Week 6 intro to derm
1/210
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
211 Terms
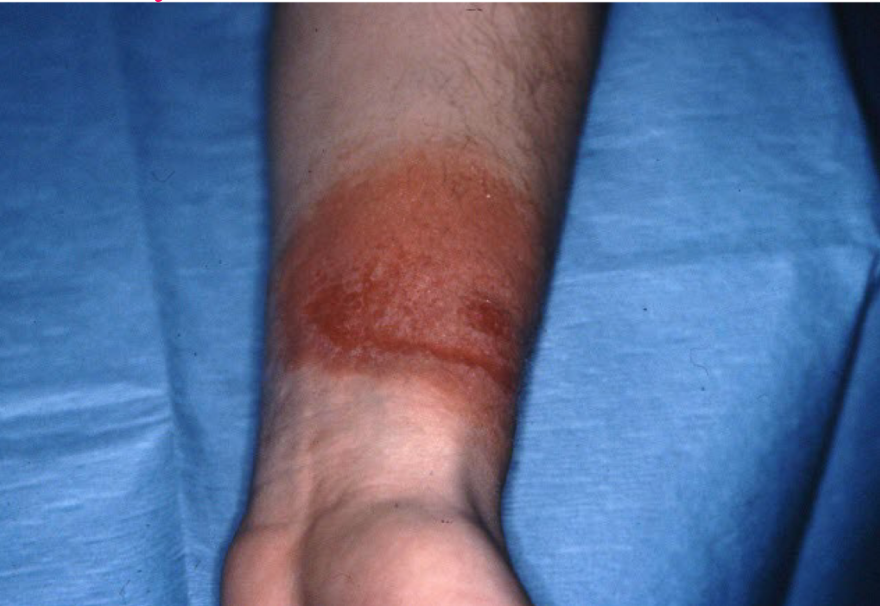
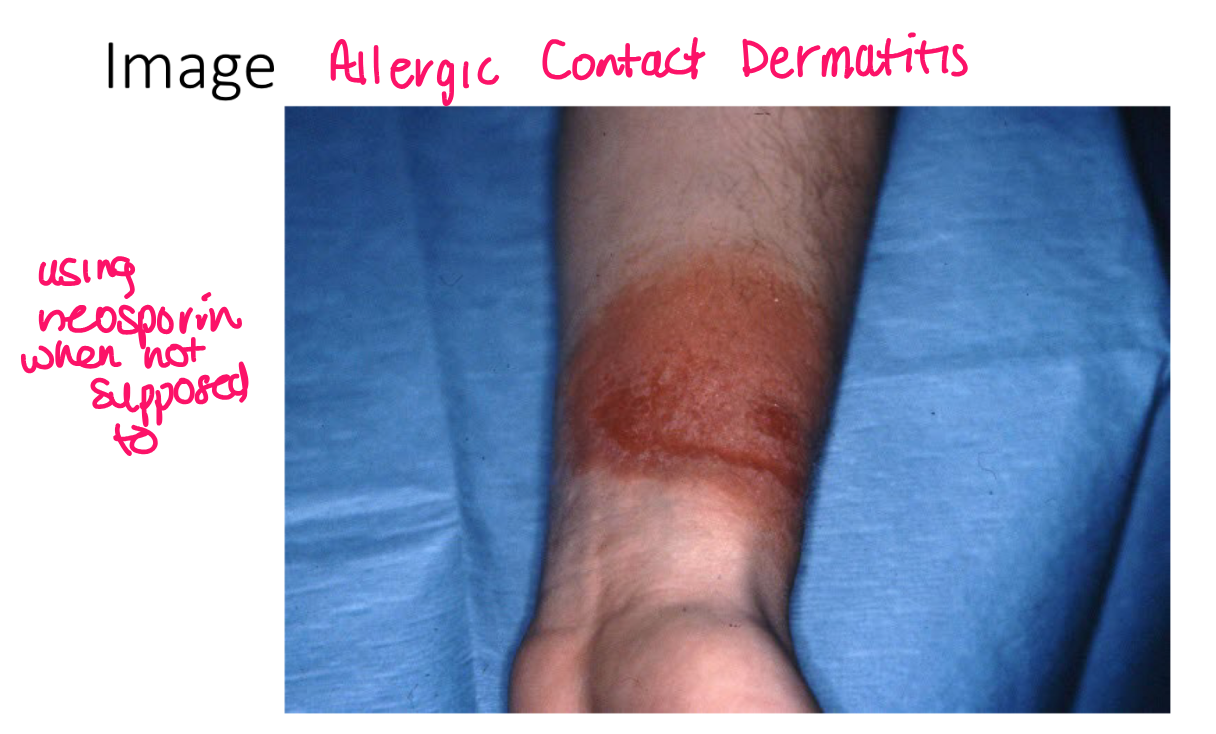
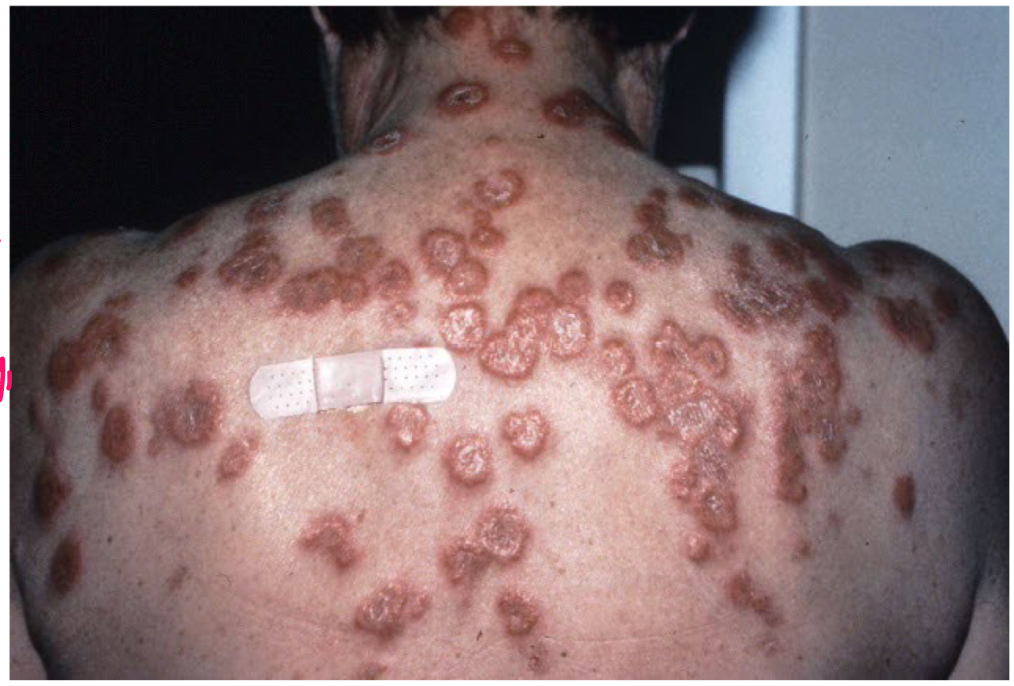
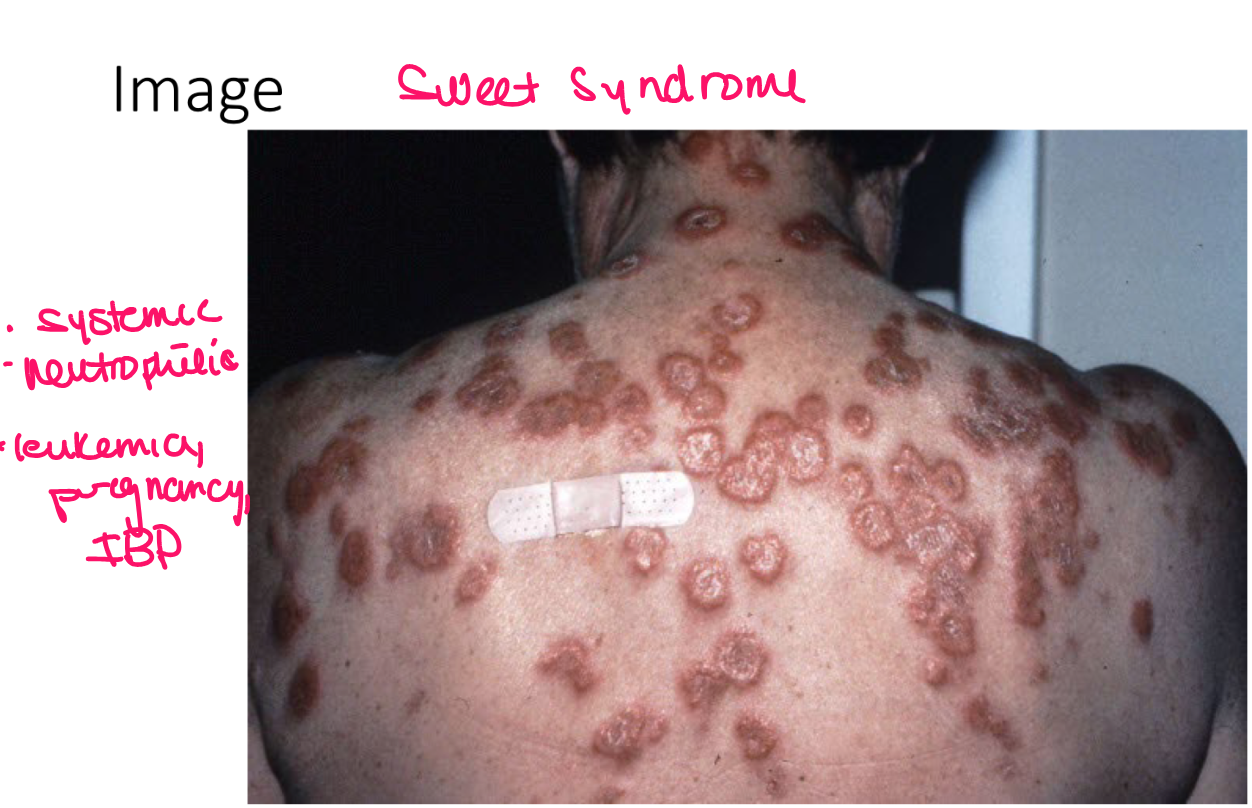
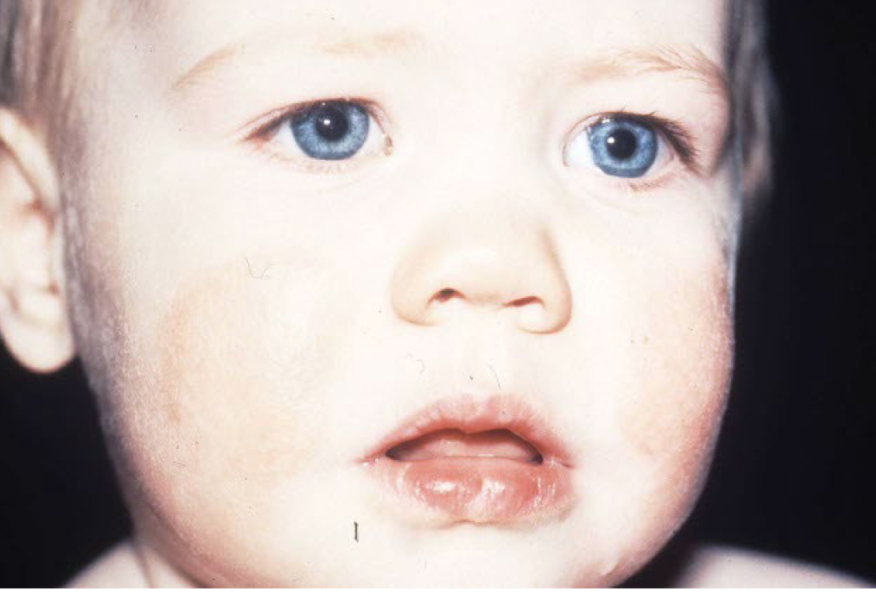
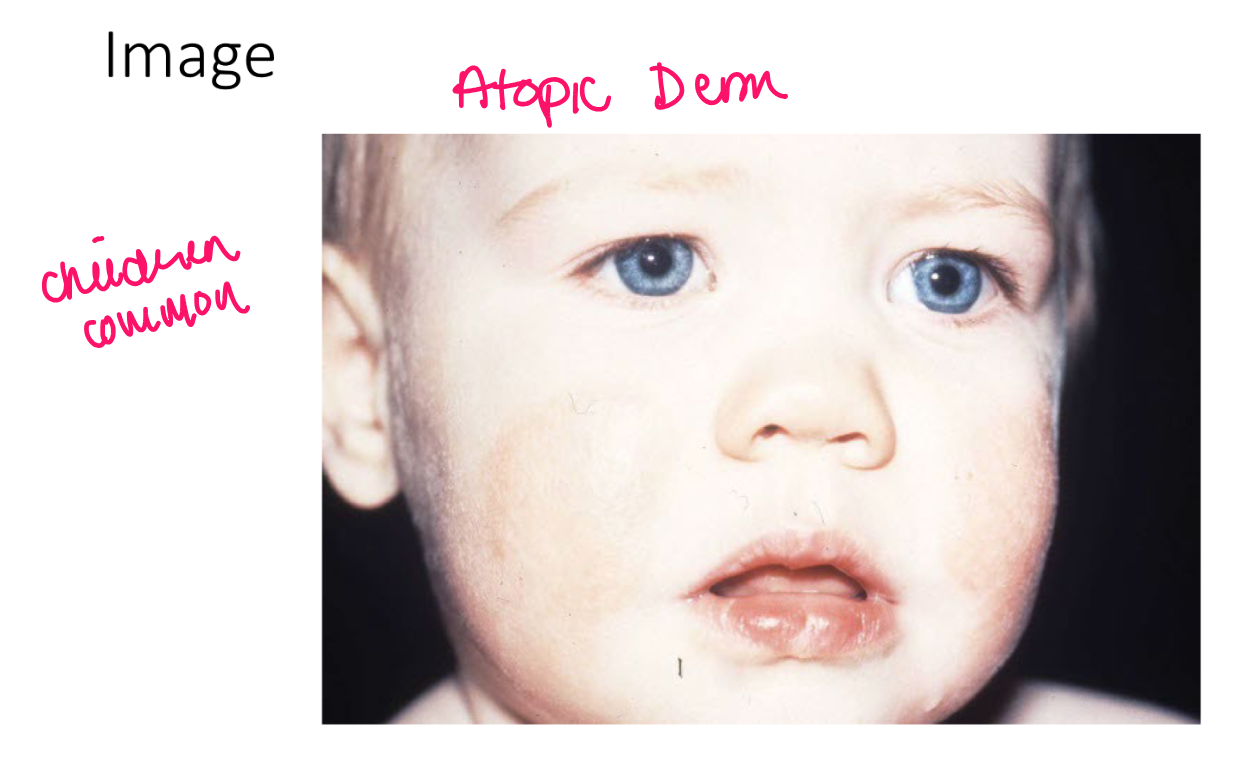
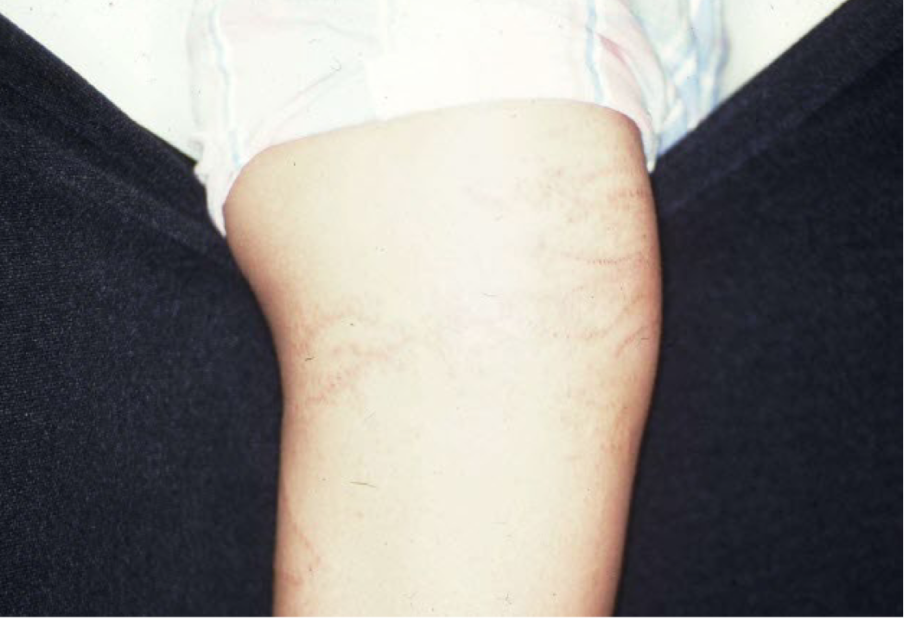
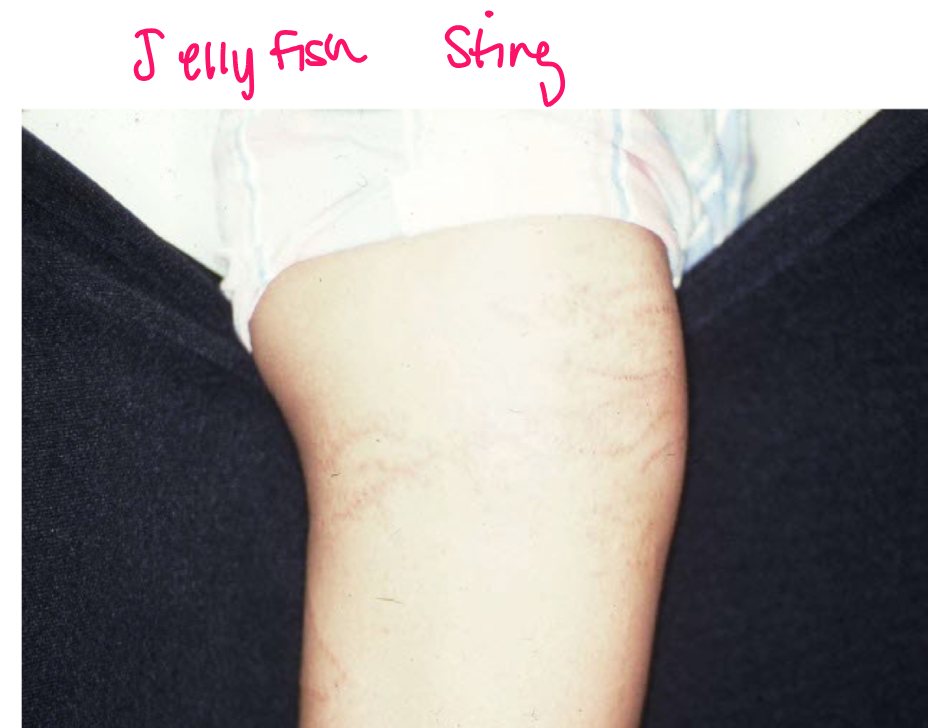
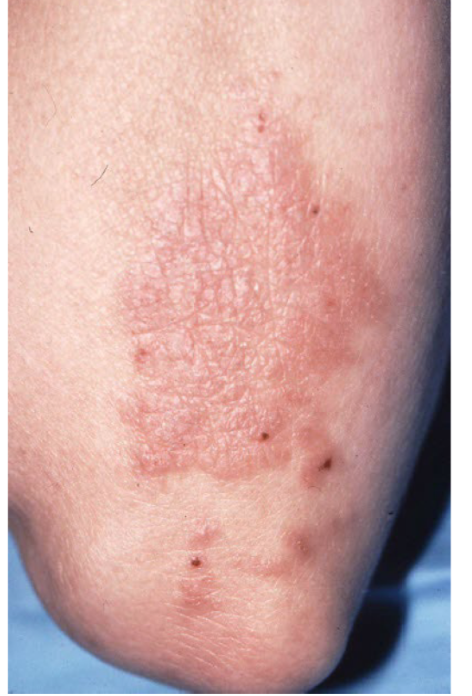
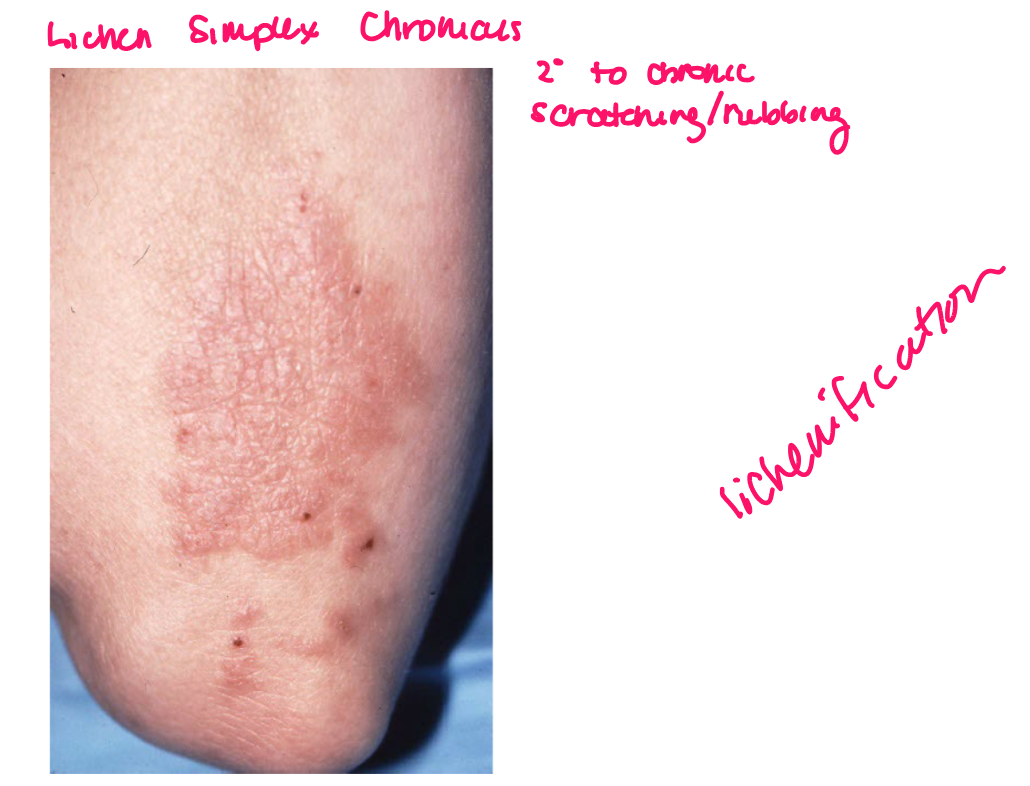
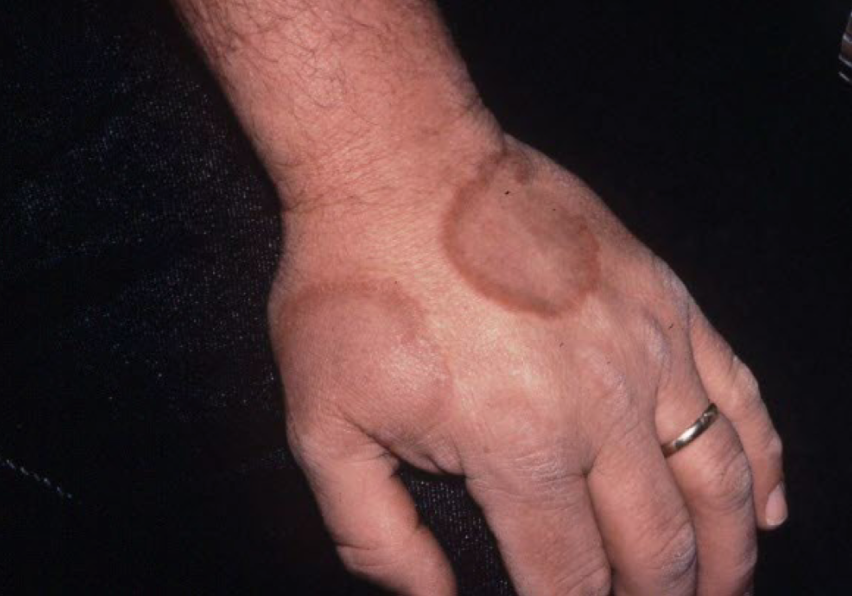
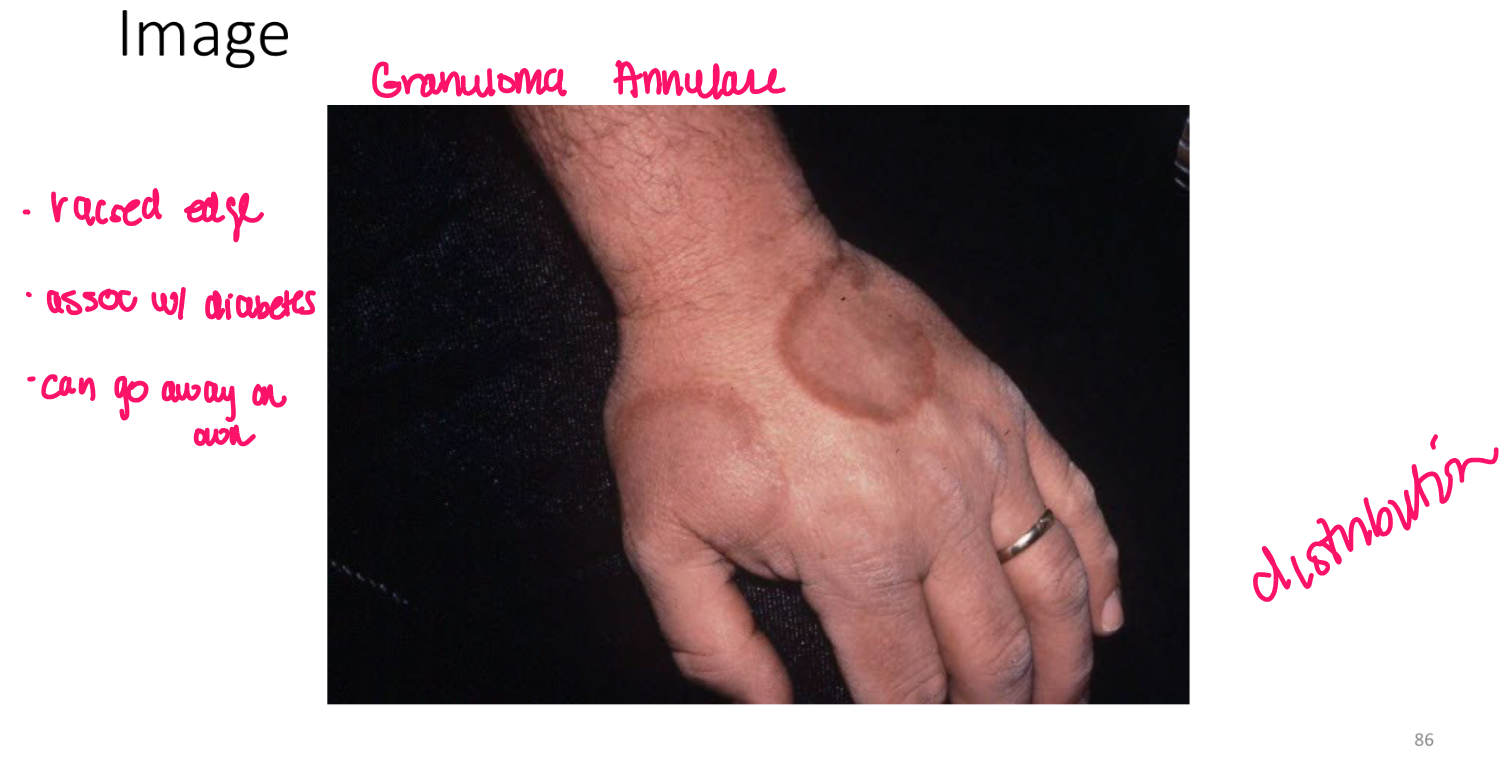
example of primary vs secondary lesion
primary: plaque from eczema
secondary: scratching —> bleeding and erythema
Papule
superficial elevated solid lesion less than 1 cm in diam
small, circumscribed
Plaque
superficial flat topped lesion greater than 1 cm in diam
