human endocrine system
1/31
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
32 Terms
Endocrine system
The blood transports the hormones to the target organs where they perform their function
Exocrine system
Glands release their secretions via ducts to a body cavity or to the outside
Hormone
Chemical substance that is produced and secreted in a very small amount into the bloodstream by endocrine glands
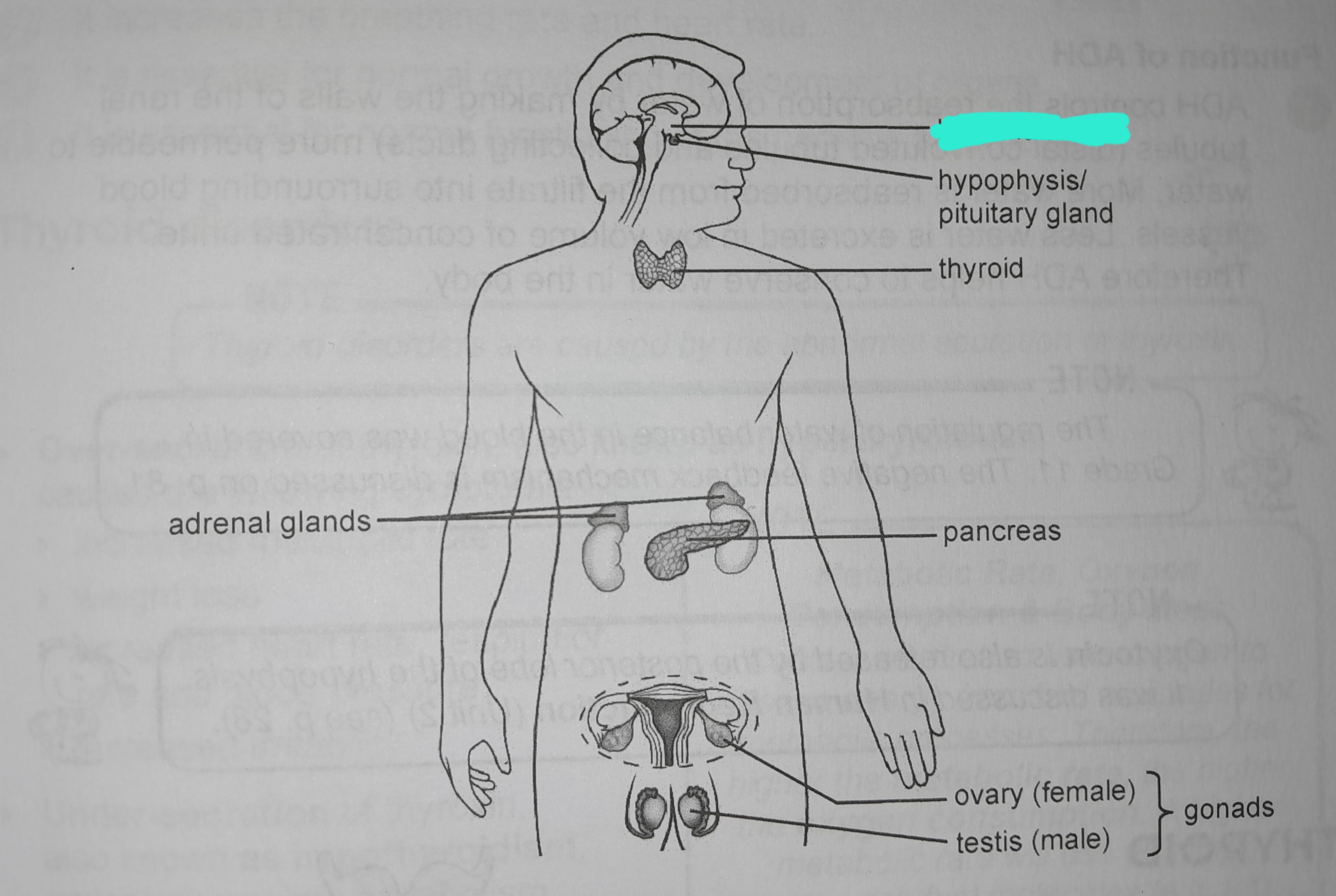
