Anatomy and Physiology Lecture Unit #2
1/121
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
122 Terms
Histology
Study of structure and function of tissues
Tissue Types
Epithelium
Connective
Muscle
Neural
Epithelium/Epithelial Tissue Characteristics (1)
Cover structure, lines body cavities and hollow organs
Has free surface and basement membrane
Connective tissues lies below the basement membrane
Epithelium/Epithelial Tissue Characteristics (2)
Nonvascular
Little intercellular (between cells) material, tightly packed
Rapid healing, frequent cell replacement
Epithelium/Epithelial Tissue Functions
Absorption: epithelial cells absorb nutrients from food
Secretion: cell releases substance
Excretion: excess substance cell needs to get rid of
Diffusion: cells can move one way or another
Protection
Distention: specialized for being stretched
Epithelium/Epithelial Tissue Classification
Simple: 1 cell layer (can be squamous, cuboidal, or columnar)
Stratified: 2 or more cell layers (can be squamous, cuboidal, or columnar)
Pseudo-Stratified Columnar: simple but looks stratified (columnar)
Transitional: number of layers depend on stretching (no cell shape)
Epithelial Cell Shape
Squamous
Cuboidal
Columnar
Stratified epithelium
(Squamous) Flat and pancake-shaped
(Cuboidal) Tall as wide (square)
(Columnar) Taller than wide (rectangle standing up)
(Stratified) Cell shape term refers to free surface
Connective Tissue Characteristics
Abundant intercellular material called matrix
Matrix contains ground substance and fibers
Generally vascular
Cells
(cyte - name of cell type)
Fibroblasts: produce fibers
Macrophages: phagocytes
Adipocytes: in adipose
Chondrocytes: in cartilage
Osteocytes: in bone
Fibers
Collagenous: collagen protein - strong
Elastic: elastin protein - stretchy
Reticular: collagen protein - branching
Ground Substance
Gel-like
Reduced
Firm-solid: solid but flexible
Hard-solid: solid can’t bend
Fluid: plasma (blood)
Epithelia
Simple Squamous Epithelium
Locations
Functions
Locations: lines alveoli, forms capillary walls, lines blood and lymph vessels, covers body cavity membranes
Functions: Diffusion (gases), filtration, decrease friction (smooth)
Epithelia
Stratified Squamous Epithelium
Locations
Functions
Features
Locations: surface of skin, linings of oral cavity, vagina, anal canal, and part of pharynx (where swallowing occurs)
Functions: Protection
Features: May be non-keratinizing (alive, moist) or keratinizing (dry, dead cells filled with keratin protein that makes skin waterproof)
Epithelia
Simple Cuboidal Epithelium
Locations
Functions
Locations: covers ovaries, lines kidney tubules and ducts of many glands
Functions: Absorption, secretion (release of cell product), excretion (cell waste)
Epithelia
Stratified Cuboidal Epithelium
Locations
Functions
Locations: linings of larger ducts of mammary glands, sweat glands, salivary glands, and pancreas
Functions: protection, secretion
Transitional Epithelium
Locations:
Functions:
Locations: lining of urinary bladder, ureters, and part of urethra
Functions: protection, distention
Epithelia
Simple Columnar Epithelium
