Conversions, Formulas and When to Use Them (copy)
1/16
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
17 Terms
What is the miles to kilometres conversion?
1 mile ≈ 1.6 km or 5 miles ≈ 8 km.
What is the kilograms to pounds conversion?
1 kg ≈ 2.2 lbs.
What is the litres to pints conversion?
1 litre ≈ 1.75 pints.
When can you use the cosine rule?
When you are given 2 sides and the included angle or all 3 sides.
What is the formula for calculating the frequency density? (histograms)
frequency density = frequency ÷ class width.
What are the angles in a corresponding (F) angle?
Angles are equal (the same).
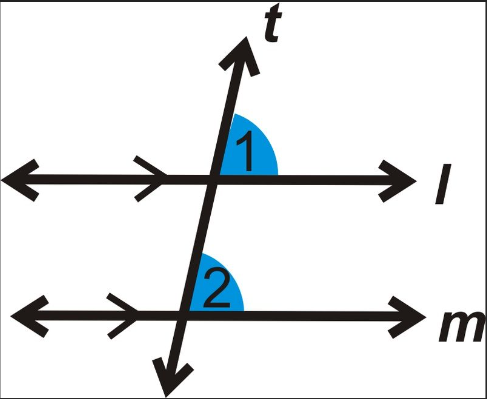
What are the angles in an alternate (Z) angle?
Angles are equal (the same).
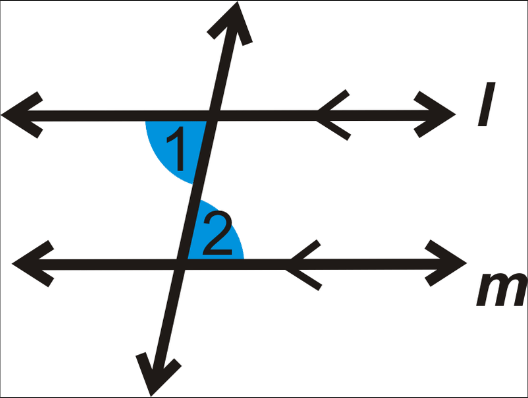
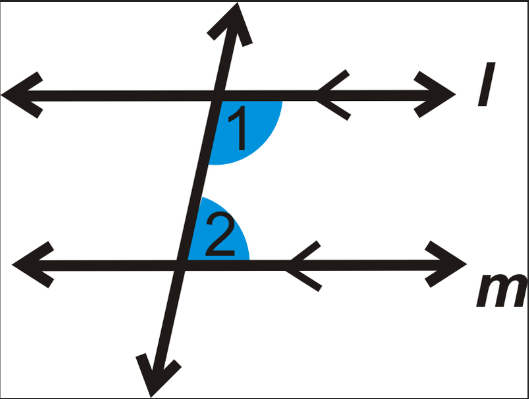
What are the angles in an co-interior (C) angle?
Angles add up to 180°.
What are the bearing rules?
Always measure from North.
Always measure in a clockwise direction.
Always write three figures (e.g. 41° —> 041°).
How do you find the acceleration on a velocity-time graph?
Find the gradient of a line (tangent).
To do this - draw line touching the curve. From this, draw right angle triangle and calculate using rise÷run.
How do you find the distance travelled using a velocity time graph?
Find the area under the curve, usually using the trapezium rule.
How do you find the area of a trapezium?
(a+b ÷ 2) x h.
What should your standard form number be between?
1-10 (e.g. 17 × 106 —> 1.7 x 107).
What is random sampling?
All data that has equal chance of being selected. For example, picking names out of a hat.
What is systematic sampling?
Choosing the sample based on the position. For example, choosing every 10th person.
What is stratified sampling?
Where the size of the sample is selected based on the proportion of different groups.
How can you tell if one of two shapes is an enlargement of the other?
The angles are identical.