M1 - Intro to Structure and Function
1/35
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
36 Terms
Anatomy
is the study of the body's structures (what it's made of)
Physiology
Physiology is the scientific study of the chemistry and physics of the structures of the body and the ways in which they work together to support the functions of life.
Gross Anatomy
Study of the larger structures of the body, typically with the unaided eye; also referred to as macroscopic anatomy
Regional Anatomy
Focuses on studying the body in sections or parts (e.g., head and neck, thorax, abdomen, etc.)
Microscopic Anatomy
Study of very small structures of the body using magnification
Systemic anatomy
Focuses on studying the body by organ systems (e.g., skeletal, muscular, nervous, etc.)
Homeostasis
Steady state of body systems that living organisms maintain
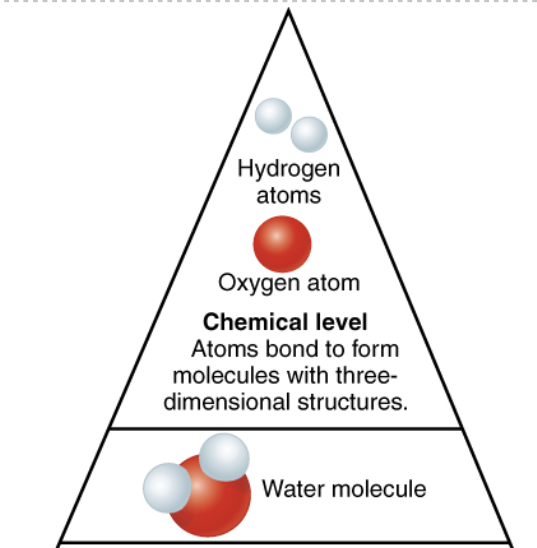
Chemical Level
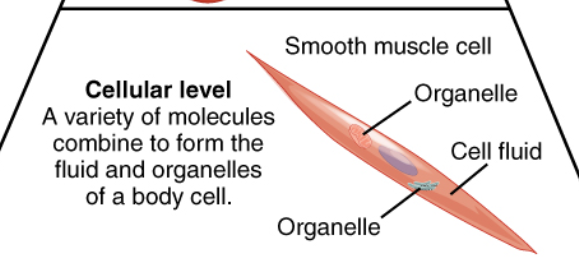
Cellular Level
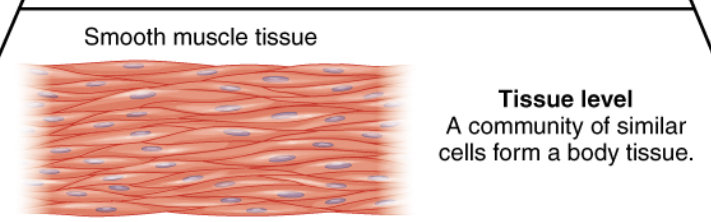
Tissue Level
Organ Level
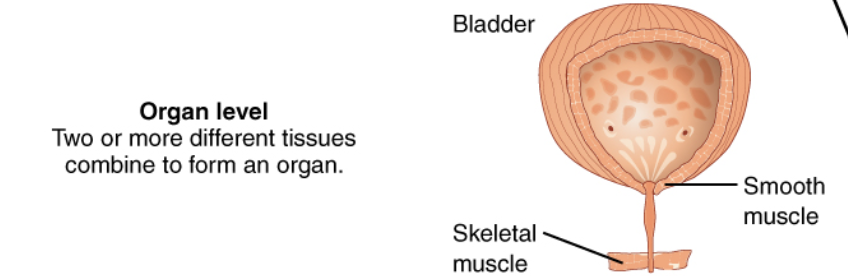
Organ System Level
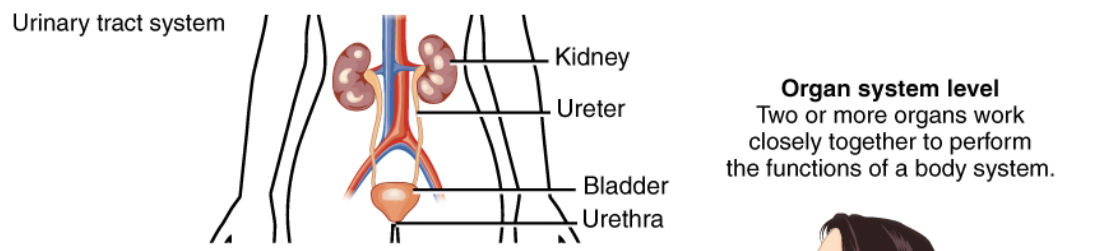
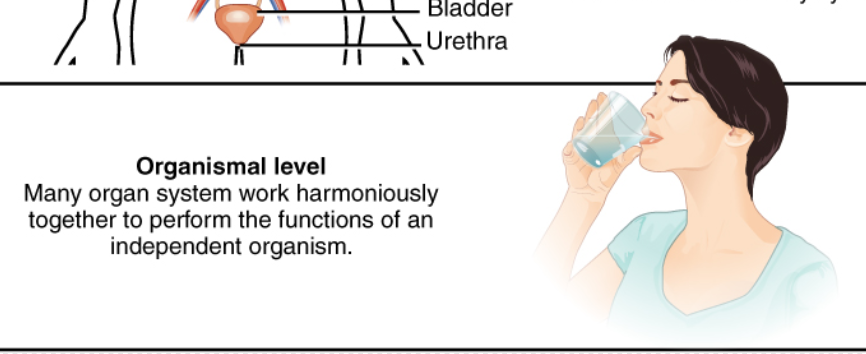
Organismal Level
Set point
is the physiological value around which the normal range fluctuates.
Negative feedback