Locations
Functions
Features
Locations: lines uterus, stomach, intestines, uterine tubes
Functions: secretion, absorption, protection production of movement (move an egg into tube)
Features: may have cilia for movement or microvilli for absorption (brush border), and mucus secreting goblet cells
Epithelia
Stratified Columnar Epithelium
Locations
Functions
Locations: lining ductus deferens, part of male urethra, part of pharnyx
Functions: protection, secretion
Epithelia
Pseudo-stratified Columnar Epithelium
Locations
Functions
Features
Locations: lines respiratory passages
Functions: protection, secretion, production of movement
Features: may be ciliated with mucus secreting goblet cells
Connective
Areolar
Locations
Functions
Locations: below skin and below basement membrane of most epithelia
Functions: binds structures
Connective
Adipose
Locations
Functions
Locations: beneath skin, between muscles, around kidneys and heart, behind eyes, in abdominal membranes
Functions: adipocytes accumulate triglycerides for energy storage, insulation, and protection
Connective
Reticular Connective
Locations
Functions
Locations: liver, spleen, lymph nodes
Functions: structural support
Connective
Dense Connective Tissue
Locations
Functions
Features
Locations: regular (tendons, ligaments) irregular (dermis of the skin)
Functions: provides strength
Features: regular is slow to heal because it is mainly nonvascular (poor blood supply), irregular is vascular
Connective
Elastic Connective
Locations
Functions
Locations: walls of larger arteries, heart chambers, and larger airways, and between vertebrae
Functions: provides strength with elasticity
Connective
Blood
Locations:
Functions:
Features:
Locations: Cardiovascular System
Functions: transport, protection from infection, prevention of blood loss
Features: formed elements (cells) in plasma (matrix)
Connective
Hyaline Cartilage
Locations:
Functions:
Features:
Locations: ends of bones, tracheal rings, bone models in fetus and child
Functions: support, bone development
Feature of all Cartilage: chondrocytes occupy lacunae (caves), tissue is nonvascular but surrounded by vascular perichondrium (region around cartilage)
Connective
Elastic Cartilage
Locations:
Functions:
Locations: external ears, part of larynx
Functions: support with elasticity
Connective
Fibrocartilage
Locations:
Functions:
Locations: intervertebral disks (cushion), menisci of knee joints
Functions: support with increased strength and durability (strongest of cartilages)
Connective
Bone
Locations:
Functions:
Features:
Locations: skeleton
Functions: support, protection, attachment sites for muscles, mineral storage
Features: osteocytes occupy lacunae (bone cells live in caves). Compact bone has osteons with central canals, lamellae, and canailiculi
Gland Classification
Endocrine Glands:
Exocrine Glands:
Endocrine Glands: secrete products directly into blood or tissue fluid (hormones)
Exocrine Glands: secrete products directly onto a surface, usually via ductE
Exocrine divided into 3
Cell Number
Structural Complexity
Method of Secretion
Exocrine
Cell Number
