Foundations Exam 3 Material - Nucleotide Metabolism, DNA Replication, DNA Repair
1/195
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
196 Terms
What is chronic/delayed toxic exposure?
more than 3 months, repeated doses
What is an informational pathway?
pathway in which genetic information is stored as the nucleotide sequence is maintained and expressed
How is information from parenteral DNA copied to daughter DNA with high fidelity?
DNA replication
How is RNA synthesized using DNA as a template?
transcription
How are viruses able to make RNA and DNA using RNA as a template?
Reverse transcription
Define gene
segments of DNA that code for peptides and RNA; different from regulatory sequences, DNA can be expressed differently to yield different products
How is DNA involved in transcription?
one strand of double-stranded DNA acts as the molecular template for RNA synthesis
What happens in translation?
triplets of nucleotides in mRNA bind complementary triplets in tRNA
What determines biological function?
the protein sequence
Human somatic cells have how many chromosomes?
46 (22 diploid pairs plus X and Y)
Do mitochondria and chloroplasts have DNA?
Yes; double stranded circles
What is the majority of eukaryotic DNA?
non-coding DNA
(T/F) The total length of DNA, nor the number of chromosomes correlates strongly with the complexity of an organism.
False
How is eukaryotic DNA organized?
into a complex called chromatin
How much of the total genome encodes for proteins?
a small fraction (1.5%)
What are some non-protein things that are encoded in the total genome?
things that are involved in regulation of gene expression (promoted, terminations signals, etc), small regulatory RNA, junk DNA (pieces of unwanted genes, remnants of viral infections)
What are exons?
expressed sequences that are translated into the amino acid sequence
What are introns
regions of genes that are transcribed but not translated; do not encode polypeptide sequence
What happens to introns?
they are removed after transcription and the exon mRNA sequences are spliced together; creates mature transcripts
What are transposons?
sequences that can move around within the genome of a single cell
Describe transposon characteristics
ends of transposons contain terminal repeats, these repeats hybridize with complementary regions of target DNA during insertion; account for 50% of human genome
Describe simple sequence repeats (SSRs)
short sequences with millions of repeats also known as satellite DNA, associated with centromeres and telomeres
What are telomere sequences for?
may form special loop structures to keep DNA ends from unraveling
What adds telomere sequences to chromosomes?
telomerase
Describe cellular DNA aging
in many tissues, telomeres are shortened after each round of replication
What is the hayflick limit?
normal human cells divide about 52 times before losing the ability to divide again
What are centromere sequences?
AT-rich repeated sequences essential for equal distribution of chromosome sets to daughter cells; region where two daughter chromosomes are held together during mitosis
What is DNA supercoiling?
the formation of additional coils in DNA due to twisting forces
Why does DNA need to be organized?
packing of large DNA molecules within cells; access of proteins to read the information in DNA sequences
What is non-supercoiled DNA called?
relaxed
Supercoiling has great influence on ________ and ________ of DNA
transcription and replication
Is supercoiling regulated?
Yes
Most cellular DNA is under-wound in what form?
normal B-form
(T/F) Closed circular DNA is rarely relaxed
True
How is linear DNA underwound?
With the help of proteins to prevent strands from rotating
What additional DNA structural changes are facilitated by underwinding?
maintain structure of cruciforms at palindromes (cruciforms rarely occur in relaxed DNA), facilitate formation of stretches of left-handed Z-form
What are topoisomers?
Different forms of DNA that differ only in the degree and nature of supercoiling
What is required for conversion between topoisomers?
a DNA strand break
What type of supercoiled DNA travels faster in agarose gel electrophoresis experiment than relaxed or nicked DNA?
negatively supercoiled DNA
What do topoisomerases do?
cur DNA strands for DNA unwinding and rewinding during transcription and replication
What are the major types of topoisomerases?
type 1 and type 2
Describe Type 1 topoisomerase
makes a transient cut in one DNA strand
Describe type 2 topoisomerase
makes a transient cut in 2 DNA strands;
What is the type 1 topoisomerase mechanism?
Tyrosine reside attacks phosphate and cuts one strand; forms new bond to DNA strand, enzyme changes to an open conformation, unbroken DNA strand passes through the break in the first strand, enzyme in closed conformation, liberated OH attacks the linkage to re-ligate the cleaved DNA strand
What are the main eukaryotic topoisomerases?
Topo 1, 2alpha, 2beta, 3
What eukaryotic topoisomerases are type 1
Topo 1 and Topo 3
What are the two subfamilies of type 2 topoisomerases?
2a and 2b; can relax both positive and negative supercoils
What is the mechanism of eukaryotic type 2a topoisomerase?
Two tyrosines attack double stranded DNA, Second segment of the same DNA molecule (double stranded) passes through break, breaks are re-ligated via two ATP molecules
What are coumarins (novobiocin, coumermycin A1)?
drug that inhibits bacterial type 2 topoisomerases from binding ATP
What are quinolones(nalidixic acid, ciprofloxacin)?
inhibit the last step of topoisomerase, which is resealing the DNA strand breaks, wide-spectrum and mostly selective for bacterial enzymes (antibiotics)
How are topoisomerases used as chemotherapy agents?
target cancer because most rapidly growing cells (tumors, others) express topoisomerases
How do eukaryotic type 1 topoisomerase inhibitors work?
trap the enzyme-DNA complex in its cleaved state
What is chromatin?
fibers of DNA and protein where DNA associates tightly with proteins called histones
What are histones?
small proteins with lots of basic (Lys, Arg) residues (often positively charged)
What are nucleosomes?
DNA and protein packed into discrete units
What does wrapping of DNA around the histone core require?
the removal of one helical turn
When under-winding occurs without a strand break, what forms?
a compensatory positive supercoil
How is the positive supercoil relaxed?
By a topoisomerase, leaving DNA with a net negative supercoil
Where does histone binding occur more often?
AT rich regions, staggering at 10bp intervals that facilitate its binding around the histone core
What are some roles of nucleic acids?
cellular energetics, messengers (within the cell/mRNA from nucleus) and from outside the cell (in response to hormones), molecular repositories of information
How are nucleic acids involved in biotechnological processes?
genetic testing, vaccine development, drug development, nutraceuticals, metabolic engineering, etc
Nucleic acids have what properties?
ordinal and informative
What is a nucleotide?
nitrogenous base, pentose, and phosphate
What is a nucleoside?
nitrogenous base and pentose
What is a nucleobase?
only nitrogenous abse
What is the phosphate group charge at neutral pH?
negatively charged, in nucleotides at 5' position
What pentose sugar is in RNA?
beta-D-ribofuranose
What pentose sugar is in DNA?