is a mechanism that reverses a deviation from the set point, and in turn, maintains body parameters within their normal range.
Positive feedback
intensifies a change in the body’s physiological condition rather than reversing it.
A sensor, also referred to a receptor
monitors a physiological value, which is then reported to the control center.
The control center
compares the value to the normal range. If the value deviates too much from the set point, then the control center activates an effector.
An effector
causes a change to reverse the situation and return the value to the normal range.
Homeostasis
is the activity of cells throughout the body to maintain the physiological state within a narrow range that is compatible with life. Homeostasis is regulated by negative feedback loops and, much less frequently, by positive feedback loops.
A body that is lying face down is described as
prone
A body that is lying face up is described as
supine
Anterior (or ventral)
describes the front or direction toward the front of the body. The toes are anterior to the foot.
Remember Audio and Visual is towards the front
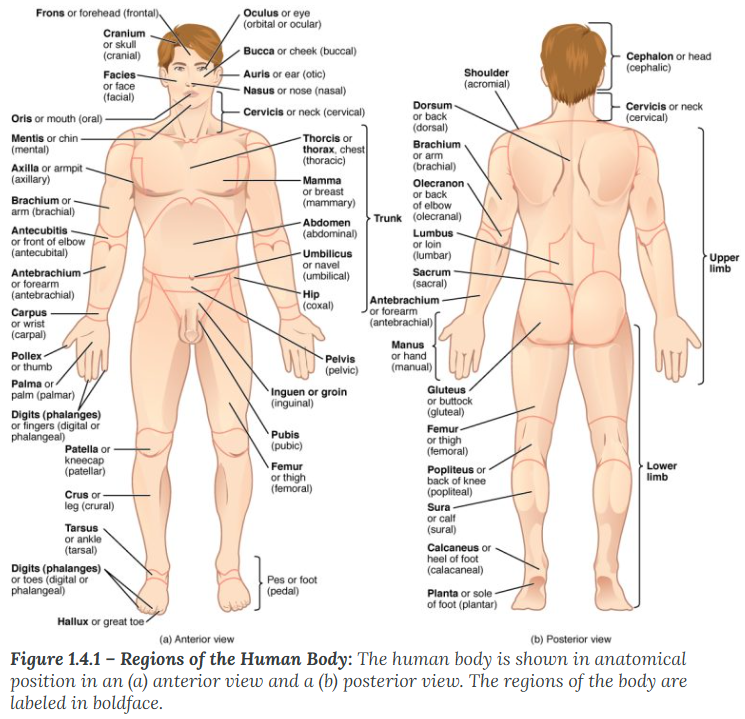
Posterior (or dorsal)
describes the back or direction toward the back of the body. The popliteus is posterior to the patella.