Unicellular (goblet cell)
Multicellular
Exocrine
Structural Complexity
Simple (duct does not branch)
Compound (duct branches)
Exocrine
Method of Secretion
Merocrine (cellular secretion/exocytosis)
Apocrine (cell apex (top) breaks off)
Holocrine (gland releases whole cells which disintegrate)
Types of Membranes
Serous membranes
Locations:
Secretion:
Tissues:
Line and cover organs within the ventral cavity
Secretion: serous fluid
Tissues: simple squamous mesothelium, areolar
Types of Membranes
Mucous membranes
Locations:
Secretion:
Tissues:
Locations: line cavities that open to the outside of the body
Secretion: mucus
Tissues: various epithelia, areolar
Types of Membranes
Synovial membranes
Locations:
Secretion:
Tissues:
Locations: line cavities of freely movable joints
Secretion: synovial fluid (lubrication)
Tissues: areolar, adipose
Types of Membranes
Cutaneous membrane, integumentary membrane, integument, skin
Locations:
Secretion:
Tissues:
Locations: Covers the body
Secretion: sweat, sebum (oil)
Tissues: stratified squamous, epithelium, areolar, irregular dense connective
Integumentary System
Cutaneous membrane (skin)
- Accessory structures/organs:
Hair follicles
Sebaceous glands
Nails
Epidermis (—- layer of skin)
Thickness?
Superficial layer of skin
0.08-0.5 mm thick
Strata
Stratum basale: single layer of cuboidal or columnar stem cells
Stratum spinosum: 8-10 layers of flatter cells, some of which are stem cells
Stratum granulosum: missing in thin areas
Stratum lucidum: only in palms and soles
Stratum corneum: 15-30 layers of flattened, dead, keratinized cells
Epidermis
Cell Types
Keratinocytes: produce keratin
Melanocytes: produce melanin
Dendritic cells: protect against microorganisms and superficial cancers
Epidermis
Keratinization
Keratinocytes produce and accumulate keratin and eventually die as they are pushed away from the blood vessels of the dermis and toward the skin surface by the reproductive actions of the cells of the strata basale and spinosum
Epidermis
Epidermal Ridges
Are present on hands and feet to increase friction
Skin Color
3 pigments responsible for skin color
Melanin
Hemoglobin
Carotene
Melanin
(Brown, yellow-brown, black) produced by melanocytes in the epidermis
- people have similar numbers of melanocytes but differ in their activity level
- production promoted by UV radiation
- protects DNA molecules in deeper cells from UV radiation
Hemoglobin
(Bright red, dark red) in red blood cells in the dermis
Carotene
(Orange-yellow) from vegetables can accumulate in the epidermis and in subcutaneous adipose
Dermis (deep layer of skin)
Tissues
Areolar - papillary layer
Dense irregular connective - reticular layer
1-2 mm thick
Dermal papillae contain capillary loops and sensory receptors
Highly vascular
Hypodermis
Region below skin
Areolar and adipose tissue
Separates skin from underlying structures
Integumentary System Accessory Organs
Hair Follicles
follicle wall formed from epidermal cells
usually associated with an arrector pilli muscle (makes hair stand up)
Integumentary System Accessory Organs
Sebaceous Glands