B-2'-deoxy-ribofuranose
Identify adenine
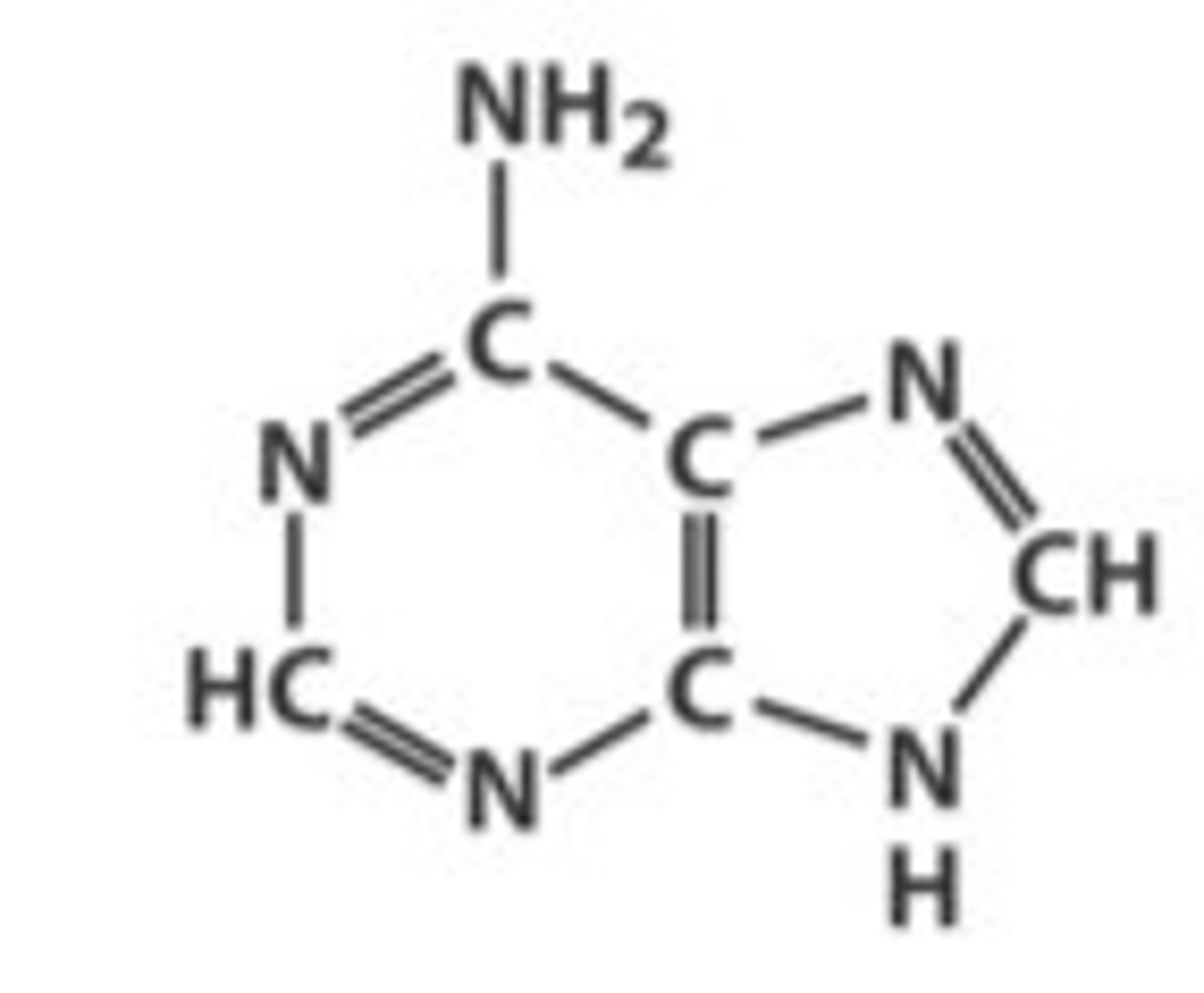
Identify guanine

What are the purines?
adenine and guanine
Identify cytosine
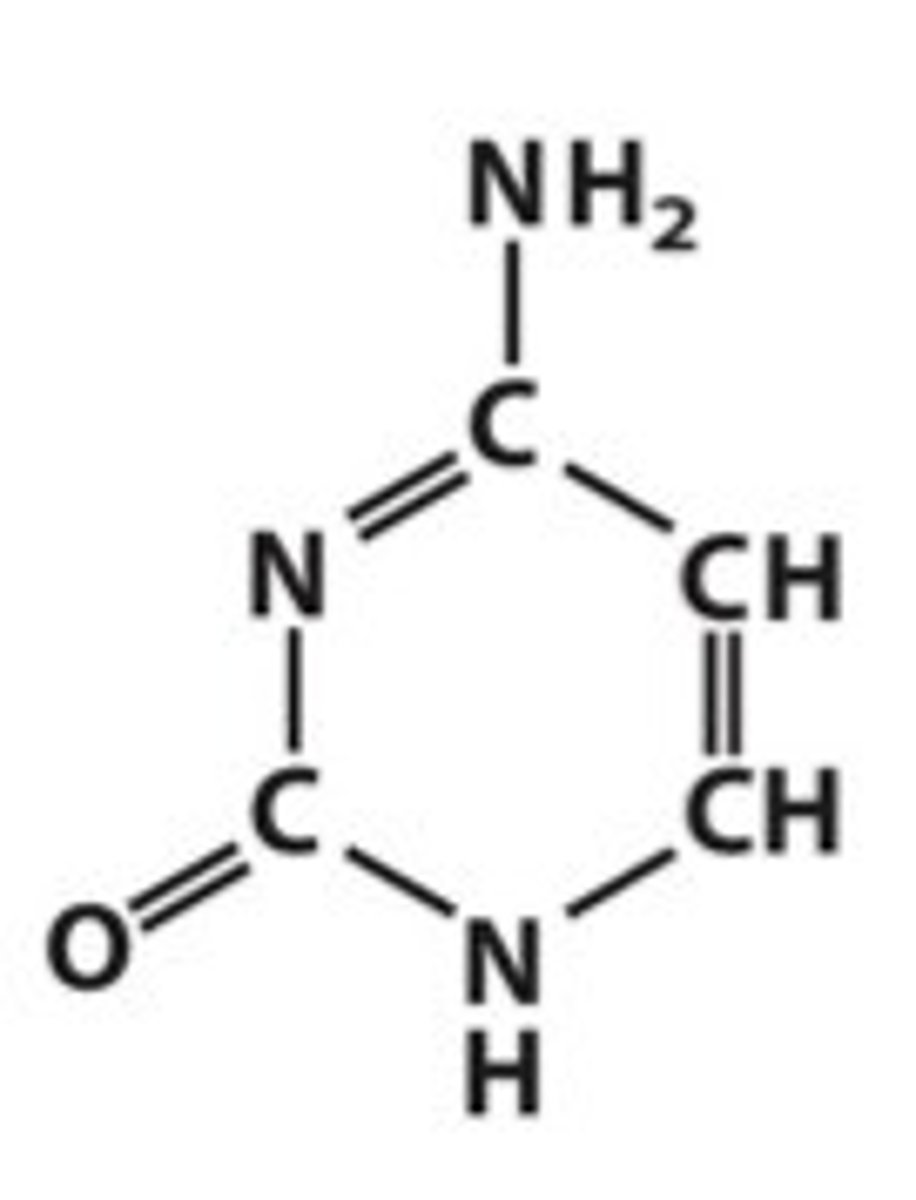
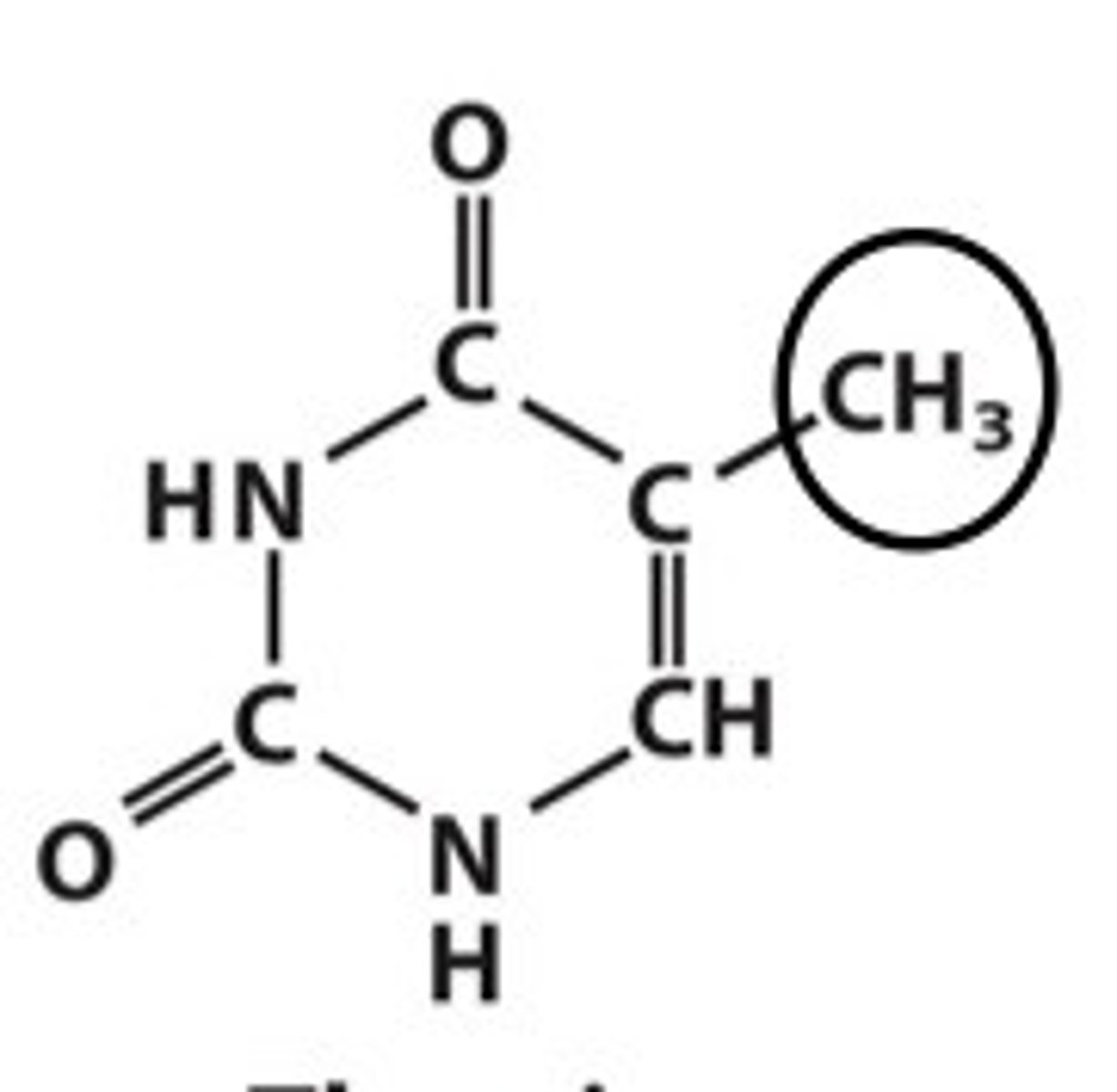
Identify thymine
Identify uracil
