Biology - Ch : 6 Tissue
1/52
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
53 Terms
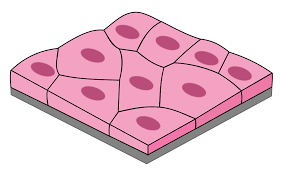
What is a tissue?
A group of cells similar in structure and function.
Why are tissues useful in multicellular organisms?
They allow division of labour and efficient functioning.
What are the two main types of plant tissues?
Meristematic tissue and Permanent tissue.
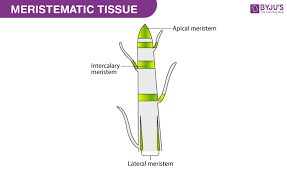
What is meristematic tissue?
Dividing tissue present in growing regions of plants.
Types of meristematic tissues?
Apical, Intercalary, Lateral.
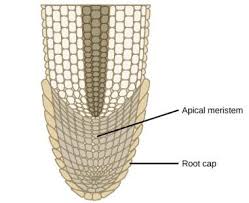
Function of apical meristem?
Increases length of stem and root.
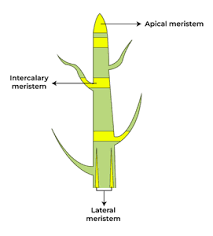
Function of lateral meristem?
Increases girth/thickness.
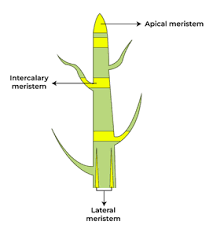
Function of intercalary meristem?
Increases length of internodes.
Key features of meristematic cells?
Dense cytoplasm, thin walls, prominent nuclei, no vacuoles.
What is differentiation?
Process by which meristematic cells become permanent and lose ability to divide.
Types of simple permanent tissues?
Parenchyma, Collenchyma, Sclerenchyma.
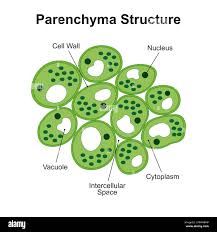
Features of parenchyma?
Living, thin-walled, loosely packed, large intercellular spaces.
Function of parenchyma?
Storage; photosynthesis (chlorenchyma); floating (aerenchyma).

Features of collenchyma?
Living, elongated, uneven thickening at corners, little intercellular space.
Function of collenchyma?
Flexibility and mechanical support.
Features of sclerenchyma?
Dead, thick lignified walls, narrow lumen.
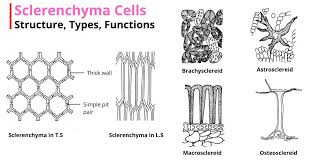
Function of sclerenchyma?
Provides strength and stiffness.
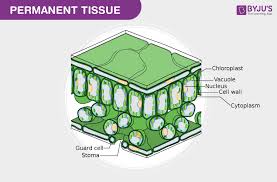
What is epidermis?
Outermost protective layer of cells without intercellular spaces.
What is cutin?
Waxy, water-proof layer on epidermis.
What are stomata?
Pores in leaf epidermis for gas exchange.
What controls stomatal opening?
Guard cells.
Role of stomata?
Gas exchange, transpiration.
What is cork?
Dead, compact cells with suberin.
Function of cork?
Protection from water loss, mechanical injury, microbes.
Examples of complex tissues?
Xylem and phloem.
Elements of xylem?
Tracheids, vessels, xylem parenchyma, xylem fibres.
Function of xylem?
Transport of water and minerals.
Elements of phloem?
Sieve tubes, sieve cells, companion cells, phloem parenchyma, phloem fibres.
Function of phloem?
Transport of food.
What are the four types of animal tissues?
Epithelial, Connective, Muscular, Nervous.
What is epithelial tissue?
Protective covering that forms body surfaces and linings.
Types of epithelial tissue?
Squamous, cuboidal, columnar, ciliated, glandular, stratified.
Function of squamous epithelium?
Diffusion and protection.
Function of cuboidal epithelium?
Secretion and absorption (e.g., kidney tubules).
Function of columnar epithelium?
Absorption (intestine).
Function of ciliated epithelium?
Moves mucus or fluids (respiratory tract).
What is glandular epithelium?
Epithelium that secretes substances.
What is the main feature of connective tissue?
Cells loosely placed in a matrix.
Types of connective tissue?
Blood, bone, cartilage, ligament, tendon, adipose, areolar.
Matrix of blood?
Plasma.
Function of blood?
Transport of substances.
Features of bone?
Hard matrix of calcium & phosphorus, supports body.
Features of cartilage?
Flexible, smoothens surfaces at joints.
What does ligament connect?
Bone to bone.
What does tendon connect?
Muscle to bone.
Function of adipose tissue?
Stores fat; insulation.
Function of areolar tissue?
Fills spaces, supports organs, repairs tissues.
Features of striated muscles?
Striped, voluntary, multinucleate, attached to bones.
Features of smooth muscle?
Non-striated, involuntary, spindle-shaped, single nucleus.
Features of cardiac muscle?
Branched, involuntary, single nucleus, rhythmic contraction.
What is a neuron?
Structural and functional unit of nervous system.
Parts of neuron?
Dendrite, cell body, axon.
What is a nerve impulse?
Electrical signal transmitted through neurons.