holocrine glands that secrete sebum for lubrication, moisture, and protection from bacterial infection
Integumentary System Accessory Organs (1)
Sweat Glands: Apocrine
Apocrine (body odor)
mainly located in axillae and pubic region
secrete into hair follicles
holocrine glands with secretion that may function in olfactory communication
Integumentary System Accessory Organs (2)
Sweat Glands: Merocrine
found in most areas of skin
secrete onto skin’s surface
secretion functions in thermoregulation and protection from bacterial infection
Functions of Integumentary System
protects underlying tissue and organs against impact, abrasion, fluid loss, chemical attack, and infection by pathogens
excrete salts, water, and organic wastes by integumentary glands (sweat glands)
maintain normal body temp (insulation, evaporative cooling)
produce melanin, protects underlying tissue (and their DNA) from UV radiation
Functions of Integumentary System
produces keratin, protects against abrasion and serves as water repellant
synthesize vitamin D3, steroid converted to calcitriol, hormone important to normal calcium metabolism
store lipids in adipocytes in dermis and adipose tissue in hypo-dermis
detect touch, pressure, pain, and temp stimuli, relay that info to nervous system
Organs of Skeletal System?
bone and joints
each bone and joint is considered an organ because it consists of more than 1 type of tissue
Functions of Skeletal System
support
store minerals and lipids
produce blood cells
protection
leverage
Bone classification by shape
Long: large limb bones (femur or thighbone)
Short: wrist and ankle bones (carpal or wrist bone)
Flat: sternum and cranium bones (parietal bone from roof of skull)
Irregular: vertebrae and facial bones (sphenoid bone from skull)
Parts of a Long Bone
Diaphysis (pl. diaphyses)
Metaphysis (pl. metaphyses)
Epiphysis (pl. epiphyses)
Articular cartilage - hyaline cartilage (decreases friction)
Periosteum - covers outer surface
Medullary cavity
Endospeum - lines all internal cavities
Compact bone - diaphysis and surface of epiphyses
Spongy bone - cores of epiphyses
Marrow
- Red: blood cell production
- Yellow: adipose for energy storage

Bone Tissue Structure: Compact Bone
osteon = central canal + concentric lamellae
lamellae may also be circumferential or interstitial
osteocytes live in lacunae
canaliculi connect neighboring lacunae
perforating canals connect central canal

Bone Tissue Structure: Spongy Bone
Trabeculae
Canaliculi
Trabeculae are small interconnecting bars or plates containing osteocytes in lacunae and lamellae
Canaliculi open onto surface of each trabecula which supply nutrients to the osteocytes
Joints =
Articulations (where bones connect)
Joints are…
Classified to extent of movement
Synarthrosis: no movement (red)
Amiphiarthrosis: slight movement (yellow)
Diarthrosis: free movement (green)
Joints are…
Classified according to articulating tissue
- Fibrous (ligaments)
Syndesmosis: interosseous [between bone] ligament (yellow)
Suture: sutural ligament (red)
Gomphosis: periodontal ligament (red)
Joints are…
Classified according to articulating tissue
- Cartilaginous (cartilage)
