Highschool Thermo
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
27 Terms
Temperature
Measure of average kinetic energy of particles in a sample of matter
Joule
Amount of energy transferred as heat kg*m²/s²
Heat
Energy transferred between samples of matter due to temperature differences
How does Heat flow
From high temperature (energy) to low temperature (energy)
Specific heat
Energy required to raise the temperature of one gram of the substance by one degree (celsius or kelvin)
Energy lost or gained equation
q = cp*m* (change in temperature)
Enthalpy Change
amount of energy absorbed by a system as heat during a process at constant pressure
Enthalpy equation
delta H = Hproducts - Hreactants
Enthalpy of reaction (delta Hreaction)
The quantity of energy transferred as heat during a chemical reaction
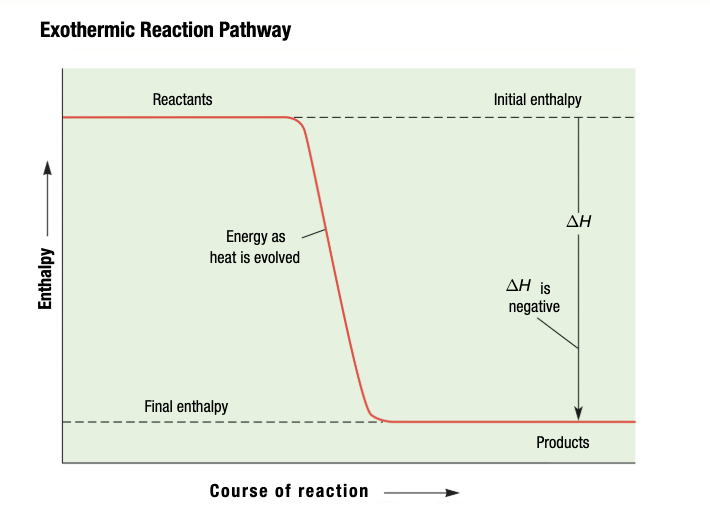
Negative for Exothermic Reactions
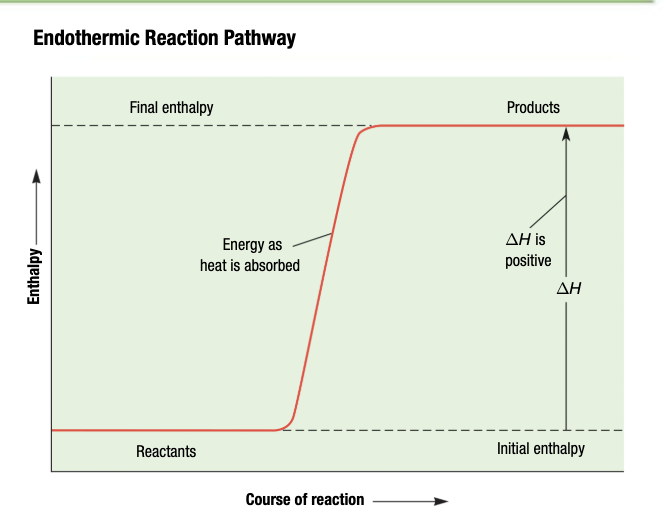
Positive for Endothermic Reactions
Thermochemical Equation
Normal Chemical Equation that includes the quantity of energy (Joules) as a term
Endothermic Reaction: energy is a reactant and absorbed from surroundings; delta H is positive
Exothermic Reaction: energy is a product and released to surroudings; delta H is negative
Thermochemical Equation Specifics
Each term in the equation represents moles of a substance
Physical state (s, l, g) matters include it when you write equations
If you multiply the equation by a factor make sure to multiply the change in enthalpy too
Enthalpy change usually isn’t influenced that much by temperature
Exothermic Reaction
System releases energy to the surroundings
Endothermic Reaction
System absorbs energy from surroundings
Molar Enthalpy of Formation
Enthalpy change that occurs when 1 mole of a compound is formed from its elements at STP (25 degress Celcius and 1 atm of pressure)
Enthalpies of formation are given at room temperature and standard pressure. So water is a liquid (does not freeze or boil at 25 degrees celcius)\
Elements in their standard state have an enthalpy of formation = 0
The most stable compounds…
Have a large negative enthalpy of formation. Anything w/ a positive enthalpy of formation is unstable
Hess’s Law Tips
Use it if they give you a bunch of thermochemical equations
Manipulate the equation so you can cross out things that appear on both sides until you get the final equation
If you flip the equation, flip the sign of the enthalpy
If you multiply the equation by a factor, multiply the enthalpy by the same factor
Add up all the enthalpies at the end and that is the total enthalpy change of the reaction (your answer)
Reactions depend on…
Both Enthalpy (delta H) & Entropy (delta S)
A spontaneous reaction can either go from
a high-energy state to a low-energy state (negative delta H)
a highly ordered state to a more “chaotic” state (positive delta S)
Entropy (S)
a measure of the degree of randomness of the particles in a system
Entropy and Phase Changes
Least Entropy S < L < G Most Entropy
Solids: Particles are fixed in position; low randomness low entropy
Liquids: Particles are close together but can move; medium randomness medium entropy
Gas: Particles are far apart and can move; high randomness high entropy
3rd Law of Thermodynamics
The entropy of a pure crystalline solid at 0 kelvin (absolute 0) is 0
Entropy change ( delta S )
Sproducts - Sreactants
Increase in Entropy + delta S
Decrease in Entropy - delta S
Forming Solutions & Entropy
Increase in Entropy, + delta S
ex. mixing gasses, dissolving a liquid in another liquid, and dissolving a solid in a liquid
Free Energy equation
delta G = delta H - T* delta S
Positive delta G = non-spontaneous reaction ( will not occur naturally)
Negative delta G = spontaneous reaction ( will occur naturally )
Natural processes proceed in the direction that lowers free energy
If delta H is negative & delta S is positive
delta G is always negative; reaction is spontaneous at the conditions provided and will proceed
If delta H is negative & delta S is negative
delta G is negative at lower temperatures; reaction is spontaneous at lower temperatures
If delta H is positive & delta S is positive
delta G is negative at higher temperatures; reaction is spontaneous at higher temperatures
If delta H is positive & delta S is negative
delta G is always positive; reaction is never spontaneous & will never proceed (in nature)