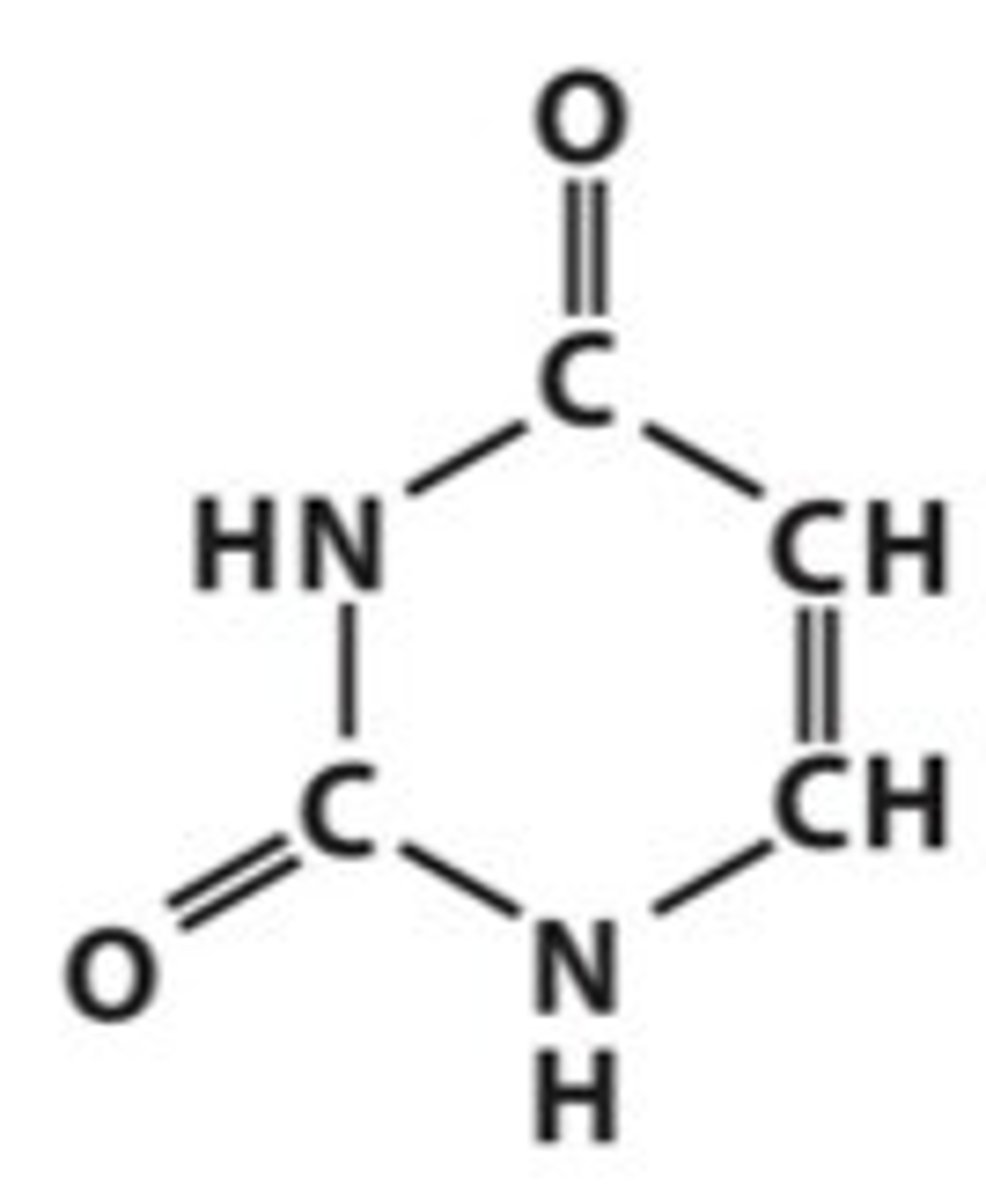
What are the pyrimidines?
cytosine, thymine, and uracil
Where do you find cytosine?
in both DNA and RNA
Where do you find thymine?
only in DNA
Where do you find Uracil?
only in RNA
What are some common characteristics of pyrimidine bases?