Remember PO and DO is towards the back
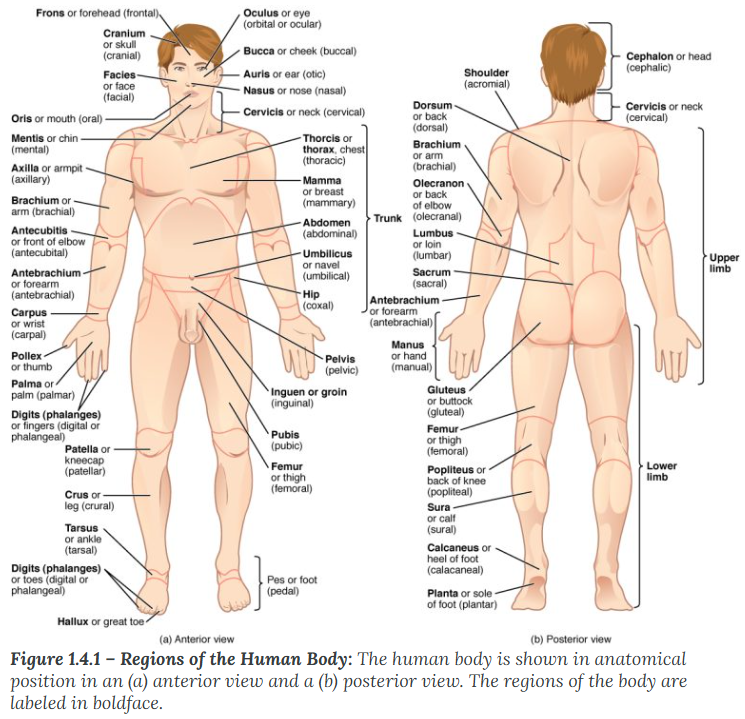
Superior (or cranial)
describes a position above or higher than another part of the body proper. The orbits are superior to the oris.
Superior / Cranial (Above): * Superior: A Supervisor is "above" you.
Cranial: Your Cranium (skull) is at the very top.
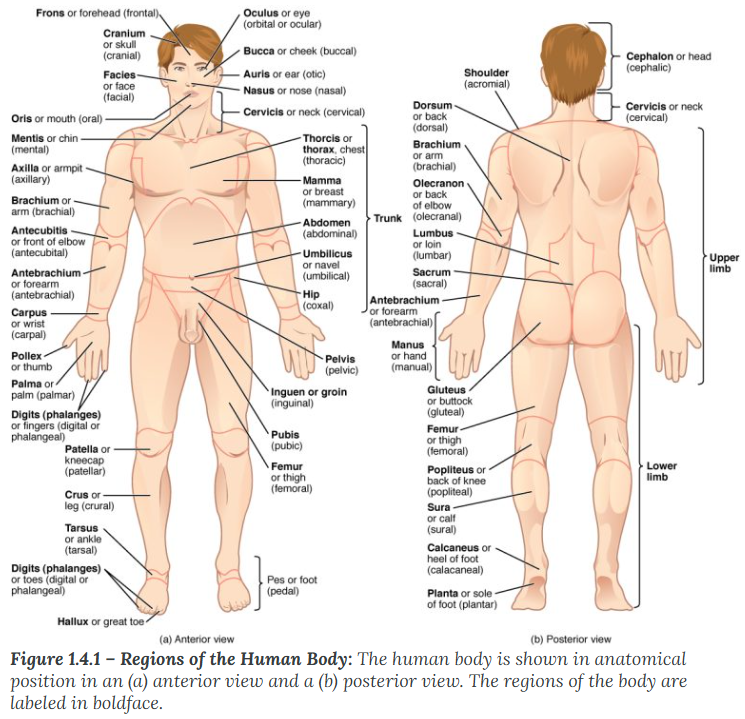
Inferior (or caudal)
describes a position below or lower than another part of the body proper; near or toward the tail (in humans, the coccyx, or lowest part of the spinal column). The pelvis is inferior to the abdomen.
Inferior: If you feel "inferior," you feel "down."