palpable lesion elevated above skin
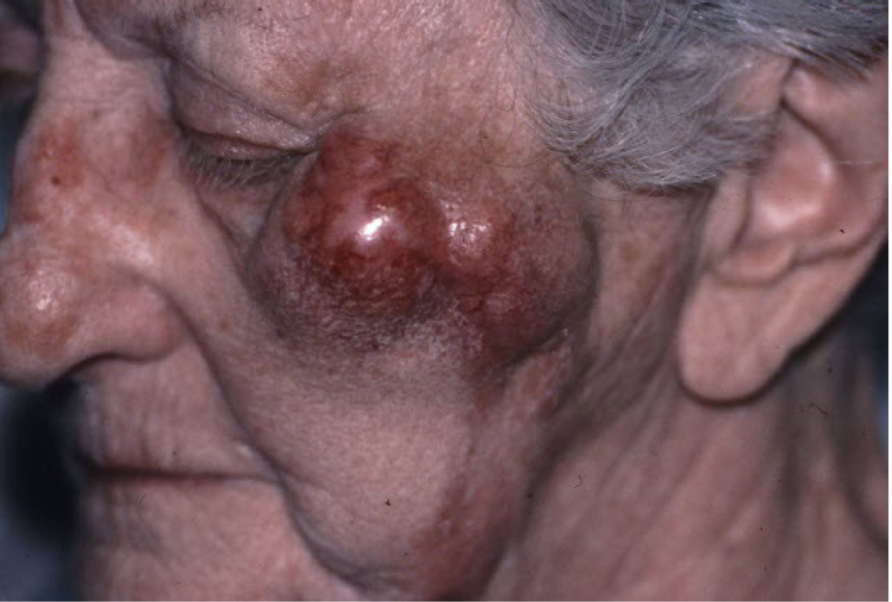
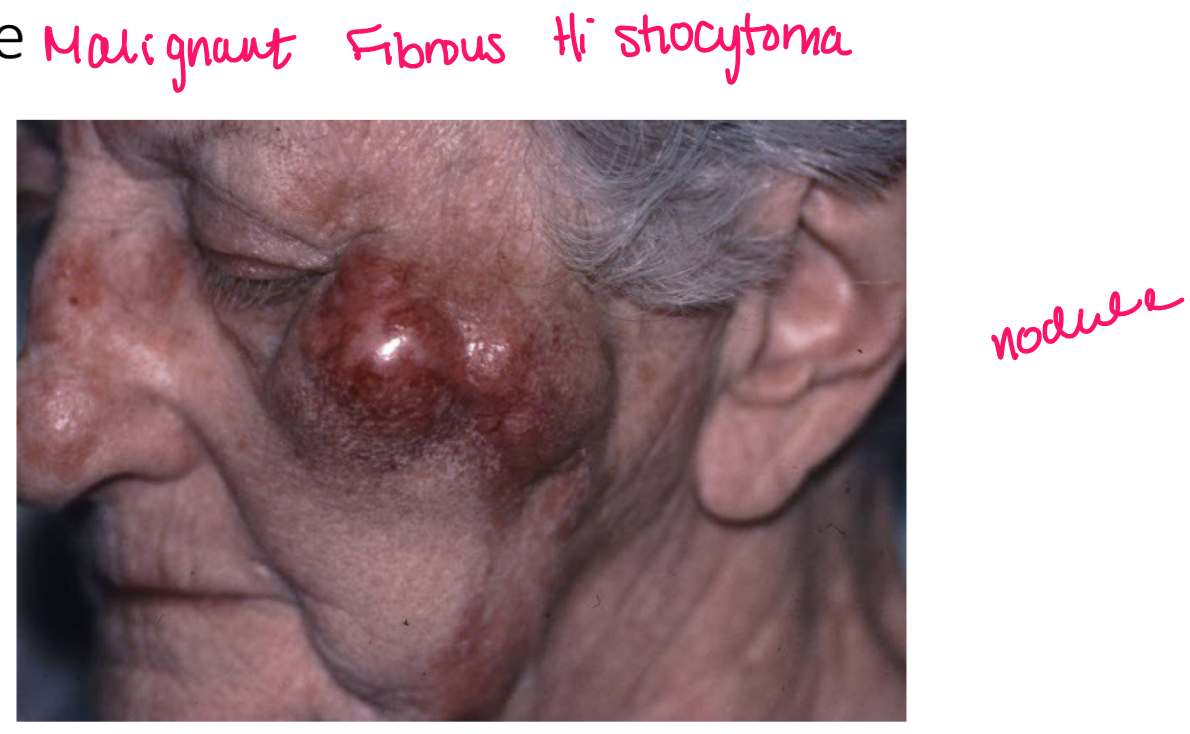
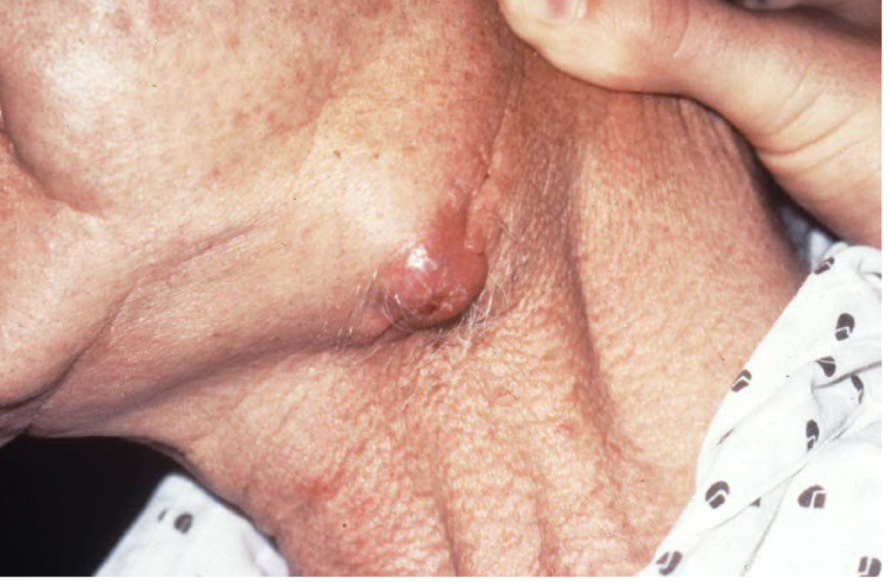
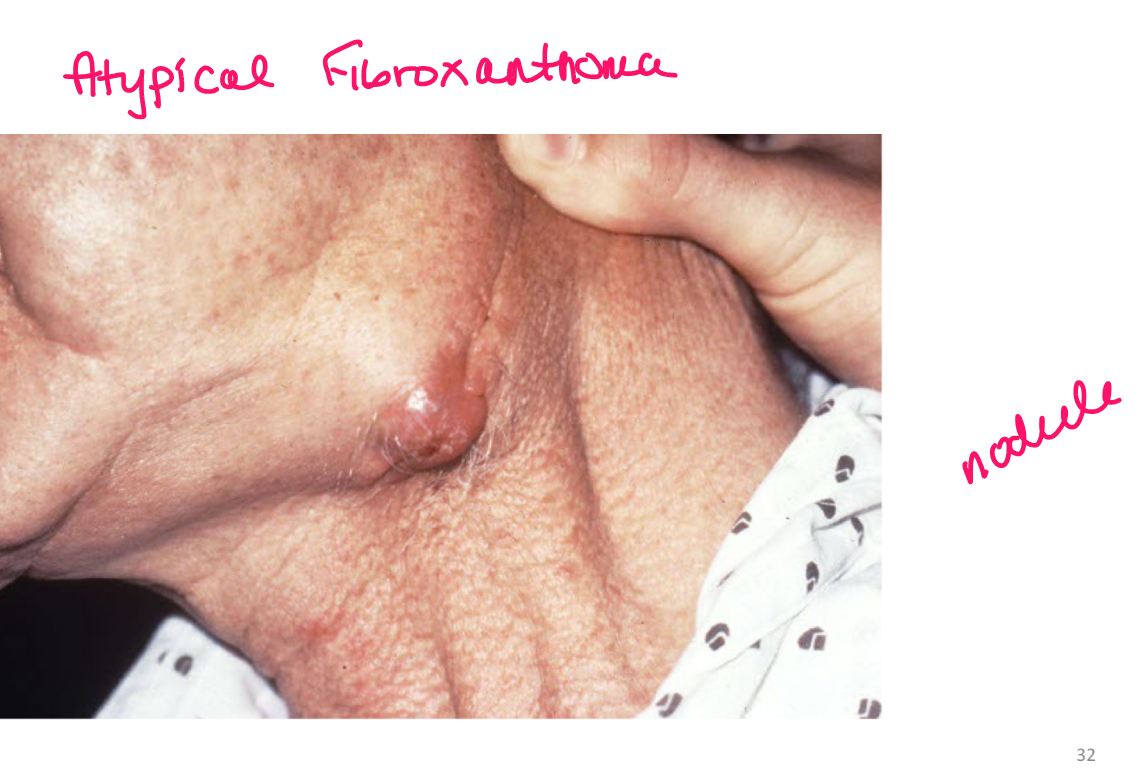
nodule
deep solid lesion usually greater than 1 cm in diam
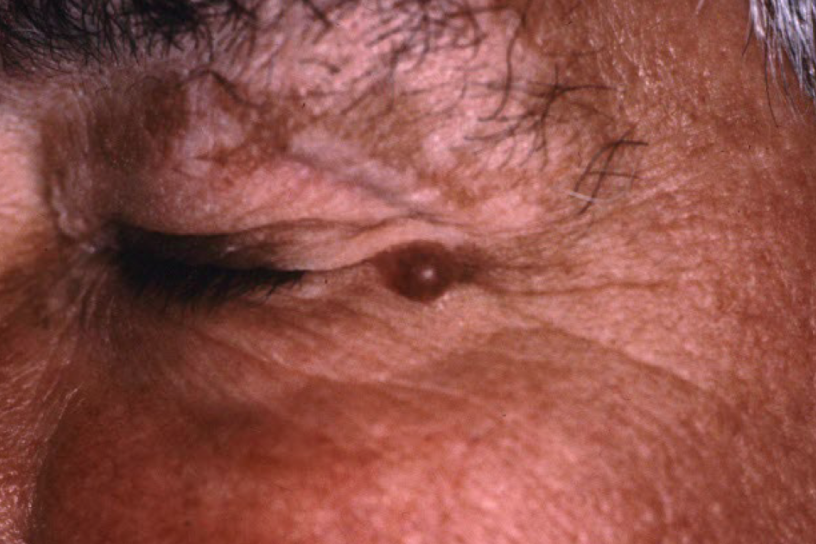
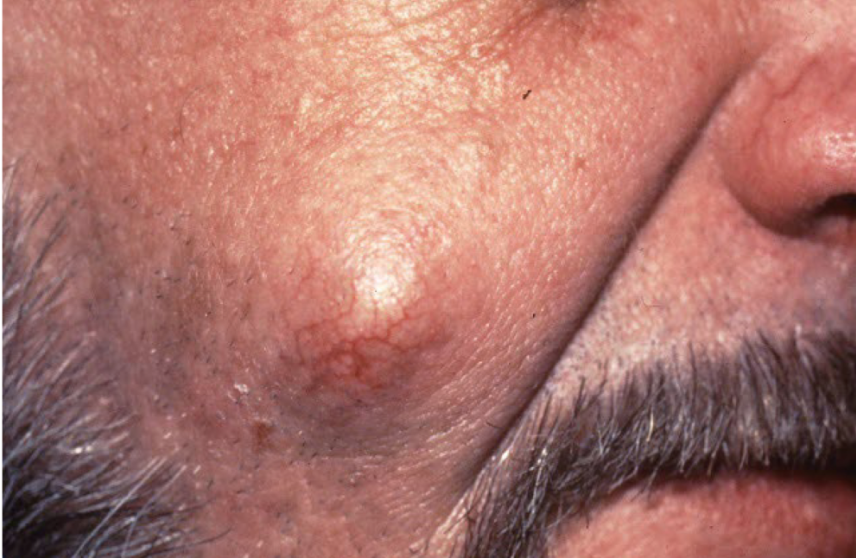
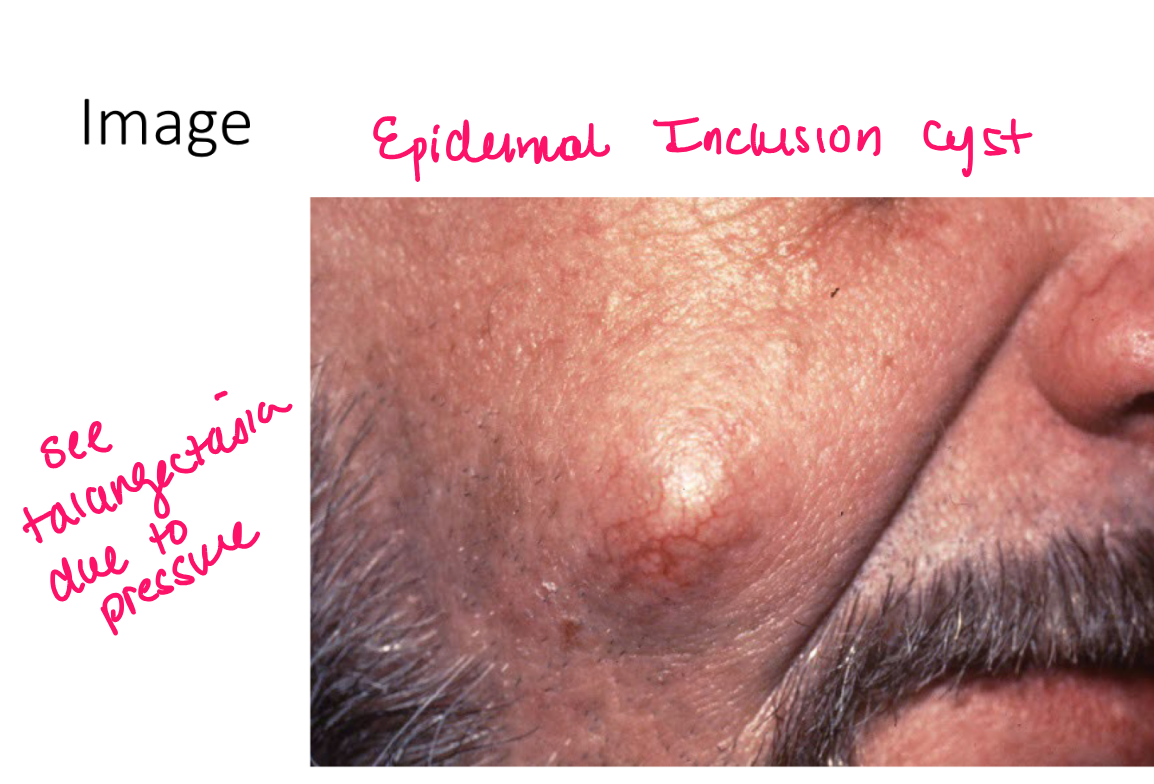
cyst
walled cavity containing keratin, mucin, or fluid
a nodule is under
epidermis
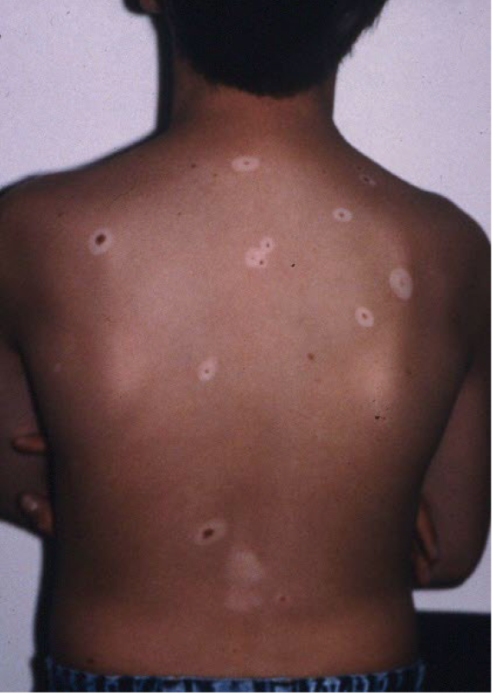
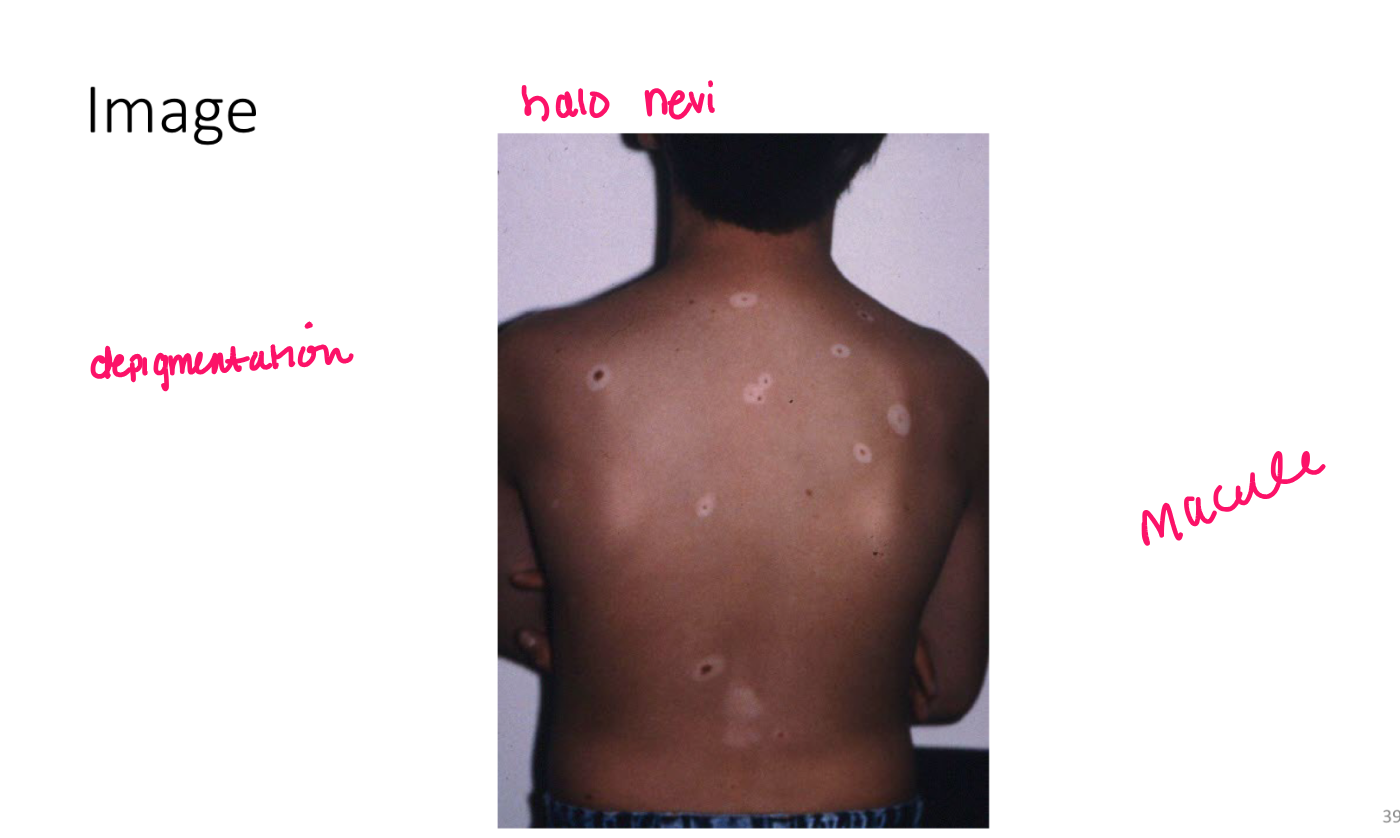
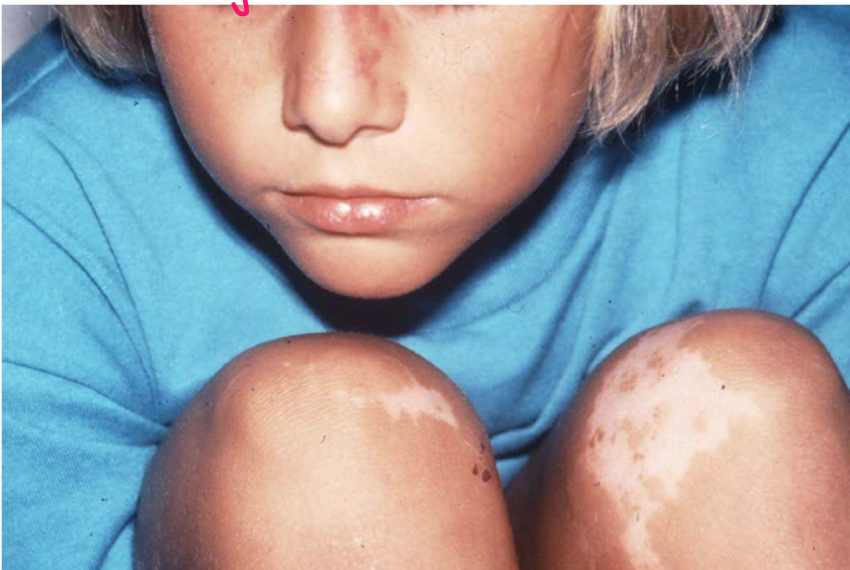
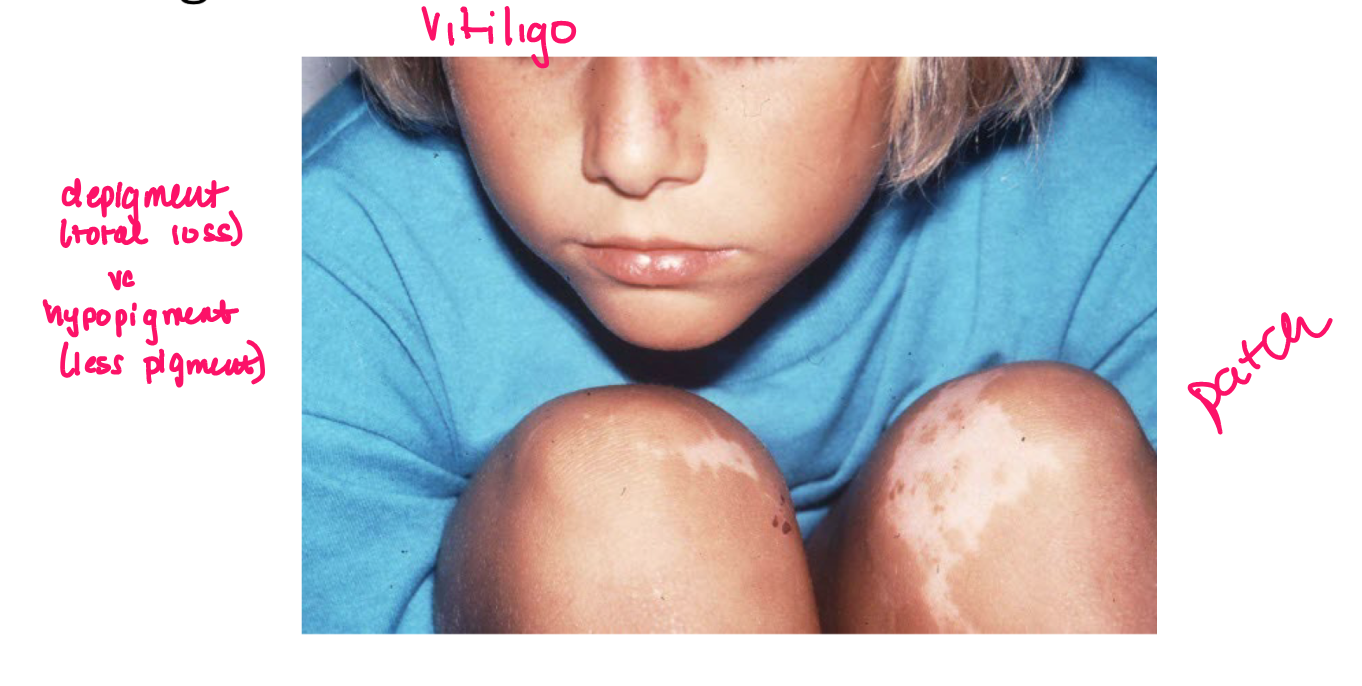
Macule
nonpalpable FLAT lesion less than 1 cm in diam
lesion w color change or texture change
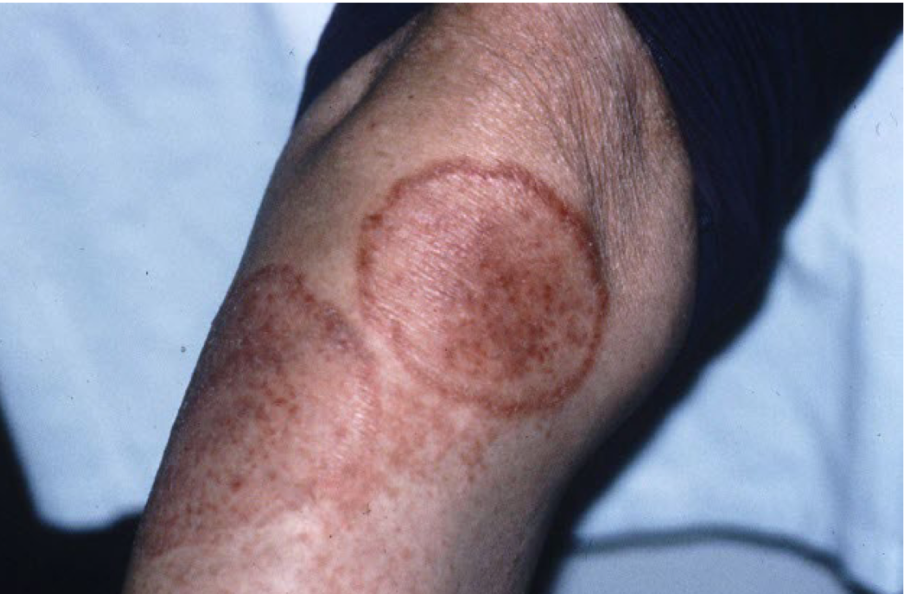
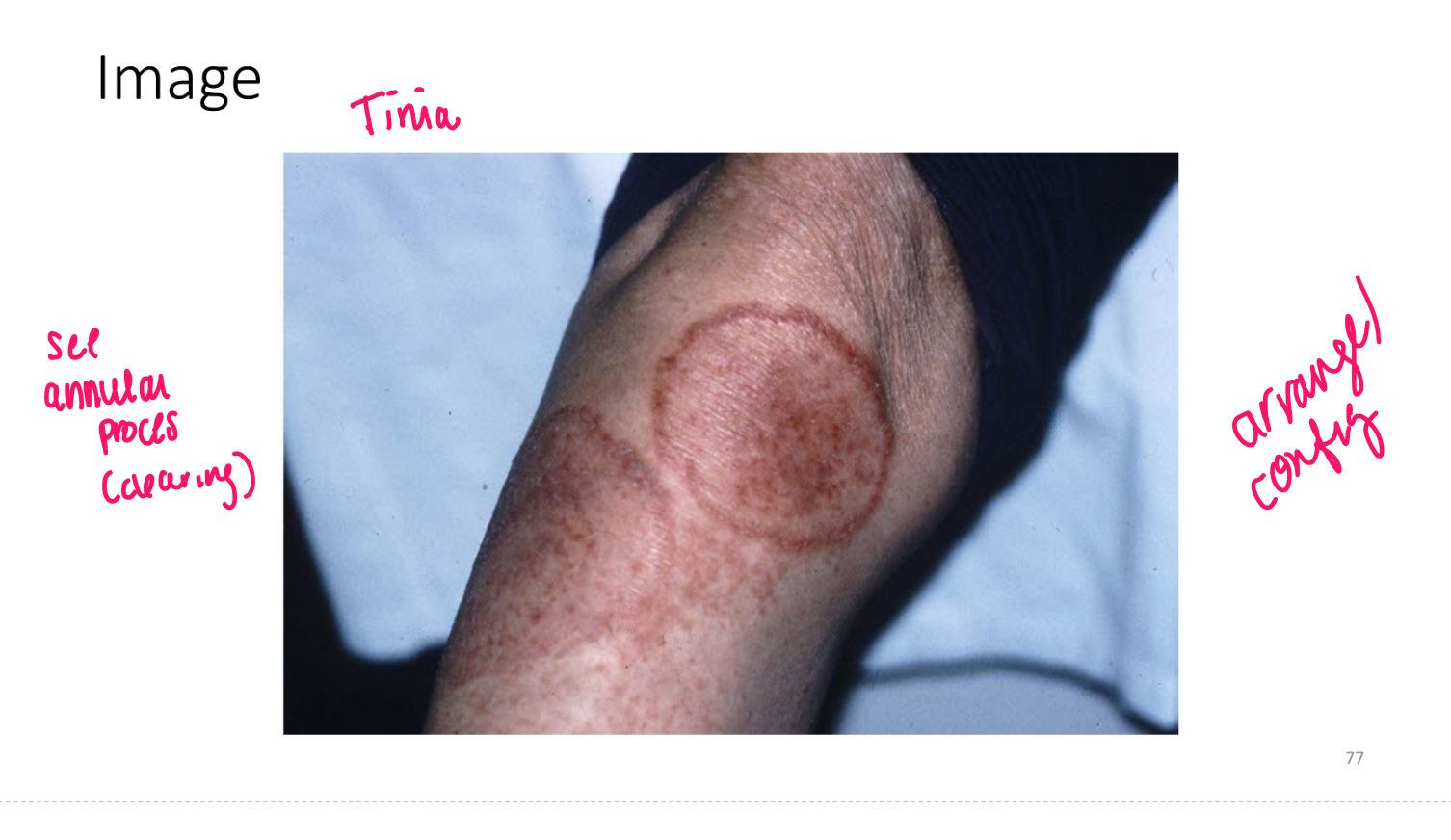
patch