Synchondrosis: hyaline cartilage (red)
Symphysis: hyaline cartilage and fibrocartilage disc (yellow)
Joints are…
Classified according to articulating tissue
- Synovial (joint capsule)
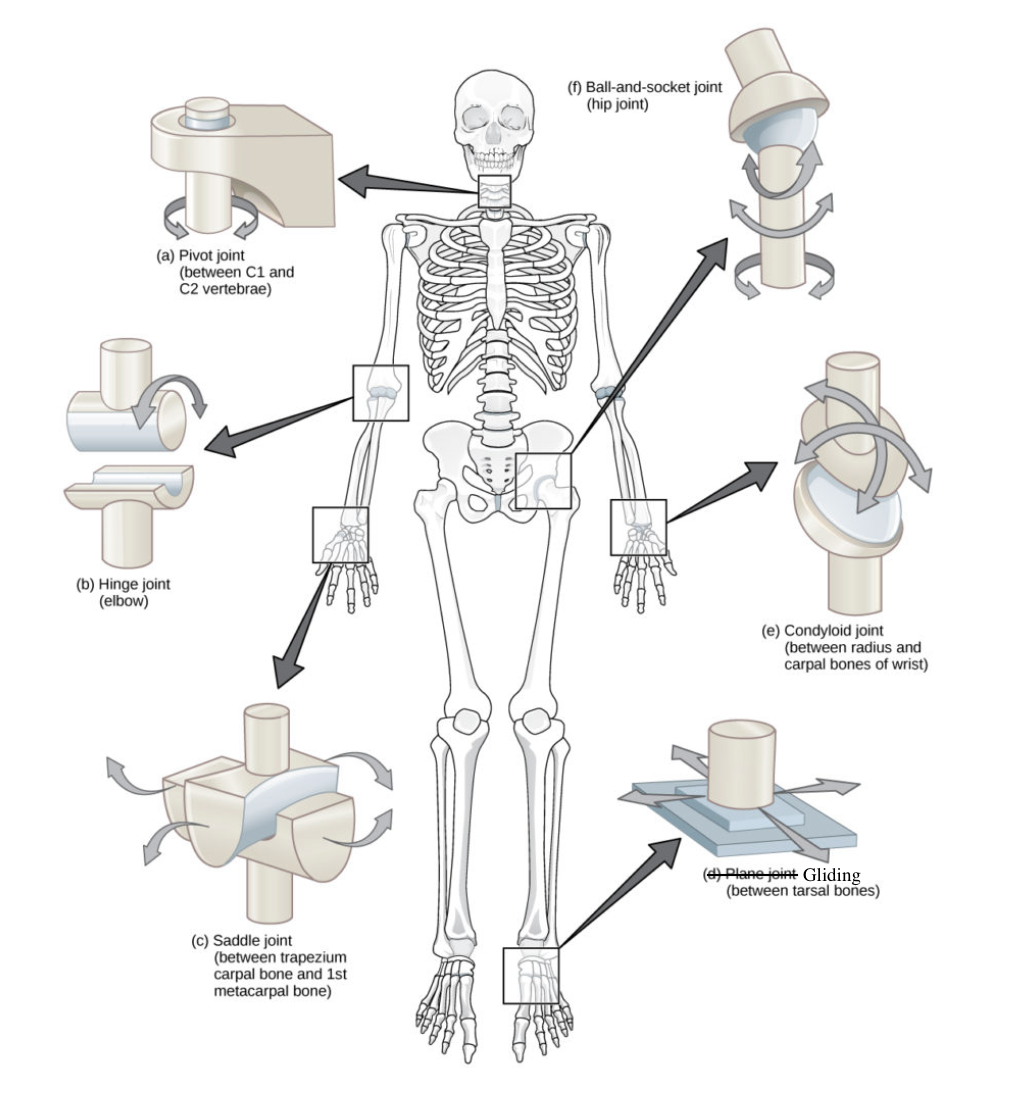
Classified according to shapes of the articulating surfaces
Ball and socket (hip joint)
Conclyloid (wrist)
Gliding (carpals, tarsals)
Hinge (elbow, knee)
Pivot (rotational) (neck)
Saddle (thumb)
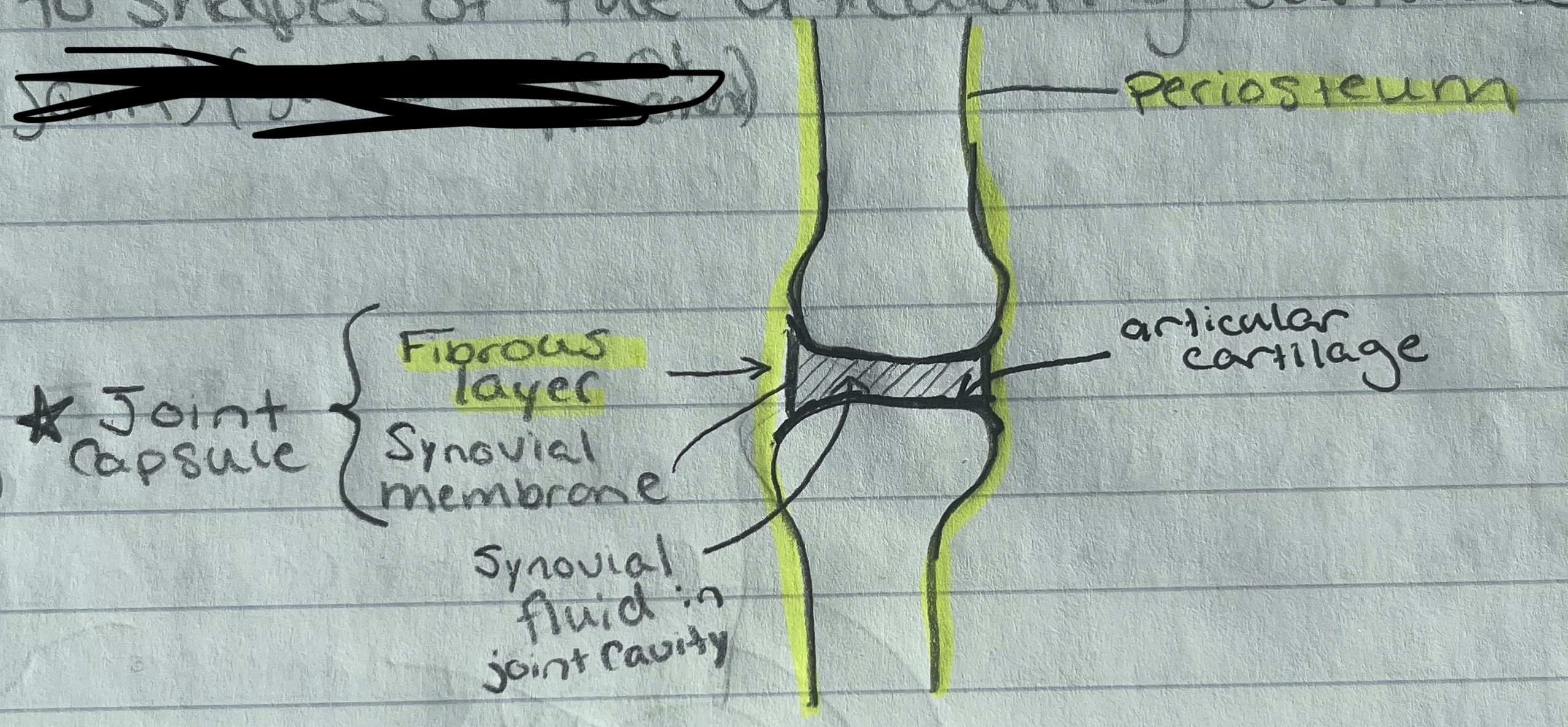
Synovial Joint Structure
Articular cartilage
Joint capsule
- Fibrous layer (dense regular connective) that is continuous with periostium
Synovial membrane (areolar) that secretes synovial fluid for lubrication and cushioning
Synovial Joint Structure
Ligaments
Ligaments: bind bones together and limit movement
Some are part of the fibrous layer, some are separate, some run within joint, some surround
Synovial Joint Structure
Menisci
Bursae
Menisci: fibrocartilage pads between articulating surfaces that provide cushioning
Contains thing, branching fibers and is found within the liven, spleen, and lymph nodes
Reticular Connective
Forms the lining of the urinary bladder
Transitional epithelium
Supports the external ear
Elastic cartilage
Lines some respiratory passages (ex. trachea), appears multilayered but is not
Pseudo-stratified columnar epithelium
Forms the superficial layer of the skin
Stratified squamous epithelium
Lines the larger ducts of several glands and has several layers of cells that are about as tall as they are wide
Stratified cuboidal epithelium
Lines the vas deferens and part of the male urethra and has several layers of cells with those at the apical surface being taller than they are wide
Stratified columnar epithelium
Forms the intervertebral disks
Fibrocartilage
Binds the skin to underlying organs and contains both collagenous and elastic fibers
Areolar
Forms tendons and ligaments
Dense regular connective
Forms the walls of capillaries and linings of other blood vessels
Simple squamous epithelium
Allows the larger arteries and the chambers of the heart to expand and recoil
Elastic connective
Found beneath the skin and around the heart and kidneys. Also stores energy in triglycerides
Adipose
Lines the stomach and uterus
Simple columnar epithelium
Covers the ovaries and lines kidney tubules and the ducts of many glands
Simple cuboidal epithelium
Covers the ends of bones where they articulate
Hyaline cartilage
The basic structural unit for compact bone
Osteon
The basic structural unit for spongy bone
Trabecula
Cavity whereto find a bone cell
Lacunae
Name for a bone cell
Osteocyte
Matrix layer in compact bone
Lamella
Contains blood vessels and nerve fibers
Central canal
Term for an end of a long bone
Epiphysis
Term for the central shaft of a long bone
Diaphysis
Decreases friction on the surface of a bone at a joint
Articular cartilage
Covers a bone
Periosteum
Contains yellow bone marrow in an adult
Medullary cavity
Fills the cores of a long bone’s ends
Spongy bone
Forms the wall of a long bone’s shaft and the surface of it’s ends
Compact bone
Lines the cavity in a long bone’s shaft
Endosteum