Caudal: means moving away from the head
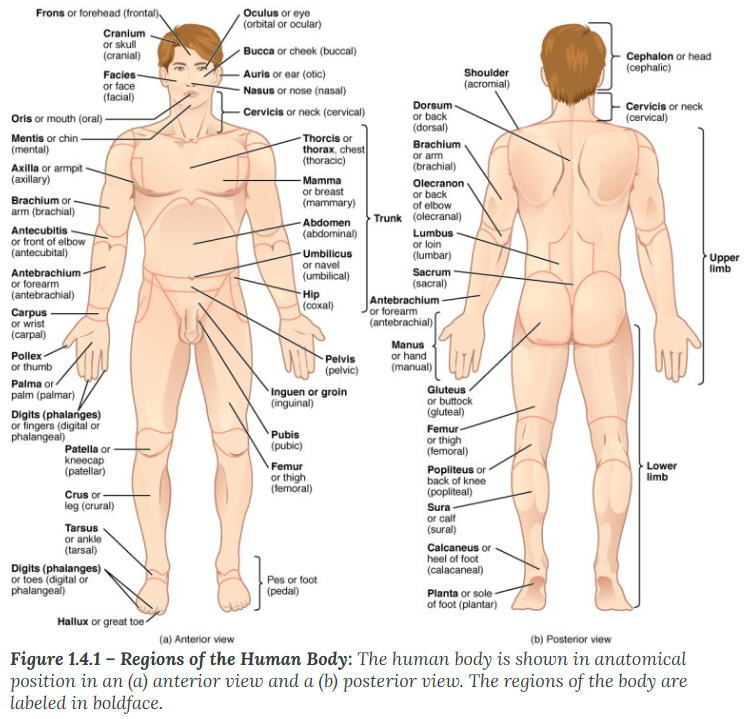
Lateral
describes the side or direction toward the side of the body. The thumb (pollex) is lateral to the digits.
Lateral: Think of a "Ladder"—you have to hold the sides of the ladder to climb.
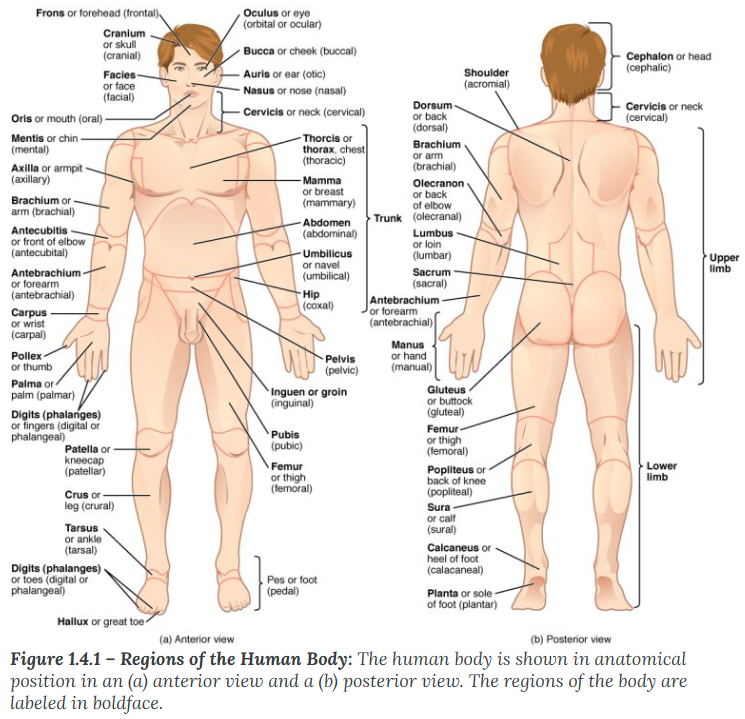
Medial
describes the middle or direction toward the middle of the body. The hallux is the medial toe.