nonpalp lesion greater than 1 cm diam
FLAT, essentially larger macule
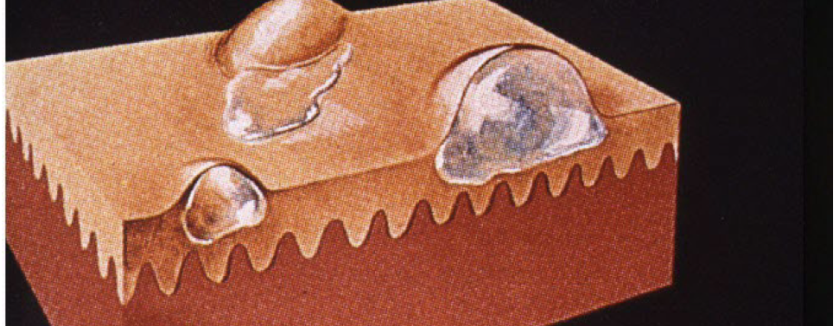
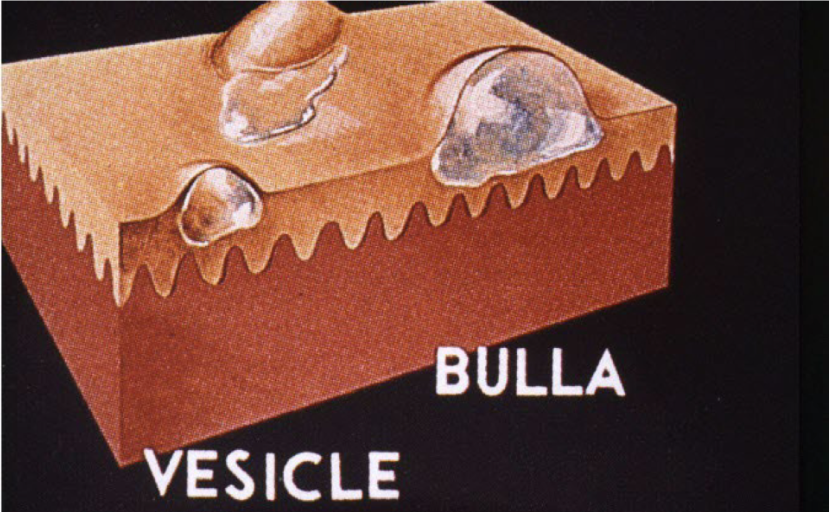
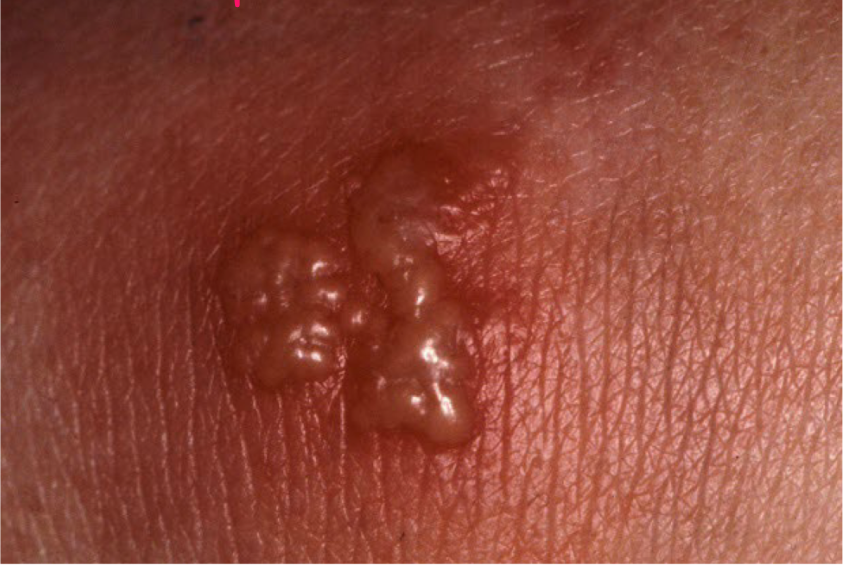
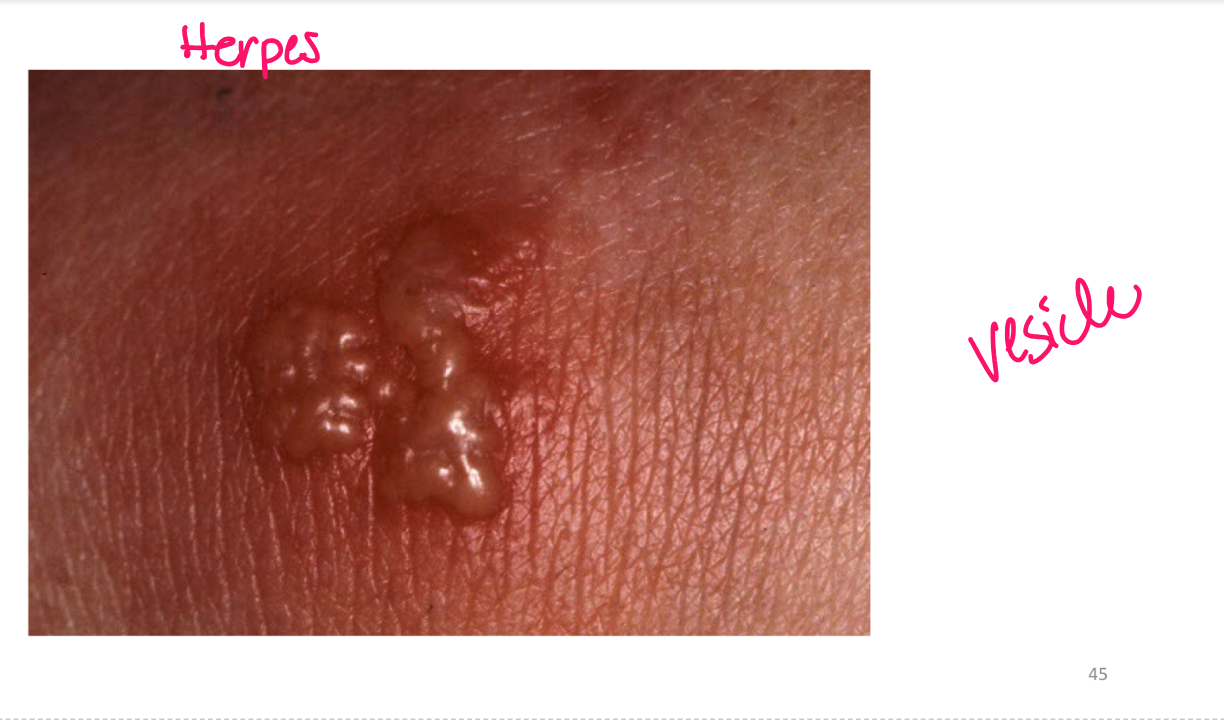
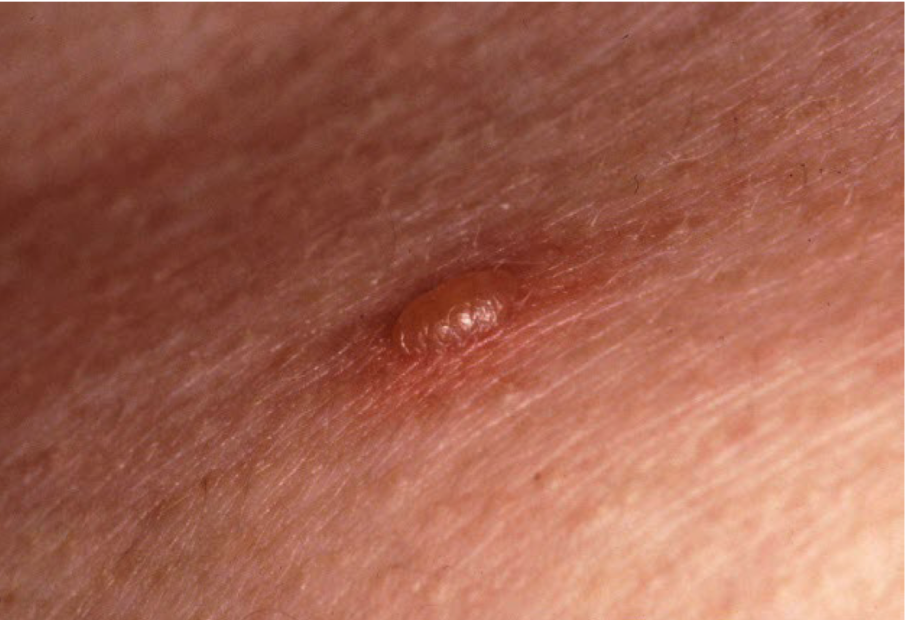
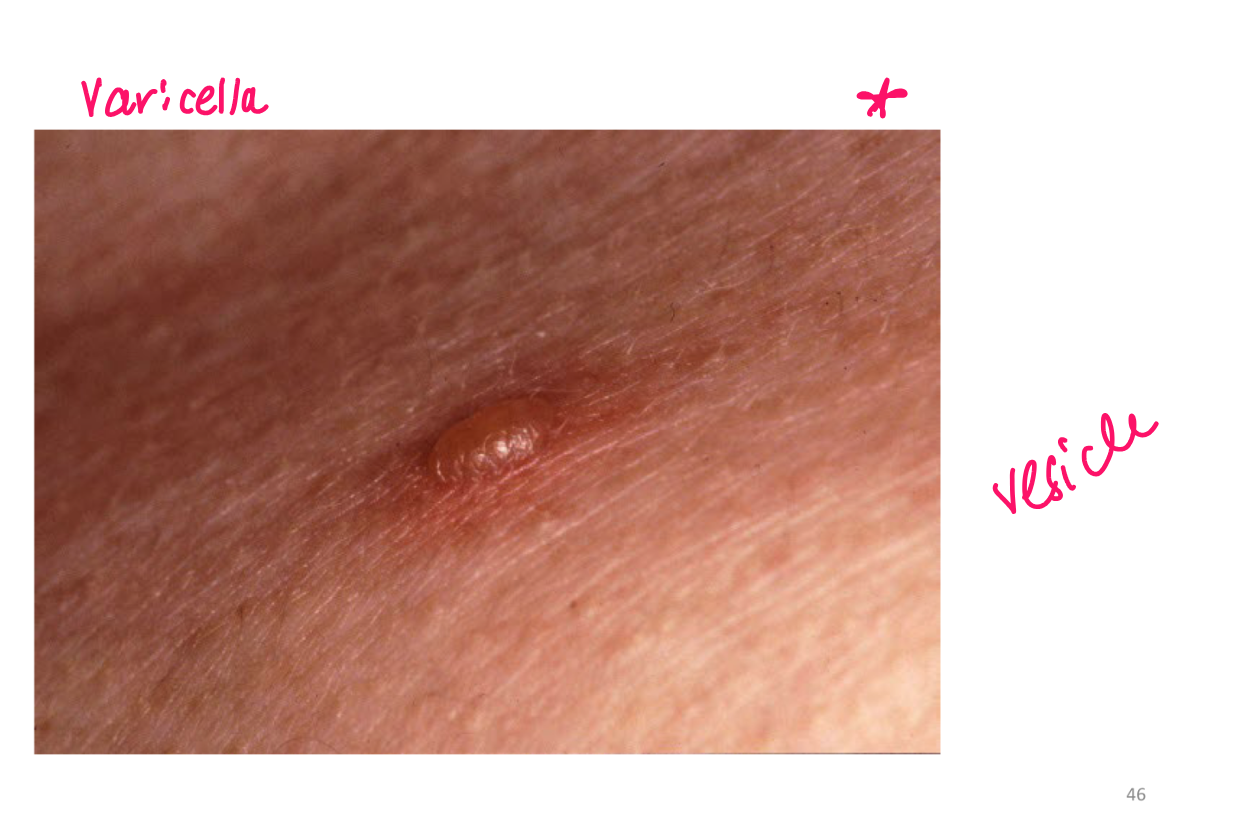
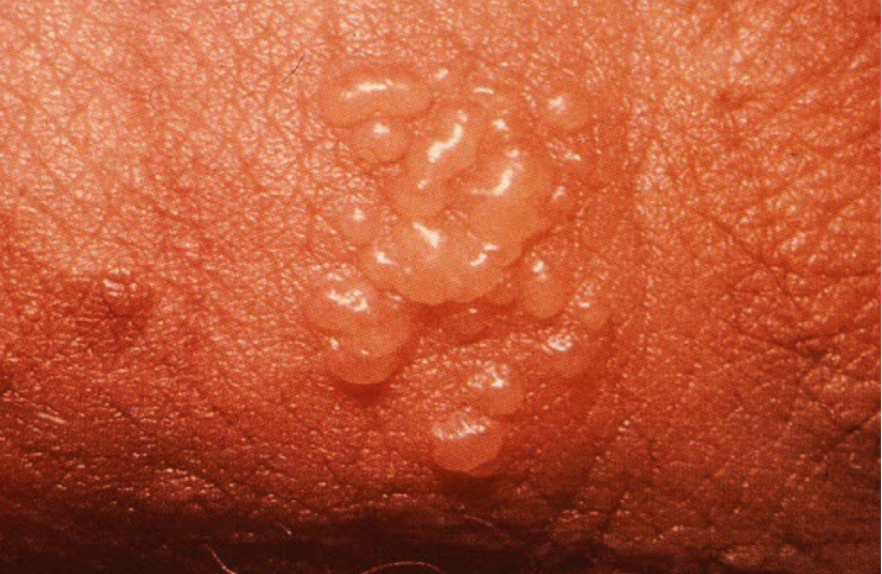
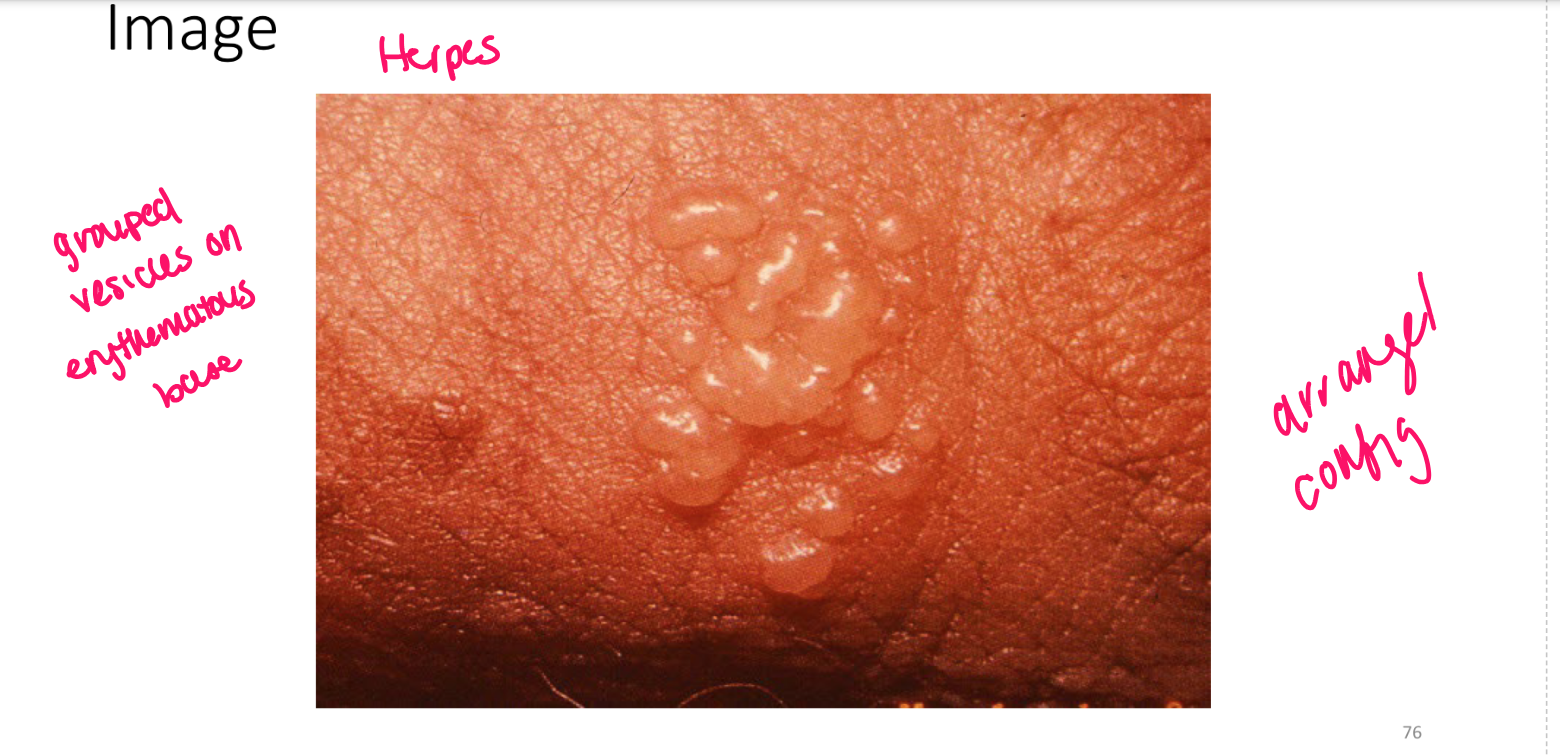
Vesicle
superficial fluid filled lesion less than 1 cm
elevated lesion, clear fluid
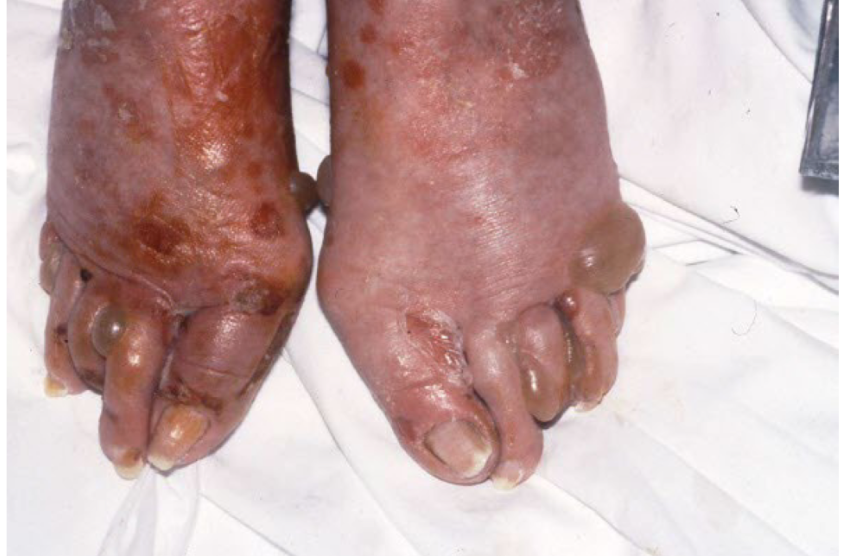
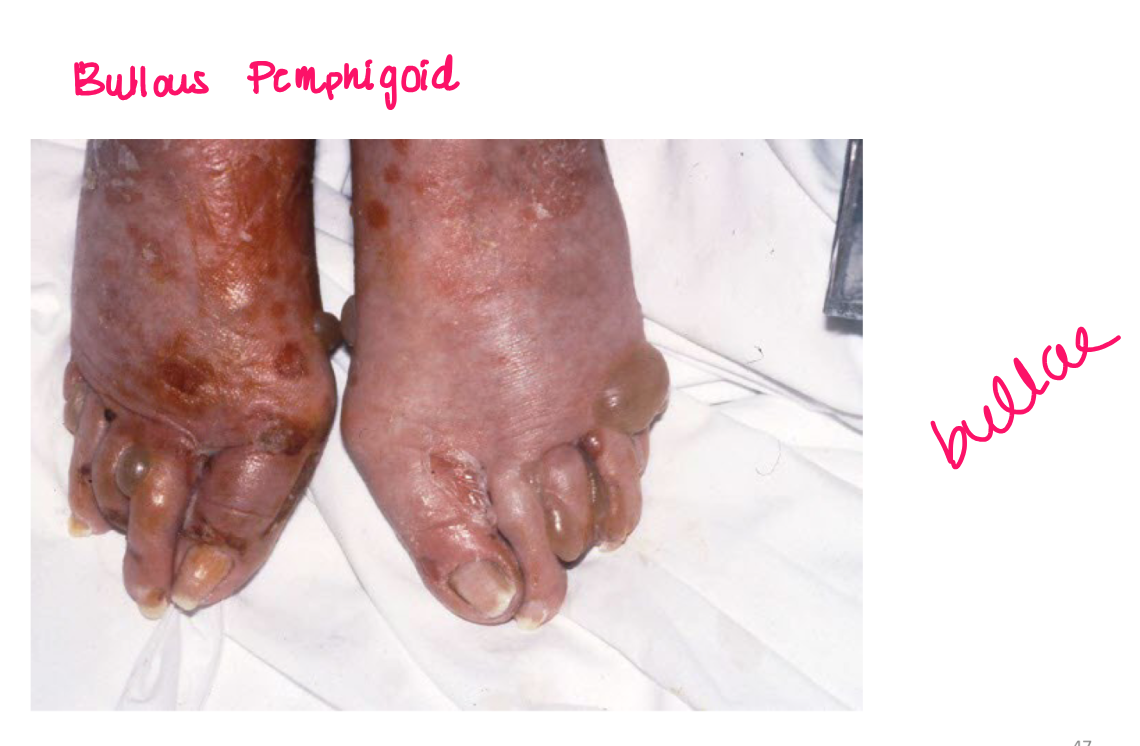
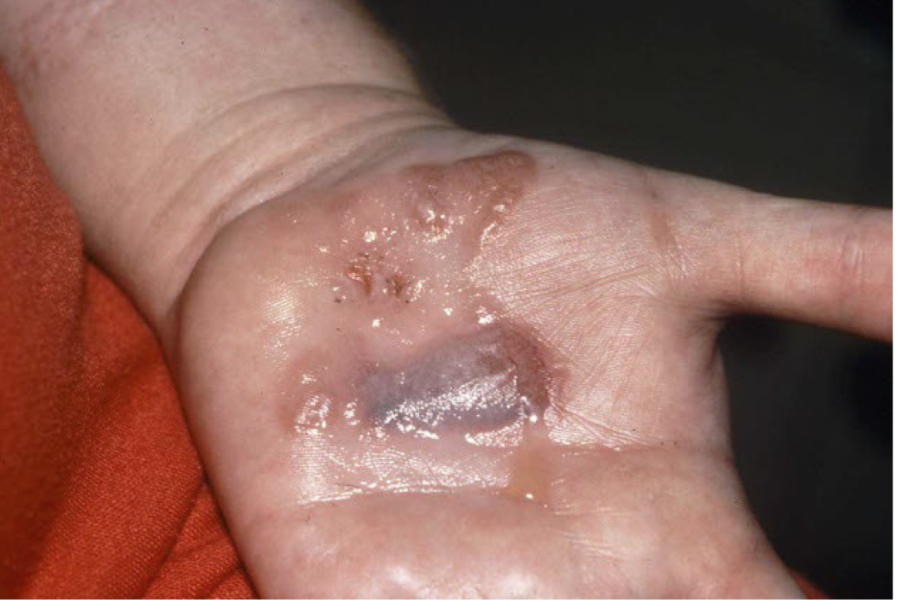
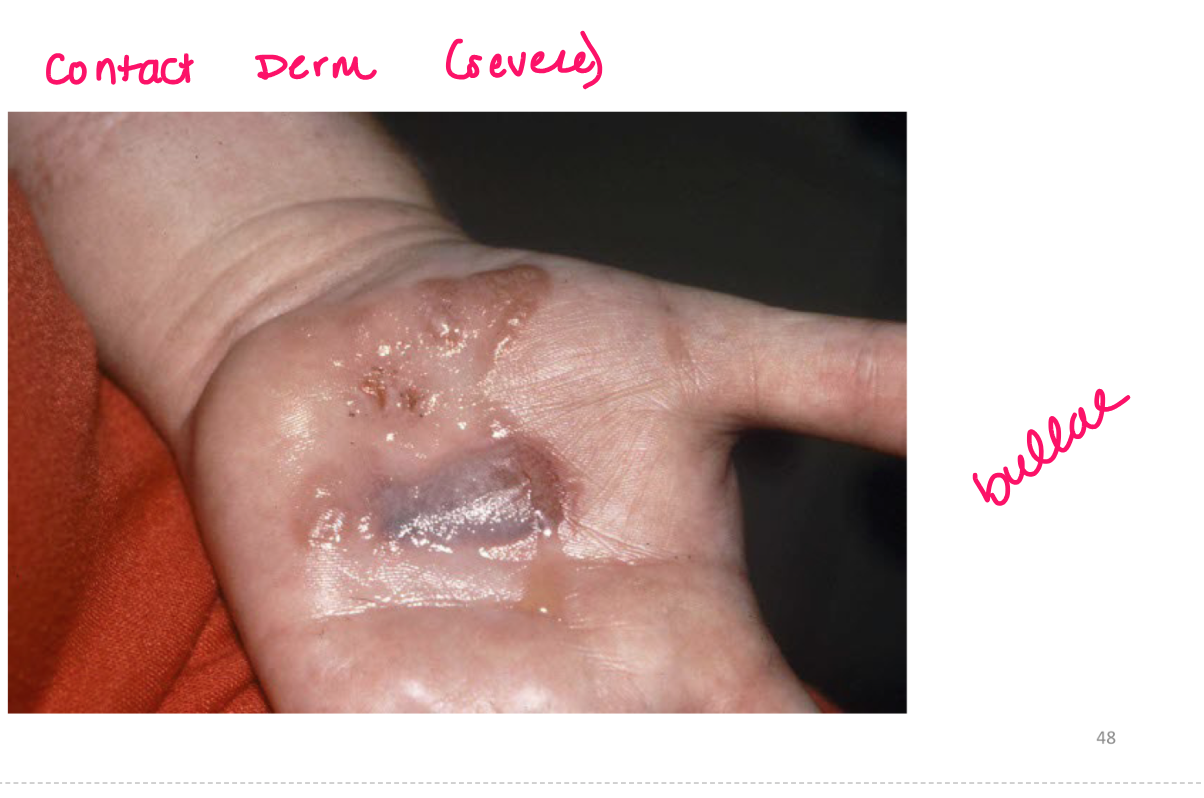
bullae
superficial fluid filled lesion greater than 1 cm
elevated, clear fluid
pustule
superficial localized accumulation of pus
less than 1 cm
elevated lesion
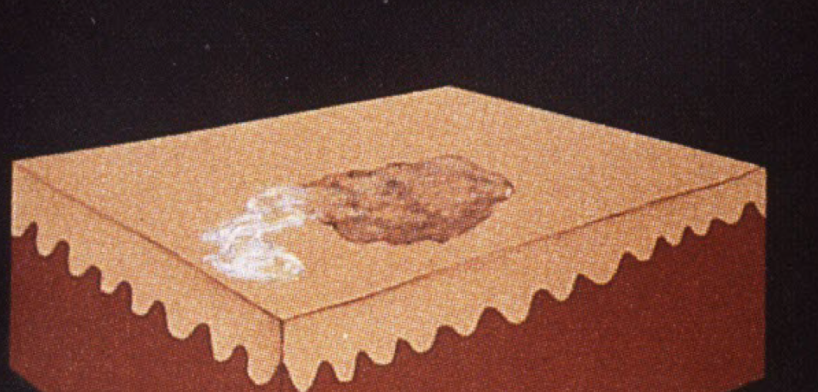