all are good H-bond donors and acceptors
Pyrimidine bases are neutral molecules at what pH?
7
Where are adenine and guanine found?
in both RNA and DNA
What are some characteristics of purine bases?
good H-bond donors and acceptors
Purine bases are neutral molecules at what pH?
7
How are pentose rings attached to nucleobases?
via N-glycosidic bonds
Where are N-glycosidic bonds formed?
formed to the anomeric carbon of the sugar in the b conformation
In pyrimidines, where is the N-glycosidic bond formed?
position N1
In purines, where is the N-glycosidic bond formed?
position N9
Are N-glycosidic bonds stable toward hydrolysis?
Yes, especially in pyrimidines
What is the rotation like for N-glycosidic bonds in free nucleotides?
free rotation
Identify deoxyadenylate
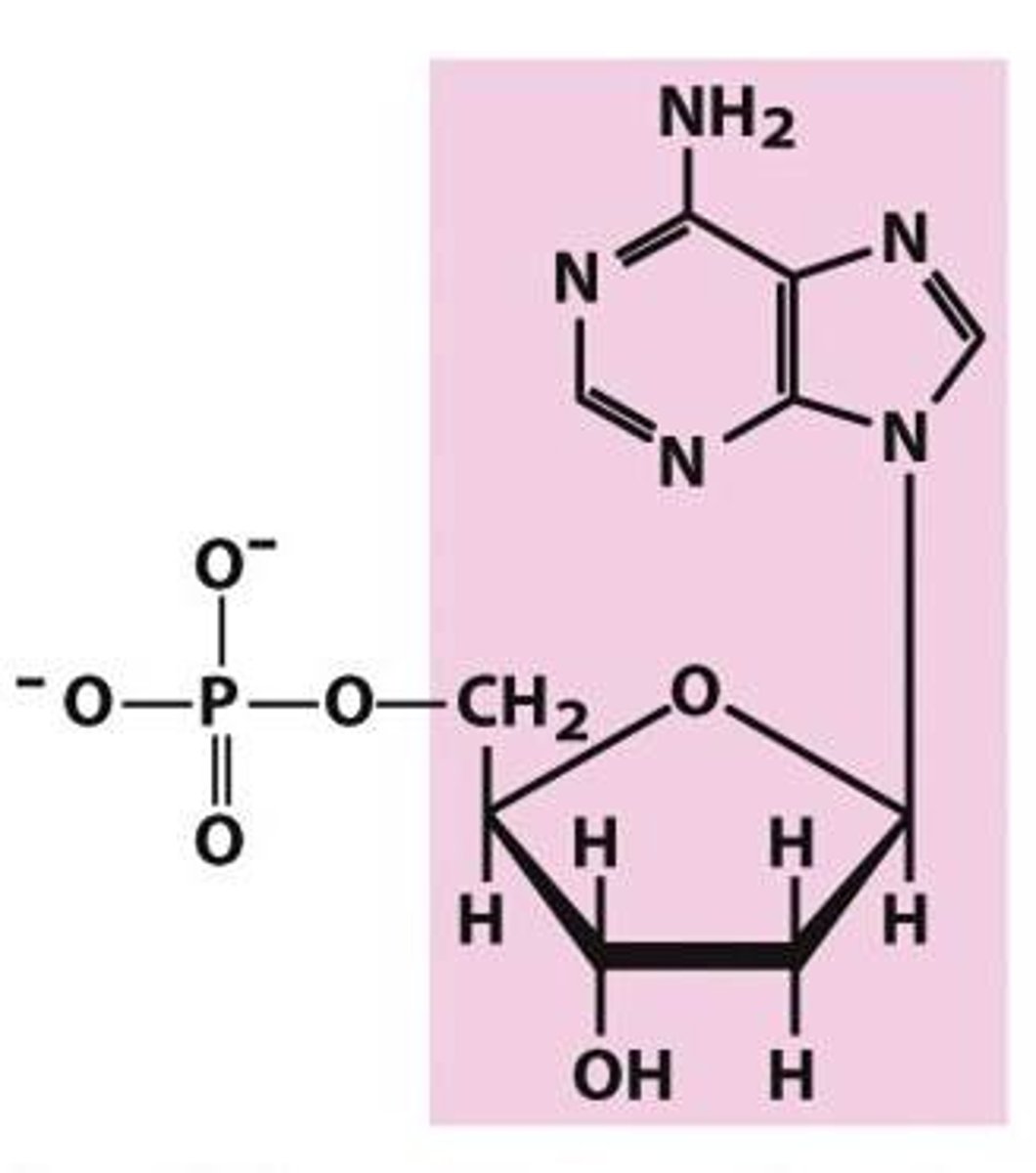
Identify deoxyguanylate

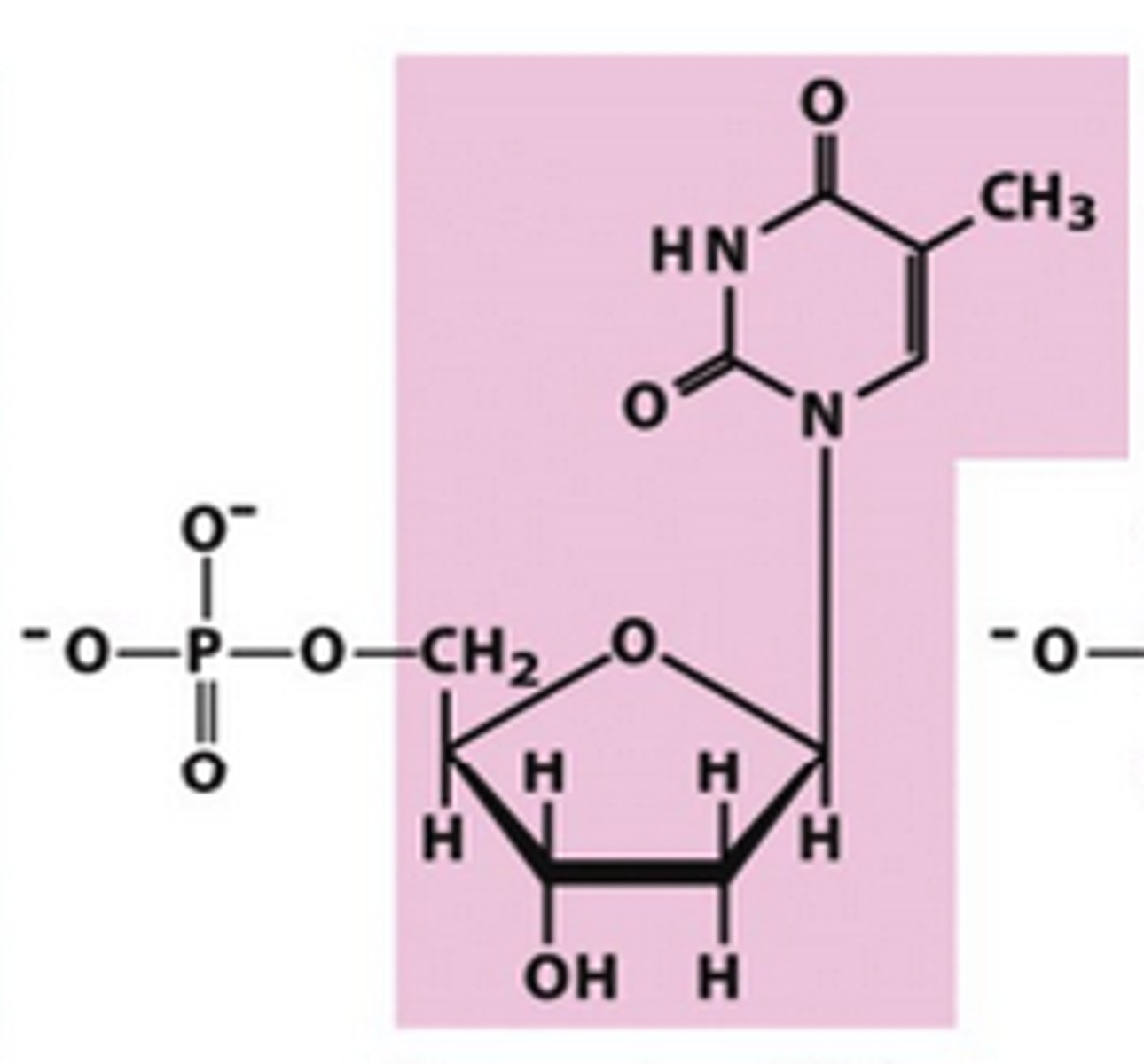
