Chapter 5, 6, 7
1/54
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Homework Questions
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
55 Terms
The working-age population is defined as the number of
people over the age of 16 who are not in jail, hospital, or other institution
Full-time students and prisoners are
not in the labor force.
Which is NOT considered to be in the labor force?
a person who is not working and who has not tried to find a job
The unemployment rate is the ________ who are unemployed.
percentage of people in the labor force
The percentage of people employed aged 16 years and older divided by the working-age population is known as the
employment-to-population ratio.
Who of the following is counted as unemployed?
Glenn, a student who just graduated from college last week and is currently looking for a job
Suppose that Matt quits a job with the XYZ Corporation in order to look for more rewarding employment. Matt is best be considered as
frictionally unemployed
The best example of a cyclically unemployed individual is
Charles who lost his job as a real estate salesperson when the housing market went soft because of a recession.
Full employment occurs when
cyclical unemployment is zero
The economy is at full employment when
all unemployment is frictional or structural.
The unemployment rate generally falls during ________ in the business cycle.
an expansion
The cost of inflation to society includes
I. The opportunity costs of resources used by people to protect themselves against inflation.
II. The diversion of productive resources to forecasting inflation.
both I and II
In a period of rapid, unexpected inflation, resources can be lost
when firms use resources to forecast inflation
Hyperinflation is defined as
very high inflation rates.
If the CPI for this year is 220 and the CPI for last year was 215, the inflation rate is
just over 2 percent.
The currently used method for calculating the CPI
probably overstates inflation
The best definition for economic growth is
a sustained expansion of production possibilities measured as the increase in real GDP over a given period.
We are interested in long-term growth primarily because it brings
higher standards of living.
The Rule of 70 is used to
estimate how long it will take the level of any variable to double.
Using the Rule of 70, if China's current growth rate of real GDP per person was 7 percent a year, how long would it take the country's real GDP per person to double?
10 years
A country in which real GDP per person has grown more slowly than the United States since 1980 would be
Mexico
Over the last 120 years, the average U.S. growth rate in real GDP per person was about
2 percent per year
The real wage rate measures the
quantity of goods and services that an hour of work will buy
Because the productivity of labor decreases as the quantity of labor employed increases
the quantity of labor a firm demands increases as the real wage rate decreases.
Which of the following is TRUE regarding the labor market?
I. The labor supply curve slopes upward because firms maximize profits as they hire more workers.
II. If the real wage rate falls, the quantity of labor firms demand increases.
III. The demand for labor curve slopes downward because as the real wage rate falls, workers demand to work fewer hours.
II only
If the price level falls by 5 percent and workers' money wage rates remain constant, firms'
quantity of labor demanded will decrease.
If the price level increases and workers' money wage rates remain constant, which of the following will occur?
I. The quantity of labor supplied will decrease
II. The real wage rate will decrease
III. The labor supply curve will shift rightward
I and II
If the labor market is in equilibrium and then the labor supply curve shifts rightward
there will be a surplus of labor at the original equilibrium wage rate.
Employment and (total) potential GDP increase if the
labor supply curve shifts rightward and the labor demand curve does not shift.
If the population increases, then potential GDP ________ and employment ________.
increases; increases
Potential GDP per labor hour can increase due to
increases in labor productivity.
Labor productivity is
real GDP per hour of labor.
If both the supply of labor and the demand for labor increase, then
potential GDP increases.
Technological change
increases potential GDP.
Human capital is the
skill and knowledge accumulated by humans.
The nominal interest rate approximately equals which of the following?
the real interest rate plus the inflation rate
If you lend a dollar for a year and at the end of the year the price level has risen by 10 percent
you must have earned a nominal interest rate of 10 percent to maintain the purchasing power of your loan.
When the inflation rate is zero, the
real interest rate equals the nominal interest rate.
When the inflation rate is negative, the
real interest rate is greater than the nominal interest rate.
Suppose that you took out a $1,000 loan in January and had to pay $75 in annual interest. During the year, inflation was 6 percent. Which of the following statements is CORRECT?
The nominal interest rate is 7.5 percent and the real interest rate is 1.5 percent.
Assume you save $1,000 in a bank account that pays 8 percent interest per year and the inflation rate is 3 percent. At the end of the year you have earned
a real return of $50.
Other things remaining the same, the greater the expected profit
the greater the amount of investment.
The demand for loanable funds curve shows that as the ________ interest rate increases, there will be ________ the curve.
real; movement up along
A movement downward along the demand for loanable funds curve occurs when
the real interest rate falls
Greater optimism about the expected profits from investment projects
shifts the demand for loanable funds curve rightward.
Which of the following shifts the demand for loanable funds curve leftward?
a decrease in the expected profit
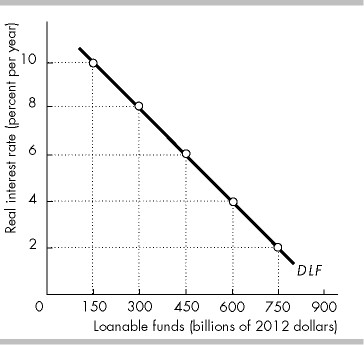
In the above figure, if the real interest rate is 6 percent, the quantity of loanable funds demanded is
$450 billion.
If households' disposable income decreases, then
households' saving will decrease.
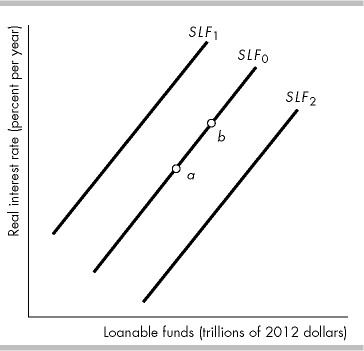
In the above figure, the economy is at point a on the initial supply of loanable funds curve SLF0. What happens if the real interest rate rises?
There would be a movement to a point such as b on supply of loanable funds curve SLF0.
Technological progress that increases the expected profit shifts the demand for loanable funds curve
rightward and increases the real interest rate.
When a government has a budget surplus, the surplus
helps finance investment.
The idea that a government budget deficit decreases investment is called
the crowding-out effect.
If the government has a budget deficit, crowding out might occur. Crowding out is associated with all of the following EXCEPT
decreased private saving.
If China's government runs a budget surplus and there is no Ricardo-Barro effect, there will be ________ in the supply of loanable funds, private saving ________ and investment ________.
an increase; decreases; increases
The Ricardo-Barro effect of a government budget deficit refers to
a change in private savings supply.