Hypothalamus
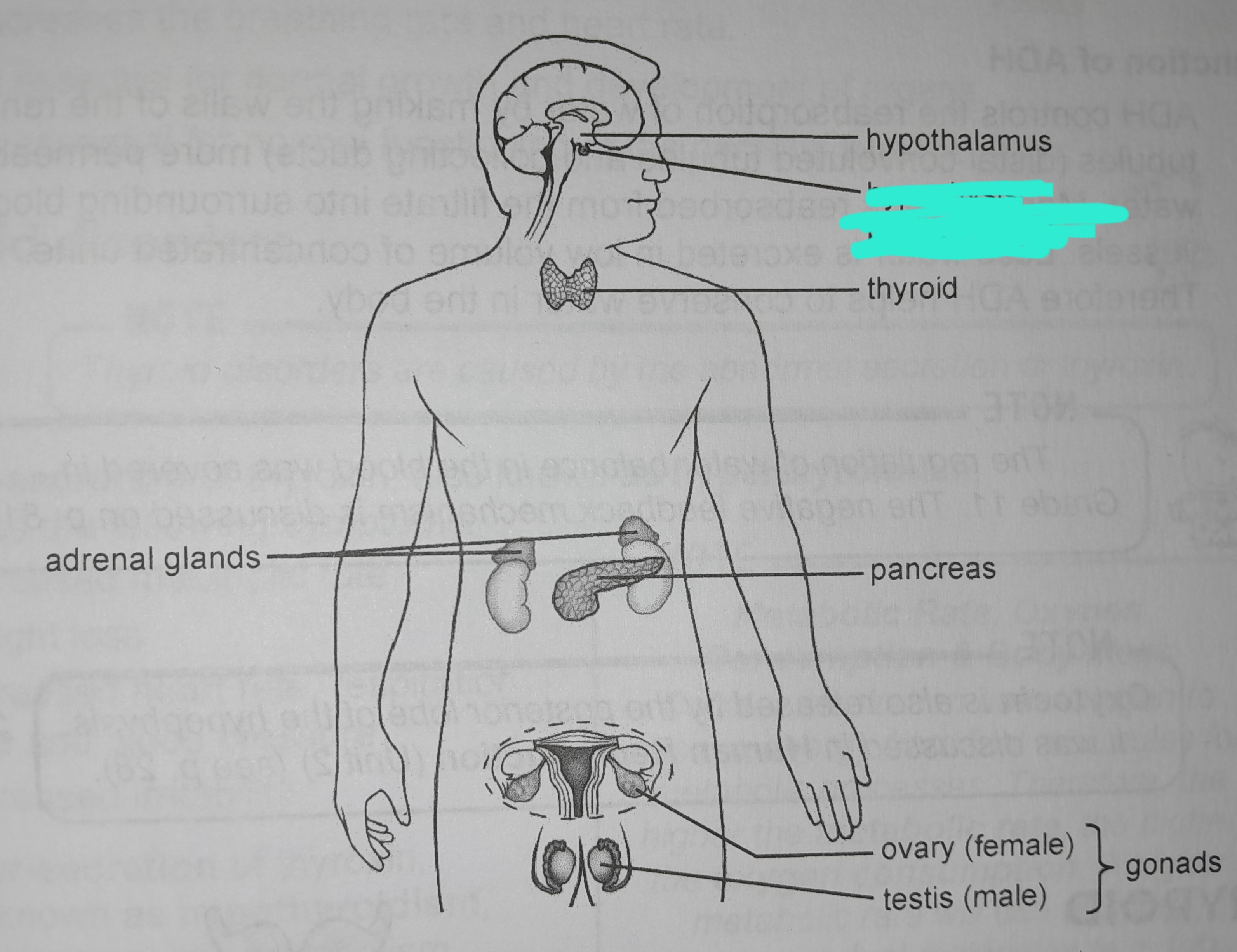
Hypophysis
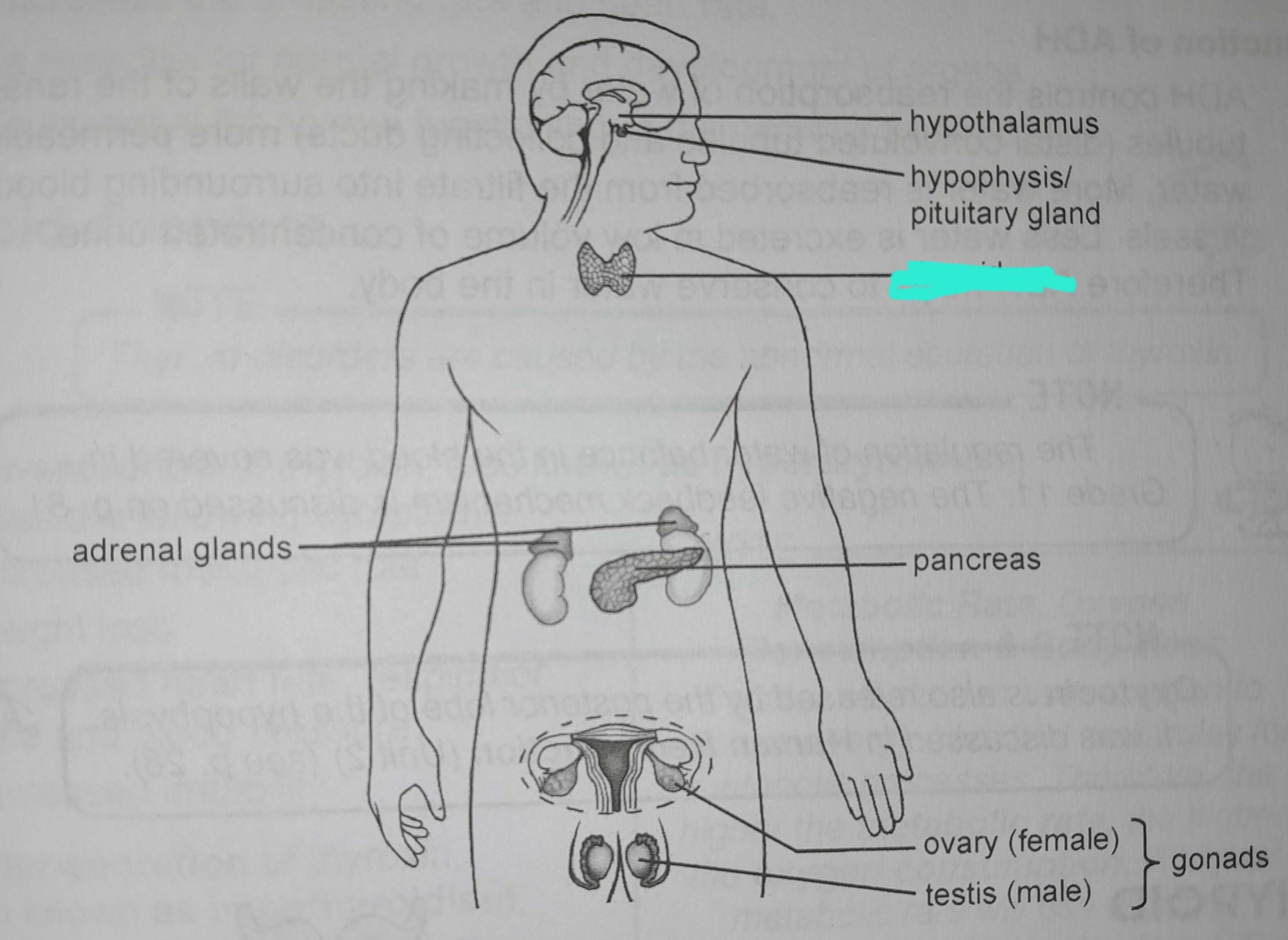
Thyroid
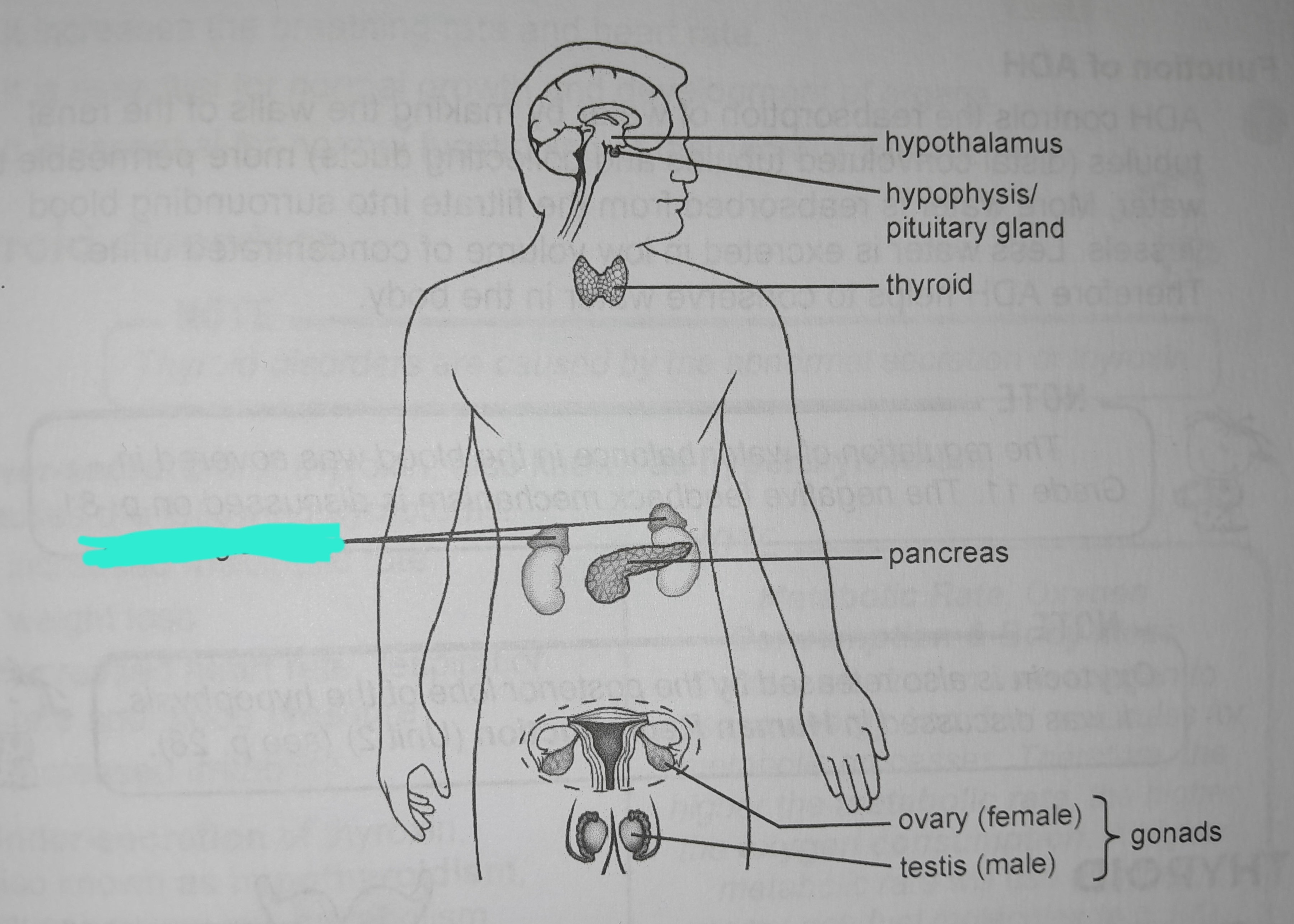
Adrenal glands
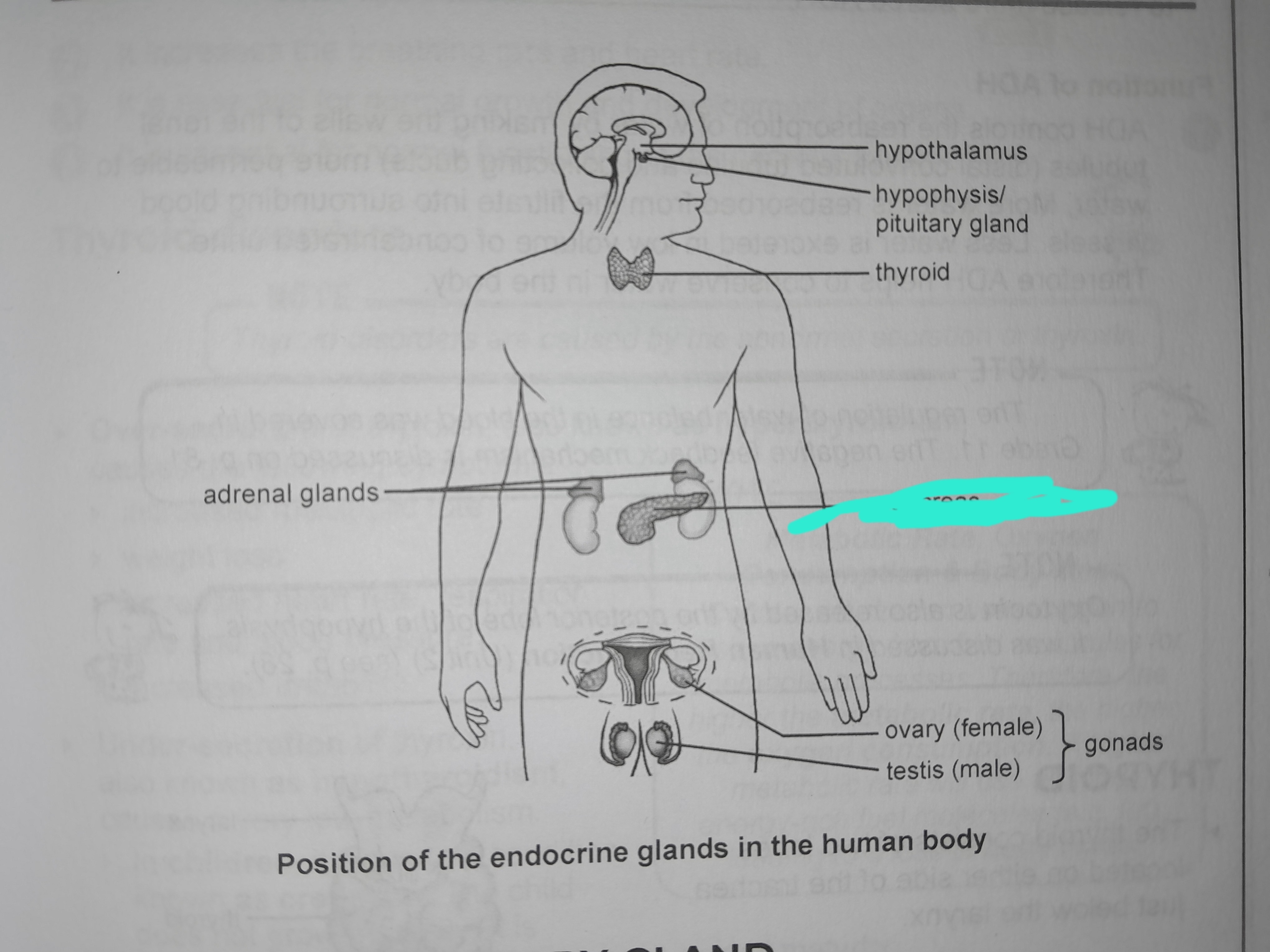
Pancreas
Hypophysis hormones
Thyroid stimulating hormone, Growth hormone (somatotropic hormone), FSH, LH, prolactin
Hypothalamus hormones
Antidiuretic hormone
Thyroid hormone
Thyroxin
Islet of langerhans hormone in the pancreas
Insulin, glucagon