Medial meaning towards the middle of the body
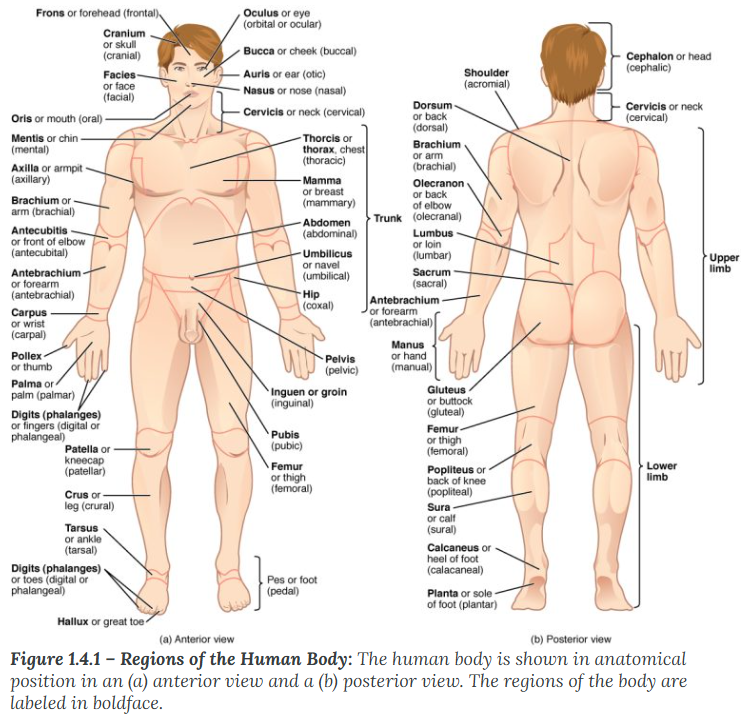
Proximal
describes a position in a limb that is nearer to the point of attachment or the trunk of the body. The brachium is proximal to the antebrachium.
Proximal (Near attachment): * Proximal: Think of "Proximity" or "Approximately." It is close to the trunk.
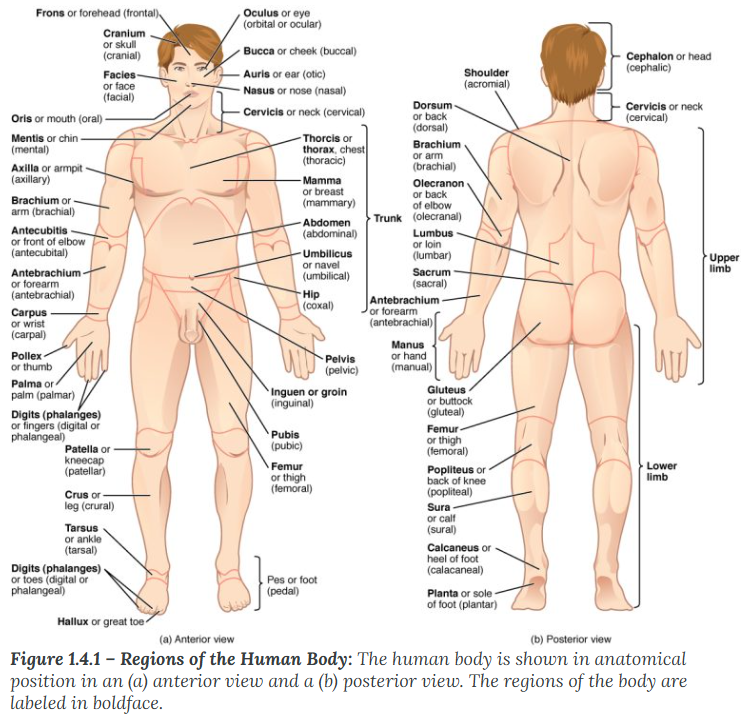
Distal
describes a position in a limb that is farther from the point of attachment or the trunk of the body. The crus is distal to the femur.
Distal (Far from attachment): * Distal: Think of "Distance." It is distant from the trunk.
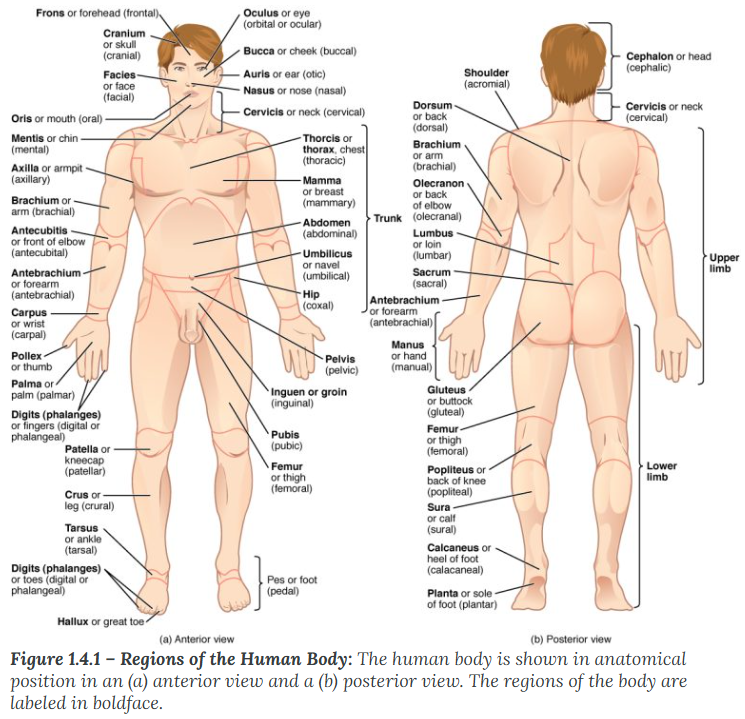
Superficial
describes a position closer to the surface of the body. The skin is superficial to the bones.
