hunger
thirst
pupillary dilation
(No.2)
what is the condition called when all ANS reflexes involving spinal levels, medulla oblongata, hypothalamus, and higher centers are working to keep organ systems alive but there is no consciousness?
vegetative state