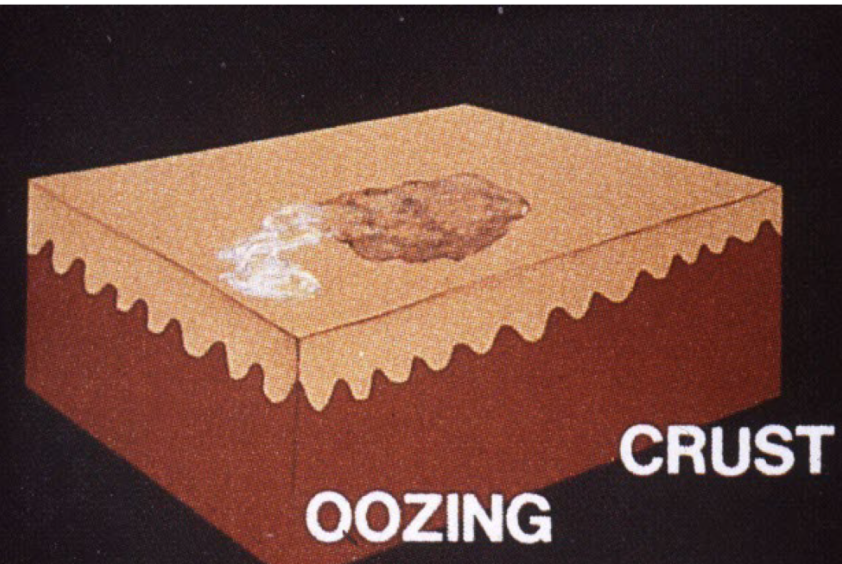
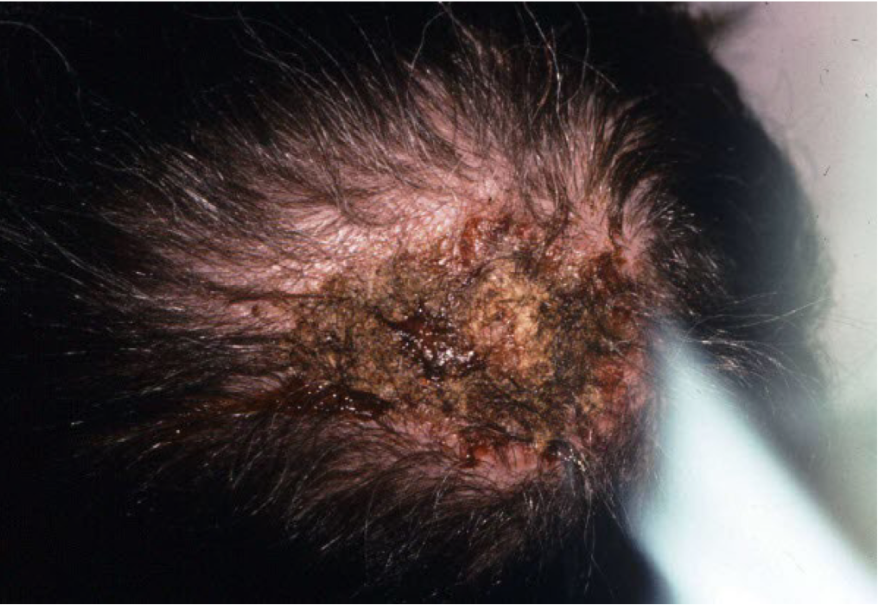
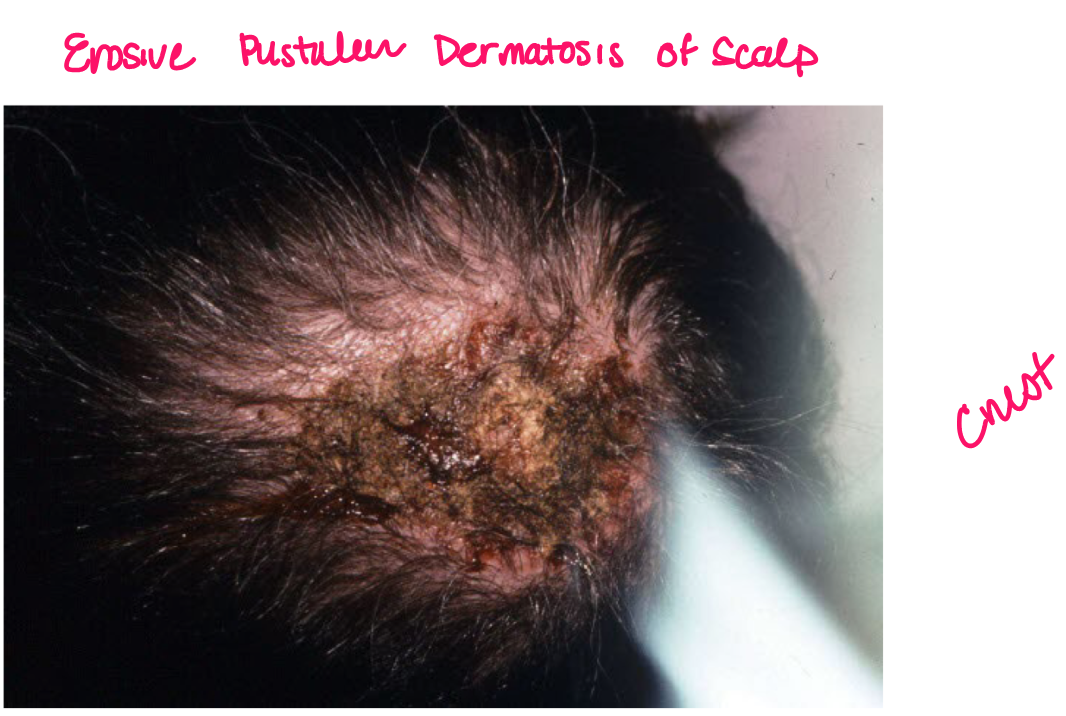
Crust
scab dried exudate of plasma/blood on surface of skin
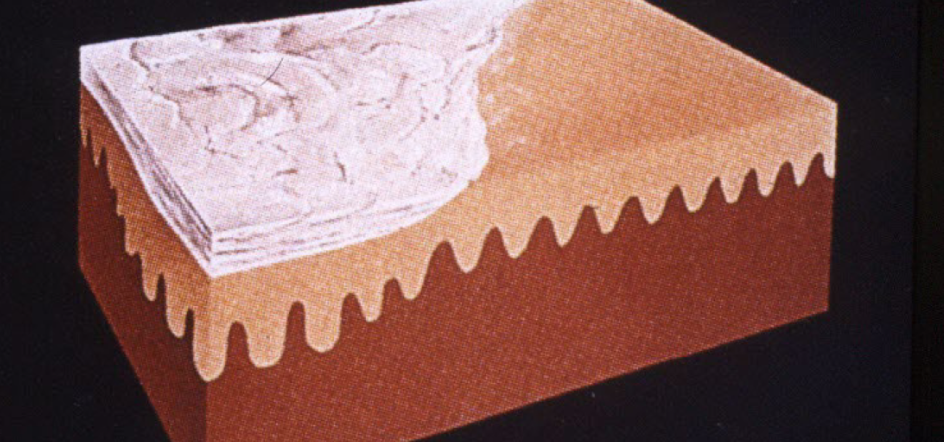
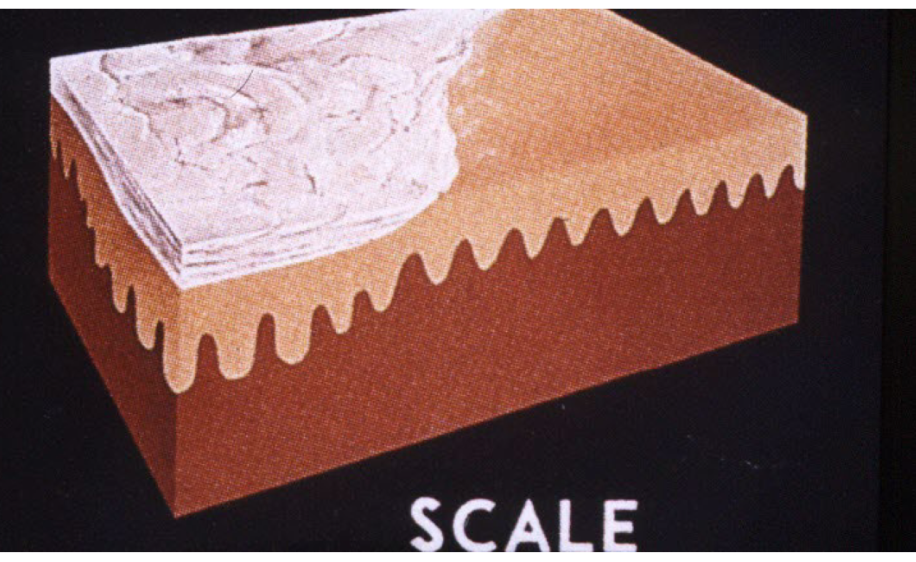
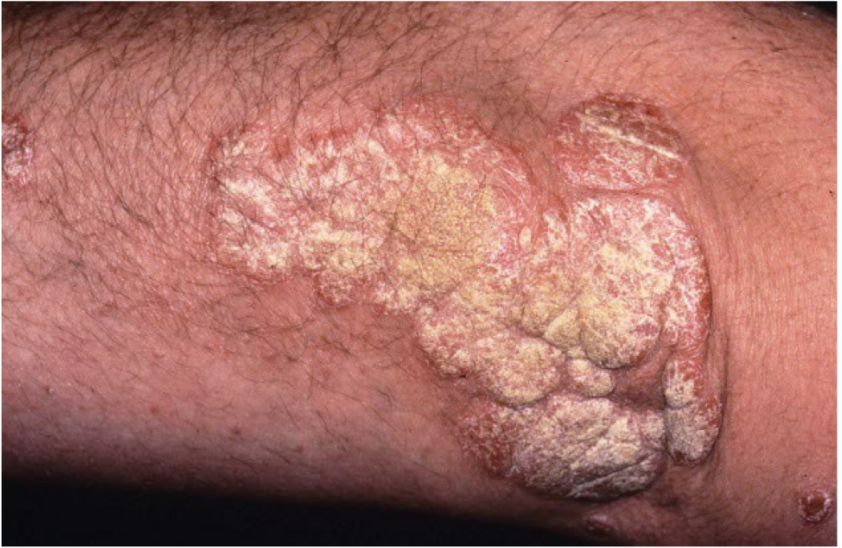
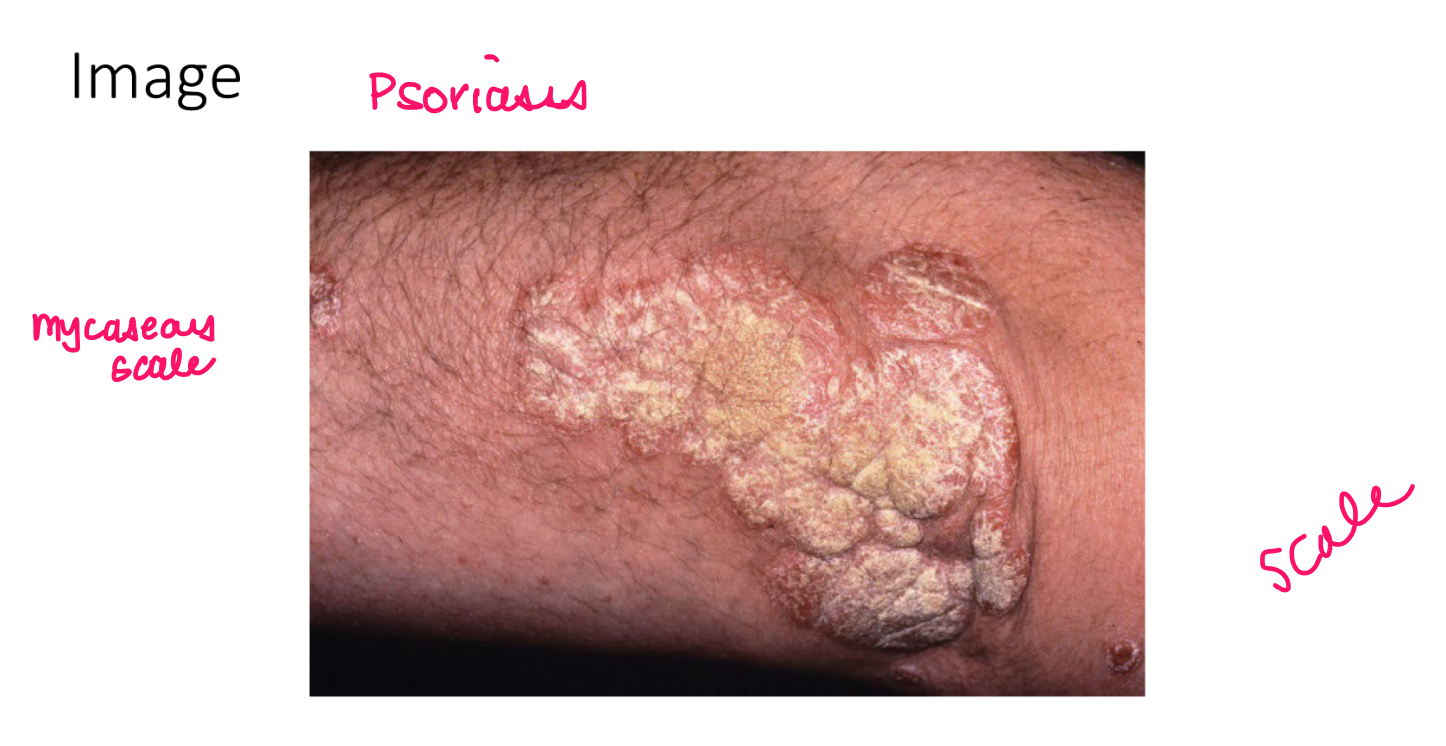
scale
thickened stratum corneum
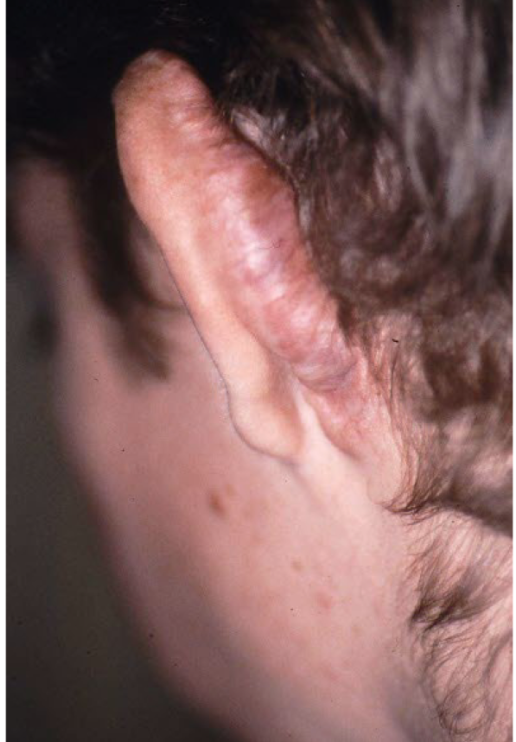
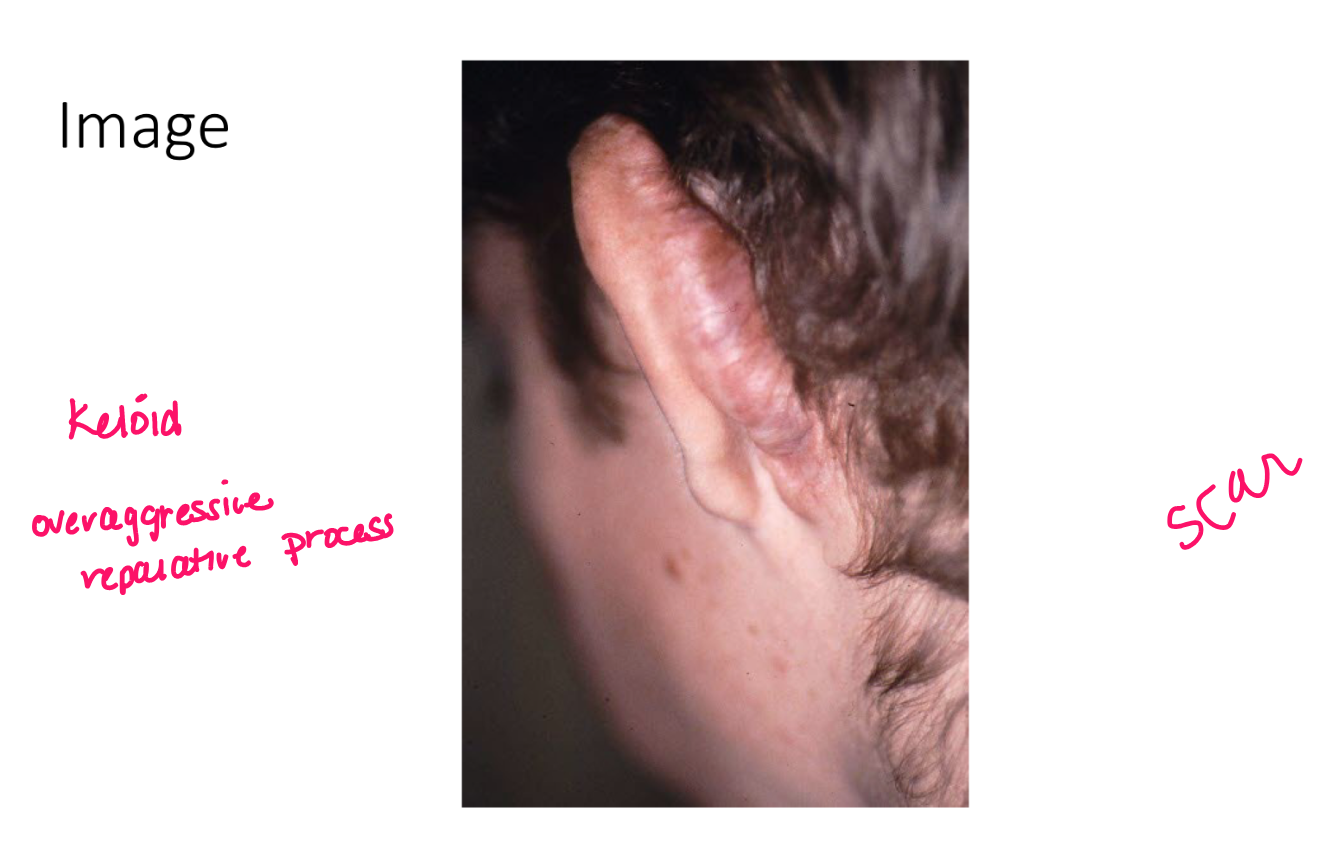
scar
visible alteration of skin following repair of injury
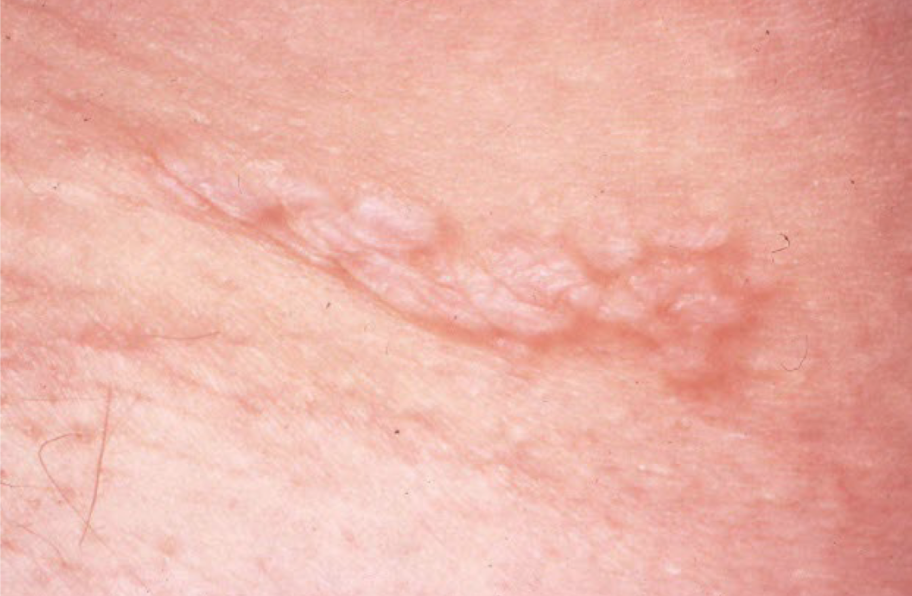
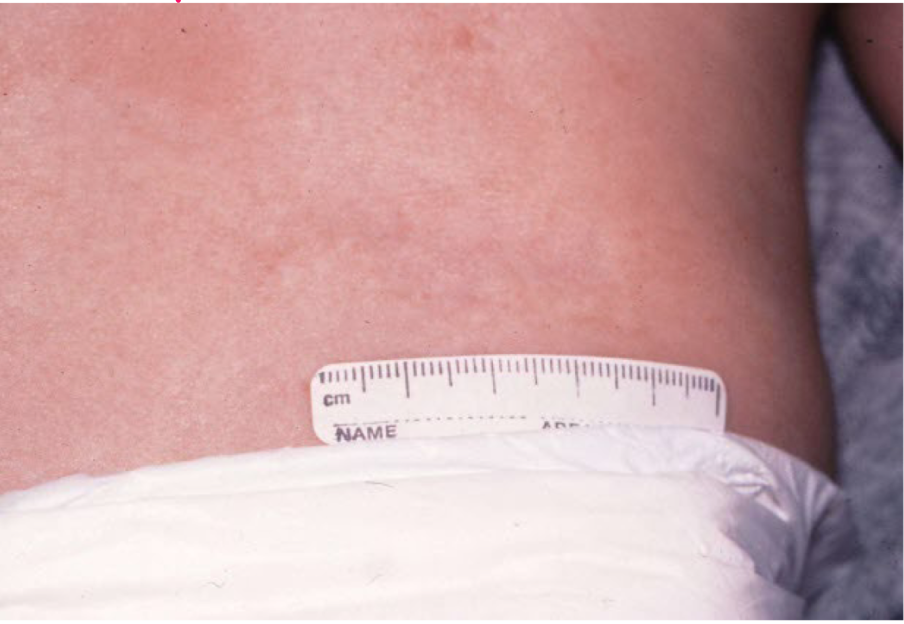
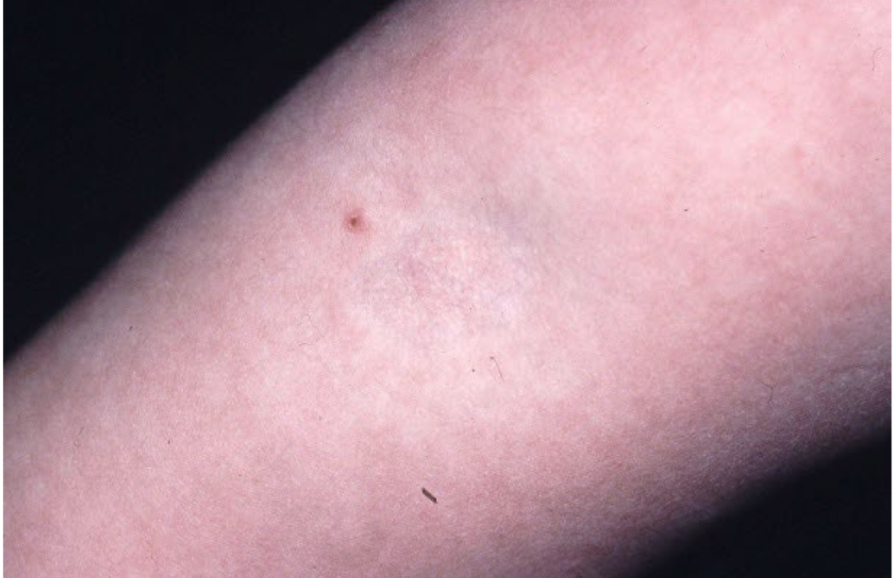
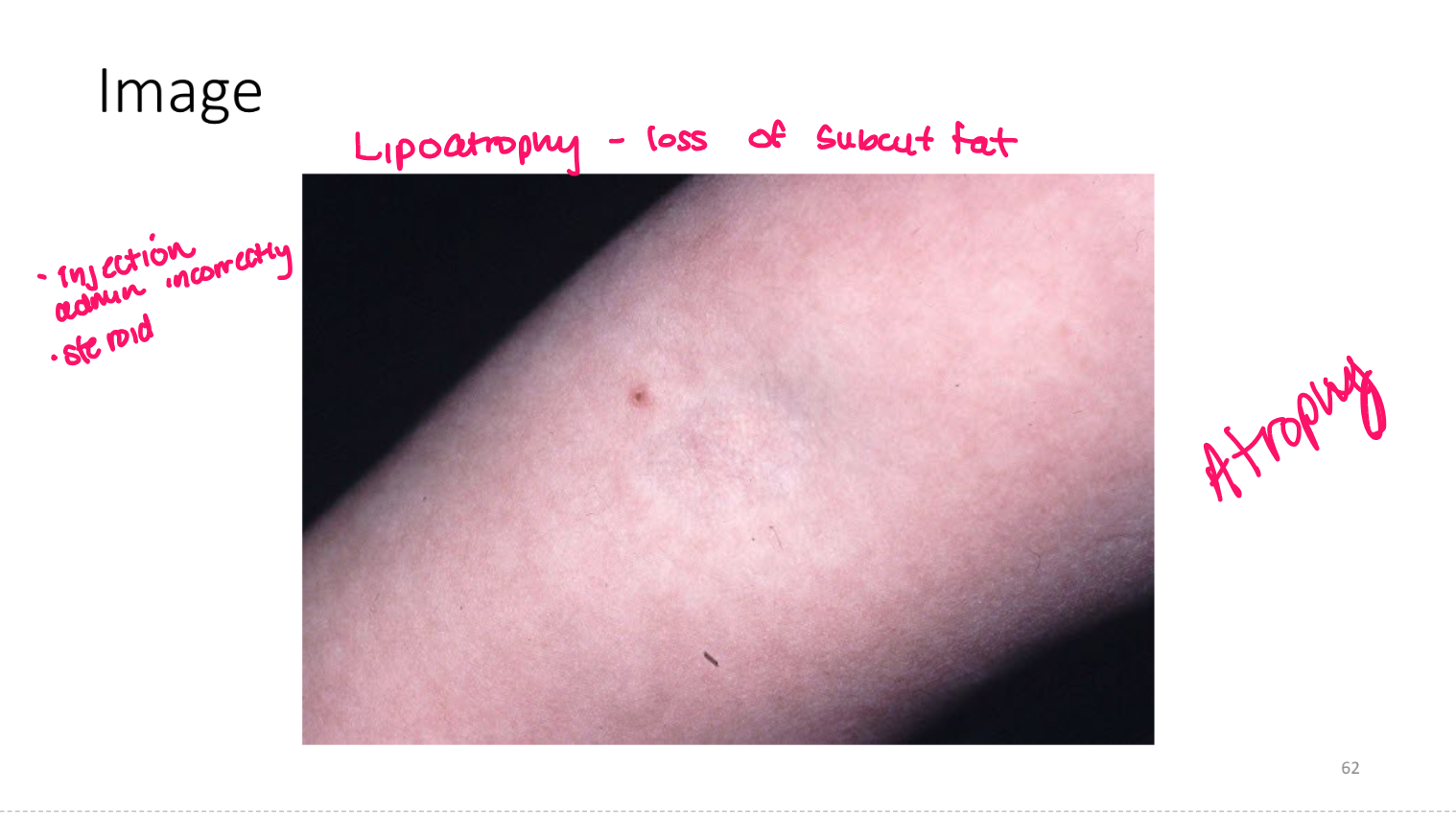
atrophy
loss of tissue (epidermal, dermal, subcutaneous)
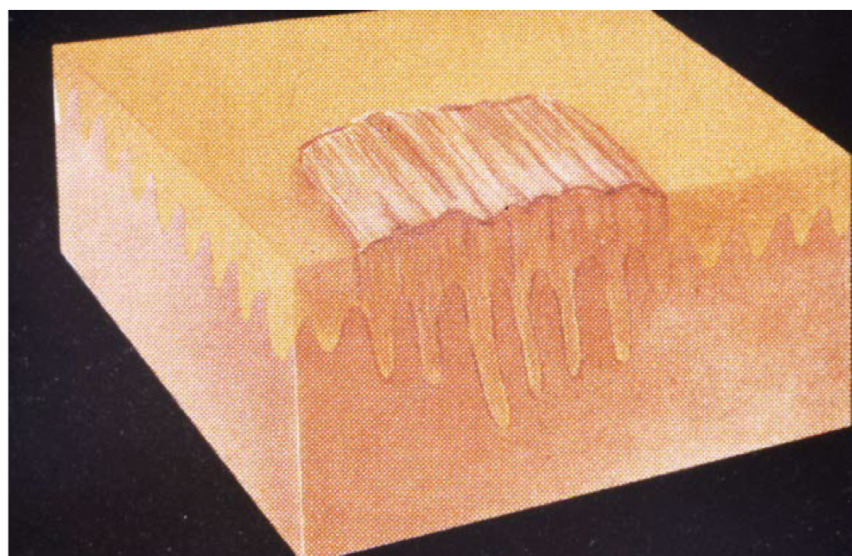
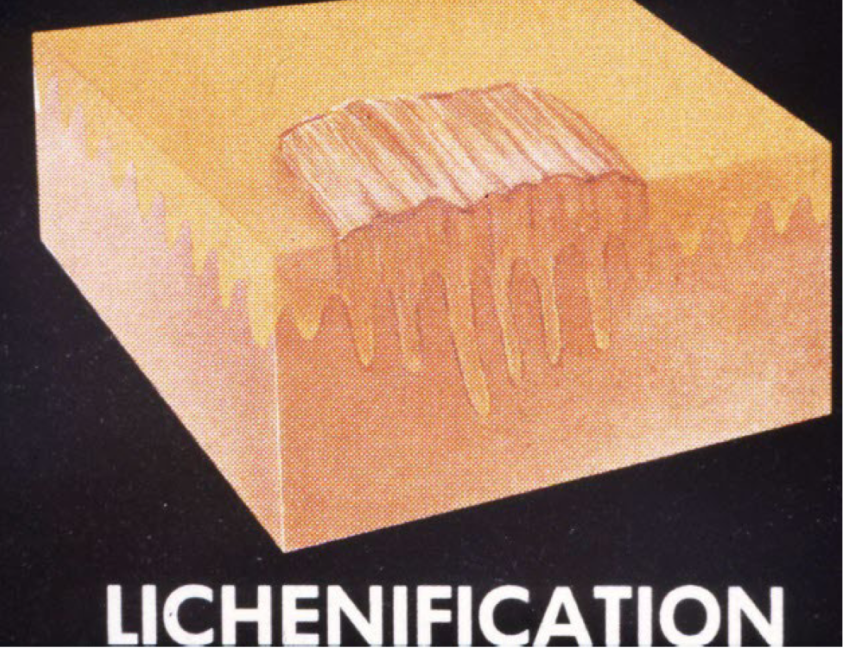
