FBS 10 LAB 2
1/64
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
65 Terms
plant roots
“the part of a plant which attaches it to the ground or
to a support, typically underground, conveying water
and nourishment to the rest of the plant via numerous
branches and fibers.”
Anchor plants
Food reserves
Absorb water and dissolved minerals
Transport materials
Root system (characteristics)
Root cap
region of cell division
region of cell elongation
region of cell maturation
Root hair
External structure of roots
Region of maturation
cells begin to
differentiate into special cell types; root hairs
are found in this region
Region of elongation
newly formed cells increase in length
Region of cell division
location of actively dividing cells.
Root cap
protects the root tip
absence of nodes
uncutinized
protective covering in the tip
arrangement of primary tissues on early stages
Can be distinguished from the stem
by the following:
Primary Root
Adventitious Roots
Root Classification: Based on Origin
Primary Root
directly emanating from the
embryonic root (radicle) (secondary and
tertiary roots arise from the primary root, and
so on)
Adventitious Roots
arising
not from the radicle, but from
any other plant parts
Fibrous Root System
Taproot System
Root Classification: Based on form and structure
Fibrous Root System

Taproot System

Fibrous Root System
Does not penetrate deeply into the soil
Prevents soil erosion
Common among monocot species
Taproot System
Penetrates deeply into the soil
Functions as a storage organ
Good at anchoring the plant in place
Root Hairs
extension of the roots that
absorb a considerable amount
of water by forming an intimate
association with soil particles.

Trichoblast cells
the
particular cells that produce root
hairs.

Underground culms (Rhizomes)
Bamboo Root System
Clumping
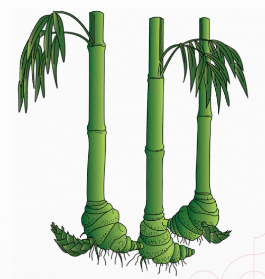
Running

pachymorph rhizomes
form clumps(non invasive)
sympodial type
Clumping Bamboo(root characteristics)
Sympodial type
Rhizomes always turn upward and become culms
Clumping Bamboo

leptomorph (Horizontal rhizome)
monopodial type (running)
Running Bamboo
Monopodial type
Any new rhizome will
grow horizontally underground and
produce more new culms and rhizomes
and this behaviour gave this type of growth
‘running.’
Running bamboo

Running bamboo

Clumping bamboo

Running bamboo

adventitious emerging from a region of the trunk
Palm Root System
Modifications
defined
as morphological changes
in an organ to perform
certain special functions
other than or in addition to
the normal functions.
Storage
Mechanical support
Vital functions
others
Types of root modifications
Fleshy Tap Roots
intended for
storage of (starch) and come in several
forms and shapes. Most fleshy types
are considered edible hence, the term
“root crops”.
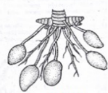
Tuberous Root
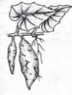
Fasciculated fleshy root
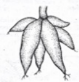
nodulose
moniliform

Annulated
Tuberous Root
do not assume a definite shape and occur singly, e.g., Sweet Potato
Fasciculated Fleshy Roots
clusters and they lie at the base of the stem
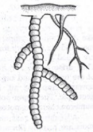
Moniliform
swollen at regular intervals
like beads of a necklace e.g., Basella (Portulaca)
rubra, Momordica
Nodulose
the swellings occur only near the tips
e.g., Curcuma amada (Mango ginger), Maranta sp.
Tuberous Root

Fasciculated Fleshy Roots

Moniliform

Nodulose

Annulated

Tuberous Root
Fasciculated
Moniliform
Nodulose
Annulated
Modification: Storage
Prop roots
Stilt roots
Clinging
Buttress
Modification: Mechanical Support
Prop roots

Stilt roots

Clinging

Buttress

Assimilatory Roots
Epiphytic Roots
Floating Roots
Contractile
Reproductive Roots
Haustoria or Parasitic Roots
Pneumatophores
Modification: Vital Functions
Assimilatory Roots

Epiphytic Roots

Floating Roots

Contractile

Reproductive Roots

Haustoria

Parasitic Roots

Pneumatophores

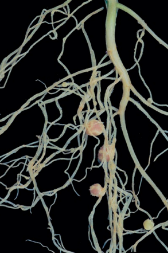
Mycorrhiza

Root Nodules (Rhizobium)