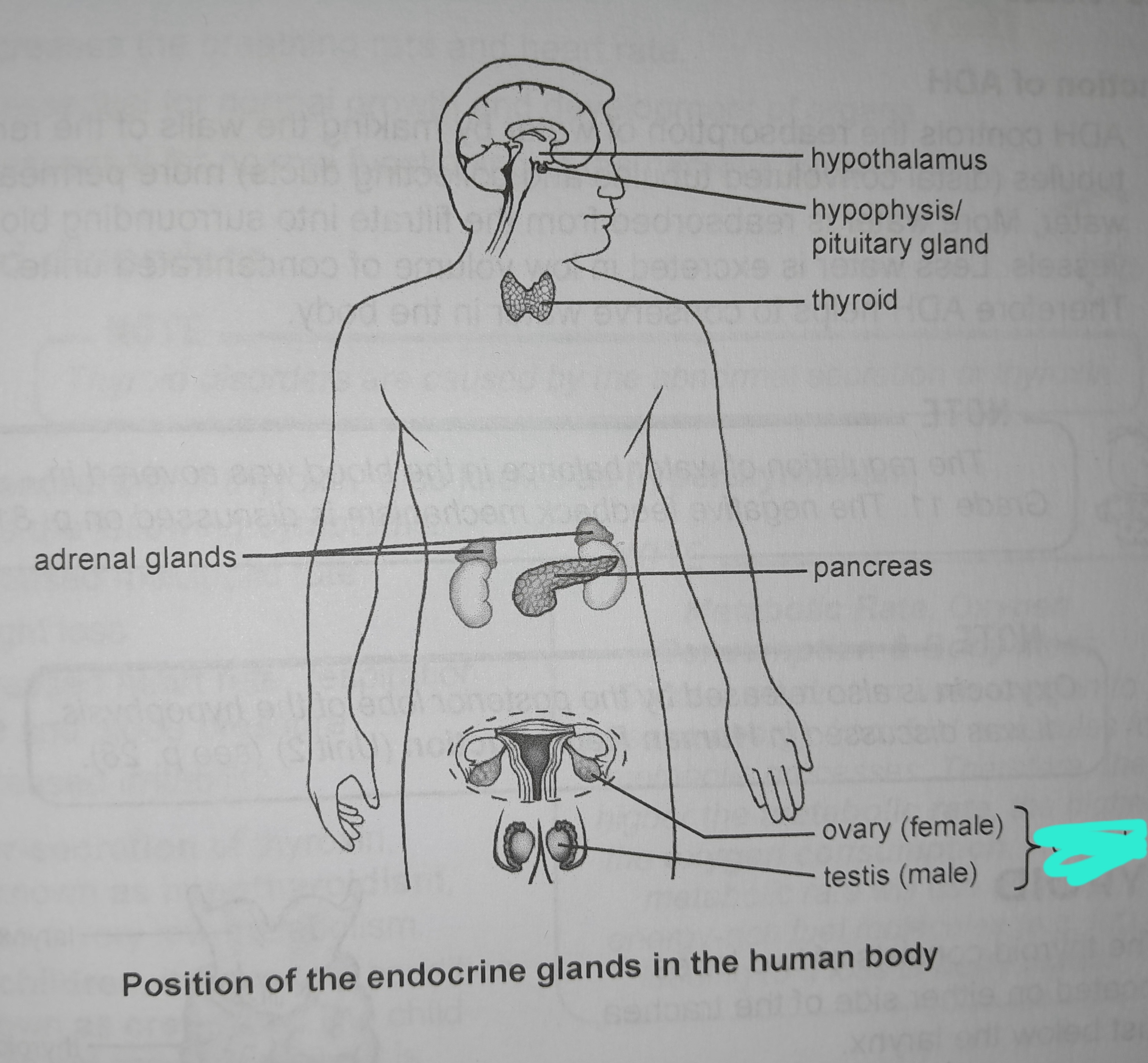
Ovary hormone
Oestrogen, progesterone
Testis hormone
Testosterone
Adrenal gland hormones
Aldosterone, adrenalin
Thyroid stimulating hormone function
Stimulates thyroid to secrete thyroxin
Function of growth hormone (somatotropic hormone)
Promotes the growth of the skeleton and muscles by stimulating the synthesis of proteins
FSH function in females
Stimulates the development of primary follicles in the female ovary into mature Graafian follicles
FSH function in males
Activates the germinal epithelium that produces sperm cells in the testes
LH function in females
Stimulates ovulation and the development of the corpus luteum in the ovary
LH function in males
Stimulates the cells of leydig to produce testosterone
Prolactin function
Stimulates the mammary glands to produce milk after the birth of a baby
Antidiuretic hormone (ADH) function
Controls the reabsorption of water by making walls of the renal tubules more permeable to water
Function of thyroxin
Increases basal metabolic rate so respiration occurs faster, increases breathing rate and heart rate.
Function of insulin
Decreases glucose level when blood glucose rises above normal
Glucagon function
Increases glucose level when blood glucose level drops below normal.
Aldosterone function
Regulates salt balance of the tissue fluid
Adrenalin function
Prepares the body for action in an emergency by accelerating heart rate and increasing blood pressure
Function of testosterone
Necessary for the maturation of sperm and contributes to quality of sperm
Function of oestrogen
Responsible for thickening of endometrium and preparation of uterus for implantation
Function of progesterone
Responsible for the thickening of the endometrium and maintenance of the endometrium during pregnancy