lichenification
epidermal thickening characterized by thickening and accentuation of skin markings


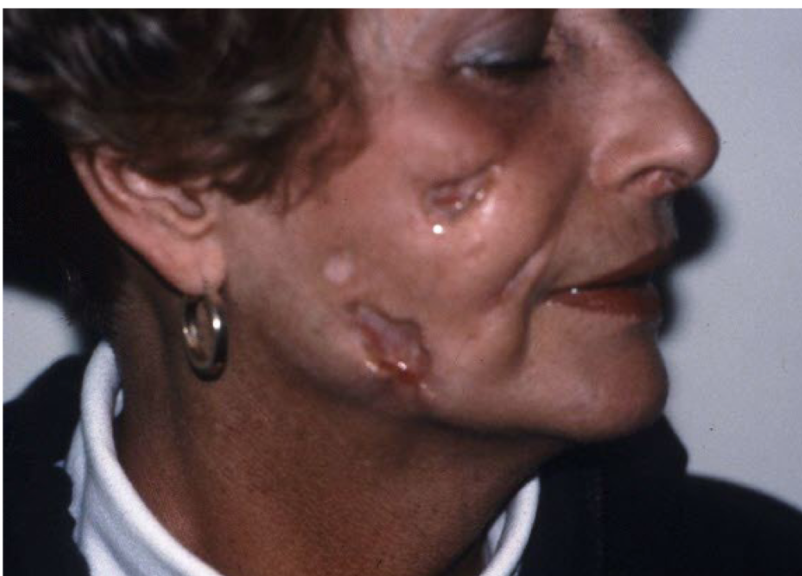
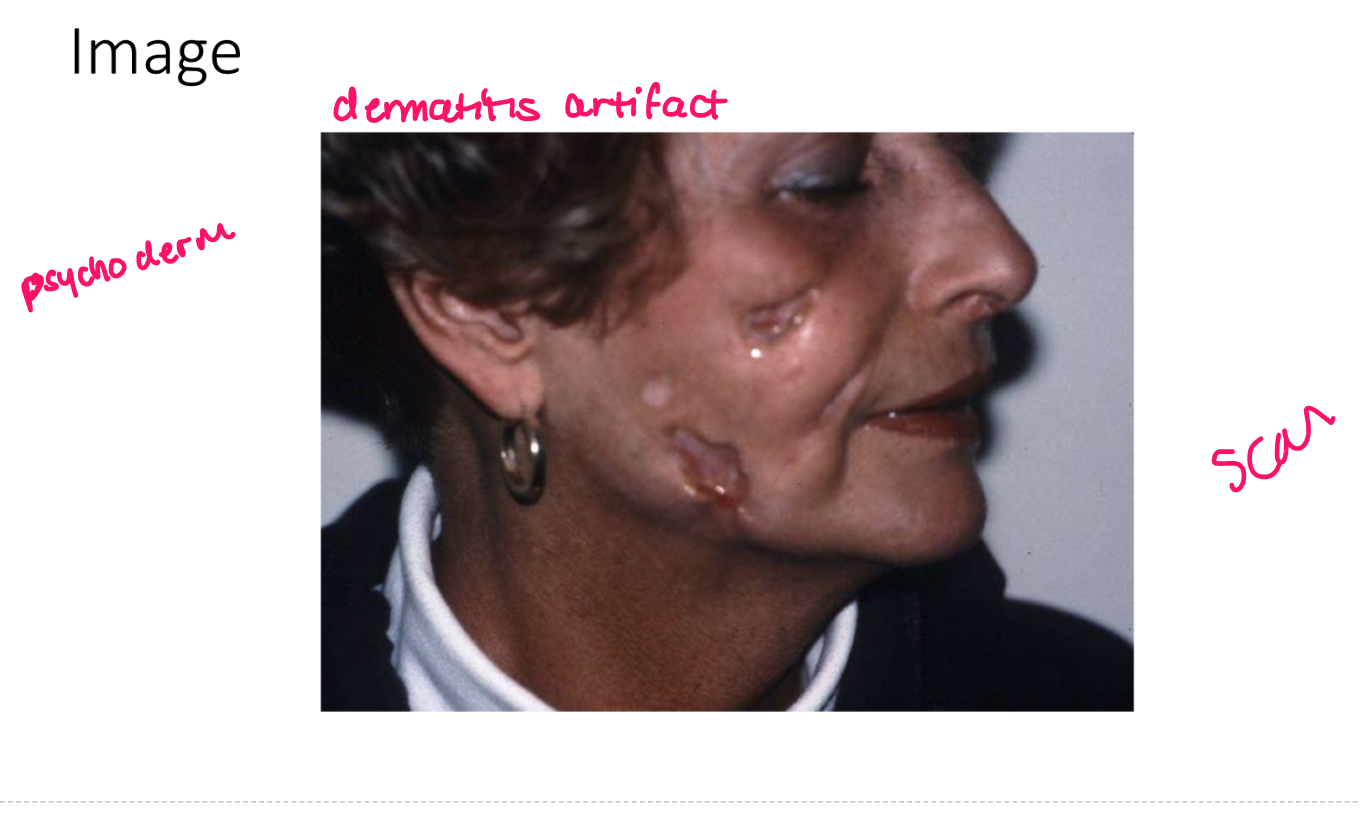
Excoriation
oval or linear depressions in skin w/ complete removal of epidermis
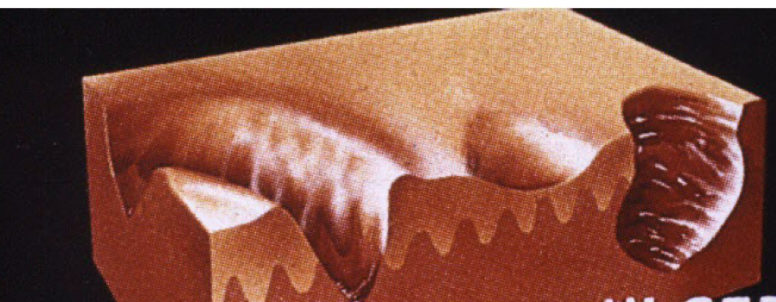
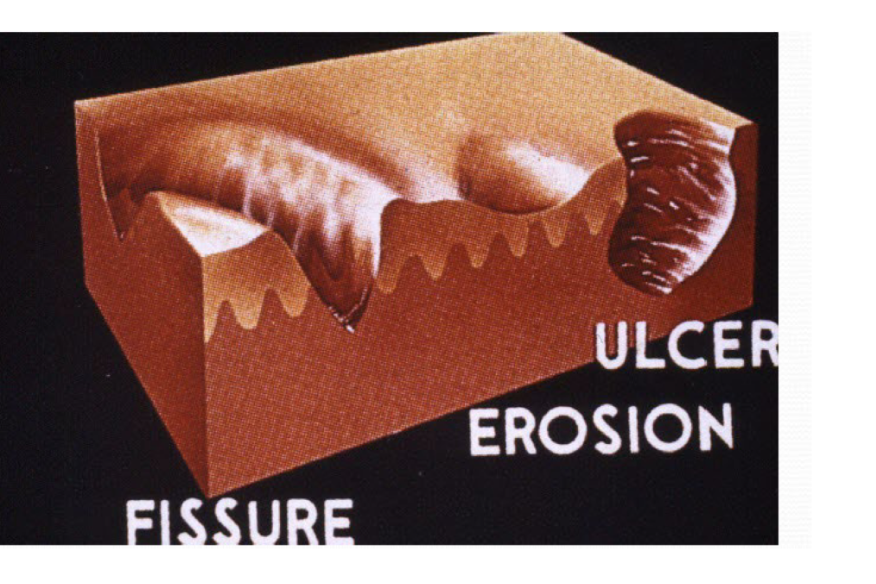
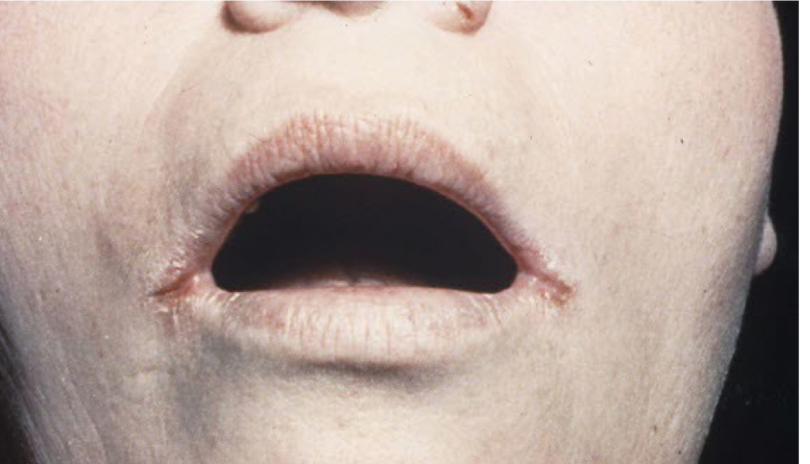
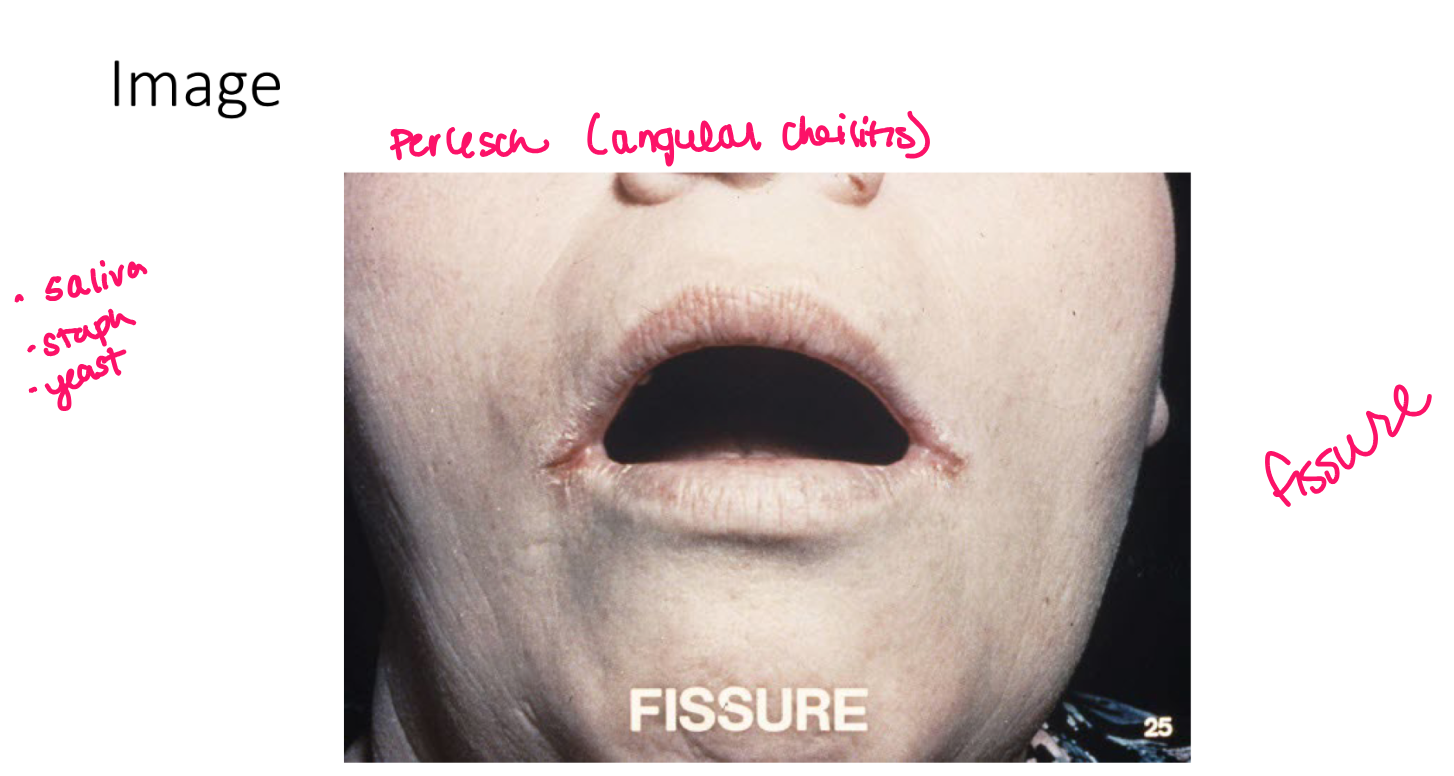
Fissure
linear wedge shaped breaks in epidermis extending down to dermis
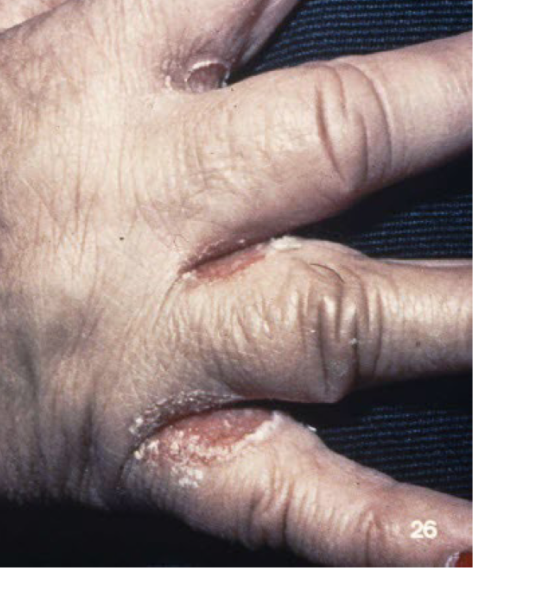
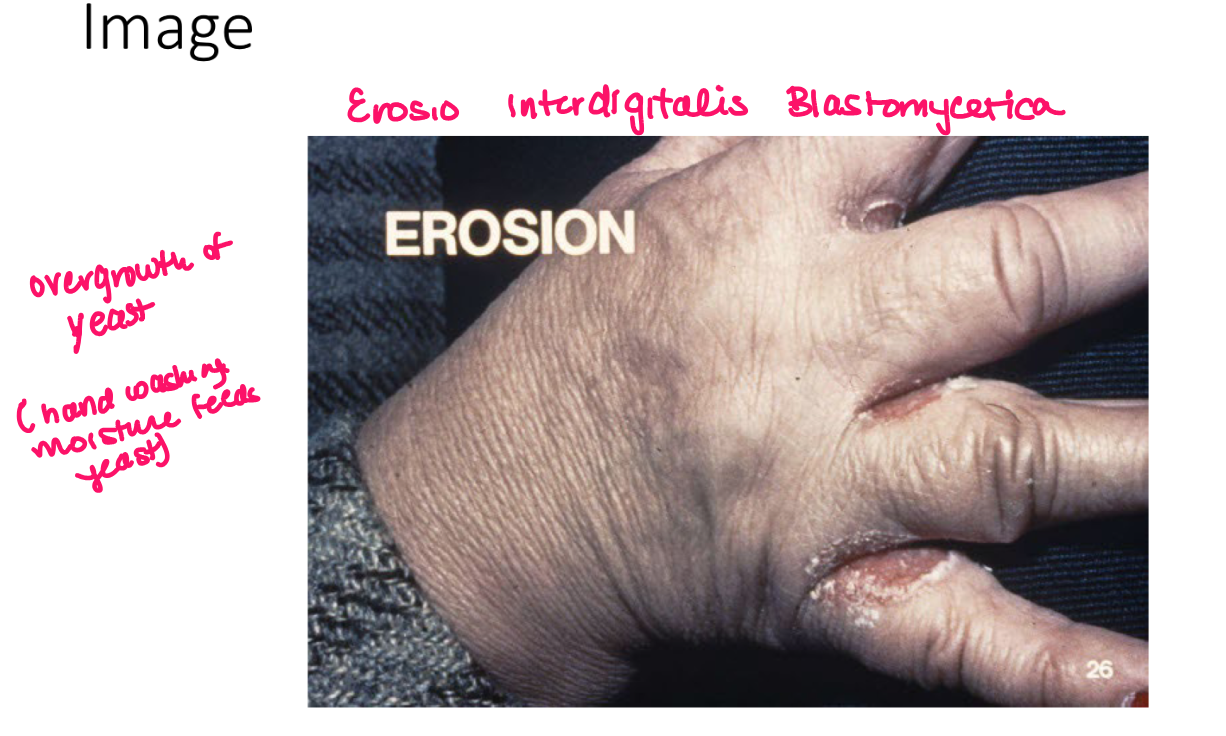
erosion
moist circumscribed depressed area limited to epidermis
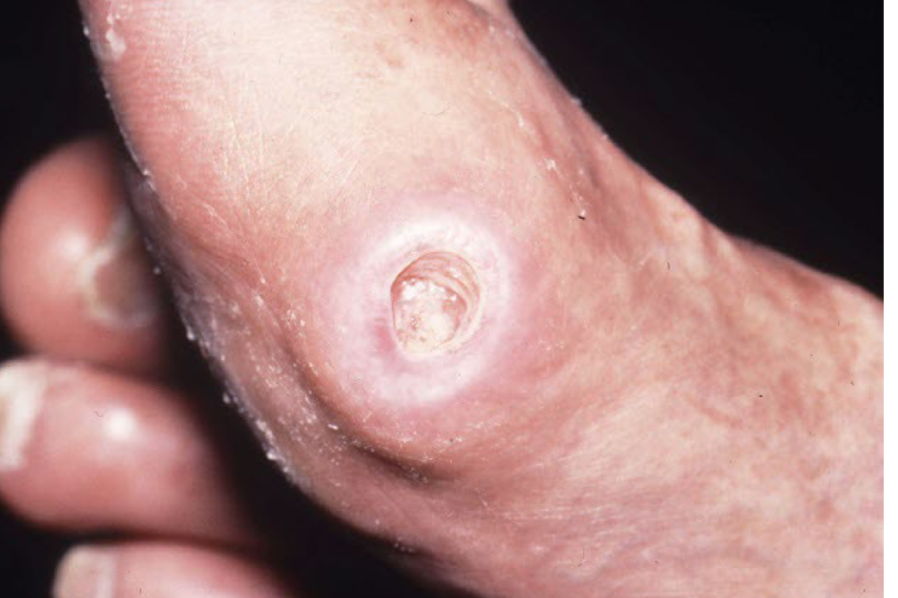
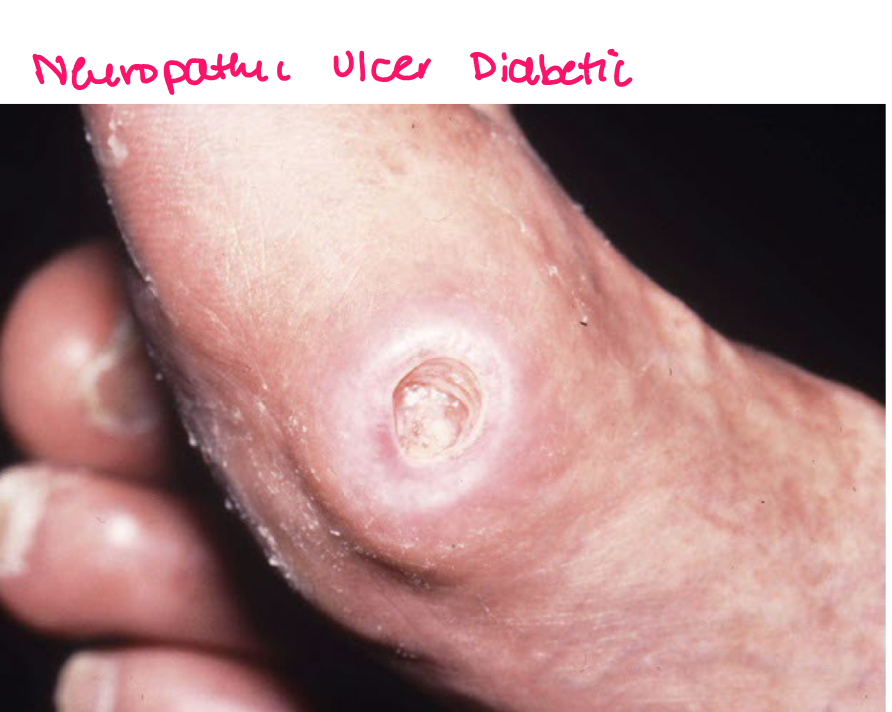
Ulcer
defect devoid of epidermis extending into dermis of subcut tissue
