Chapter 6 RNA directed RNA synthesis
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
19 Terms
Viruses with (-) ss RNA genomes
RdRp
RNA coated with protein (nucleocapsid)
ex: VSV (unimolecular); Influenza (segmented)
Viruses with dsRNA genomes
RdRp
Naked RNA
mRNAs and genomic RNAs are produced from distinct templates in different viral particles
ex: Reoviridae, reovirus, rotavirus
Reovirus
(+) strand is not accessible by ribosome because it is double stranded
Rotavirus
Each dsRNA segment is attached to RdRp via the 5’ cap
Viruses with (+) ssRNA genomes
No RdRp
Naked RNA (exceptions include retroviruses and coronavirus)
ex: Polio virus
RNA structure
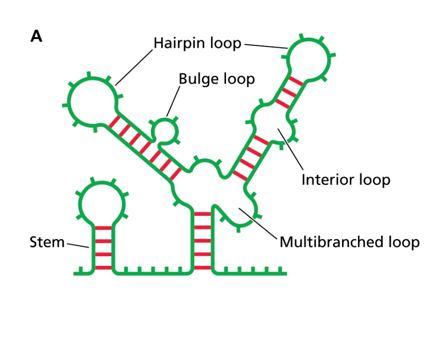
Rules for Viral RNA Synthesis
RNA genome must be copied end to end with no loss of nucleotide sequence
Viral mRNAs must be produced that can efficiently translated by cellular protein synthesis machinery
Rules for RNA-directed RNA synthesis
RNA synthesis initiates and terminates at specific sites
RdRp may initiate synthesis w/ or w/out a primer
Other viral and cell proteins may be required
RNA is synthesized by adding NTPs one by one from the 5’ end to the 3’ end.
There is some non-templated synthesis
De novo
Without a primer
NTP added to 3’ end
Primer-dependent
Protein linked primer (polio)
or nucleic acid primer (influenza)
Two-metal mechanism of polymerase catalysis
Polymerases synthesize nucleic acids
Polymerase enzyme contains two Asp residues which coordinate two Mg2+ ions.
A phosphodiester bond forms, extending the sugar-phosphate backbone
Template sequence determines next NTP
UTP
Are bound to polio virus RdRp
D328 & D329 are 2 aspartates in active site of RdRp that coordinate metal ions
Hydrogen bond between 2’-OH of ribose and D238 (only UTP of RNA works)
Poliovirus Replication: VPg
Linked to first base in RNA at 5’ end by phosphodiester bond
Acts as a primer for RNA synthesis
Why copies of viral RNAs are made
Cloverleaf, cre stemloop, and pseudoknot structures
(-) strand RNA Virus Replication
Viral genome is not mRNA
There must be a switch from mRNA to genome RNA synthesis
A specific protein acts as that molecular switch (N protein)
N protein
With this viral nucleocapsid bound to the (-) strand genome RNA, the RdRp reads through the intergenic juctions where termination occurs during mRNA synthesis
Activation of influenza virus RNA Polymerase
Influenza has a (-) strand RNA genome
PB2 binds to capped primer, activating binding of(-) strand genome RNA at conserved sequence
Endonuclease cleaves host cell RNAs, producing primers for viral mRNA synthesis
Diversity among RNA viruses
Lack of proofreading in RdRp
Exchange of nucleotide sequences among different genomic RNA molecules (Shapes RNA virus world by rearranging genomes and creating new ones)
Nidovirales
exoN protein is 3’ to 5’ exonuclease that corrects RNA polymerase errors and allows replication of large RNA genomes