Superficial (Near surface): * Superficial: Think of a "Superficial person." They only care about what’s on the surface (the outside).
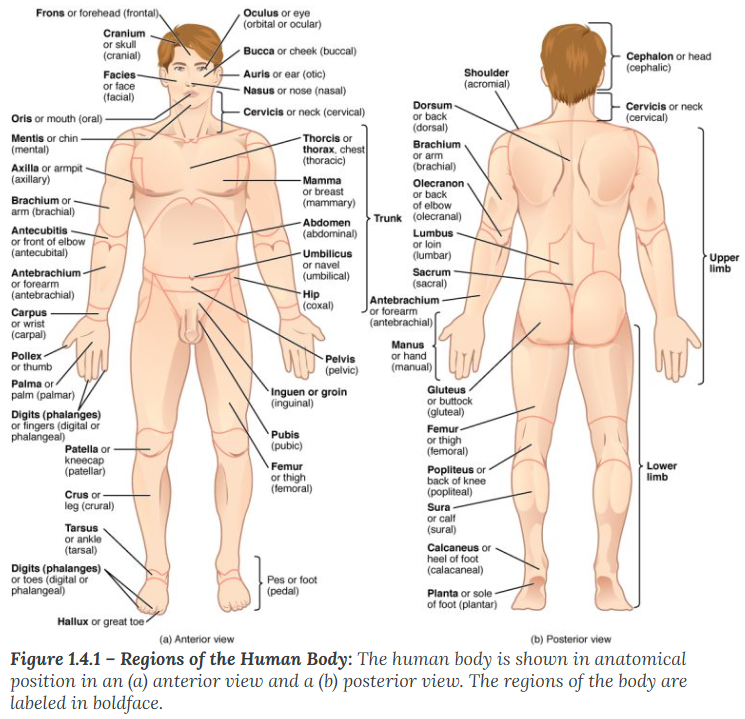
Deep
describes a position farther from the surface of the body. The brain is deep to the skull.
Deep (Away from surface): * Deep: Think of a "Deep-sea diver." They go far below the surface.
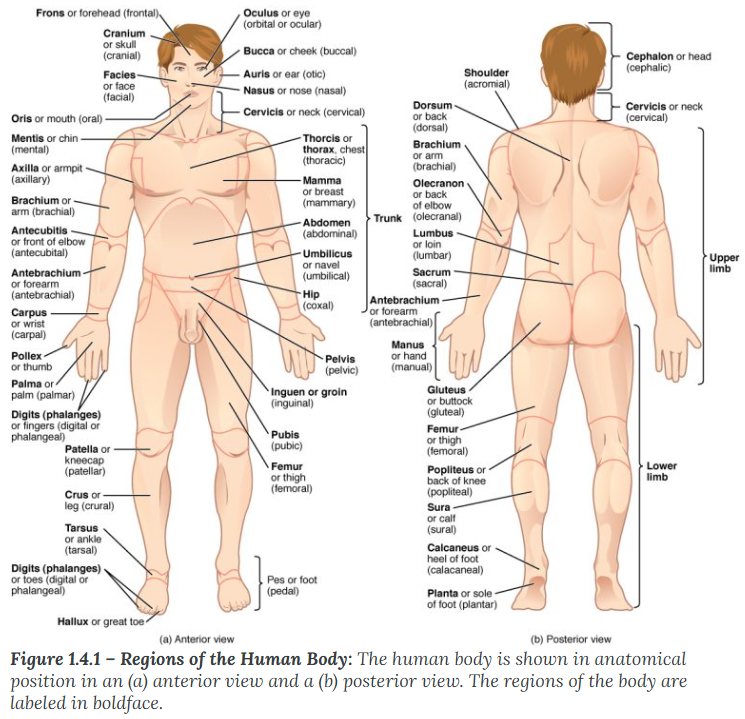
The sagittal plane
divides the body or an organ vertically into right and left sides. If this vertical plane runs directly down the middle of the body, it is called the midsagittal or median plane. If it divides the body into unequal right and left sides, it is called a parasagittal plane or less commonly a longitudinal section.