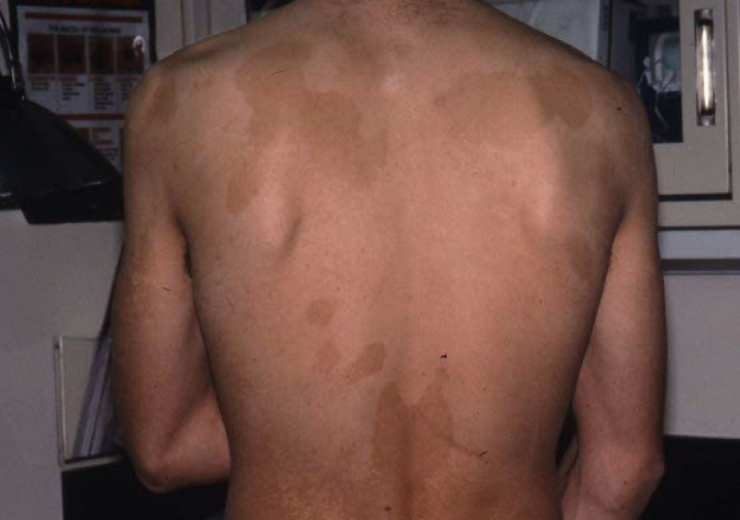
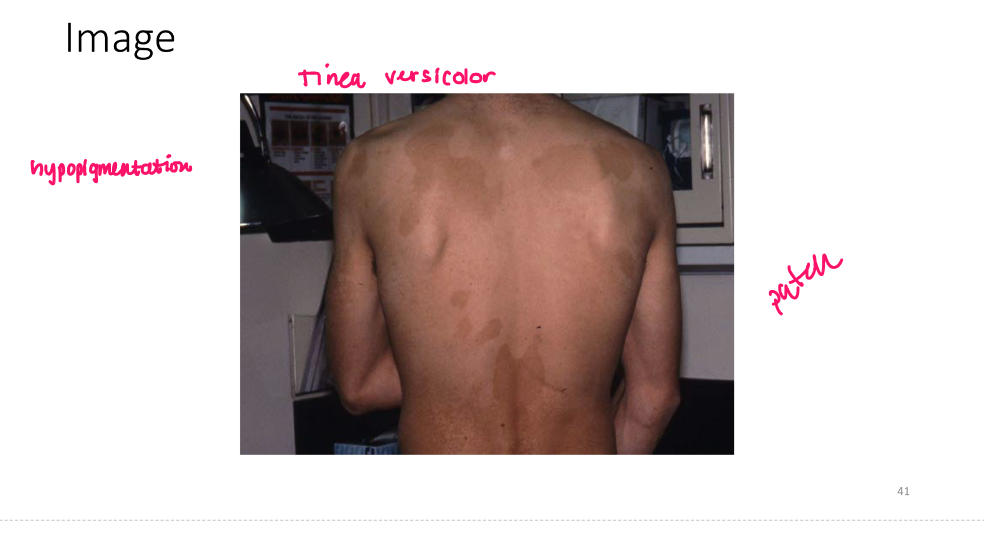
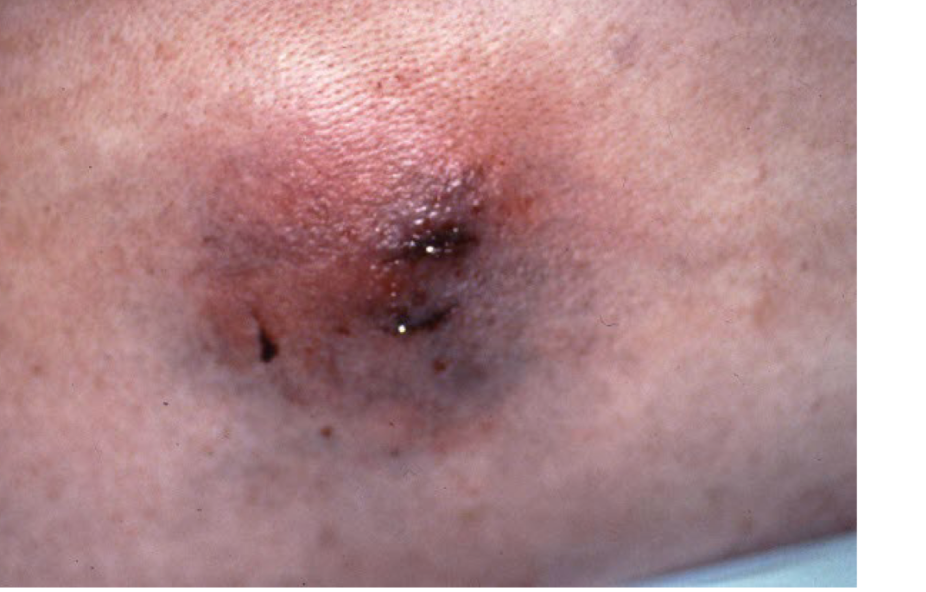
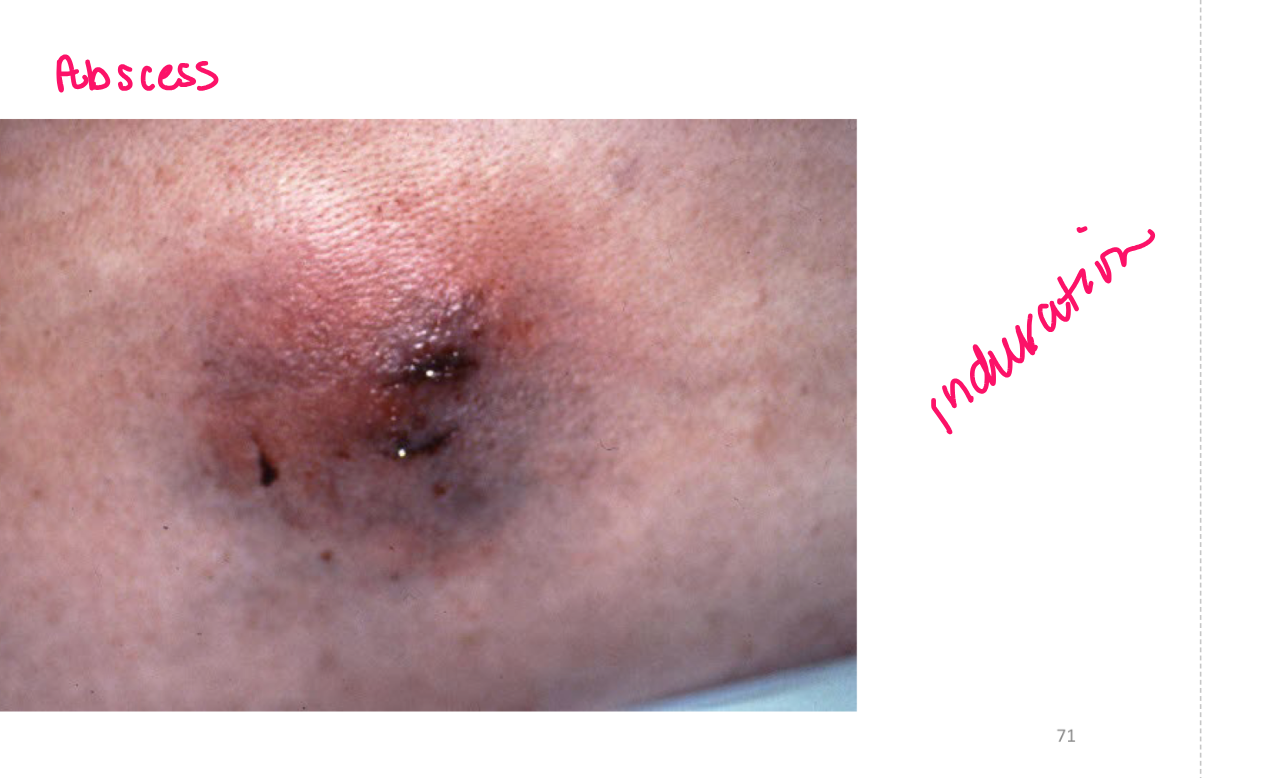


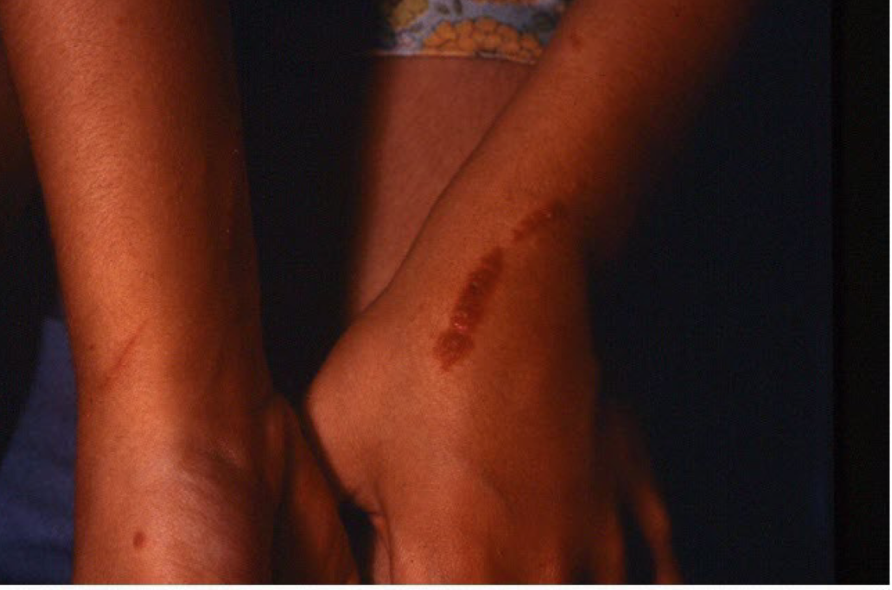
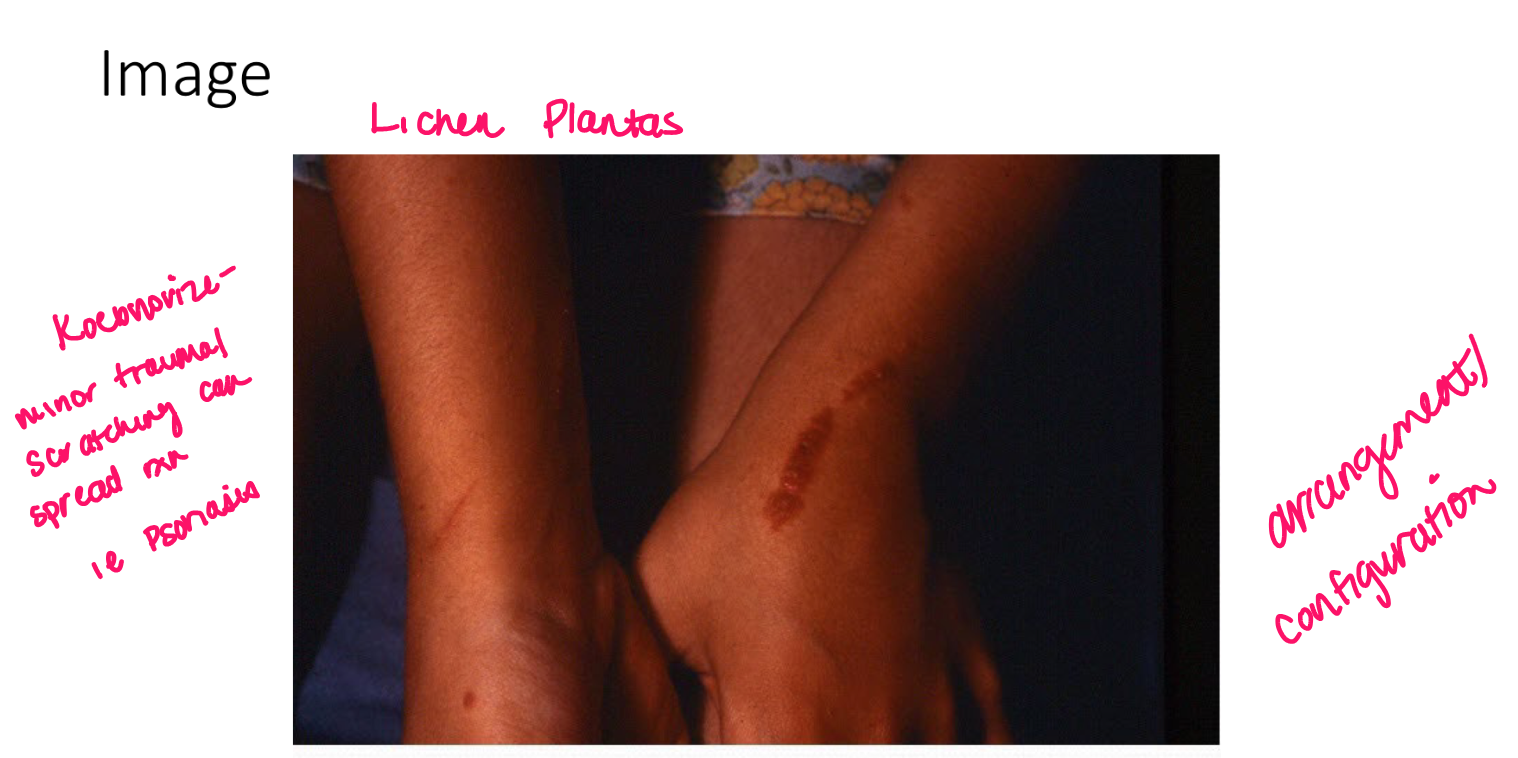
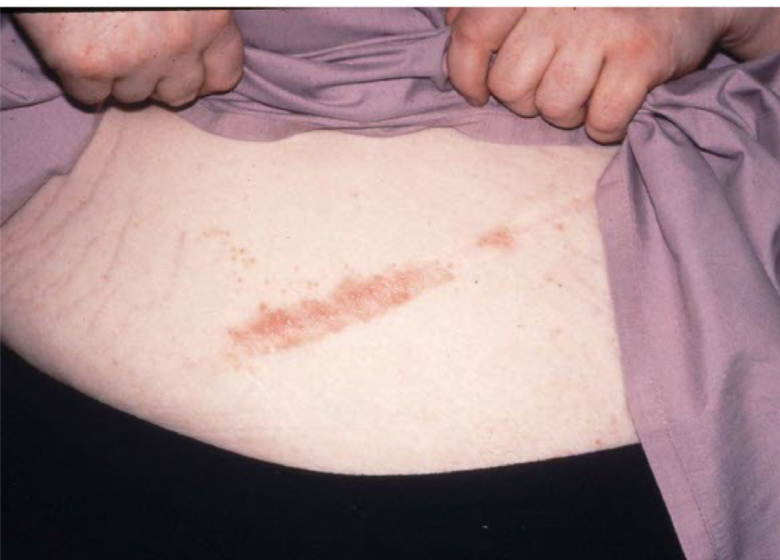
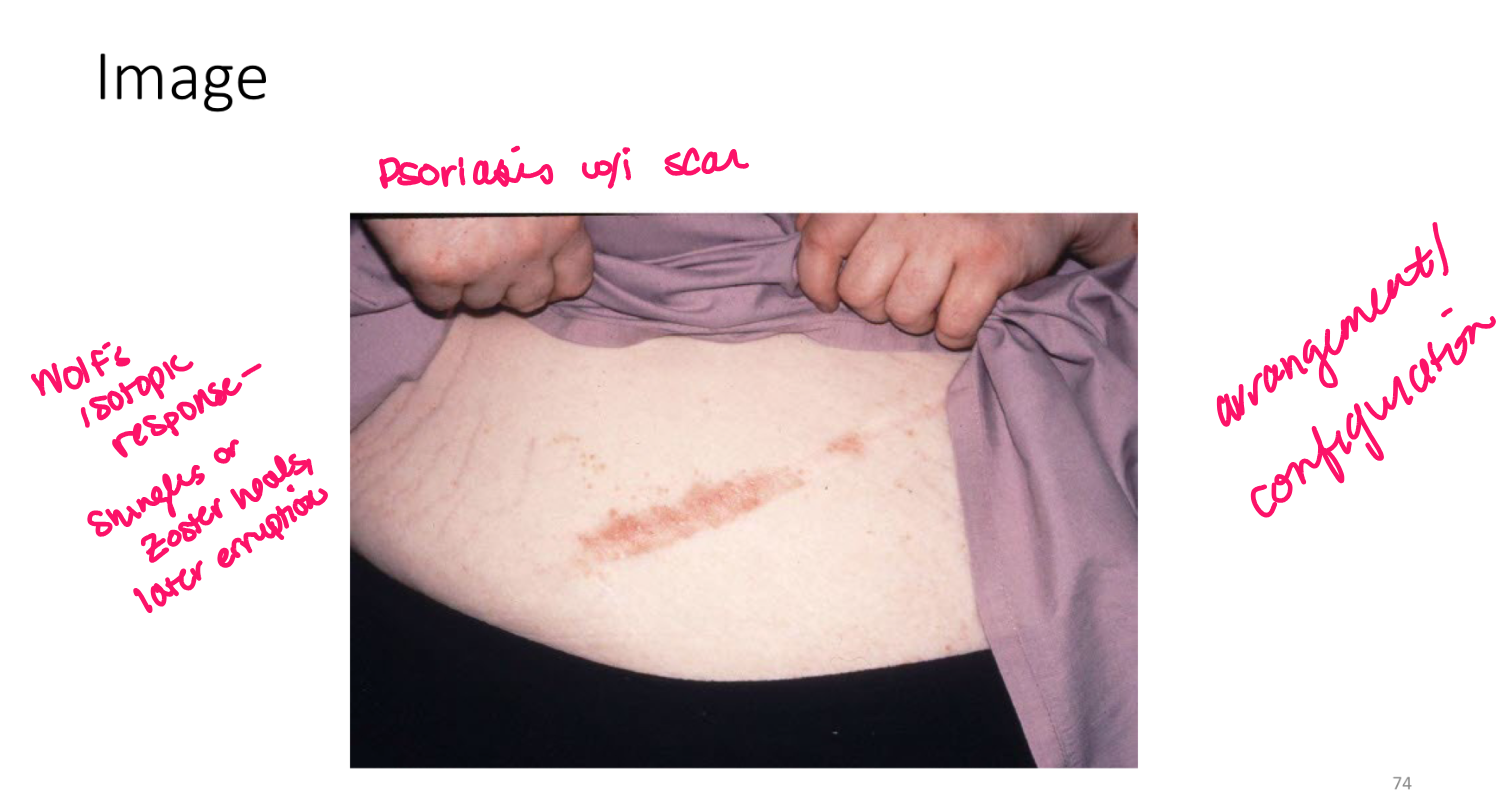
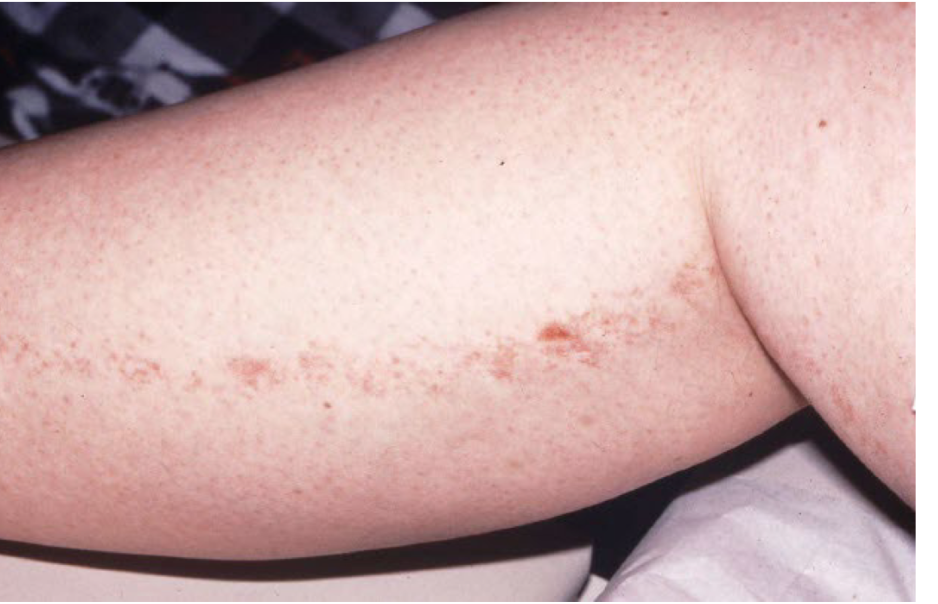
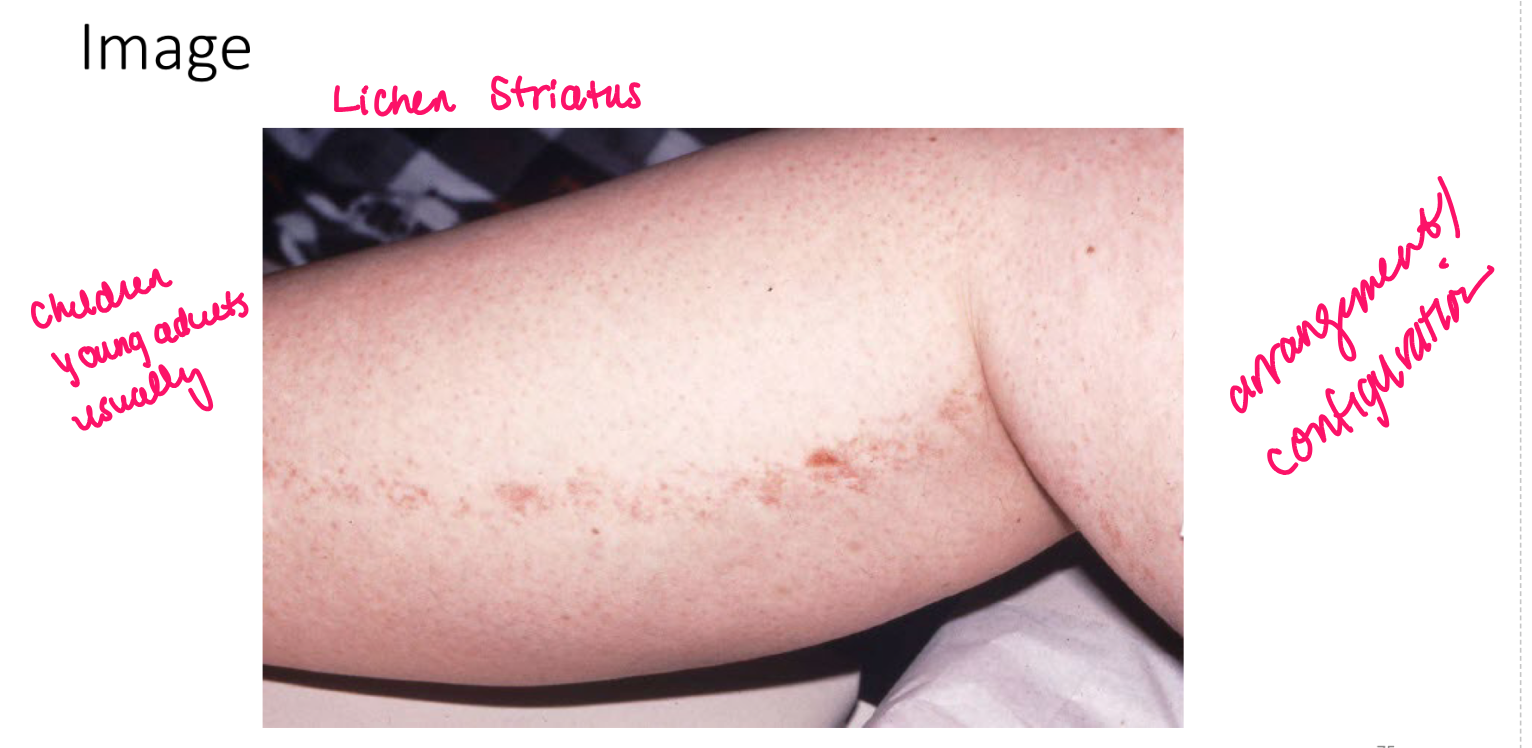
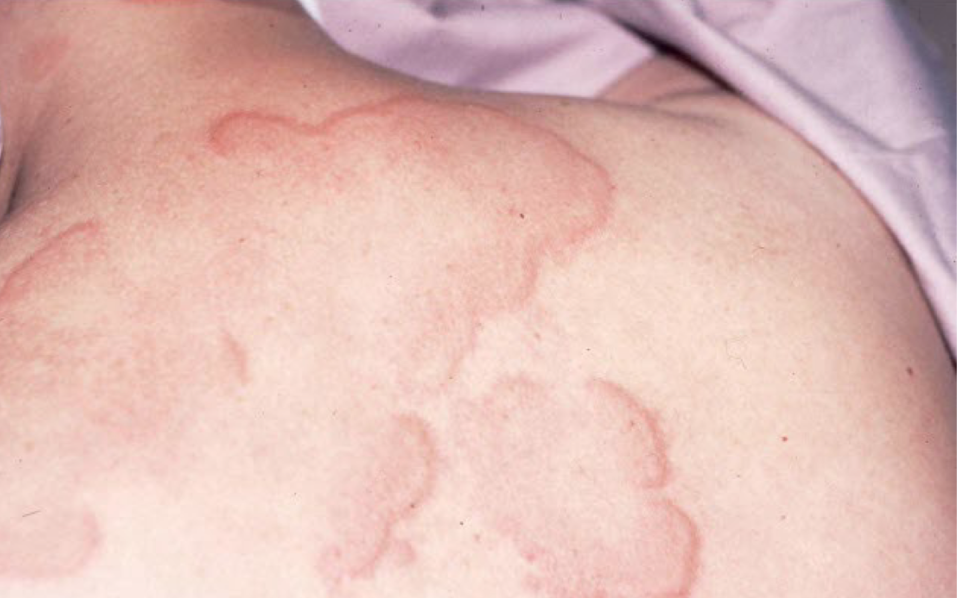
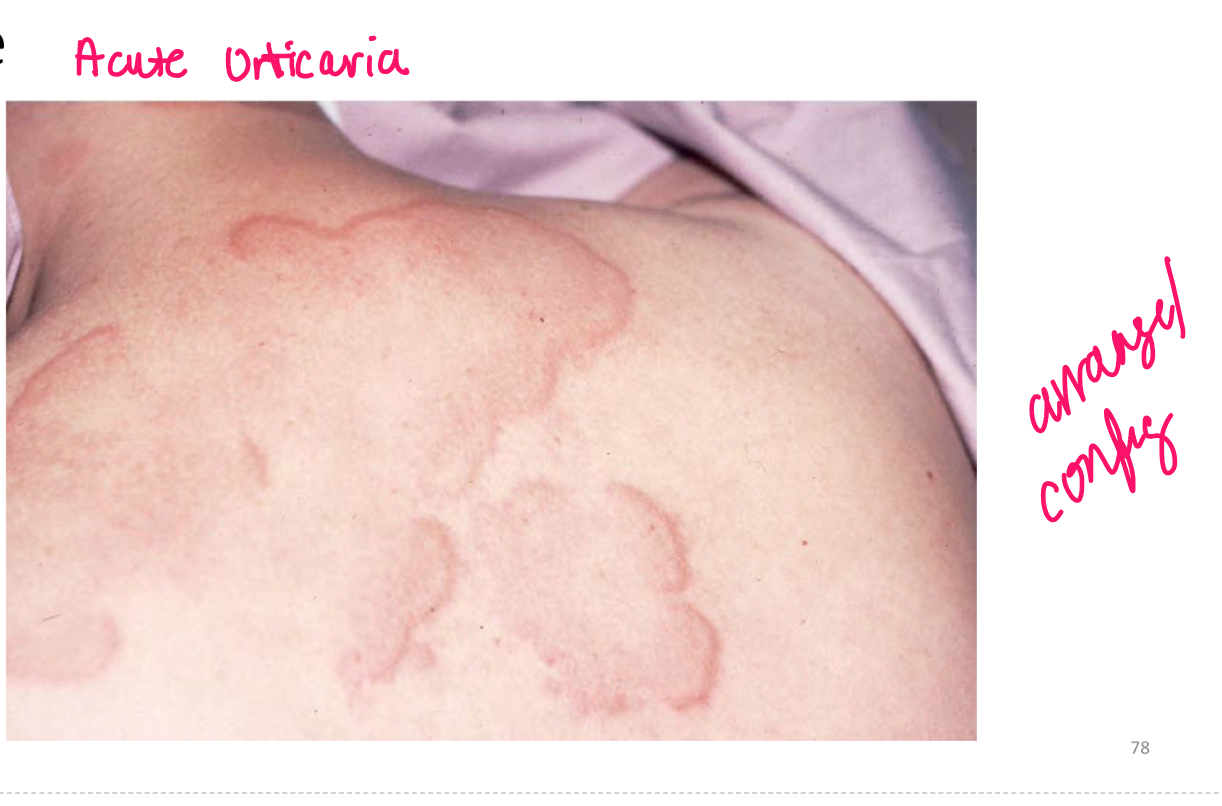
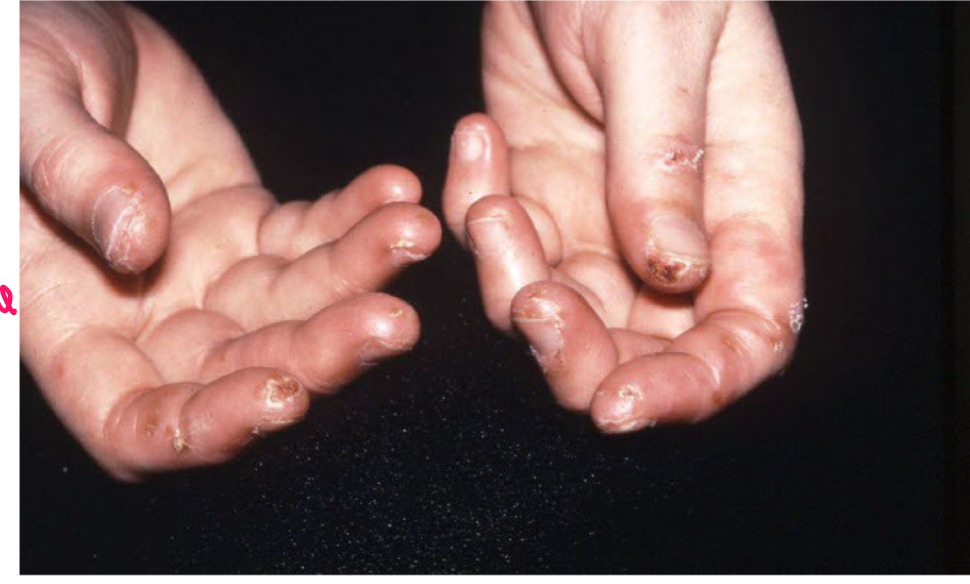
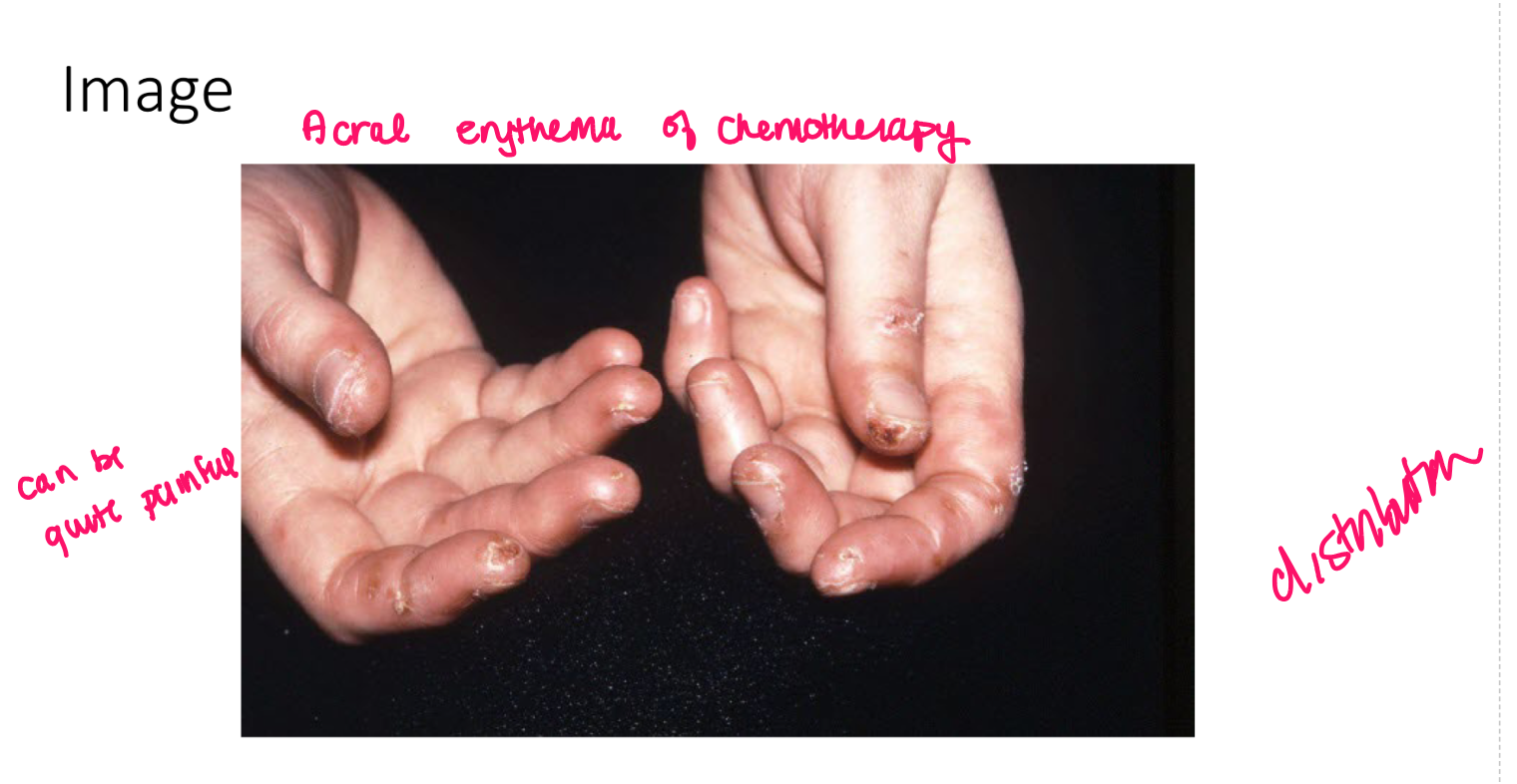


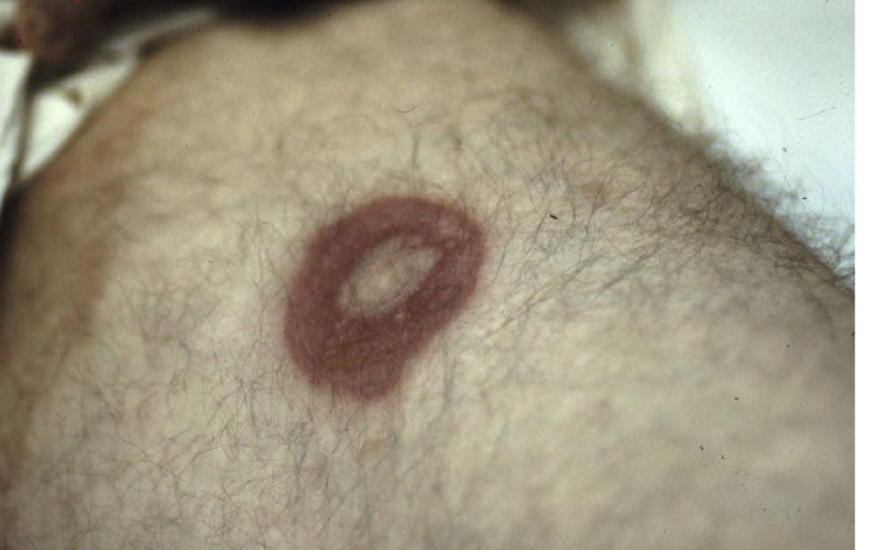
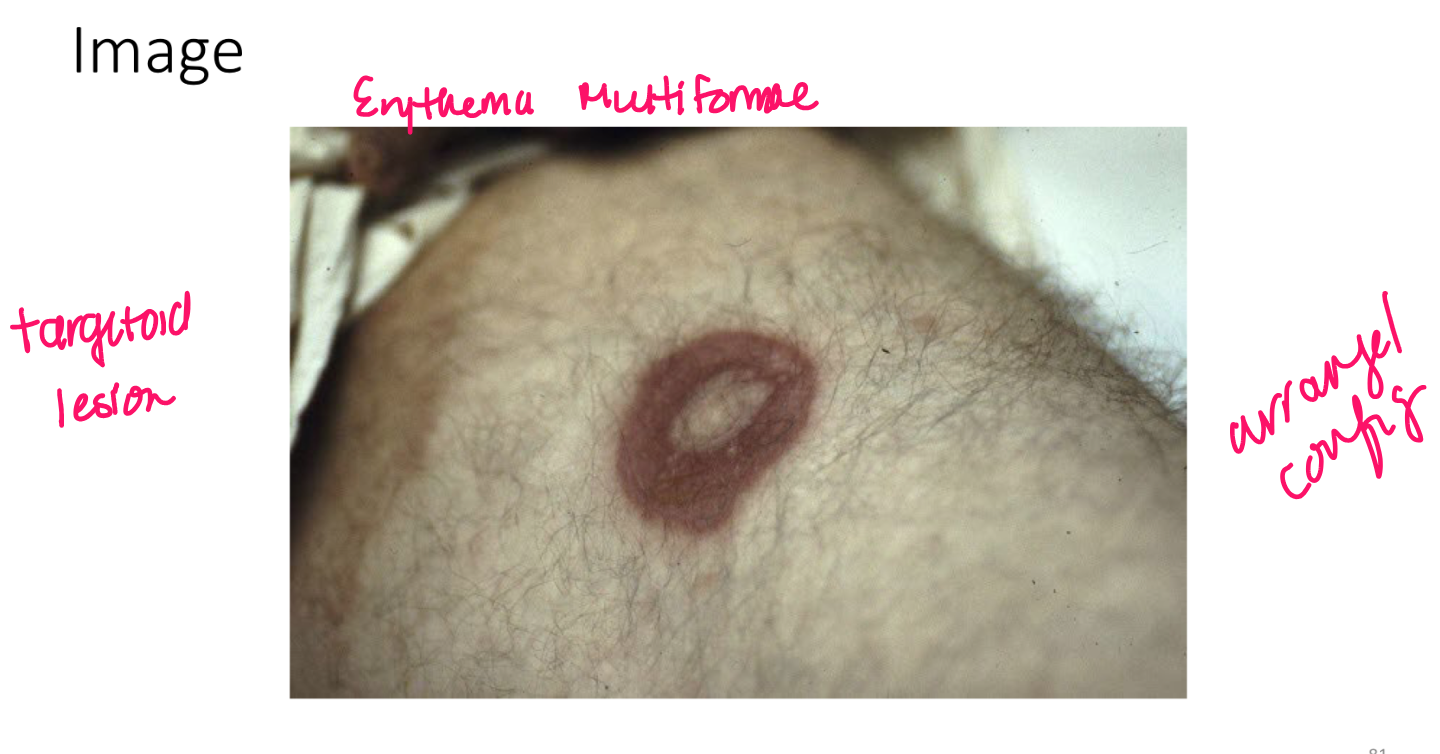
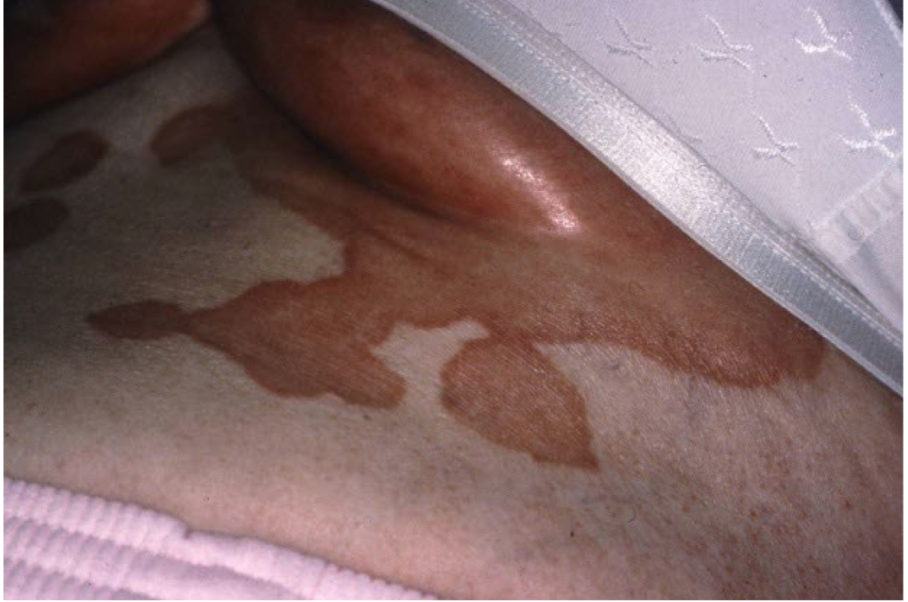
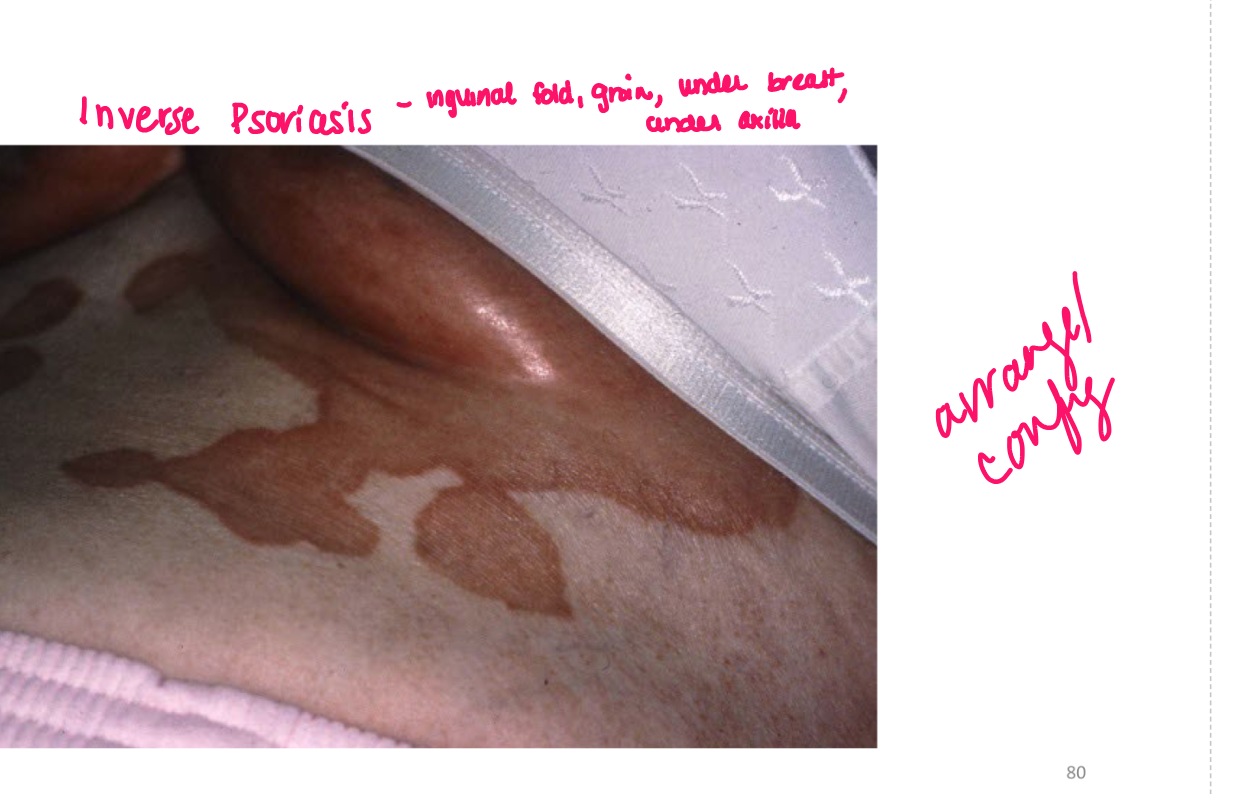
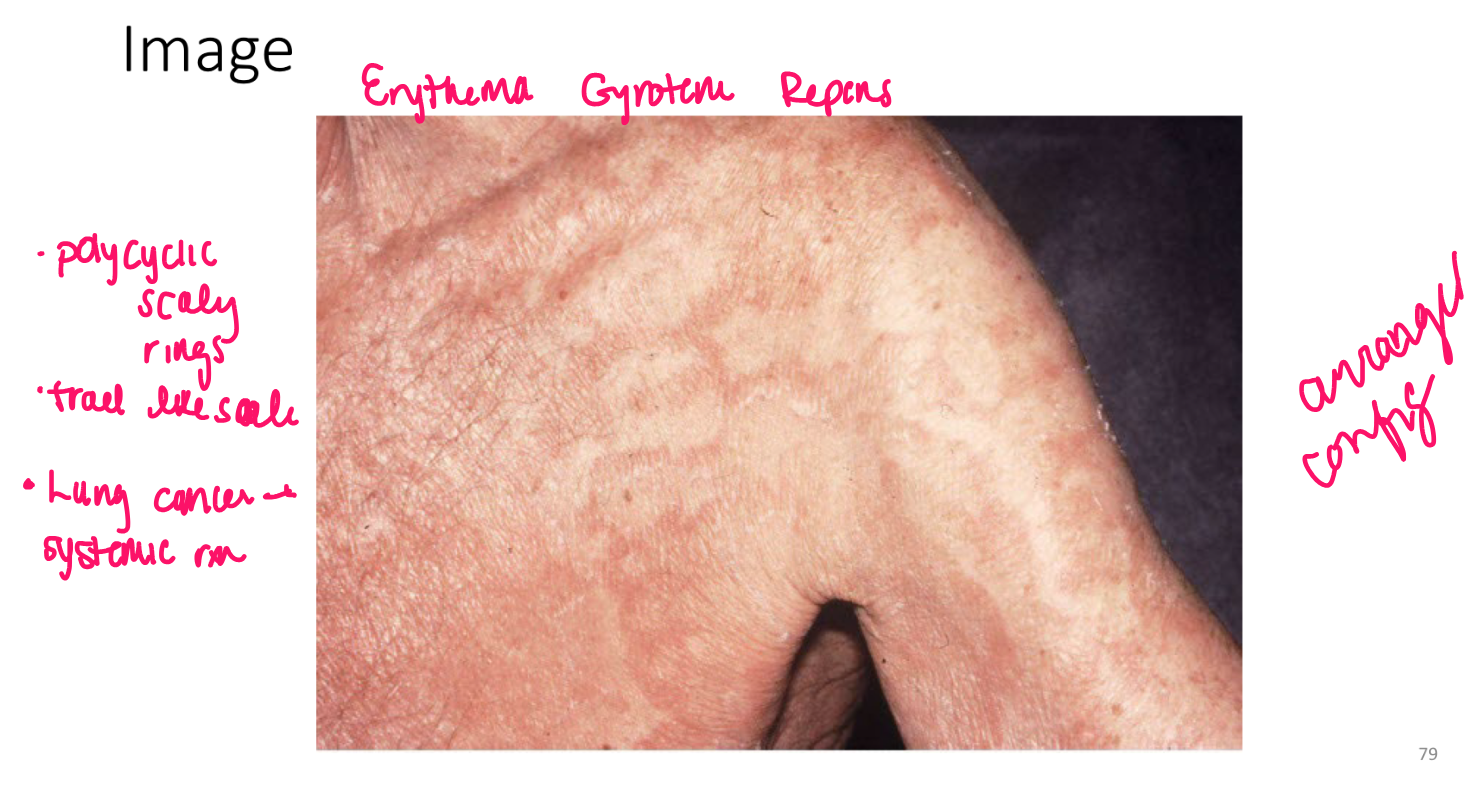
Turgor
slowness to return to normal position when pinched