Identify deoxythymidylate
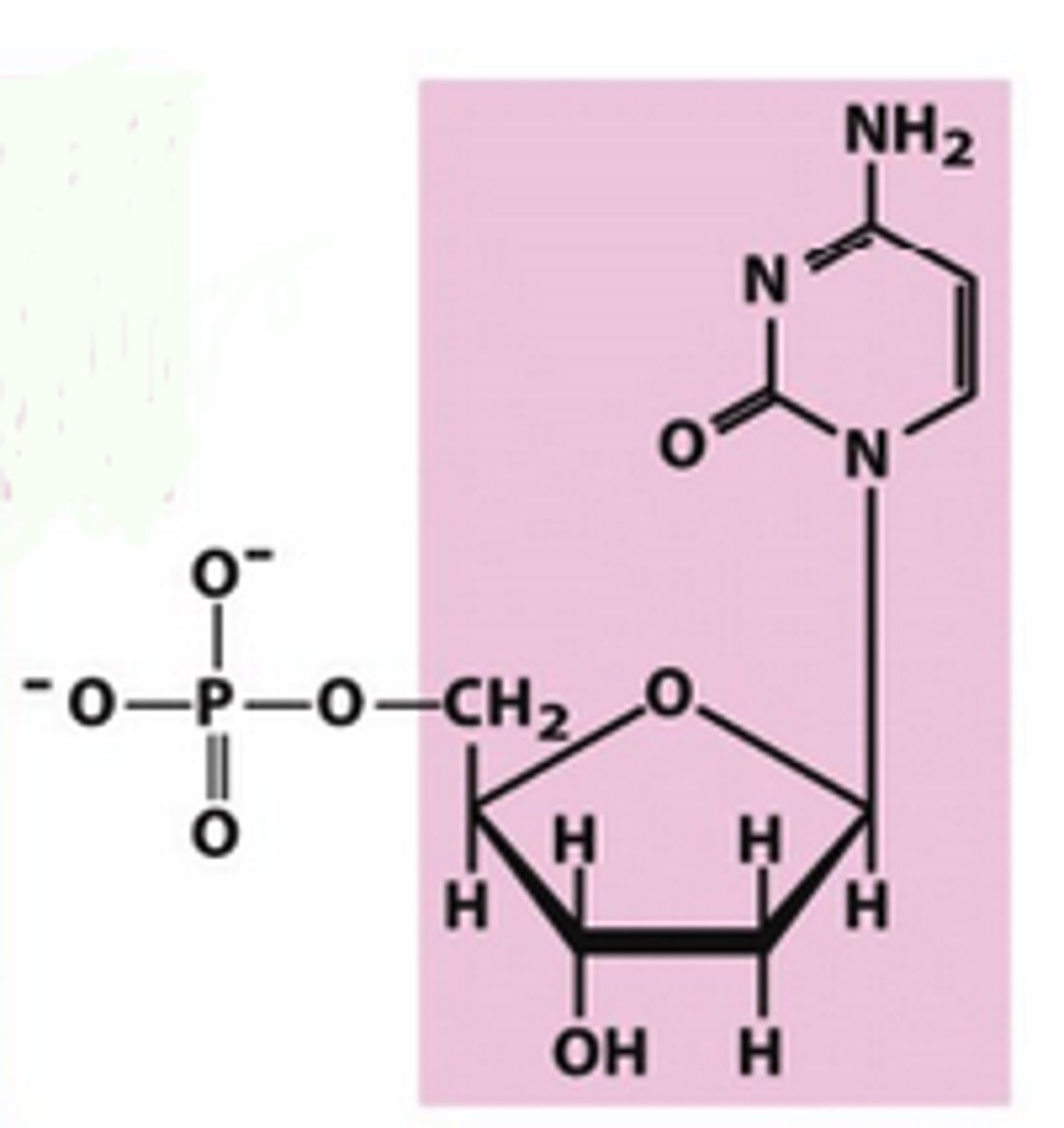
Identify deoxycytidylate
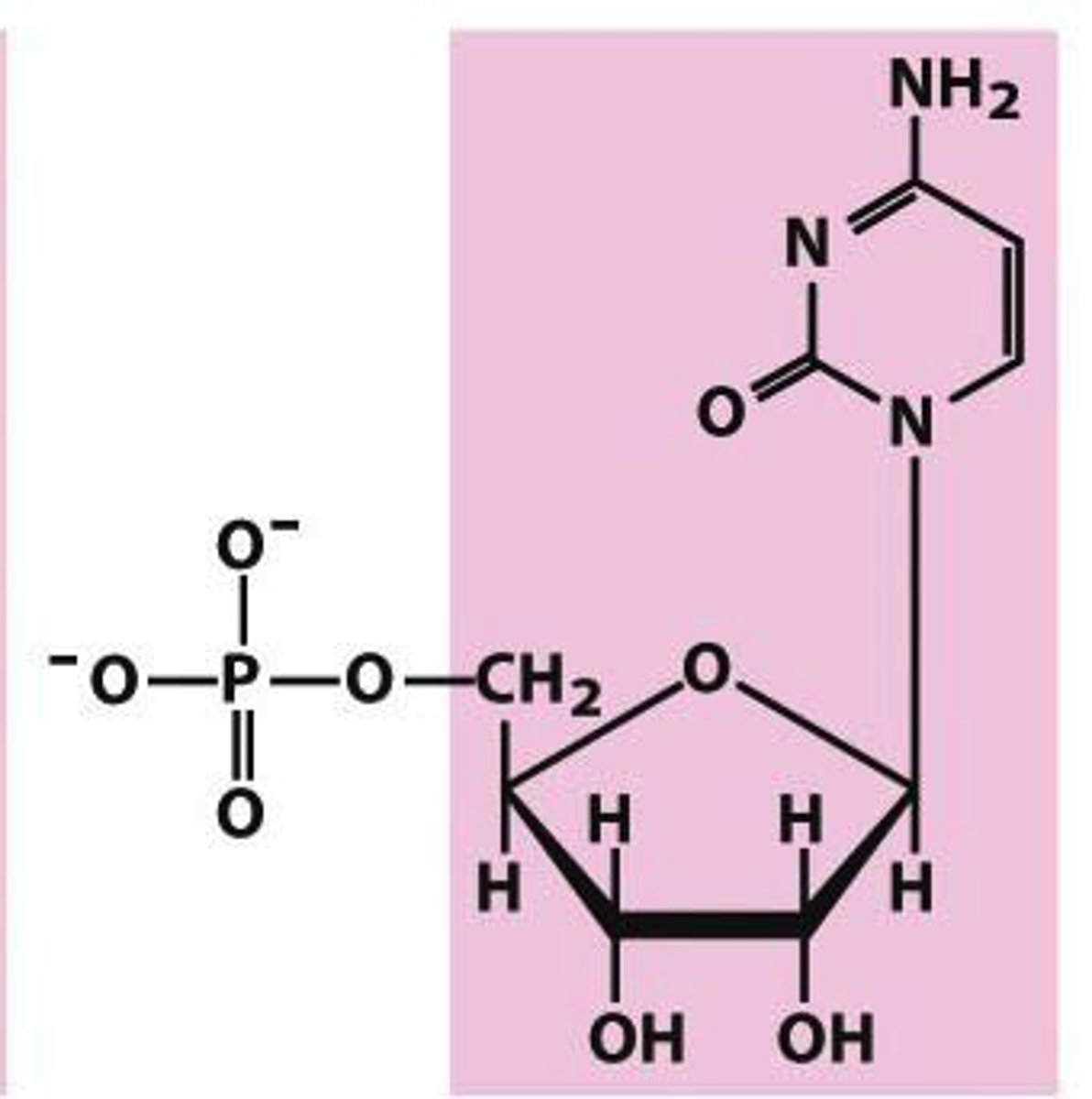
Identify adenylate
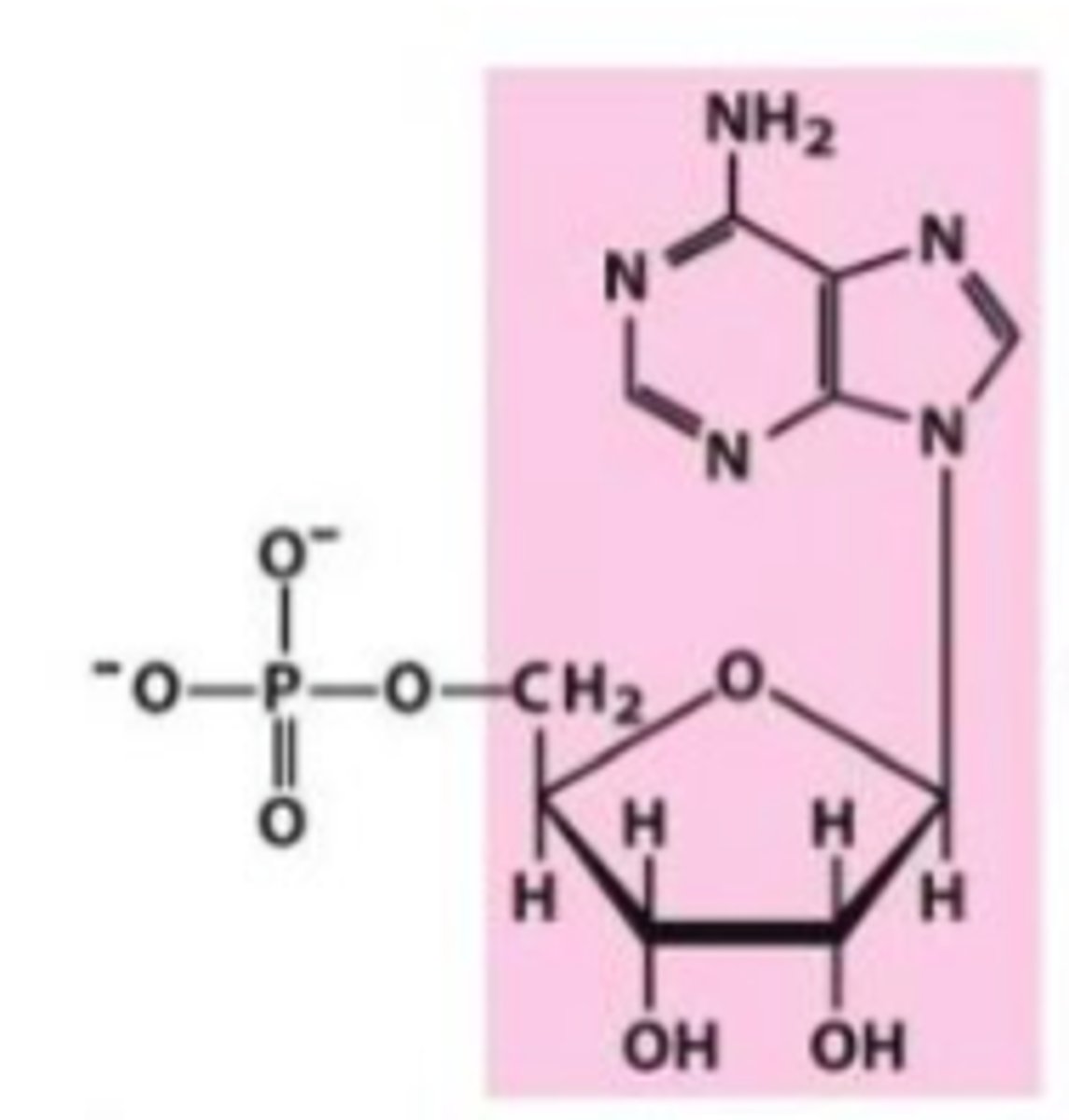
Identify guanylate
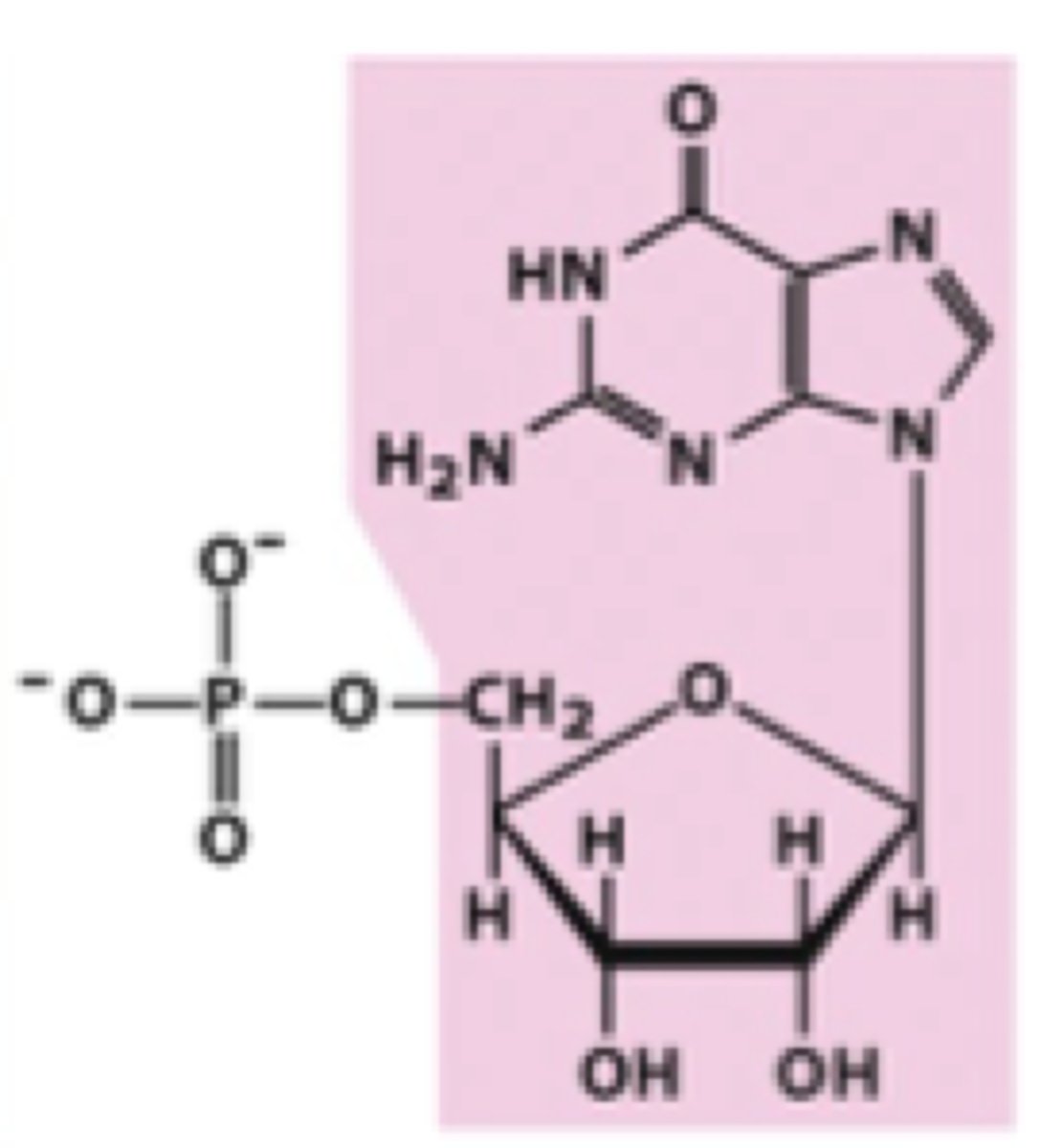
Identify uridylate
