architecture of the CPU flashcards
1/18
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
19 Terms
what is a computer?
an electronic device that takes input, processes data and outputs a result. it may also communicate and store processed data.
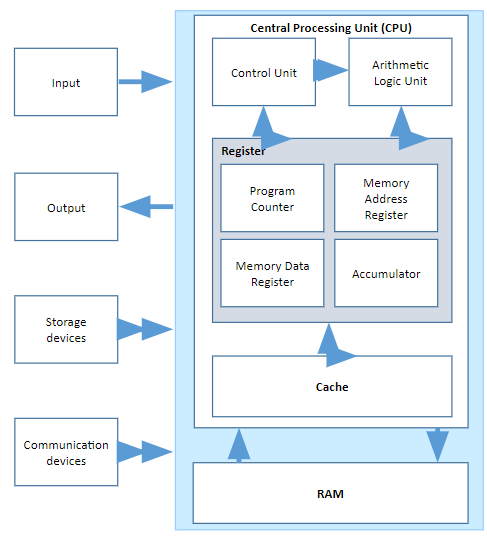
CPU
Central Processing Unit
purpose is to process and execute instructions
main components of the CPU and functions
Arithmetic Logic Unit (ALU) - performs calculations
Control Unit (CU)- decodes instructions and sends signals to control how data moves around the CPU.
what are registers?
tiny, super-fast pieces of onboard memory, inside the CPU, each with a specific purpose
registers in the CPU
Memory Address Register (MAR)
Memory Data Register (MDR)
Program Counter (PC)
Accumulator (ACC)
MAR
Memory Address Register
stores the memory address where data is to be stored or fetched
MDR
Memory Data Register
holds data fetched from or to be written to the main memory
PC
Program Counter
holds the address of the next instruction
ACC
Accumulator
holds the results of calculations
cache
memory that provides fast access to frequently used instructions and data without having to go back to the main memory (RAM)
why do we need cache?
improves performance of computer - reduces number of times that the processor has to access main memory
by storing frequently accessed data in cache, the processor can access data more quickly
what factors affect CPU performance?
clock speed
number of cores
cache size
how does clock speed affect the CPU’s performance?
the faster the clock speed, the faster instructions are processed. (the faster the CPU will run)
how does cache size affect the CPU’s performance?
cache is faster than main memory (RAM).
the larger the cache size, the less time will be spent accessing the RAM and for the processor to wait for instructions to be fetched → CPU will work faster
how does the number of cores affect the CPU’s performance?
the more cores a CPU has, the greater the number of instructions it can process in a given space of time.
von Neumann architecture
based on the stored-program concept, meaning both instruction data and program data are stored in the same memory in binary form
fetch-execute cycle
Data is fetched from main memory (RAM) into the CPU/registers to be decoded
CPU decodes instructions to be ready for processing
CPU performs/process instructions
embedded system
a computer system with a dedicated function within a larger mechanical system. examples:
traffic lights
hospital equipment
factory equipment
typical properties of embedded systems
Low power consumption
Small size
Rugged operating ranges
Low cost per unit