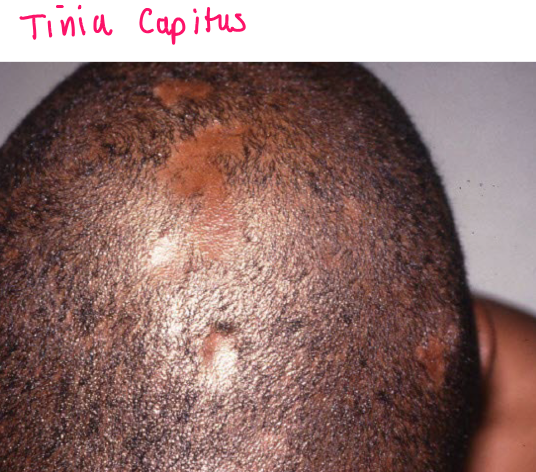
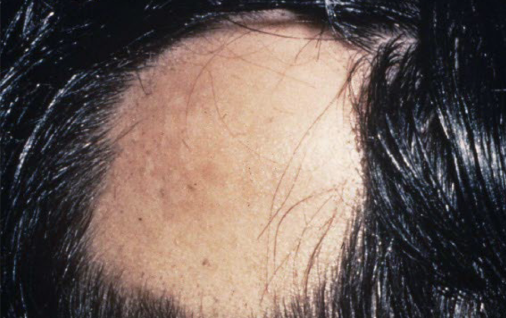
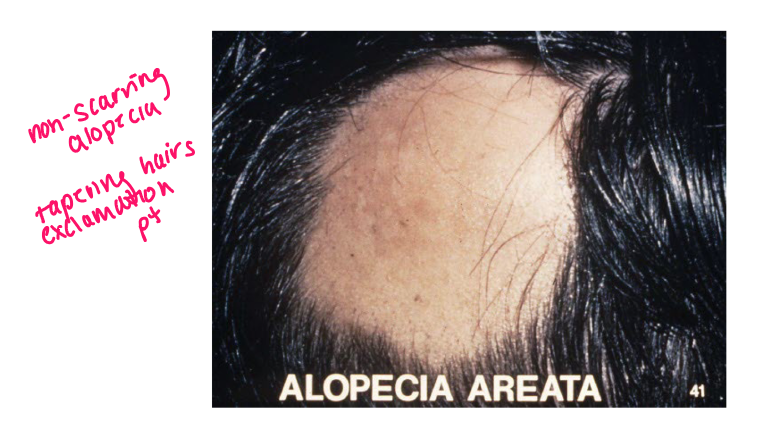
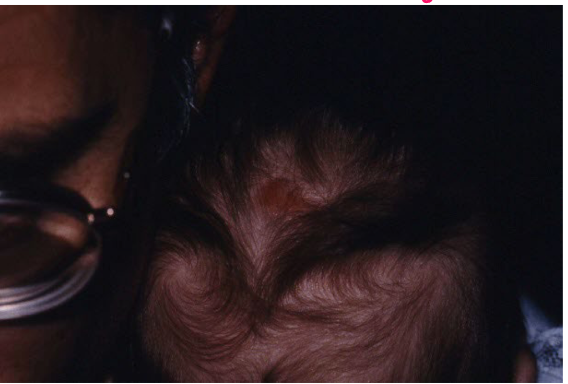
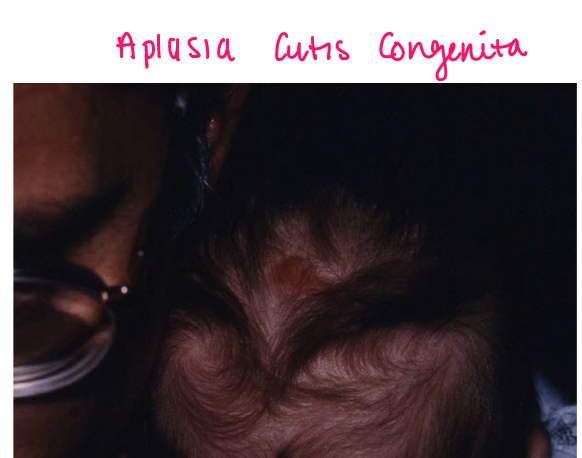
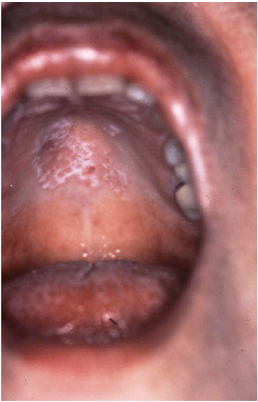
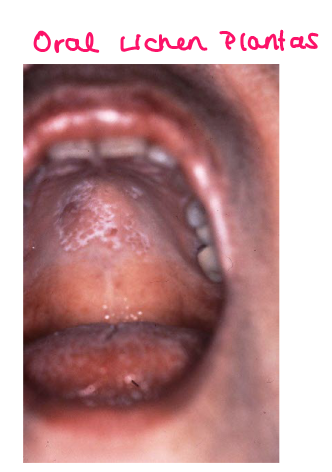
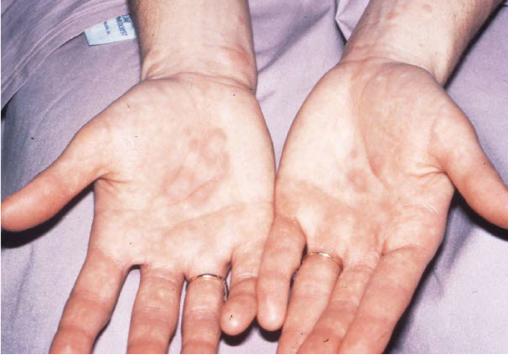
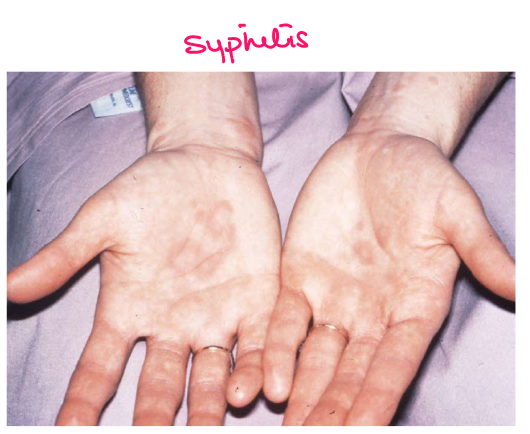
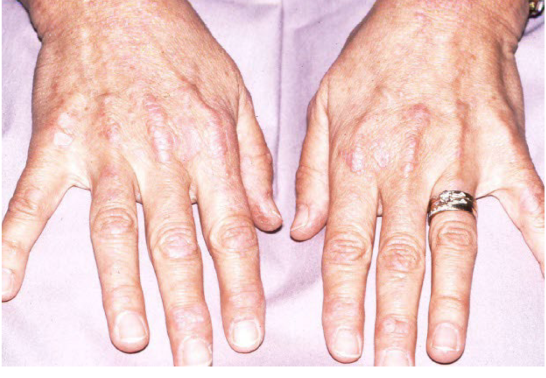
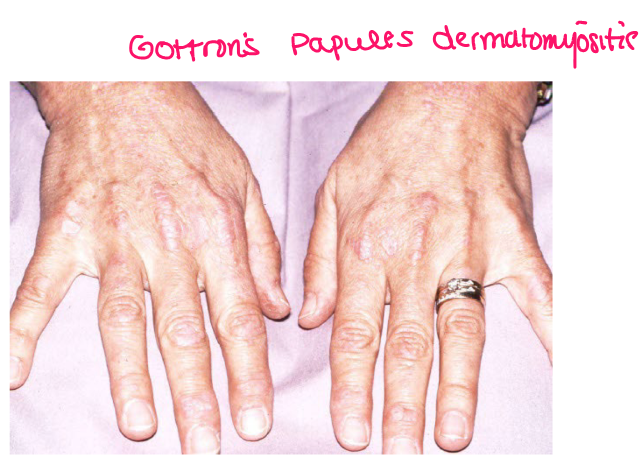
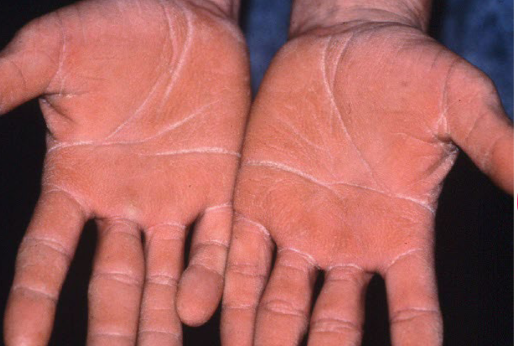
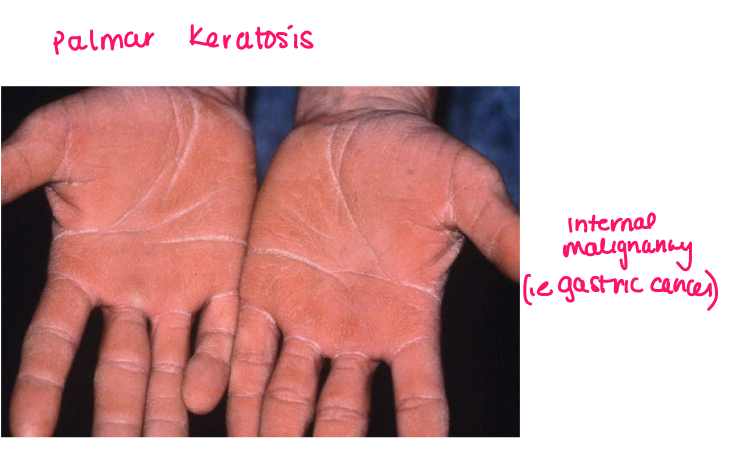
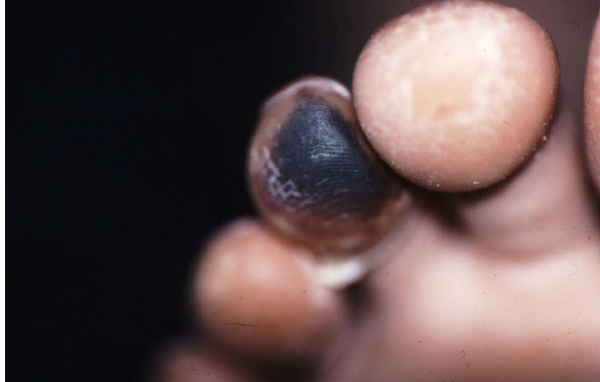
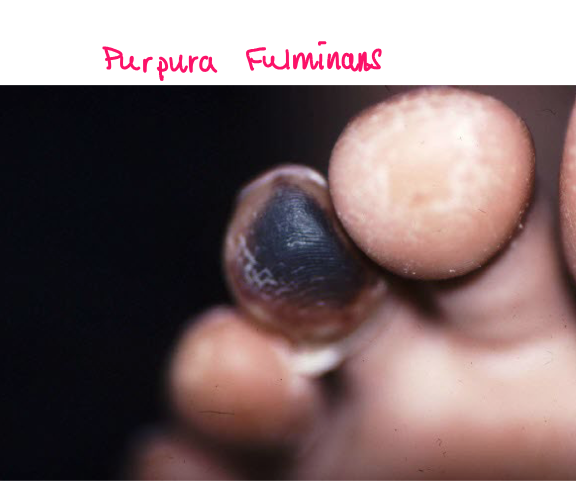
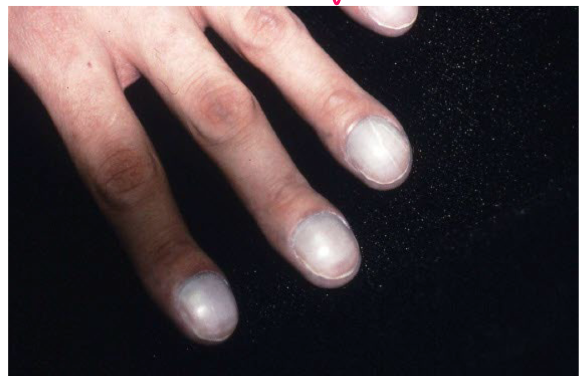
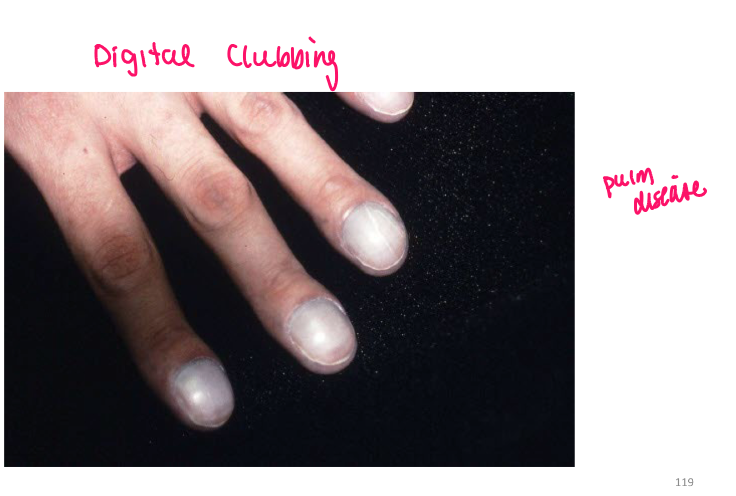
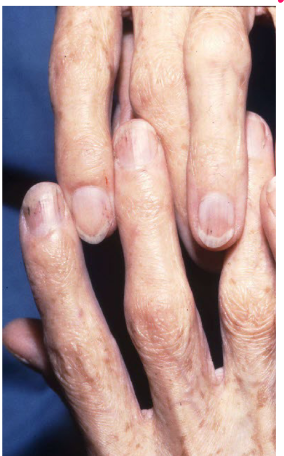
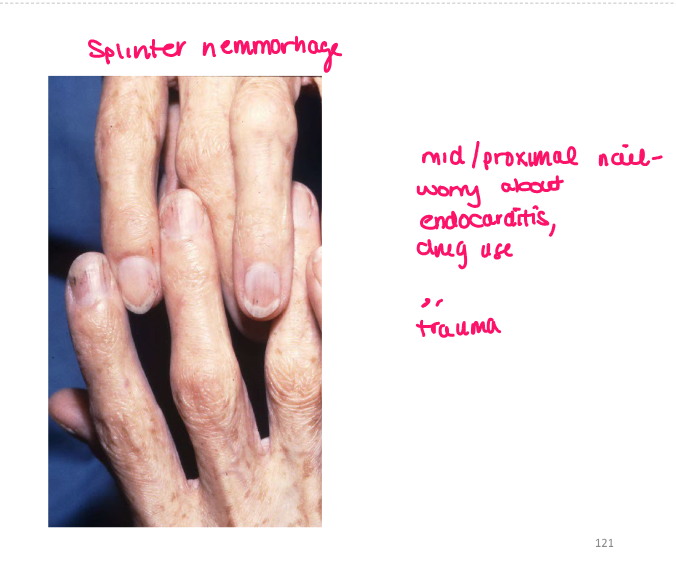
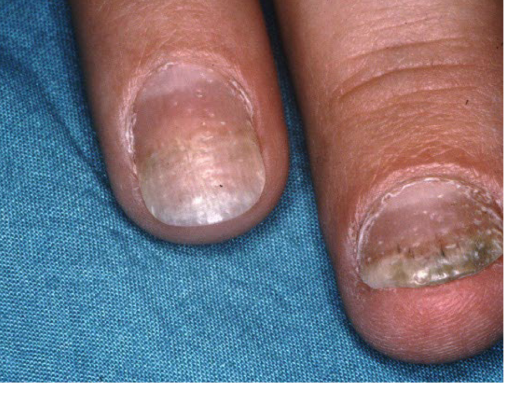