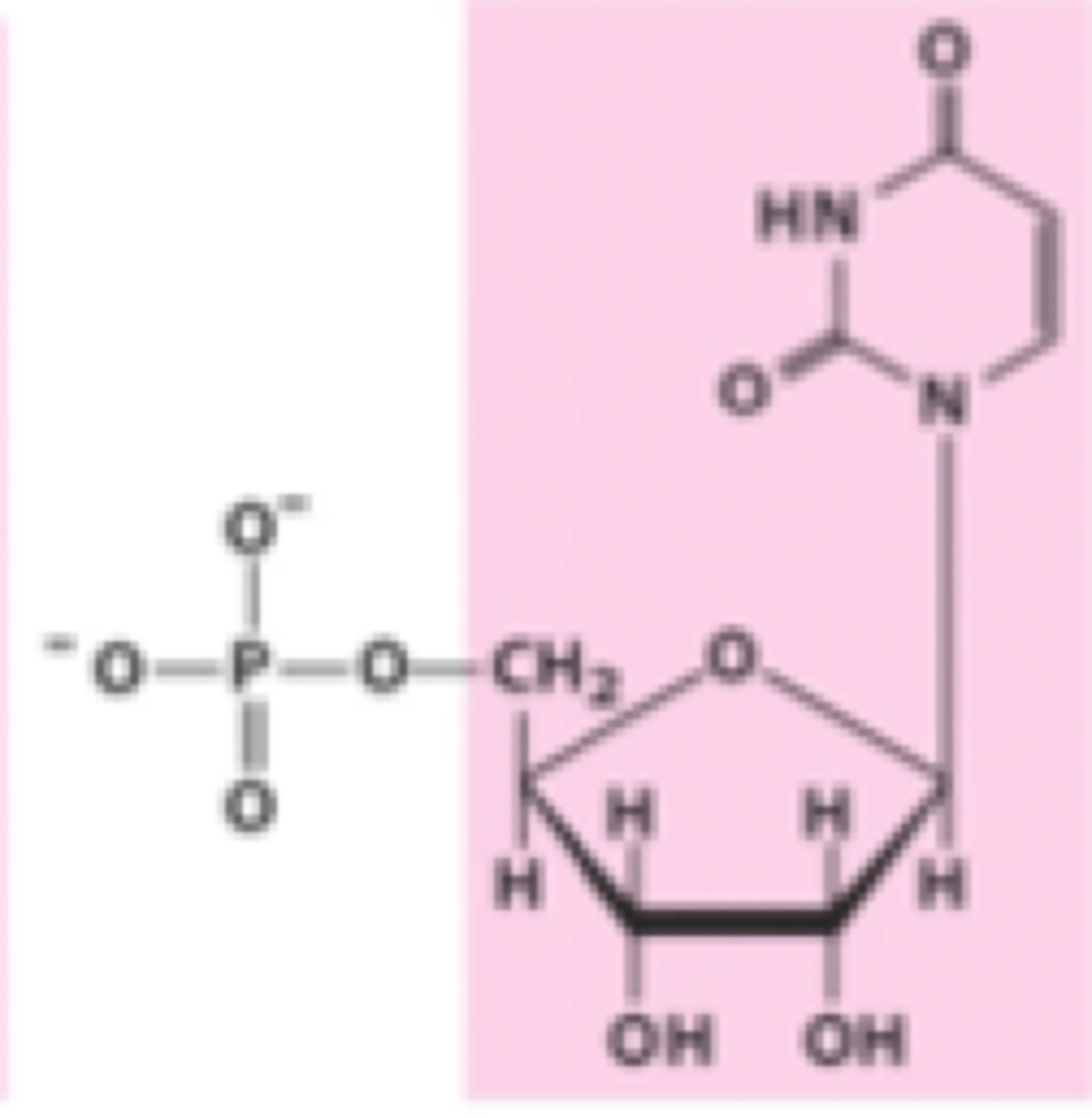
Identify cytidylate
What is 5-Methylcytidine?
common minor nucleoside in DNA found in eukaryotes and bacteria; is an epigenetic marker
What is an epigenetic marker?
way to mark which genes should be active
What turns genes off from being expressed?
methylation