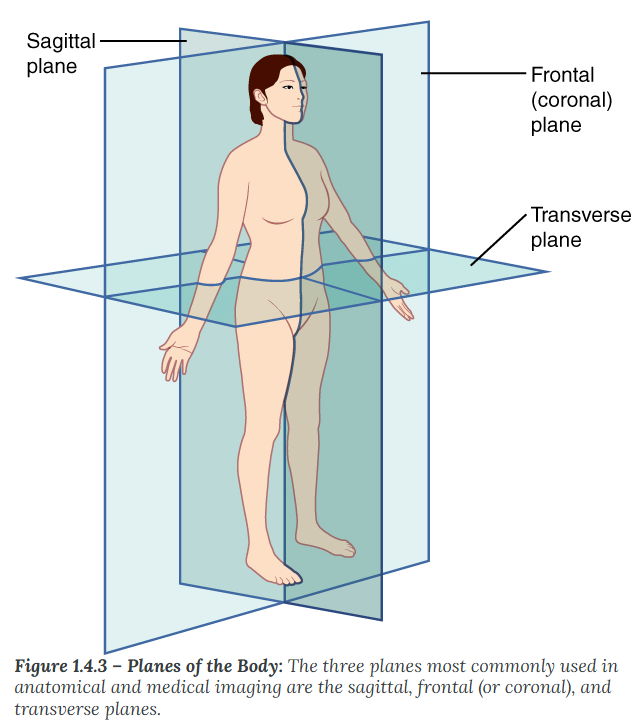
The frontal (coronal) plane
divides the body or an organ into an anterior (front) portion and a posterior (rear) portion. The frontal plane is often referred to as a coronal plane. (“Corona” is Latin for “crown.”)
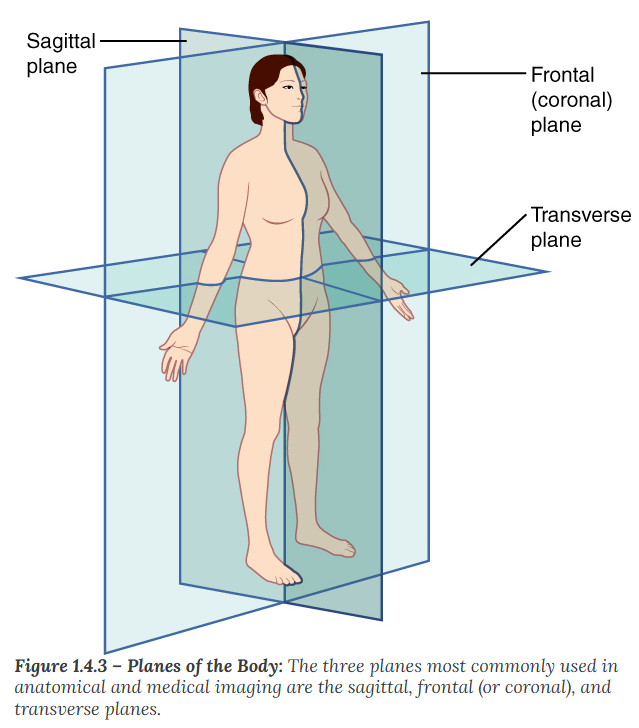
The transverse (or horizontal) plane
divides the body or organ horizontally into upper and lower portions. Transverse planes produce images referred to as cross sections.
Abdominal Regions and Quadrants
To promote clear communication, for instance, about the location of a patient’s abdominal pain or a suspicious mass, health care providers typically divide up the cavity into either nine regions or four quadrants.