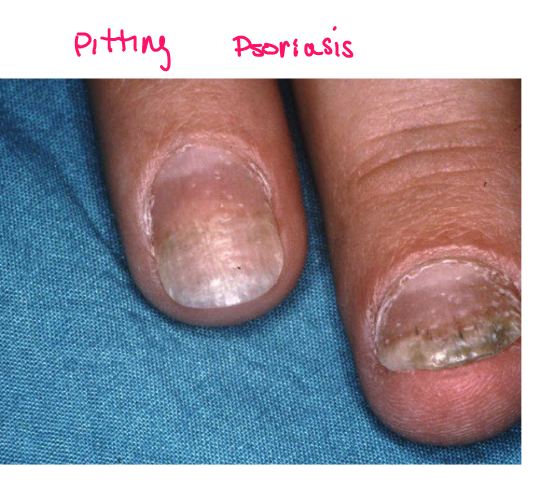
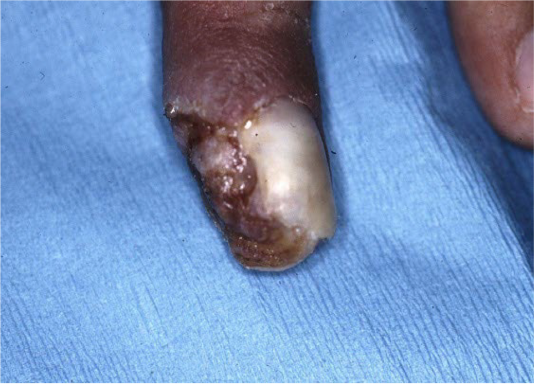
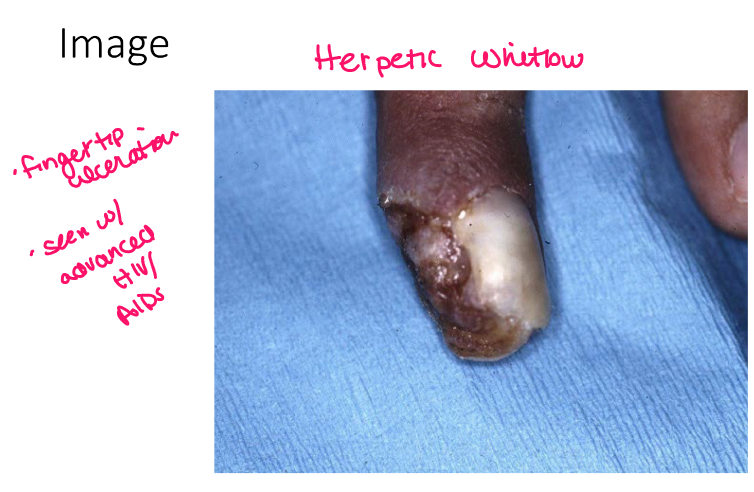
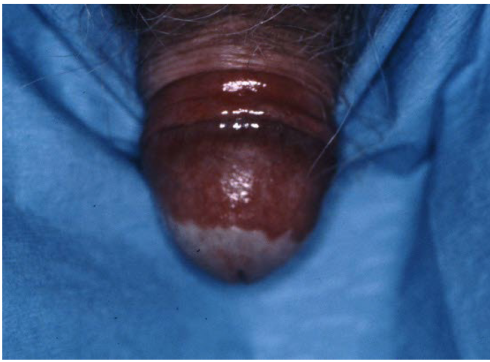
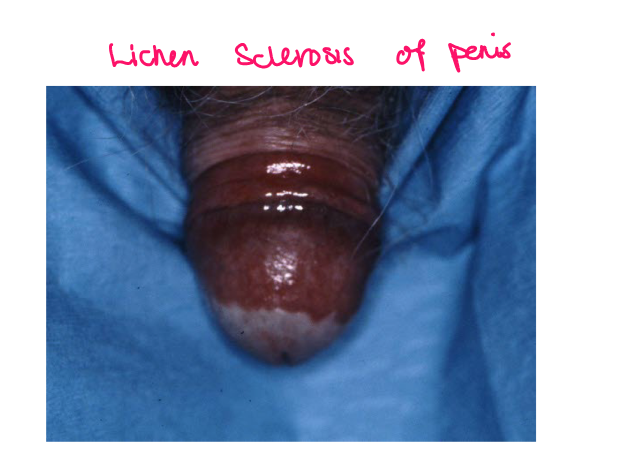
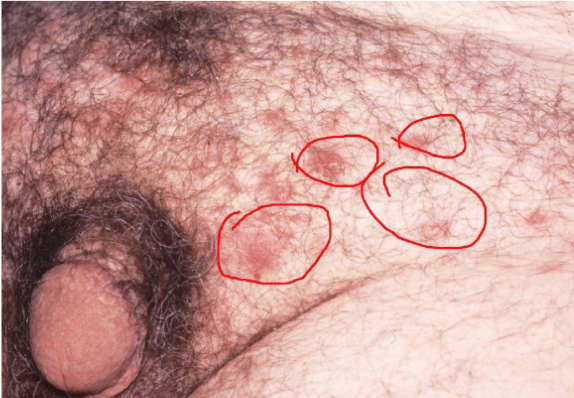
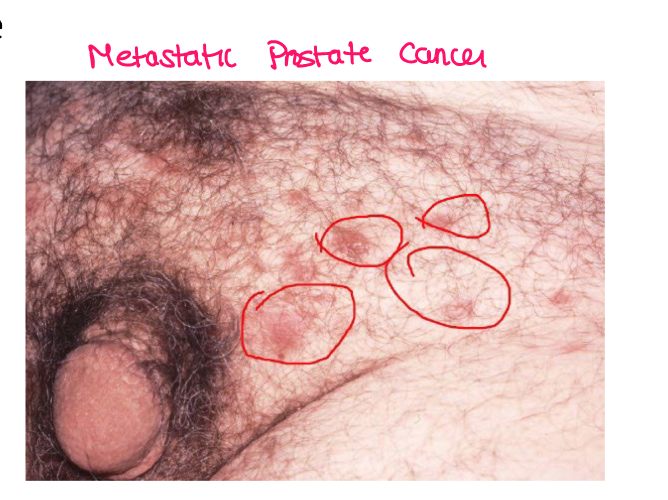
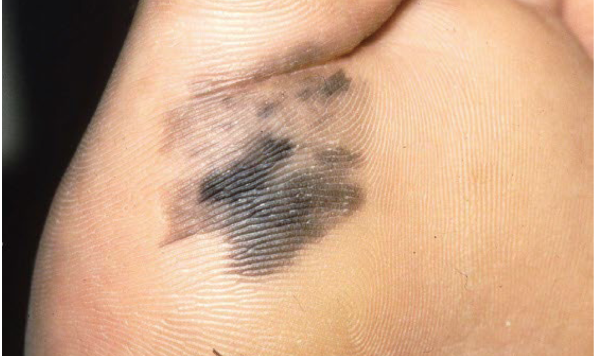
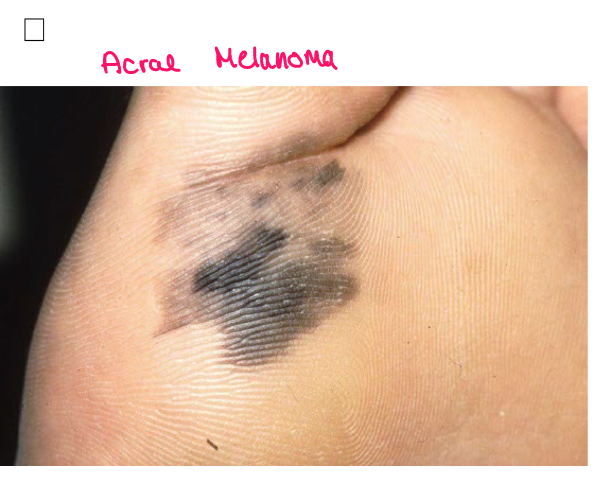
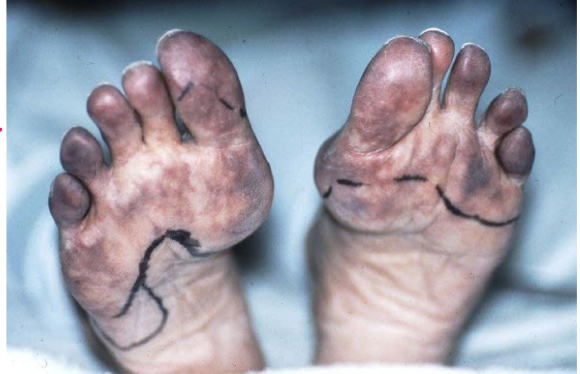
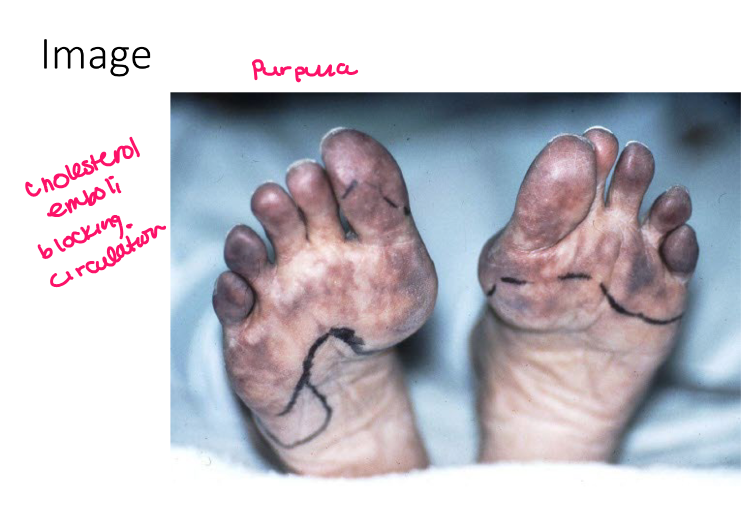
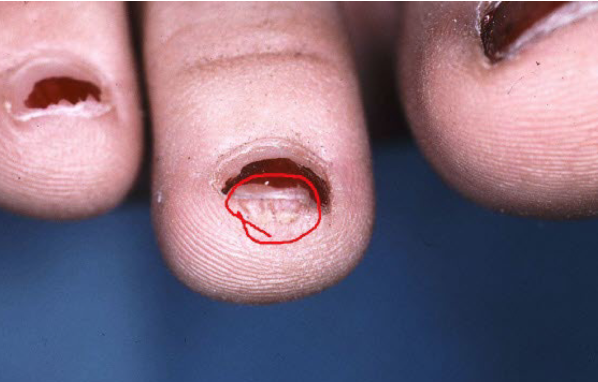
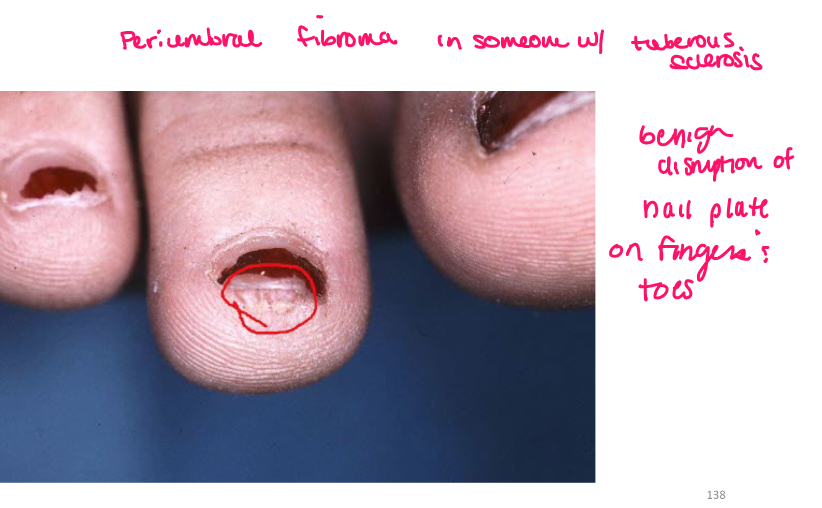
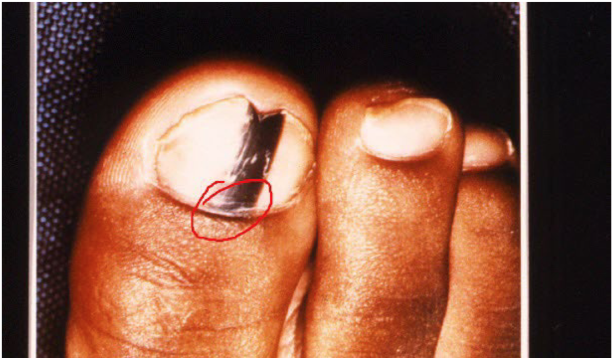
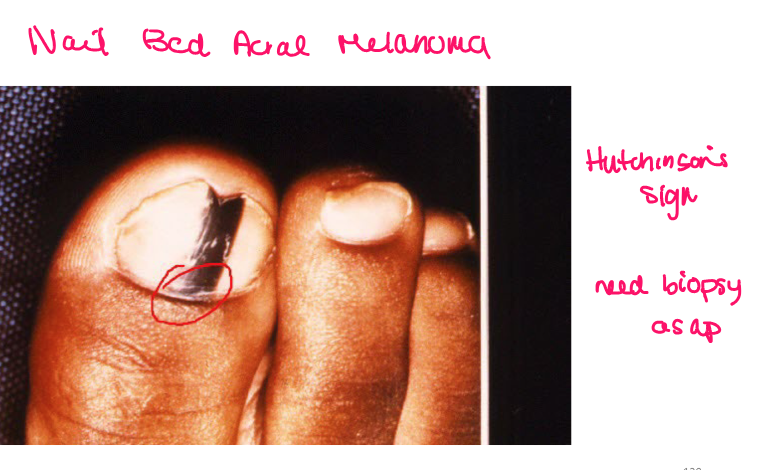
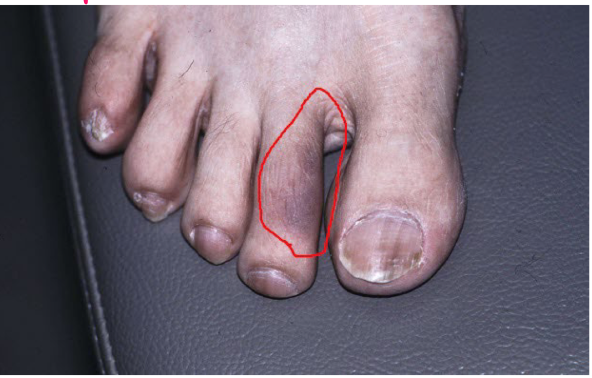
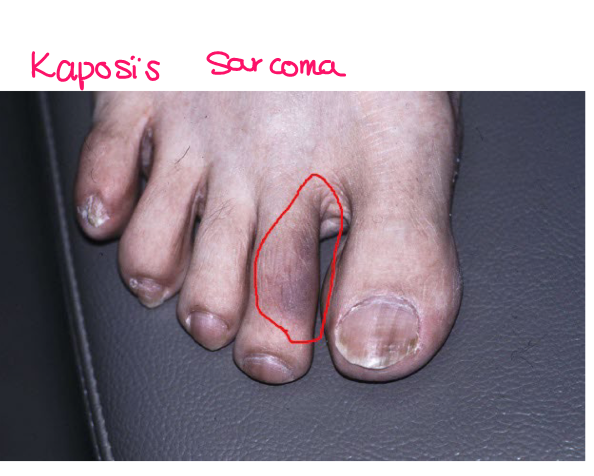
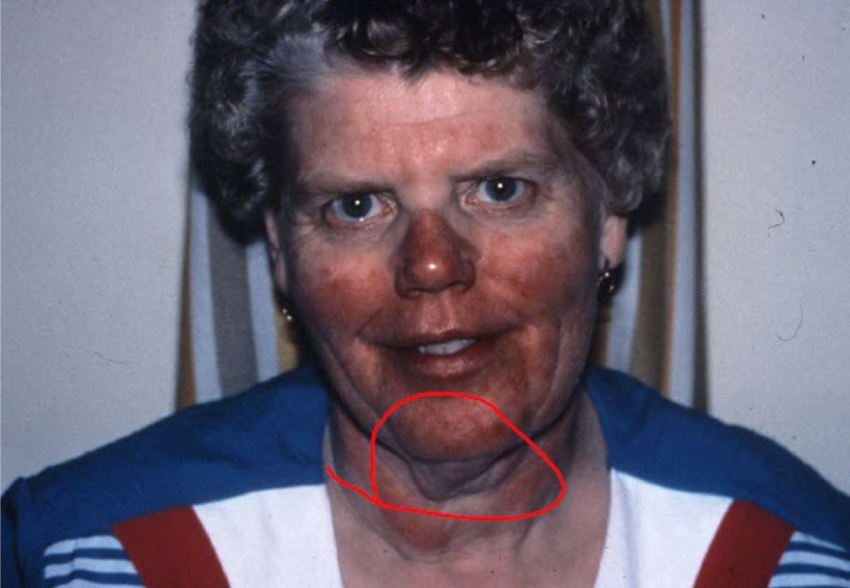
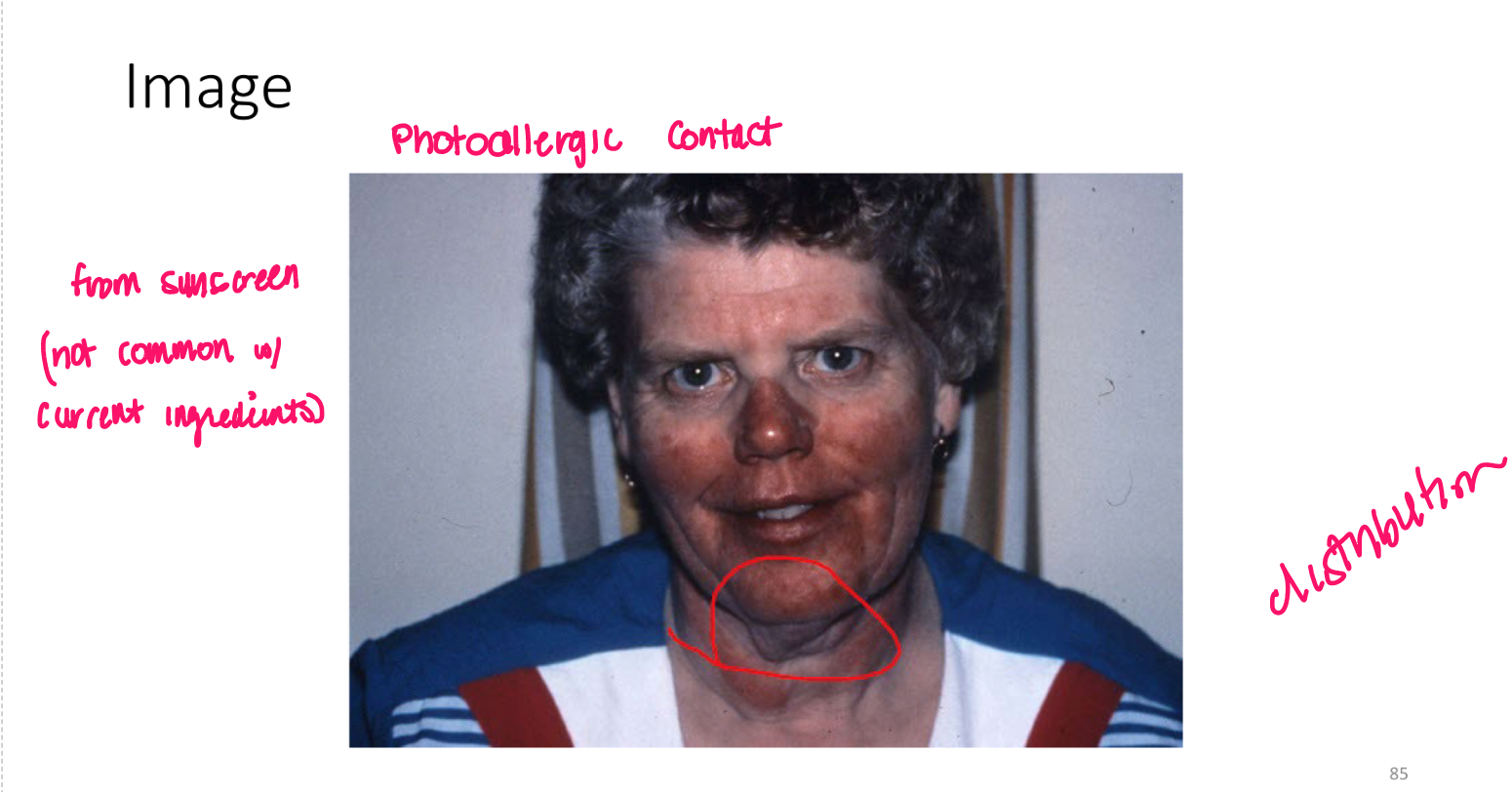
Most viral exanthems are caused by
enteroviruses
Viral exanthems
