other metals
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
26 Terms
what are radionuclides
Radioisotopes of elements from all parts of the periodic table find both clinical and research applications
what happens in diagnostic imaging?
exploiting the tissue penetration of gamma rays derived from nuclear decay or positron annihilation
what happens in targeted therapy?
exploiting the cellular toxicity of non-penetrating alpha and beta particles and secondary electrons.
types of particles
alpha
beta
positron
proton
neutron
gamma ray
what is the description of an alpha particle?
high energy helium nuclei consising of two protons and two neutrons
what is the description of a beta particle?
high energy electrons
what is the description of a positron?
particles with the same mass as an electron but with 1 unit of positive charge
what is the description of a proton?
nuclei of hydrogen atoms
what is a neutron?
particles with a mass approximately equal to that of a proton but with no charge
what is a gamma ray?
very high-energy electromagnetic radiation
what is a cyclotron?
a particle accelerator
- electrically powered machine producing a beam of charged particles
- accelerates in a spiral path
Medical cyclotrons produce?
proton beams to manufacture radioisotopes used in medical diagnosis.
Radioisotopes produced in a cyclotron decay by either?
by either positron emission or electron capture.
What are Positron Emission Tomography (PET) and Single Photon Emission Computed Tomography (SPECT), and how do they work?
PET and SPECT are imaging techniques using gamma rays from electron capture
Both rely on cyclotron-produced radioisotopes
PET: Detects positrons emitted by the radioisotopes
SPECT: Detects gamma rays emitted by the radioisotopes
How do modern cyclotrons accelerate particles?
Negative ions are created in a plasma and accelerated
When they reach the outer edge, electrons are stripped off, forming positive particles like protons or deuterons
These positive particles are then extracted as a beam
What is SPECT, and how does it work?
Dual-mode imaging technique:
Single Photon Emission: Detects a single gamma ray (compared to PET's pair of gamma emissions)
Computer Tomography: Uses sectional X-ray images
Why is 99mTc commonly used in SPECT imaging?
why are Nearly 80% of all radio-pharmaceuticals used in clinical studies 99mTc
Easy availability: Eluted from a generator
Optimal nuclear properties:
Half-life (t½) = 6.05 hours
Low-energy γ rays
Low cost:
What is Positron Emission Tomography (PET), and how does it work?
PET involves the emission of a positron (positive electron) which annihilates to produce two identical gamma rays
Often combined with CT or MRI to overlay organ or body structures
: What isotopes are commonly used in PET for diagnostics?
Fluorine-18 ([18F]FDG), an analogue of glucose, used in 90% of clinical oncology PET scans
what is Zirconium89 used for?
Diagnostic PET
Zirconium-89 labeled antibodies: A new Tool for molecular imaging in cancer patients
What is Gallium-68 used for in PET imaging?
Gallium-68 used for imaging gastroenteropancreatic neuroendocrine tumors (GEP-NETs)
Can the metal radioisotope in a diagnostic agent be changed?
Yes, Lutetium can be exchanged for Gallium
This changes the agent from a diagnostic positron-emitting isotope to a therapeutic beta emitter
what is positron decay?
Breakdown of a proton into a neutron, positron, and neutrino.
Positron is annihilated when exposed to an electron, releasing gamma radiation. Releases heat
what is Beta decay?
-the breakdown of a neutron into a proton and an electron
Converts to another element,
emits some low energy gamma photons in some directions, but also a high ionising electron
What are the two common components of therapeutic radiotherapy or theranostic agents?
Chelated radioisotope (e.g., Lutetium-177 or Yttrium-90)
Targeting group (e.g., peptide sequence or antibody) that is internalised by diseased cells
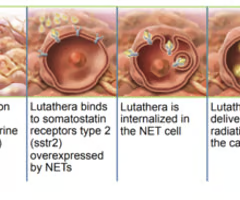
what is the mode of action of Lutathera?
through binding of Somostatin receptor